The Uptake of Rare Trace Elements by Perennial Ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Preparation
2.2. Plant Growth
2.3. Digestion and Measurement
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of RTEs and Cd on the Biomass of L. perenne
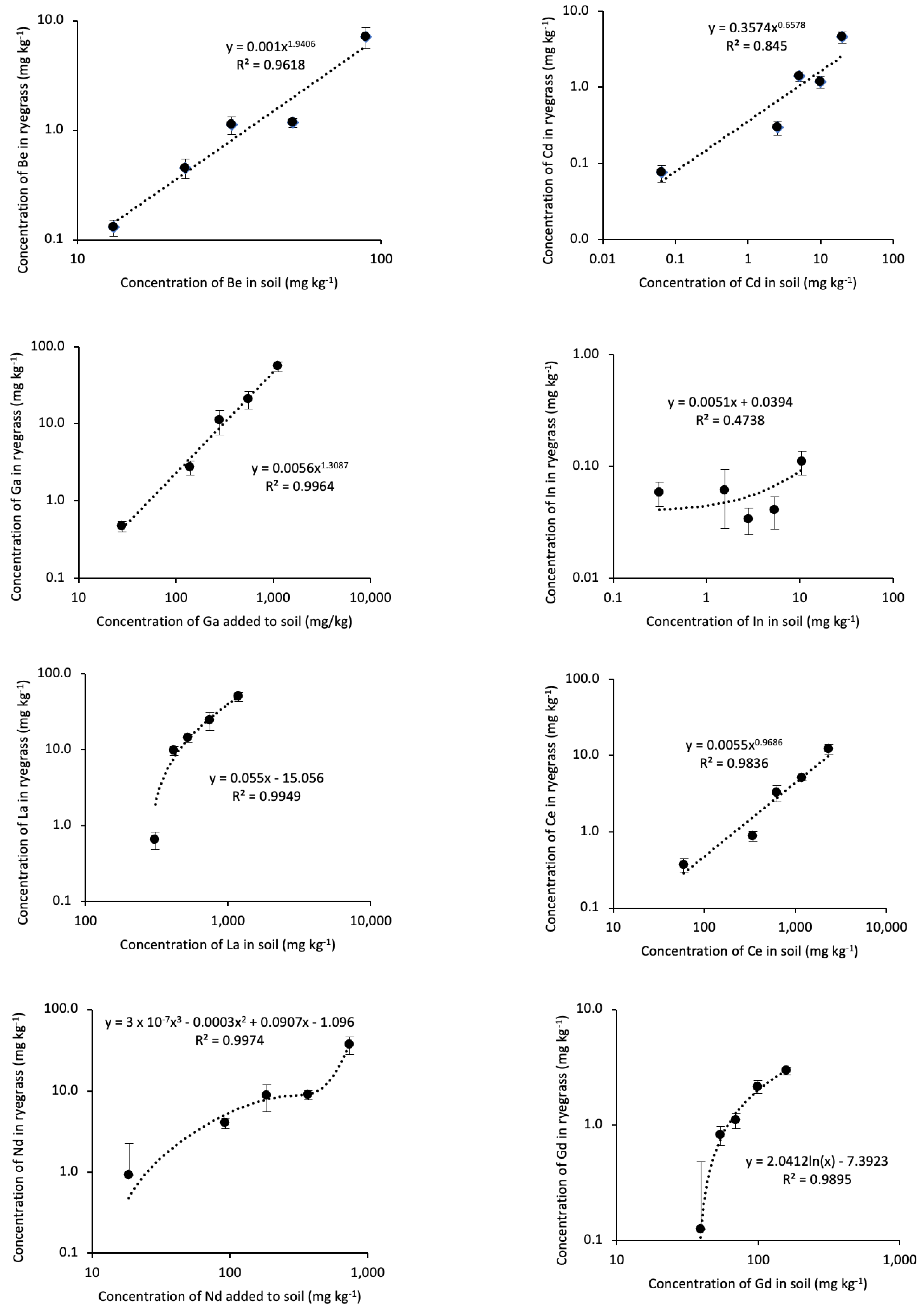
3.2. Uptake and bioaccumulation of RTEs in L. perenne
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of the RTEs and Cd Contaminants on the Biomass of L. perenne
| Element | Plant Concentrations (mg kg−1) in Unspiked Soil | Uptake in Plants Spiked with ETECs (mg kg−1, μmol kg−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Background | Elevated (without Visible Toxicity) | Before Toxicity | With Toxicity | |
| Be | 0.1–10.1, 11–1121 [44,49] | 0.4–32, 44–3551 [49,50] | ||
| Ga | 2–74, 29–1061 [18,53] | 5–16, 72–229 [17,21] | ||
| In | 1.1–4.2, 9.6–37 [17,18] | 2.5–6.6, 22–57 [17,21] | ||
| La | 0.44–6.5, 3.2–47 [43,60] | 0.95–120, 6.8–864 [43,45] | ||
| Ce | 6.7, 48 [60] | 16, 114 [60] | ||
| Nd | 1.79–13, 12–90 [42] | 6.69–221, 46–1532 [42,45] | ||
| Gd | - | - | ||
4.2. Uptake of the RTEs and Cd in L. perenne
4.3. Bioaccumulation Coefficients of the RTEs and Cd in L. perenne
4.4. Effect of the Concentration of RTEs and Cd Added to Soil on Bioaccumulation in L. perenne
4.5. Risk of RTEs Entering the Food Chain
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robinson, B.H. E-Waste: An Assessment of Global Production and Environmental Impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, N.N.; Agusa, T.; Ramu, K.; Tu, N.P.C.; Murata, S.; Bulbule, K.A.; Parthasaraty, P.; Takahashi, S.; Subramanian, A.; Tanabe, S. Contamination by Trace Elements at E-Waste Recycling Sites in Bangalore, India. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.H.; Sakakibara, M.; Sano, S.; Mai, T.N. Uptake of Metals and Metalloids by Plants Growing in a Lead-Zinc Mine Area, Northern Vietnam. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hong, M.; Yin, X.; Liu, J. Effects of the Accumulation of the Rare Earth Elements on Soil Macrofauna Community. J. Rare Earths 2010, 28, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumaru, T.; Ozaki, H.; Onwona-Agyeman, S.; Ofosu-Anim, J.; Watanabe, I. Determination of the Extent of Trace Metals Pollution in Soils, Sediments and Human Hair at E-Waste Recycling Site in Ghana. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 73, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, H. A Comparative Assessment of Lesser-Studied Trace Elements in the Soil-Plant System: Implications for Environmental Quality. Doctor Thesis, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bradl, H.B. Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions on Soils and Soils Constituents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 277, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooda, P. Trace Elements in Soils; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 9781444319484. [Google Scholar]
- Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012; ISBN 9789400744707. [Google Scholar]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Mukherjee, A.B. Trace Elements from Soil to Human; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2007; ISBN 9783540327134. [Google Scholar]
- Bañuelos, G.S.; Ajwa, H.A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants: An Overview. J. Environ. Sci. Health 1999, 34, 951–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, R.; Hayes, J. Mechanisms and Control of Nutrient Uptake in Plants. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2003, 229, 73–114. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, L.R. 31Ga Therapeutic Gallium Compounds. In Metallotherapeutic Drugs and Metal-Based Diagnostic Agents; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2005; pp. 259–277. ISBN 9780470864050. [Google Scholar]
- Tyler, G. Rare Earth Elements in Soil and Plant Systems—A Review. Plant Soil 2004, 267, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.N.; Tanveer, M.; Hussain, S.; Yang, G. Beryllium in the Environment: Whether Fatal for Plant Growth? Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 15, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laaouidi, Y.; Bahmed, A.; Naylo, A.; El Khalil, H.; Ouvrard, S.; Schwartz, C.; Boularbah, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Vegetables from Market Gardens of Urban Areas in Marrakech City. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 195, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.-Y.; Syu, C.-H.; Lee, D.-Y. Growth Inhibition of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Seedlings in Ga- and In-Contaminated Acidic Soils Is Respectively Caused by Al and Al+In Toxicity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syu, C.-H.; Chien, P.-H.; Huang, C.-C.; Jiang, P.-Y.; Juang, K.-W.; Lee, D.-Y. The Growth and Uptake of Ga and In of Rice (Oryza sative L.) Seedlings as Affected by Ga and In Concentrations in Hydroponic Cultures. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 135, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.-Z.; Feng, X.-H.; Feng, Y.-X. Phytotoxicity and Transport of Gallium (Ga) in Rice Seedlings for 2-Day of Exposure. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 95, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kärnbränslehantering, S.; Sheppard, S.; Long, J.; Sanipelli, B.; Sohlenius, G. Solid/liquid Partition Coefficients (Kd) for Selected Soils and Sediments at Forsmark and Laxemar-Simpevarp. Available online: https://www.skb.com/publication/1951648/R-09-27.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Syu, C.-H.; Chen, L.-Y.; Lee, D.-Y. The Growth and Uptake of Gallium (Ga) and Indium (In) of Wheat Seedlings in Ga- and In-Contaminated Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Chen, Y.; Gu, Z.; Wang, X. Determination of Trace Rare Earth Elements in Plant and Soil Samples by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2000, 76, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Yang, X.; Beiyuan, J.; Yin, M.; Xiao, T.; Jiang, Y.; Lin, W.; et al. Emerging Risks of Toxic Metal(loid)s in Soil-Vegetables Influenced by Steel-Making Activities and Isotopic Source Apportionment. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterlot, C.; Bidar, G.; Pelfrêne, A.; Roussel, H.; Fourrier, H.; Douay, F. Contamination, Fractionation and Availability of Metals in Urban Soils in the Vicinity of Former Lead and Zinc Smelters, France. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Yuan, D.-A.; Shan, X.-Q.; Li, F.-L.; Zhang, S.-Z. The Influence of Rare Earth Element Fertilizer Application on the Distribution and Bioaccumulation of Rare Earth Elements in Plants under Field Conditions. Chem. Spec. Bioavail. 2001, 13, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M. Accumulation, Uptake and Bioavailability of Rare Earth Elements (Rees) in Soil Grown Plants from Ex-Mining Area in Perak, Malaysia. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2017, 15, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, G. Changes in the Concentrations of Major, Minor and Rare-Earth Elements during Leaf Senescence and Decomposition in a Fagus sylvatica Forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 206, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, G.; Olsson, T. Plant Uptake of Major and Minor Mineral Elements as Influenced by Soil Acidity and Liming. Plant Soil 2001, 230, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, H.; Gaw, S.; Lehto, N.J.; Hassall, L.; Robinson, B.H. The Mobility and Plant Uptake of Gallium and Indium, Two Emerging Contaminants Associated with Electronic Waste and Other Sources. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.D.; Beckett, P.H.T.; Wollan, E. Critical Levels of Twenty Potentially Toxic Elements in Young Spring Barley. Plant Soil 1978, 49, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, B.; Moore, C.B. Principles of Geochemistry; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Reiser, R.; Simmler, M.; Portmann, D.; Clucas, L.; Schulin, R.; Robinson, B. Cadmium Concentrations in New Zealand Pastures: Relationships to Soil and Climate Variables. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, R.G.; Cameron, K.C. Soil Science: Sustainable Production and Environmental Protection; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1996; ISBN 9780195583458. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, P.J.; Blumenthal, M.J.; Anderson, M.W.; Prakash, K.S.; Leonforte, A. Perennial Ryegrass Improvement in Australia. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 1994, 37, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grogan, D.; Gilliland, T.J. A Review of Perennial Ryegrass Variety Evaluation in Ireland. Ir. J. Agric. Food Res. 2011, 50, 65–81. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, R.P.G.; Bradshaw, A.D. Heavy Metal Tolerance in Populations of Agrostis Tenuis Sibth. and Other Grasses. New Phytol. 1965, 64, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartler, J.; Robinson, B.; Burton, K.; Clucas, L. Carbonaceous Soil Amendments to Biofortify Crop Plants with Zinc. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 465, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIST Standard Reference Material 1573a; Leaves, Tomato. National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2018.
- Al Mamun, S.; Lehto, N.J.; Cavanagh, J.; McDowell, R.; Aktar, M.; Benyas, E.; Robinson, B.H. Effects of Lime and Organic Amendments Derived from Varied Source Materials on Cadmium Uptake by Potato. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, M.A.; Elyamine, A.M.; Moussa, M.G.; Cai, M.; Zhao, X.; Hu, C. Cadmium in Plants: Uptake, Toxicity, and Its Interactions with Selenium Fertilizers. Metallomics 2019, 11, 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, H.L.; Seekamp, G. Beryllium Effects on Potatoes and Oats in Acid Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1979, 11, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, D.; Boutin, C.; Allison, J.E.; Parsons, J.L.; Ellis, D.M. Uptake and Effects of Six Rare Earth Elements (REEs) on Selected Native and Crop Species Growing in Contaminated Soils. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, B.; Diao, F.; Zhang, J.; Bao, Z.; Guo, W. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Alter Microbiome Structure of Rhizosphere Soil to Enhance Maize Tolerance to La. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 212, 111996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.I.; Sajwan, K.S.; Adriano, D.C.; Gettier, S. Phytoavailability and Toxicity of Beryllium and Vanadium. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1990, 53, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, A.; Hale, B.; Santos, R.M.; Chiang, Y.W. Accumulation and Toxicity of Lanthanum and Neodymium in Horticultural Plants (Brassica Chinensis L. and Helianthus Annuus L.). Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 96, 2263–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poschenrieder, C.; Cabot, C.; Martos, S.; Gallego, B.; Barceló, J. Do Toxic Ions Induce Hormesis in Plants? Plant Sci. 2013, 212, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Samson, I.M. The Aqueous Geochemistry of Gallium, Germanium, Indium and Scandium. Ore Geol. Rev. 2006, 28, 57–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, J. Concentrations of 61 Trace Elements in Sewage Sludge, Farmyard Manure, Mineral Fertiliser, Precipitation and in Oil and Crops; Swedish Environmental Protection Agency: Stockholm, Sweden, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.J.B.; Le Riche, H.H. The Effect of Traces of Beryllium on the Growth of Kale, Grass, and Mustard. Plant Soil 1968, 29, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajwan, K.S.; Ornes, W.H.; Youngblood, T.V. Beryllium Phytotoxicity in Soybeans. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1996, 86, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Choi, J. Adverse Outcome Pathways Potentially Related to Hazard Identification of Microplastics Based on Toxicity Mechanisms. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, N.; Özcan, M.M.; Kaşık, G.; Öztürk, C. Mineral Contents of 34 Species of Edible Mushrooms Growing Wild in Turkey. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.M.; Power, I.L. Comparison of Plant Uptake and Plant Toxicity of Various Ions in Wheat. Plant Soil 1995, 172, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-F.; Yang, P.-T.; Lin, H.-W.; Yeh, K.-C.; Chen, M.-N.; Wang, S.-L. Indium Uptake and Accumulation by Rice and Wheat and Health Risk Associated with Their Consumption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14946–14954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedzielski, P.; Mleczek, M.; Budka, A.; Rzymski, P.; Siwulski, M.; Jasińska, A.; Gąsecka, M.; Budzyńska, S. A Screening Study of Elemental Composition in 12 Marketable Mushroom Species Accessible in Poland. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laul, J.C.; Weimer, W.C.; Rancitelli, L.A. Biogeochemical Distribution of Rare Earths and Other Trace Elements in Plants and Soils. Phys. Chem. Earth. 1979, 11, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fu, F.; Akagi, T.; Yabuki, S.; Iwaki, M. The Variation of REE (rare Earth Elements) Patterns in Soil-Grown Plants: A New Proxy for the Source of Rare Earth Elements and Silicon in Plants. Plant Soil 2001, 235, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.; Liu, D.; Wang, K.; Xiao, P.; Yu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Song, J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Concentrations and Health Risk Assessment of Rare Earth Elements in Vegetables from Mining Area in Shandong, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotelnikova, A.; Fastovets, I.; Rogova, O.; Volkov, D.S. La, Ce and Nd in the Soil-Plant System in a Vegetation Experiment with Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ding, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Dai, L. Bioaccumulation of Lanthanum and Cerium and Their Effects on the Growth of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Seedlings. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Shan, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, S. Evaluation of Plant Availability of Rare Earth Elements in Soils by Chemical Fractionation and Multiple Regression Analysis. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 102, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiche, O.; Székely, B.; Kummer, N.-A.; Moschner, C.; Heilmeier, H. Effects of Intercropping of Oat (Avena sativa L.) with White Lupin (Lupinus albus L.) on the Mobility of Target Elements for Phytoremediation and Phytomining in Soil Solution. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2016, 18, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmuc, N.R.; Dolenec, T.; Serafimovski, T.; Dolenec, M.; Vrhovnik, P. Geochemical Characteristics of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) in the Paddy Soil and Rice (Oryza sativa L.) System of Kočani Field, Republic of Macedonia. Geoderma 2012, 183–184, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalla, S.; Baffi, C.; Barbante, C.; Turetta, C.; Cozzi, G.; Beone, G.M.; Bettinelli, M. Determination of Rare Earth Elements in Tomato Plants by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry Techniques. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 23, 3285–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, J.A.; Tejera, N.A.; Sánchez, C.J. Substrate Role in the Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Sporocarps of Wild Fungi. Biometals 2009, 22, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wairich, A.; de Oliveira, B.H.N.; Arend, E.B.; Duarte, G.L.; Ponte, L.R.; Sperotto, R.A.; Ricachenevsky, F.K.; Fett, J.P. The Combined Strategy for Iron Uptake Is Not Exclusive to Domesticated Rice (Oryza sativa). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, R.D.; Stangoulis, J.C.R. Trace Element Uptake and Distribution in Plants. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1502S–1505S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, T.; Furuta, T.; Sonoda, Y.; Iwai, I. Growth Response of Cabbage Plants to Beryllium and Strontium under Water Culture Conditions. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1977, 23, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, G.; Olsson, T. Concentrations of 60 Elements in the Soil Solution as Related to the Soil Acidity. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2001, 52, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, N.; Saifullah; Malhi, S. S.; Zia, M.H.; Naeem, A.; Bibi, S.; Farid, G. Role of Mineral Nutrition in Minimizing Cadmium Accumulation by Plants. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinraide, T.B. Improved Scales for Metal Ion Softness and Toxicity. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopittke, P.M.; Blamey, F.P.C.; Menzies, N.W. Toxicity of Cd to Signal Grass (Brachiaria decumbens Stapf.) and Rhodes Grass (Chloris gayana Kunth.). Plant Soil 2010, 330, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Element | Concentration in Experimental Soil (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|
| Be | 13 (0.55) |
| Cd | 0.064 (0.0018) |
| Ga | 89 (1.1) |
| In | 0.31 (0.0081) |
| La | 308 (1.5) |
| Ce | 60 (0.53) |
| Nd | 256 (4.0) |
| Gd | 39 (0.56) |
| RTE or Cd Added to Soil | Treatment and Concentration Added (mg kg−1) | Biomass Index | Significance | Toxicity Threshold in Plant Biomass | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg kg−1) | (μmol kg−1) | |||||
| Be | Control | 0 | 1 | ab | >7.1 | >790 |
| T1 | 9.5 | 1.1 (0.28) | abc | |||
| T2 | 19 | 1.9 (0.52) | c | |||
| T3 | 38 | 1.6 (0.053) | bc | |||
| T4 | 76 | 0.56 (0.11) | a | |||
| Cd | Control | 0 | 1 | c | 0.06–0.30 | 0.54–2.6 |
| T1 | 2.5 | 0.70 (0.046) | b | |||
| T2 | 5 | 0.81 (0.078) | bc | |||
| T3 | 10 | 0.76 (0.012) | b | |||
| T4 | 20 | 0.47 (0.11) | a | |||
| Ga | Control | 0 | 1 | bc | 11–21 | 159–300 |
| T1 | 140 | 1.3 (0.27) | c | |||
| T2 | 280 | 0.83 (0.061) | ab | |||
| T3 | 560 | 0.56 (0.056) | a | |||
| T4 | 1120 | 0.69 (0.060) | ab | |||
| In | Control | 0 | 1 | a | >0.11 | >0.98 |
| T1 | 1.275 | 1.1 (0.42) | a | |||
| T2 | 2.55 | 1.0 (0.20) | a | |||
| T3 | 5.1 | 1.3 (0.20) | a | |||
| T4 | 10.2 | 0.84 (0.064) | a | |||
| La | Control | 0 | 1 | ab | >50 | >362 |
| T1 | 109.25 | 0.88 (0.18) | ab | |||
| T2 | 218.5 | 1.5 (0.25) | b | |||
| T3 | 437 | 1.2 (0.43) | ab | |||
| T4 | 874 | 0.71 (0.22) | a | |||
| Ce | Control | 0 | 1 | b | >12 | >87 |
| T1 | 283 | 0.37 (0.058) | a | |||
| T2 | 566 | 0.87 (0.081) | b | |||
| T3 | 1132 | 0.85 (0.22) | b | |||
| T4 | 2264 | 0.84 (0.22) | b | |||
| Nd | Control | 0 | 1 | c | 8.7–9.0 | 60–62 |
| T1 | 92.25 | 0.80 (0.019) | bc | |||
| T2 | 184.5 | 0.75 (0.10) | abc | |||
| T3 | 369 | 0.51 (0.041) | a | |||
| T4 | 738 | 0.72 (0.15) | ab | |||
| Gd | Control | 0 | 1 | b | 1.1–2.1 | 6.0–14 |
| T1 | 15.075 | 1.7 (0.31) | c | |||
| T2 | 30.15 | 0.58 (0.045) | ab | |||
| T3 | 60.3 | 0.44 (0.069) | a | |||
| T4 | 120.6 | 0.69 (0.025) | ab | |||
| Be | Cd | Ga | In | La | Ce | Nd | Gd | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Be | ||||||||
| Na | 0.50 S | 0.48 S | 0.48 S | |||||
| Mg | 0.69 S** | 0.52 S* | ||||||
| Al | 0.67 S** | |||||||
| P | −0.54 S* | −0.47 S | ||||||
| K | ||||||||
| Ca | 0.53 S* | 0.51 S | ||||||
| Cr | 0.54 S* | |||||||
| Mn | −0.53 S* | |||||||
| Fe | −0.14 S | 0.62 S* | 0.60 S* | |||||
| Co | 0.58 S* | 0.56 S* | 0.47 S | |||||
| Ni | 0.59 S* | 0.58 S* | 0.53 S* | |||||
| Cu | 0.49 S | 0.42 S | ||||||
| Zn | 0.78 S** | 0.44 S | 0.58 S* | 0.55 S* | ||||
| Ga | 0.50 S | |||||||
| As | −0.82 S** | |||||||
| Cd | 0.49 S | 0.57 S* | 0.50 S* | 0.50 S | 0.42 S | 0.45 S | ||
| In | ||||||||
| Te | ||||||||
| I | −0.76 S** | |||||||
| La | 0.49 S | 0.52 S | 0.65 S** | 0.72 S** | ||||
| Ce | 0.64 S** | |||||||
| Nd | 0.44 S | 0.58 S* | 0.37 S | 0.77 S** | ||||
| Gd | 0.41 S | 0.53 S* | 0.79 S** | 0.56 S* |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jensen, H.; Lehto, N.; Almond, P.; Gaw, S.; Robinson, B. The Uptake of Rare Trace Elements by Perennial Ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Toxics 2023, 11, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110929
Jensen H, Lehto N, Almond P, Gaw S, Robinson B. The Uptake of Rare Trace Elements by Perennial Ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Toxics. 2023; 11(11):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110929
Chicago/Turabian StyleJensen, Hayley, Niklas Lehto, Peter Almond, Sally Gaw, and Brett Robinson. 2023. "The Uptake of Rare Trace Elements by Perennial Ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.)" Toxics 11, no. 11: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110929
APA StyleJensen, H., Lehto, N., Almond, P., Gaw, S., & Robinson, B. (2023). The Uptake of Rare Trace Elements by Perennial Ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Toxics, 11(11), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110929







