Cognitive Performance and Exposure to Organophosphate Flame Retardants in Children: Evidence from a Cross-Sectional Analysis of Two European Mother–Child Cohorts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Study Outcomes
2.3. Exposure
2.4. Chemical Analysis
2.4.1. Organophosphate Flame Retardants
2.4.2. Creatinine
2.5. Potential Confounders
2.6. Statistical Analysis
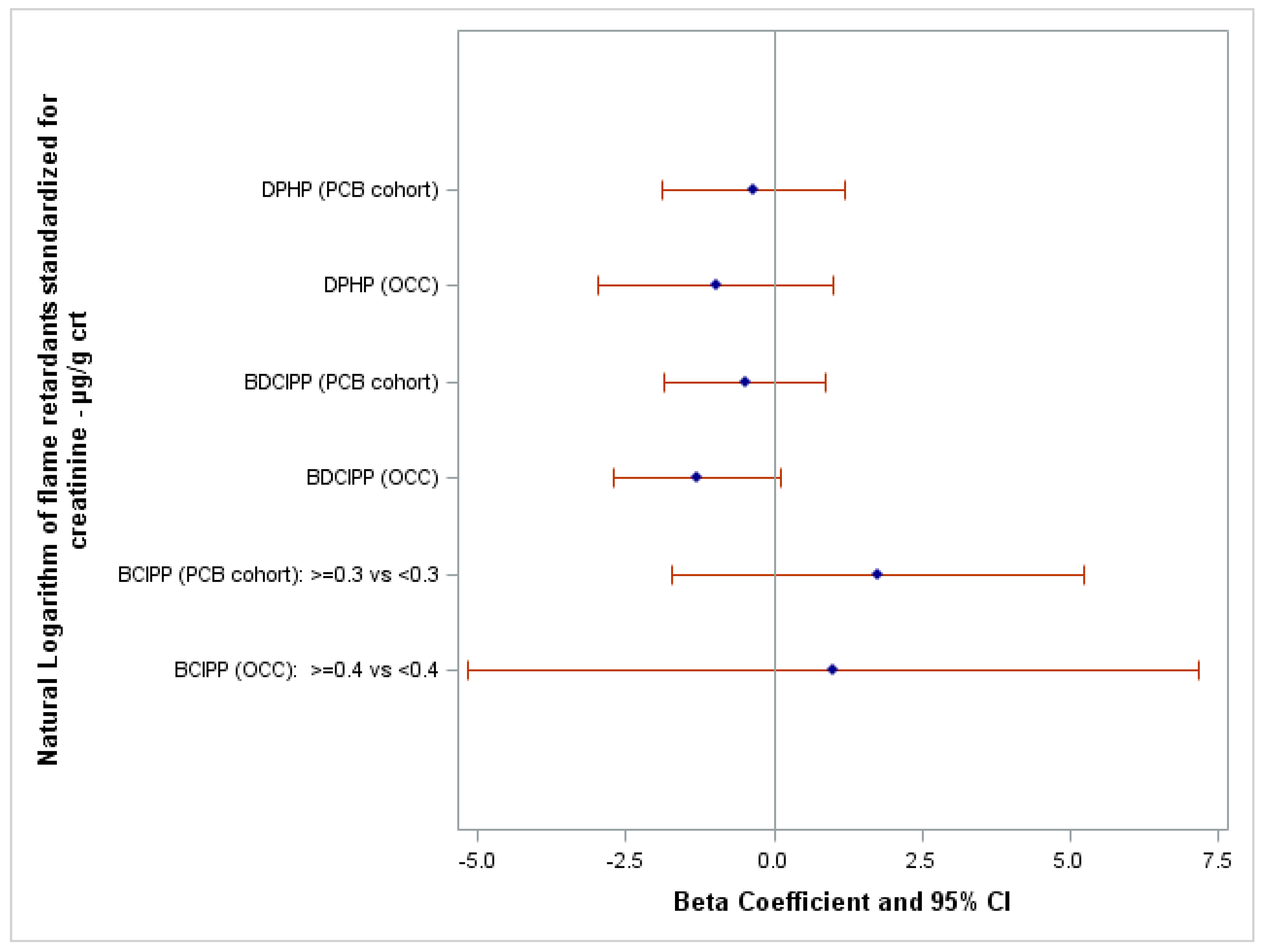
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Internal Consistency
4.2. External Consistency
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jotterand, F. Childhood Brain Development, the Educational Achievement Gap, and Cognitive Enhancement. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lövdén, M.; Fratiglioni, L.; Glymour, M.M.; Lindenberger, U.; Tucker-Drob, E.M. Education and Cognitive Functioning Across the Life Span. Psychol. Sci. Public Interest 2020, 21, 6–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronfani, L.; Vecchi Brumatti, L.; Mariuz, M.; Tognin, V.; Bin, M.; Ferluga, V.; Knowles, A.; Montico, M.; Barbone, F. The Complex Interaction between Home Environment, Socioeconomic Status, Maternal IQ and Early Child Neurocognitive Development: A Multivariate Analysis of Data Collected in a Newborn Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, J.M. Early-Life Exposure to EDCs: Role in Childhood Obesity and Neurodevelopment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona, A.; Roudeau, S.; Ortega, R. Molecular Mechanisms of Environmental Metal Neurotoxicity: A Focus on the Interactions of Metals with Synapse Structure and Function. Toxics 2021, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, E.; Gunier, R.; Bradman, A.; Harley, K.; Kogut, K.; Molitor, J.; Eskenazi, B. Association between Pesticide Profiles Used on Agricultural Fields near Maternal Residences during Pregnancy and IQ at Age 7 Years. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dórea, J.G. Environmental Exposure to Low-Level Lead (Pb) Co-Occurring with Other Neurotoxicants in Early Life and Neurodevelopment of Children. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandjean, P.; Landrigan, P.J. Neurobehavioural Effects of Developmental Toxicity. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurewicz, J.; Polańska, K.; Hanke, W. Exposure to Widespread Environmental Toxicants and Children’s Cognitive Development and Behavioral Problems. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2013, 26, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivollier, F.; Krebs, M.O.; Kebir, O. Perinatal Exposure to Environmental Endocrine Disruptors in the Emergence of Neurodevelopmental Psychiatric Diseases: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simhadri, J.J.; Loffredo, C.A.; Trnovec, T.; Murinova, L.P.; Nunlee-Bland, G.; Koppe, J.G.; Schoeters, G.; Jana, S.S.; Ghosh, S. Biomarkers of Metabolic Disorders and Neurobehavioral Diseases in a PCB- Exposed Population: What We Learned and the Implications for Future Research. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, M.; Wu, J. The Association between Prenatal Exposure to Phthalates and Cognition and Neurobehavior of Children-Evidence from Birth Cohorts. Neurotoxicology 2019, 73, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HBM4EU Web Page the European Human Biomonitoring Initiative (HBM4EU) Web Page. Available online: https://www.hbm4eu.eu/hbm4eu-substances/flame-retardants/ (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- Sharkey, M.; Harrad, S.; Abou-Elwafa Abdallah, M.; Drage, D.S.; Berresheim, H. Phasing-out of Legacy Brominated Flame Retardants: The UNEP Stockholm Convention and Other Legislative Action Worldwide. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 106041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, H.M.; Misenheimer, J.; Hoffman, K.; Webster, T.F. Flame Retardant Associations between Children’s Handwipes and House Dust. Chemosphere 2014, 116, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.L.; Li, D.Q.; Zhuo, M.N.; Liao, Y.S.; Xie, Z.Y.; Guo, T.L.; Li, J.J.; Zhang, S.Y.; Liang, Z.Q. Organophosphorus Flame Retardants and Plasticizers: Sources, Occurrence, Toxicity and Human Exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 196, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Veen, I.; de Boer, J. Phosphorus Flame Retardants: Properties, Production, Environmental Occurrence, Toxicity and Analysis. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1119–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajard, L.; Negi, C.K.; Mustieles, V.; Melymuk, L.; Jomini, S.; Barthelemy-Berneron, J.; Fernandez, M.F.; Blaha, L. Endocrine Disrupting Potential of Replacement Flame Retardants—Review of Current Knowledge for Nuclear Receptors Associated with Reproductive Outcomes. Environ. Int. 2021, 153, 106550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, A.; Behl, M.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Diamond, M.L.; Phillips, A.; Singla, V.; Sipes, N.S.; Stapleton, H.M.; Venier, M. Organophosphate Ester Flame Retardants: Are They a Regrettable Substitution for Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers? Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECHA Web Page the European Chemicals Agency Web Page. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/ (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- Poma, G.; Glynn, A.; Malarvannan, G.; Covaci, A.; Darnerud, P.O. Dietary Intake of Phosphorus Flame Retardants (PFRs) Using Swedish Food Market Basket Estimations. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 100, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Guardia, M.J.; Schreder, E.D.; Uding, N.; Hale, R.C. Human Indoor Exposure to Airborne Halogenated Flame Retardants: Influence of Airborne Particle Size. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, E.A.; Stapleton, H.M.; Calero, L.; Holmes, D.; Burke, K.; Martinez, R.; Cortes, B.; Nematollahi, A.; Evans, D.; Herbstman, J.B. Flame Retardant Exposure Assessment: Findings from a Behavioral Intervention Study. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, C.M.; Congleton, J.; Hoffman, K.; Fang, M.; Stapleton, H.M. Metabolites of Organophosphate Flame Retardants and 2-Ethylhexyl Tetrabromobenzoate in Urine from Paired Mothers and Toddlers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10432–10438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cequier, E.; Sakhi, A.K.; Marcé, R.M.; Becher, G.; Thomsen, C. Human Exposure Pathways to Organophosphate Triesters—A Biomonitoring Study of Mother-Child Pairs. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, E.A.; Stapleton, H.M.; Calero, L.; Holmes, D.; Burke, K.; Martinez, R.; Cortes, B.; Nematollahi, A.; Evans, D.; Anderson, K.A.; et al. Differential Exposure to Organophosphate Flame Retardants in Mother-Child Pairs. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Toms, L.M.L.; Thai, P.; Van den Eede, N.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Baduel, C.; Harden, F.A.; Heffernan, A.L.; Hobson, P.; et al. Urinary Metabolites of Organophosphate Esters: Concentrations and Age Trends in Australian Children. Environ. Int. 2018, 111, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, K.; Butt, C.M.; Chen, A.; Limkakeng, A.T.; Stapleton, H.M. High Exposure to Organophosphate Flame Retardants in Infants: Associations with Baby Products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14554–14559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, E.M.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Trasande, L. Effects of Early Exposure to Phthalates and Bisphenols on Cardiometabolic Outcomes in Pregnancy and Childhood. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 68, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Eede, N.; Heffernan, A.L.; Aylward, L.L.; Hobson, P.; Neels, H.; Mueller, J.F.; Covaci, A. Age as a Determinant of Phosphate Flame Retardant Exposure of the Australian Population and Identification of Novel Urinary PFR Metabolites. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Lu, Z.; Xu, L.; Li, F.; Cong, M.; Shan, X.; Wu, H. Global Responses to Tris(1-Chloro-2-Propyl)Phosphate (TCPP) in Rockfish Sebastes Schlegeli Using Integrated Proteomic and Metabolomic Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, H.; Mi, C.; Feng, C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, B. The Adverse Effect of TCIPP and TCEP on Neurodevelopment of Zebrafish Embryos/Larvae. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, A.J.; Kapps, V.A.; Cai, Y.; Rai, M.R.; St. Armour, G.; Horman, B.M.; Rock, K.D.; Witchey, S.K.; Greenbaum, A.; Patisaul, H.B. Maternal Organophosphate Flame Retardant Exposure Alters the Developing Mesencephalic Dopamine System in Fetal Rat. Toxicol. Sci. 2023, 191, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noyes, P.D.; Haggard, D.E.; Gonnerman, G.D.; Tanguay, R.L. Advanced Morphological—Behavioral Test Platform Reveals Neurodevelopmental Defects in Embryonic Zebrafish Exposed to Comprehensive Suite of Halogenated and Organophosphate Flame Retardants. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 145, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri, A.N.; Ortiz, E.; Levin, E.D. Developmental Exposure to an Organophosphate Flame Retardant Alters Later Behavioral Responses to Dopamine Antagonism in Zebrafish Larvae. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2018, 67, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, K.D.; Armour, G.S.; Horman, B.; Phillips, A.; Ruis, M.; Stewart, A.K.; Jima, D.; Muddiman, D.C.; Stapleton, H.M.; Patisaul, H.B. Effects of Prenatal Exposure to a Mixture of Organophosphate Flame Retardants on Placental Gene Expression and Serotonergic Innervation in the Fetal Rat Brain. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 176, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Xu, W.; Peng, T.; Chen, H.; Ren, L.; Tan, H.; Xiao, D.; Qian, H.; Fu, Z. Developmental Exposure of Zebrafish Larvae to Organophosphate Flame Retardants Causes Neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2016, 55, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Qian, Q.; Gao, M.; Wang, H. Tris (1-Chloro-2-Propyl) Phosphate Exposure to Zebrafish Causes Neurodevelopmental Toxicity and Abnormal Locomotor Behavior. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castorina, R.; Bradman, A.; Stapleton, H.M.; Butt, C.; Avery, D.; Harley, K.G.; Gunier, R.B.; Holland, N.; Eskenazi, B. Current-Use Flame Retardants: Maternal Exposure and Neurodevelopment in Children of the CHAMACOS Cohort. Chemosphere 2017, 189, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.M.; Keil, A.P.; Choi, G.; Ramos, A.M.; Richardson, D.B.; Olshan, A.F.; Martin, C.L.; Villanger, G.D.; Reichborn-Kjennerud, T.; Zeiner, P.; et al. Prenatal Organophosphate Ester Exposure and Executive Function in Norwegian Preschoolers. Environ. Epidemiol. 2023, 7, E251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipscomb, S.T.; McClelland, M.M.; MacDonald, M.; Cardenas, A.; Anderson, K.A.; Kile, M.L. Cross-Sectional Study of Social Behaviors in Preschool Children and Exposure to Flame Retardants. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percy, Z.; Chen, A.; Yang, W.; Braun, J.M.; Lanphear, B.; Ospina, M.; Calafat, A.M.; Xie, C.; Cecil, K.M.; Vuong, A.M.; et al. Childhood Urinary Organophosphate Esters and Cognitive Abilities in a Longitudinal Cohort Study. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percy, Z.; Vuong, A.M.; Xu, Y.; Xie, C.; Ospina, M.; Calafat, A.M.; Lanphear, B.P.; Braun, J.M.; Cecil, K.M.; Dietrich, K.N.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to a Mixture of Organophosphate Esters and Intelligence among 8-Year-Old Children of the HOME Study. Neurotoxicology 2021, 87, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tierney, A.L.; Nelson, C.A., III. Brain Development and the Role of Experience in the Early Years. Zero Three 2009, 30, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gilles, L.; Govarts, E.; Rambaud, L.; Vogel, N.; Castaño, A.; Esteban López, M.; Rodriguez Martin, L.; Koppen, G.; Remy, S.; Vrijheid, M.; et al. HBM4EU Combines and Harmonises Human Biomonitoring Data across the EU, Building on Existing Capacity—The HBM4EU Survey. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 237, 113809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilles, L.; Govarts, E.; Martin, L.R.; Andersson, A.M.; Appenzeller, B.M.R.; Barbone, F.; Castaño, A.; Coertjens, D.; Hond, E.D.; Dzhedzheia, V.; et al. Harmonization of Human Biomonitoring Studies in Europe: Characteristics of the HBM4EU-Aligned Studies Participants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govarts, E.; Gilles, L.; Rodriguez Martin, L.; Santonen, T.; Apel, P.; Alvito, P.; Anastasi, E.; Andersen, H.R.; Andersson, A.-M.; Andryskova, L.; et al. Harmonized Human Biomonitoring in European Children, Teenagers and Adults: EU-Wide Exposure Data of 11 Chemical Substance Groups from the HBM4EU Aligned Studies (2014–2021). Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2023, 249, 114119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HBM4EU Web Page the European Human Biomonitoring Initiative (HBM4EU) Web Page. Available online: https://www.Hbm4eu.Eu/ (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Beck, I.H.; Bilenberg, N.; Davidsen, K.A.; Rasmussen, A.A.; Boye, H.; Jensen, T.K. Prenatal and Early Childhood Predictors of Intelligence Quotient (IQ) in 7-Year-Old Danish Children from the Odense Child Cohort. Scand. J. Public Health 2022, 51, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyhl, H.B.; Jensen, T.K.; Barington, T.; Buhl, S.; Norberg, L.A.; Jørgensen, J.S.; Jensen, D.F.G.; Christesen, H.T.; Lamont, R.F.; Husby, S. The Odense Child Cohort: Aims, Design, and Cohort Profile. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2015, 29, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Trnovec, T.; Kočan, A.; Charles, M.J.; Čižnar, P.; Langer, P.; Sovčikova, E.; James, R. PCBs and Early Childhood Development in Slovakia: Study Design and Background. Fresenius Environ. Bull 2003, 12, 208–214. [Google Scholar]
- Simeone, R.M.; Howards, P.P.; Anderson, E.; Jusko, T.A.; Drobná, B.; Kočan, A.; Čonka, K.; Fabišiková, A.; Murínová, Ľ.P.; Canfield, R.L.; et al. Pre- and Postnatal Polychlorinated Biphenyl Exposure and Cognitive and Behavioral Development at Age 45 Months in a Cohort of Slovak Children. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, D. Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children; The Psychological Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Dočkal, V.; Kretová, E.; Kundrátová, B.; Sedlačková, B.; Tesař, M. WISC-III—Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children Adapted Slovak Version; Testcentrum—Hogrefe: Prague, Slovakia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler, D. WISC-V Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children—Fifth Edition. Vejledning Del 1 Dansk Version, 1st ed.; NCS Pearson, Inc.: Bloomington, MN, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rosolen, V.; Giordani, E.; Mariuz, M.; Parpinel, M.; Ronfani, L.; Vecchi Brumatti, L.; Bin, M.; Calamandrei, G.; Mustieles, V.; Gilles, L.; et al. Concurrent Assessment of Phthalates/HEXAMOLL® DINCH Exposure and Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children Performance in Three European Cohorts of the HBM4EU Aligned Studies. Toxics 2022, 10, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Eede, N.; Neels, H.; Jorens, P.G.; Covaci, A. Analysis of Organophosphate Flame Retardant Diester Metabolites in Human Urine by Liquid Chromatography Electrospray Ionisation Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1303, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastiaensen, M.; Xu, F.; Been, F.; Van den Eede, N.; Covaci, A. Simultaneous Determination of 14 Urinary Biomarkers of Exposure to Organophosphate Flame Retardants and Plasticizers by LC-MS/MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 7871–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorakova, D.; Pulkrabova, J.; Gramblicka, T.; Polachova, A.; Buresova, M.; López, M.E.; Castaño, A.; Nübler, S.; Haji-Abbas-Zarrabi, K.; Klausner, N.; et al. Interlaboratory Comparison Investigations (ICIs) and External Quality Assurance Schemes (EQUASs) for Flame Retardant Analysis in Biological Matrices: Results from the HBM4EU Project. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban López, M.; Göen, T.; Mol, H.; Nübler, S.; Haji-Abbas-Zarrabi, K.; Koch, H.M.; Kasper-Sonnenberg, M.; Dvorakova, D.; Hajslova, J.; Antignac, J.P.; et al. The European Human Biomonitoring Platform—Design and Implementation of a Laboratory Quality Assurance/Quality Control (QA/QC) Programme for Selected Priority Chemicals. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 234, 113740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Textor, J.; van der Zander, B.; Gilthorpe, M.S.; Liśkiewicz, M.; Ellison, G.T. Robust Causal Inference Using Directed Acyclic Graphs: The R Package “Dagitty”. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNESCO Institute for Statistics. International Standard Classification of Education ISCED 2011; UNESCO Institute for Statistics: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2012; Volume 88. [Google Scholar]
- De Onis, M.; Onyango, A.W.; Borghi, E.; Siyam, A.; Nishida, C.; Siekmann, J. Development of a WHO Growth Reference for School-Aged Children and Adolescents. Bull. World Health Organ. 2007, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harel, O.; Perkins, N.; Schisterman, E.F. The Use of Multiple Imputation for Data Subject to Limits of Detection. Sri. Lankan J. Appl. Stat. 2014, 5, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohai, V.J. High Breakdown-Point and High Efficiency Robust Estimates for Regression. Ann. Stat. 1987, 15, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, J.; Gregory, S.; Iles-Caven, Y.; Hibbeln, J.; Emond, A.; Taylor, C.M. Associations between Prenatal Mercury Exposure and Early Child Development in the ALSPAC Study. Neurotoxicology 2016, 53, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Schyff, V.; Kalina, J.; Govarts, E.; Gilles, L.; Schoeters, G.; Castaño, A.; Esteban-López, M.; Kohoutek, J.; Kukučka, P.; Covaci, A.; et al. Exposure to Flame Retardants in European Children—Results from the HBM4EU Aligned Studies. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2023, 247, 114070. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, J.L.; Jacobson, S.W. Dose-Response in Perinatal Exposure To Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs): The Michigan and North Carolina Cohort Studies. Toxicol. Ind. Health 1996, 12, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, P.W.; Lonky, E.; Reihman, J.; Pagano, J.; Gump, B.B.; Darvill, T. The Relationship between Prenatal PCB Exposure and Intelligence (IQ) in 9-Year-Old Children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.Y.; Park, J.S.; Sovcikova, E.; Kocan, A.; Linderholm, L.; Bergman, A.; Trnovec, T.; Hertz-Picciotto, I. Exposure to Hydroxylated Polychlorinated Biphenyls (OH-PCBs) in the Prenatal Period and Subsequent Neurodevelopment in Eastern Slovakia. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AdminStat Denmark Web Page. Available online: https://ugeo.urbistat.com/AdminStat/en/dk/demografia/famiglie/odense/20367970/4 (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- HBM4EU Web Page the European Human Biomonitoring Initiative (HBM4EU) Web Page. Available online: https://www.hbm4eu.eu/work-packages/deliverable-10-12-update-statistical-analysis-plan-for-the-co-funded-studies-of-wp8/ (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- Totsika, V.; Sylva, K. The Home Observation for Measurement of the Environment Revisited. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health Vol. 2004, 9, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastiaensen, M.; Gys, C.; Malarvannan, G.; Fotache, M.; Bombeke, J.; Ait Bamai, Y.; Araki, A.; Covaci, A. Short-Term Temporal Variability of Urinary Biomarkers of Organophosphate Flame Retardants and Plasticizers. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nader, A.M.; Jelenic, P.; Soulières, I. Discrepancy between WISC-III and WISC-IV Cognitive Profile in Autism Spectrum: What Does It Reveal about Autistic Cognition? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, D. Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children, 3rd ed.; Canadian (WISC-III); Psychological Corporation: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Olivier, T.W.; Mahone, E.M.; Jacobson, L.A. Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children. In Encyclopedia of Clinical Neuropsychology; Kreutzer, J.S., DeLuca, J., Caplan, B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | OCC | PCB Cohort |
|---|---|---|
| Child’s sex, N (%): | ||
| Male | 142 (53.8) | 131 (44.1) |
| Female | 122 (46.2) | 166 (55.9) |
| Highest education level of the household of the child, N (%): | ||
| Low education (ISCED 0–2) | 37 (14.0) | 16 (5.4) |
| Medium education (ISCED 3–4) | 141 (53.4) | 219 (73.7) |
| High education (ISCED ≥ 5) | 86 (32.6) | 45 (15.2) |
| Missing | 0 (0.0) | 17 (5.7) |
| Child’s age, mean ± SD (N): | 7.0 ± 0.1 (264) | 11.1 ± 0.4 (297) |
| Child’s BMI z-score, mean ± SD (N): | −0.1 ± 1.0 (259) | 0.7 ± 1.3 (297) |
| FSIQ score, mean ± SD (N): | 98 ± 12 (264) | 81 ± 15 (297) |
| Biomarkers of Exposure | N | Geometric Mean (95%CI) | 25th Percentile | Median | 75th Percentile | 90th Percentile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPFRs (µg/g crt) | ||||||
| DPHP: | ||||||
| OCC | 264 | 1.44 (1.31; 1.58) | 0.86 | 1.39 | 2.34 | 3.82 |
| PCB cohort | 296 | 2.24 (2.00; 2.52) | 1.32 | 2.21 | 3.45 | 5.06 |
| BDCIPP: | ||||||
| OCC | 264 | 0.52 (0.49; 0.60) | 0.25 | 0.49 | 0.92 | 2.21 |
| PCB cohort | 296 | 0.18 (0.16; 0.20) | 0.08 | 0.17 | 0.35 | 10.73 |
| Crt (g/L) | ||||||
| OCC | 264 | 0.70 (0.65; 0.75) | 0.51 | 0.78 | 1.05 | 1.32 |
| PCB cohort | 296 | 1.21 (1.12; 1.31) | 0.88 | 1.31 | 1.82 | 2.39 |
| BCIPP µg/L | N (%) |
|---|---|
| OCC: | |
| <0.4 | 247 (93.6) |
| ≥0.4 | 17 (6.4) |
| PCB cohort: | |
| <0.3 | 210 (70.7) |
| ≥0.3 | 87 (29.3) |
| FSIQ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | OCC | p-Value | PCB Cohort | p-Value |
| Highest education level of the household of the child,mean ± SD(N): | ||||
| Low education (ISCED 0–2) | 95 ± 14 (38) | 0.20 a | 56 ± 9 (16) | <0.01 a |
| Medium education (ISCED 3–4) | 98 ± 12 (141) | 81 ± 13 (219) | ||
| High education (ISCED ≥5) | 99 ± 11 (86) | 91 ± 16 (45) | ||
| Child’s sex, mean ± SD(N): | ||||
| Male | 97 ± 12 (142) | 0.07 a | 79 ± 16 (131) | 0.09 a |
| Female | 100 ± 12 (122) | 82 ± 15 (166) | ||
| Child’s BMI z-score, correlation (N): | 0.03 (259) | 0.66 b | 0.16 (297) | 0.01 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosolen, V.; Giordani, E.; Mariuz, M.; Parpinel, M.; Mustieles, V.; Gilles, L.; Govarts, E.; Rodriguez Martin, L.; Baken, K.; Schoeters, G.; et al. Cognitive Performance and Exposure to Organophosphate Flame Retardants in Children: Evidence from a Cross-Sectional Analysis of Two European Mother–Child Cohorts. Toxics 2023, 11, 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110878
Rosolen V, Giordani E, Mariuz M, Parpinel M, Mustieles V, Gilles L, Govarts E, Rodriguez Martin L, Baken K, Schoeters G, et al. Cognitive Performance and Exposure to Organophosphate Flame Retardants in Children: Evidence from a Cross-Sectional Analysis of Two European Mother–Child Cohorts. Toxics. 2023; 11(11):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110878
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosolen, Valentina, Elisa Giordani, Marika Mariuz, Maria Parpinel, Vicente Mustieles, Liese Gilles, Eva Govarts, Laura Rodriguez Martin, Kirsten Baken, Greet Schoeters, and et al. 2023. "Cognitive Performance and Exposure to Organophosphate Flame Retardants in Children: Evidence from a Cross-Sectional Analysis of Two European Mother–Child Cohorts" Toxics 11, no. 11: 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110878
APA StyleRosolen, V., Giordani, E., Mariuz, M., Parpinel, M., Mustieles, V., Gilles, L., Govarts, E., Rodriguez Martin, L., Baken, K., Schoeters, G., Sepai, O., Sovcikova, E., Fabelova, L., Kohoutek, J., Jensen, T. K., Covaci, A., Roggeman, M., Melymuk, L., Klánová, J., ... Barbone, F. (2023). Cognitive Performance and Exposure to Organophosphate Flame Retardants in Children: Evidence from a Cross-Sectional Analysis of Two European Mother–Child Cohorts. Toxics, 11(11), 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110878











