Water Quality Criteria of Dieldrin for the Protection of Aquatic Organisms and Wildlife Using a Tissue Residue Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Toxicity Data Screening
2.2. Derivation of Tissue-Based Criteria
2.3. Obtaining the WQC for Dieldrin
2.4. Ecological Risk Assessment
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. WQC for the Protection of Aquatic Life
| Species | Common Name | NOEC (mg/kg, WW *) | Taxa | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palaemonetes pugio | Grass shrimp | 0.09 | Crustaceans | [50] |
| Micropterus salmoides | Largemouth bass | 1.01 | Fishes | [51] |
| Ictalurus punctatus | Channel catfish | 2 | Fishes | [52] |
| Lepomis macrochirus | Bluegill | 3.7 | Fishes | [53] |
| Carassius auratus | Goldfish | 3.8 | Fishes | [53] |
| Poecilia reticulata | Guppy | 10.7 | Fishes | [54] |
| Cyprinodon variegatus | Sheepshead minnow | 12.8 | Fishes | [50] |
| Crassostrea virginica | Eastern oyster | 18.6 | Mollusks | [55] |
| Morone saxatilis | Striped bass | 25 | Fishes | [56] |
| Gambusia affinis | Mosquito fish | 28 | Fishes | [57] |
| Oncorhynchus mykiss | Rainbow trout | 43 | Fishes | [58] |
| Leuciscus idus | Golden ide | 151 | Fishes | [59] |
3.2. WQC for Protection of Aquatic-Dependent Wildlife
3.3. Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boland, M.P. Dieldrin. In Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 4th ed.; Wexler, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2024; pp. 685–689. [Google Scholar]
- Bus, J.S.; Leber, A.P. Miscellaneous Chlorinated Hydrocarbon Pesticides. In Patty’s Toxicology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- ASTDR. Toxicological Profile for Aldrin and Dieldrin; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Petrocelli, S.R.; Anderson, J.W.; Hanks, A.R. Controlled food-chain transfer of dieldrin residues from phytoplankters to clams. Mar. Biol. 1975, 31, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrocelli, S.R.; Anderson, J.W.; Hanks, A.R. Biomagnification of dieldrin residues by food-chain transfer from clams to blue crabs under controlled conditions. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1975, 13, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Jandric, Z.; Chhem-Kieth, S.; Vreysen, M.J.; Rathor, M.N.; Gilles, J.R.; Cannavan, A. Anopheles arabiensis egg treatment with dieldrin for sex separation leaves residues in male adult mosquitoes that can bioaccumulate in goldfish (Carassius auratus auratus). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 2786–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, A.H. Hazard identification of the potential for dieldrin carcinogenicity to humans. Environ. Res. 2014, 131, 188–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martyniuk, C.J.; Mehinto, A.C.; Denslow, N.D. Organochlorine pesticides: Agrochemicals with potent endocrine-disrupting properties in fish. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelista de Duffard, A.M.; Duffard, R. Behavioral toxicology, risk assessment, and chlorinated hydrocarbons. Env. Health Perspect 1996, 104 (Suppl. 2), 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deck, A.T.; Reinke, E.N.; McCain, W.C. Wildlife Toxicity Assessment for Aldrin and Dieldrin. In Wildlife Toxicity Assessments for Chemicals of Military Concern; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 367–384. [Google Scholar]
- Ulugov, U.A.; Bobritskaya, L.S.; Sinitsky, J. Inventory of Obsolete Pesticide Warehouses in Tajikistan and Implications for Removal of Contaminated Soil. J. Health Pollut. 2018, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarrete, I.A.; Tee, K.A.M.; Unson, J.R.S.; Hallare, A.V. Organochlorine pesticide residues in surface water and groundwater along Pampanga River, Philippines. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogbeide, O.; Uhunamure, G.; Okundaye, F.; Ejeomo, C. First report on probabilistic risk assessment of pesticide residues in a riverine ecosystem in South-South Nigeria. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 546–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snow, D.D.; Chakraborty, P.; Uralbekov, B.; Satybaldiev, B.; Sallach, J.B.; Thornton Hampton, L.M.; Jeffries, M.; Kolok, A.S.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.B. Legacy and current pesticide residues in Syr Darya, Kazakhstan: Contamination status, seasonal variation and preliminary ecological risk assessment. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oginawati, K.; Susetyo, S.H.; Rahmawati, S.I.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Abdullah, S.R.S. Distribution of organochlorine pesticide pollution in water, sediment, mollusk, and fish at Saguling Dam, West Java, Indonesia. Toxicol. Res. 2022, 38, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, R.C.; Portella, R.B.; Almeida, P.; Pinto, C.O.; Gubert, P.; Santos da Silva, J.D.; Nakamura, T.C.; do Rego, E.L. Human milk contamination by nine organochlorine pesticide residues (OCPs). J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2020, 55, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Saeid, M.H.; Hassanin, A.S.; Bazeyad, A.Y. Levels of pesticide residues in breast milk and the associated risk assessment. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 3741–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Antary, T.M.; Alawi, M.A.; Kiwan, R.; Haddad, N.A. Monitoring of Organochlorine Pesticide Residues in Human Breast Milk in the Northern Governorates of Jordan in 2019/2020 Compared with the Results of 2015 Study. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padayachee, K.; Reynolds, C.; Mateo, R.; Amar, A. A global review of the temporal and spatial patterns of DDT and dieldrin monitoring in raptors. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, A.F.; Dietz, R.; Sonne, C.; Letcher, R.J.; Roos, A.M.; Simon, M.; Rosing-Asvid, A.; Ferguson, S.H.; McKinney, M.A. Feeding and biological differences induce wide variation in legacy persistent organic pollutant concentrations among toothed whales and polar bear in the Arctic. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CCME. Canadian Sediment Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life-dieldrin; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Procedures for the Derivation of Equilibrium Partitioning Sediment Benchmarks (ESBs) for the Protection of Benthic Organisms: Dieldrin; Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Wildlife Fact Sheet for Dieldrin: (Wildlife); Indiana Department of Environmental Management: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Meharg, A.; Wright, J.; Osborn, D. The frequency of Environmental Quality Standard (EQS) exceedance for chlorinated organic pollutants in rivers of the Humber catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 210–211, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Xu, C.; Zhu, S.; Liu, W. Residue patterns of currently, historically and never-used organochlorine pesticides in agricultural soils across China and associated health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Cao, G.; Liu, L.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Jia, S.-M.; Fu, M.-Q.; Ma, W.-L. Cross-regional scale studies of organochlorine pesticides in air in China: Pollution characteristic, seasonal variation, and gas/particle partitioning. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, R.; Guan, Y.; Zhuang, T.; Wang, Y.; Tan, R.; Wang, J.; Zhou, R.; Wang, B.; Xu, J.; et al. The profiling of elements and pesticides in surface water in Nanjing, China with global comparisons. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhan, F.; Yu, R.-Q.; Sun, X.; Wu, Y. Bioaccumulation of legacy organic contaminants in pregnant Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins (Sousa chinensis): Unique features on the transplacental transfer. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wu, J.; Fan, C. Residual levels, tissue distribution and risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in edible fishes from Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 9265–9277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Fang, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Yuan, H.; Jantunen, L.; Li, Y.-F. Residues of Currently and Never Used Organochlorine Pesticides in Agricultural Soils from Zhejiang Province, China. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2982–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Xu, L.; Deng, A.; Xing, P.; Xu, Y. Centurial deposition records of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in sediment cores from a plateau deep-water lake of China: Significance of anthropogenic impacts, transformation signals and ecological risks revealed by full congener analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water. State Environmental Protection Administration: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 1–8.
- Yang, M.; Mu, Y.; Wu, F. Derivation on Criteria Maximum Concentration of Four Typical Organochlorine Pesticides for Protecting Aquatic Organisms. J. Kunming Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2019, 44, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhart, B.; Flinders, C.; Ragsdale, R.; Johnson, G.; Wiegand, P. Deriving Human Health and Aquatic Life Water Quality Criteria in the United States for Bioaccumulative Substances: A Historical Review and Future Perspective. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 2394–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meador, J.P.; Warne, M.S.J.; Chapman, P.M.; Chan, K.M.; Yu, S.; Leung, K.M.Y. Tissue-based environmental quality benchmarks and standards. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 21, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.J. Rationale for a tissue-based selenium criterion for aquatic life. Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 57, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckvar, N.; Dillon, T.M.; Read, L.B. Approaches for linking whole-body fish tissue residues of mercury or DDT to biological effects thresholds. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 2094–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steevens, J.A.; Reiss, M.R.; Pawlisz, A.V. A methodology for deriving tissue residue benchmarks for aquatic biota: A case study for fish exposed to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and equivalents. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2005, 1, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meador, J. Rationale and Procedures for Using the Tissue-Residue Approach for Toxicity Assessment and Determination of Tissue, Water, and Sediment Quality Guidelines for Aquatic Organisms. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2006, 12, 1018–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.R.; van Dam, R.A.; Fisher, R.; Batley, G.E.; Tillmanns, A.R.; Thorley, J.; Schwarz, C.J.; Spry, D.J.; McTavish, K. Recent Developments in Species Sensitivity Distribution Modeling. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, J.R.; Grist, E.P.M.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Morritt, D.; Crane, M. Species sensitivity distributions: Data and model choice. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 45, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Tissue-Based Criteria for “Bioaccumulative” Chemicals; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- CCME. Protocol for the Derivation of Canadian Tissue Residue Guidelines for the Protection of Wildlife that Consume Aquatic Biota; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, MB, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mackay, D.; Fraser, A. Kenneth Mellanby Review Award. Bioaccumulation of persistent organic chemicals: Mechanisms and models. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 110, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnot, J.A.; Gobas, F.A.P.C. A Generic QSAR for Assessing the Bioaccumulation Potential of Organic Chemicals in Aquatic Food Webs. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2003, 22, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruijn, J.; Busser, F.; Seinen, W.; Hermens, J. Determination of octanol/water partition coefficients for hydrophobic organic chemicals with the “slow-stirring” method. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1989, 8, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorley, J.; Schwarz, C. ssdtools: An R package to fit Species Sensitivity Distributions. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, 4.1.0; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Arnot, J.A.; Gobas, F.A.P.C. A review of bioconcentration factor (BCF) and bioaccumulation factor (BAF) assessments for organic chemicals in aquatic organisms. Environ. Rev. 2006, 14, 257–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, P.R.; Couch, J.A.; Forester, J.; Patrick, J.M., Jr.; Cook, G.H. Dieldrin: Effects on Several Estuarine Organisms. J. Southeast. Assoc. Fish Wildl. Agencies 1977, 427–434. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, K.G.; Muller, J.K.; Price, B.; Ware, A.; Sepúlveda, M.S.; Borgert, C.J.; Gross, T.S. Influence of seasonality and exposure on the accumulation and reproductive effects of p,p′-dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane and dieldrin in largemouth bass. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, L.R. Accumulation and elimination of dieldrin in muscle tissue of channel catfish. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1977, 17, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gakstatter, J.H.; Weiss, C.M. The Elimination of DDT-C14, Dieldrin-C14, and Lindane-C14 from Fish following a Single Sublethal Exposure in Aquaria. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1967, 96, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, K.M.; Liss, W.J. Multi-steady-state toxicant fate and effect in laboratory aquatic ecosystems. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1990, 9, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, J.W.; Rowe, D.R. The accumulation and loss of dieldrin and endrin in the Eastern oyster. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1976, 4, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santerre, C.R.; Blazer, V.S.; Khanna, N.; Reinert, R.E.; Barrows, F.T. Absorption of Dietary Dieldrin by Striped Bass. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1997, 58, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, R.L. Chapter 2—A Laboratory Model Ecosystem to Evaluate Compounds Producing Biological Magnification. In Essays in Toxicology; Hayes, W.J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1974; Volume 5, pp. 17–38. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrle, P.; Mayer, F.; Johnson, W.; Mayer, F.; Hamelink, J. Diet Quality in Fish Toxicology: Effects on Acute and Chronic Toxicity. In Aquatic Toxicology and Hazard Evaluation; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Freitag, D.; Ballhorn, L.; Geyer, H.; Korte, F. Environmental hazard profile of organic chemicals: An experimental method for the assessment of the behaviour of organic chemicals in the ecosphere by means of simple laboratory tests with 14C labelled chemicals. Chemosphere 1985, 14, 1589–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Mu, Y.; Feng, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, F.; Giesy, J.P. Tissue Residue Guideline for ∑DDT for Protection of Aquatic Birds in China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2014, 20, 1629–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Feng, C.; Chang, H.; Mu, Y.; Wu, F. Study on Tissue Residue Guidelines of DDTs for Protection of Aquatic Mammalian Species in China. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2015, 10, 110–118. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, C.L.H.; Lau, R.K.F.; Lam, J.C.W.; Jefferson, T.A.; Hung, S.K.; Lam, M.H.W.; Lam, P.K.S. Risk assessment of trace elements in the stomach contents of Indo-Pacific Humpback Dolphins and Finless Porpoises in Hong Kong waters. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferson, T.A. Population biology of the Indo-Pacific Humpacked dolphin in Hong Kong waters. J. Wildl. Manag. 2000, 64, 1–65. [Google Scholar]
- Mendenhall, V.M.; Klaas, E.E.; McLane, M.A.R. Breeding success of barn owls (Tyto alba) fed low levels of DDE and dieldrin. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1983, 12, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, I.H.; Basson, N.C.J.; Van Der Vyver, J.H.; Van Der Merwe, J.H. Toxicology and Dynamics of Dieldrin in the Crowned Guinea-fowl, Numida Meleagris (L). Phytophylactica 1969, 1, 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- Atkins, T.D. Effects of Dieldrin on Reproduction of Penned Hen Pheasants. J. Wildl. Manag. 1967, 31, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergin, T.J.; Schafer, E.C. Toxicity of dieldrin to bobwhite quail in relation to sex and reproductive status. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1977, 6, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinz, G.H.; Hill, E.F.; Contrera, J.F. Dopamine and norepinephrine depletion in ring doves fed DDE, dieldrin, and Aroclor 1254. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1980, 53, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reading, C.M.; Arscott, G.H.; Tinsley, I.J. Effect of Dieldrin and Calcium on the Performance of Adult Japanese Quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Poult. Sci. 1976, 55, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, R.B.; Linder, R.L. Effects of Dieldrin in Penned Pheasants through the Third Generation. J. Wildl. Manag. 1974, 38, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitzer, J.F.; Heinz, G.H. The effect of sublethal dosages of five pesticides and a polychlorinated biphenyl on the avoidance response of coturnix quail chicks. Environ. Pollut. (1970) 1974, 6, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferies, D.J.; French, M.C. Changes Induced in the Pigeon Thyroid by p,p prime -DDE and Dieldrin. J. Wildl. Manag. 1972, 36, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, K.L.; Sell, J.L. DDT thins shells of eggs from mallard ducks maintained onad libitum or controlled-feeding regimens. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1974, 2, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eden, W.G. Toxicity of Dieldrin to Chickens. J. Econ. Entomol. 1951, 44, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.I.T.; Stevenson, D.E.; Robinson, J.; Thorpe, E.; Roberts, M. The toxicology and pharmacodynamics of dieldrin (HEOD): Two-year oral exposures of rats and dogs. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1969, 15, 345–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, A.I.T.; Thorpe, E.; Stevenson, D.E. The toxicology of dieldrin (HEOD). I. Long-term oral toxicity studies in mice. Food Cosmet. Toxicol. 1973, 11, 415–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiese, I.; Basson, N.C.J.; Basson, P.; Naudé, T.W.; Maartens, B.P. The toxicology and pathology of dieldrin and photodieldrin poisoning in two antelope species. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1973, 40 1, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, D.A.; Korschgen, L.J. Reproduction, growth, and tissue residues of deer fed dieldrin. J. Wildl. Manag. 1970, 34, 887–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, K.L. Growth, Hemoglobin, Body Composition and Vitamin A of Sheep Fed Dieldrin. J. Anim. Sci. 1970, 31, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildstein, K.L.; Forsyth, D.J. Effects of dietary dieldrin on behavior of white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus) towards an avian predator. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1979, 21, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotonya, R.; Jensen, N.-E. No effect of dieldrin on progesterone production in gilts. Toxicology 1993, 81, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurkat, P.C.; Joshi, G.P. Some Physiological and Behavior Studies on Rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) after Dieldrin Administration. Indian Vet. J. 1977, 54, 709–714. [Google Scholar]
- Uzoukwu, M.; Sd, S. Dieldrin toxicosis: Fetotoxicosis, tissue concentrations, and microscopic and ultrastructural changes in guinea pigs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1972, 33 3, 579–583. [Google Scholar]
- Klump, D.W.; Huasheng, H.; Humphrey, C.; Xinhong, W.; Codi, S. Toxic contaminants and their biological effects in coastal waters of Xiamen, China. I. Organic pollutants in mussel and fish tissues. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamai, S.L.; Warner, G.F.S.; Walker, C.H. Effects of dieldrin on life stages of the African catfish, Clarias gariepinus (Burchell). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1999, 42 1, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Ruan, X.; van der Hoek, J.P. Residues of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in aquatic environment and risk assessment along Shaying River, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2525–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisner, O.; Arle, J.; Liebmann, L.; Link, M.; Schafer, R.B.; Schneeweiss, A.; Schreiner, V.C.; Vormeier, P.; Liess, M. Three reasons why the Water Framework Directive (WFD) fails to identify pesticide risks. Water Res. 2022, 208, 117848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

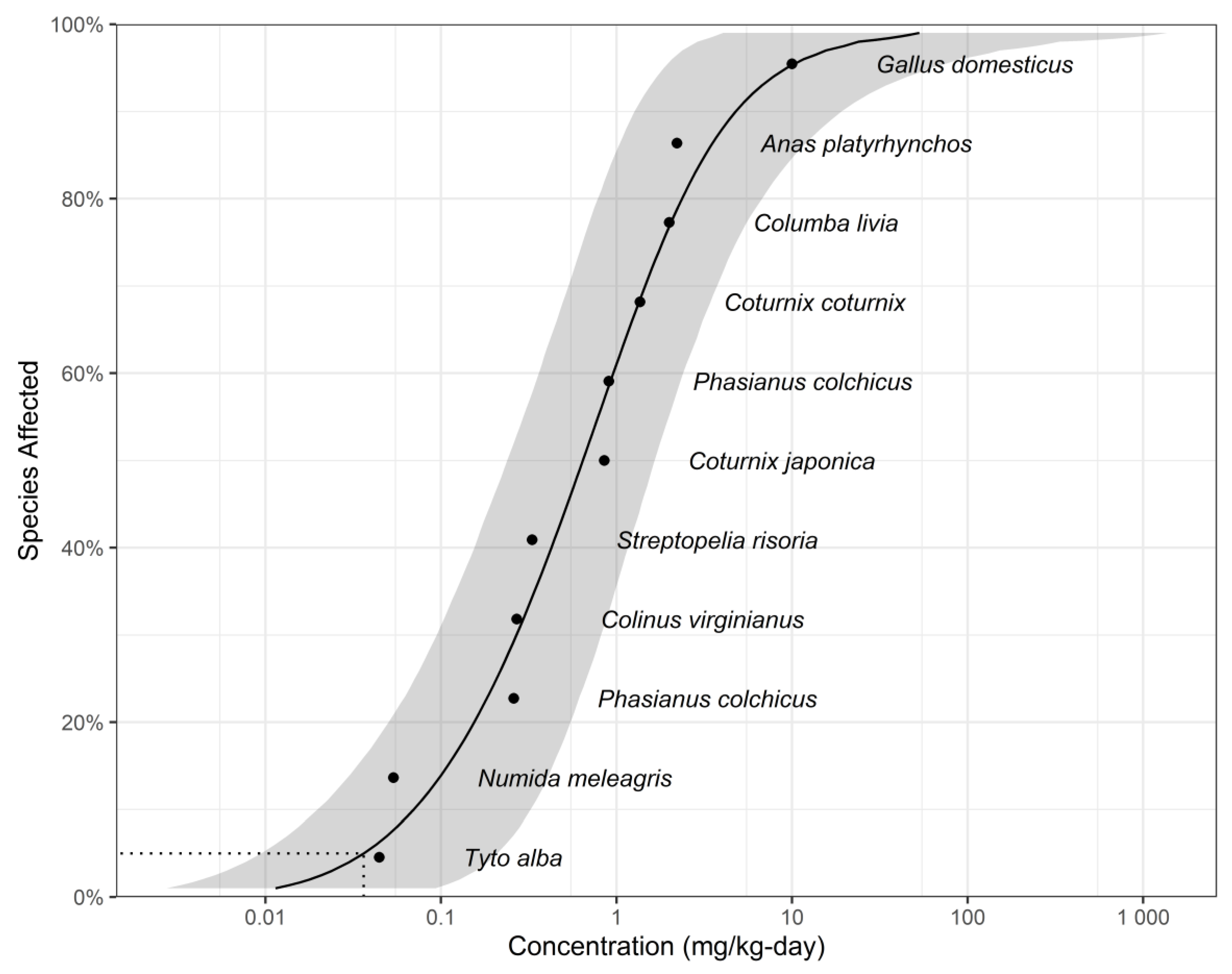
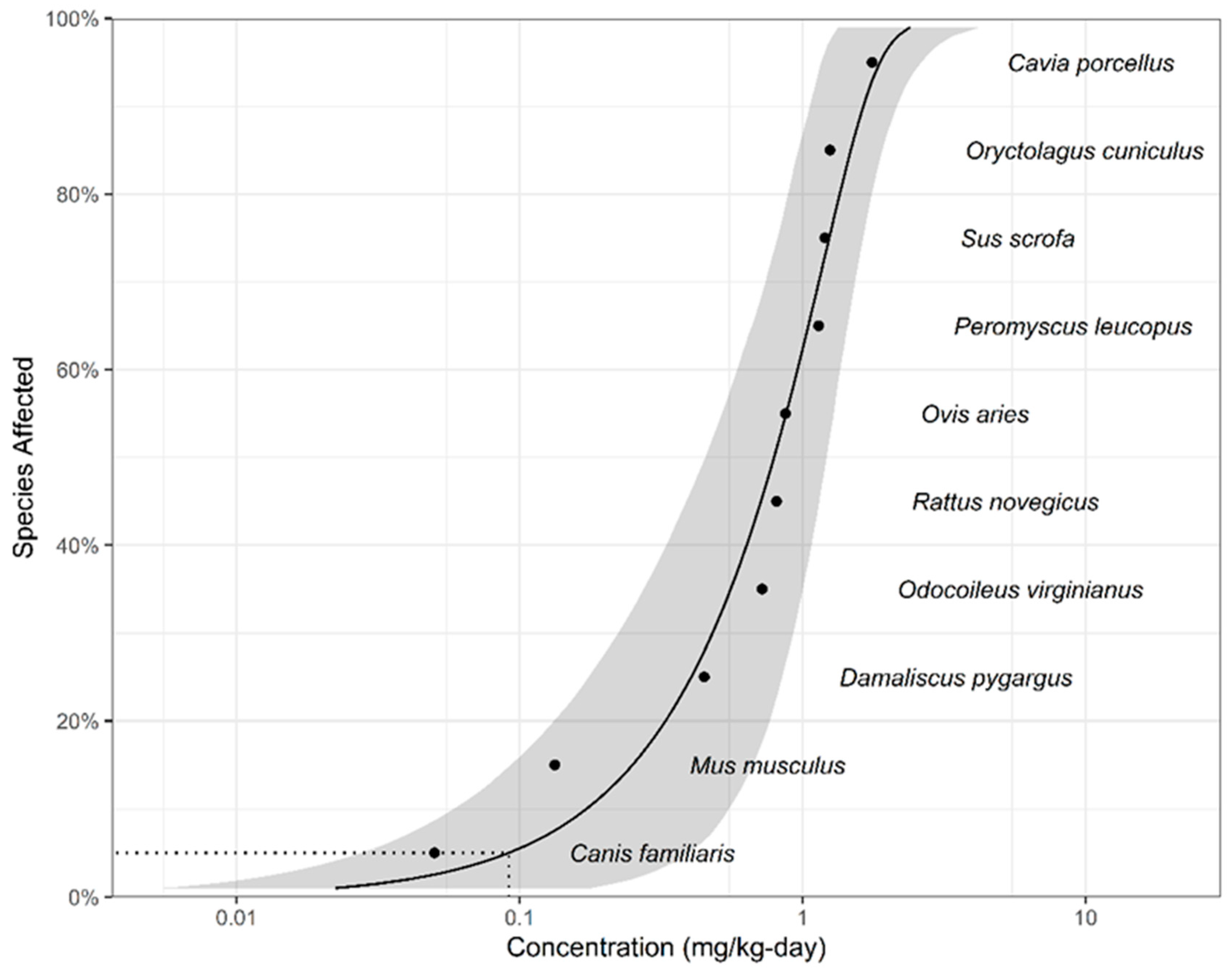
| Species | Common Name | NOEC (mg/kg bw/day, WW) * | Taxa | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tyto alba | Barn owl | 0.0445 | Avian | [64] |
| Numida meleagris | Crowned guinea fowl | 0.0537 | Avian | [65] |
| Phasianus colchicus | Ring-necked pheasant | 0.26 | Avian | [66] |
| Colinus virginianus | Bobwhite quail | 0.27 | Avian | [67] |
| Streptopelia risoria | Ring dove | 0.331 | Avian | [68] |
| Coturnix japonica | Japanese quail | 0.852 | Avian | [69] |
| Phasianus colchicus | Pheasant | 0.905 | Avian | [70] |
| Coturnix coturnix | Quail | 1.36 | Avian | [71] |
| Columba livia | Homing pigeon | 2 | Avian | [72] |
| Anas platyrhynchos | Mallard | 2.21 | Avian | [73] |
| Gallus domesticus | Chicken | 10 | Avian | [74] |
| Canis familiaris | Dog | 0.05 | Mammalian | [75] |
| Mus musculus | Mouse | 0.133 | Mammalian | [76] |
| Damaliscus pygargus | Blesbuk | 0.449 | Mammalian | [77] |
| Odocoileus virginianus | White-tailed deer | 0.72 | Mammalian | [78] |
| Rattus novegicus | Rat | 0.81 | Mammalian | [75] |
| Ovis aries | Sheep | 0.87 | Mammalian | [79] |
| Peromyscus leucopus | White-footed mouse | 1.14 | Mammalian | [80] |
| Sus scrofa | Pig | 1.20 | Mammalian | [81] |
| Oryctolagus cuniculus | Rabbit | 1.25 | Mammalian | [82] |
| Cavia porcellus | Guinea pig | 1.76 | Mammalian | [83] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, L.; Li, X.; Bao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Su, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, F.; Wei, Y.; Ji, N.; Zhou, M. Water Quality Criteria of Dieldrin for the Protection of Aquatic Organisms and Wildlife Using a Tissue Residue Approach. Toxics 2025, 13, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030173
Xie L, Li X, Bao L, Zhang Y, Su H, Liu X, Wang F, Wei Y, Ji N, Zhou M. Water Quality Criteria of Dieldrin for the Protection of Aquatic Organisms and Wildlife Using a Tissue Residue Approach. Toxics. 2025; 13(3):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030173
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Li, Xuemei Li, Liangwen Bao, Yuexin Zhang, Hailei Su, Xuesong Liu, Fanfan Wang, Yuan Wei, Ningning Ji, and Min Zhou. 2025. "Water Quality Criteria of Dieldrin for the Protection of Aquatic Organisms and Wildlife Using a Tissue Residue Approach" Toxics 13, no. 3: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030173
APA StyleXie, L., Li, X., Bao, L., Zhang, Y., Su, H., Liu, X., Wang, F., Wei, Y., Ji, N., & Zhou, M. (2025). Water Quality Criteria of Dieldrin for the Protection of Aquatic Organisms and Wildlife Using a Tissue Residue Approach. Toxics, 13(3), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030173






