In Situ Evaluation of the GSH Depletion Ability of Various Alkylating Agents and the Protective Effect of Several Active Thiol Compounds Based on High-Content Cell Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.3. Fluorescent Probe Preferences
2.4. Optimization of Probe Incubation Concentration and Time
2.5. Fluorescence Analysis of Intracellular GSH Changes
2.6. Measurement of Reactive Oxygen Species Generation
2.7. Screening of Protective Drugs and Optimization of Conditions
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
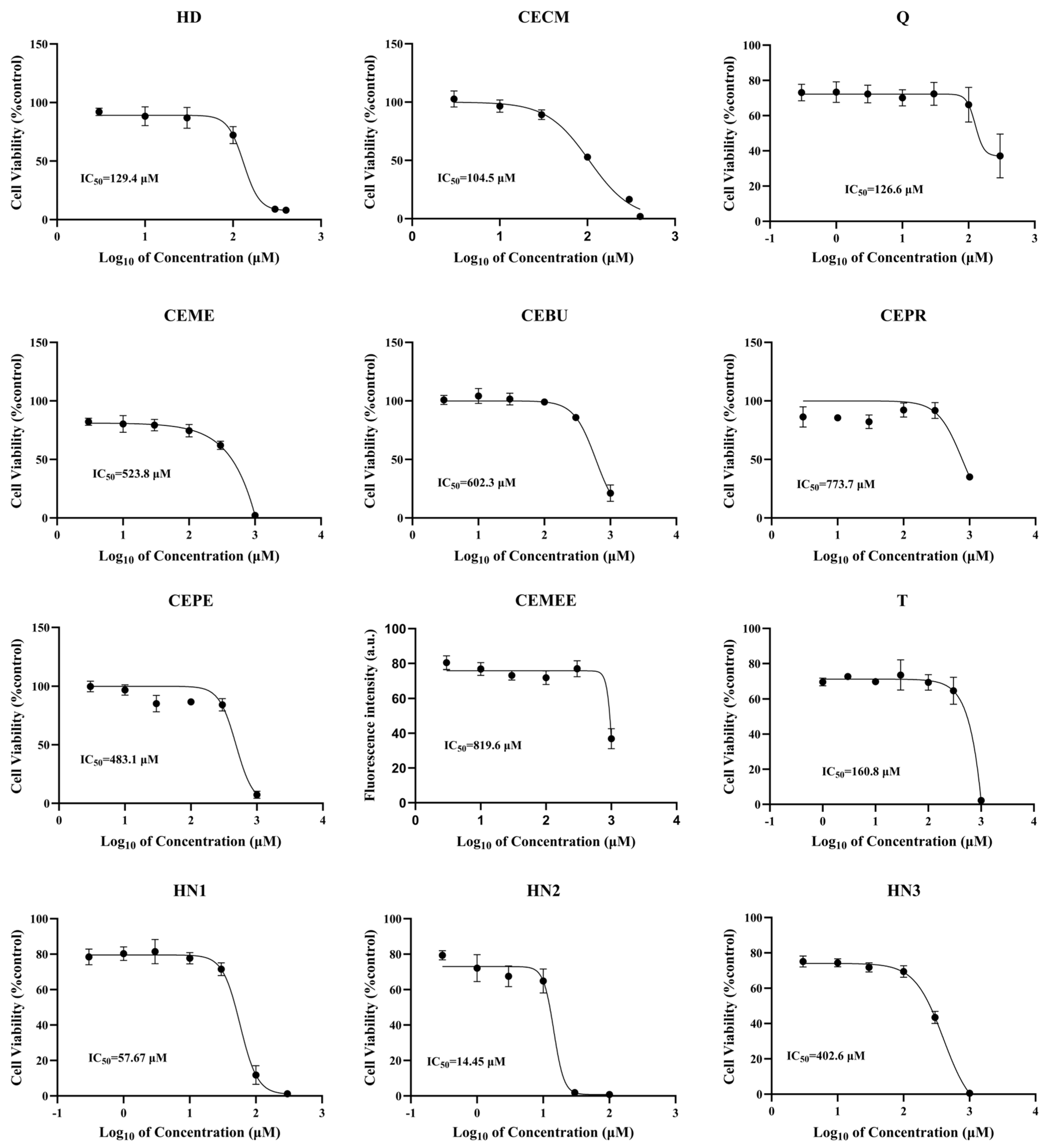
3.1. Cytotoxicity Induced by Series of Alkylating Agents
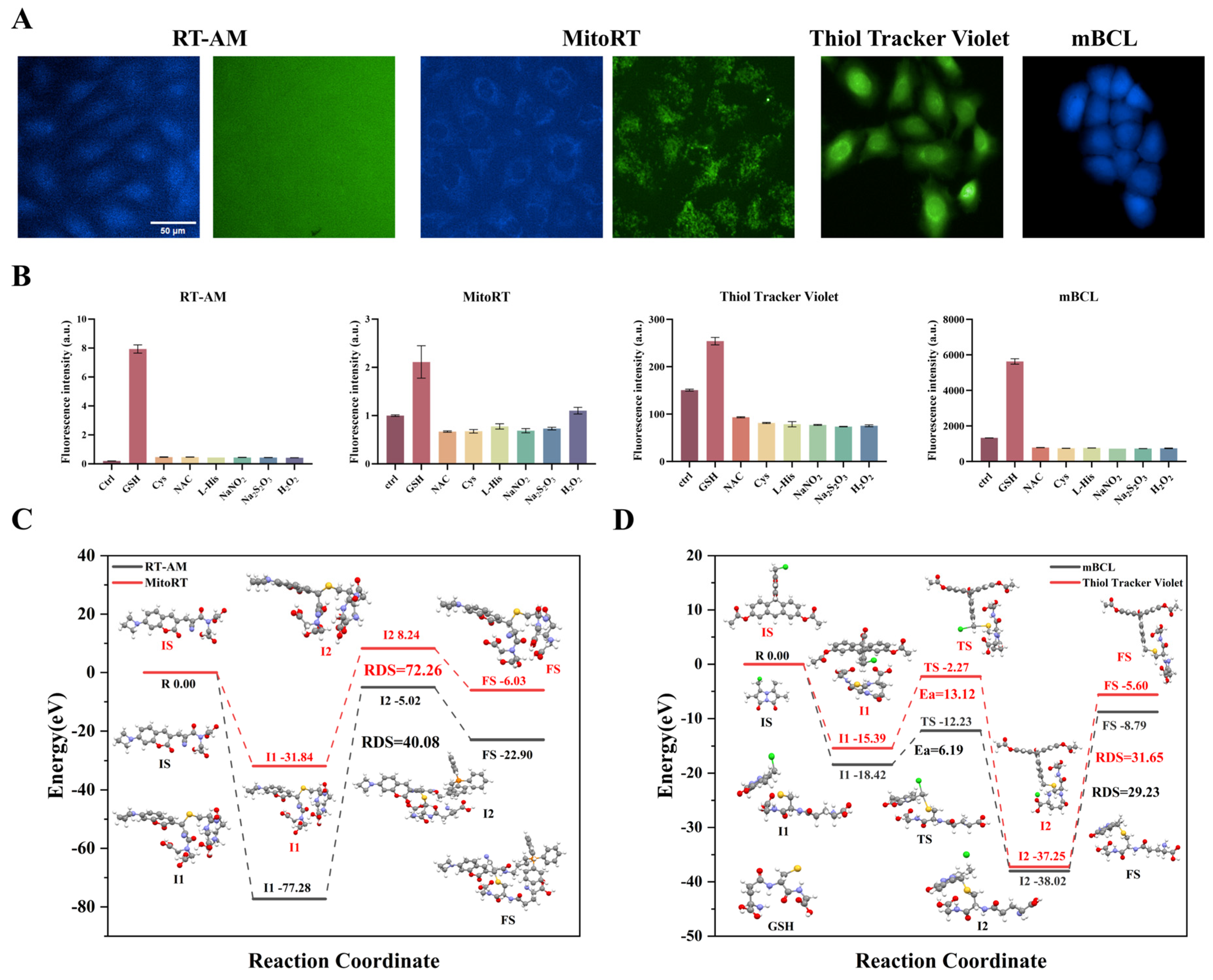
3.2. Preferred Specific Recognition of GSH Fluorescent Probes
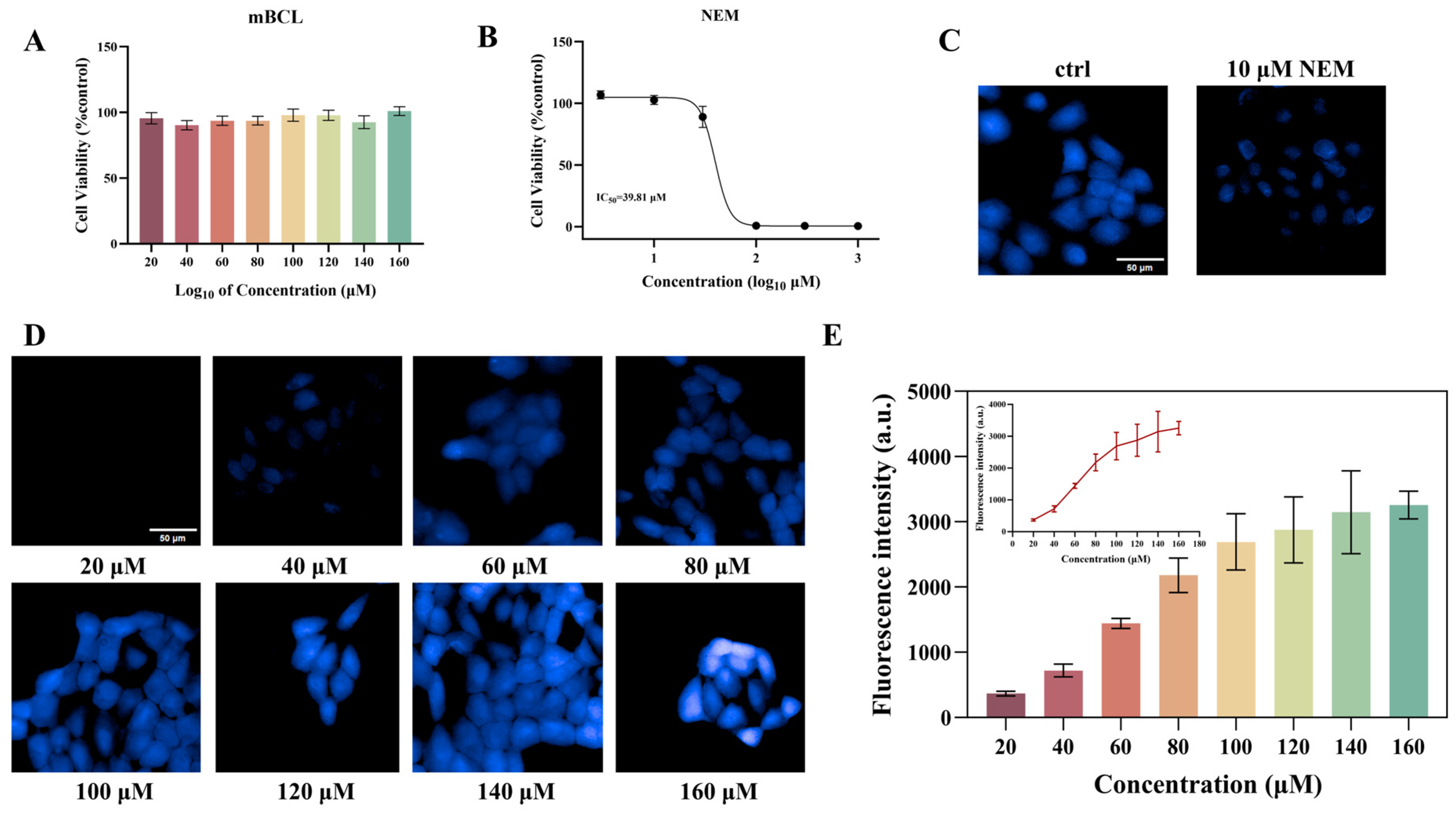
3.3. Optimization of Imaging Conditions for Fluorescent Probes
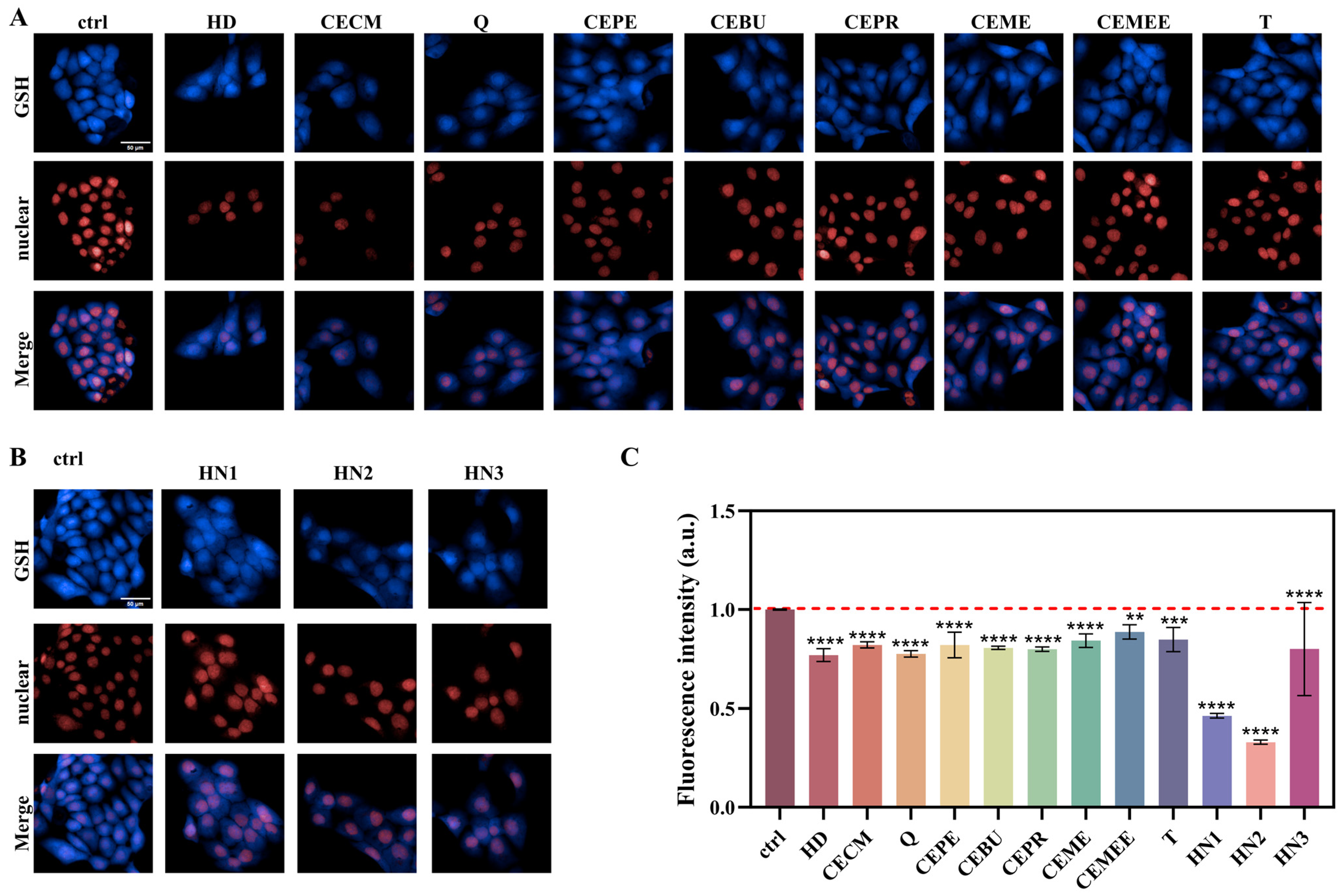
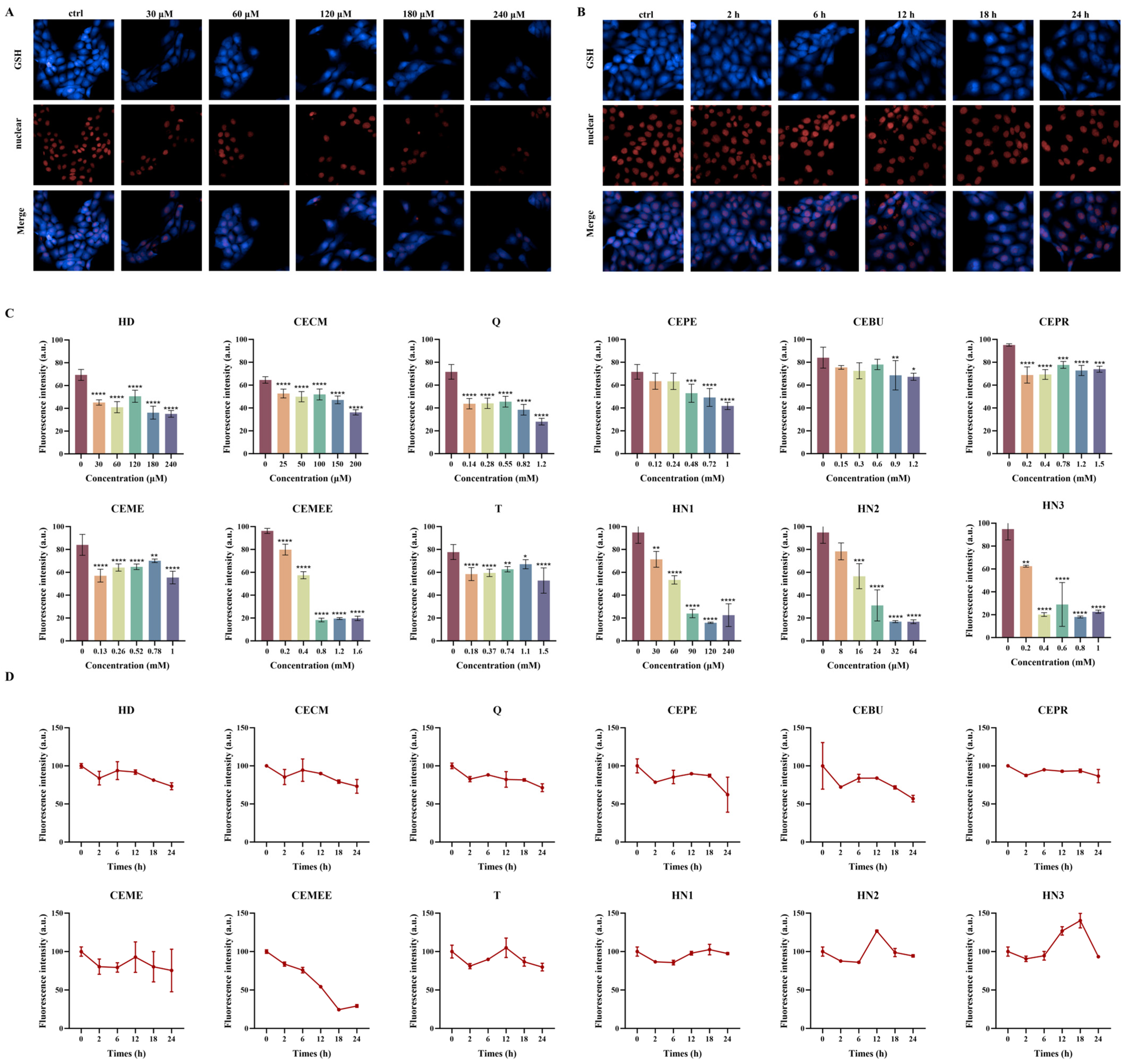
3.4. Evaluation of Different Alkylating Agents on the Capacity of Intracellular GSH Depletion
3.5. Dose- and Time-Dependent Depletion of Intracellular GSH by Alkylating Agent
3.6. Alkylating Agents Induce the Production of Reactive Oxygen Species
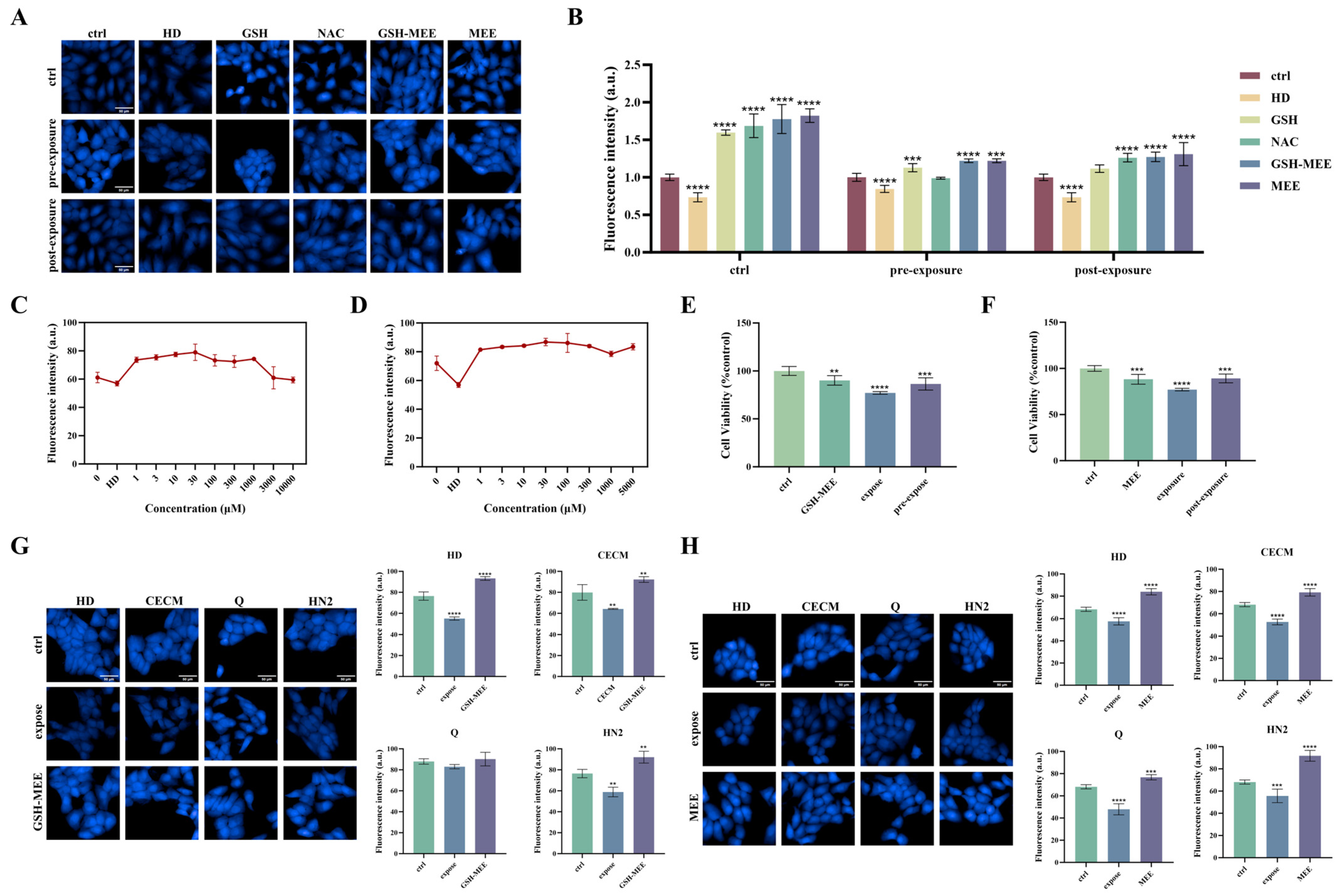
3.7. Evaluation of the Antagonistic Effect of Different Exogenous GSH Modulators
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, K.Y.; Shang, H.M.; Kong, X.Q.; Lin, W.Y. A novel near-infrared fluorescent probe with a large Stokes shift for biothiol detection and application in in vitro and in vivo fluorescence imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3836–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.Y.; Guan, Y.S.; Chen, Y.Z.; Wu, L.Z.; Tung, C.H.; Yang, Q.Z. BODIPY-Based Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensor for Highly Selective Detection of Glutathione over Cysteine and Homocysteine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 18928–18931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ji, X.; Zhou, J.L.; Chen, Z.J.; Dong, X.C.; Zhao, W.L. Pyridinium substituted BODIPY as NIR fluorescent probe for simultaneous sensing of hydrogen sulphide/glutathione and cysteine/homocysteine. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2018, 257, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.P.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.M.; Li, M.J.; Yi, C.Q.; Yang, M.S. A dual-mode nanosensor based on carbon quantum dots and gold nanoparticles for discriminative detection of glutathione in human plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 56, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Sun, Y.Q.; Huo, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.X.; Wang, L.F.; Zhang, P.; Song, D.; Shi, Y.W.; Guo, W. Simultaneous Fluorescence Sensing of Cys and GSH from Different Emission Channels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 574–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.Y.; Liao, K.X.; Zhou, Y.X.; Wen, T.; Quan, G.L.; Pan, X.; Wu, C.B. Application of glutathione depletion in cancer therapy: Enhanced ROS-based therapy, ferroptosis, and chemotherapy. Biomaterials 2021, 277, 121110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balendiran, G.K.; Dabur, R.; Fraser, D. The role of glutathione in cancer. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2004, 22, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, S.; Yoshikawa, M.; Nagano, O.; Yoshimi, K.; Saya, H.; Einaga, Y. In vivo assessment of cancerous tumors using boron doped diamond microelectrode. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.Y.; Fang, Y.Z.; Yang, S.; Lupton, J.R.; Turner, N.D. Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, R.; Schoneveld, O.J.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I. The central role of glutathione in the pathophysiology of human diseases. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 113, 234–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, T.W.; McNeely, K.; Louis, K.; Lecavalier, P.; Song, Y.F.; Villanueva, M.; Clewley, R. Comparative toxicity of mono- and bifunctional alkylating homologues of sulphur mustard in human skin keratinocytes. Toxicology 2017, 382, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, Y.H.; Heck, D.E.; An, Y.Q.; Laskin, D.L.; Laskin, J.D. Nitrogen Mustard Alkylates and Cross-Links p53 in Human Keratinocytes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 35, 636–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Liang, M.; Li, C.; Wang, D.; Gong, X.; Zheng, K. Synthesis of nitrogen mustard-based fluorophores for cell imaging and cytotoxicity studies. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2023, 14, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudabad, A.B.Z.; Saberi, M.; Pirzad, J. Critical role of GSH in sulfur mustard-induced oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in human skin fibroblast cell line. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2008, 7, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, H.; Li, B.F.; Zhao, X.; Zhuang, Y.L.; Ren, G.Y.; Yan, M.Y.; Cai, Y.P.; Zhang, X.K.; Chen, L. The effect of pacific cod (Gadus macrocephalus) skin gelatin polypeptides on UV radiation-induced skin photoaging in ICR mice. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Chen, J.; Qiao, Q.L.; Liu, X.G.; Xu, Z.C. A TICS-fluorophore based probe for dual-color GSH imaging. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 4943–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge, M.E.; Martinefski, M.R.; Bollini, M.; Pontel, L.B. UHPLC-HRMS-Based Analysis of S-Hydroxymethyl-Glutathione, GSH, and GSSG in Human Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2675, 117–132. [Google Scholar]
- De Mattia, G.; Bravi, M.C.; Laurenti, O.; Moretti, A.; Cipriani, R.; Gatti, A.; Mandosi, E.; Morano, S. Endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress in type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients without clinical macrovascular complications. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2008, 79, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorincz, T.; Szarka, A. The determination of hepatic glutathione at tissue and subcellular level. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2017, 88, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.W.; Cheng, D.; Li, P.P.; Xu, Z.J.; Zhu, X.H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, H.T.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, M.L.; Yao, S.Z. Au/Metal-Organic Framework Nanocapsules for Electrochemical Determination of Glutathione. Acs Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 4853–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodáková, J.; Preisler, J.; Foret, F.; Kubán, P. Sensitive determination of glutathione in biological samples by capillary electrophoresis with green (515 nm) laser-induced fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1391, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Mao, S.F.; Wang, S.Q.; Li, H.F.; Lin, J.M. Chip-based SALDI-MS for rapid determination of intracellular ratios of glutathione to glutathione disulfide. Sci. China-Chem. 2019, 62, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Gao, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhu, A.N.; Ying, Y.; Guo, X.Y.; Wu, Y.P.; Wen, Y.; Yang, H.F. MnO2 coated Au nanoparticles advance SERS detection of cellular glutathione. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 215, 114388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.H.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y.; Wu, Y.P.; Guo, X.Y.; Ying, Y.; Wen, Y.; Yang, H.F. Thiol-Disulfide Exchange Reaction for Cellular Glutathione Detection with Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11333–11339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, I.; Kode, A.; Biswas, S.K. Assay for quantitative determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide levels using enzymatic recycling method. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 3159–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, D.; Dalle-Donne, I.; Milzani, A.; Fanti, P.; Rossi, R. Analysis of GSH and GSSG after derivatization with N-ethylmaleimide. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1660–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.; Li, P.P.; Xu, Z.J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, M.L.; Yao, S.Z. Signal On-Off Electrochemical Sensor for Glutathione Based on a AuCu-Decorated Zr-Containing Metal-Organic Framework via Solid-State Electrochemistry of Cuprous Chloride. ACS Sens. J. 2022, 7, 2465–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.J.; Wu, J.F.; Wang, K.; Xu, H.; Qu, M.M.; Gao, Z.C.; Guo, L.; Xie, J.W. Facile and sensitive measurement of GSH/GSSG in cells by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Talanta 2021, 224, 121852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogel, A.I.; Martin, S.E.; Hasson, S.A. Application of Imaging-Based Assays in Microplate Formats for High-Content Screening. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1439, 273–304. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, L.H.J.; Beck, A.; Flockerzi, V.; Maurer, H.H.; Meyer, M.R. Cytotoxicity of new psychoactive substances and other drugs of abuse studied in human HepG2 cells using an adopted high content screening assay. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 301, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Gong, Y.X.; Jeong, E.M. Measuring Glutathione Regeneration Capacity in Stem Cells. Int. J. Stem Cells 2023, 16, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, J.; Okamura, A.; Takeuchi, K.; Hanioka, K.; Okada, A.; Ohata, T. High content analysis assay for prediction of human hepatotoxicity in HepaRG and HepG2 cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2016, 33, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohan, G.; Espinosa, J.A.; Chen, S.; Ang, K.K.; Arkin, M.R.; Markossian, S. Multiparametric High-Content Assays to Measure Cell Health and Oxidative Damage as a Model for Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Curr. Protoc. Chem. Biol. 2020, 12, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.Q.; Chen, J.W.; Bajic, A.; Zhang, C.W.; Song, X.Z.; Carroll, S.L.; Cai, Z.L.; Tang, M.L.; Xue, M.S.; Cheng, N.H.; et al. Quantitative real-time imaging of glutathione. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.W.; Jiang, X.Q.; Zhang, C.W.; MacKenzie, K.R.; Stossi, F.; Palzkill, T.; Wang, M.C.; Wang, J. Reversible Reaction-Based Fluorescent Probe for Real-Time Imaging of Glutathione Dynamics in Mitochondria. Acs. Sens. 2017, 2, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuwelt, A.; Wu, J.; Knap, N.; Losin, M.; Neuwelt, E.; Pagel, M.; Warmann, S.; Fuchs, J.; Czauderna, P.; Wozniak, M. Using Acetaminophen’s Toxicity Mechanism to Enhance Cisplatin Efficacy in Hepatocarcinoma and Hepatoblastoma Cell Lines. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastia, J.; Cristofol, R.; Martin, M.; Rodriguez-Farre, E.; Sanfeliu, C. Evaluation of fluorescent dyes for measuring intracellular glutathione content in primary cultures of human neurons and neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y. Cytom. Part A J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2003, 51, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangerich, A.; Debiak, M.; Birtel, M.; Ponath, V.; Balszuweit, F.; Lex, K.; Martello, R.; Burckhardt-Boer, W.; Strobelt, R.; Siegert, M.; et al. Sulfur and nitrogen mustards induce characteristic poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation responses in HaCaT keratinocytes with distinctive cellular consequences. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 244, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16 Rev. A.03; ScienceOpen: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Goerigk, L.; Hansen, A.; Bauer, C.; Ehrlich, S.; Najibi, A.; Grimme, S. A look at the density functional theory zoo with the advanced GMTKN55 database for general main group thermochemistry, kinetics and noncovalent interactions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 32184–32215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgül, C.; Nazıroğlu, M. TRPM2 channel protective properties of N-acetylcysteine on cytosolic glutathione depletion dependent oxidative stress and Ca2+ influx in rat dorsal root ganglion. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 106, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Mi, T.Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Y.Y.; Huang, N.; Gao, P.; Lee, J.M.; Guelakis, M.; Gu, X.L. Topical glutathione amino acid precursors protect skin against environmental and oxidative stress. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, B.Y.; Zhou, Y.X.; Liao, K.X.; Wen, T.; Lao, S.X.; Quan, G.L.; Pan, X.; Wu, C.B. “Pincer movement”: Reversing cisplatin resistance based on simultaneous glutathione depletion and glutathione S-transferases inhibition by redox-responsive degradable organosilica hybrid nanoparticles. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2074–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donovan, D.J.; Katkin, J.P.; Tamura, T.; Husser, R.; Xu, X.D.; Smith, C.V.; Welty, S.E. Gene transfer of mitochondrially targeted glutathione reductase protects H441 cells from t-butyl hydroperoxide-induced oxidant stresses. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1999, 20, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Xie, J. In Situ Evaluation of the GSH Depletion Ability of Various Alkylating Agents and the Protective Effect of Several Active Thiol Compounds Based on High-Content Cell Analysis. Toxics 2025, 13, 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121016
Guo J, Li Z, Wang J, Ma B, Zhang L, Wang H, Wu J, Xie J. In Situ Evaluation of the GSH Depletion Ability of Various Alkylating Agents and the Protective Effect of Several Active Thiol Compounds Based on High-Content Cell Analysis. Toxics. 2025; 13(12):1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121016
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jing, Zhi Li, Jiao Wang, Bo Ma, Liang Zhang, Hairui Wang, Jianfeng Wu, and Jianwei Xie. 2025. "In Situ Evaluation of the GSH Depletion Ability of Various Alkylating Agents and the Protective Effect of Several Active Thiol Compounds Based on High-Content Cell Analysis" Toxics 13, no. 12: 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121016
APA StyleGuo, J., Li, Z., Wang, J., Ma, B., Zhang, L., Wang, H., Wu, J., & Xie, J. (2025). In Situ Evaluation of the GSH Depletion Ability of Various Alkylating Agents and the Protective Effect of Several Active Thiol Compounds Based on High-Content Cell Analysis. Toxics, 13(12), 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121016







