Gut–Liver Axis Mediates the Combined Hepatointestinal Toxicity of Triclosan and Polystyrene Microplastics in Mice: Implications for Human Co-Exposure Risks
Highlights
- Co-exposure to TCS and PS exacerbated mouse hepatointestinal toxicity, oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Co-exposure to TCS and PS aggravated the destruction of gut microbiota homeostasis.
- Co-exposure to TCS and PS reduced the abundance of SCFA-producing bacteria.
- Gut-liver axis dysregulation mediated the cross-organ toxicity of the combined exposure.
- The results provide novel mechanistic evidence that co-exposure to microplastics and triclosan induces synergistic toxicity via the gut–liver axis.
- These findings critically advance the risk assessment of combined environmental pollutants by elucidating a central pathophysiological pathway, underscoring the imperative for regulatory frameworks to address mixture toxicity.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Histological Analysis
2.4. Immunohistochemistry Analysis
2.5. Serum Biochemical Indices
2.6. Assessment of Inflammatory Factors in Colon
2.7. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress Levels in Colon and Liver
2.8. Integrated Biomarker Response (IBR) Analysis
2.9. Gut Microbiome Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
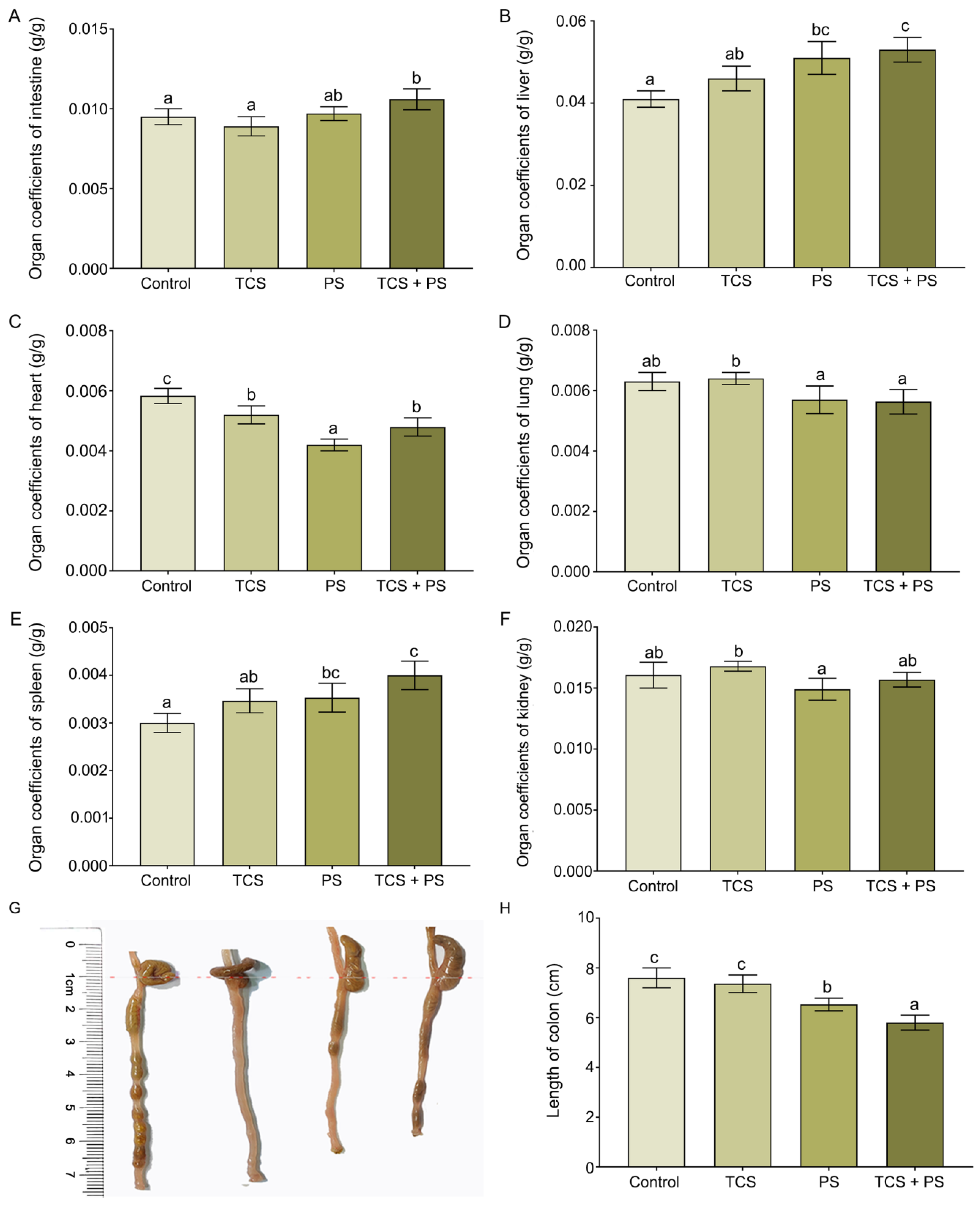
3.1. Changes in the Organ Coefficients of Mice Exposed to Polystyrene and Triclosan
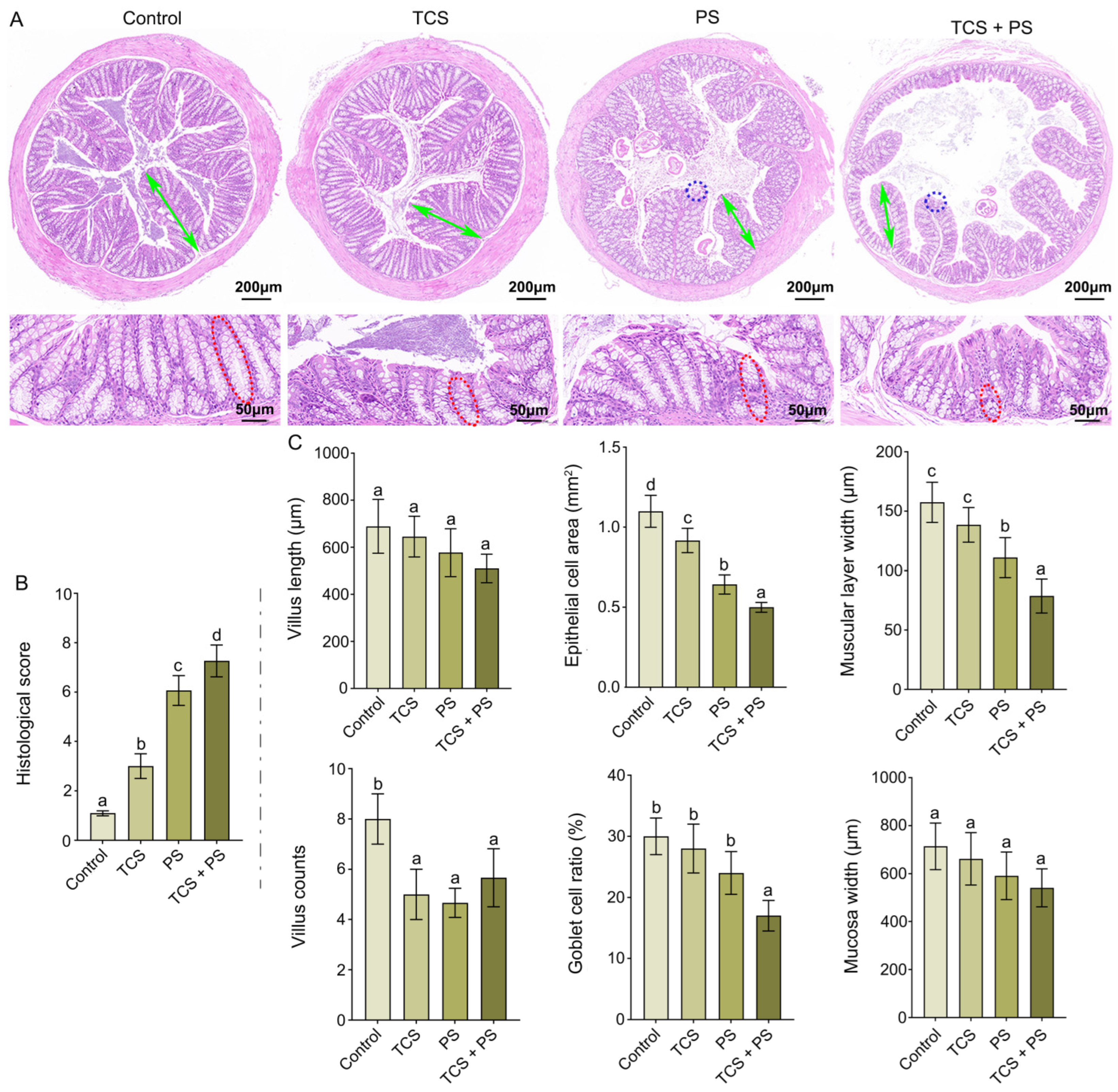
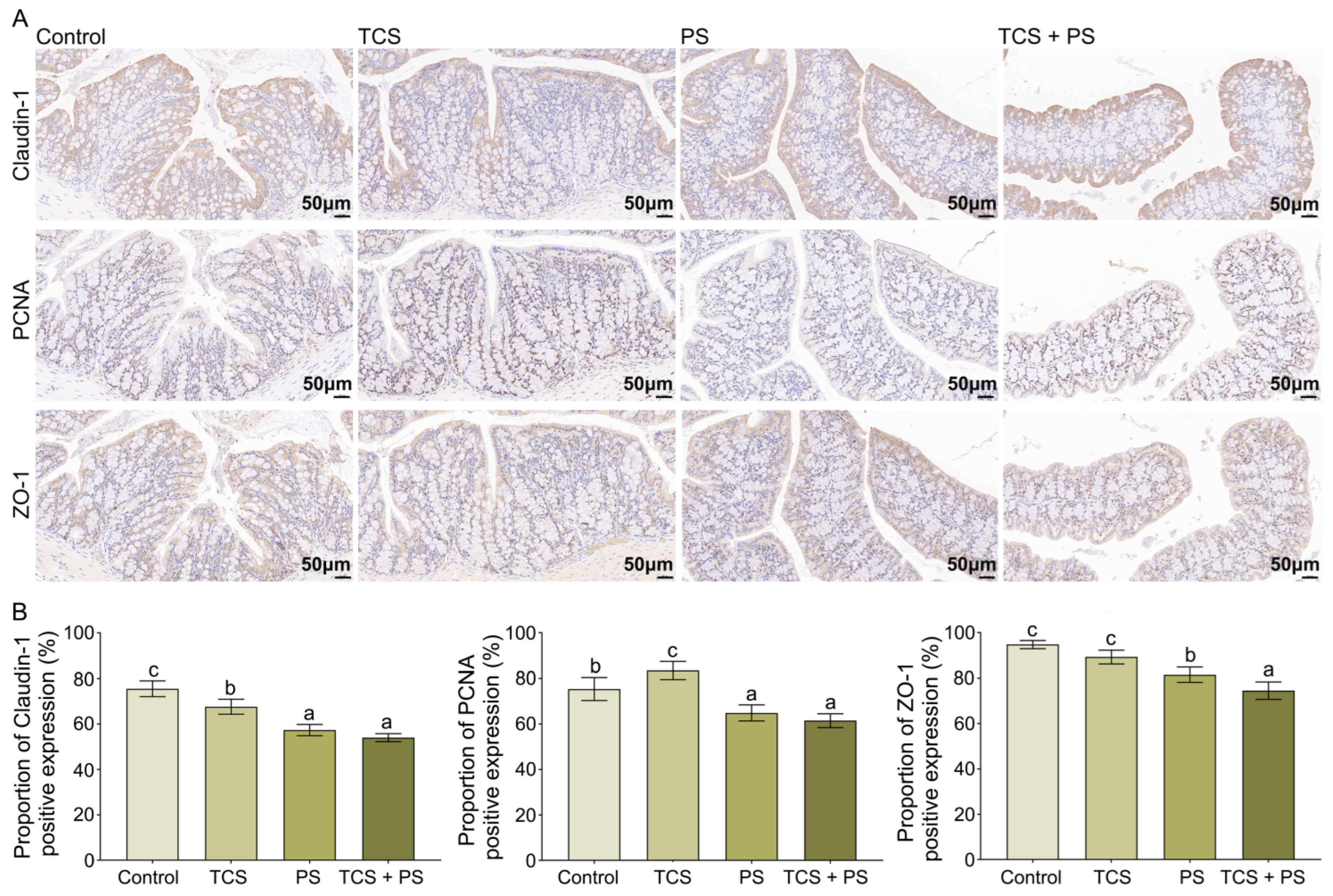
3.2. Destruction of the Intestinal Barrier
3.3. The Combined Effect of TCS and PS Aggravated Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in the Colon
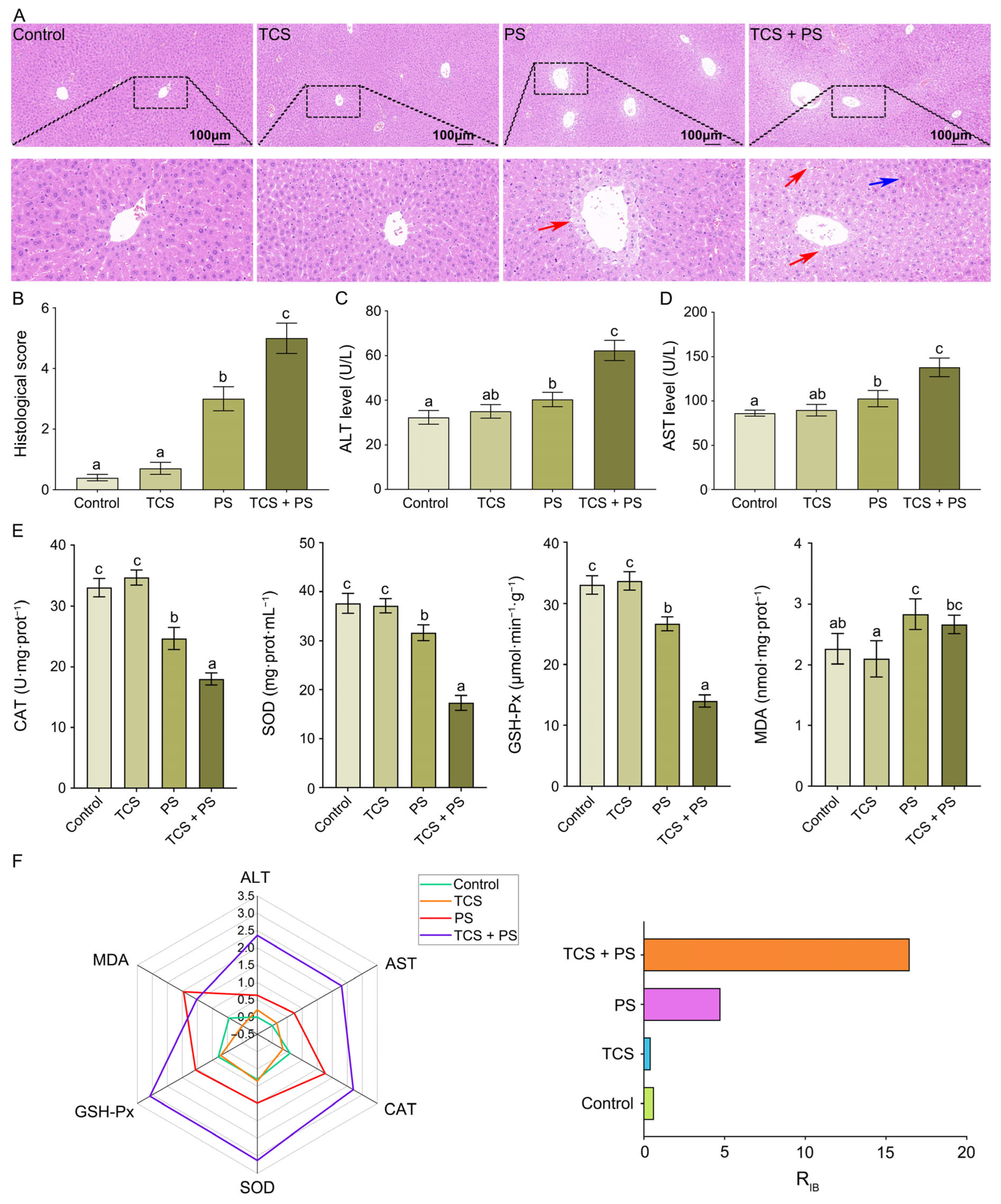
3.4. The Combined Effect of TCS and PS Aggravated Tissue Damage and Oxidative Stress of Liver
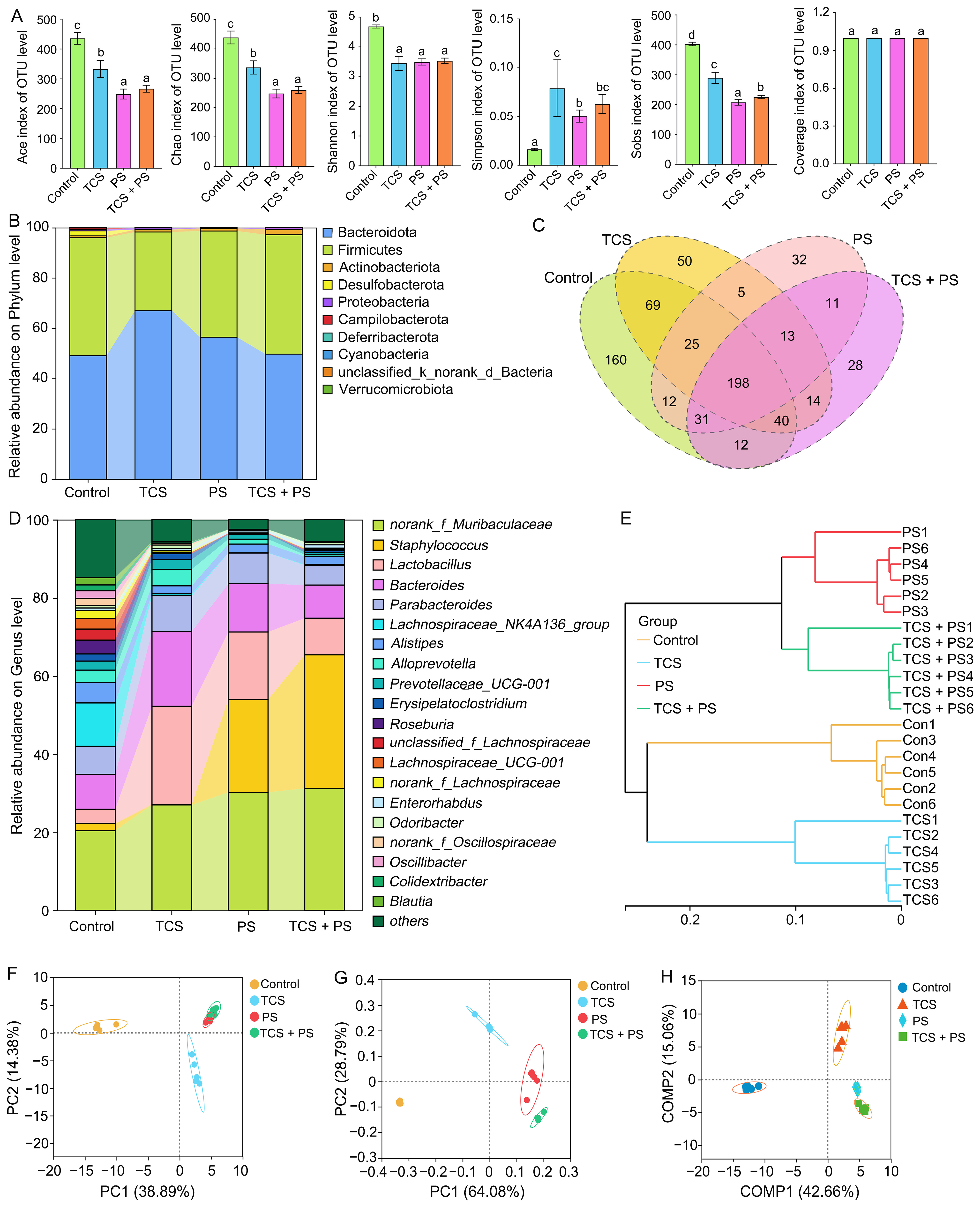
3.5. The Combined Effect of TCS and PS Aggravated Gut Dysbiosis
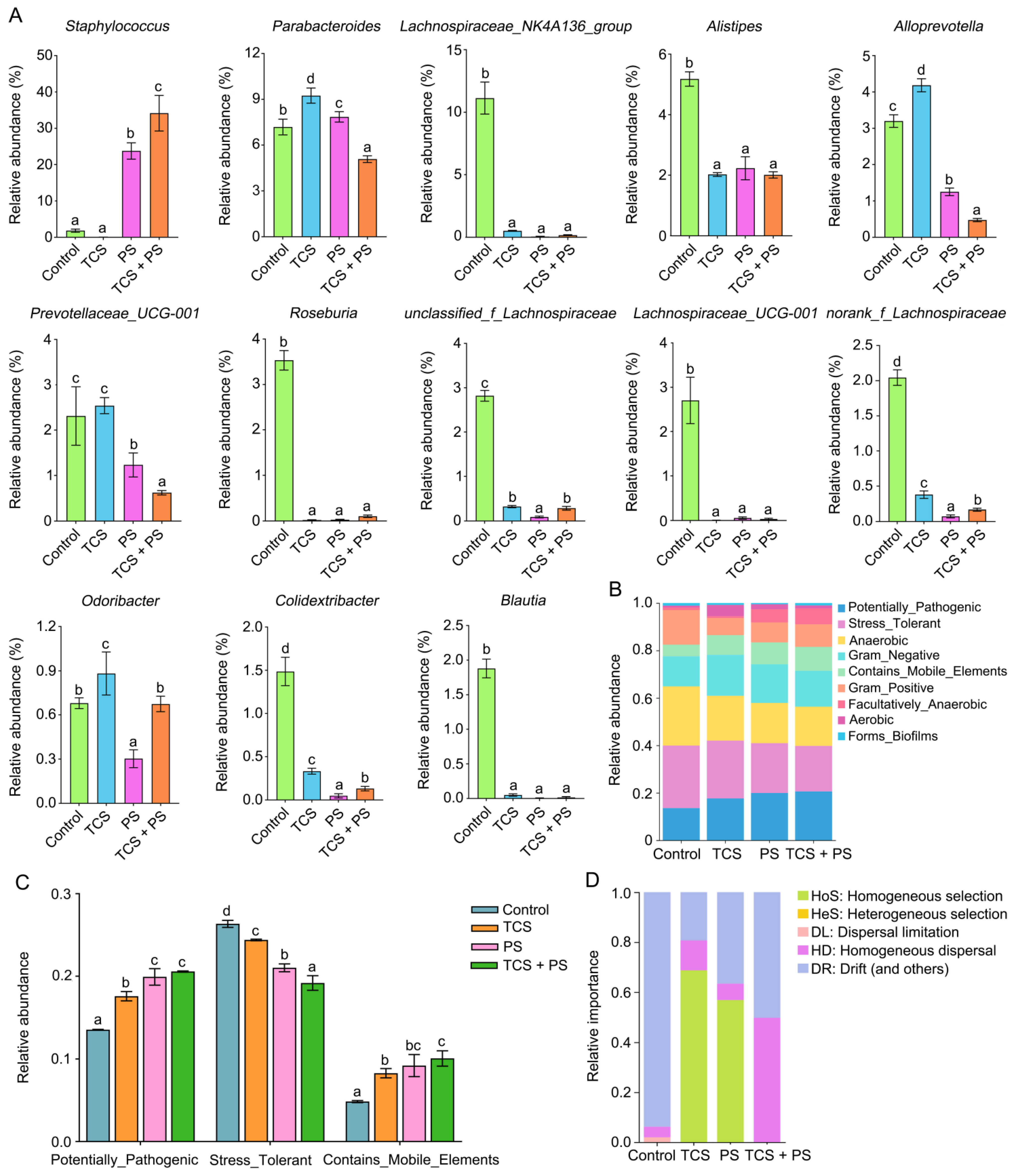
3.6. The Combined Effect of TCS and PS on the Key Genera Related to SCFA Production
3.7. The Combined Effect of TCS and PS on Gut Microbiota Assembly Mechanisms and Phenotypic Profiles
3.8. Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frias, J.P.G.L.; Nash, R. Microplastics: Finding a consensus on the definition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, G.D.; Rodríguez-Seijo, A.; Parati, M.; Johnston, B.; Erdem, E.; Cernava, T.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, X.; Axmann, I.M.; Lindblad, P.; et al. Harnessing photosynthetic microorganisms for enhanced bioremediation of microplastics: A comprehensive review. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 20, 100407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, A.; You, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, H.; Jiang, G.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Research progress on distribution, sources, identification, toxicity, and biodegradation of microplastics in the ocean, freshwater, and soil environment. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Xing, B. Environmental source, fate, and toxicity of microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, N.B.; Hüffer, T.; Thompson, R.C.; Hassellöv, M.; Verschoor, A.; Daugaard, A.E.; Rist, S.; Karlsson, T.; Brennholt, N.; Cole, M.; et al. Are We Speaking the Same Language? Recommendations for a Definition and Categorization Framework for Plastic Debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellos, D.M.C.; Chien, M.; Inoue, C.; Nakano, H.; Isobe, A.; Onda, D.F.L.; Watanabe, K.; Bacosa, H.P. Mesoplastics: A review of contamination status, analytical methods, pollution sources, potential risks, and future perspectives of an emerging global environmental pollutant. Toxics 2025, 13, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Feng, Q.; Wang, J. Mini-review of microplastics in the atmosphere and their risks to humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenner, L.C.; Rotchell, J.M.; Bennett, R.T.; Cowen, M.; Tentzeris, V.; Sadofsky, L.R. Detection of microplastics in human lung tissue using muFTIR spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borriell, L.; Scivicco, M.; Cacciola, N.A.; Esposito, F.; Severino, L.; Cirillo, T. Microplastics, a global issue: Human exposure through environmental and dietary sources. Foods 2023, 12, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvatits, T.; Tamminga, M.; Liu, B.; Sebode, M.; Carambia, A.; Fischer, L.; Püschel, K.; Huber, S.; Fischer, E.K. Microplastics detected in cirrhotic liver tissue. eBioMedicine 2022, 82, 104147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhu, L.; Weng, J.; Jin, Z.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z. Detection and characterization of microplastics in the human testis and semen. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, E.; Etienne-Mesmin, L.; Grootaert, C.; Jelsbak, L.; Syberg, K.; Blanquet-Diot, S.; Mercier-Bonin, M. Microplastics in the human digestive environment: A focus on the potential and challenges facing In Vitro gut model development. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, T.; Hamaguchi, M.; Hasegawa, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Majima, S.; Senmaru, T.; Ushigome, E.; Nakanishi, N.; Asano, M.; Yamazaki, M.; et al. Oral exposure to polystyrene microplastics of mice on a normal or high-fat diet and intestinal and metabolic outcomes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 27006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, J.; Zhang, L.; Han, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Gao, A. Polystyrene micro-/nanoplastics induced hematopoietic damages via the crosstalk of gut microbiota, metabolites, and cytokines. Environ. Int. 2022, 161, 107131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, H.; Chu, C.; Huang, C.; Chia, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lee, Y. Polystyrene microplastics induce hepatic lipid metabolism and energy disorder by upregulating the NR4A1-AMPK signaling pathway. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 369, 125850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.C.; Pan, X.Q.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lai, K.P.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.X. Unraveling the impact of micro- and nano-sized polymethyl methacrylate on gut microbiota and liver lipid metabolism: Insights from oral exposure studies. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 373, 126157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yueh, M.F.; Tukey, R.H. Triclosan: A widespread environmental toxicant with many biological effects. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 56, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Yang, F.; Luo, P.; Xie, L.; Chen, J.; Guan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xu, T.; Hao, H.; Chen, B.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomic dissection of the cellular and molecular events underlying the triclosan-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Mil. Med. Res. 2023, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, J.; Nishimura, N.; Shimada, Y. Toxicological interactions of microplastics/nanoplastics and environmental contaminants: Current knowledge and future perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 123913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geens, T.; Neels, H.; Covaci, A. Distribution of bisphenol-A, triclosan and n-nonylphenol in human adipose tissue, liver and brain. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Tian, Y.; Pan, Y.; Sheng, N.; Dai, H.; Fan, X.; Liu, X.; Bai, X.; Dai, J. Exposure and potential risks of thirteen endocrine-disrupting chemicals in pharmaceuticals and personal care products for breastfed infants in China. Environ. Int. 2024, 192, 109032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanidad, K.Z.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, G. Triclosan, a common antimicrobial ingredient, on gut microbiota and gut health. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, W.; Romano, K.A.; Gu, M.; Sanidad, K.Z.; Kim, D.; Yang, J.; Schmidt, B.; Panigrahy, D.; Pei, R.; et al. A common antimicrobial additive increases colonic inflammation and colitis-associated colon tumorigenesis in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaan4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yueh, M.; He, F.; Chen, C.; Vu, C.; Tripathi, A.; Knight, R.; Karin, M.; Chen, S.; Tukey, R.H. Triclosan leads to dysregulation of the metabolic regulator FGF21 exacerbating high fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 31259–31266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yueh, M.F.; Taniguchi, K.; Chen, S.; Evans, R.M.; Hammock, B.D.; Karin, M.; Tukey, R.H. The commonly used antimicrobial additive triclosan is a liver tumor promoter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17200–17205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, R.; Tian, W.; Qin, C.; Li, P.; Sun, Y.; Long, M.; Yang, S. Polystyrene microplastics and cadmium drive the gut-liver axis through the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway to cause toxic effects on broilers. Toxics 2025, 13, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.C. The gut is a potential trigger of exercise-induced inflammatory responses. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1998, 76, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xiang, D.; Zhou, J.; Xie, J. Protective effect of Dictyophora rubrovolvata extract on intestinal and liver tissue toxicity induced by metformin disinfection byproducts. Toxics 2025, 13, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Lv, W. The role of gut microbiota in some liver diseases: From an immunological perspective. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 923599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Oh, Y.; Park, H.E.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.S. Synergistic toxic mechanisms of microplastics and triclosan via multixenobiotic resistance (MXR) inhibition-mediated autophagy in the freshwater water flea Daphnia magna. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 165214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Wang, Z.; Pan, X.; Zheng, L.; Xu, Y.; Qiao, Q. Effects of triclosan adsorption on intestinal toxicity and resistance gene expression in Xenopus tropicalis with different particle sizes of polystyrene. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 146, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Cen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Lin, X.; Liang, T.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Qiao, Q.; Huang, L.; Xiong, K. Triclosan-loaded aged microplastics exacerbate oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in Xenopus tropicalis tadpoles via increased bioaccumulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xian, H.; Ye, R.; Zhong, Y.; Liang, B.; Huang, Y.; Dai, M.; Guo, J.; Tang, S.; Ren, X.; et al. Gender-specific effects of polystyrene nanoplastic exposure on triclosan-induced reproductive toxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 932, 172876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhao, F.; Wang, S.; Liu, F.; Liu, G. Joint toxicity of microplastics with triclosan to marine microalgae Skeletonema costatum. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pu, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, J.; Yan, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Qian, Q. Comparative impact of pristine and aged microplastics with triclosan on lipid metabolism in larval zebrafish: Unveiling the regulatory role of miR-217. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 929, 172580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zheng, L.; Gao, H.; Mao, D.; Luo, Y. Triclosan exposure exaggerates injury of intestine and liver function induced by high fat diet in mice. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2021, 16, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, B.; Wu, D. A comparative study of effects of short-term oral exposure to ozone-aged polystyrene microplastics and standard polystyrene microplastic beads on gut microbiota structure and energy metabolism-related hormones in mice. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2022, 17, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, X.; Ding, Z.; Xu, M.; Wu, L.; Li, X.; Xing, M.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Differential impacts of environmentally relevant microplastics on gut barrier integrity in mice fed high-fat diet versus normal chow diet. Metabolites 2025, 15, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, W.; Chan, H.; Peng, J.; Zhu, P.; Li, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Z.; et al. Polystyrene microplastics induce size-dependent multi-organ damage in mice: Insights into gut microbiota and fecal metabolites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wu, K.; Xu, L.; Cen, Y.; Ni, J.; Chen, J.; Zheng, W.; Liu, W. Methanol extract of Inonotus obliquus improves type 2 diabetes mellitus through modifying intestinal flora. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 13, 1103972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, M.; Mianabadi, M.; Zargari, M.; Karimpour, A.; Khalafi, M.; Amiri, F.T. Effects of olive oil supplementation on sodium arsenate-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milart, P.; Paluszkiewicz, P.; Dobrowolski, P.; Tomaszewska, E.; Smolinska, K.; Debinska, I.; Gawel, K.; Walczak, K.; Bednarski, J.; Turska, M.; et al. Kynurenic acid as the neglected ingredient of commercial baby formulas. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Yan, S.; Meng, Z.; Tian, S.; Jia, M.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Diao, J.; Zhu, W. Combined ingestion of polystyrene microplastics and epoxiconazole increases health risk to mice: Based on their synergistic bioaccumulation In Vivo. Environ. Int. 2022, 166, 107391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zheng, L.; Duan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Gao, H.; Mao, D.; Luo, Y. Gut microbiota exaggerates triclosan-induced liver injury via gut-liver axis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Chen, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, C.; Liang, T.; Zheng, L.; Xu, Y.; Huang, L.; Qiao, Q.; Xiong, K. New insight into intestinal toxicity accelerated by aged microplastics with triclosan: Inflammation regulation by gut microbiota-bile acid axis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 492, 138308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Shen, M.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wen, H.; Lu, H.; Chen, S.; Xie, J. Purple red rice anthocyanins alleviate intestinal damage in cyclophosphamide-induced mice associated with modulation of intestinal barrier function and gut microbiota. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Chen, Q.; Xu, L.; Chen, X. Combined exposure to polyvinyl chloride and polystyrene microplastics induces liver injury and perturbs gut microbial and serum metabolic homeostasis in mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Liu, H.; Ma, H.; Hu, T.; Luo, P.; Wei, S. Grifola frondosa polysaccharide’s therapeutic potential in oxazolone-induced ulcerative colitis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 344, 122517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.K.; Meena, A.S.; Gangwar, R.; Szabo, E.; Balogh, A.; Lee, S.C.; Vandewalle, A.; Tigyi, G.; Rao, R. LPAR2 receptor activation attenuates radiation-induced disruption of apical junctional complexes and mucosal barrier dysfunction in mouse colon. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 11641–11657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, L.; Dong, J.; Yuan, Z.; Yao, W.; Ji, P.; Hua, Y.; Wei, Y. Shaoyao decoction improves damp-heat colitis by activating the AHR/IL-22/STAT3 pathway through tryptophan metabolism driven by gut microbiota. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 326, 117874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lv, X.; He, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. Chronic exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics induces intestinal mechanical and immune barrier dysfunction in mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 269, 115749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Tian, S.; Sun, W.; Liu, L.; Yan, S.; Huang, S.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, Z. Effects of exposure to prothioconazole and its metabolite prothioconazole-desthio on oxidative stress and metabolic profiles of liver and kidney tissues in male mice. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shao, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Wei, J.; Yang, C.; Cai, Z. Integration of metabolomics and lipidomics reveals metabolic mechanisms of triclosan-induced toxicity in human hepatocytes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5406–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Nie, J.; Beyea, J.; Rudra, C.B.; Browne, R.W.; Bonner, M.R.; Mu, L.; Trevisan, M.; Freudenheim, J.L. Exposure to traffic emissions: Associations with biomarkers of antioxidant status and oxidative damage. Environ. Res. 2013, 121, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Sun, H.; Yang, J.; et al. The effects of combined environmental factors on the intestinal flora of mice based on ground simulation experiments. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Kou, B.; Cai, M.; Wu, J.; Dong, J.; Meng, Q.; Wang, Y.; et al. Dysregulated hepatic lipid metabolism and gut microbiota associated with early-stage NAFLD in ASPP2-deficiency mice. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 974872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Cui, L.; Liao, H.; Junaid, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Gao, D.; Zheng, Y.; Lu, S.; Qiu, J.; et al. Combined exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics and bisphenol A induces hepato- and intestinal-toxicity and disturbs gut microbiota in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatelier, E.L.; Nielsen, T.; Qin, J.; Prifti, E.; Hildebrand, F.; Falony, G.; Almeida, M.; Arumugam, M.; Batto, J.; Kennedy, S.; et al. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature 2013, 500, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Microbiota and diabetes: An evolving relationship. Gut 2014, 63, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, M.A.; Schloss, P.D. Looking for a signal in the noise: Revisiting obesity and the microbiome. mBio 2016, 7, e01018-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, Y.; He, Y. The variation characteristics of fecal microbiota in remission UC patients with anxiety and depression. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1237256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Yokoyama, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Benegiamo, G.; Hirayama, A.; Zhu, Q.; Kitamura, N.; Sugizaki, T.; Morimoto, K.; Itoh, H.; et al. Asperuloside improves obesity and type 2 diabetes through modulation of gut microbiota and metabolic signaling. iScience 2020, 23, 101522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, K.; Shen, J.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Xiao, P. Huangqin tea total flavonoids-gut microbiota interactions: Based on metabolome and microbiome analysis. Foods 2023, 12, 4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velotti, F.; Bernini, R. Hydroxytyrosol interference with inflammaging via modulation of inflammation and autophagy. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Xue, Y.; Cao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Pang, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, W. Raffinose ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice by modulating gut microbiota and targeting the inflammatory TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB signaling pathway. Foods 2024, 13, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Feng, Y.; Liu, H.; Kong, D.; Hsueh, C.; Shi, X.; Wu, Q.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Gut microbiome and metabolome changes in mice with acute vestibular deficit. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 821780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Liu, Y.; Hoang, T.K.; Tian, X.; Taylor, C.M.; Luo, M.; Tran, D.Q.; Tatevian, N.; Rhoads, J.M. Antibiotic-modulated microbiome suppresses lethal inflammation and prolongs lifespan in Treg-deficient mice. Microbiome 2019, 7, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marttinen, M.; Ala-Jaakkola, R.; Laitila, A.; Lehtinen, M.J. Gut microbiota, probiotics and physical performance in athletes and physically active individuals. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; He, Y.; Luo, M.; Liu, S.; Hou, J.; Cao, B.; An, X. Transfer toxicity of polystyrene microplastics In Vivo: Multi-organ crosstalk. Environ. Int. 2025, 202, 109604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Ling, Z.; Nie, X.; Liu, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S. Microbial diversity and community structure of Chinese fresh beef during cold storage and their correlations with off-flavors. Foods 2024, 13, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ning, D.; Yu, W.; Chen, G.; Tao, X.; Zhou, J.; Du, Z.; Mu, D. Niche modification by sulfate-reducing bacteria drives microbial community assembly in anoxic marine sediments. mBio 2023, 14, e03535-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, W.; Xie, J. Gut–Liver Axis Mediates the Combined Hepatointestinal Toxicity of Triclosan and Polystyrene Microplastics in Mice: Implications for Human Co-Exposure Risks. Toxics 2025, 13, 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110977
Liu H, Zhou J, Cheng Z, Liu W, Xie J. Gut–Liver Axis Mediates the Combined Hepatointestinal Toxicity of Triclosan and Polystyrene Microplastics in Mice: Implications for Human Co-Exposure Risks. Toxics. 2025; 13(11):977. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110977
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Huijuan, Jie Zhou, Zhifei Cheng, Wenhao Liu, and Jiao Xie. 2025. "Gut–Liver Axis Mediates the Combined Hepatointestinal Toxicity of Triclosan and Polystyrene Microplastics in Mice: Implications for Human Co-Exposure Risks" Toxics 13, no. 11: 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110977
APA StyleLiu, H., Zhou, J., Cheng, Z., Liu, W., & Xie, J. (2025). Gut–Liver Axis Mediates the Combined Hepatointestinal Toxicity of Triclosan and Polystyrene Microplastics in Mice: Implications for Human Co-Exposure Risks. Toxics, 13(11), 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110977






