Prediction of Cell Survival Rate Based on Physical Characteristics of Heavy Ion Radiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Radiation Parameters
2.2. Supervised Learning
2.3. Compilation of Datasets
2.4. Applied Methods
3. Results
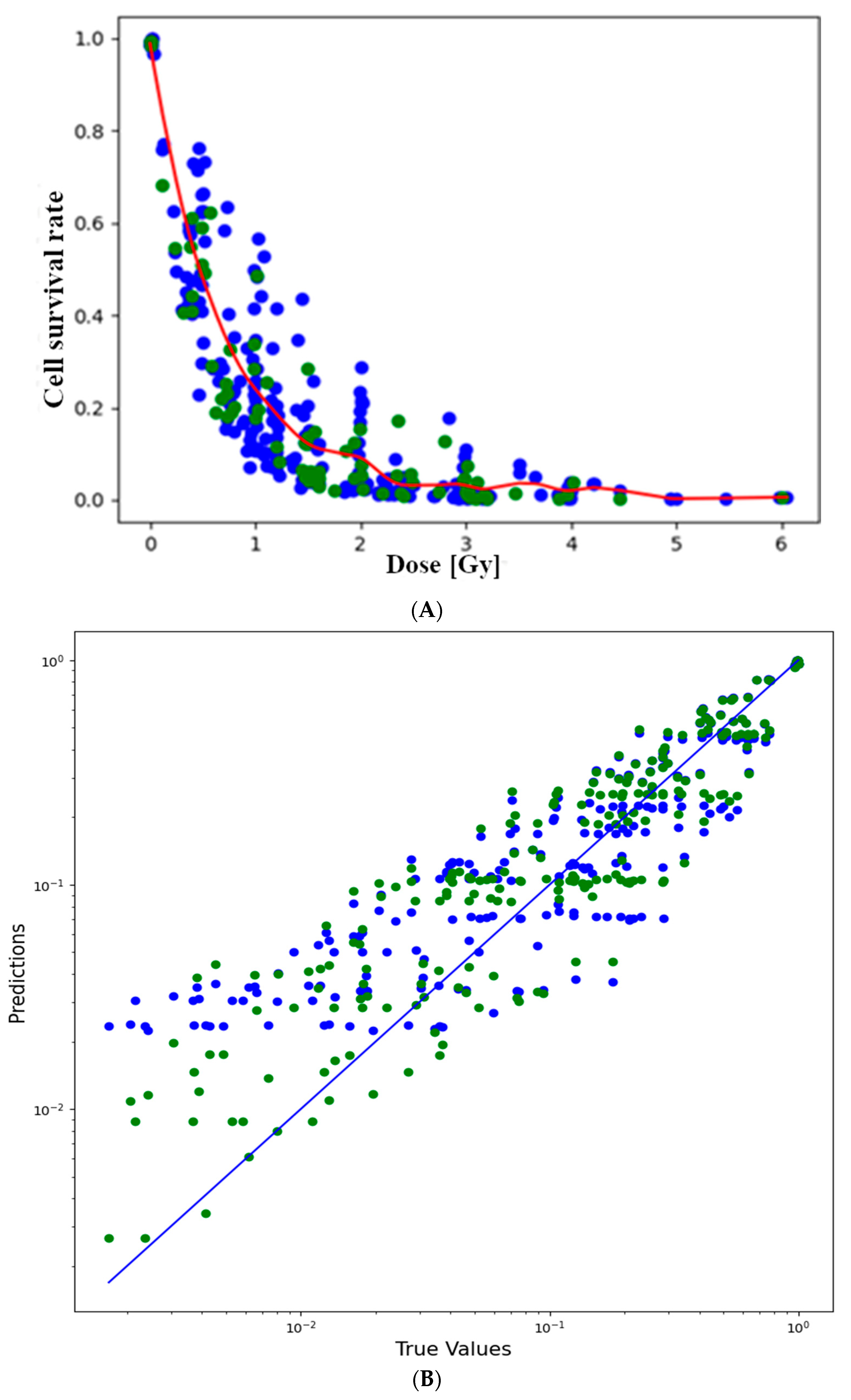
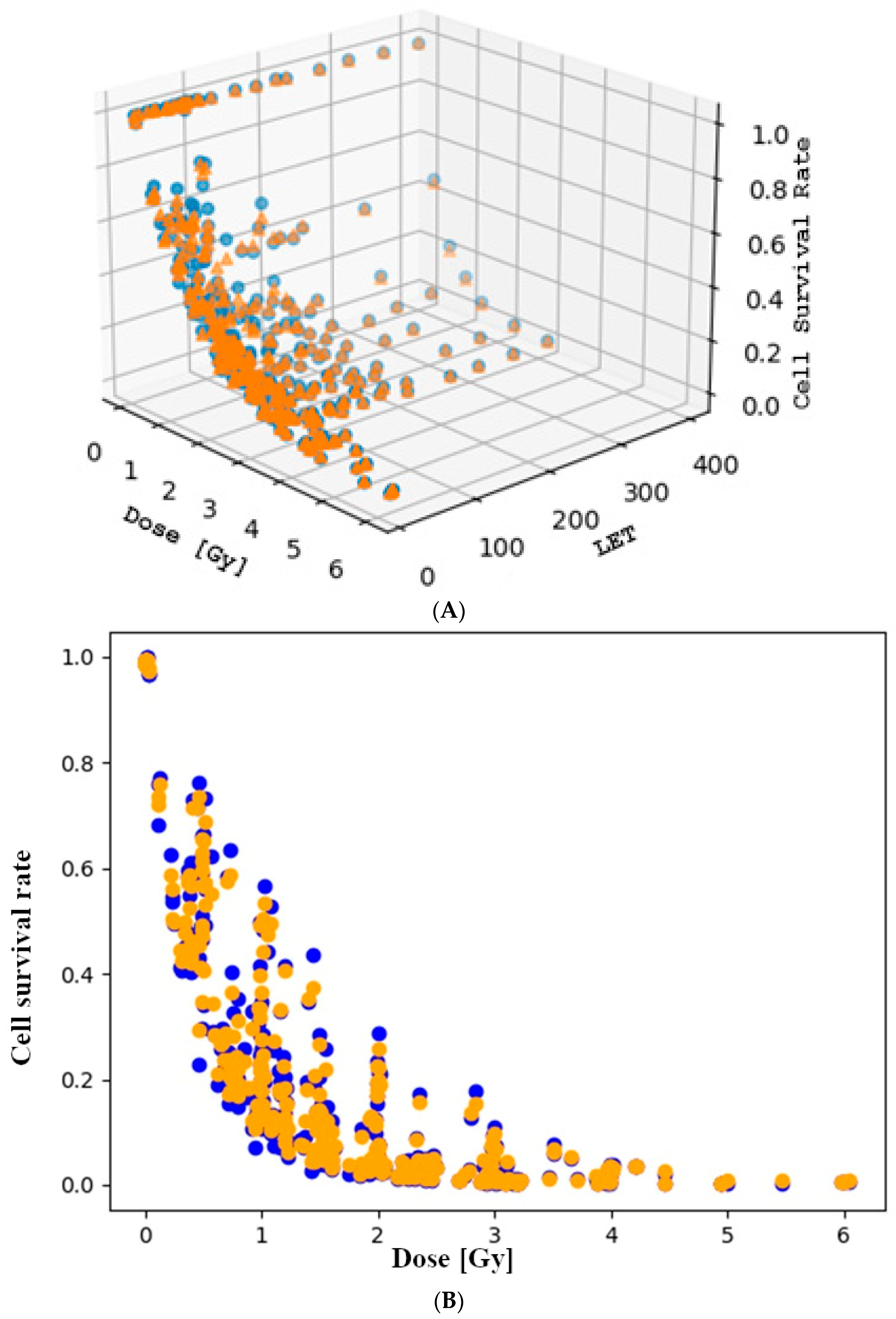
3.1. Cell Survival Rate and Dose Relationship
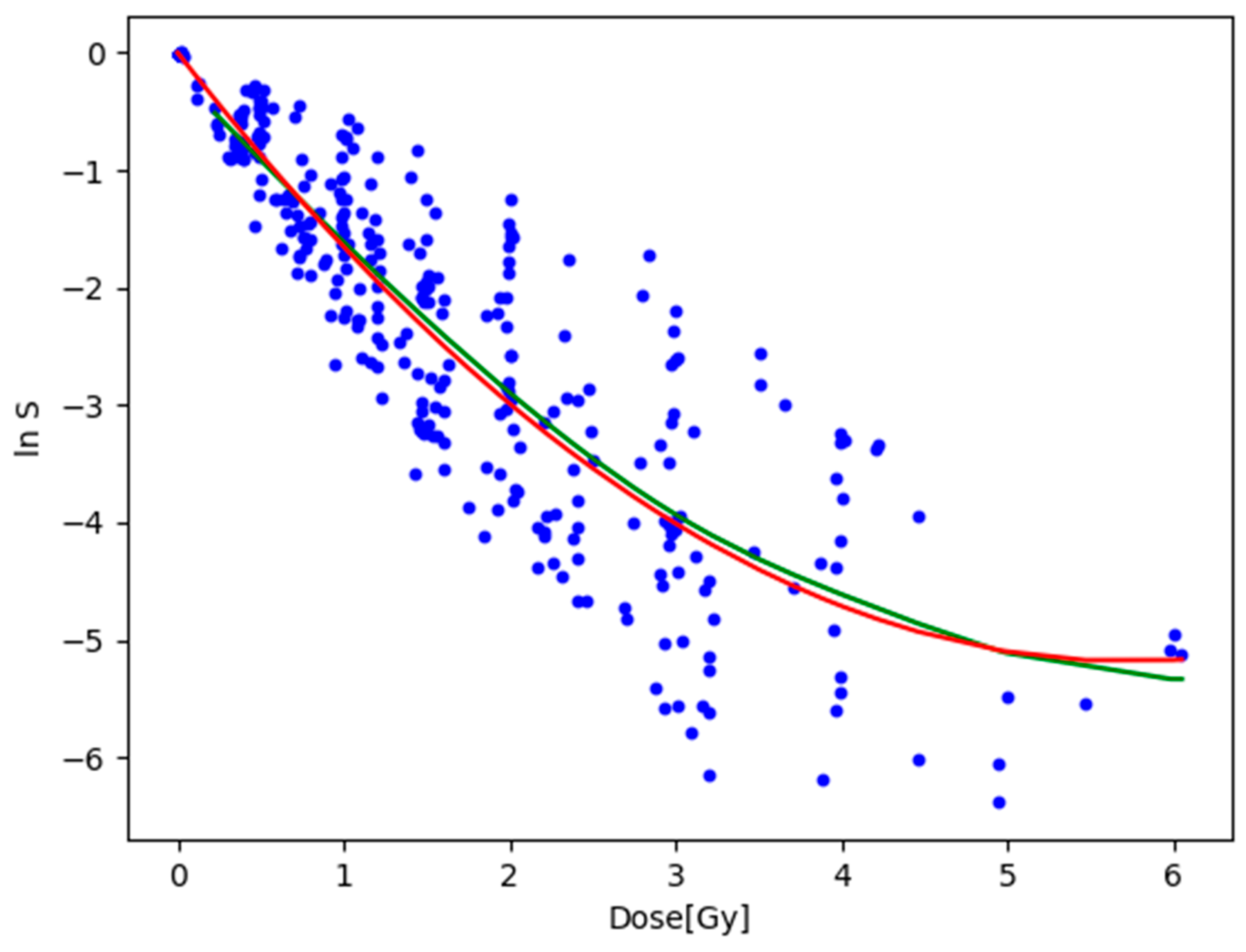
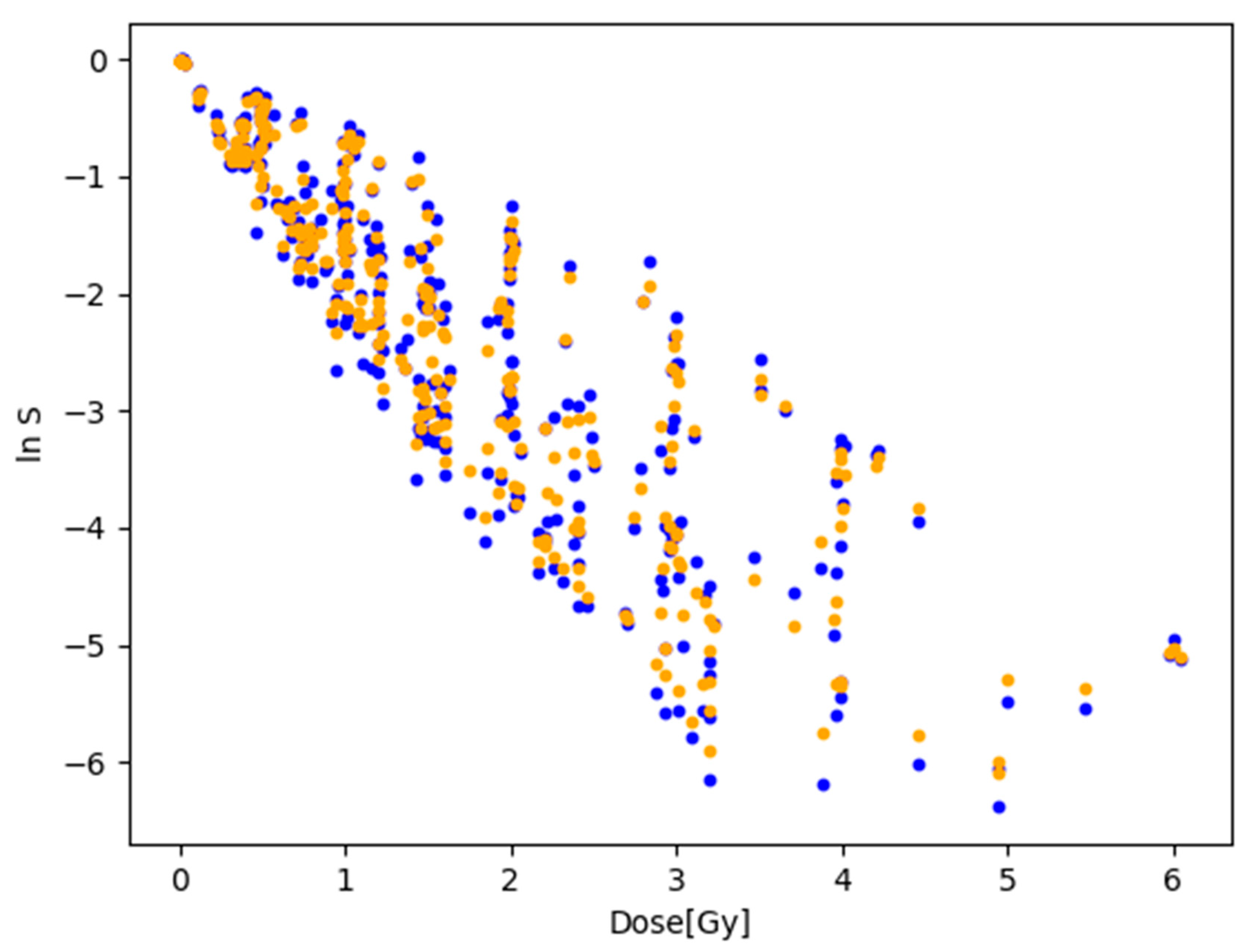
3.2. Fitting to the Natural Logarithm of the Cell Survival Rate
3.3. The Role of Linear Energy Transfer in the Rate of Cell Death
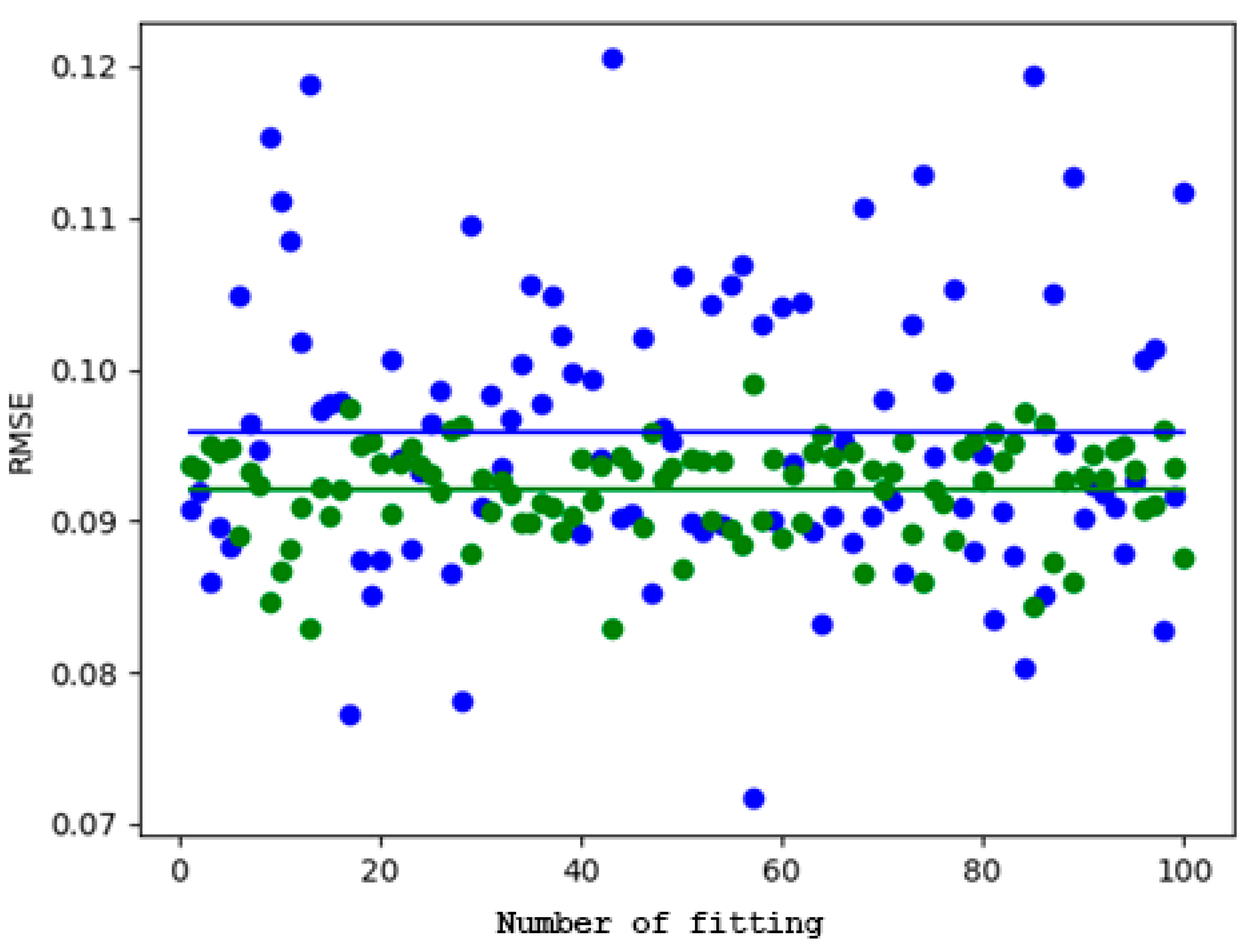
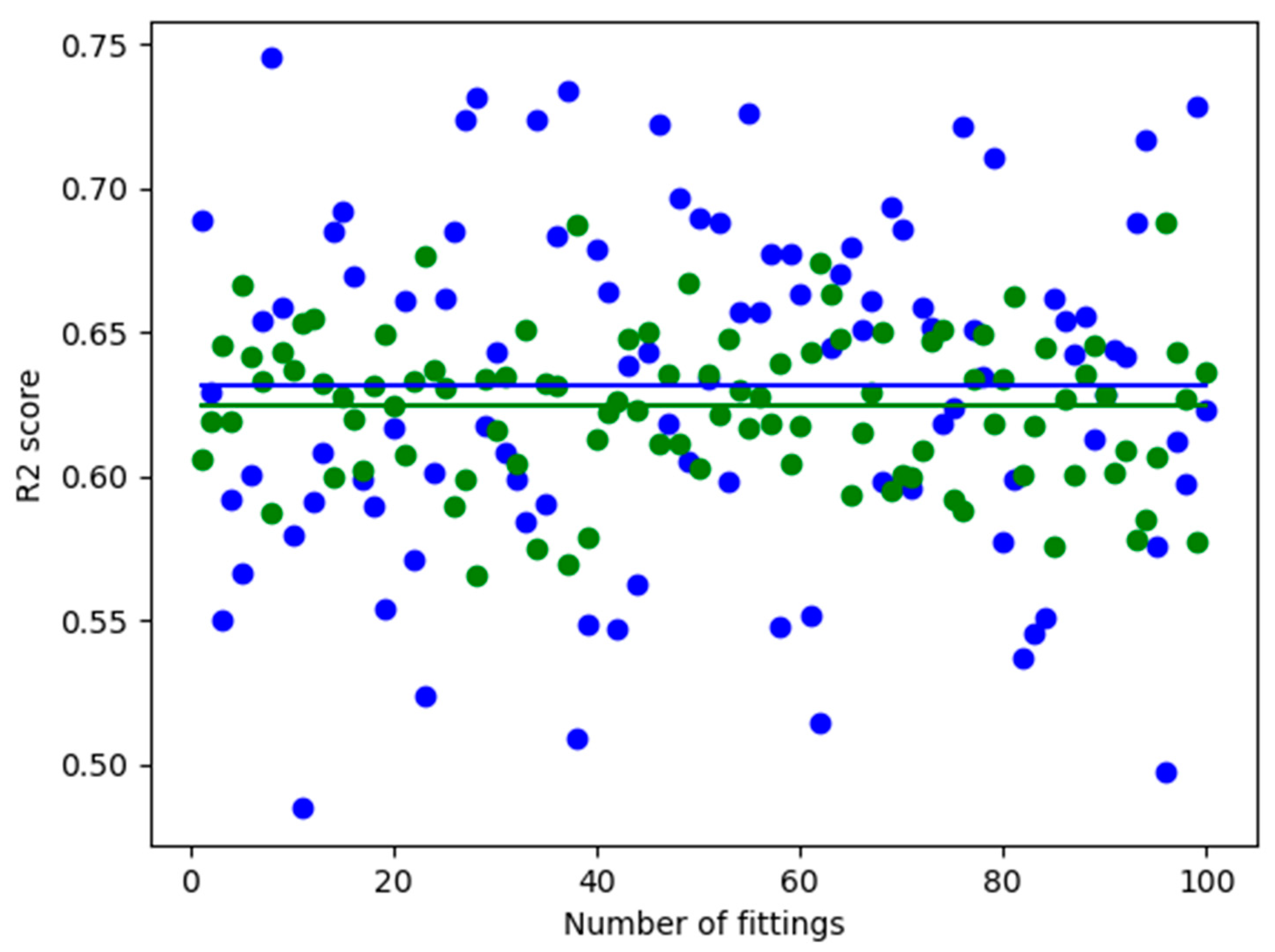
3.4. Comparison of the Performances in the Case of the Log-Transformed Dataset
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abu Bakar, N.F.; Othman, S.A.; Azman, N.F.A.N.; Jasrin, N.S. Effect of ionizing radiation towards human health: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 268, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, C.M.; Oei, A.L.; Crezee, J.; Bel, A.; Franken, N.A.P.; Stalpers, L.J.A.; Kok, H.P. The alfa and beta of tumours: A review of parameters of the linear-quadratic model, derived from clinical radiotherapy studies. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaccorso, G. Machine Learning Algorithms: A Reference Guide to Popular Algorithms for Data Science and Machine Learning; Packt Publishing: Birmingham, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ICRP. The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP publication 103. Ann. ICRP 2007, 37, 1–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettler, F.A.; Upton, A.C. Medical Effects of Ionizing Radiation; Saunders/Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Malouff, T.D.; Mahajan, A.; Krishnan, S.; Beltran, C.; Seneviratne, D.S.; Trifiletti, D.M. Carbon Ion Therapy: A Modern Review of an Emerging Technology. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäkel, O. Physical advantages of particles: Protons and light ions. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, N. Recent Insights into the Biological Action of Heavy-Ion Radiation. J. Radiat. Res. 2009, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, N.; Imaoka, T.; Masunaga, S.-I.; Ogata, T.; Okayasu, R.; Takahashi, A.; Kato, T.A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Ono, K.; et al. Recent Advances in the Biology of Heavy-Ion Cancer Therapy. J. Radiat. Res. 2010, 51, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vapnik, V.N. An overview of statistical learning theory. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1999, 10, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gareth, J.; Daniela, W.; Trevor, H.; Robert, T. An Introduction to Statistical Learning: With Applications in R; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vabalas, A.; Gowen, E.; Poliakoff, E.; Casson, A.J. Machine learning algorithm validation with a limited sample size. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthaharan, S. Machine Learning Models and Algorithms for Big Data Classification: Thinking with Examples for Effective Learning. Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Gradus, J.L.; Rosellini, A.J. Supervised Machine Learning: A Brief Primer. Behav. Ther. 2020, 51, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, T.; Pfuhl, T.; Scholz, M. Update of the particle irradiation data ensemble (PIDE) for cell survival. J. Radiat. Res. 2021, 62, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalev-Shwartz, S.; Ben-David, S. Understanding Machine Learning: From Theory to Algorithms; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Eertink, J.J.; Heymans, M.W.; Zwezerijnen, G.J.C.; Zijlstra, J.M.; de Vet, H.C.W.; Boellaard, R. External validation: A simulation study to compare cross-validation versus holdout or external testing to assess the performance of clinical prediction models using PET data from DLBCL patients. EJNMMI Res. 2022, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stańczyk, U.; Jain, L.C. Feature Selection for Data and Pattern Recognition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tsujii, H.; Kamada, T. A Review of Update Clinical Results of Carbon Ion Radiotherapy. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 42, 670–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinganelli, W.; Durante, M. Carbon Ion Radiobiology. Cancers 2020, 12, 3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, S.J. The linear quadratic model: Usage, interpretation and challenges. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 64, 01TR01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joiner, M.; Kogel, A.v.d. Basic Clinical Radiobiology, 4th ed.; Hodder Arnold London: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, L.; Hoban, P.; Metcalfe, P. The use of the linear quadratic model in radiotherapy: A review. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2001, 24, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, S.J.; Prise, K.M. Mechanistic Modelling of Radiation Responses. Cancers 2019, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, D.; Maclin, R. Popular Ensemble Methods: An Empirical Study. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 1999, 11, 169–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohri, M.; Rostamizadeh, A.; Talwalkar, A. Foundations of Machine Learning; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ghojogh, B.; Crowley, M. The Theory Behind Overfitting, Cross Validation, Regularization, Bagging, and Boosting: Tutorial. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.12787. [Google Scholar]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction, 2nd ed.; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, J.M.; Hastie, T. Statistical Models in S; Wadsworth & Brooks/Cole Advanced Books & Software: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher, J.; Mac Namee, B.; D’Arcy, A. Fundamentals of Machine Learning for Predictive Data Analytics: Algorithms, Worked Examples, and Case Studies; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.-S.; Liang, Y.-Z. Monte Carlo cross validation. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 56, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, D.; Butler, D. Statistical validation. Ecol. Model. 1993, 68, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Warrens, M.J.; Jurman, G. The coefficient of determination R-squared is more informative than SMAPE, MAE, MAPE, MSE and RMSE in regression analysis evaluation. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draper, N.R.; Smith, H. Applied Regression Analysis; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hodson, T.O. Root-mean-square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE): When to use them or not. Geosci. Model Dev. 2022, 15, 5481–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Koehler, A.B. Another look at measures of forecast accuracy. Int. J. Forecast. 2006, 22, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, D.; Zanni, V.; Nikitaki, Z.; Vasileiou, C.; Kousouris, K.; Georgakilas, A.G. Using Machine Learning Techniques for Asserting Cellular Damage Induced by High-LET Particle Radiation. Radiation 2021, 1, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, Y.; Tsuboi, K.; Ohyama, H.; Ohno, T.; Nose, T.; Ando, K. Cell death induced by high-linear-energy transfer carbon beams in human glioblastoma cell lines. Brain Tumor Pathol. 1998, 15, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordoni, F.G.; Missiaggia, M.; Scifoni, E.; La Tessa, C. An artificial intelligence-based model for cell killing prediction: Development, validation and explainability analysis of the ANAKIN model. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 085017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekking, F.M.; Kraaikamp, C.; Lopuhaä, H.P.; Meester, L.E. A Modern Introduction to Probability and Statistics, Understanding Why and How; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.; Zou, J. Data-OOB: Out-of-bag Estimate as a Simple and Efficient Data Value. In Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, 2023. Available online: https://proceedings.mlr.press/v202/kwon23e.html (accessed on 15 March 2024).



| α Coefficient | β Coefficient | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean (AM) | 1.6939 | −0.1827 |
| Variance | 0.0154 | 0.00178 |
| Standard deviation | 0.041 | 0.0137 |
| Minimum | 1.5804 | −0.2177 |
| Maximum | 1.8257 | −0.1281 |
| LQM | Local Regression | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean(AM) | 0.8843 | 0.8986 |
| Variance | 0.03614 | 0.00924 |
| Minimum | 0.7329 | 0.8738 |
| Maximum | 0.9477 | 0.9248 |
| CV | 0.04087 | 0.01028 |
| LQM | Local Regression | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean(AM) | 0.0959 | 0.0921 |
| Variance | 0.009382 | 0.0032 |
| Minimum | 0.0717 | 0.08286 |
| Maximum | 0.121 | 0.0986 |
| CV | 0.198 | 0.09901 |
| LQM | Local Regression | LQM ln | Local Regression ln | Linear Regression ln | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.8843 | 0.8986 | 0.6316 | 0.6245 | 0.5531 |
| RMSE | 0.0959 | 0.0921 | 0.7689 | 0.76174 | 0.8952 |
| n_ Estimators | Min_ Samples_Split | Min_ Samples_Leaf | Max_ Depth | R2 Score | RMSE Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 2 | 1 | 100 | 0.9685 | 0.0196 |
| 200 | 2 | 1 | 100 | 0.9511 | 0.129 |
| 600 | 2 | 1 | 100 | 0.9511 | 0.130 |
| 800 | 2 | 1 | 60 | 0.9509 | 0.131 |
| 400 | 2 | 1 | 100 | 0.9509 | 0.130 |
| LQM | Local Regression | Random Forest | |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.8843 | 0.8986 | 0.9685 |
| RMSE | 0.959 | 0.921 | 0.0196 |
| n_ Estimators | Min_ Samples_Split | Min_ Samples_Leaf | Max_ Depth | R2 Score | RMSE Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 2 | 1 | 40 | 0.941318 | 0.132077 |
| 600 | 2 | 1 | 20 | 0.940821 | 0.130237 |
| 400 | 2 | 1 | 40 | 0.940702 | 0.130339 |
| 800 | 2 | 1 | 100 | 0.940699 | 0.130532 |
| 1000 | 2 | 1 | 60 | 0.940498 | 0.131342 |
| n_ Estimators | Min_ Samples_Split | Min_ Samples_Leaf | Max_ Depth | R2 Score | RMSE Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 | 10 | 4 | 80 | 0.92887905 | 800 |
| 600 | 10 | 4 | 20 | 0.928749352 | 600 |
| 600 | 10 | 4 | 100 | 0.928730675 | 600 |
| 400 | 10 | 4 | 40 | 0.928686579 | 400 |
| 200 | 2 | 4 | 80 | 0.928535596 | 200 |
| Coefficients | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| n_estimators | 1.264 × 10−7 | 0.836 |
| min_samples_split | −0.0007 | 1.2 × 10−22 |
| min_samples_leaf | −0.0025 | 4.2 × 10−30 |
| max_depth | 5.17 × 10−6 | 0.403 |
| LQM ln Transformed | Local Regression ln Transformed | Random Forest ln Transformed | |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.6316 | 0.6245 | 0.9413 |
| RMSE | 0.7689 | 0.76174 | 0.1321 |
| LQM ln Transformed R2 | Random Forest ln Transformed R2 | LQM ln Transformed RMSE | Random Forest ln Transformed RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB1RGB | 0.6316 | 0.9413 | 0.7689 | 0.1321 |
| Other | 0.6258 | 0.8884 | 0.9957 | 0.2708 |
| Difference | −0.0058 | −0.0529 | 0.2268 | 0.1387 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Debreceni, A.; Buri, Z.; Csige, I.; Bodzás, S. Prediction of Cell Survival Rate Based on Physical Characteristics of Heavy Ion Radiation. Toxics 2024, 12, 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12080545
Debreceni A, Buri Z, Csige I, Bodzás S. Prediction of Cell Survival Rate Based on Physical Characteristics of Heavy Ion Radiation. Toxics. 2024; 12(8):545. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12080545
Chicago/Turabian StyleDebreceni, Attila, Zsolt Buri, István Csige, and Sándor Bodzás. 2024. "Prediction of Cell Survival Rate Based on Physical Characteristics of Heavy Ion Radiation" Toxics 12, no. 8: 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12080545
APA StyleDebreceni, A., Buri, Z., Csige, I., & Bodzás, S. (2024). Prediction of Cell Survival Rate Based on Physical Characteristics of Heavy Ion Radiation. Toxics, 12(8), 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12080545







