Distribution of Micro-Nano PS, DEHP, and/or MEHP in Mice and Nerve Cell Models In Vitro after Exposure to Micro-Nano PS and DEHP
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PS and DEHP
2.2. In Vitro Adsorption of DEHP by PS
2.3. Animals and Treatment
2.4. Distribution of PS in Mice
2.4.1. Distribution of PS in Tissues In Vivo
2.4.2. Quantitative Detection of PS Distribution In Vivo
2.5. Quantitative Detection of DEHP and MEHP Distribution in Mice
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. In Vitro Cell Culture
2.8. Detection of Cell Viability Using CCK8 Assay
2.9. Confocal Observation of PS Uptake by Cells
2.10. GC-MS Detection of MEHP Uptake by Cells
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of PS
3.2. In Vitro Adsorption of DEHP by PS
3.3. Distribution of PS in Mice
3.4. Distribution of DEHP and MEHP in Mice
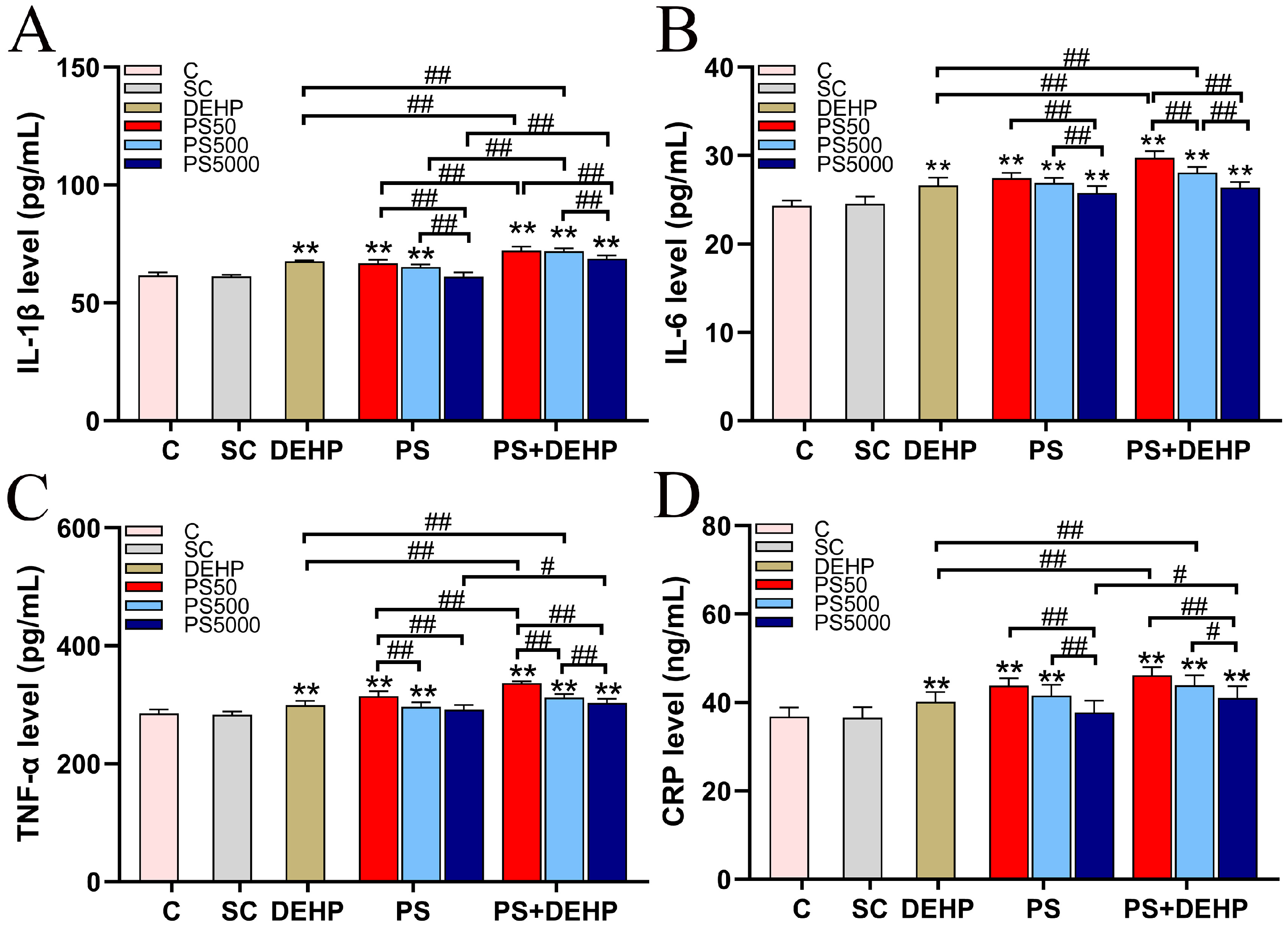
3.5. Combined Exposure to PS and DEHP Induces Systemic Inflammation
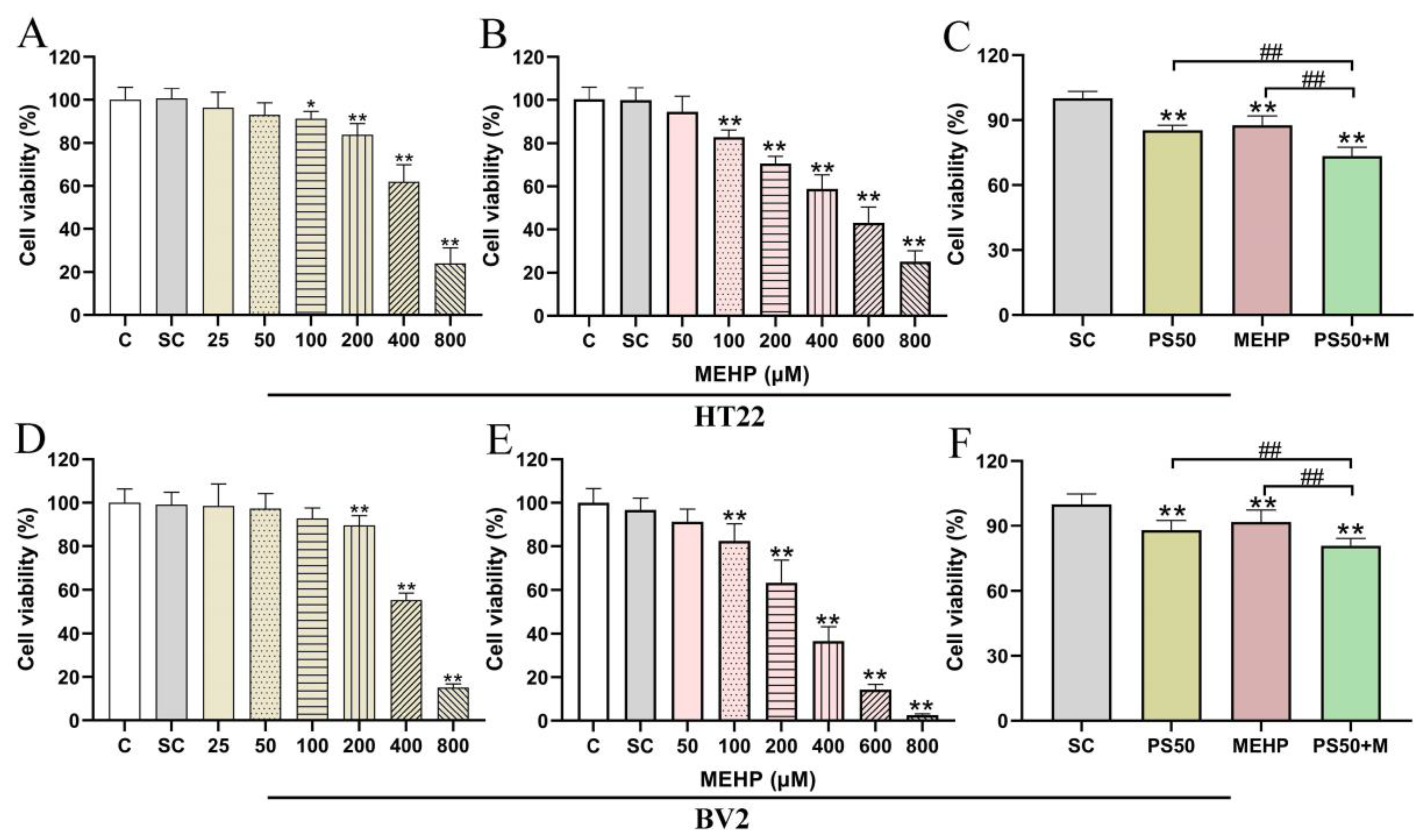
3.6. Effects of PS50 and MEHP Exposure Alone and in Combination on the Viability of HT22 and BV2 Cells
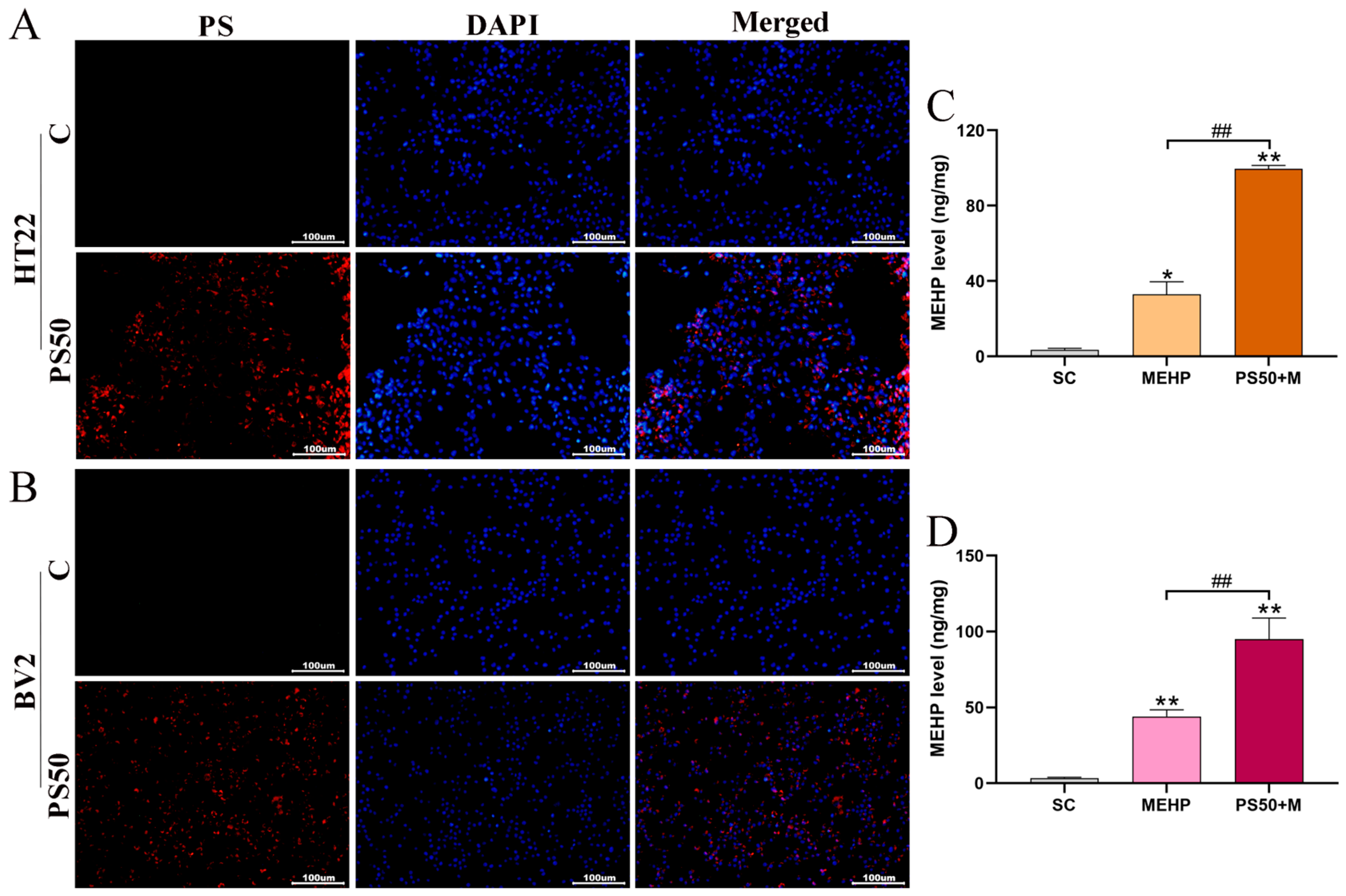
3.7. Accumulation of PS and MEHP in HT22 and BV2 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tiseo, I. Global Plastic Production 1950–2020. Retrieved on 27 May 2022. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/282732/global-production-of-plastics-since-1950 (accessed on 29 April 2022).
- Richard, C.T.; Ylva, O.; Richard, P.M.; Anthony, D.; Steven, J.R.; Anthony, W.G.J.; Daniel, M.; Andrea, E.R. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Lopes, C.; Oliveira, P.; Bessa, F.; Otero, V.; Henriques, B.; Raimundo, J.; Caetano, M.; Vale, C.; Guilhermino, L. Microplastics in wild fish from North East Atlantic Ocean and its potential for causing neurotoxic effects, lipid oxidative damage, and human health risks associated with ingestion exposure. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 717, 134625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.; Deng, H.; Li, B.; Chen, Q.; Pettigrove, V.; Wu, C.; Shi, H. The occurrence of microplastic in specific organs in commercially caught fishes from coast and estuary area of east China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalbone, L.; Cincotta, F.; Giarratana, F.; Ziino, G.; Panebianco, A. Microplastics in fresh and processed mussels sampled from fish shops and large retail chains in Italy. Food Control 2021, 125, 108003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Shim, W.J.; Jang, M.; Han, G.M.; Hong, S.H. Nationwide monitoring of microplastics in bivalves from the coastal environment of Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, J.C.; Paço, A.; Reis, V.; da Costa, J.P.; Fernandes, A.J.S.; da Costa, F.M.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Identification of microplastics in white wines capped with polyethylene stoppers using micro-Raman spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, K.D.; Covernton, G.A.; Davies, H.L.; Dower, J.F.; Juanes, F.; Dudas, S.E. Human Consumption of Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7068–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, L.M.; Xu, E.G.; Larsson, H.C.E.; Tahara, R.; Maisuria, V.B.; Tufenkji, N. Response to Comment on “Plastic Teabags Release Billions of Microparticles and Nanoparticles into Tea”. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14136–14137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shi, Y.; Yang, L.; Xiao, L.; Kehoe, D.K.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Boland, J.J.; Wang, J.J. Microplastic release from the degradation of polypropylene feeding bottles during infant formula preparation. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danopoulos, E.; Twiddy, M.; Rotchell, J.M. Microplastic contamination of drinking water: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Y.S.; Tuan Anuar, S.; Azmi, A.A.; Wan Mohd Khalik, W.M.A.; Lehata, S.; Hamzah, S.R.; Ismail, D.; Ma, Z.F.; Dzulkarnaen, A.; Zakaria, Z.; et al. Detection of microplastics in human colectomy specimens. JGH Open 2021, 5, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabl, P.; Köppel, S.; Königshofer, P.; Bucsics, T.; Trauner, M.; Reiberger, T.; Liebmann, B. Detection of Various Microplastics in Human Stool: A prospective case series. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; He, S.; Yang, C.; Zhang, T.; Tang, C.; Zhang, C.; et al. A review: Research progress on microplastic pollutants in aquatic environments. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 766, 142572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wan, Z.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Polystyrene microplastics induce gut microbiota dysbiosis and hepatic lipid metabolism disorder in mice. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 631–632, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lu, L.; Tu, W.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z. Impacts of polystyrene microplastic on the gut barrier, microbiota and metabolism of mice. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 649, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Ma, T.; Sha, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, X.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Ding, J. Polystyrene microplastics induced male reproductive toxicity in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Lee, Y.-H.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Chiu, I.-J.; Huang, C.C.-Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Chia, Z.-C.; Lee, C.-P.; Lin, Y.-F.; Chiu, H.-W. The Kidney-Related Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics on Human Kidney Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells HK-2 and Male C57BL/6 Mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 057003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-W.; Hsu, L.-F.; Wu, I.-L.; Wang, Y.-L.; Chen, W.-C.; Liu, Y.-J.; Yang, L.-T.; Tan, C.-L.; Luo, Y.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; et al. Exposure to polystyrene microplastics impairs hippocampus-dependent learning and memory in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Bakir, A.; Burton, G.A.; Janssen, C. Microplastic as a Vector for Chemicals in the Aquatic Environment: Critical Review and Model-Supported Reinterpretation of Empirical Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3315–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennecke, D.; Duarte, B.; Paiva, F.; Caçador, I.; Canning-Clode, J. Microplastics as vector for heavy metal contamination from the marine environment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 178, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhrhoff, T.J.; Scholz-Böttcher, B.M. Qualitative impact of salinity, UV radiation and turbulence on leaching of organic plastic additives from four common plastics—A lab experiment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithner, D.; Larsson, Å.; Dave, G. Environmental and health hazard ranking and assessment of plastic polymers based on chemical composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3309–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.-J.; Xu, J.-K.; Yan, Z.-H.; Ren, H.-Q.; Zhang, Y. Microplastics enhance the developmental toxicity of synthetic phenolic antioxidants by disturbing the thyroid function and metabolism in developing zebrafish. Environ. Int. 2020, 140, 105750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouda, S.; Missawi, O.; Cappello, T.; Boughattas, I.; De Marco, G.; Maisano, M.; Banni, M. Toxicological impact of environmental microplastics and benzo[a]pyrene in the seaworm Hediste diversicolor under environmentally relevant exposure conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 310, 119856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romdhani, I.; De Marco, G.; Cappello, T.; Ibala, S.; Zitouni, N.; Boughattas, I.; Banni, M. Impact of environmental microplastics alone and mixed with benzo[a]pyrene on cellular and molecular responses of Mytilus galloprovincialis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 128952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilhermino, L.; Vieira, L.R.; Ribeiro, D.; Tavares, A.S.; Cardoso, V.; Alves, A.; Almeida, J.M. Uptake and effects of the antimicrobial florfenicol, microplastics and their mixtures on freshwater exotic invasive bivalve Corbicula fluminea. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 622–623, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Yan, X.; Xu, S.; Fan, Y.; Xu, H.; Ma, Y.; Hou, W.; Javed, R.; Zhang, Y. Co-exposure of polystyrene microplastics and iron aggravates cognitive decline in aging mice via ferroptosis induction. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 233, 113342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierens, T.; Servaes, K.; Van Holderbeke, M.; Geerts, L.; De Henauw, S.; Sioen, I.; Vanermen, G. Analysis of phthalates in food products and packaging materials sold on the Belgian market. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 2575–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Du, Q. Uptake of Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate of Vegetables from Plastic Film Greenhouses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11585–11588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransohoff, R.; Engelhardt, B. The anatomical and cellular basis of immune surveillance in the central nervous system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallmann, R.; Horn, N.; Selg, M.; Wendler, O.; Pausch, F.; Sorokin, L.M. Expression and Function of Laminins in the Embryonic and Mature Vasculature. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 979–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.; Alvarez, X.; Lackner, A.A. Central nervous system perivascular cells are immunoregulatory cells that connect the CNS with the peripheral immune system. Glia 2001, 36, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Liu, Z.-H.; Yin, H.; Dang, Z.; Wu, P.-X.; Zhu, N.-W.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Y. Migration and potential risk of trace phthalates in bottled water: A global situation. Water Res. 2018, 147, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, H.M.; Bolt, H.M.; Preuss, R.; Angerer, J. New metabolites of di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) in human urine and serum after single oral doses of deuterium-labelled DEHP. Arch. Toxicol. 2005, 79, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildenbrand, S.; Gabrio, T.; Volland, G. Inter-Day Variability of Metabolites of DEHP and DnBP in Human Urine—Comparability of the Results of Longitudinal Studies with a Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventrice, P.; Ventrice, D.; Russo, E.; De Sarro, S.G. Phthalates: European regulation, chemistry, pharmacokinetic and related toxicity. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 36, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.J.; Lee, B.M. Toxicokinetic Relationship Between Di(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) and Mono(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate in Rats. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2007, 70, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, F.; Wang, F.; Leng, J.; Wang, K.; Héroux, P.; Shen, H.-M.; Wu, Y.; et al. Mono-2-ethylhexyl phthalate drives progression of PINK1-parkin-mediated mitophagy via increasing mitochondrial ROS to exacerbate cytotoxicity. Redox Biol. 2021, 38, 101776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kim, K.H. Effects of Mono-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate on Fetal and Neonatal Rat Testis Organ Cultures. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 69, 1964–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.S.; Rozati, R.; Reddy, B.V.R.; Raman, N.V.V.S.S. General gynaecology: Association of phthalate esters with endo metriosis in Indian women. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2006, 113, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meruvu, S.; Zhang, J.; Bedi, Y.S.; Choudhury, M. Mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate induces apoptosis through miR-16 in human first trimester placental cell line HTR-8/SVneo. Toxicol. 2016, 31, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Xu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Guo, S.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, L.; Ye, L. Effect of Notch pathway on lipid accumulation induced by mono-2-ethylhexyl phthalate on 3T3-L1 cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bility, M.T.; Thompson, J.T.; McKee, R.H.; David, R.M.; Butala, J.H.; Vanden Heuvel, J.P.; Peters, J.M. Activation of Mouse and Human Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) by Phthalate Monoesters. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 82, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Jiang, W.; Xin, H.; Luo, Y.; Loya-López, S.; Gu, H.; Ran, D. Distinct Role of Mono-2-ethylhexyl Phthalate in Neuronal Transmission in Rat CA3 Hippocampal Neurons: Involvement of Ion Channels. Molecules 2022, 27, 3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.-F.; Liu, G.-Z.; Zhu, Z.-L.; Wang, S.-C.; Zhao, F.-F. Interactions between microplastics and phthalate esters as affected by microplastics characteristics and solution chemistry. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senathirajah, K.; Attwood, S.; Bhagwat, G.; Carbery, M.; Wilson, S.; Palanisami, T. Estimation of the mass of microplastics ingested—A pivotal first step towards human health risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efsa Panel on Food Contact Materials, E.; Processing, A.; Silano, V.; Barat Baviera, J.M.; Bolognesi, C.; Chesson, A.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Crebelli, R.; Gott, D.M.; Grob, K.; et al. Update of the risk assessment of di-butylphthalate (DBP), butyl-benzyl-phthalate (BBP), bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP), di-isononylphthalate (DINP) and di-isodecylphthalate (DIDP) for use in food contact materials. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, T.; Zhao, X. Polystyrene nanoplastics penetrate across the blood-brain barrier and induce activation of microglia in the brain of mice. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, T.F.; O’brien, A.M.; Zargartalebi, M.; Sinton, D. Nanoplastic State and Fate in Aquatic Environments: Multiscale Modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 4017–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Phthalates released from microplastics inhibit microbial metabolic activity and induce different effects on intestinal luminal and mucosal microbiota. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 310, 119884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ma, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, Y. Systematic toxicity evaluation of polystyrene nanoplastics on mice and molecular mechanism investigation about their internalization into Caco-2 cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, B.; Du, Y.; Li, J.; Tong, X.; Wu, Y.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y. Tissue distribution of polystyrene nanoplastics in mice and their entry, transport, and cytotoxicity to GES-1 cells. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, J.; García, I.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Cellular Uptake of Nanoparticles versus Small Molecules: A Matter of Size. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2305–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, J.; Lin, L.; Hu, M.; Jiang, J.; Dai, M.; Wang, B.; et al. Underestimated health risks: Polystyrene micro- and nanoplastics jointly induce intestinal barrier dysfunction by ROS-mediated epithelial cell apoptosis. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, M.; Kutscher, H.L.; Gao, D.; Sunil, V.R.; Malaviya, R.; Vayas, K.; Stein, S.; Laskin, J.D.; Laskin, D.L.; Sinko, P.J. Biodistribution and renal clearance of biocompatible lung targeted poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) nanogel aggregates. J. Control Release 2012, 164, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa de Almeida, M.; Susnik, E.; Drasler, B.; Taladriz-Blanco, P.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Understanding nano particle endocytosis to improve targeting strategies in nanomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 5397–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, S.B.; D’errico, J.N.; Adler, D.S.; Kollontzi, S.; Goedken, M.J.; Fabris, L.; Yurkow, E.J.; Stapleton, P.A. Nanopolystyrene translocation and fetal deposition after acute lung exposure during late-stage pregnancy. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Lopes, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Environmental exposure to microplastics: An overview on possible human health effects. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 702, 134455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schettler, T. Human exposure to phthalates via consumer products. Int. J. Androl. 2006, 29, 134–139, discussion 181–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yan, Z.; Shen, R.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lemos, B. Microplastics release phthalate esters and cause aggravated adverse effects in the mouse gut. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Guan, J.; Feng, Y.; Nie, L.; Xu, Y.; Xu, H.; Fu, F. Polystyrene microplastics induced nephrotoxicity associated with oxidative stress, inflammation, and endoplasmic reticulum stress in juvenile rats. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1059660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Yu, Z.; Feng, P.; Ye, Z.; Li, R.; Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Kakade, A.; Liu, P.; Li, X. Lactobacillus plantarum TW1-1 Alleviates Diethylhexylphthalate-Induced Testicular Damage in Mice by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Decreasing Inflammation. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
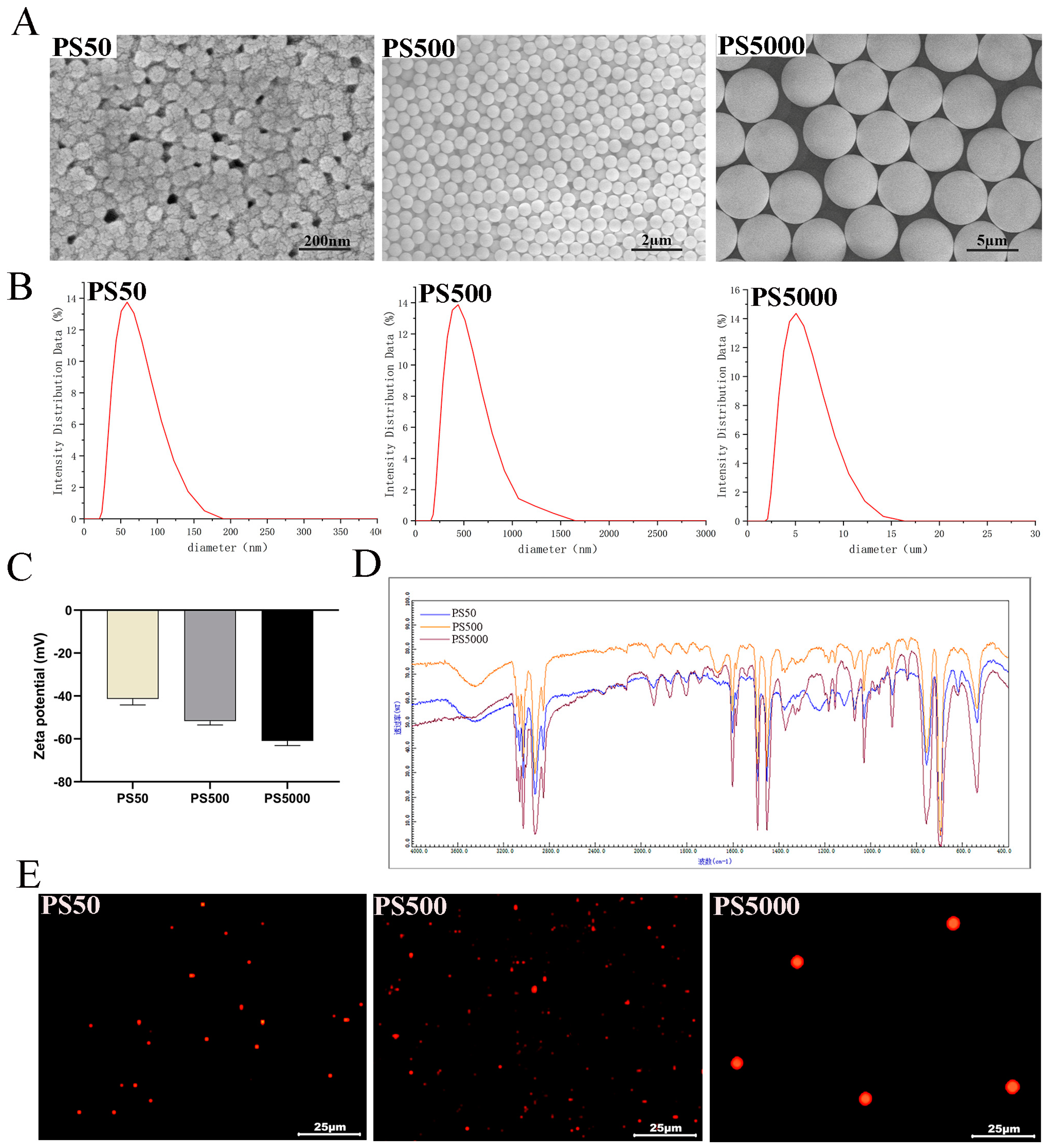
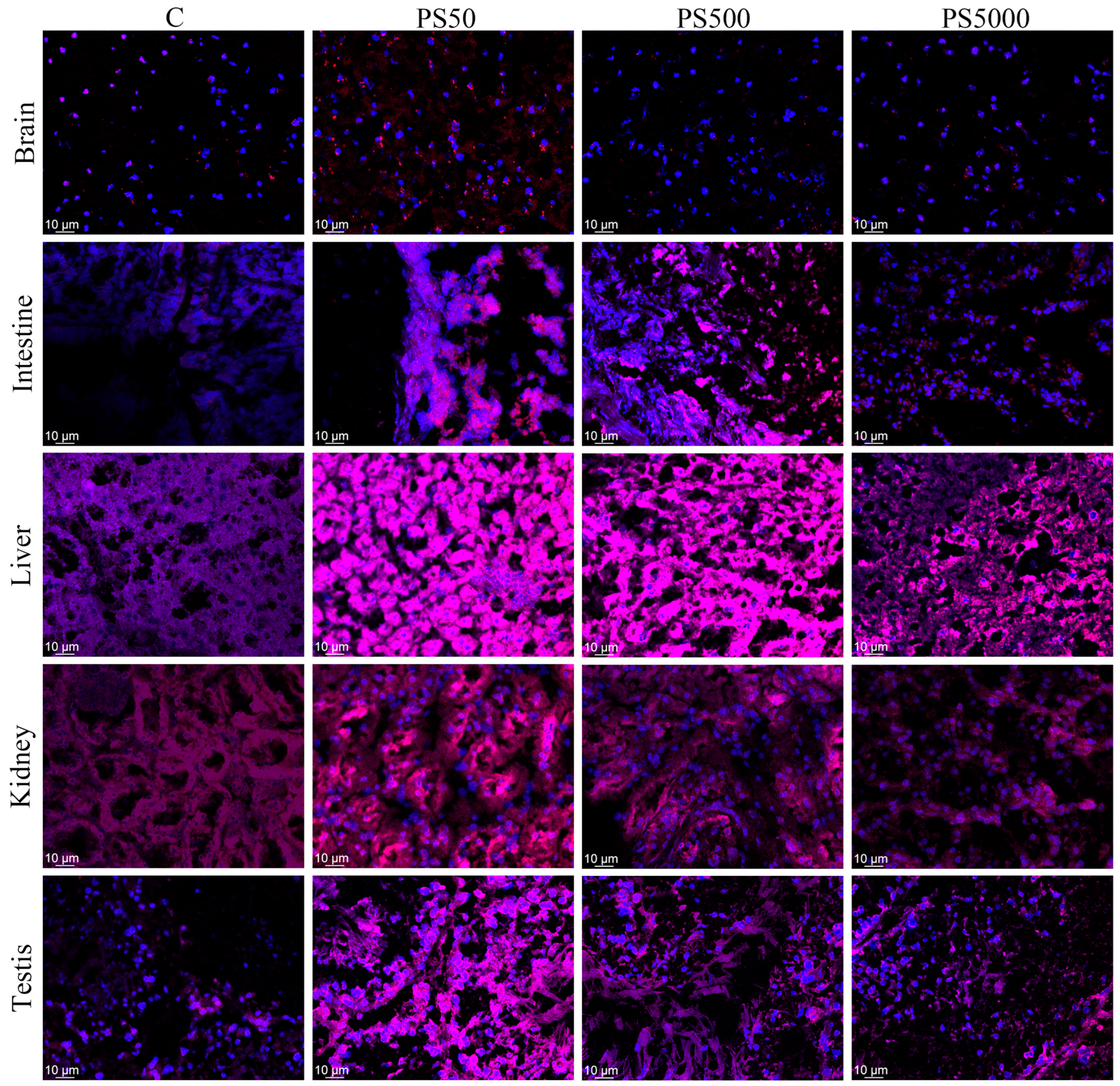
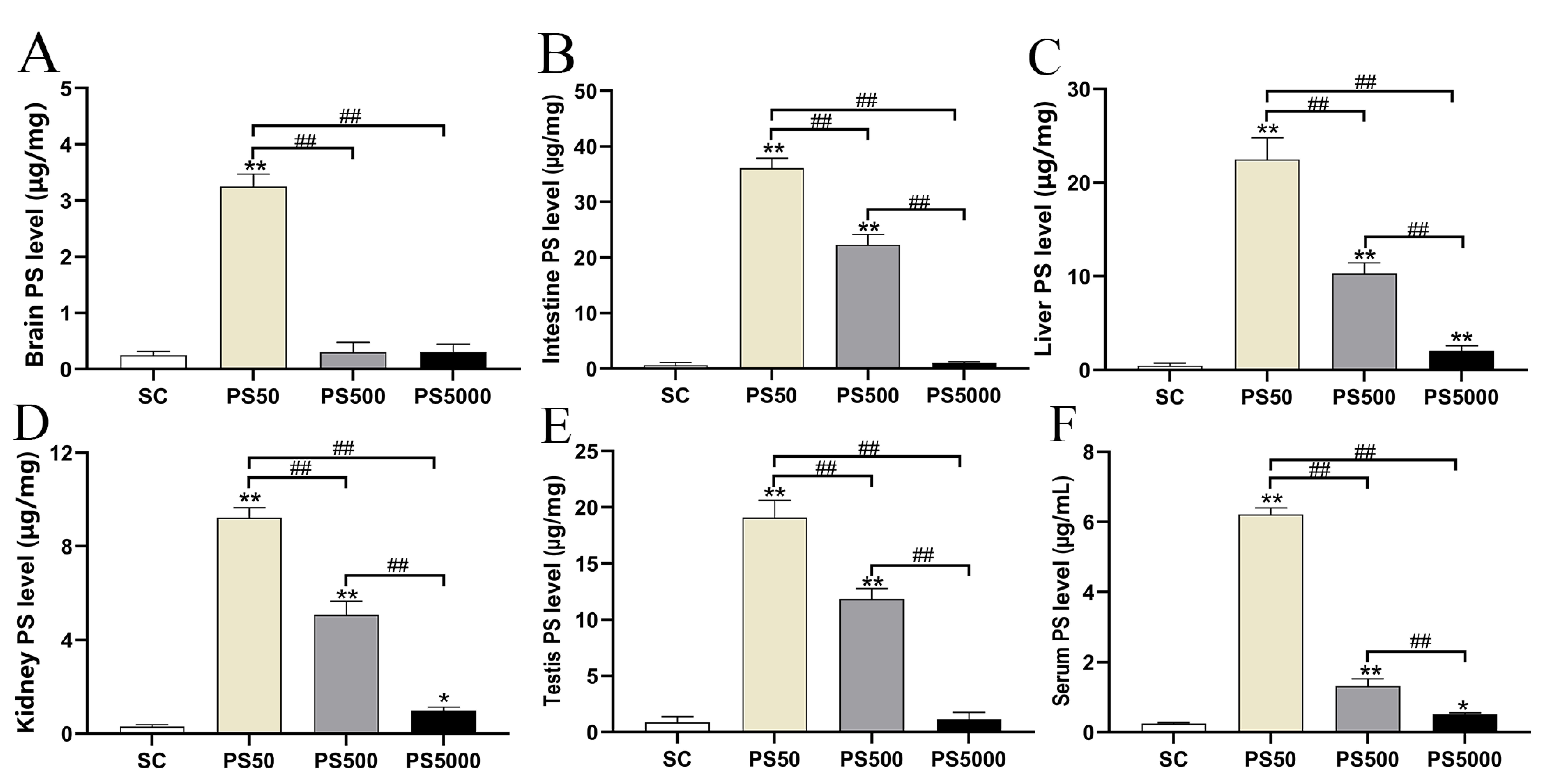
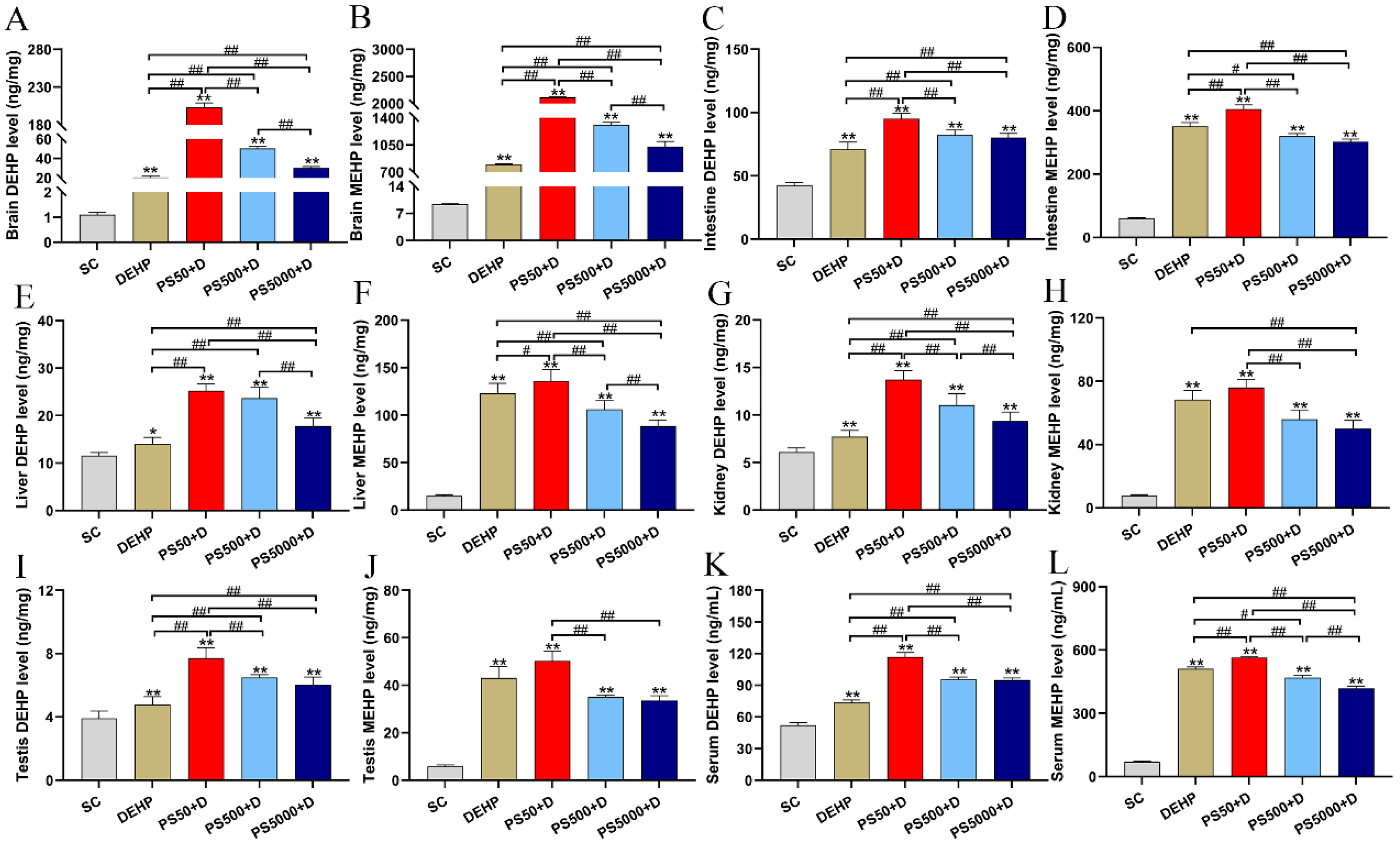
| Group | Brain (μg mg−1) | Intestine (μg mg−1) | Liver (μg mg−1) | Kidney (μg mg−1) | Testis (μg mg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS50 | 3.0053 | 35.4827 | 22.026 | 8.9173 | 18.2173 |
| PS500 | 0.0533 | 21.6607 | 9.814 | 4.7713 | 10.9733 |
| PS5000 | 0.0613 | 0.3767 | 1.588 | 0.6833 | 0.2633 |
| Group | Brain (ng mg−1) | Intestine (ng mg−1) | Liver (ng mg−1) | Kidney (ng mg−1) | Testis (ng mg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEHP | 19.39 | 28.33 | 2.41 | 1.62 | 0.87 |
| PS50+D | 201.53 | 52.55 | 13.66 | 7.62 | 3.81 |
| PS500+D | 49.28 | 39.62 | 12.08 | 4.93 | 2.59 |
| PS5000+D | 29.24 | 37.58 | 6.21 | 3.26 | 2.14 |
| Group | Brain (ng mg−1) | Intestine (ng mg−1) | Liver (ng mg−1) | Kidney (ng mg−1) | Testis (ng mg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEHP | 789.04 | 291.81 | 108.04 | 60.50 | 37.26 |
| PS50+D | 2099.64 | 345.60 | 120.98 | 68.06 | 44.40 |
| PS500+D | 1303.59 | 260.28 | 91.21 | 48.08 | 29.17 |
| PS5000+D | 1021.50 | 241.99 | 73.47 | 42.14 | 27.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Yan, J.; Li, K.; Lin, B.; Lai, W.; Bian, L.; Jia, R.; Liu, X.; Xi, Z. Distribution of Micro-Nano PS, DEHP, and/or MEHP in Mice and Nerve Cell Models In Vitro after Exposure to Micro-Nano PS and DEHP. Toxics 2023, 11, 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050441
Han J, Yan J, Li K, Lin B, Lai W, Bian L, Jia R, Liu X, Xi Z. Distribution of Micro-Nano PS, DEHP, and/or MEHP in Mice and Nerve Cell Models In Vitro after Exposure to Micro-Nano PS and DEHP. Toxics. 2023; 11(5):441. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050441
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Jie, Jun Yan, Kang Li, Bencheng Lin, Wenqing Lai, Liping Bian, Rui Jia, Xiaohua Liu, and Zhuge Xi. 2023. "Distribution of Micro-Nano PS, DEHP, and/or MEHP in Mice and Nerve Cell Models In Vitro after Exposure to Micro-Nano PS and DEHP" Toxics 11, no. 5: 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050441
APA StyleHan, J., Yan, J., Li, K., Lin, B., Lai, W., Bian, L., Jia, R., Liu, X., & Xi, Z. (2023). Distribution of Micro-Nano PS, DEHP, and/or MEHP in Mice and Nerve Cell Models In Vitro after Exposure to Micro-Nano PS and DEHP. Toxics, 11(5), 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050441






