PAH Contamination, Sources and Health Risks in Black Soil Region of Jilin Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Sample Acquisition
2.3. Main Reagents and Materials
2.4. Soil Tests and Extracting the PAHs
2.5. Quality Control
2.6. Risk Assessment of PAHs
2.7. Source Apportionment
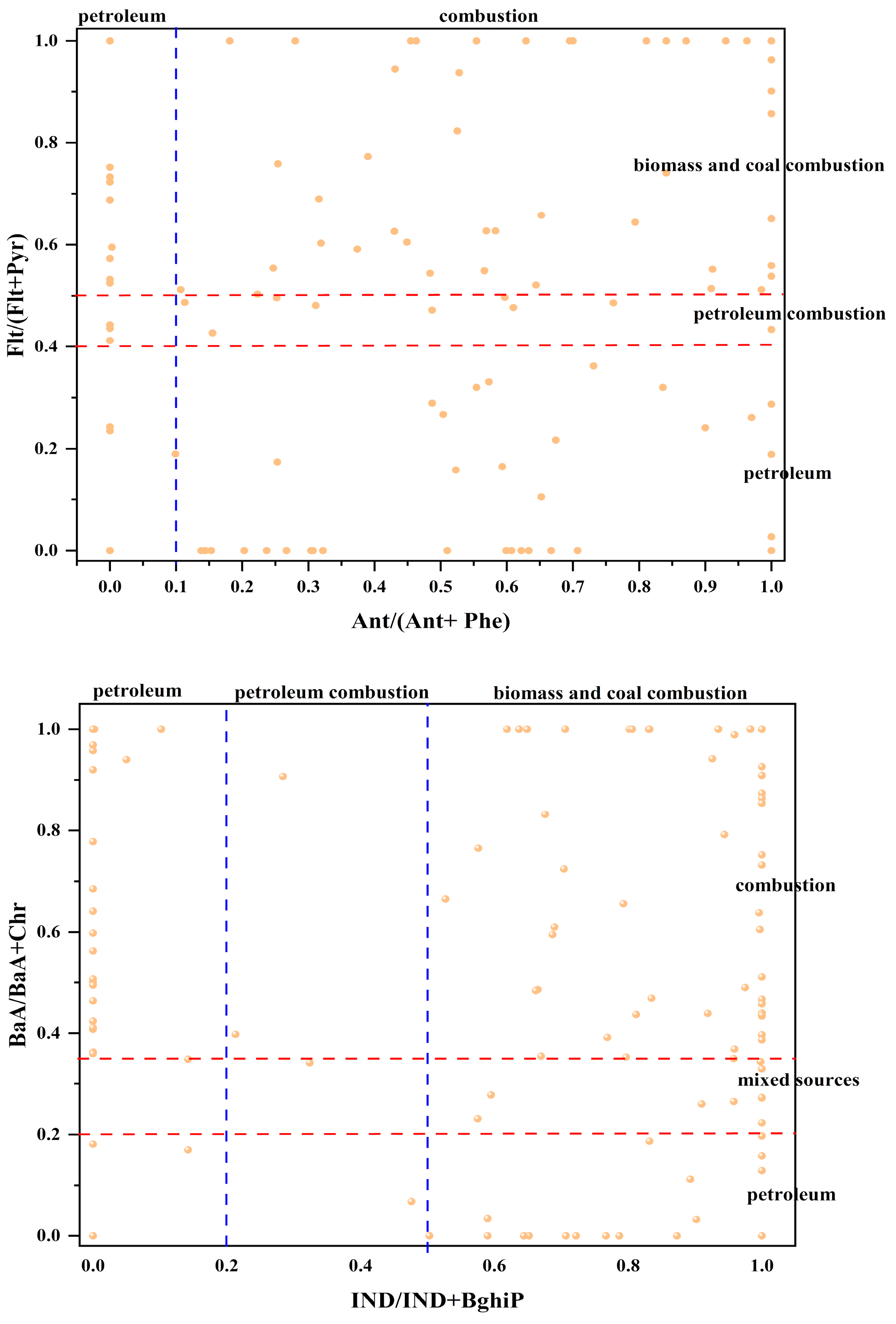
2.7.1. Feature Ratio Method
2.7.2. Positive Matrix Factorization Method (PMF)
3. Results and Discussion
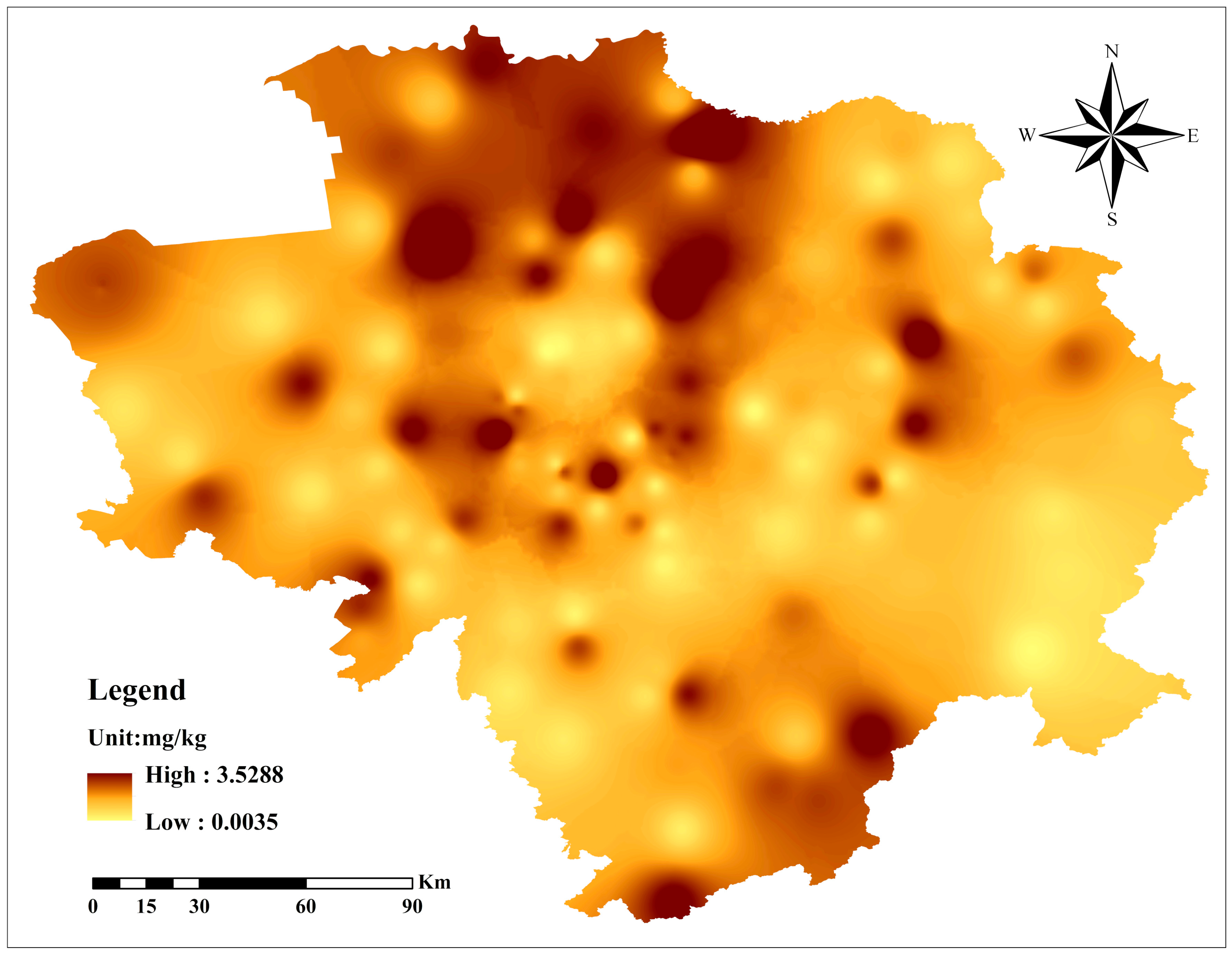
3.1. Pollution Level and PAHs Locations
| Placements | Soil Type | Total Concentration Range | Mean | Cited Material |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huanghuai, China | Agricultural soils | 0.0157–1.2476 | 0.1295 | [52] |
| Shanghai, China | Agricultural soils | 0.0223–8.214 | 1.552 | [36] |
| Xinzhou, China | Agricultural soils | 0.00–0.782 | 0.202 | [53] |
| Junggar Basin, Xinjiang | Agricultural soils | 0.0139–0.1974 | 0.0455 | [54] |
| Fujian, China | Agricultural soils | 0.0129–2.271 | 0.2239 ± 0.3243 | [55] |
| Yichang, China | Surface soils | 0.0083–0.397 | 0.0558 | [56] |
| Shanghai, China | Agricultural soils | 0.0172–3.775 | 0.339 ± 0.594 | [57] |
| Changbai Mountain range, China | Mountain soil | 0.239–2.433 | 1.047 | [58] |
| Beijing, China | Urban soil | 0.066–6.867 | 0.460 | [59] |
| London, UK | Urban soils | 4.000–67.000 | 18.000 | [60] |
| Delhi, India | Agricultural soils | 0.830–3.880 | 1.910 ± 1.020 | [61] |
| Lucknow, India | Urban soils | 0.4789–8.1641 | 3.7482 | [62] |
| King GeorgeIsland, Antarctica | Surface soils | 0.0018–0.0329 | 0.0119 ± 0.0081 | [63] |
| Australia | Industrial soils | 0.0529–6.2401 | 0.7514 | [64] |
| South Korea | Agricultural soils | 0.0223–2.834 | 0.236 | [65] |
| Japan | Agricultural soils | 0.0046–2.000 | 0.465 | [66] |
| Switzerlan | Agricultural soils | 0.05–0.619 | 0.225 | [67] |
| West PalmBeach, USA | Urban soils | 0.922–17.698 | 4.055 | [68] |
| Lesser himalayan, Pakistan | Surface soils | 0.0145–0.4374 | 0.492 | [69] |
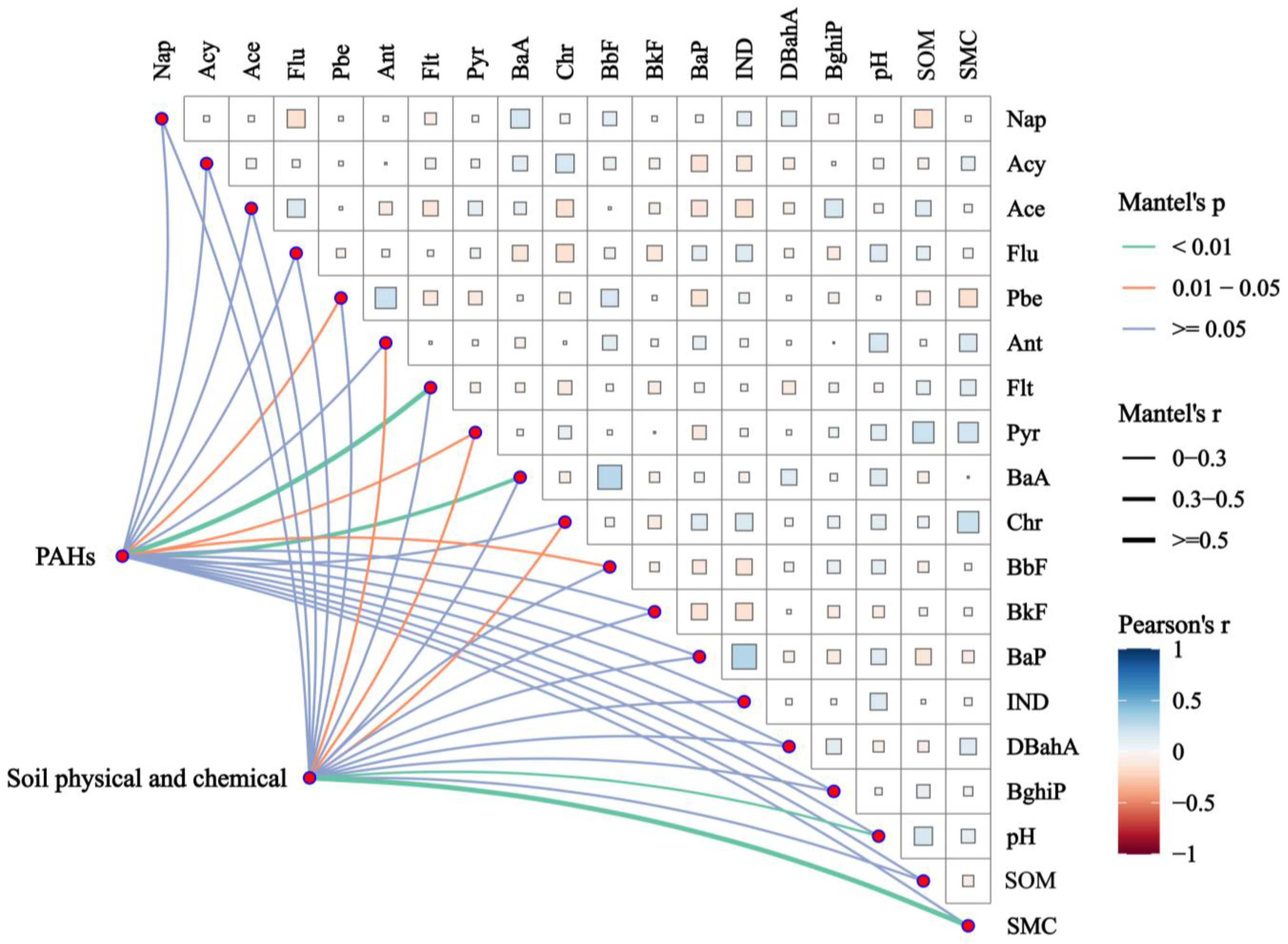
3.2. Correlation Analysis Between PAHs and Soil Properties
3.3. Analysis of the PAH Sources
3.3.1. Feature Ratio Method Source Analysis
3.3.2. PMF Source Analysis
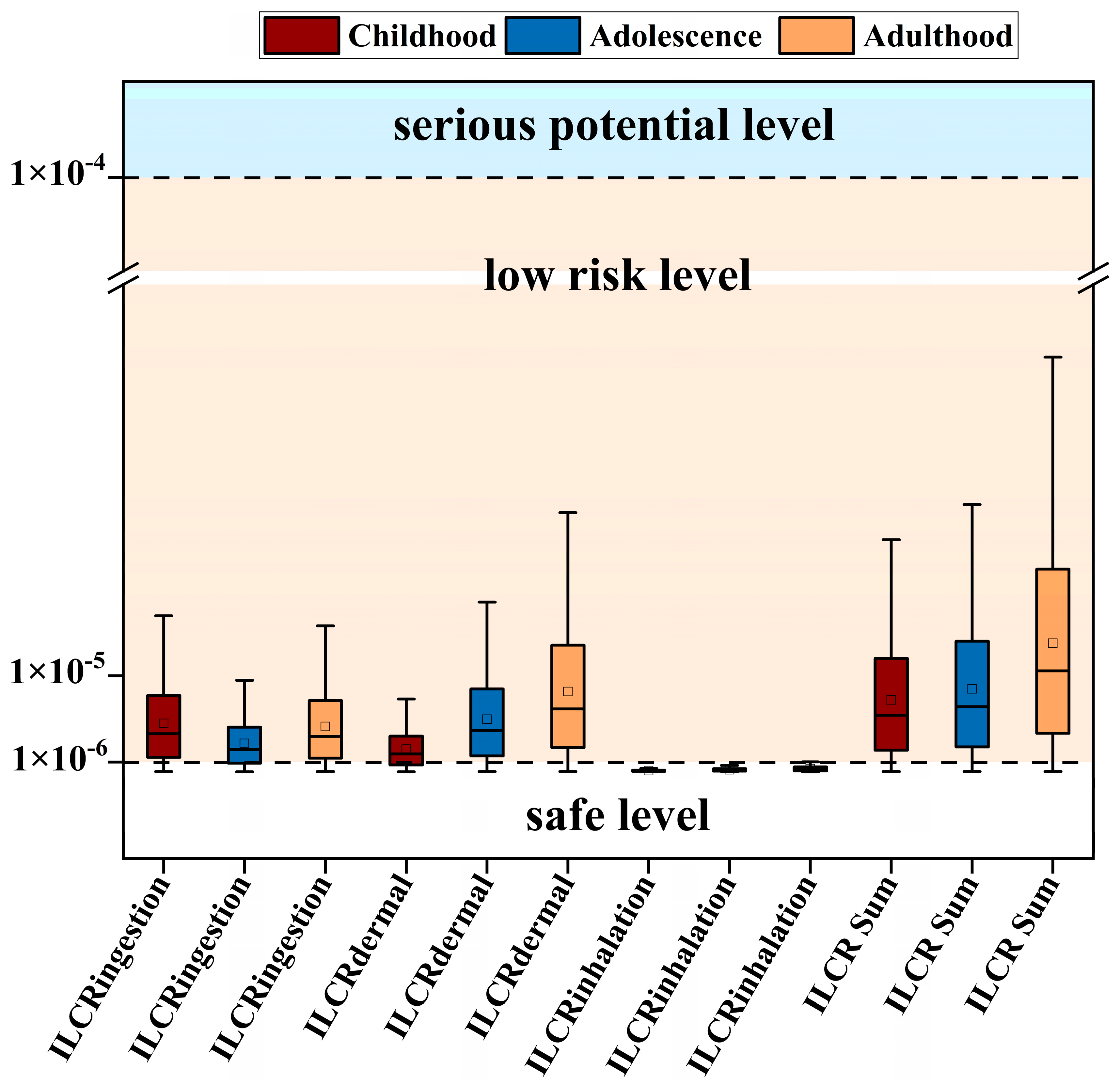
3.4. Human Health Risk Assessment
3.5. Uncertainly Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PAHs | Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| PMF | Positive matrix factorization method |
| ILCR | Incremental lifetime cancer risk |
| TEFs | Toxicity equivalence factors |
| TEQBaP | Toxic equivalent concentration |
| Nap | Naphthalene |
| Acy | Acenaphthylene |
| Ace | Acenaphthene |
| Flu | Fluorene |
| Phe | Phenanthrene |
| Ant | Anthracene |
| Flt | Fluoranthene |
| Pyr | Pyrene |
| BaA | Benz(a)anthracene |
| Chr | Chrysene |
| BbF | Benzo(b)fluoranthene |
| BkF | Benzo(k)fluoranthene |
| BaP | Benzo(a)pyrene |
| IND | Indeno (1,2,3-cd) pyrene |
| DBahA | Dibenz (a,h)anthracene |
| BghiP | Benzo (g,h,i)perylene |
References
- Ortega Albero, N.; Vallejo Sardon, S.; Lupuţ, I.; Boscaiu, M.; Donat-Torres, M.P.; Fita, A.; González-Orenga, S. Sarcocornia fruticosa, a Potential Candidate for Saline Agriculture: Antioxidant Levels in Relation to Environmental Conditions in the Eastern Iberian Peninsula. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, D.C.S.; Yunta, F.; Baragaño, D.; Evrard, O.; Reiff, T.; Silva, V.; de la Torre, A.; Zhang, C.; Panagos, P.; Jones, A.; et al. Soil pollution in the European Union—An outlook. Environ. Sci. Policy 2024, 161, 103876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushkova, S.; Minkina, T.; Deryabkina, I.; Rajput, V.; Antonenko, E.; Nazarenko, O.; Yadav, B.K.; Hakki, E.; Mohan, D. Environmental pollution of soil with PAHs in energy producing plants zone. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enshaey Nezhad, M.; Goudarzi, G.; Babaei, A.A.; Mohammadi, M.J. Characterization, ratio analysis, and carcinogenic risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon compounds bounded PM10 in a southwest of Iran. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2023, 24, 101419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhu, X.; Si, S.; Kou, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Shen, B. Remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons polluted soil by biochar loaded humic acid activating persulfate: Performance, process and mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 399, 130633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Sun, C.; Xu, L.; Xu, L.; Tu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bai, R.; Liu, J. Copper-catalyzed aerobic oxidative dehydrogenative cyclization to construct polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Tetrahedron Lett. 2024, 140, 155040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wan, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Q.; Zhu, K.; Xiang, Z.; Liu, R.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Song, R. Dyslexia is associated with urinary polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolite concentrations of children from China: Data from the READ program. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 346, 123538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soladoye, O.P.; Shand, P.; Dugan, M.E.R.; Gariépy, C.; Aalhus, J.L.; Estévez, M.; Juárez, M. Influence of cooking methods and storage time on lipid and protein oxidation and heterocyclic aromatic amines production in bacon. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Zhang, H.; Lv, X.; Xie, R.; Chen, B.; Lai, Y.; Chen, L.; Teng, H.; Cao, H. A systematic study on the chemical model of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons formation from nutrients (glucose, amino acids, fatty acids) in food. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 138849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaoui, M.; Louadj, L.; Ferrand, N.; Nehme, R.; Sabbah, M.; Abdennebi-Najar, L. Carcinogenic effect of low doses of polycyclic and heterocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and amines and lack of protection by inulin supplementation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 185, 114454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mörchen, R.; Rahimova, H.; Siegmund, B.F.; Diaz, F.A.; Roland, B.; Lehndorff, E. Organic matter imports to the Atacama Desert using polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons as tracer. Glob. Planet. Change 2024, 235, 104394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Pan, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z. Source and health risk assessment of soil polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons under straw burning condition in Changchun City, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 165057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Lan, J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, R.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z. Spatiotemporal variations in soil pollution by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons over a 20-year economic boom in different districts of a heavy industrial city in North China. Environ. Res. 2024, 247, 118134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Huang, C.; Chen, C.; Lam, S.S.; Sonne, C.; Kang, C.; Hung, C. Facile heteroatoms modification biochar production from mahogany (Swietenia macrophylla King) pericarps for enhanced the suppression of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollutants. Env. Pollut (1987) 2024, 343, 123173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, G.; Liao, X. Negative role of biochars in the dissipation and vegetable uptake of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in an agricultural soil: Cautions for application of biochars to remediate PAHs-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 213, 112075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L. Spatial distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contamination in urban soil of China. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Du, Y.; Allinson, G.; Zeng, X.; Li, X.; Fang, H. Metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons pollutants in industrial parks under valley landforms in Tibetan Plateau: Spatial pattern, ecological risk and interaction with soil microorganisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 471, 134411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, H.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Hao, H.; Zhao, C.; Xing, S.; Yu, H.; Liang, X.; Lu, J.; Chen, X.; et al. Large-scale soil application of hydrochar: Reducing its polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon content and toxicity by heating. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 471, 134467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łyszczarz, S.; Lasota, J.; Staszel, K.; Błońska, E. Effect of forest and agricultural land use on the accumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in relation to soil properties and possible pollution sources. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 490, 119105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dong, J.; Long, J.; Jiang, J.; Lin, C. Characteristics, sources analysis, and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contamination in surface sediments surrounding tourist island. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 206, 116735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatami, A.; Moghaddam, A.D.; Talatappeh, H.D.; Mohammadimehr, M. Simultaneous extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and tetracycline antibiotics from honey samples using dispersive solid phase extraction combined with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction before their determination with HPLC-DAD. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2024, 131, 106179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaashikaa, P.R.; Karishma, S.; Kamalesh, R.; Saravanan, A.; Vickram, A.S.; Anbarasu, K. A systematic review on enhancement strategies in biochar-based remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chemosphere 2024, 355, 141796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Yan, K.; Yuan, Z.; Feng, D.; Wang, H.; Wu, L.; Xu, J. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) pollution and risk assessment of soils at contaminated sites in China over the past two decades. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 450, 141876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruifei, L.; Jin, Z.; Peter, K. Consumption- and Income-Based Sectoral Emissions of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in China from 2002 to 2017. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3582–3592. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Chen, R.; Xu, Y.; Chen, C.; Xiong, J.; Tan, W.; Fang, L. Examining diverse remediation mechanisms of biochar in soil contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) of various ring structures: A global meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 171178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Chao, Y.; Shi, Z.; Lin, D.; Yang, K. Effects of Chinese “double carbon strategy” on soil polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons pollution. Environ. Int. 2024, 188, 108741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, Y. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contamination in surface soil of China: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605–606, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Hu, W.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Feng, T.; Hong, Z.; Jiang, J.; Xu, R. Exchangeable acidity characteristics of farmland black soil in northeast China. Geoderma Reg. 2024, 38, e852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhengwu, C.; Yang, W.; Rui, Y.U.; Guanghui, X.U.; Yong, Y.U. Content characteristics and risk assessment of PAHs in agricultural soils around power plants in Jilin Province. Environ. Pollut. Control 2018, 40, 806–811. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Deng, X.; Yue, H. Black soil conservation will boost China’s grain supply and reduce agricultural greenhouse gas emissions in the future. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 106, 107482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Hu, W.; Jia, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Huang, B.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shukla, M.K.; et al. Soil degradation: A global threat to sustainable use of black soils. Pedosphere 2024, in press. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, C.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y.; Teng, Y. Developing an integrated framework for source apportionment and source-specific health risk assessment of PAHs in soils: Application to a typical cold region in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ma, T.; Song, R.; Lu, M.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Risk effects of meteorological factors on human brucellosis in Jilin province, China, 2005–2019. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Huo, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Pang, C.; Ma, C.; Zheng, J.; Wu, F. Intensive land-based activities increase the potential risk of benzo[α]pyrene (BaP) to aquatic ecosystems and human health in coastal areas of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 371, 133571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Aniagu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, T. AHR-mediated DNA damage contributes to BaP-induced cardiac malformations in zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, R.; Yang, X.; Su, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Long, M. Levels, sources and probabilistic health risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the agricultural soils from sites neighboring suburban industries in Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Peng, C.; He, Y. Introducing a land use-based weight factor in regional health risk assessment of PAHs in soils of an urban agglomeration. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 887, 163833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, G.; Chen, H.; Zhai, Y.; Teng, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, R. Source apportionment and source specific health risk assessment of HMs and PAHs in soils with an integrated framework in a typical cold agricultural region in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 167337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Pang, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, X.; Fu, K.; Zhang, T.; Han, J.; Yang, L.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, S. Distribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Pesticides in Danjiangkou Reservoir and Evaluation of Ecological Risk. Toxics 2024, 12, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knafla, A.; Phillipps, K.A.; Brecher, R.W.; Petrovic, S.; Richardson, M. Development of a dermal cancer slope factor for benzo[a]pyrene. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 45, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund (RAGS) Part A. Saúde Pública 1989, 804, 636–640. [Google Scholar]
- Adesina, O.A.; Kolawole, O.M.; Lala, M.A.; Omofoyewa, M.G.; Igbafe, A.I. Characterization and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from the emission of different power generator. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Ma, S.; Zhao, W.; Tian, M.; Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, Z. Calculated cancer risks for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon mixtures in mainstream smoke of cigarettes sold in China. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 142, 105427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziyaei, K.; Mokhtari, M.; Hashemi, M.; Rezaei, K.; Abdi, F. Association between exposure to water sources contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and cancer risk: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, M.A.; Hassan, S.K.; Shetaya, W.H.; Al, S.M.; Nawab, J.; Khoder, M.I. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in indoor mosques dust in Saudi Arabia: Levels, source apportionment, human health and carcinogenic risk assessment for congregators. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimkowicz-Pawlas, A.; Smreczak, B.; Maliszewska-Kordybach, B. Integrated Ecological Risk Assessment of the Agricultural Area under a High Anthropopressure Based on Chemical, Ecotoxicological and Ecological Indicators. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, B.; Wang, G.; Gao, W.; Zheng, L.; Chi, W.; Shi, Y. Analysis of PAHs content, source and risk assessment in surface sediments from Laizhou Bay and Bohai Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 197, 115698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, Y.P. Long-term (1993–2018) particulate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) concentration trend in the atmosphere of Seoul: Changes in major sources and health effects. Atmos. Environ. (1994) 2024, 325, 120418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Bai, Y.; Cao, P.; Hua, P. Vehicular contribution of PAHs in size dependent road dust: A source apportionment by PCA-MLR, PMF, and Unmix receptor models. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, M.; Yu, G. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban soils of the megacity Shanghai: Occurrence, source apportionment and potential human health risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Sun, Q.; Bian, Y.; Han, J.; Jiang, X.; Xue, J.; Song, Y. Predicting the bioavailability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rhizosphere soil using a new novel in situ solid-phase microextraction technique. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Xue, N.; Zhou, L.; Li, F.; Cong, X.; Han, B.; Li, H.; Yan, Y.; Liu, B. Risk assessment and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in agricultural soils of Huanghuai plain, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 84, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Shao, S.; Deng, W.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Wen, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.; et al. Occurrence of BTX and PAHs in underground drinking water of coking contaminated sites: Linkage with altitude and health risk assessment by boiling-modified models. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuerla, A.; Xie, X.; Hua, Z.; Ma, J.; Abliz, A.; Mamtimin, Y.; Mamat, A.; Fan, Y.; Jiang, N.; An, J. Distribution, sources, and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface soils and plants from industrial and agricultural areas, Junggar Basin, Xinjiang. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 369, 122340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zeng, F.; Chen, W.; Qu, C.; Li, X.; Xing, X.; Qi, S.; et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in agricultural soils from northwest Fujian, southeast China; spatial distribution, source apportionment, and toxicity evaluation. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 195, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, C.; Xiong, J.; Zhao, R.; Fang, J.; Liao, Y.; Song, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, W.; et al. Levels, sources, and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soils of karst trough zone, central China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 614, 128568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, P.; Zhang, X.; Wei, X.; Huang, Y.; Du, W.; Qadeer, A.; Liu, M.; Huang, Y. Source apportionment of PAHs in roadside agricultural soils of a megacity using positive matrix factorization receptor model and compound-specific carbon isotope analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, T. Characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soil horizon from high-altitude mountains in Northeastern China. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Ma, J.; Wei, H.; Liu, Q.; Liu, L.; Wu, H.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y. Potential sources, influencing factors, and health risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the surface soil of urban parks in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vane, C.H.; Kim, A.W.; Beriro, D.J.; Cave, M.R.; Knights, K.; Moss-Hayes, V.; Nathanail, P.C. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) in urban soils of greater London, UK. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 51, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, T.; Khillare, P.S.; Shridhar, V.; Ray, S. Pattern, sources and toxic potential of PAHs in the agricultural soils of Delhi, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Khan, R.; Bhattacharya, P.; Devanesan, S.; AlSalhi, M.S. Concentration, source apportionment and potential carcinogenic risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in roadside soils. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deelaman, W.; Pongpiachan, S.; Tipmanee, D.; Choochuay, C.; Suttinun, O.; Charoenkalunyuta, T.; Promdee, K. Ecotoxicological risk and health risk characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in terrestrial soils of King George Island, Antarctica. Polar Sci. 2021, 29, 100715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, O.; Semple, K.T.; Ramadass, K.; O’Connor, W.; Hansbro, P.; Thavamani, P. Analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their polar derivatives in soils of an industrial heritage city of Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.J.; Song, B.H.; Eom, K.C.; Lee, S.H.; Smith, A. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in agricultural soils in South Korea. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, K.; Mizukami, M.; Ueda, Y.; Hamada, N.; Seike, N. Residue level of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Japanese paddy soils from 1959 to 2002. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucheli, T.D.; Blum, F.; Desaules, A.; Gustafsson, O. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, black carbon, and molecular markers in soils of Switzerland. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 1061–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Da, S.E.; Xiang, P.; Ma, L.Q. Emerging and legacy PAHs in urban soils of four small cities: Concentrations, distribution, and sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, R.; Ali, U.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Alam, K.; Sweetman, A.J.; Jones, K.C.; Malik, R.N. Assessing the level and sources of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soil and sediments along Jhelum riverine system of lesser Himalayan region of Pakistan. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliszewska-Kordybach, B.; Fuge, R.; Selinus, O.E.; Billett, M.; Fuge, R.; Billett, M.; Selinus, O. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in agricultural soils in Poland; preliminary proposals for criteria to evaluate the level of soil contamination. Appl. Geochem. 1996, 11, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cui, L.; Wang, J.; Zuo, X.; Lei, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhai, X.; Li, J.; Li, W. Distribution, source diagnostics, and factors influencing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Yellow River Delta wetland. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 67, 103181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathankumar, A.K.; Saikia, K.; Ramachandran, K.; Batista, R.A.; Cabana, H.; Vaidyanathan, V.K. Effect of soil organic matter (SOM) on the degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons using Pleurotus dryinus IBB 903-A microcosm study. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kögel-Knabner, I.; Amelung, W. Soil organic matter in major pedogenic soil groups. Geoderma 2021, 384, 114785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Dong, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, M.; Kong, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, R. Abundance and sources of particulate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and aromatic acids at an urban site in central China. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 142, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hopke, P.K.; Han, Y.; Yi, S.; Holsen, T.M.; Cybart, S.; Kozlowski, K.; Milligan, M. Application of receptor modeling to atmospheric constituents at Potsdam and Stockton, NY. Atmo. Environ. (1994) 2003, 37, 4997–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, L.; Li, Q.; Li, R.; Zhang, D.; Xu, W.; Feng, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Huang, L.; et al. Hourly measurement of PM (2.5)-bound nonpolar organic compounds in Shanghai: Characteristics, sources and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 148070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, T. Traffic contribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the center of a large city. Atmo. Environ. (1994) 1996, 30, 3481–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Dong, Z.; Duan, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, S. Variation tendency of pollution characterization, sources, and health risks of PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in an emerging megacity in China: Based on three-year data. Atmos. Res. 2019, 217, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, N.R.; Scheff, P.A.; Holsen, T.M. PAH source fingerprints for coke ovens, diesel and, gasoline engines, highway tunnels, and wood combustion emissions. Atmo. Environ. (1994) 1995, 29, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, H. Characterization and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) pollution in particulate matter in rural residential environments in China-A review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 96, 104690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, P.; Yu, G.; Chen, C.; Qin, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Li, R.; Zhang, L.; et al. Unveiling the pollution and risk of atmospheric (gaseous and particulate) polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a heavily polluted Chinese city: A multi-site observation research. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 428, 139454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulun, T. Study on Soil Contamination Characteristics and Environmental Risks of Key Industrial Sites in Heavy Industrial Zone of Northeast China. Master’s Thesis, JiLin Universty, Changchun, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, R.; Liao, J.; Zhang, P.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, Y. Distribution and source identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) with PCA-MLR and PMF methods in the topsoil of Chengdu at SW, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zheng, T.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ren, M.; Gao, Z.; Lin, B.; Feng, X. Identification and health risk evaluation of soil contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons at shale gas extraction sites based on positive matrix factorization. Chemosphere 2024, 356, 141962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Liang, W.; Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X. The occurrence, sources, and health risks of substituted polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (SPAHs) cannot be ignored. Environ. Int. 2024, 183, 108390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinpelumi, V.K.; Kumi, K.G.; Onyena, A.P.; Sam, K.; Ezejiofor, A.N.; Frazzoli, C.; Ekhator, O.C.; Udom, G.J.; Orisakwe, O.E. A comparative study of the impacts of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and soils in Nigeria and Ghana: Towards a framework for public health protection. J. Hazard Mater. Adv. 2023, 11, 100336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


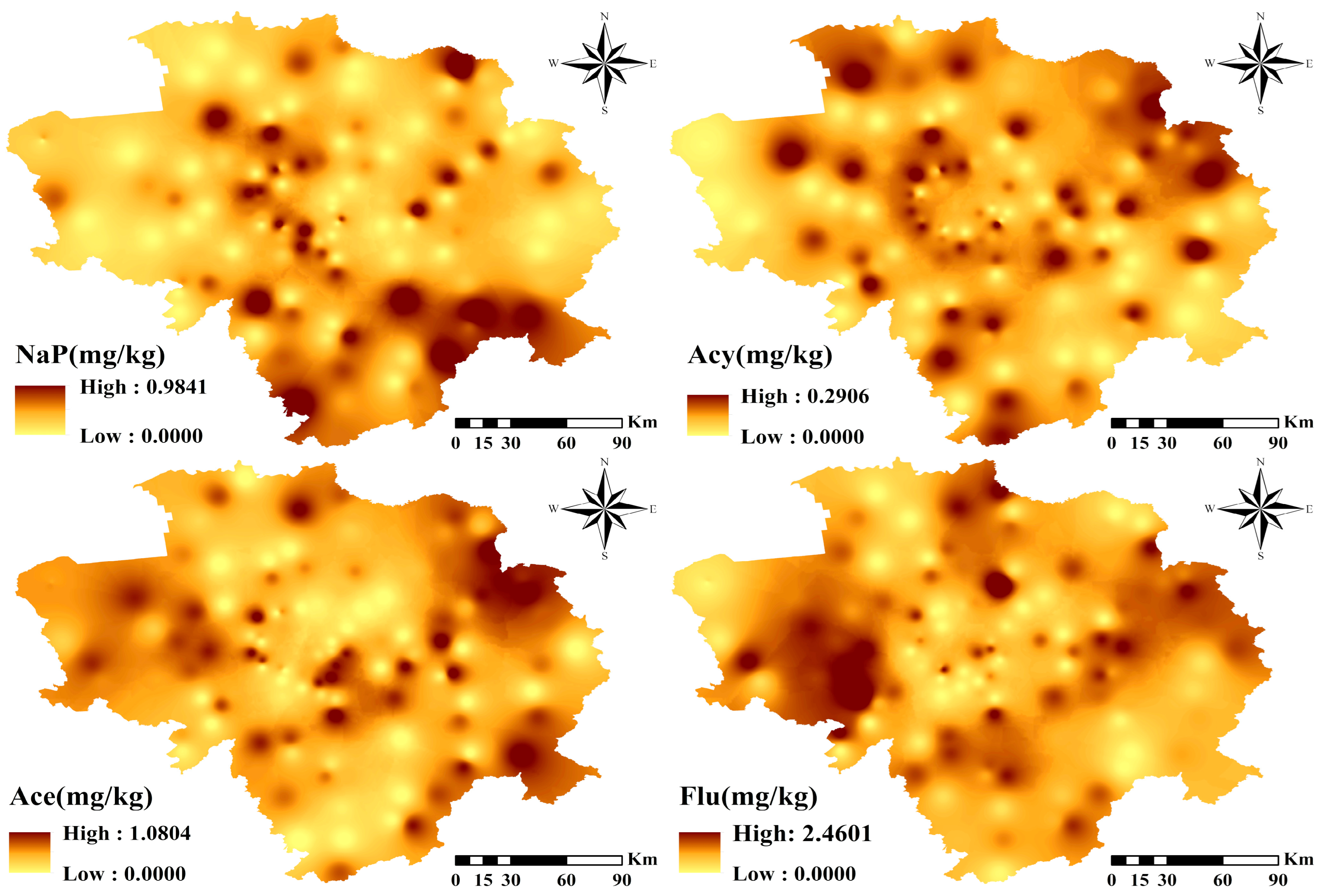
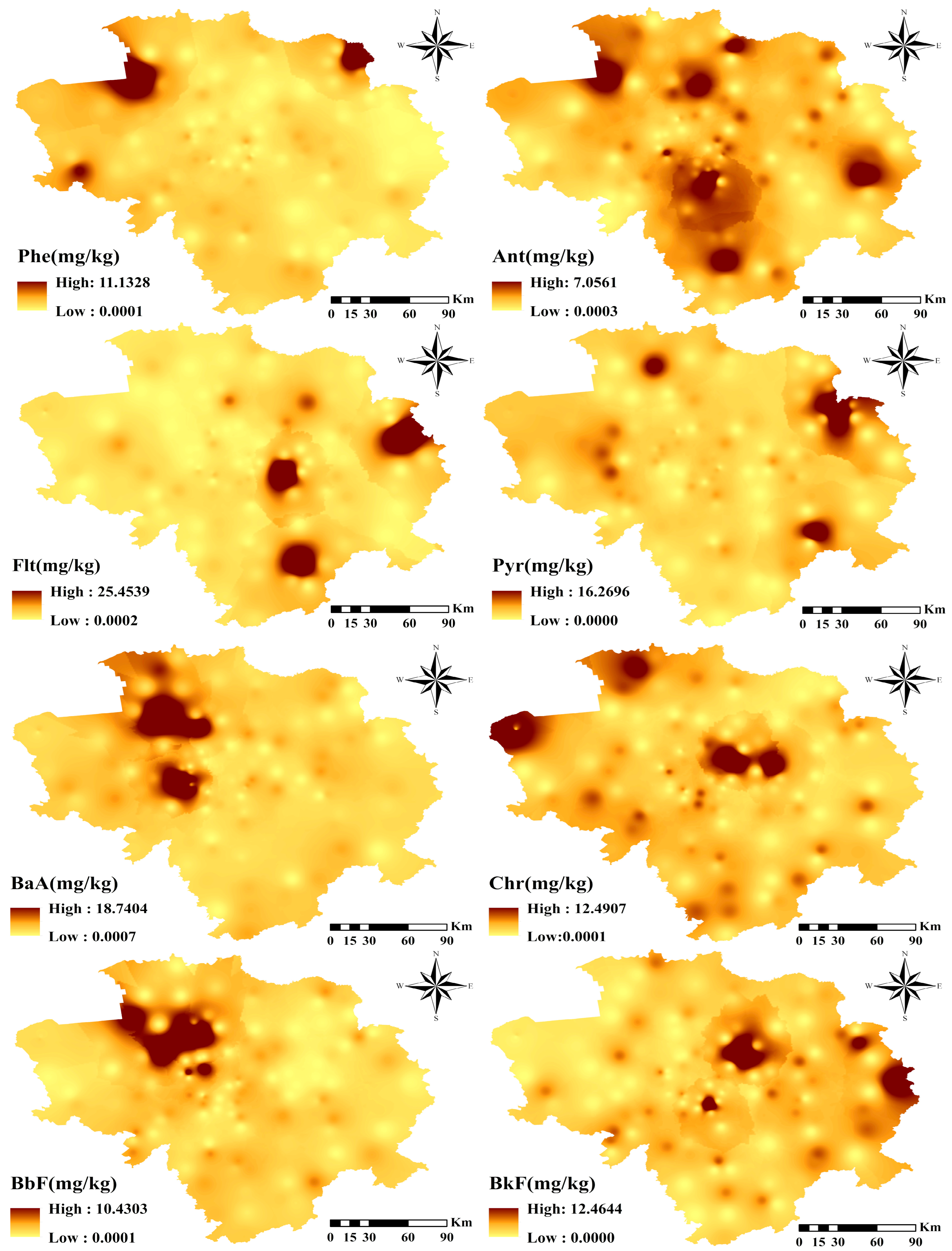
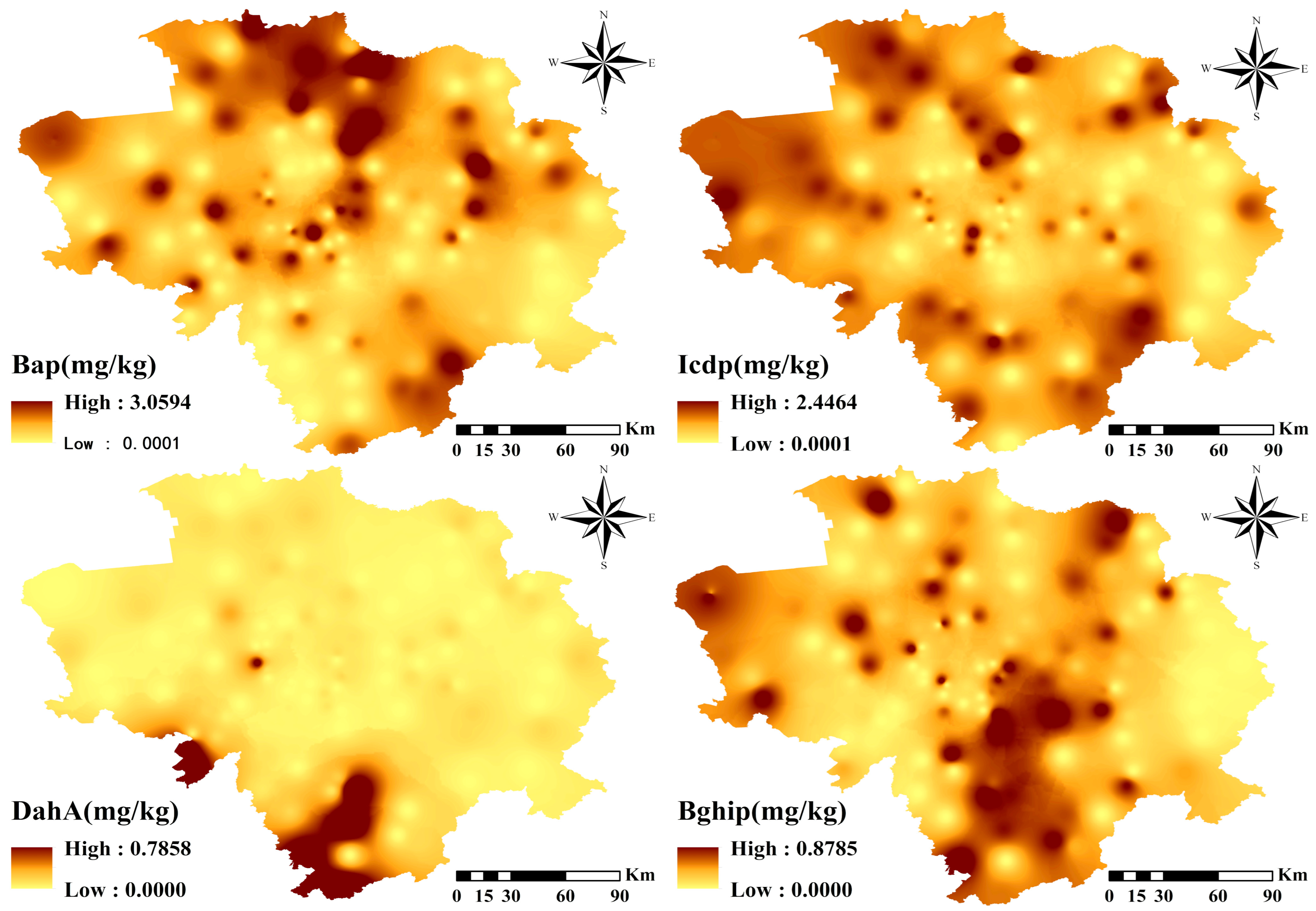

| PAHs | Aromatic Ring | TEF 1 | Min | Max | Mean | Median | SD | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nap | 2 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.984 | 0.264 | 0.178 | 0.272 | 0.764 | −0.589 |
| Acy | 3 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.291 | 0.111 | 0.099 | 0.099 | 0.301 | −1.342 |
| Ace | 3 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 1.080 | 0.436 | 0.419 | 0.359 | 0.189 | −1.348 |
| Flu | 3 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 1.609 | 0.628 | 0.574 | 0.539 | 0.646 | 0.351 |
| Phe | 3 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 2.460 | 0.790 | 0.607 | 1.463 | 6.134 | 41.909 |
| Ant | 3 | 0.01 | 0.000 | 11.163 | 0.744 | 0.587 | 0.928 | 3.417 | 18.389 |
| Flt | 4 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 25.454 | 1.082 | 0.531 | 3.129 | 6.220 | 41.103 |
| Pyr | 4 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 16.270 | 0.756 | 0.578 | 1.603 | 8.050 | 75.899 |
| BaA | 4 | 0.1 | 0.000 | 18.740 | 1.191 | 0.727 | 2.337 | 5.736 | 36.359 |
| Chr | 4 | 0.01 | 0.000 | 12.491 | 0.948 | 0.606 | 1.487 | 4.984 | 33.336 |
| BbF | 5 | 0.1 | 0.000 | 10.430 | 0.548 | 0.328 | 1.31 | 6.512 | 51.892 |
| BkF | 5 | 0.1 | 0.000 | 12.464 | 0.677 | 0.316 | 1.381 | 6.364 | 49.179 |
| BaP | 5 | 1 | 0.000 | 3.074 | 0.689 | 0.455 | 0.77 | 0.874 | −0.158 |
| IND | 5 | 0.1 | 0.000 | 2.446 | 0.744 | 0.616 | 0.677 | 0.362 | −1.186 |
| DBahA | 6 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.786 | 0.069 | 0.026 | 0.157 | 3.670 | 12.804 |
| BghiP | 6 | 0.01 | 0.000 | 0.879 | 0.274 | 0.139 | 0.306 | 0.729 | −0.982 |
| LMW PAHs 2 | 0.250 | 16.346 | 2.973 | 2.714 | 1.978 | 4.040 | 22.943 | ||
| HMW PAHs 3 | 1.689 | 30.327 | 6.977 | 5.994 | 4.660 | 2.568 | 7.856 | ||
| ∑7Car PAHs 4 | 0.000 | 22.316 | 4.866 | 4.288 | 3.466 | 2.952 | 11.281 | ||
| ∑16PAHs 5 | 2.546 | 31.993 | 9.950 | 9.057 | 4.863 | 2.089 | 5.729 |
| PAHs | TEFi | Min | Max | Mean | PAHs | TEFi | Min | Max | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nap | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.0010 | 0.0003 | BaA | 0.1 | 0.000 | 1.8740 | 0.1191 |
| Acy | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.0003 | 0.0001 | Chr | 0.01 | 0.000 | 0.1249 | 0.0095 |
| Ace | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.0011 | 0.0004 | BbF | 0.1 | 0.000 | 1.0430 | 0.0548 |
| Flu | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.0025 | 0.0006 | BkF | 0.1 | 0.000 | 1.2464 | 0.0677 |
| Phe | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.0112 | 0.0008 | BaP | 1.00 | 0.000 | 3.0739 | 0.6888 |
| Ant | 0.010 | 0.000 | 0.0706 | 0.0074 | IND | 0.10 | 0.000 | 0.2446 | 0.0744 |
| Flt | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.0255 | 0.0011 | DBahA | 1.00 | 0.000 | 0.7858 | 0.0694 |
| Pyr | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.0163 | 0.0008 | BghiP | 0.010 | 0.000 | 0.0088 | 0.0027 |
| Site | Description | ILCRing | ILCRder | ILCRinh | ILCRs | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sichuan, China | Children | 6.08 × 10−9 | 2.44 × 10−12 | 7.58 × 10−8 | 8.19 × 10−8 | [84] |
| Adult | 7.78 × 10−9 | 3.12 × 10−12 | 1.38 × 10−5 | 1.38 × 10−5 | ||
| Chongqing, China | Children | 7.08 × 10−9 | 2.84 × 10−12 | 8.83 × 10−8 | 9.53 × 10−8 | [84] |
| Adult | 9.06 × 10−9 | 3.63 × 10−12 | 1.61 × 10−5 | 1.61 × 10−5 | ||
| Chengdu, China | Children | 8.05 × 10−6 | 5.84 × 10−6 | 1.56 × 10−6 | 1.39 × 10−5 | [83] |
| Adolescents | 7.95 × 10−6 | 6.53 × 10−6 | 8.07 × 10−6 | 1.46 × 10−5 | ||
| Adult | 8.88 × 10−6 | 8.95 × 10−6 | 1.39 × 10−6 | 1.79 × 10−5 | ||
| Dongying, China | Children | 4.76 × 10−7 | 1.05 × 10−5 | 3.48 × 10−5 | 4.58 × 10−5 | [85] |
| Adult | 6.78 × 10−7 | 3.13 × 10−5 | 1.37 × 10−5 | 1.73 × 10−4 | ||
| Nigeria, Africa | Children | 2.95 × 10−2 | 3.68 × 10−3 | 5.73 × 10−3 | 6.42 × 10−4 | [86] |
| Adult | 2.31 × 10−3 | 4.10 × 10−3 | 1.79 × 10−7 | 6.19 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aihemaitijiang, G.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, C. PAH Contamination, Sources and Health Risks in Black Soil Region of Jilin Province, China. Toxics 2024, 12, 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120937
Aihemaitijiang G, Zhang L, Li M, Chen Y, Zhang J, Zhang F, Zhao C. PAH Contamination, Sources and Health Risks in Black Soil Region of Jilin Province, China. Toxics. 2024; 12(12):937. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120937
Chicago/Turabian StyleAihemaitijiang, Guzailinuer, Lujuan Zhang, Mingtang Li, Yanan Chen, Jiquan Zhang, Feng Zhang, and Chunli Zhao. 2024. "PAH Contamination, Sources and Health Risks in Black Soil Region of Jilin Province, China" Toxics 12, no. 12: 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120937
APA StyleAihemaitijiang, G., Zhang, L., Li, M., Chen, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, F., & Zhao, C. (2024). PAH Contamination, Sources and Health Risks in Black Soil Region of Jilin Province, China. Toxics, 12(12), 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120937








