First Human Biomonitoring Evidence of Strobilurin Fungicide Exposure in South China: Impact on Oxidative Stress and Liver Damage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Study Population and Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Extraction and Instrumental Analysis
2.4. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
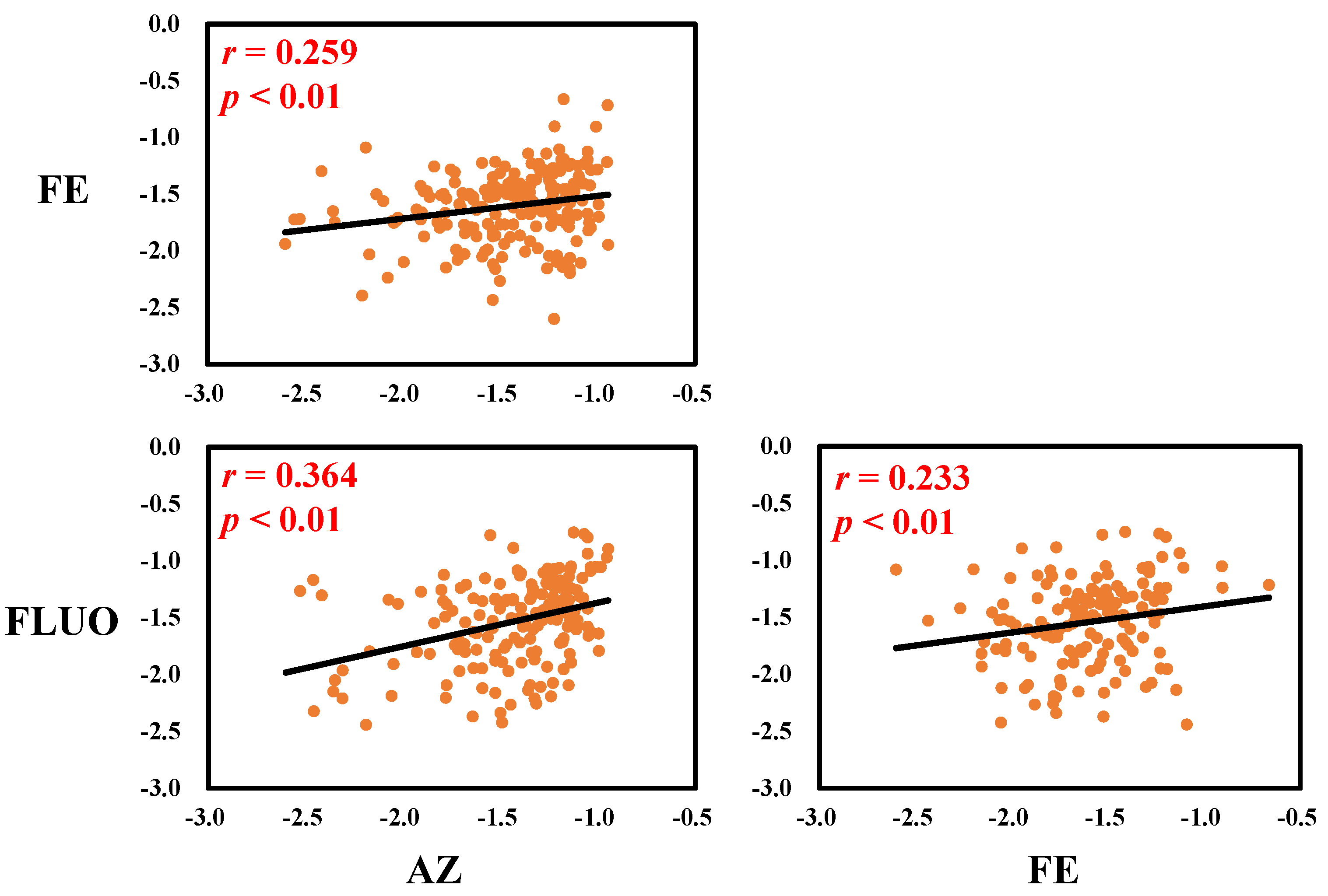
3.1. Serum Concentrations and Correlations of SFs in Serum
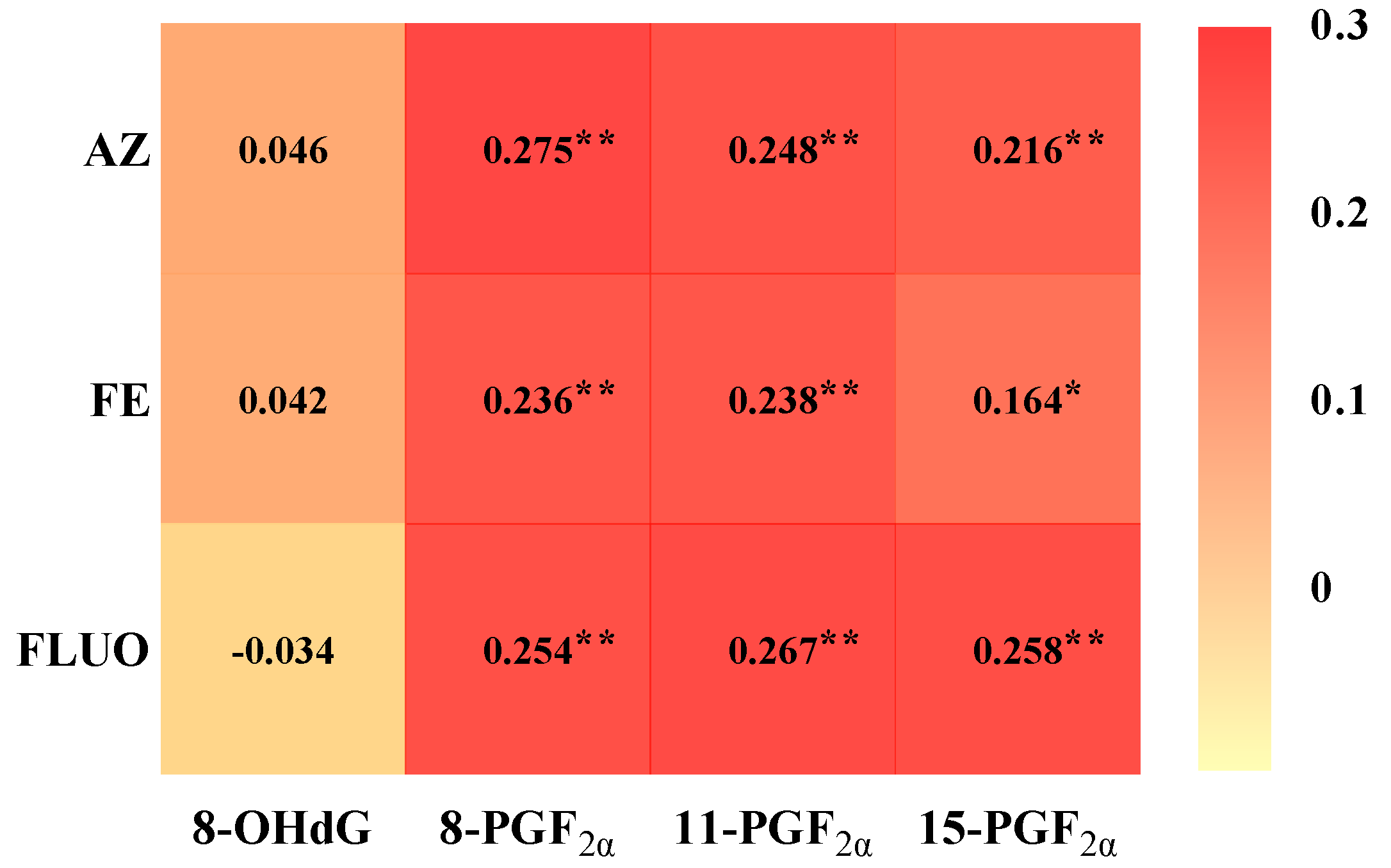
3.2. Associations Between Serum Concentrations of SFs and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers
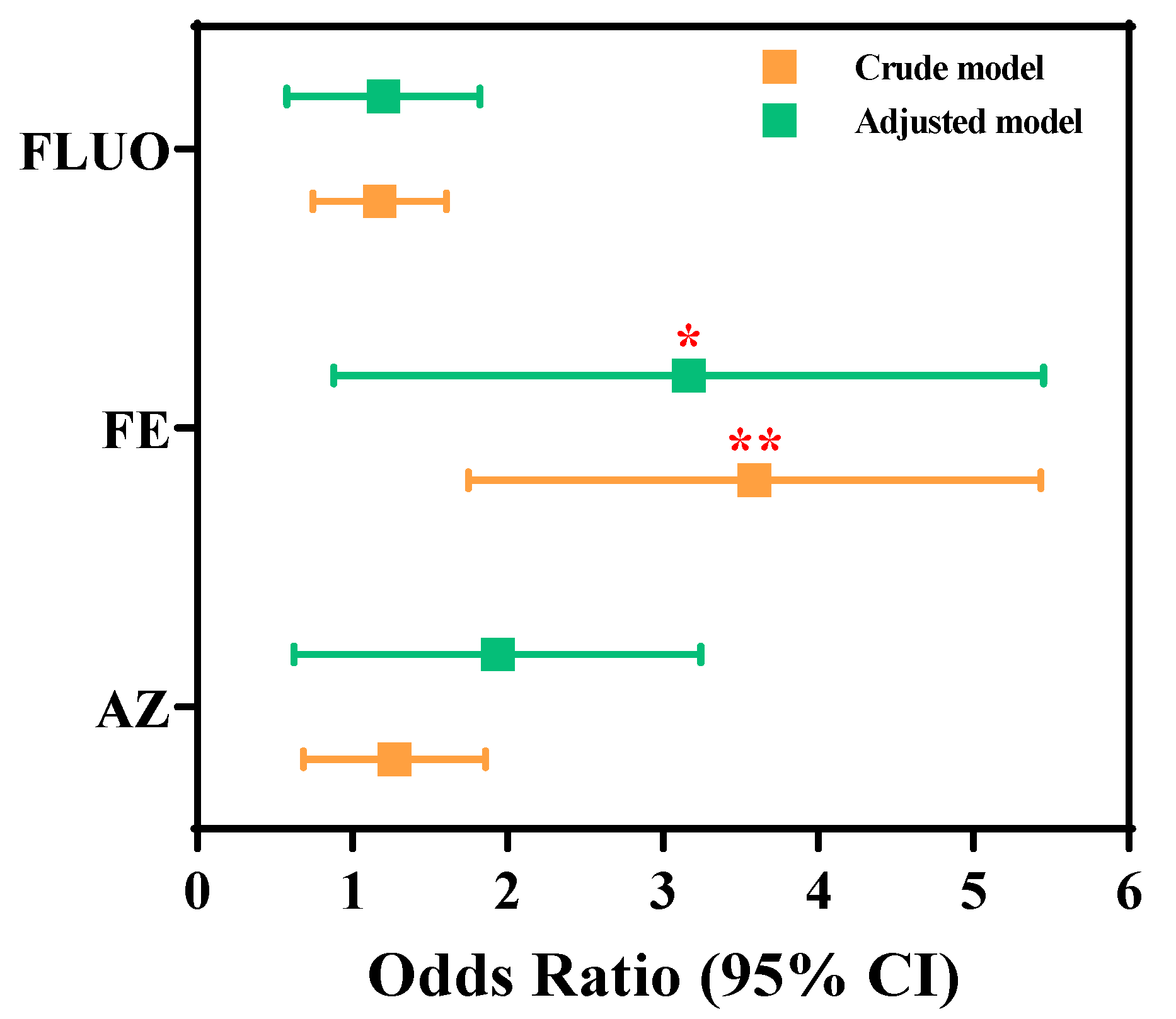
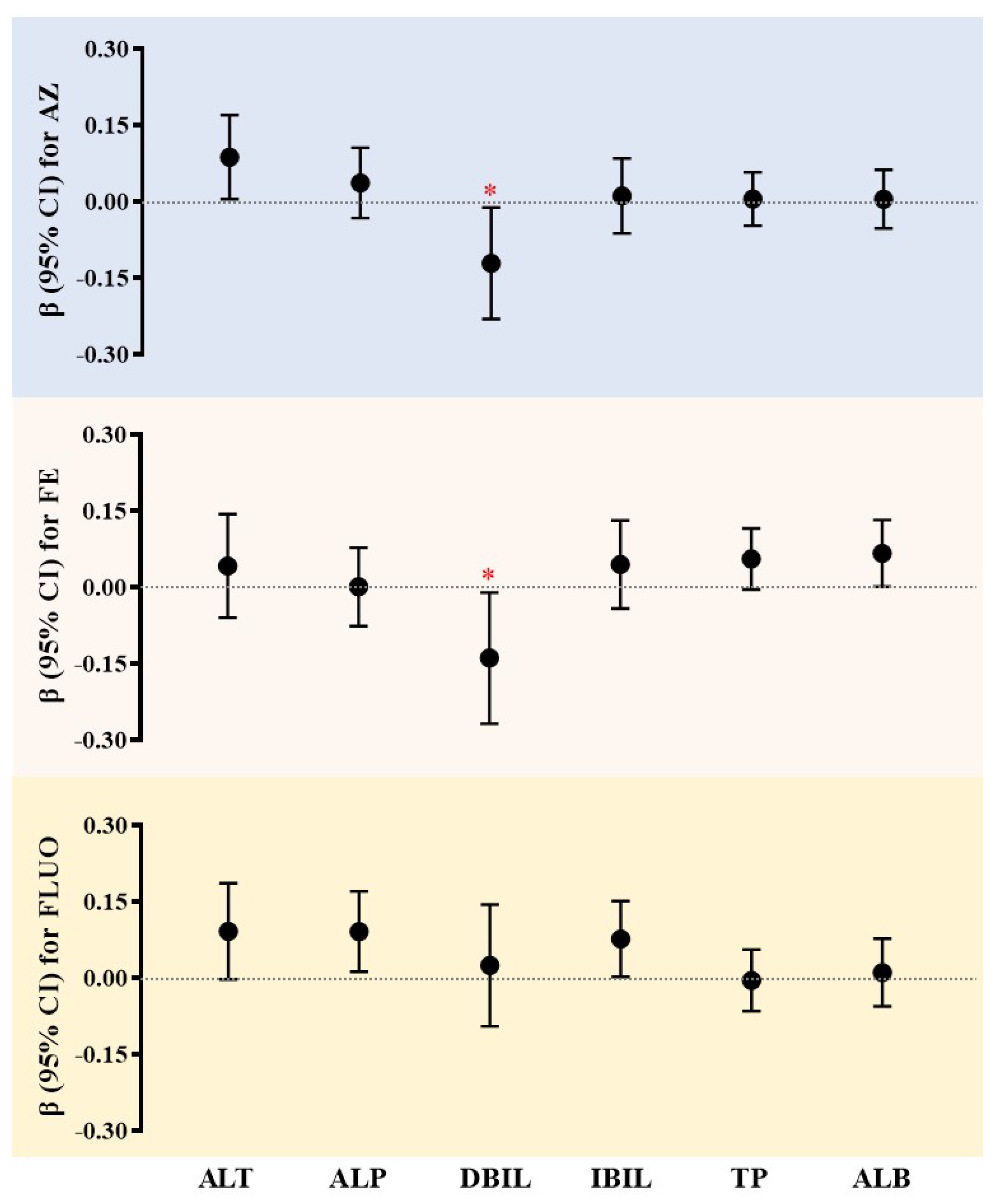
3.3. Associations Between SF Exposure and the Occurrence of Liver Damage
4. Discussion
5. Strengths and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, T.; Xu, Y.; Du, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L. Ecotoxicology of Strobilurin Fungicides. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Jia, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Sial, M.U.; Jiang, H. Embryonic Development and Oxidative Stress Effects in the Larvae and Adult Fish Livers of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Exposed to the Strobilurin Fungicides, Kresoxim-Methyl and Pyraclostrobin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Geological Survey. Estimated Annual Agricultural Pesticide Use. 2019. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/tools/estimated-annual-agricultural-pesticide-use (accessed on 4 March 2019).
- Leite, F.G.; Sampaio, C.F.; Pires, J.A.C.; de Oliveira, D.P.; Dorta, D.J. Toxicological Impact of Strobilurin Fungicides on Human and Environmental Health: A Literature Review. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 2024, 59, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, E.M.; Rushing, R.; Hoffman, K.; Phillips, A.L.; Hammel, S.C.; Zylka, M.J.; Stapleton, H.M. Strobilurin Fungicides in House Dust: Is Wallboard a Source? J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2020, 30, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Qin, Y.J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, T.; Zhao, Y.H.; Wang, X.H.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Yan, B. Relative Comparison of Strobilurin Fungicides at Environmental Levels: Focus on Mitochondrial Function and Larval Activity in Early Staged Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxicology 2021, 452, 152706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, E.E.; Hladik, M.L.; Main, A.R.; Cahn, M.; Orlando, J.L.; Teerlink, J. Comparing Imidacloprid, Clothianidin, and Azoxystrobin Runoff from Lettuce Fields Using a Soil Drench or Treated Seeds in the Salinas Valley, California. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 315, 120325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esser, L.; Yu, C.-A.; Xia, D. Structural Basis of Resistance to Anti-Cytochrome Bc1 Complex Inhibitors: Implication for Drug Improvement. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 704–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.; Chai, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, C. Toxicity of Three Strobilurins (Kresoxim-Methyl, Pyraclostrobin, and Trifloxystrobin) on Daphnia Magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.T.; Wen, Y.; He, J.; Zhao, Y.H. Freshwater Quality Criteria of Four Strobilurin Fungicides: Interspecies Correlation and Toxic Mechanism. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, F.; Zhao, F.; Yang, Y.; Teng, M.; Wang, C.; Qiu, L. Developmental Toxicity, Oxidative Stress and Immunotoxicity Induced by Three Strobilurins (Pyraclostrobin, Trifloxystrobin and Picoxystrobin) in Zebrafish Embryos. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, E.; Galougahi, K.K.; Liu, C.-C.; Bhindi, R.; Figtree, G.A. Biological Markers of Oxidative Stress: Applications to Cardiovascular Research and Practice. Redox Biol. 2013, 1, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Eryani, L.; Wahlang, B.; Falkner, K.C.; Guardiola, J.J.; Clair, H.B.; Prough, R.A.; Cave, M. Identification of Environmental Chemicals Associated with the Development of Toxicant-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Rodents. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 43, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Li, H.; Zhao, F.; Wu, P.; Qian, L.; Huang, L.; Pang, S.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Qiu, L. Parental Exposure to Azoxystrobin Causes Developmental Effects and Disrupts Gene Expression in F1 Embryonic Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Wu, P.; Huang, L.; Li, H.; Qian, L.; Pang, S.; Qiu, L. Short-Term Developmental Effects and Potential Mechanisms of Azoxystrobin in Larval and Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 198, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.M.; Paranjape, S.R.; Wolter, J.M.; Salazar, G.; Zylka, M.J. High-Throughput Screening and Classification of Chemicals and Their Effects on Neuronal Gene Expression Using RASL-Seq. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serim, I.; Demirel, H.H.; Zemheri-Navruz, F.; Ince, S. Taurine Exhibits Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antiapoptotic Effects against Pyraclostrobin Exposure in Rats. Toxicol. Res. 2024, 13, tfae120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodkin, I.; Valasek, M.A.; Bettencourt, R.; Cachay, E.; Loomba, R. Clinical, Biochemical and Histological Differences between HIV-Associated NAFLD and Primary NAFLD: A Case-Control Study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 41, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulds, C.E.; Trevino, L.S.; York, B.; Walker, C.L. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Fatty Liver Disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heindel, J.J.; Blumberg, B.; Cave, M.; Machtinger, R.; Mantovani, A.; Mendez, M.A.; Nadal, A.; Palanza, P.; Panzica, G.; Sargis, R.; et al. Metabolism Disrupting Chemicals and Metabolic Disorders. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 68, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global Epidemiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Meta-Analytic Assessment of Prevalence, Incidence, and Outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, C.; Anstee, Q.M.; Teresa Arias-Loste, M.; Bantel, H.; Bellentani, S.; Caballeria, J.; Colombo, M.; Craxi, A.; Crespo, J.; Day, C.P.; et al. Modeling NAFLD Disease Burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the Period 2016–2030. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.D.; Hill, K.E.; Burk, R.F.; Nammour, T.M.; Badr, K.F.; Roberts, L.J., 2nd. A Series of Prostaglandin F2-like Compounds Are Produced in Vivo in Humans by a Non-Cyclooxygenase, Free Radical-Catalyzed Mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 9383–9387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.J., II; Morrow, J.D. Measurement of F2-Isoprostanes as an Index of Oxidative Stress in Vivo. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavanidis, A.; Vlachogianni, T.; Fiotakis, C. 8-Hydroxy-2′ -Deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG): A Critical Biomarker of Oxidative Stress and Carcinogenesis. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2009, 27, 120–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Y.; Song, S.; Zhang, T. Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances, Neonicotinoid Insecticides, Benzotriazoles and Benzothiazoles: Associations with Human Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2024, 6, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Gao, Y.; Feng, S.; Cheng, Z.; Huang, H.; Xue, J.; Zhang, T.; Sun, H. Widespread Occurrence of Two Typical N, N’-Substituted p-Phenylenediamines and Their Quinones in Humans: Association with Oxidative Stress and Liver Damage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 468, 133835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, Q. Secondary Factors and Diagnosis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Chin. Hepatol. 2022, 27, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Fan, J.G. Guidelines of Prevention and Treatment for Alcoholic Liver Disease (2018, China). J. Dig. Dis. 2019, 20, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, B.; He, Y.; Hong, D.; Song, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T. Triclosan and Triclocarbon in Maternal-Fetal Serum, Urine, and Amniotic Fluid Samples and Their Implication for Prenatal Exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Bai, X.; Zhang, T.; Xue, J.; Lu, S.; Kannan, K. Placental Transfer of Bisphenol Diglycidyl Ethers (BDGEs) and Its Association with Maternal Health in a Population in South of China. Eco-Environ. Health 2022, 1, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, E.T.; Lopes, I.; Pardal, M.A. Occurrence, Fate and Effects of Azoxystrobin in Aquatic Ecosystems: A Review. Environ. Int. 2013, 53, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xia, W.; Wan, Y.; Xu, S. Azole and Strobilurin Fungicides in Source, Treated, and Tap Water from Wuhan, Central China: Assessment of Human Exposure Potential. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Hsiao, Y.-C.; Morrison-Welch, N.; Lamberti, S.; Liu, C.-W.; Lin, W.; Engel, S.M.; Lu, K.; Zylka, M.J. Co-Detection of Azoxystrobin and Thiabendazole Fungicides in Mold and Mildew Resistant Wallboards and in Children. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wan, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xia, W.; He, Z.; Xu, S. Occurrence of Azole and Strobilurin Fungicides in Indoor Dust from Three Cities of China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 304, 119168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, C.; Qin, R.; Lu, X. Determination of Strobilurin Fungicide Residues in Food by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2008, 36, 1471–1475. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, Y.B.; Shabeer, T.P.A.; Jadhav, M.; Banerjee, K.; Hingmire, S.; Saha, S.; Rai, A.B. Analytical Method Validation, Dissipation and Safety Evaluation of Combination Fungicides Fenamidone plus Mancozeb and Iprovalicarb plus Propineb in/on Tomato. J. Food Sci. Technol.-Mysore 2020, 57, 2061–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, S.; Song, S.; Zhao, Q.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, T. First Evidence in the Association of Phenolic Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals with Secondary Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Case-Control Study in South China. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 373, 126086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogahed, E.; Sayed, A.; Khalifa, S.; El-Hennawy, A.; El-Raziky, M. Causes of Secondary Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Non-Obese Children below 10 Years. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2020, 179, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Liu, C.-W.; Jimenez, J.A.; McCoy, E.S.; Hsiao, Y.-C.; Lin, W.; Engel, S.M.; Lu, K.; Zylka, M.J. Detection of Azoxystrobin Fungicide and Metabolite Azoxystrobin-Acid in Pregnant Women and Children, Estimation of Daily Intake, and Evaluation of Placental and Lactational Transfer in Mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 27013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Han, L.; Qin, F.; Song, S.; Lv, X.; Dong, Q.; Qiao, C.; Ren, B. Method Validation, Residue Analysis and Dietary Risk Assessment of Trifloxystrobin and Trifloxystrobin Acid in Milk, Eggs and Pork. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2022, 36, e5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, M.; Auteri, D.; Barmaz, S.; Bellisai, G.; Brancato, A.; Brocca, D.; Bura, L.; Byers, H.; Chiusolo, A.; Marques, D.C.; et al. Peer Review of the Pesticide Risk Assessment of the Active Substance Trifloxystrobin. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Conclusion on the Peer Review of the Pesticide Risk Assessment of the Active Substance Azoxystrobin. 2010. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/1542 (accessed on 12 March 2010).
- European Food Safety Authority. Conclusion Regarding the Peer Review of the Pesticide Risk Assessment of the Active Substance Fluoxastrobin. 2007. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/rn-102 (accessed on 13 June 2007).
- Martinez-Moral, M.-P.; Kannan, K. How Stable Is Oxidative Stress Level? An Observational Study of Intra- and Inter-Individual Variability in Urinary Oxidative Stress Biomarkers of DNA, Proteins, and Lipids in Healthy Individuals. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, M.; Stjepanovic, N.; Hackenberger, D.K.; Loncaric, Z.; Hackenberger, B.K. Comprehensive Study of the Effects of Strobilurin-Based Fungicide Formulations on Enchytraeus Albidus. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 1554–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Pang, S. Acute Toxicity and Associated Mechanisms of Four Strobilurins in Algae. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 60, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemheri-Navruz, F.; Ince, S.; Arslan-Acaroz, D.; Acaroz, U.; Demirel, H.H.; Demirkapi, E.N. Resveratrol Alleviates Pyraclostrobin-Induced Lipid Peroxidation, Oxidative Stress, and DNA Damage in Rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 6414–6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollan, J.L.; Zucker, S.D. A New Voyage of Discovery: Transport through the Hepatocyte. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 1996, 107, 48–55, discussion 55–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gan, C.; Yuan, Y.; Shen, H.; Gao, J.; Kong, X.; Che, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Dong, E.; Xiao, J. Liver Diseases: Epidemiology, Causes, Trends and Predictions. SIGNAL Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hak, H.N.G.; Al-Eisa, R.A.; Ryad, L.; Halawa, E.; El-Shenawy, N.S. Mechanisms and Histopathological Impacts of Acetamiprid and Azoxystrobin in Male Rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 43114–43125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, L. Genotoxicity and Oxidative Stress Induced by the Fungicide Azoxystrobin in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Livers. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 133, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Souders, C.L., II; Wang, S.; Ganter, J.; He, J.; Zhao, Y.H.; Cheng, H.; Martyniuk, C.J. Behavioral and Developmental Toxicity Assessment of the Strobilurin Fungicide Fenamidone in Zebrafish Embryos/Larvae (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 228, 112966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uckun, A.A.; Oz, O.B. Evaluation of the Acute Toxic Effect of Azoxystrobin on Non-Target Crayfish (Astacus leptodactylusEschscholtz, 1823) by Using Oxidative Stress Enzymes, ATPases and Cholinesterase as Biomarkers. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 44, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, M.; Bakhtawar, N. Vitamin E as an Adjuvant Treatment for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Adults: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Cureus J. Med. Sci. 2020, 12, e9018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | All Participants | Group | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 281) | Healthy (n = 143) | S-NAFLD (n = 138) | |
| Age (years) | 37.1 ± 11.8 | 30.0 ± 7.93 | 44.4 ± 10.6 |
| BMI [kg/m2, n (%)] | |||
| BMI < 18 | 10 (3%) | 10 (7%) | 0 (0%) |
| 18 ≤ BMI < 24 | 157 (56%) | 109 (76%) | 48 (35%) |
| ≥24 | 114 (41%) | 24 (17%) | 90 (65%) |
| Gender [n (%)] | |||
| Female | 134 (48%) | 91 (64%) | 43 (31%) |
| Male | 147 (52%) | 52 (36%) | 95 (69%) |
| ALT (U/L) | 36.5 ± 27.9 | 25.7 ± 7.39 | 48.5 ± 35.8 |
| AST (U/L) | 38.7 ± 17.5 | 25.6 ± 5.27 | 53.2 ± 14.5 |
| GGT (U/L) | 36.5 ± 23.4 | 26.1 ± 8.92 | 47.5 ± 28.3 |
| ALP (U/L) | 84.3 ± 28.1 | 79.0 ± 23.3 | 89.2 ± 31.8 |
| TBIL (μmol/L) | 16.4 ± 6.21 | 12.9 ± 3.47 | 20.0 ± 6.42 |
| DBIL (μmol/L) | 6.90 ± 3.39 | 5.64 ± 1.82 | 8.18 ± 4.12 |
| IBIL (μmol/L) | 9.49 ± 3.93 | 7.28 ± 2.35 | 11.9 ± 4.01 |
| TP (g/L) | 68.9 ± 11.1 | 72.1 ± 5.47 | 65.1 ± 14.0 |
| ALB (g/L) | 40.1 ± 7.19 | 42.1 ± 4.61 | 37.8 ± 8.52 |
| GLB (g/L) | 28.7 ± 6.66 | 30.0 ± 5.15 | 27.3 ± 7.76 |
| LOD | LOQ | Range | All (n = 281) | Health (n = 143) | S-NAFLD (n = 138) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DF | Median | Geomean | DF | Median | Geomean | DF | Median | Geomean | ||||
| AZ | 0.0012 | 0.004 | <LOQ-0.118 | 89% | 0.042 | 0.030 | 83% | 0.049 | 0.028 | 94% | 0.034 | 0.032 |
| FE | 0.0015 | 0.005 | <LOQ-0.218 | 75% | 0.019 | 0.014 | 62% | 0.016 | 0.011 | 88% | 0.021 | 0.018 |
| FLUO | 0.0012 | 0.004 | <LOQ-0.178 | 65% | 0.016 | 0.012 | 60% | 0.014 | 0.011 | 70% | 0.016 | 0.012 |
| ORY | 0.0003 | 0.001 | <LOQ-0.024 | 49% | <LOQ | 0.002 | 73% | 0.006 | 0.004 | 25% | <LOQ | 0.0014 |
| PICO | 0.0006 | 0.002 | <LOQ-0.075 | 47% | <LOQ | 0.003 | 58% | 0.008 | 0.005 | 35% | <LOQ | 0.0021 |
| TRIF | 0.0009 | 0.003 | <LOQ-0.025 | 17% | <LOQ | <LOQ | 34% | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0% | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| AZ-acid | 0.0003 | 0.001 | <LOQ-0.023 | 22% | <LOQ | <LOQ | 36% | <LOQ | <LOQ | 7% | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| TRIF-acid | 0.0003 | 0.001 | <LOQ-0.062 | 21% | <LOQ | <LOQ | 38% | <LOQ | <LOQ | 3% | <LOQ | <LOQ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Feng, S.; Gao, Y.; Xie, W.; Chen, Y.; Song, S. First Human Biomonitoring Evidence of Strobilurin Fungicide Exposure in South China: Impact on Oxidative Stress and Liver Damage. Toxics 2025, 13, 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110908
Zhang B, Feng S, Gao Y, Xie W, Chen Y, Song S. First Human Biomonitoring Evidence of Strobilurin Fungicide Exposure in South China: Impact on Oxidative Stress and Liver Damage. Toxics. 2025; 13(11):908. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110908
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bo, Shuai Feng, Yanxia Gao, Wenxi Xie, Yiyu Chen, and Shiming Song. 2025. "First Human Biomonitoring Evidence of Strobilurin Fungicide Exposure in South China: Impact on Oxidative Stress and Liver Damage" Toxics 13, no. 11: 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110908
APA StyleZhang, B., Feng, S., Gao, Y., Xie, W., Chen, Y., & Song, S. (2025). First Human Biomonitoring Evidence of Strobilurin Fungicide Exposure in South China: Impact on Oxidative Stress and Liver Damage. Toxics, 13(11), 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110908