Effects of Fireworks Burning on Air Quality during the Chinese Spring Festival—Evidence from Zhengzhou, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
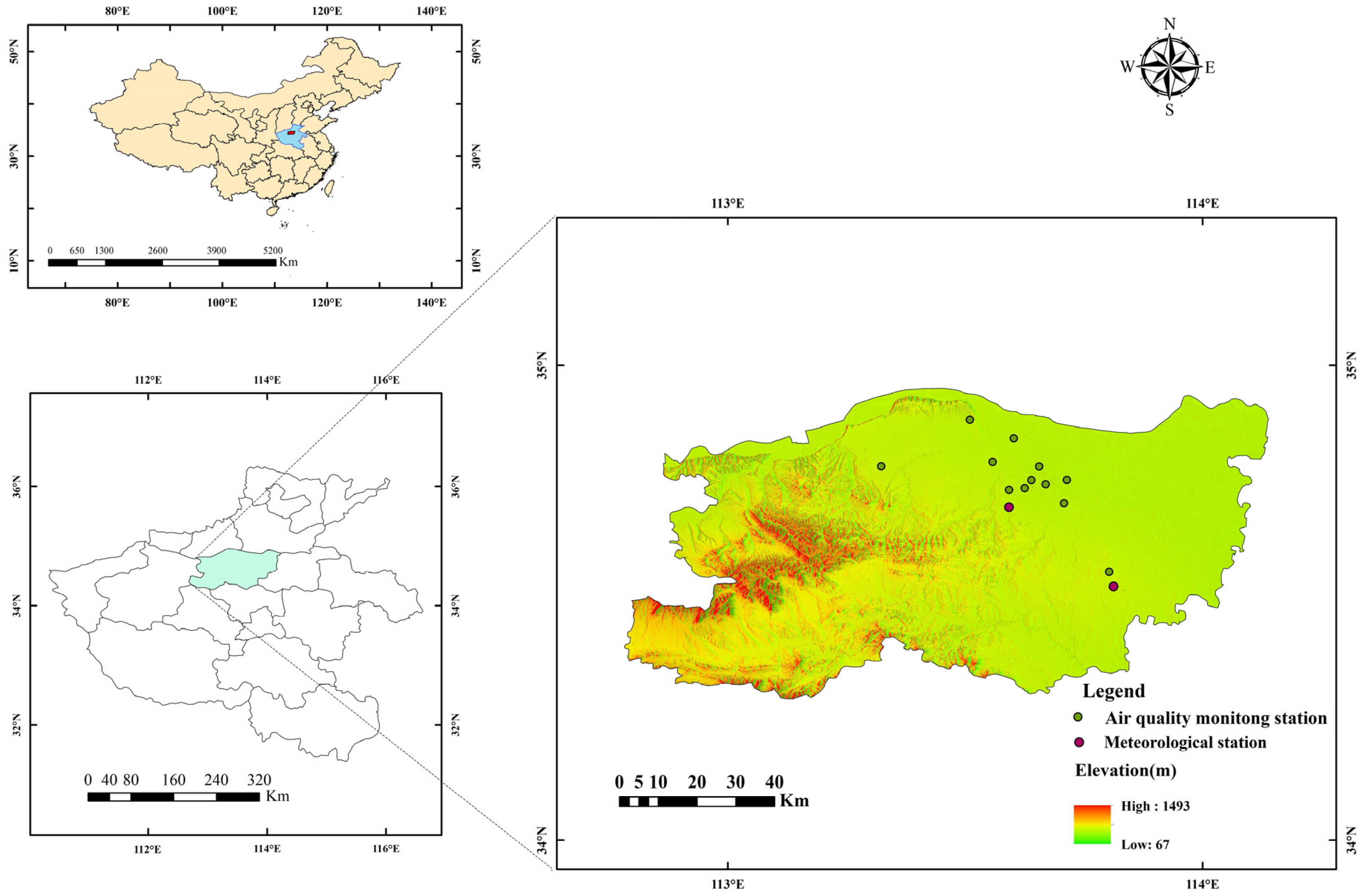
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Data Processing and Analysis
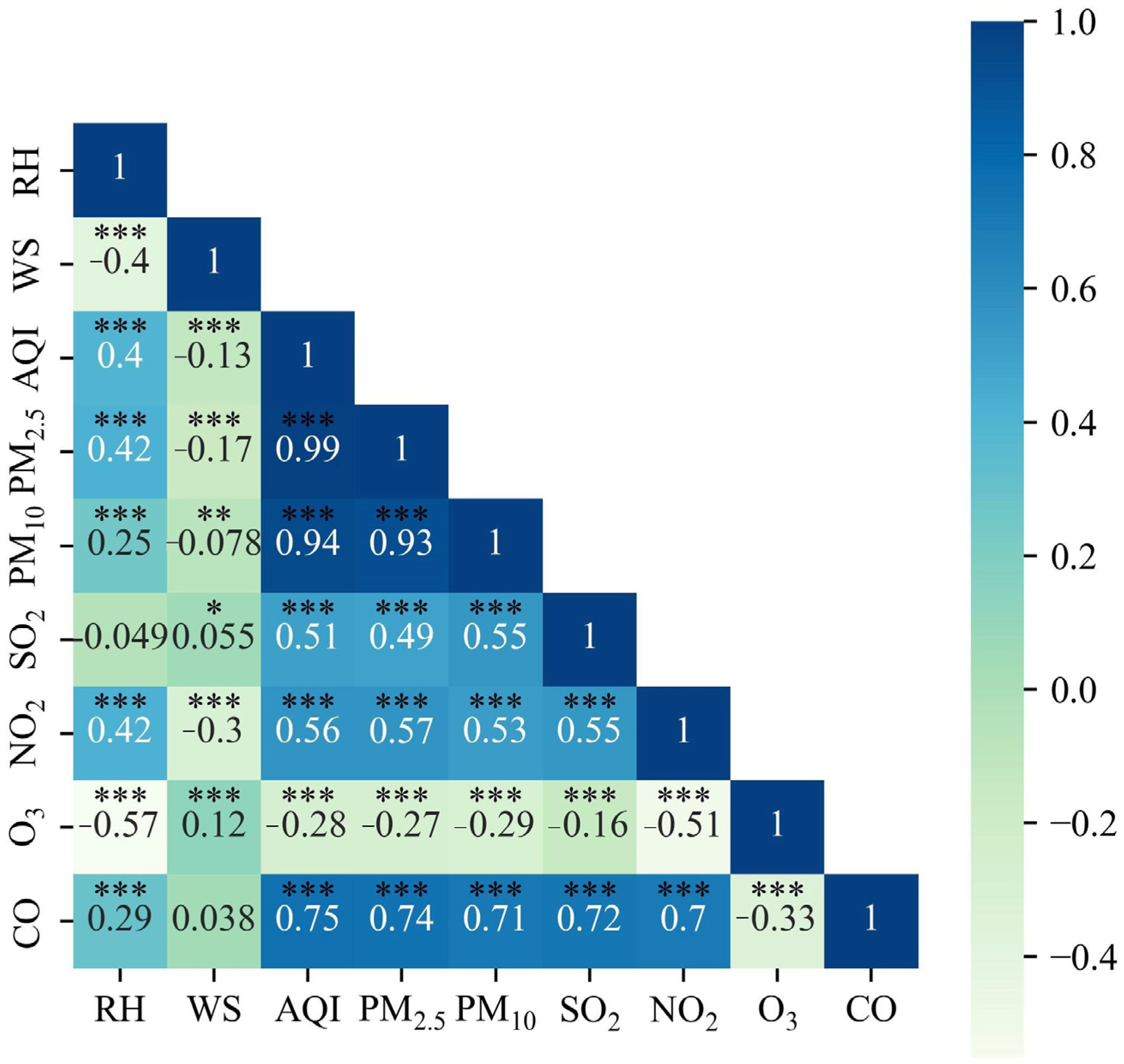
2.3.2. Correlation Analysis
2.3.3. Relative Ratio Method
3. Results
3.1. Air Quality Index(AQI) Characteristics
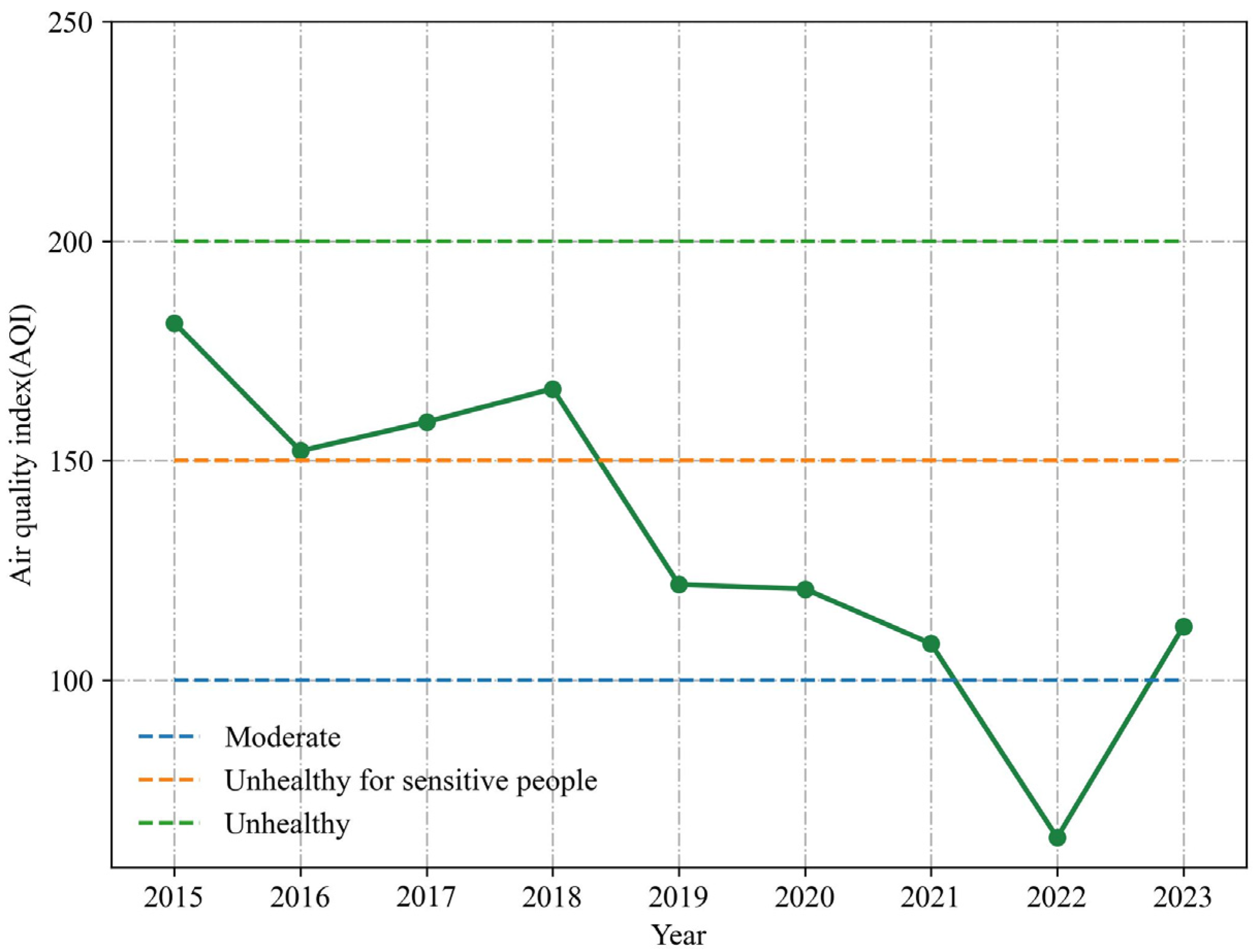
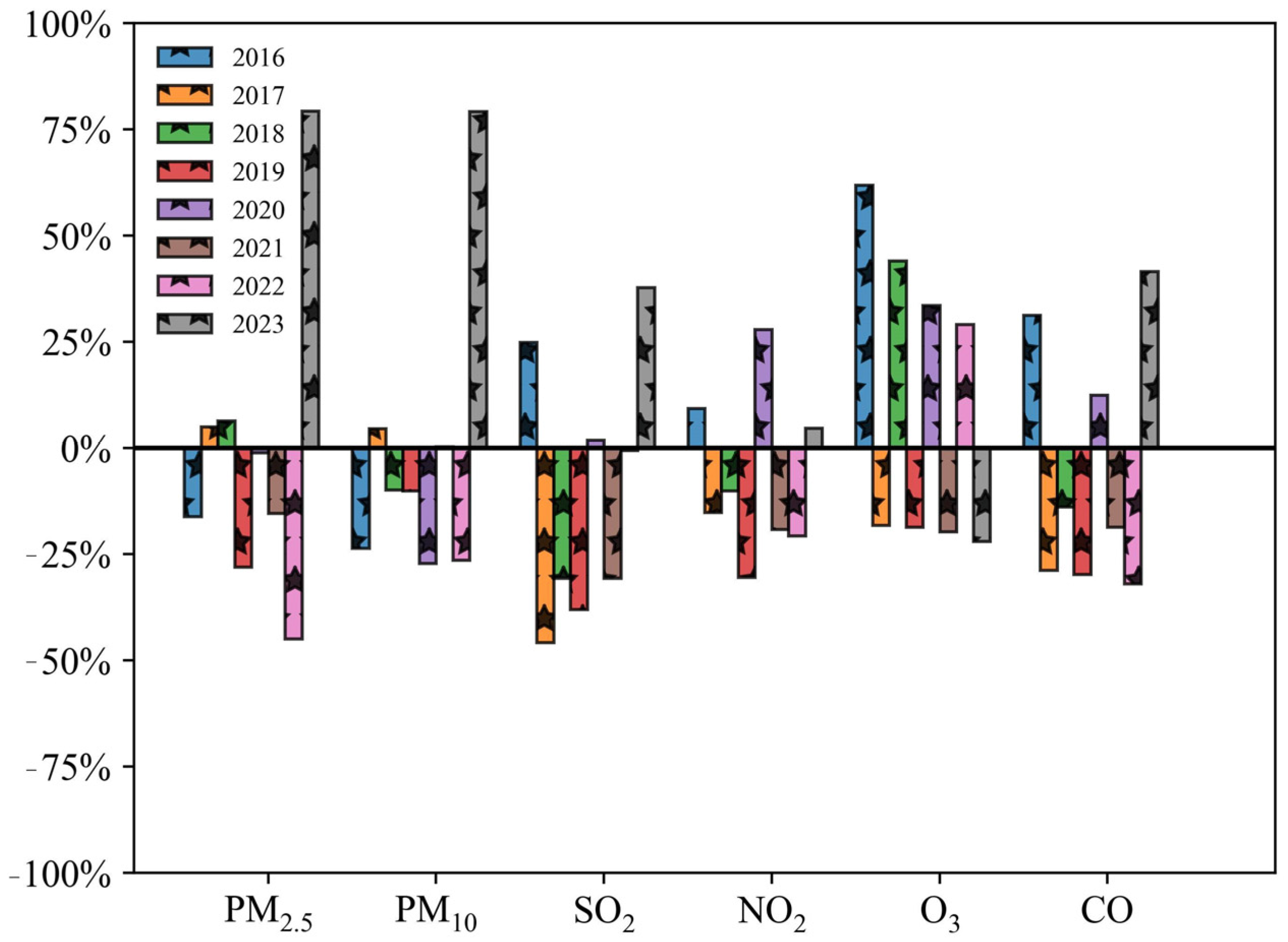
3.1.1. Variation of Annual Spring Festival AQI Average
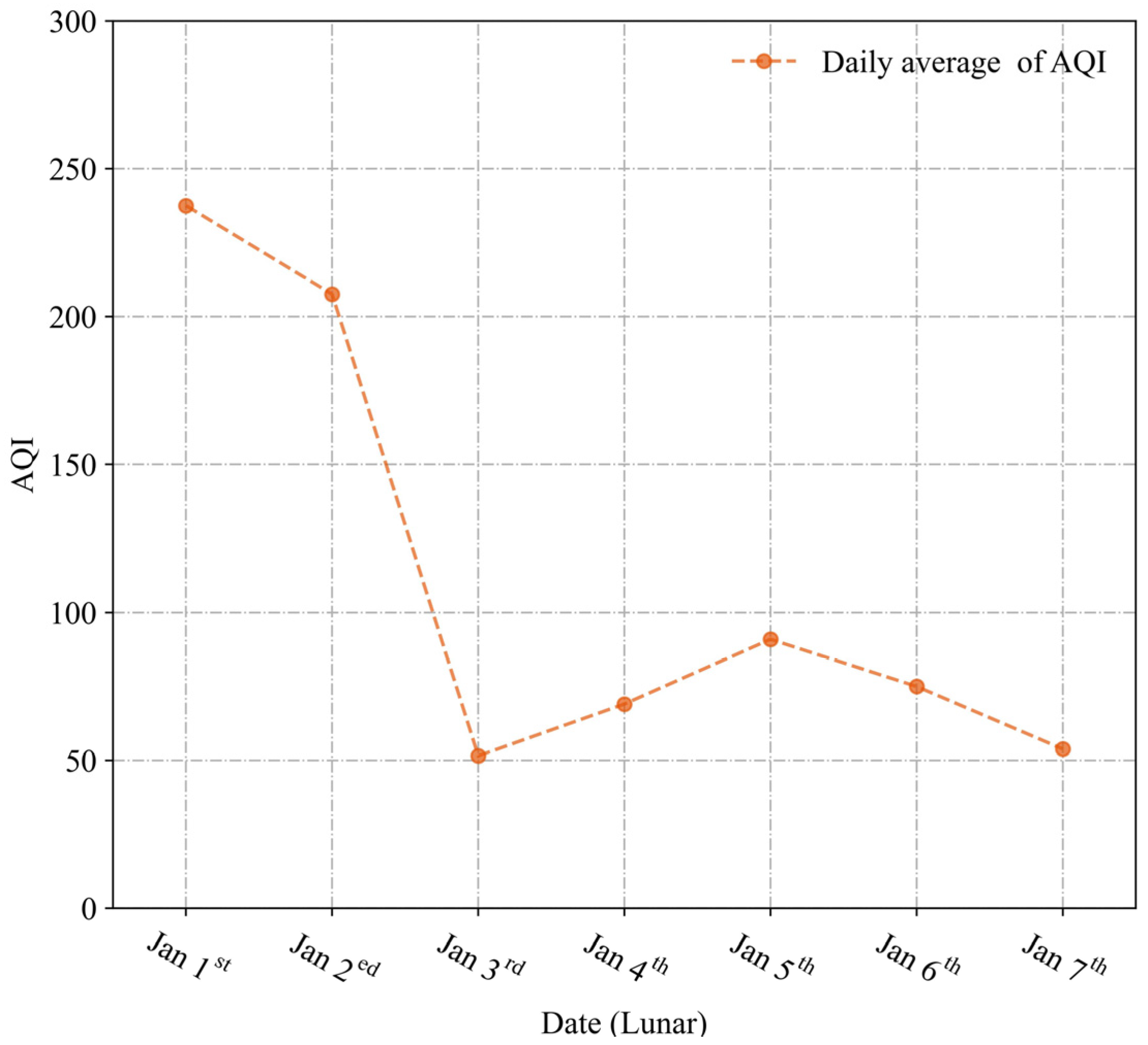
3.1.2. Variation of Daily AQI Average
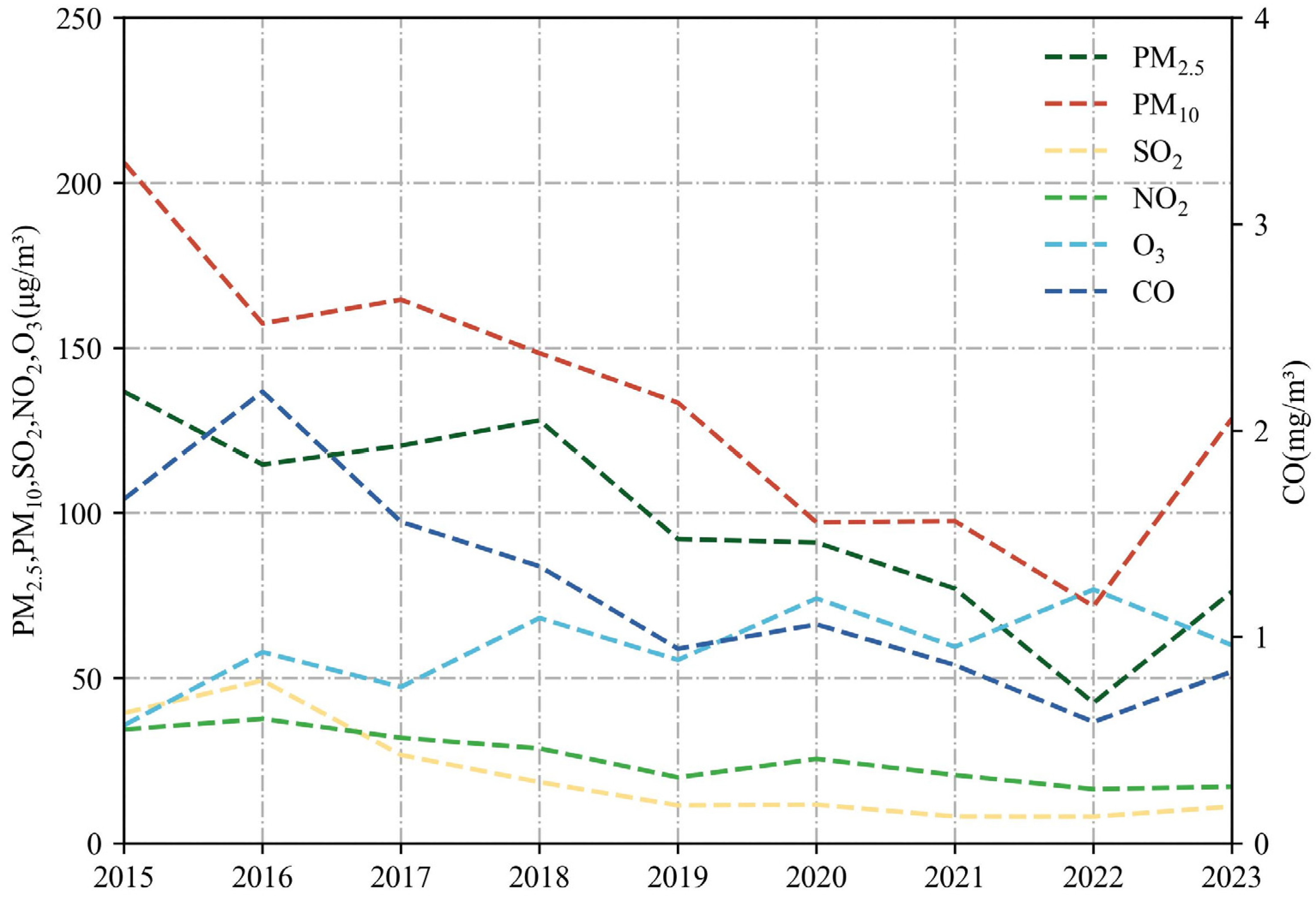
3.2. Variation of Concentrations in Main Pollutants
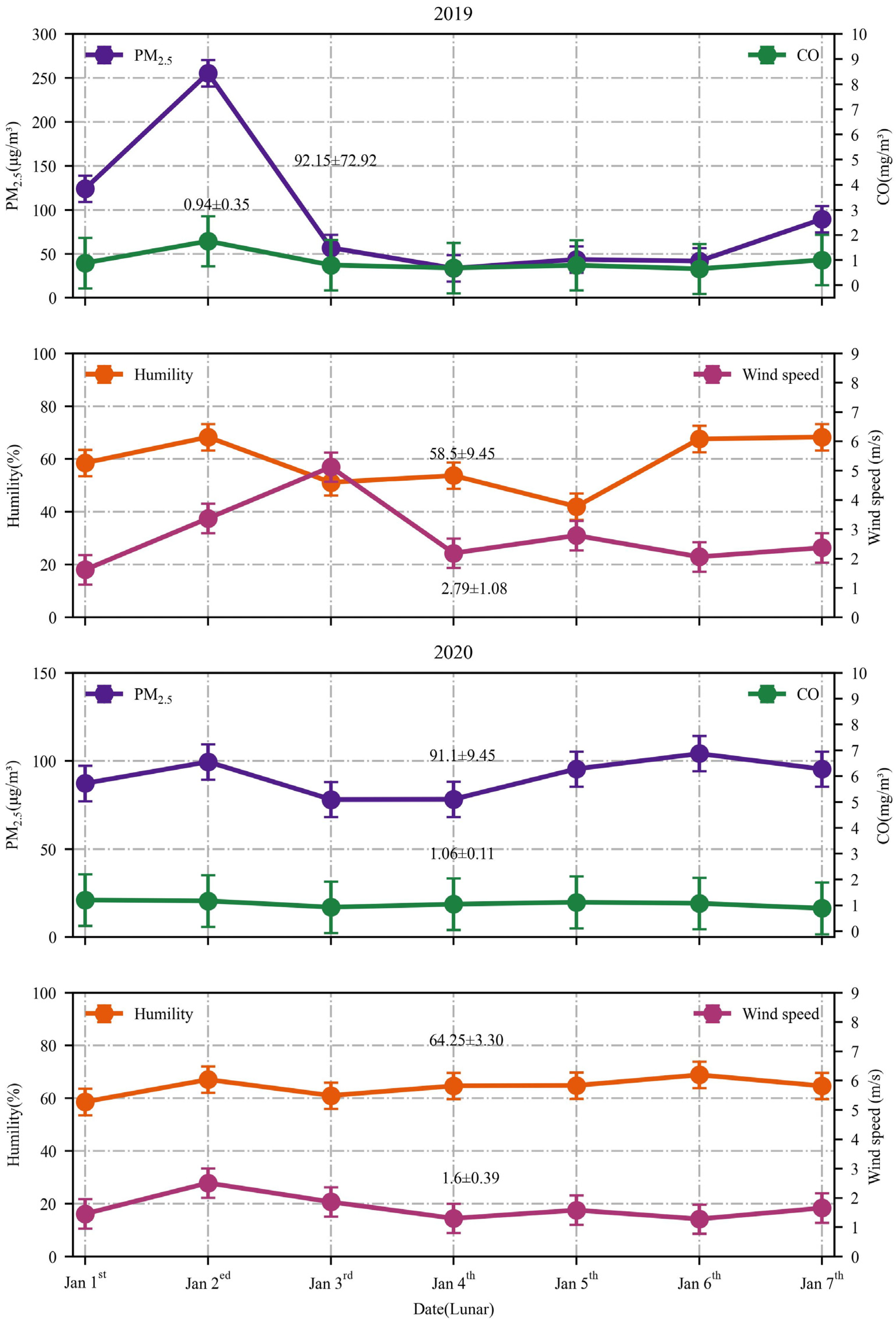
3.2.1. Variation before and after Implementation of POFB Policy (2015–2016)
3.2.2. Variation of before and after Implementation of RHFB Policy (2022–2023)
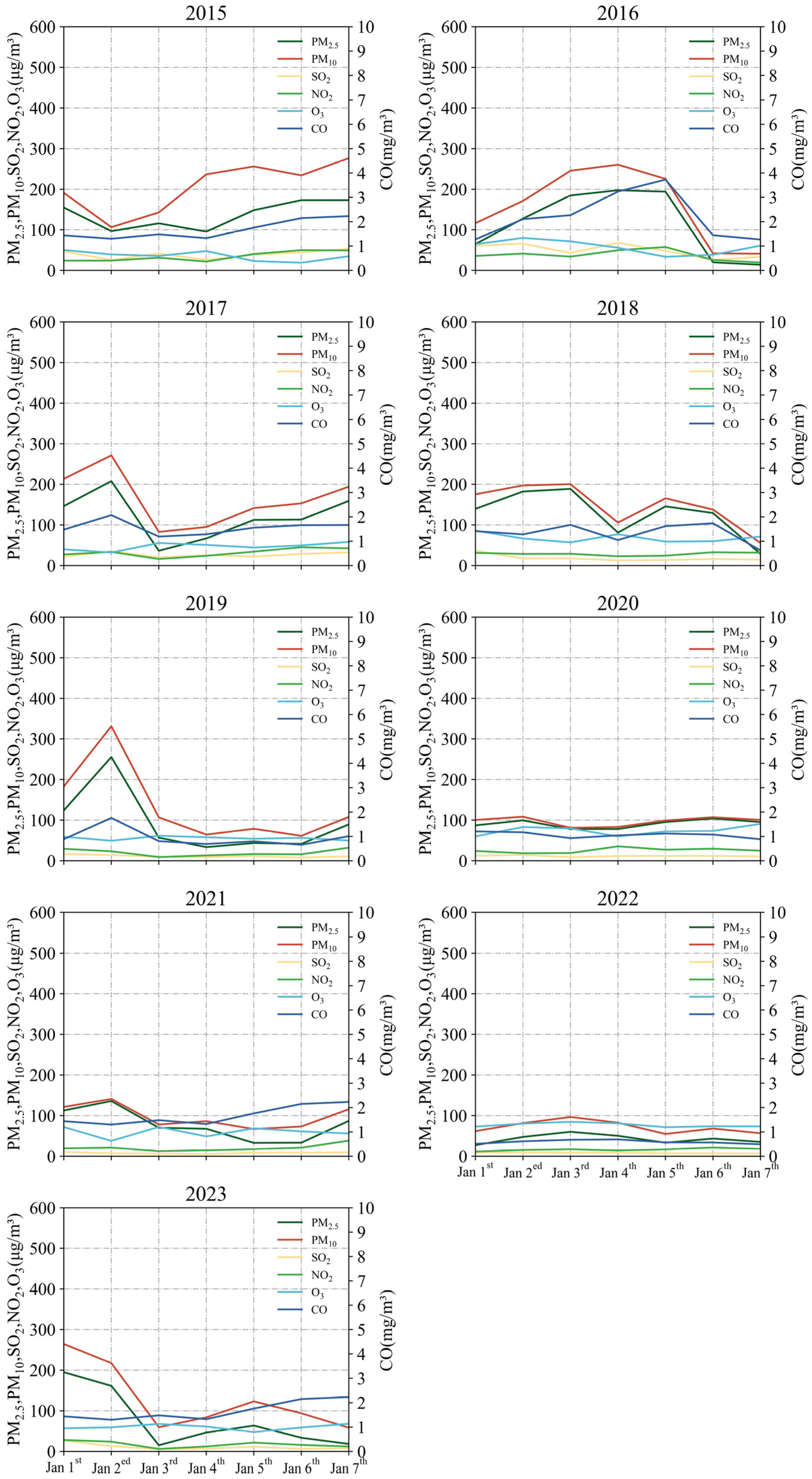
3.3. Variation of Hourly Concentrations of Main Pollutants
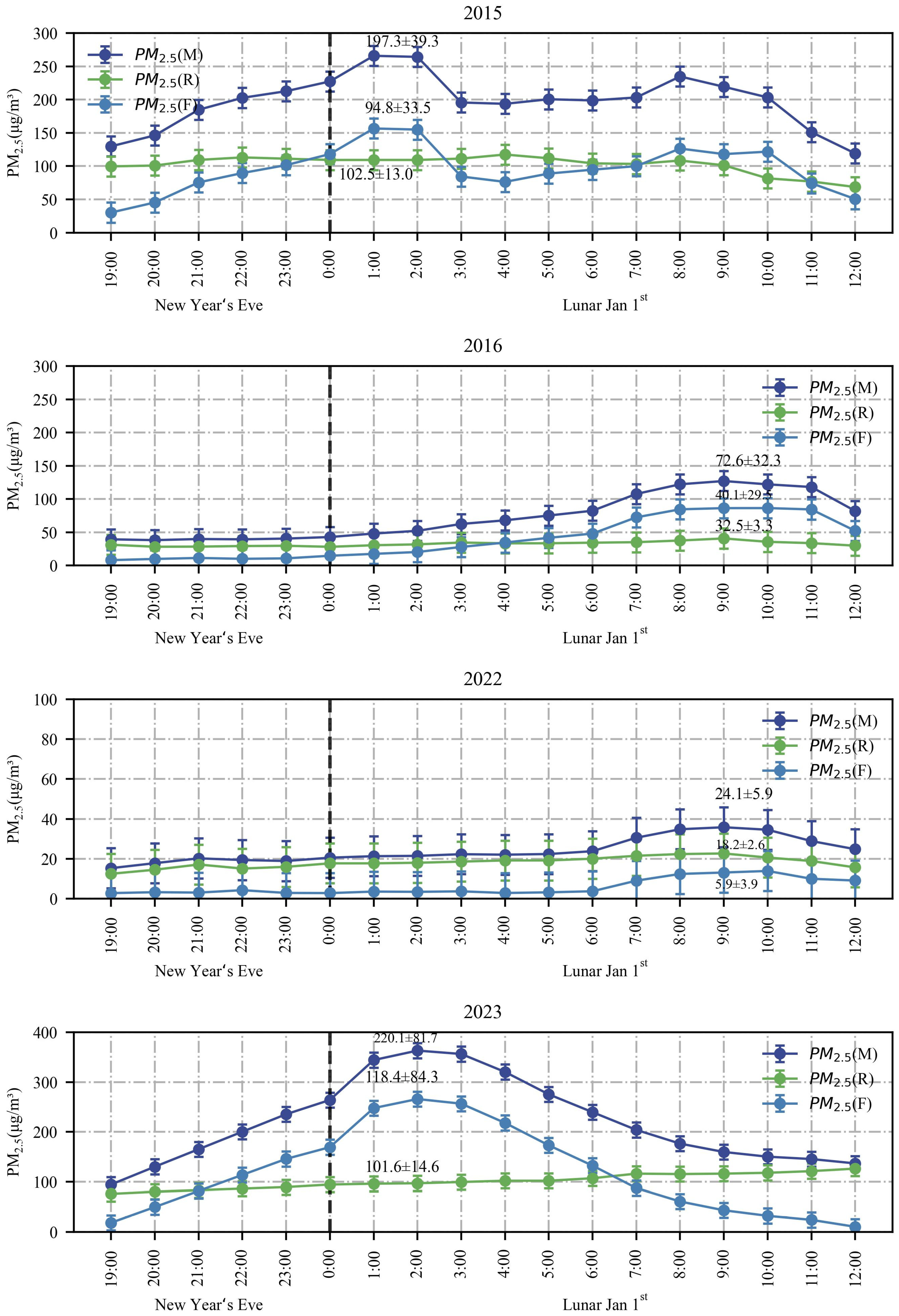
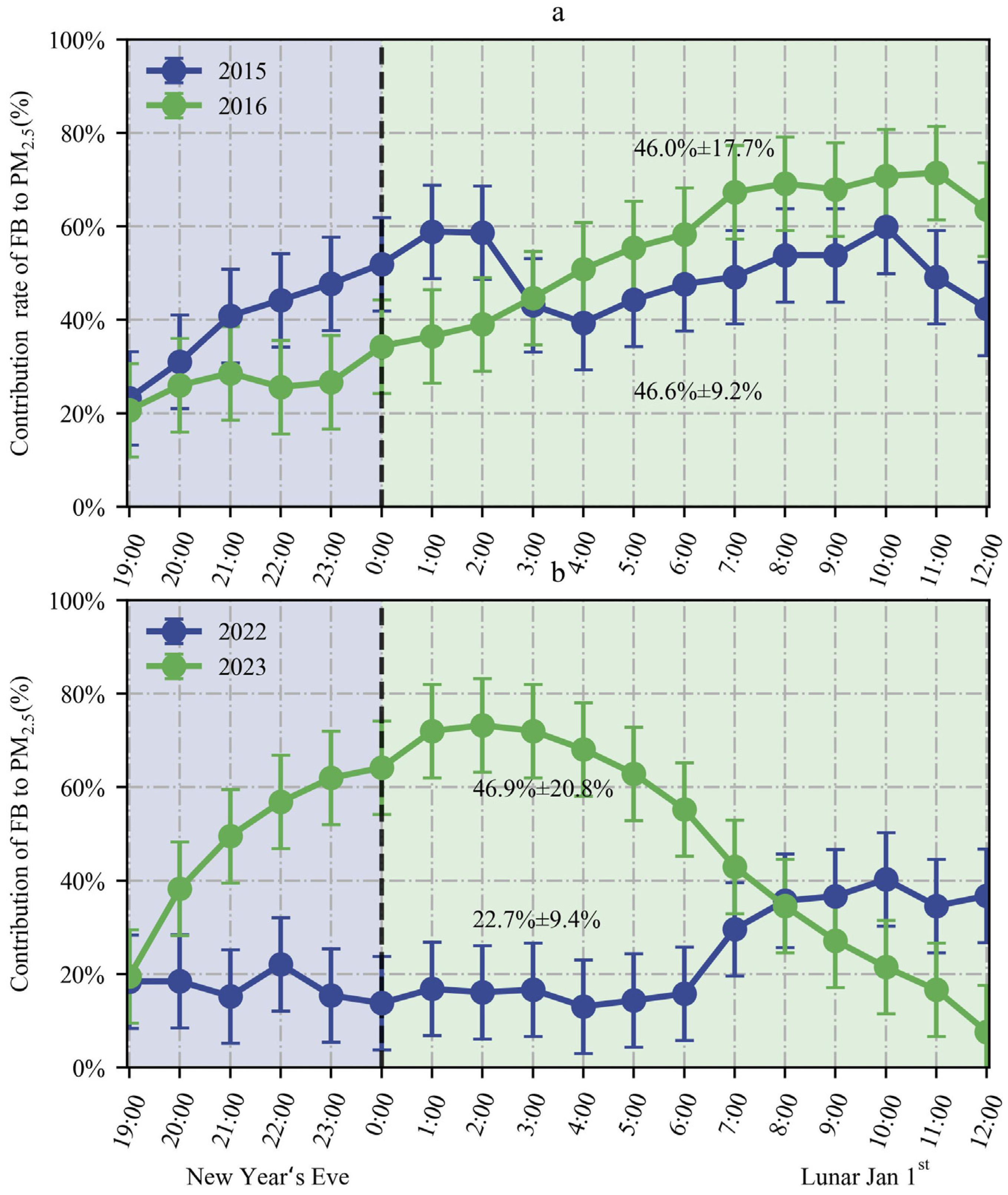
3.4. Contributions of Fireworks Burning to PM2.5 Concentrations during the FBP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nasir, U.P.; Brahmaiah, D. Impact of fireworks on ambient air quality: A case study. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, T.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Amato, F.; Pey, J.; Pandolfi, M.; Kuenzli, N.; Bouso, L.; Rivera, M.; Gibbons, W. Effect of fireworks events on urban background trace metal aerosol concentrations: Is the cocktail worth the show? J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Chate, D.M.; Srivastava, M.K.; Safai, P.D.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bisht, D.S.; Padmanabhamurty, B. Statistical evaluation of PM10 and distribution of PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 in ambient air due to extreme fireworks episodes (Deepawali festivals) in megacity Delhi. Nat. Hazards 2011, 61, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beig, G.; Chate, D.M.; Ghuade, S.D.; Ali, K.; Satpute, T.; Sahu, S.K.; Parkhi, N.; Trimbake, H.K. Evaluating population exposure to environmental pollutants during Deepavali fireworks displays using air quality measurements of the SAFAR network. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, S.; Green, D.; Heo, J. Evaluation of health risk associated with fireworks activity at Central London. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2015, 9, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greven, F.E.; Vonk, J.M.; Fischer, P.; Duijm, F.; Vink, N.M.; Brunekreef, B. Air pollution during New Year’s fireworks and daily mortality in the Netherlands. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, D.J.; Birnbaum, A.N. Effects of Independence Day fireworks on atmospheric concentrations of fine particulate matter in the United States. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 115, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godri, K.J.; Green, D.C.; Fuller, G.W.; Dall’Osto, M.; Beddows, D.C.; Kelly, F.J.; Harrison, R.M.; Mudway, I.S. Particulate oxidative burden associated with firework activity. Particulate Oxidative Burden Associated with Firework Activity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8295–8301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewnick, F.; Hings, S.S.; Curtius, J.; Eerdekens, G.; Williams, J. Measurement of fine particulate and gas-phase species during the New Year’s fireworks 2005 in Mainz, Germany. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 4316–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, B.; Wiedensohler, A.; Heintzenberg, J. Submicrometer aerosol size distributions and mass concentration of the Millennium fireworks 2000 in Leipzig, Germany. J. Aerosol Sci. 2000, 12, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchi, R.; Bernardoni, V.; Cricchio, D.; D’Alessandro, A.; Fermo, P.; Lucarelli, F.; Nava, S.; Piazzalunga, A.; Valli, G. The impact of fireworks on airborne particles. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, W.; Cheng, S.; Wang, R.; Zhu, J. Evaluation of continuous emission reduction effect on PM2.5 pollution improvement through 2013-2018 in Beijing. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecconi, A.; Navarrete, G.; Garcia-Guimaraes, M.; Vera, A.; Blanco-Dominguez, R.; Sanz-Garcia, A.; Lozano-Prieto, M.; Lopez-Melgar, B.; Rivero, F.; Martin, P.; et al. Influence of air pollutants on circulating inflammatory cells and microRNA expression in acute myocardial infarction. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, R.; Saud, C.; Espinoza, C. Simulating PM2.5 Concentrations during New Year in Cuenca, Ecuador: Effects of Advancing the Time of Burning Activities. Toxics 2022, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C. A Review of the Impact of Fireworks on Particulate Matter in Ambient Air. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2016, 66, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Singh, R.K.; Murari, V.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, R.S.; Banerjee, T. Fireworks induced particle pollution: A Spatio-temporal analysis. Atmos. Res. 2016, 180, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, J.; Tang, A.; Zheng, A.; Shao, Z.; Liu, X. Chemical Characteristics of PM2.5 during 2015 Spring Festival in Beijing, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yu, H.; Su, X.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Sun, J.H. Chemical composition and source apportionment of PM2.5 during Chinese Spring Festival at Xinxiang, a heavily polluted city in North China: Fireworks and health risks. Atmos. Res. 2016, 182, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, R.; Shen, H.; Wang, S.; Hu, Q.; Cui, J.; Yan, Y.; Huang, H.; Hu, G. Chemical characteristics, sources, and formation mechanisms of PM2.5 before and during the Spring Festival in a coastal city in Southeast China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shao, P. Ecological and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in dust affected by fireworks during the Spring Festival in Beijing. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 14, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Cui, Y.; Li, L.; He, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Zhou, L.; Maenhaut, W.; Wen, T.; et al. Characterization and source identification of fine particulate matter in urban Beijing during the 2015 Spring Festival. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Pant, P.; Pope, F.D. Air quality during and after festivals: Aerosol concentrations, composition and health effects. Atmos. Res. 2019, 227, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; Ghissassi, F.E.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Talla, L.; Guha, N.; Baan, R.; Mattock, H.; Straif, K. The Carcinogenicity of Outdoor Air Pollution. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1262–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeples, L. News Feature: How Air Pollution Threatens Brain Heath. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 13856–13860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rindelaub, J.D.; Davy, P.K.; Talbot, N.; Pattinson, W.; Miskelly, G.M. The contribution of commercial fireworks to both local and personal air quality in Auckland, New Zealand. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 21650–21660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, T.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Minguillón, M.C.; Pey, J.; Rodriguez, S.; Miró, J.V.; Felis, C.; Gibbons, W. Recreational atmospheric pollution episodes: Inhalable metalliferous particles from firework displays. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerramsetti, V.S.; Sharma, A.R.; Navlur, N.G.; Rapolu, V.; Dhulipala, N.S.K.C.; Sinha, P.R. The impact assessment of Diwali fireworks emissions on the air quality of a tropical urban site, Hyderabad, India, during three consecutive years. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 7309–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhashini, R.; Samhitha, B.K.; Mana, S.C.; Jose, J. Data Analytics to Find Out the Effect of Firework Emissions on Quality of Air: A case study. Second International Conference on Material Science. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2201, 020008. [Google Scholar]
- Shivani; Gadi, R.; Saxena, M.; Sharma, S.K.; Mandal, T.K. Short-term degradation of air quality during major firework events in Delhi, India. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2018, 131, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, G.R.; Bañaga, P.A.; Cambaliza, M.O.; Cruz, M.T.; AzadiAghdam, M.; Arellano, A.; Betito, G.; Braun, R.; Corral, A.F.; Dadashazar, H.; et al. Measurement report: Firework impacts on air quality in Metro Manila, Philippines, during the 2019 New Year revelry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 6155–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, T.; Lu, X.; Chen, H.; Nizkorodov, S.A.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Mo, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liu, H.; et al. Online single particle measurement of fireworks pollution during Chinese New Year in Nanning. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 53, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, S.F.; Li, L.; Li, X.X.; Yin, Y.; Chen, K.; Liu, D.T.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Shan, Y.P.; Ji, Y.Q. The impacts of firework burning at the Chinese Spring Festival on air quality: Insights of tracers, source evolution and aging processes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 2167–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.; Feng, M.; Liu, X.; Che, Y.; Xu, H.; Schaefer, K.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y. Size-resolved hygroscopic behaviour and mixing state of submicron aerosols in a megacity of the Sichuan Basin during pollution and fireworks episodes. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 226, 117393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Huang, B.; He, Q.; Chen, B.; Wei, J.; Mahmood, R. Dynamic Assessment of PM2.5 exposure and health risk using remote sensing and geo-spatial big Data. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickey, C.; Gordon, C.; Galdanes, K.; Blaustein, M.; Horton, L.; Chillrud, S.; Ross, J.; Yinon, L.; Chen, L.C.; Gordon, T. Toxicity of particles emitted by fireworks. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecconi, A.; Franco, E.; Agustín, J.A.; Vilchez, J.P.; Palacios-Rubio, J.; Sánchez-Enrique, C.; Fernández-Ortiz, A.; Macaya, C.; Fernández-Jiménez, R. Hyponatremia-induced stress cardiomyopathy due to psychogenic polydipsia. Int J Cardiol. 2016, 202, 618–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Luo, D.; Liu, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, F.; Li, B.; Li, L. Effects of PM2.5 Exposure on Reproductive System and Its Mechanisms. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, X.; Song, H.; Tao, B.; Qiu, B.; Tian, D.; Zhan, M.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J. Effects of short-term ambient PM2.5 exposure on the blood cell count and hemoglobin concentration among 82, 431 people in eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 146046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, C. Are Environmentally Friendly Fireworks Really “Green” for Air Quality? A Study from the 2019 National Day Fireworks Display in Shenzhen. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3520–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, W.; Peng, J.; Ma, Q. The Effect of Banning Fireworks on Air Quality in a Heavily Polluted City in Northern China During Chinese Spring Festival. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 872226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Wang, G.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Tian, G.; Liu, Y.; Gao, W.; Lang, J. Impact of fireworks burning on air quality during the Spring Festival in 2021–2022 in Linyi, a central city in the North China Plain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 17915–17925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Wang, D.; Fu, Q.; Qiao, L.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Sun, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; et al. The effects of firework regulation on air quality and public health during the Chinese Spring Festival from 2013 to 2017 in a Chinese megacity. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Fan, H.; Zhao, K. Fine-Grained Spatiotemporal Analysis of the Impact of Restricting Factories, Motor Vehicles, and Fireworks on Air Pollution. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Nagda, C.; Kumar, K.; Kain, T.; Jhala, L.S.; Rathore, D.S. COVID-19 Implicated ban on Diwali fireworks: A case study on the air quality of Rajasthan, India. EQA-Int. J. Environ. Qual. 2022, 47, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Yang, L. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of PM2.5 Pollution and the Influential Meteorological Factors in the Henan Province, China, 2021. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 6, 5211–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zheng, Z. Optimal Allocation of Control Targets for PM2.5 Pollution in China’s Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Regions. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 3941–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Chen, R.; Chen, M. The impacts of Chinese Nian culture on air pollution. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jiménez, Y.S.; Rodríguez, J.V.P.; Hernández, J.M. Air pollution and tourism demand: A case study of Beijing, China. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2019, 21, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, B.; Li, H. Research on Computer Forecast Model Using BP Neural Network and Pearson Correlation Coefficient. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2033, 012091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, N.; Gao, J.; Zhao, P.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Chai, F. Impact of fireworks control on air quality in four Northern Chinese cities during the Spring Festival. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 117958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Yuan, X.; Dou, W.; Hu, J.; Xia, J.; Li, D.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, P.; Quan, Q.; Li, Y. Effects of fireworks on air quality in the main urban area of Nanchong City during the spring festival of 2014–2019. Environ. Eng. Res. 2022, 28, 220038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Xu, C.; An, Z. The air pollution caused by the burning of fireworks during lantern festival in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Ji, D.S.; Gao, W.K.; Yu, Z.W.; Chen, K.; Cao, W. Characteristics of air quality in Tianjin during the Spring Festival period of 2015. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2016, 9, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, H.; Otjes, R.; Weijers, E. Extreme levels and chemistry of PM from the consumer fireworks in the Netherlands. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 212, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.Z.; Wang, J.; Peng, X.; Shi, G.L.; Feng, Y.C. Estimation of the direct and indirect impacts of fireworks on the physicochemical characteristics of atmospheric PM10 and PM2.5. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 9469–9479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, L. The Effects of Fireworks Discharge on Atmospheric PM2.5 Concentration in the Chinese Lunar New Year. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Tan, L.; Xu, K.; Wang, D.; Zhu, X. Characteristics of Atmospheric Volatile Organic Compounds and Photochemical Changes During an O3 Event in a County-Level City of Shaanxi Province, China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.P.; Singh, D.; Kumar, K.; Jain, V.K. Study of seasonal variation of PM2.5 concentration associated with meteorological parameters at residential sites in Delhi, India. J. Atmos. Chem. 2021, 78, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Tao, S. Interannual variability of summertime aerosol optical depth over East Asia during 2000–2011: A potential influence from El Niño Southern Oscillation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 044034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhao, C.; Kwan, M.; Cai, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Yang, J.; et al. Influence of meteorological conditions on PM2.5 concentrations across China: A review of methodology and mechanism. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juráň, S.; Grace, J.; Urban, O. Temporal Changes in Ozone Concentrations and Their Impact on Vegetation. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Air Quality | AQI Value | Grade |
|---|---|---|
| Good | 0–50 | I |
| Moderate | 51–100 | II |
| Unhealthy for sensitive people | 101–150 | III |
| Unhealthy | 151–200 | IV |
| Very healthy | 201–300 | V |
| Hazardous | 301–500 | VI |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yan, P.; Lu, Y. Effects of Fireworks Burning on Air Quality during the Chinese Spring Festival—Evidence from Zhengzhou, China. Toxics 2024, 12, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010023
Liu X, Yang L, Wang Y, Yan P, Lu Y. Effects of Fireworks Burning on Air Quality during the Chinese Spring Festival—Evidence from Zhengzhou, China. Toxics. 2024; 12(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xinzhan, Ling Yang, Yan Wang, Pengfei Yan, and Yimeng Lu. 2024. "Effects of Fireworks Burning on Air Quality during the Chinese Spring Festival—Evidence from Zhengzhou, China" Toxics 12, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010023
APA StyleLiu, X., Yang, L., Wang, Y., Yan, P., & Lu, Y. (2024). Effects of Fireworks Burning on Air Quality during the Chinese Spring Festival—Evidence from Zhengzhou, China. Toxics, 12(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010023






