Parabens, Triclosan and Bisphenol A in Surface Waters and Sediments of Baiyang Lake, China: Occurrence, Distribution, and Potential Risk Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compounds and Materials
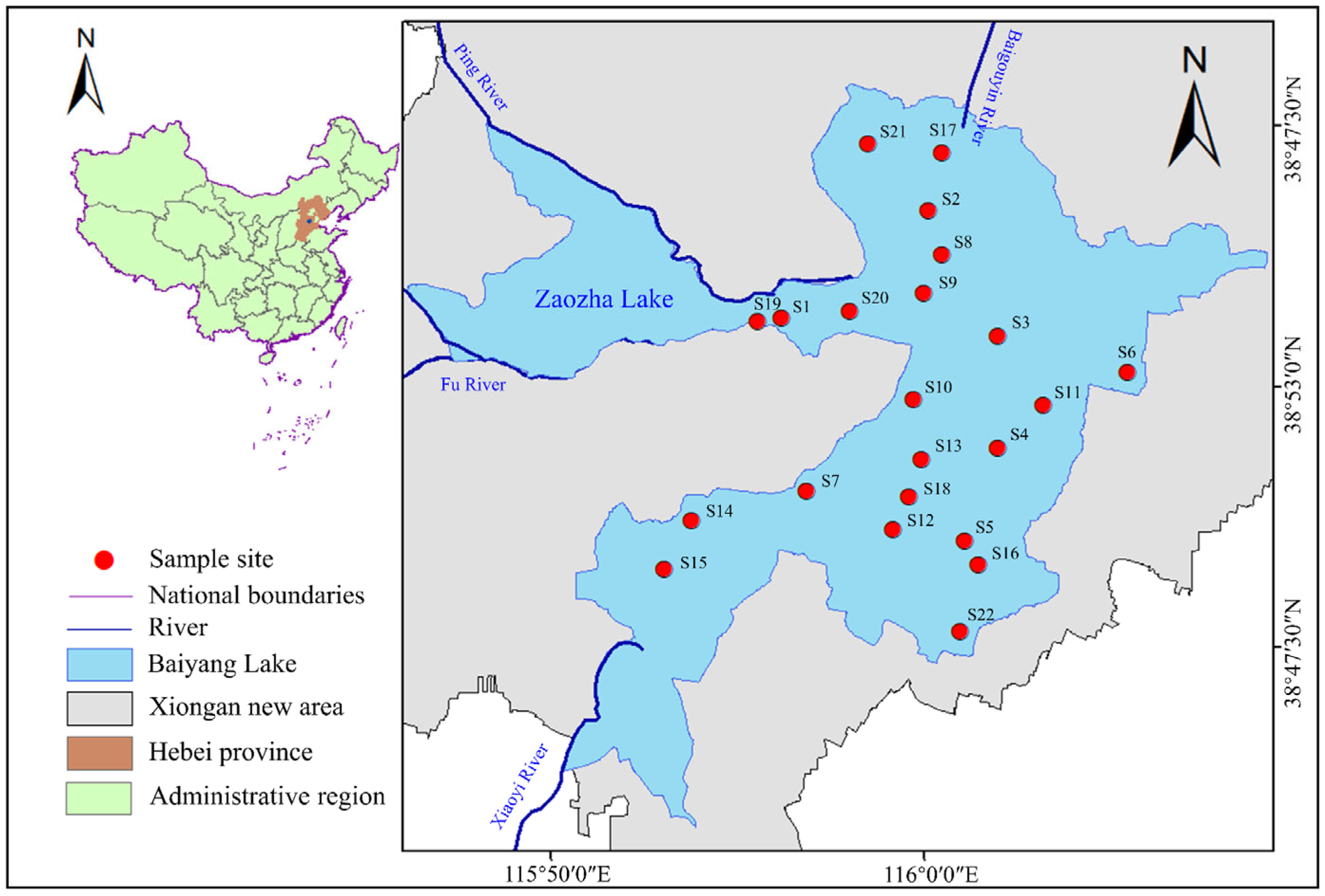
2.2. Study Area and Sampling
2.3. Sample Pretreatment and Analysis
2.4. Quality Assurance/Quality Control (QA/QC)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Risk Assessment
2.6.1. Health Risk Assessment
2.6.2. Ecological Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
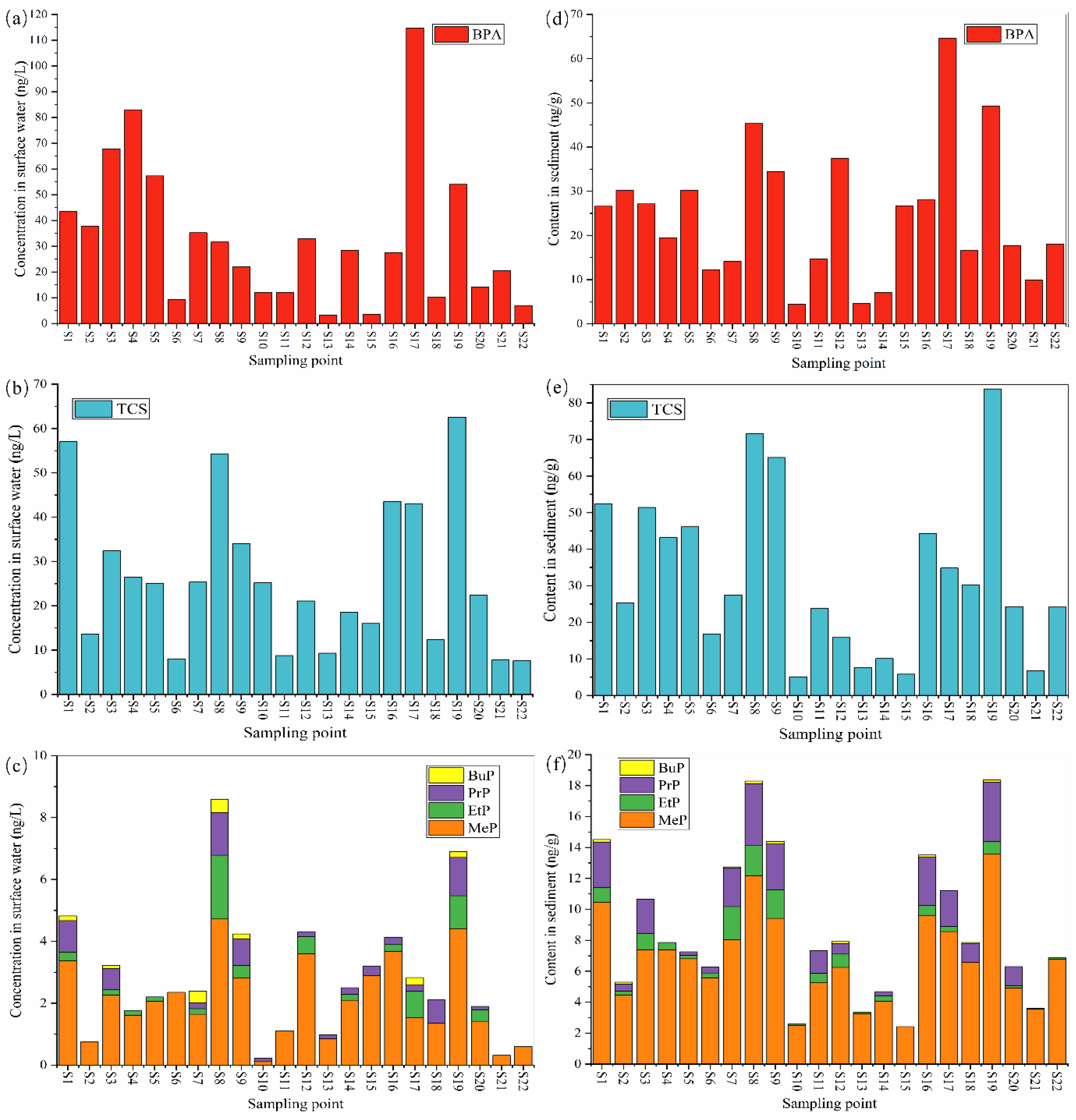
3.1. Concentrations of Parabens TCS and BPA in Surface Water
3.2. Contents of Parabens TCS and BPA in Sediment
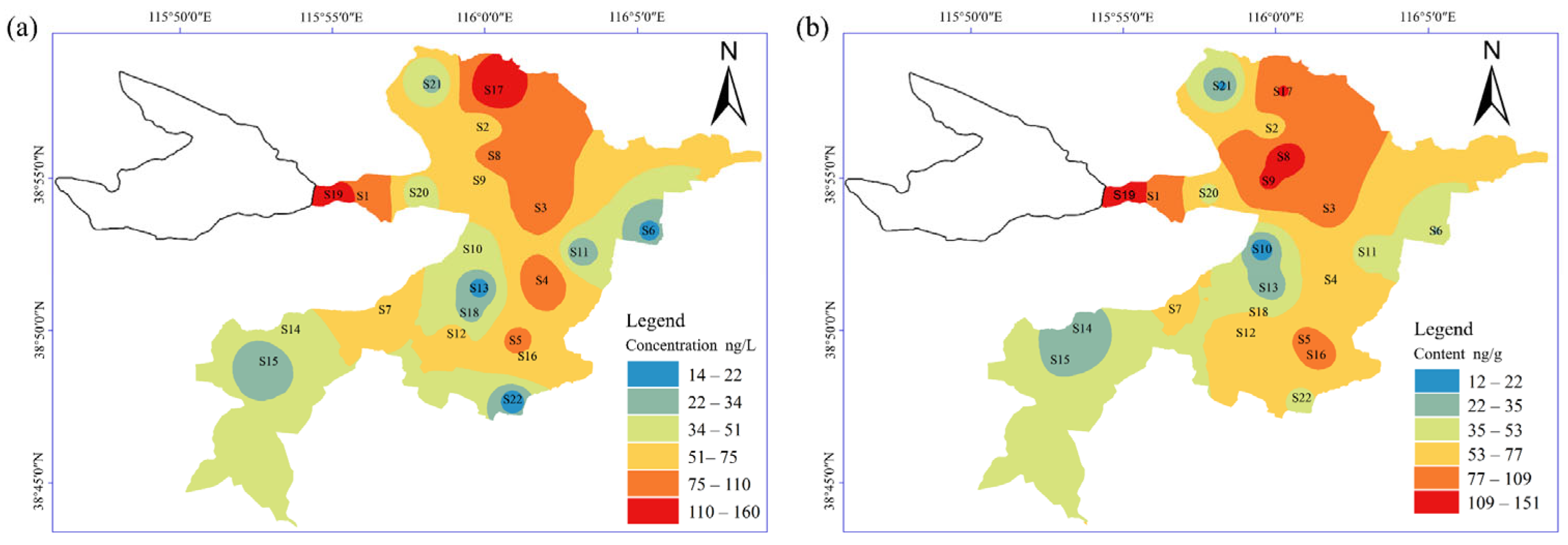
3.3. Spatial Distribution in Surface Water and Sediment
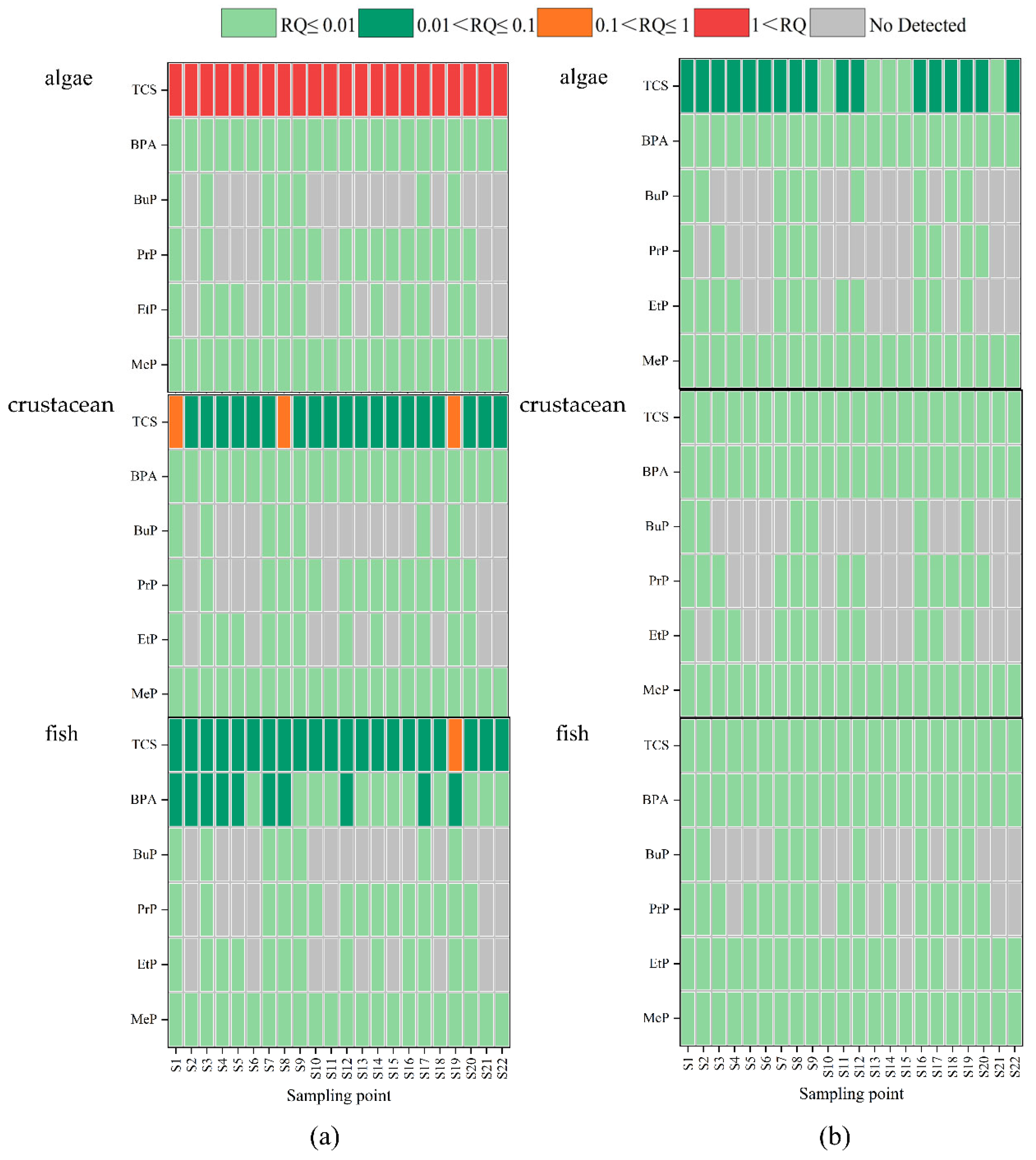
3.4. Risk Assessment
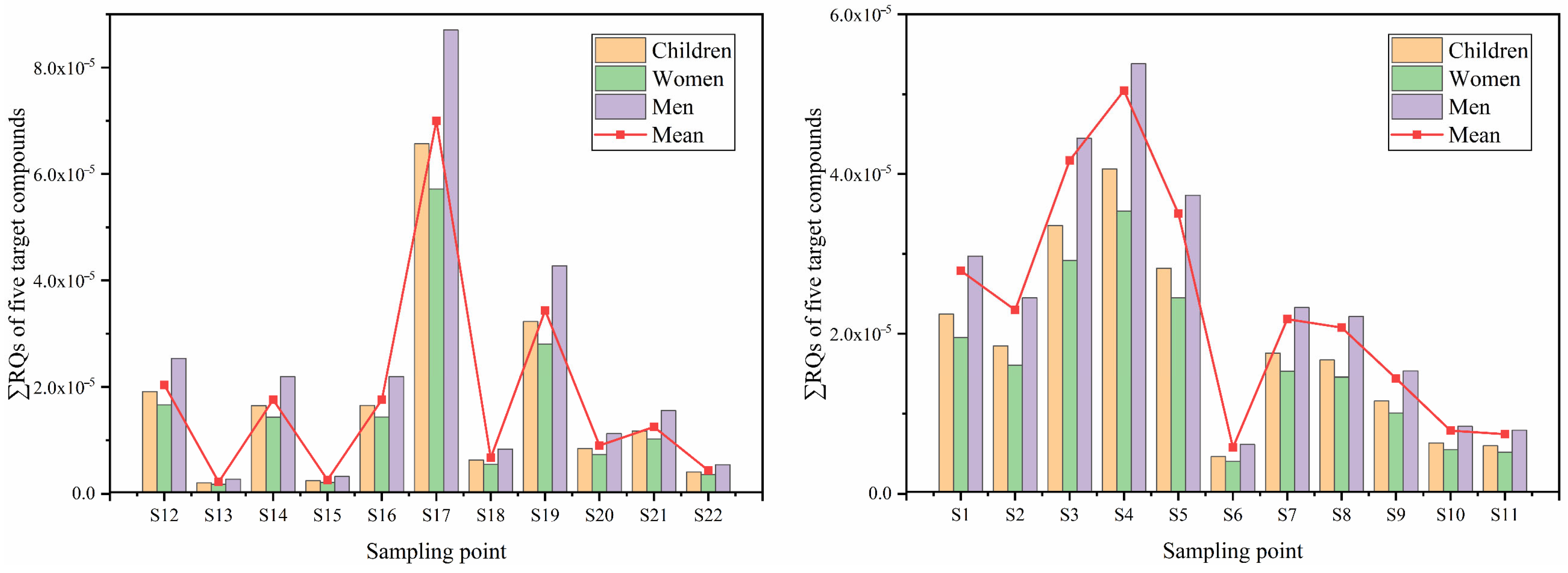
3.4.1. Health Risk Assessment
3.4.2. Ecological Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Q.; Jia, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, H.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Spatial distribution of parabens, triclocarban, triclosan, bisphenols, and tetrabromo bisphenol A and its alternatives in municipal sewage sludges in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 679, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahab, R.A.; Omar, T.F.T.; Nurulnadia, M.Y.; Rozulan, N.N.A. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of parabens in the surface water of Terengganu River, Malaysia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 115036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cun, D.; Zhang, Z.; Pu, D.; Li, X.; Liang, W.; Fang, T. Occurrence and risk assessment of triclosan in freshwater lakes in the middle Yangtze River basin (Wuhan, Central China). Water Biol. Secur. 2022, 1, 100063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.C.; Donnachie, R.L.; Sumpter, J.P.; Jurgens, M.D.; Moeckel, C.; Pereira, M.G. An alternative approach to risk rank compounds on the threat they pose to the aquatic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Zhao, J.; Xi, N.; Guo, W.; Sun, J. Parabens and their metabolite in surface water and sediment from the Yellow River and the Huai River in Henan Province: Spatial distribution, seasonal variation and risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 172, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolujoko, N.B.; Ogunlaja, O.O.; Alfred, M.O.; Okewole, D.M.; Ogunlaja, A.; Olukanni, O.D.; Msagati, T.A.M.; Unuabonah, E.I. Occurrence and human exposure assessment of parabens in water sources in Osun State, Nigeria. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandikes, G.; Pathak, P.; Razak, A.S.; Narayanamurthy, V.; Singh, L. Occurrence, environmental risks and biological remediation mechanisms of triclosan in wastewaters: Challenges and perspectives. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, N.; Pan, B.; Ni, J. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in water, sediment and freshwater mollusks of the Dongting Lake downstream the Three Gorges Dam. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumkar, P.; Verma, C.R.; Hysek, S.; Pise, M.; Zoltowska, S.; Gosavi, S.M.; Mercl, F.; Božik, M.; Praus, L.; Hanková, K.; et al. Contaminants and their ecological risk assessment in beach sediments and water along the Maharashtra coast of India: A comprehensive approach using microplastics, heavy metal(loid)s, pharmaceuticals, personal care products and plasticizers. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, M.J.S.; Barbosa, S.C.; Malinowski, M.M.; Volpato, D.; Castro, I.B.; Franco, T.; Primel, E.G. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in a Brazilian wetland of international importance: Occurrence and environmental risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadutto, D.; Andreu, V.; Ilo, T.; Akkanen, J.; Pico, Y. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in a Mediterranean coastal wetland: Impact of anthropogenic and spatial factors and environmental risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Kannan, K. Phthalates and parabens in personal care products from China: Concentrations and human exposure. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 66, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Li, X.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yang, M.; Zhang, N.; Cui, J.; Zhang, B. Hexabromocyclododecanes in surface soil-maize system around Baiyangdian Lake in North China: Distribution, enantiomer-specific accumulation, transport, temporal trend and dietary risk. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 451, 131180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnett, K.G.; Chin, A.; Schuh, S.M. BPA and BPA alternatives BPS, BPAF, and TMBPF, induce cytotoxicity and apoptosis in rat and human stem cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 216, 112210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, S.M.; Cheong, A.; Adgent, M.A.; Veevers, J.; Suen, A.A.; Tam, N.N.C.; Leung, Y.K.; Jefferson, W.N.; Williams, C.J. Environmental factors, epigenetics, and developmental origin of reproductive disorders. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 68, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brose, D.A.; Kumar, K.; Liao, A.; Hundal, L.S.; Tian, G.; Cox, A.; Zhang, H.; Podczerwinski, E.W. A reduction in triclosan and triclocarban in water resource recovery facilities’ influent, effluent, and biosolids following the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s 2013 proposed rulemaking on antibacterial products. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal, C.M.; Bhat, K.; Ramaswamy, B.R.; Kumar, V.; Singhal, R.K.; Basu, H.; Udayashankar, H.N.; Vasantharaju, S.G.; Praveenkumarreddy, Y.; Lino, Y.; et al. Seasonal occurrence and risk assessment of pharmaceutical and personal care products in Bengaluru rivers and lakes, India. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, X.; Lin, J.; Liu, J. Occurrence and fate of selected endocrine-disrupting compounds in water and sediment from an urban lake. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 68, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, G.; Guo, Q.; Yan, C. Estrogenic compounds and estrogenicity in surface water, sediments, and organisms from Yundang Lagoon in Xiamen, China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 61, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Huang, B.; Jin, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Li, F.; Hu, P.; Pan, X. Seasonal distribution, source investigation and vertical profile of phenolic endocrine disrupting compounds in Dianchi Lake, China. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Cao, W. Assessment of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) of Dalong Lake in Xuzhou by concentration monitoring and bio-effects monitoring process. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 43, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Song, N.; Guo, R.; Chen, M.; Mai, D.; Yan, Z.; Han, Z.; Chen, J. Occurrence, distribution and sources of bisphenol analogues in a shallow Chinese freshwater lake (Taihu Lake): Implications for ecological and human health risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Shan, B.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Z.; Tang, W. Spatial distribution, fractionation, toxicity and risk assessment of surface sediments from the Baiyangdian Lake in northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; You, X. Water quality assessment and contribution rates of main pollution sources in Baiyangdian Lake, northern China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 98, 106965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Xia, W.; Yang, S.; Pan, X.; He, Z.; Kannan, K. Spatial distribution of bisphenol S in surface water and human serum from Yangtze River watershed, China: Implications for exposure through drinking water. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, D.N.; Grosseli, G.M.; Mozeto, A.A.; Carneiro, R.L.; Fadini, P.S. Ultrasound-assisted extraction method for the simultaneous determination of emerging contaminants in freshwater sediments. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 3454–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Wang, D.; Zhu, C.; Wang, B.; Cen, X.; Chen, A.; Zhou, H.; Ye, Z.; Tan, Q.; Nie, X.; et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in urban adults: The mediating role of oxidatively damaged DNA. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265((Part A)), 114860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Gao, L.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y. Spatial distribution, temporal variation and risks of parabens and their chlorinated derivatives in urban surface water in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Exposure Factors Handbook: 2011 Edition; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/expobox/exposure-factors-handbook-2011-edition (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Zhao, X.; Qiu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Xiong, J.; Gao, C.; Hu, S. Occurrence, distribution, bioaccumulation, and ecological risk of bisphenol analogues, parabens and their metabolites in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Zhao, J.L.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Jiang, Y.X.; Liu, S.; Liu, W.R.; Yang, Y.Y.; Ying, G.G. Personal care products in wild fish in two main Chinese rivers: Bioaccumulation potential and human health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malnes, D.; Ahrens, L.; Kohler, S.; Forsberg, M.; Golovko, O. Occurrence and mass flows of contaminants of emerging concern (CECs) in Sweden’s three largest lakes and associated rivers. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarczynska-Goslinska, B.; Zgola-Grzeskowiak, A.; Jeszka-Skowron, M.; Frankowski, R.; Grzeskowiak, T. Detection of bisphenol A, cumylphenol and parabens in surface waters of Greater Poland Voivodeship. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 204, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picó, Y.; Alvarez-Ruiz, R.; Alfarhan, A.H.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; Alshahrani, H.O.; Barcelo, D. Pharmaceuticals, pesticides, personal care products and microplastics contamination assessment of Al-Hassa irrigation network (Saudi Arabia) and its shallow lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 135021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golovko, O.; Rehrl, A.L.; Kohler, S.; Ahrens, L. Organic micropollutants in water and sediment from Lake Malaren, Sweden. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, B.D.; Crago, J.P.; Hedman, C.J.; Klaper, R.D. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products found in the Great Lakes above concentrations of environmental concern. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2116–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pojana, G.; Gomiero, A.; Jonkers, N.; Marcomini, A. Natural and synthetic endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) in water, sediment and biota of a coastal lagoon. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Lee, S.; Moon, H.B.; Yamashita, N.; Kannan, K. Parabens in sediment and sewage sludge from the United States, Japan, and Korea: Spatial distribution and temporal trends. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10895–10902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, S.; Bakhtiari, A.R.; Sari, A.E.; Bahramifar, N.; Rahbarizade, F. Phenolic endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) in Anzali Wetland, Iran: Elevated concentrations of 4-nonylphenol, octhylphenol and bisphenol A. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Yin, L.; Yang, Z. Four typical personal care products in a municipal wastewater treatment plant in China: Occurrence, removal efficiency, mass loading and emission. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ferronato, C.; Deng, N.; Chovelon, J.-M. Study of benzylparaben photocatalytic degradation by TiO2. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 104, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, B.R.; Shanmugam, G.; Velu, G.; Rengarajan, B.; Larsson, D.G.J. GC–MS analysis and ecotoxicological risk assessment of triclosan, carbamazepine and parabens in Indian rivers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.J.; Pan, C.G.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, N.S.; Windfeld, R.; Salvito, D.; Selck, H.; Van den Brink, P.J.; Ying, G.G. Ocurrence and ecological risk assessment of emerging organic compounds in urban rivers: Guangzhou as a case study in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 589, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Pollutant | Water (n = 22) | Sediment (n = 22) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DR (%) | Concentration (ng/L) | DR (%) | Content (ng/g) | |||||
| Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | |||
| MeP | 100 | 0.11 | 4.72 | 2.07 | 100 | 2.42 | 13.56 | 6.77 |
| EtP | 59.1 | n.d. | 2.06 | 0.30 | 90.9 | n.d. | 2.16 | 0.61 |
| PrP | 68.2 | n.d. | 1.38 | 0.34 | 72.7 | n.d. | 4.01 | 1.35 |
| BuP | 31.8 | n.d. | 0.43 | 0.08 | 40.9 | n.d. | 0.17 | 0.05 |
| TCS | 100 | 7.59 | 62.54 | 26.10 | 100 | 5.07 | 83.79 | 32.54 |
| BPA | 100 | 3.24 | 114.74 | 33.09 | 100 | 4.63 | 64.59 | 24.50 |
| ∑PBs | – | 0.22 | 8.57 | 2.79 | – | 2.42 | 18.37 | 8.78 |
| Compound | HQ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children | Women | Men | ||||
| Mean | Maximum | Mean | Maximum | Mean | Maximum | |
| MeP | 1.5 × 10−8 | 3.5 × 10−8 | 1.0 × 10−8 | 2.3 × 10−8 | 1.2 × 10−8 | 2.7 × 10−8 |
| EtP | 2.3 × 10−9 | 1.5 × 10−8 | 1.5 × 10−9 | 1.0 × 10−8 | 1.7 × 10−9 | 6.0 × 10−9 |
| PrP | 1.3 × 10−7 | 5.1 × 10−7 | 8.4 × 10−8 | 3.4 × 10−7 | 9.6 × 10−8 | 3.9 × 10−7 |
| BPA | 2.5 × 10−5 | 8.6 × 10−5 | 1.6 × 10−5 | 5.6 × 10−5 | 1.9 × 10−5 | 6.5 × 10−5 |
| TCS | 8.1 × 10−7 | 1.9 × 10−6 | 5.3 × 10−7 | 1.3 × 10−6 | 6.1 × 10−7 | 1.5 × 10−6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Liang, S.-x. Parabens, Triclosan and Bisphenol A in Surface Waters and Sediments of Baiyang Lake, China: Occurrence, Distribution, and Potential Risk Assessment. Toxics 2024, 12, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010031
Fu L, Sun Y, Zhou J, Li H, Liang S-x. Parabens, Triclosan and Bisphenol A in Surface Waters and Sediments of Baiyang Lake, China: Occurrence, Distribution, and Potential Risk Assessment. Toxics. 2024; 12(1):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010031
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Liguo, Yaxue Sun, Jingbo Zhou, Hongbo Li, and Shu-xuan Liang. 2024. "Parabens, Triclosan and Bisphenol A in Surface Waters and Sediments of Baiyang Lake, China: Occurrence, Distribution, and Potential Risk Assessment" Toxics 12, no. 1: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010031
APA StyleFu, L., Sun, Y., Zhou, J., Li, H., & Liang, S.-x. (2024). Parabens, Triclosan and Bisphenol A in Surface Waters and Sediments of Baiyang Lake, China: Occurrence, Distribution, and Potential Risk Assessment. Toxics, 12(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010031






