Selenium Nanoparticles Attenuate Cobalt Nanoparticle-Induced Skeletal Muscle Injury: A Study Based on Myoblasts and Zebrafish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of Nanoparticles
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Vitality
2.4. Confocal Microscope
2.5. ROS Detection
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Flow Cytometry of Annexin V-FITC/PI Double Staining
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.9. Transmission Electron Microscope
2.10. Histological Analyses
2.11. Detection of MDA, SOD, and GSH
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
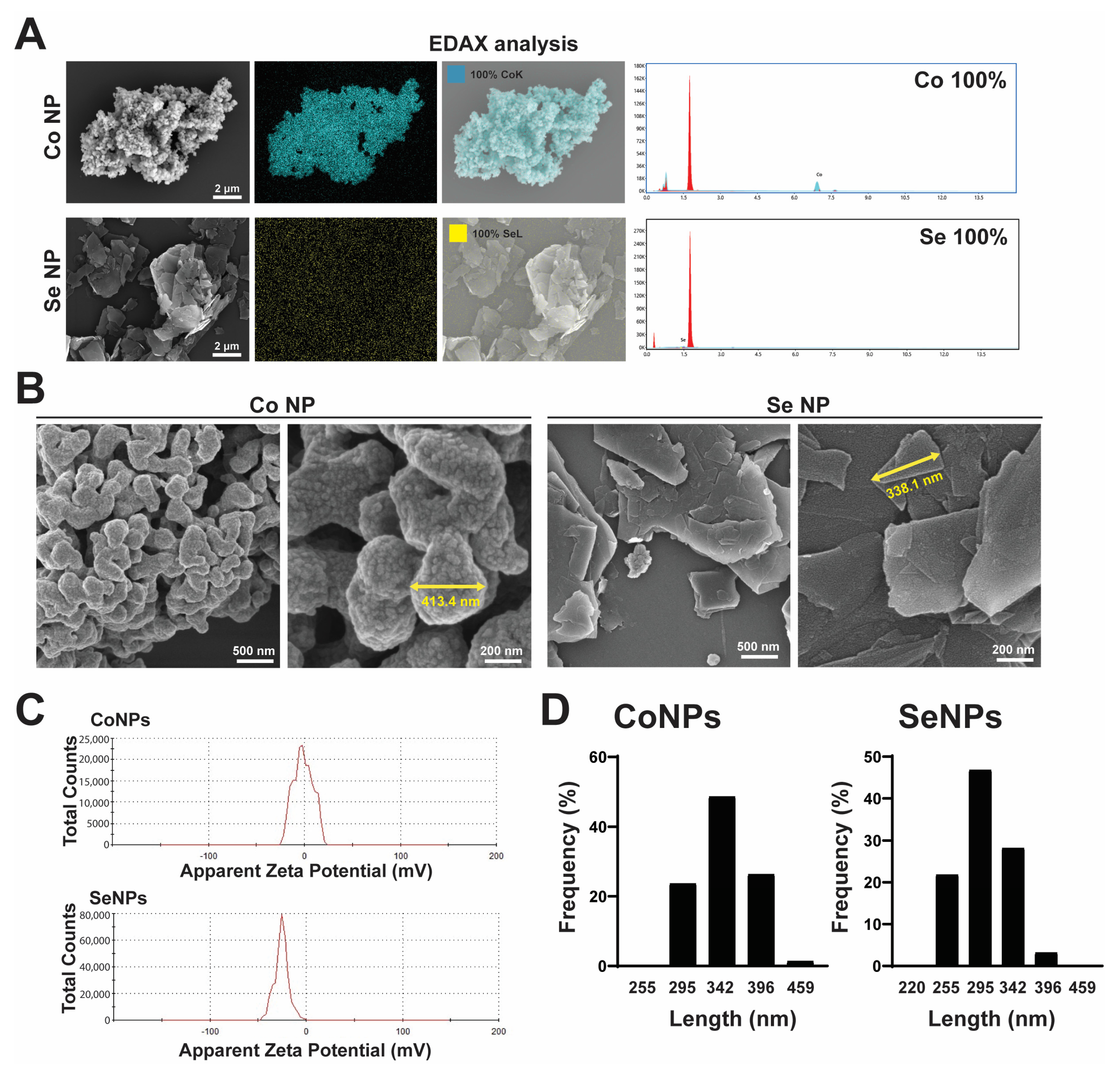
3.1. Characterization of CoNPs and SeNPs
3.2. Low-Level SeNPs Inhibited the Cytotoxic Effect of High-Dose CoNPs
3.3. Low-Dose SeNPs Inhibited CoNP-Induced Oxidative Stress in Muscle Cells
3.4. Low-Dose SeNPs Inhibited CoNP-Induced Apoptosis
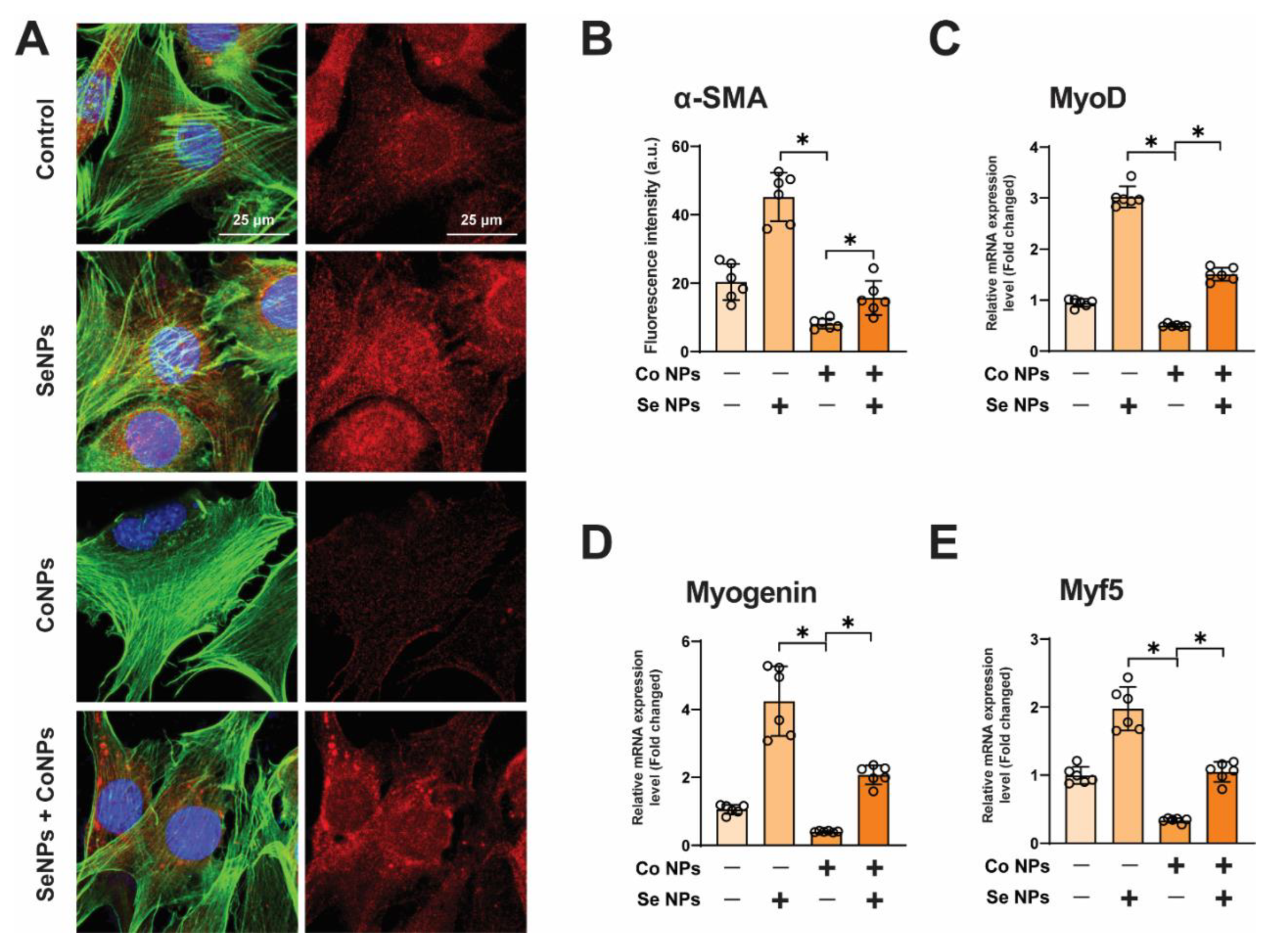
3.5. SeNPs Promote the Expression of Myogenic Markers and Protect against Muscle Damage Induced by CoNPs
3.6. Protective Effect of SeNPs against CoNP-Induced Toxicity in Zebrafish
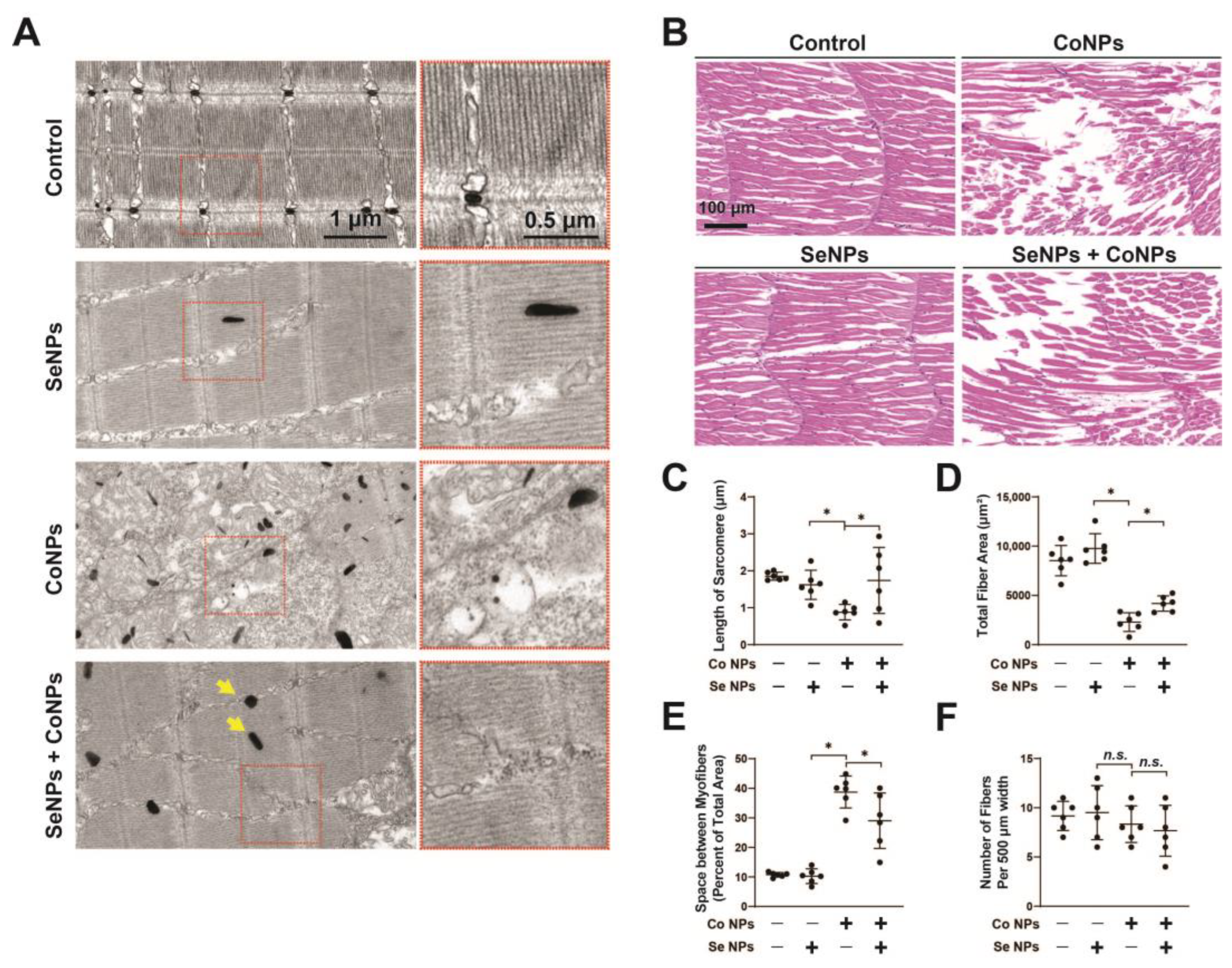
3.7. Protective Effect of SeNPs against CoNP-Induced Muscle Damage in Zebrafish
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, S.R.; Kwon, J.W.; Suk, K.S.; Kim, H.S.; Moon, S.H.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, B.H. The Clinical Use of Osteobiologic and Metallic Biomaterials in Orthopedic Surgery: The Present and the Future. Materials 2023, 16, 3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rullán, P.J.; Deren, M.E.; Zhou, G.; Emara, A.K.; Klika, A.K.; Schiltz, N.K.; Barsoum, W.K.; Koroukian, S.; Piuzzi, N.S. The Arthroplasty Surgeon Growth Indicator: A Tool for Monitoring Supply and Demand Trends in the Orthopaedic Surgeon Workforce from 2020 to 2050. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2023, 105, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balachandran, S.; Zachariah, Z.; Fischer, A.; Mayweg, D.; Wimmer, M.A.; Raabe, D.; Herbig, M. Atomic Scale Origin of Metal Ion Release from Hip Implant Taper Junctions. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.K.; Nguyen, M.K.; Lin, C.; Hoang, T.D.; Nguyen, T.C.; Lone, A.M.; Khedulkar, A.P.; Gaballah, M.S.; Singh, J.; Chung, W.J.; et al. Review on fate, transport, toxicity and health risk of nanoparticles in natural ecosystems: Emerging challenges in the modern age and solutions toward a sustainable environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 912, 169331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnear, C.; Moore, T.L.; Rodriguez-Lorenzo, L.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Petri-Fink, A. Form Follows Function: Nanoparticle Shape and Its Implications for Nanomedicine. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 11476–11521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cui, X.; Wu, J.; Bao, L.; Tan, Z.; Chen, C. Peripheral nerves directly mediate the transneuronal translocation of silver nanomaterials from the gut to central nervous system. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradberry, S.M.; Wilkinson, J.M.; Ferner, R.E. Systemic toxicity related to metal hip prostheses. Clin. Toxicol. 2014, 52, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanni, R.; Abbondante, L.; Cariati, I.; Gasbarra, E.; Tarantino, U. Metallosis after Hip Arthroplasty Damages Skeletal Muscle: A Case Report. Geriatrics 2023, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, L.R.; Marel, E.; Harbury, R.; Wearne, J. Distribution of chromium and cobalt ions in various blood fractions after resurfacing hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2008, 23, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savi, M.; Bocchi, L.; Cacciani, F.; Vilella, R.; Buschini, A.; Perotti, A.; Galati, S.; Montalbano, S.; Pinelli, S.; Frati, C.; et al. Cobalt oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and alter electromechanical function in rat ventricular myocytes. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Dash, S.K.; Tripathy, S.; Das, B.; Mandal, D.; Pramanik, P.; Roy, S. Toxicity of cobalt oxide nanoparticles to normal cells; an in vitro and in vivo study. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 226, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Khalil, S.R.; Awad, A.; Abu Zeid, E.H.; El-Aziz, R.A.; El-Serehy, H.A. Ethanolic Extract of Moringa oleifera Leaves Influences NF-κB Signaling Pathway to Restore Kidney Tissue from Cobalt-Mediated Oxidative Injury and Inflammation in Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Dong, L.; Liu, Y.M.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Liu, K.; Liu, L.; Song, Y.H.; Sun, M.; Xiang, X.C.; et al. Nickle-cobalt alloy nanocrystals inhibit activation of inflammasomes. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Lin, X.; Yang, J.; Qu, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Chang, X.; Guo, Z.; et al. Evaluation of neurotoxicity and the role of oxidative stress of cobalt nanoparticles, titanium dioxide nanoparticles, and multiwall carbon nanotubes in Caenorhabditis elegans. Toxicol. Sci. 2023, 196, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagatsuma, A.; Arakawa, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Matsuda, R.; Hoshino, T.; Mabuchi, K. Cobalt chloride, a chemical hypoxia-mimicking agent, suppresses myoblast differentiation by downregulating myogenin expression. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 470, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, P.E.; Pereira, M.R.; do Nascimento Santos, C.A.; Campos, A.P.; Esteves, T.M.; Granjeiro, J.M. Gold nanoparticles do not induce myotube cytotoxicity but increase the susceptibility to cell death. Toxicol. In Vitro 2015, 29, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.H.; Guan, P.; Zhang, T.; Lu, C.; Li, G.; Liu, J.X. Silver nanoparticles impair zebrafish skeletal and cardiac myofibrillogenesis and sarcomere formation. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 200, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skočaj, M.; Bizjak, M.; Strojan, K.; Lojk, J.; Erdani Kreft, M.; Miš, K.; Pirkmajer, S.; Bregar, V.B.; Veranič, P.; Pavlin, M. Proposing Urothelial and Muscle In Vitro Cell Models as a Novel Approach for Assessment of Long-Term Toxicity of Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Vechetti, I.J., Jr.; Alimov, A.P.; Hoffman, J.F.; Vergara, V.B.; Kalinich, J.F.; McCarthy, J.J.; Peterson, C.A. Time-course analysis of the effect of embedded metal on skeletal muscle gene expression. Physiol. Genom. 2020, 52, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, R.; Dwivedi, S.; Khan, F.; Mishra, Y.K.; Hwang, I.H.; Shin, H.S.; Musarrat, J.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A. Statistical analysis of gold nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in myoblast (C2C12) cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, L.O.; Harbak, H.; Bennekou, P. Cobalt metabolism and toxicology—A brief update. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 432, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Xu, Z.; Huang, W.; Han, D.; Dang, B.; Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Jia, W. Selenium-molybdenum interactions reduce chromium toxicity in Nicotiana tabacum L. by promoting chromium chelation on the cell wall. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozoani, H.; Ezejiofor, A.N.; Okolo, K.O.; Orish, C.N.; Cirovic, A.; Cirovic, A.; Orisakwe, O.E. Selenium and zinc alleviate hepatotoxicity induced by heavy metal mixture (cadmium, mercury, lead and arsenic) via attenuation of inflammo-oxidant pathways. Environ. Toxicol. 2023, 39, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, G.; Sang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gao, L.; Xue, J.; Zhao, M.; Yu, H.; et al. Dietary selenium excess affected spermatogenesis via DNA damage and telomere-related cell senescence and apoptosis in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2023, 171, 113556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brozmanová, J.; Mániková, D.; Vlčková, V.; Chovanec, M. Selenium: A double-edged sword for defense and offence in cancer. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 919–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Rácz, B.; Marć, M.A.; Nasim, M.J.; Szemerédi, N.; Viktorová, J.; Jacob, C.; Spengler, G. Selenium and tellurium in the development of novel small molecules and nanoparticles as cancer multidrug resistance reversal agents. Drug Resist Updat. 2022, 63, 100844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Yin, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X. Dietary Selenium Promotes Somatic Growth of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) by Accelerating the Hypertrophic Growth of White Muscle. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 2000–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.C.; Li, H.Q.; Tang, K.K.; Wang, Z.Y.; Fan, R.F. Selenium Mitigates Cadmium-Induced Adverse Effects on Trace Elements and Amino Acids Profiles in Chicken Pectoral Muscles. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 193, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, R.; Chen, X.; Hong, A.; Liu, J. The effects of luminescent ruthenium(II) polypyridyl functionalized selenium nanoparticles on bFGF-induced angiogenesis and AKT/ERK signaling. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Li, Z.; Xie, Z.; Sokolova, I.M.; Song, L.; Peijnenburg, W.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y. Rethinking Nano-TiO(2) Safety: Overview of Toxic Effects in Humans and Aquatic Animals. Small 2020, 16, e2002019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, E.T.; Khalaf, S.S.; Mesbah, N.M.; Abo-Elmatty, D.M.; Hafez, M.M. Anti-oxidant, anti-apoptotic, and mitochondrial regulatory effects of selenium nanoparticles against vancomycin induced nephrotoxicity in experimental rats. Life Sci. 2022, 288, 120098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.R.; Poland, C.A. Nanotoxicology: The Need for a Human Touch? Small 2020, 16, e2001516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.N.; Wu, P.; Jiang, W.D.; Liu, Y.; Kuang, S.Y.; Tang, L.; Ren, H.M.; Li, H.; Feng, L.; Zhou, X.Q. Aflatoxin B1 exposure induced developmental toxicity and inhibited muscle development in zebrafish embryos and larvae. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, F.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, H.; Jiang, H. The Protective Effect of Bafilomycin A1 Against Cobalt Nanoparticle-Induced Cytotoxicity and Aseptic Inflammation in Macrophages In Vitro. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 169, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.C.; Lee, N.H.; Patel, K.D.; Jun, S.K.; Park, J.H.; Knowles, J.C.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, H.H.; Lee, J.H. A Study on Myogenesis by Regulation of Reactive Oxygen Species and Cytotoxic Activity by Selenium Nanoparticles. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshta, A.T.; Fathallah, A.M.; Attia, Y.A.; Salem, E.A.; Watad, S.H. Ameliorative effect of selenium nanoparticles on testicular toxicity induced by cisplatin in adult male rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2023, 179, 113979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliya-Perumal, A.K.; Ingham, P.W. Musculoskeletal regeneration: A zebrafish perspective. Biochimie 2022, 196, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammit, P.S. Function of the myogenic regulatory factors Myf5, MyoD, Myogenin and MRF4 in skeletal muscle, satellite cells and regenerative myogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 72, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinich, J.F.; Vergara, V.B.; Hoffman, J.F. Oxidative damage in metal fragment-embedded Sprague-Dawley rat gastrocnemius muscle. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 3, 100083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, H. An in vivo evaluation of acute toxicity of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles in larval-embryo Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 166, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharawy, M.E.; Hamouda, M.; Soliman, A.A.; Amer, A.A.; El-Zayat, A.M.; Sewilam, H.; Younis, E.M.; Abdel-Warith, A.A.; Dawood, M.A.O. Selenium nanoparticles are required for the optimum growth behavior, antioxidative capacity, and liver wellbeing of Striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus). Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 7241–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, Z.; Deng, L.; Jiang, Z.; Xiang, G.; Zhang, G.; He, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Selenium Nanoparticles Attenuate Cobalt Nanoparticle-Induced Skeletal Muscle Injury: A Study Based on Myoblasts and Zebrafish. Toxics 2024, 12, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12020130
Tan Z, Deng L, Jiang Z, Xiang G, Zhang G, He S, Zhang H, Wang Y. Selenium Nanoparticles Attenuate Cobalt Nanoparticle-Induced Skeletal Muscle Injury: A Study Based on Myoblasts and Zebrafish. Toxics. 2024; 12(2):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12020130
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Zejiu, Linhua Deng, Zhongjing Jiang, Gang Xiang, Gengming Zhang, Sihan He, Hongqi Zhang, and Yunjia Wang. 2024. "Selenium Nanoparticles Attenuate Cobalt Nanoparticle-Induced Skeletal Muscle Injury: A Study Based on Myoblasts and Zebrafish" Toxics 12, no. 2: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12020130
APA StyleTan, Z., Deng, L., Jiang, Z., Xiang, G., Zhang, G., He, S., Zhang, H., & Wang, Y. (2024). Selenium Nanoparticles Attenuate Cobalt Nanoparticle-Induced Skeletal Muscle Injury: A Study Based on Myoblasts and Zebrafish. Toxics, 12(2), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12020130





