Neurotoxicity and Oxidative Stress Development in Adult Atya lanipes Shrimp Exposed to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Suspensions (TiO2 NPs)
2.2. Atya lanipes Specimens Collection
2.3. The Microcosm
2.4. Acute Toxicity Tests
2.5. Behavioral Analysis
2.6. Oxidative Stress Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Specimens of Atya lanipes and Physicochemical Parameters
3.2. Movement Assessment
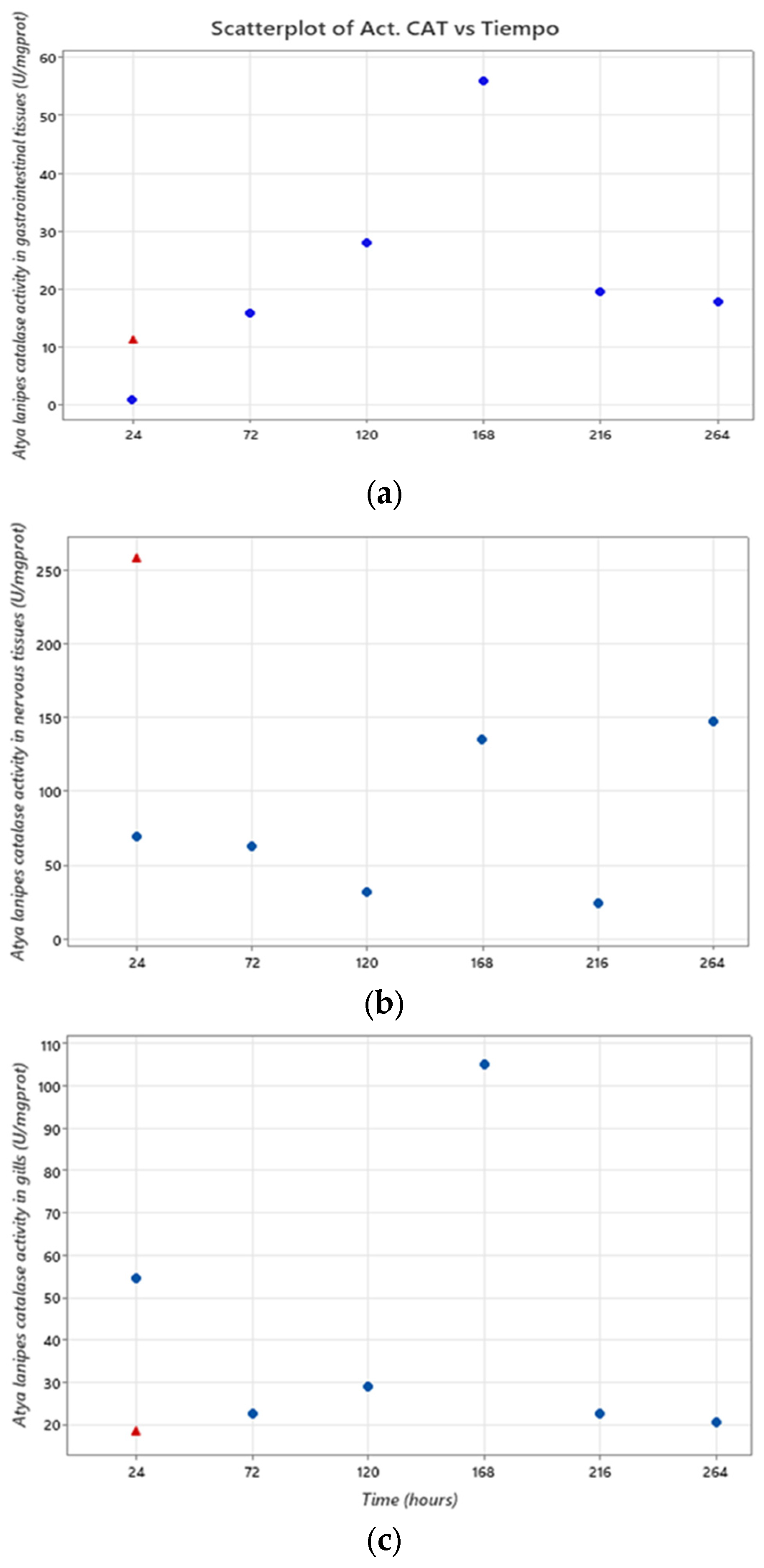
3.3. Oxidative Stress Assessment
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, X.; Li, J.; Xie, S.; Duan, P.; Zhang, H.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Y. Selectivity control in photocatalytic valorization of biomass-derived platform compounds by surface engineering of titanium oxide. Chem 2020, 6, 3038–3053. [Google Scholar]
- Tsang, C.H.A.; Li, K.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhan, Y.; Xie, R.; Leung, D.; Huang, H. Titanium oxide based photocatalytic materials development and their role of in the air pollutants degradation: Overview and forecast. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 200–228. [Google Scholar]
- Skocaj, M.; Filipic, M.; Petkovic, J.; Novak, S. Titanium dioxide in our everyday life; is it safe? Radiol. Oncol. 2011, 45, 227–247. [Google Scholar]
- Penn, R.L.; Banfield, J.F. Morphology development and crystal growth in nanocrystalline aggregates under hydrothermal conditions: Insights from titania. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar]
- Zaban, A.; Aruna, S.T.; Tirosh, S.; Gregg, B.A.; Mastai, Y. The effect of the preparation condition of TiO2 colloids on their surface structures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 4130–4133. [Google Scholar]
- Oskam, G.; Nellore, A.; Penn, R.L.; Searson, P.C. The growth kinetics of TiO2 nanoparticles from titanium (IV) alkoxide at high water/titanium ratio. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 1734–1738. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, X. Anatase/Bronze TiO2 heterojunction: Enhanced photocatalysis and prospect in photothermal catalysis. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2020, 36, 992–999. [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara, T.; Konishi, Y.; Tada, H.; Tohge, N.; Nishii, J.; Ito, S. A patterned TiO2 (anatase)/TiO2 (rutile) bilayer-type photocatalyst: Effect of the anatase/rutile junction on the photocatalytic activity. Angew. Chem. 2002, 114, 2935–2937. [Google Scholar]
- Berardinelli, A.; Parisi, F. TiO2 in the food industry and cosmetics. In Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) and Its Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 353–371. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, S.K. Engineered Nanomaterials and Phytonanotechnology: Challenges for Plant Sustainability; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 87. [Google Scholar]
- Dedman, C.J.; King, A.M.; Christie-Oleza, J.A.; Davies, G.L. Environmentally relevant concentrations of titanium dioxide nanoparticles pose negligible risk to marine microbes. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 1236–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Zahra, Z.; Habib, Z.; Hyun, S.; Sajid, M. Nanowaste: Another future waste, its sources, release mechanism, and removal strategies in the environment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2041. [Google Scholar]
- Kansara, K.; Bolan, S.; Radhakrishnan, D.; Palanisami, T.; Ala’a, H.; Bolan, N.; Vinu, A.; Kumar, A.; Karakoti, A. A critical review on the role of abiotic factors on the transformation, environmental identity and toxicity of engineered nanomaterials in aquatic environment. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 296, 118726. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, F.; Sun, T.; Nowack, B. Environmental concentrations of engineered nanomaterials: Review of modeling and analytical studies. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 181, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, F.; Sonderer, T.; Scholz, R.W.; Nowack, B. Possibilities and limitations of modeling environmental exposure to engineered nanomaterials by probabilistic material flow analysis. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Titanium-Environmental Health Criteria 24. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/37269/9241540842-eng.pdf (accessed on 16 August 2021).
- Benstead, J.P.; March, J.G.; Pringle, C.M. Estuarine larval development and upstream post-larval migration of freshwater shrimps in two tropical rivers of Puerto Rico. Biotropica 2000, 32, 545–548. [Google Scholar]
- Crowl, T.A.; McDowell, W.H.; Covich, A.P.; Johnson, S. Species-specific responses in leaf litter processing in a tropical headwater stream (Puerto Rico). Ecology 2001, 82, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Shi, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, B. Effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the bioavailability, metabolism, and toxicity of pentachlorophenol in zebrafish larvae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Deng, S.; Yu, G.; Huang, J.; Lim, V.C. As (V) and as (III) removal from water by a Ce–Ti oxide adsorbent: Behavior and mechanism. Chem. Eng. 2010, 161, 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Lazar, M.A.; Varghese, S.; Nair, S.S. Photocatalytic water treatment by titanium dioxide: Recent updates. J. Catal. 2012, 2, 572–601. [Google Scholar]
- Nel, A.; Xia, T.; Madler, L.; Li, N. Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. J. Sci. 2006, 311, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhou, J.; Cai, Z. The toxicity and oxidative stress of TiO2 nanoparticles in marine abalone (Haliotis diversicolor supertexta). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 63, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, C.D.; Vargas, C.R.; Arancibia, S.R. Estrés oxidativo y neurodegeneración. Rev. Fac. Med. 2003, 46, 229–235. [Google Scholar]
- Hund-Rinke, K.; Simon, M. Ecotoxic effect of photocatalytic active nanoparticles (TiO2) on algae and daphnids. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2006, 13, 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Rosa, S.; Pérez-Reyes, O. Titanium Oxide Nanoparticles as Emerging Aquatic Pollutants: An Evaluation of the Nanotoxicity in the Freshwater Shrimp Larvae Atya lanipes. J. Ecol. 2023, 4, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Reyes, O.; Crowl, T.A.; Hernandez-Garcia, P.J.; Ledesma-Fuste, R.; Villar-Fornes, F.A.; Covich, A.P. Freshwater decapods of Puerto Rico: A checklist and reports of new localities. Zootaxa 2013, 3717, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Minitab 17 Statistical Software. Computer Software; Minitab, Inc.: State College, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, S.; Mahyad, B.; Hashemzadeh, H.; Janfaza, S.; Gholikhani, T.; Tayebi, L. Biomedical applications of TiO2 nanostructures: Recent advances. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 3447–3470. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, E. A review on nanotoxicity and nanogenotoxicity of different shapes of nanomaterials. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 118–147. [Google Scholar]
- Lehutso, R.F.; Thwala, M. Assessment of nanopollution from commercial products in water environments. J. Nanomater. 2021, 11, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garric, J.; Thybaud, E. Toxicological Models Part B: Environmental Models; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 379–396. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Perez, W.X.; Perez-Reyes, O. Population Status of the Tropical Freshwater Shrimp Xiphocaris elongata in Urban and Forest Streams in Puerto Rico. Hydrobiol. J. 2023, 2, 277–288. [Google Scholar]
- do Amaral, D.F.; Guerra, V.; Almeida, K.L.; Signorelli, L.; Rocha, T.L.; de Melo e Silva, D. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles as a risk factor for the health of Neotropical tadpoles: A case study of Dendropsophus minutus (Anura: Hylidae). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 50515–50529. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Tseng, M.C. Behavioral effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on larval zebrafish (Danio rerio). Mar. Pollut. 2011, 63, 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Heinlaan, M.; Ivask, A.; Blinova, I.; Dubourguier, H.-C.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of nanosized and bulk ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to bacteria Vibrio fischeri and crustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Velzeboer, I.; Hendriks, A.J.; Ragas, A.M.; Van de Meent, D. Aquatic ecotoxicity tests of some nanomaterials. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1942–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffitt, R.J.; Luo, J.; Gao, J.; Bonzongo, J.C.; Barber, D.S. Effects of particle composition and species on toxicity of metallic nanomaterials in aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Ariza, A.; Peinado, J.; Pueyo, C.; Lopez-Barea, J. Biochemical indicators of oxidative stress in fish from polluted littoral areas. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1993, 50, 2568–2573. [Google Scholar]
- Onose, G.; Anghelescu, A.; Blendea, D.; Ciobanu, V.; Daia, C.; Firan, F.C.; Oprea, M.; Spinu, A.; Popescu, C.; Ionescu, A.; et al. Cellular and Molecular Targets for Non-Invasive, Non-Pharmacological Therapeutic/Rehabilitative Interventions in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 907. [Google Scholar]
- Barnham, K.J.; Masters, C.L.; Bush, A.I. Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, A.; Yan, L.J.; Jana, C.K.; Das, N. Role of catalase in oxidative stress-and age-associated degenerative diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 9613090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, I.S.; Momose, Y.; Yamamoto, A.; Kim, D.W.; Usui, K. Inhibition of catalase activity by oxidative stress and its relationship to salicylic acid accumulation in plants. Plant Growth Regul. 2003, 39, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Shen, H.; Wang, X.R.; Wu, J.C.; Xue, Y.Q. Effects of chronic exposure of 2,4-dichlorophenol on the antioxidant system in liver of freshwater fish Carassius auratus. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Covich, A.P.; Ewel, K.C.; Hall, R.O.; Giller, P.E.; Goedkoop, W.; Merritt, D.M. Ecosystem services provided by freshwater benthos. In Sustaining Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services in Soils and Sediments; Wall, D.H., Ed.; Chapter 3; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 45–72. [Google Scholar]
- Covich, A.P.; Palmer, M.A.; Crowl, T.A. The role of benthic invertebrate species in freshwater ecosystems—Zoobenthic species influence energy flows and nutrient cycling. BioScience 1999, 49, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Covich, A.P. Atyid shrimp in the headwaters of the Luquillo Mountains, Puerto Rico: Filter feeding in natural and artificial streams. Verh. Für Int. Ver. Angew. Limnol. 1988, 23, 2108–2113. [Google Scholar]
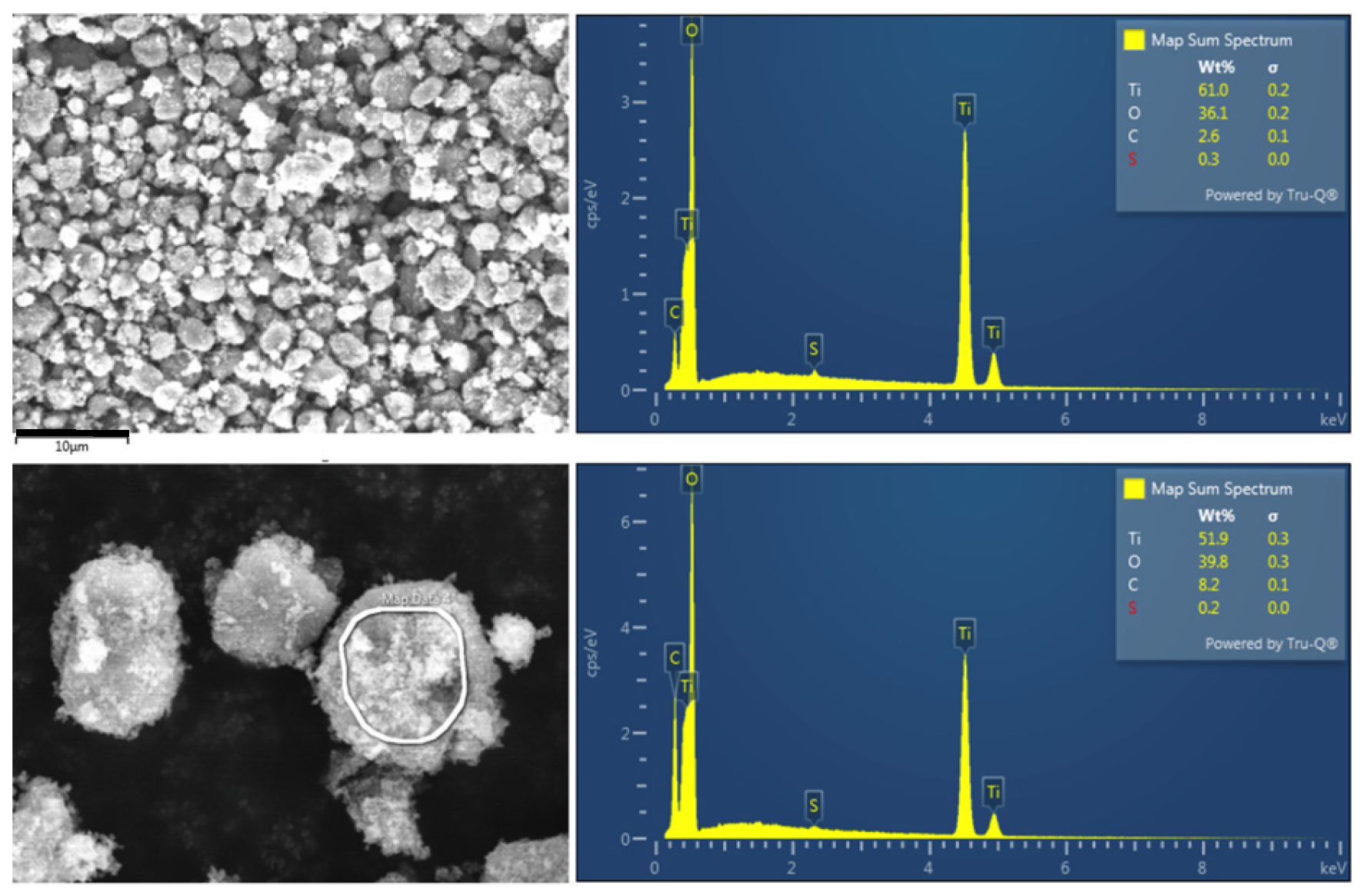
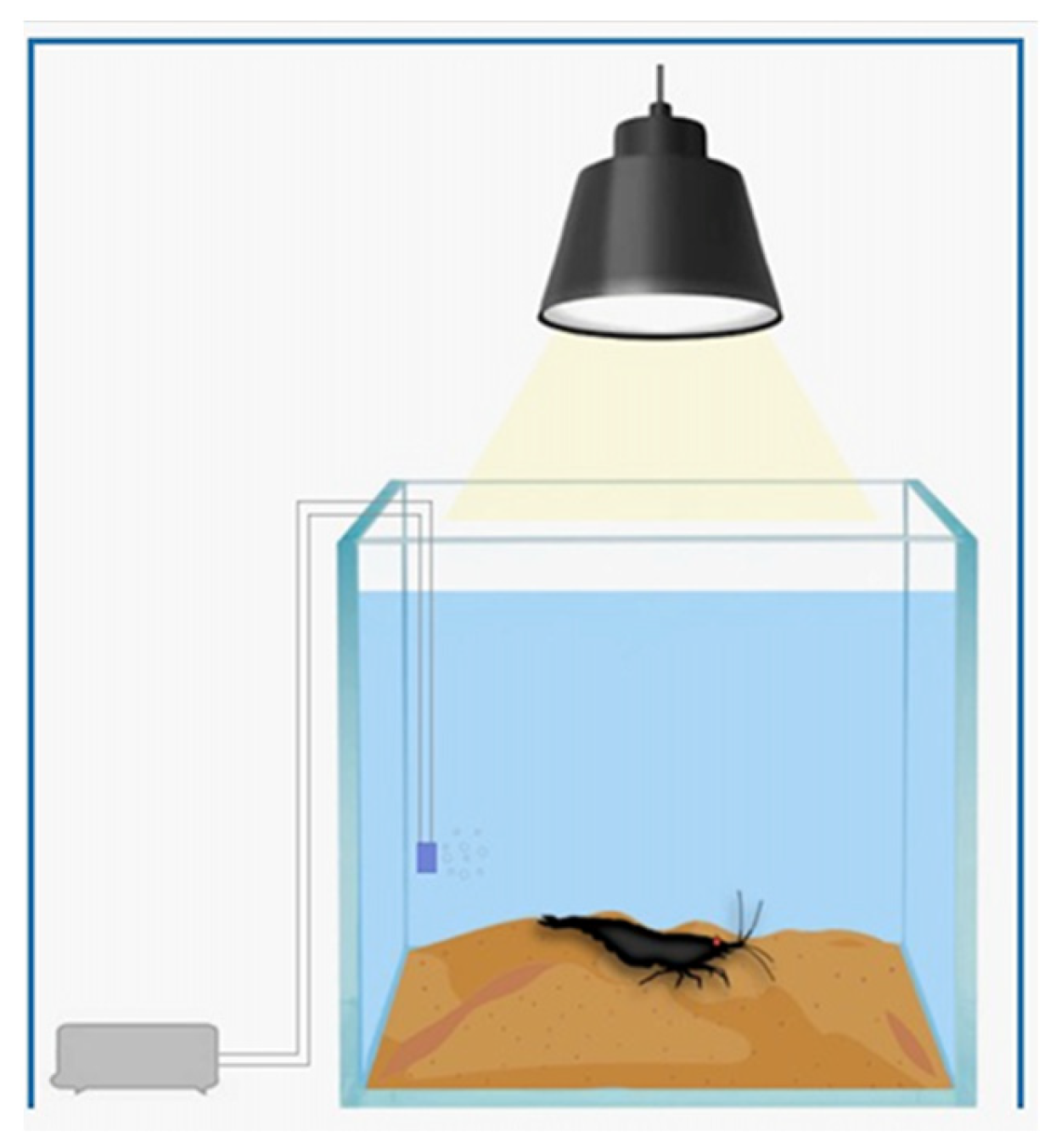
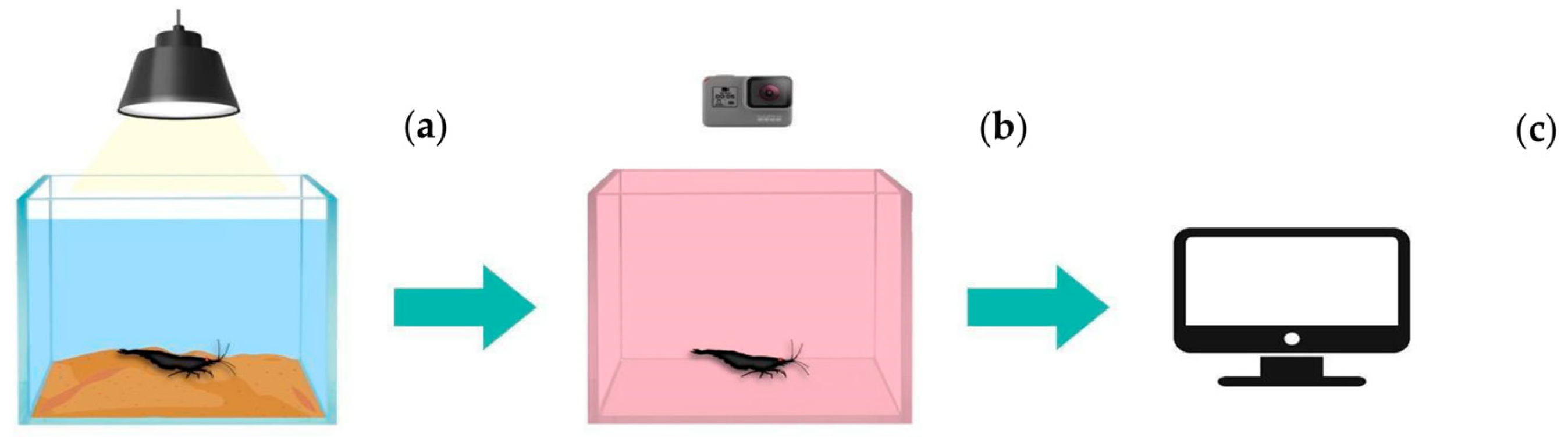


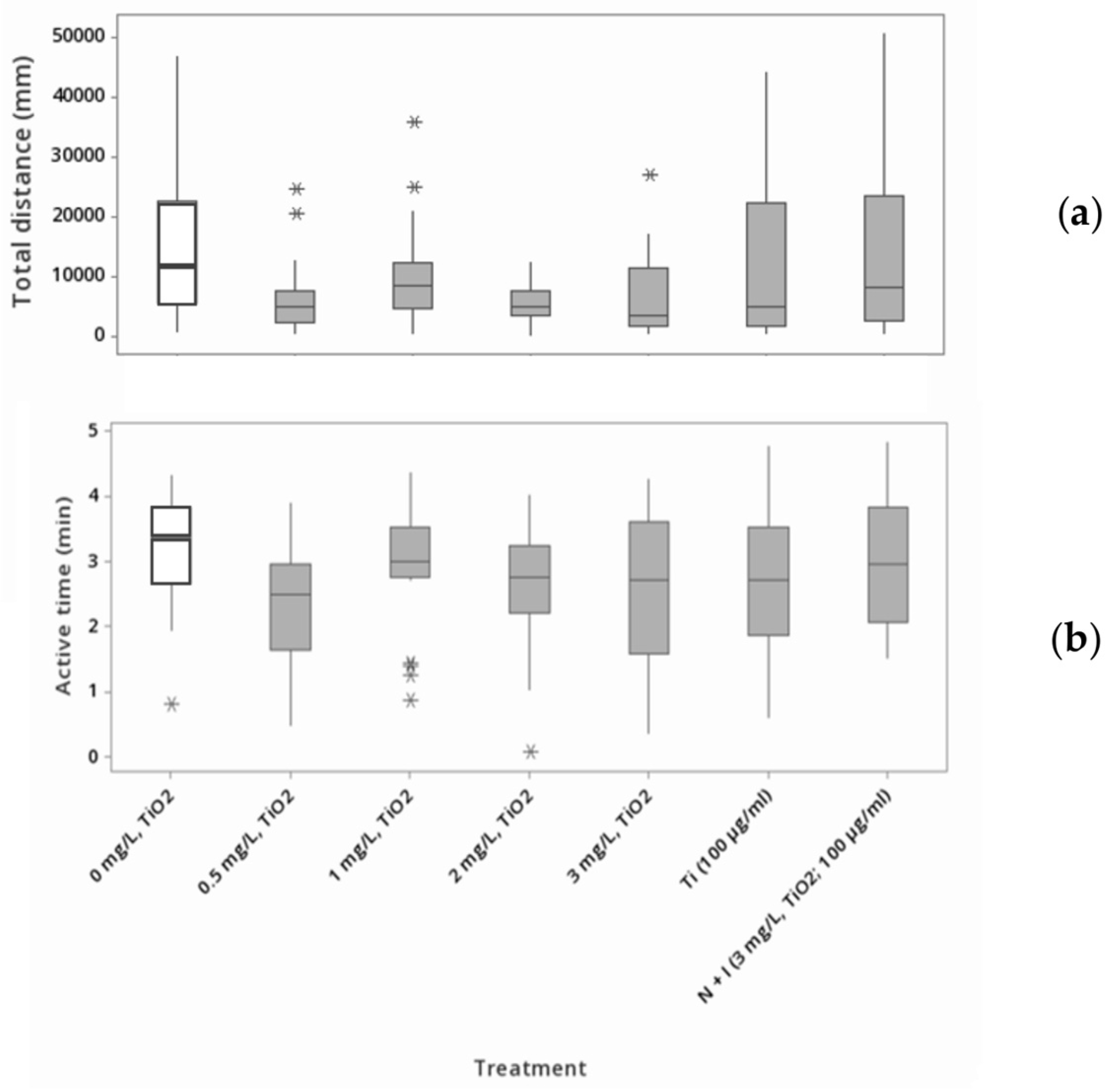
| Group | Time | pH + S.E. | Conductivity + S.E. (ms) | Salinity + S.E. (ppm) | O2, + S.E. (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 mg/L; TiO2 NPs | Pre | 8.2 ± 0.04 | 328.2 ± 19.0 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 8.7 ± 0.2 |
| Post | 8.2 ± 0.04 | 341.5 ± 15.0 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 8.8 ± 0.1 | |
| 0.50 mg/L; TiO2 NPs | Pre | 7.8 ± 0.003 | 468.7 ± 1.0 | 0.23 ± 0.001 | 9.2 ± 0.02 |
| Post | 7.7 ± 0.02 | 436.0 ± 9.1 | 0.22 ± 0.004 | 8.0 ± 0.1 | |
| 1.0 mg/L; TiO2 NPs | Pre | 8.3 ± 0.00 | 353.2 ± 0.8 | 0.23 ± 0.0001 | 9.3 ± 0.1 |
| Post | 7.7 ± 0.02 | 362.8 ± 2.3 | 0.22 ± 0.0001 | 8.4 ± 0.1 | |
| 2.0 mg/L; TiO2 NPs | Pre | 7.8 ± 0.01 | 469.6 ± 3.6 | 0.23 ± 0.002 | 9.5 ± 0.1 |
| Post | 7.7 ± 0.02 | 475.2 ± 4.2 | 0.24 ± 0.002 | 7.9 ± 0.1 | |
| 3.0 mg/L; TiO2 NPs | Pre | 8.2 ± 0.04 | 332.2 ± 17.3 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 8.6 ± 0.1 |
| Post | 8.1 ± 0.04 | 337.4 ± 16.2 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 8.9 ± 0.1 | |
| Titanium (100 mg/L) | Pre | 8.2 ± 0.04 | 332.4 ± 16.0 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 8.6 ± 0.1 |
| Post | 8.1 ± 0.04 | 367.2 ± 21.0 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 8.9 ± 0.1 | |
| TiO2 NPs (3 mg/L) ± Titanium (100 mg/L) | Pre | 8.2 ± 0.04 | 340.4 ± 21.0 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 8.6 ± 0.1 |
| Post | 8.1 ± 0.04 | 371.8 ± 22.4 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 8.9 ± 0.1 |
| Point | Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|
| 24 h | |
| EC50 | 0.143 |
| EC60 | 0.520 |
| EC70 | 2.073 |
| EC80 | 10.467 |
| EC90 | 98.868 |
| Time (Hours) | Temperature + S.E. (°C) | pH + S.E. | Conductivity + S.E. (µs) | DO + S.E. (mg/L) | Salinity + S.E. (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | 19.4 ± 0.01 | 7.0 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.01 | 8.9 ± 0.04 | 0.2 ± 0.01 |
| 24 | 19.9 ± 0.02 | 7.1 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.004 | 8.3 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.01 |
| 72 | 18.5 ± 0.1 | 6.1 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.01 | 9.0 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.01 |
| 120 | 18.8 ± 0.02 | 6.8 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.0 | 8.7 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.001 |
| 168 | 18.6 ± 0.02 | 7.1 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.0 | 7.8 ± 0.01 | 0.2 ± 0.0 |
| 216 | 19.2 ± 0.1 | 5.8 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.01 | 8.4 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.004 |
| 264 | 18.7 ± 0.1 | 6.0 ± 0.04 | 0.4 ± 0.001 | 8.9 ± 0.04 | 0.2 ± 0.01 |
| Time of Exposure (Hours) | POS + S.E. (mm) | CEF + S.E. (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 12.7 ±/−1.3 | 14.3 ±/−2.0 |
| 24 | 13.3 ±/−1.3 | 16.6 ±/−1.4 |
| 72 | 12.1 ±/−1.0 | 14.6 ±/−1.4 |
| 120 | 11.1 ±/−0.2 | 13.6 ±/−0.2 |
| 168 | 12.2 ±/−1.0 | 14.2 ±/−1.1 |
| 216 | 12.0 ±/−1.0 | 14.9 ±/−1.2 |
| 264 | 10.8 ±/−0.2 | 14.0 ±/−0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruz-Rosa, S.; Pérez-Reyes, O. Neurotoxicity and Oxidative Stress Development in Adult Atya lanipes Shrimp Exposed to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Toxics 2023, 11, 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080694
Cruz-Rosa S, Pérez-Reyes O. Neurotoxicity and Oxidative Stress Development in Adult Atya lanipes Shrimp Exposed to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Toxics. 2023; 11(8):694. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080694
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruz-Rosa, Stefani, and Omar Pérez-Reyes. 2023. "Neurotoxicity and Oxidative Stress Development in Adult Atya lanipes Shrimp Exposed to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles" Toxics 11, no. 8: 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080694
APA StyleCruz-Rosa, S., & Pérez-Reyes, O. (2023). Neurotoxicity and Oxidative Stress Development in Adult Atya lanipes Shrimp Exposed to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Toxics, 11(8), 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080694






