In Situ Toxicity Reduction and Food Safety Assessment of Pak Choi (Brassica campestris L.) in Cadmium-Contaminated Soil by Jointly Using Alkaline Passivators and Organic Fertilizer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Implementation
2.2. Sampling and Determination
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Calculation of Bioenrichment Factor, Absorption Factor, and Transport Factor
2.3.2. Grey Relational Analysis
- (1)
- First, the evaluation index X was selected as the soil pH, available Cd content, Cd content in the edible part, BAF, AF, and TF, which are denoted as X(k), k = 1, 2, 3… 6, respectively.
- (2)
- The optimal value of each evaluation index was used to establish the corresponding optimal sequence, which is denoted as X0(k) [23].
- (3)
- The original data were standardized and denoted as Xi(k):
- (4)
- The absolute deviation of grey correlation degree was calculated as:
- (5)
- The correlation coefficient (ηi (k)) between the optimal sequence and the comparison sequence was calculated as:
- (6)
- Finally, the grey correlation degree (r) between the matching application and each index was obtained as:
3. Results
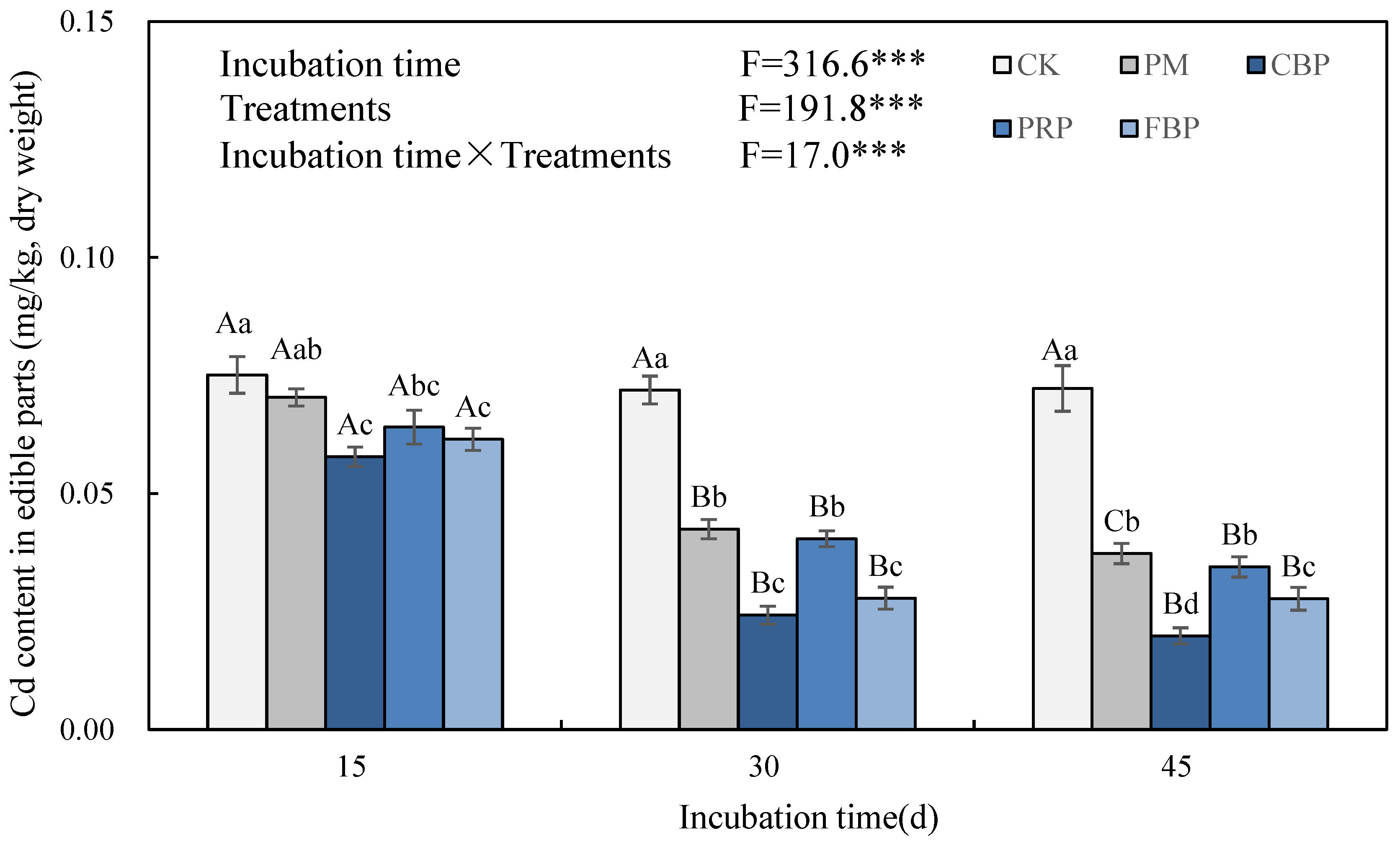
3.1. Edible Plant Biomass and Cd Content
3.2. Ability of Plants to Accumulate, Absorb, and Transport Cd
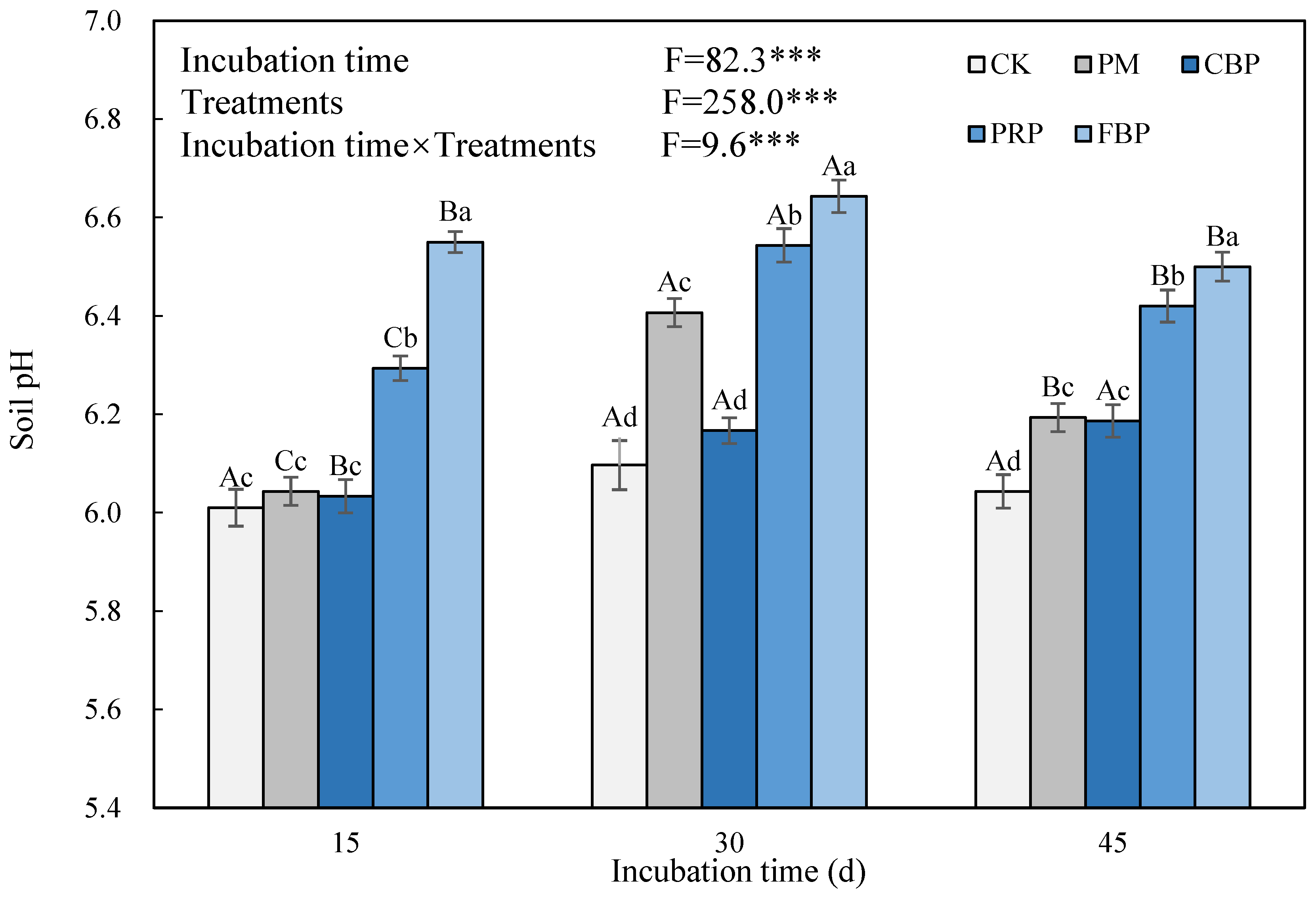
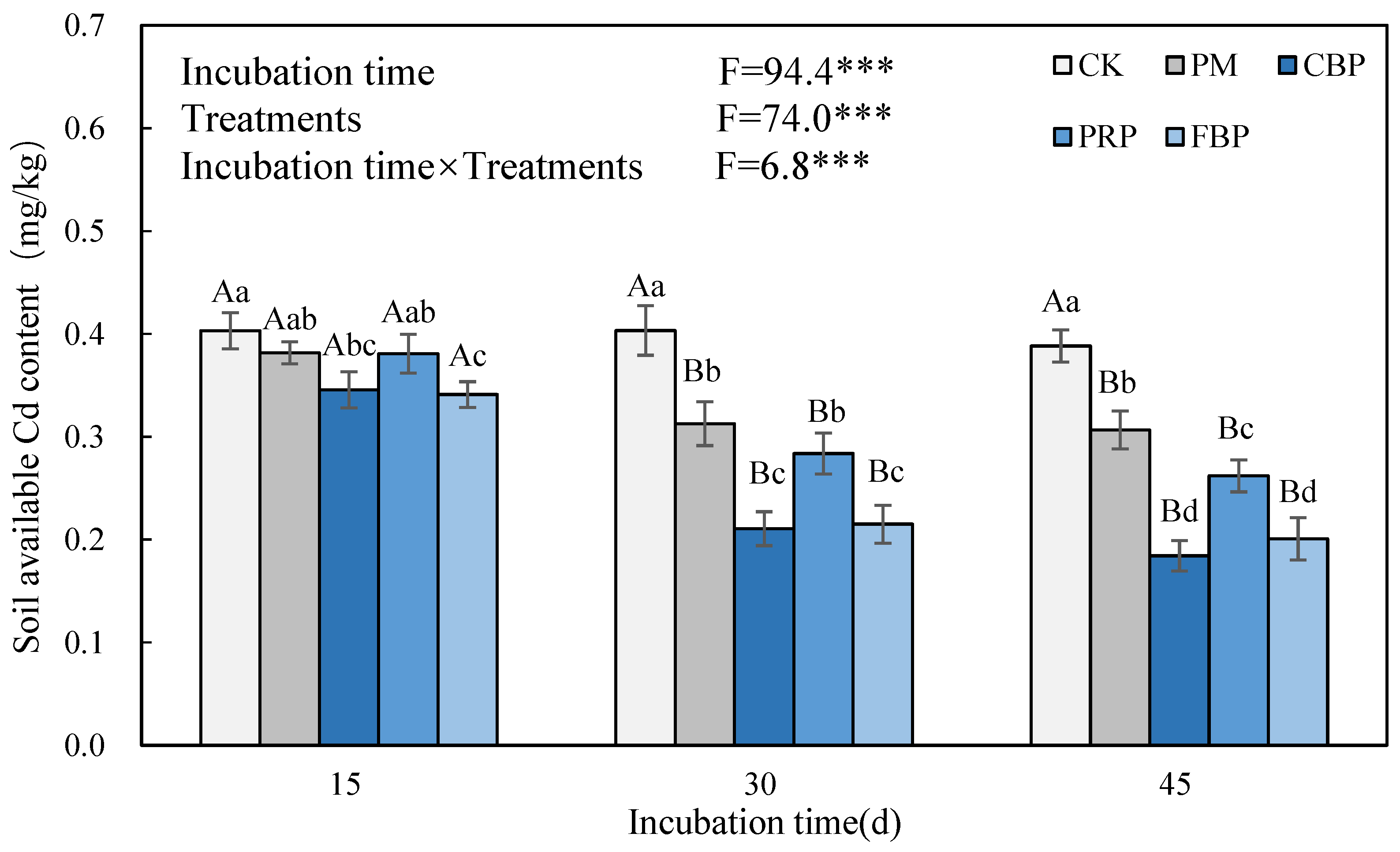
3.3. Soil pH and Available Cd Content
3.4. Food Safety Assessment via GRA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Chi, W.; Wang, P.; Hu, S.; Li, F.; Li, X.; Liu, T.; Sun, Y.; Qin, H. Modelling Evaluation of Key Cadmium Transformation Processes in Acid Paddy Soil under Alternating Redox Conditions. Chem. Geol. 2021, 581, 120409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, J.; Liang, T.; Yan, X.; Zhong, L.; Shao, J.; El-Naggar, A.; Guan, C.-Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y. A Combined Management Scheme to Simultaneously Mitigate As and Cd Concentrations in Rice Cultivated in Contaminated Paddy Soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, D.; Wu, Z.; Ji, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Ito, Y. Remediation of Cd- and Pb-Contaminated Clay Soils through Combined Freeze-Thaw and Soil Washing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibi, I.; Niazi, N.K.; Shahid, M.; Ali, F.; Masood ul Hasan, I.; Rahman, M.M.; Younas, F.; Hussain, M.M.; Mehmood, T.; Shaheen, S.M.; et al. Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Trace Elements in the Paddy Soil-Rice Ecosystem of Punjab, Pakistan. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Hu, H.; Shaheen, S.M.; Zhong, H.; Tack, F.M.G.; Wu, M.; Li, Y.-F.; Gao, Y.; Rinklebe, J.; et al. Speciation, Transportation, and Pathways of Cadmium in Soil-Rice Systems: A Review on the Environmental Implications and Remediation Approaches for Food Safety. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wu, X.; Liao, P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, N.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L. Morphological Transformation of Heavy Metals and Their Distribution in Soil Aggregates during Biotransformation of Livestock Manure. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 32, 101963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahkolaie, S.S.; Baranimotlagh, M.; Dordipour, E.; Khormali, F. Effects of Inorganic and Organic Amendments on Physiological Parameters and Antioxidant Enzymes Activities in Zea mays L. from a Cadmium-Contaminated Calcareous Soil. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 128, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zang, Y.; Li, R. Effects of Typical Modified Passivators on Speciation of Heavy Metals in Protein Extracted from Sewage Sludge. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 10875–10886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Lin, Y.; Liu, H.; Guo, S.; Xu, M.; et al. Red Mud Based Passivator Reduced Cd Accumulation in Edible Amaranth by Influencing Root Organic Matter Metabolism and Soil Aggregate Distribution. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 116543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Meng, H.; Zhao, L.; Shen, Y.; Hou, Y.; Cheng, H.; Song, L. Effect of Biochar and Humic Acid on the Copper, Lead, and Cadmium Passivation during Composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 258, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, K.; Chen, S.; Fu, X.; Feng, S.; Zhuang, Z. A Sustainable Agricultural Supply Chain Considering Substituting Organic Manure for Chemical Fertilizer. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 29, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, C.; Cardenas, L.; McDowell, R.; Morgan, S.; Blackwell, M.S.A. Effects on Soil of Grassland Management for Pasture, Hay and Silage. In Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment, 2nd ed.; Goss, M.J., Oliver, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2023; pp. 102–112. ISBN 978-0-323-95133-3. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Guo, G.; Qin, J.; Luo, J.; Zhu, Z.; Hong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Hu, S.; Hu, W.; et al. Reducing Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soil and Uptake by Maize Using Organic-Inorganic Mixed Fertilizer. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 128122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, M.S.; Riaz, M.; Shahzad, S.M.; Yasmeen, T.; Ashraf, M.; Siddique, M.; Mubarik, M.S.; Bragazza, L.; Buttler, A. Fresh and Composted Industrial Sludge Restore Soil Functions in Surface Soil of Degraded Agricultural Land. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Li, D.; Xie, C.; Zheng, X.; Yin, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, K.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, B.; Hu, Y.; et al. Combined Apatite, Biochar, and Organic Fertilizer Application for Heavy Metal Co-Contaminated Soil Remediation Reduces Heavy Metal Transport and Alters Soil Microbial Community Structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Huang, X.; Zhao, H.; Liu, F.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Gao, P.; Li, X.; Ji, P. Possibility of Using Modified Fly Ash and Organic Fertilizers for Remediation of Heavy-Metal-Contaminated Soils. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhan, Q.; Hong, L.; Bocharnikova, E.; Matichenkov, V. Regulation of As and Cd Accumulation in Rice by Simultaneous Application of Lime or Gypsum with Si-Rich Materials. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 7271–7280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Y.; Du, S.; Tian, W. Evaluation of Tar from the Microwave Co-Pyrolysis of Low-Rank Coal and Corncob Using Orthogonal-Test-Based Grey Relational Analysis (GRA). J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 337, 130362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, E.; Rehman, S. Modeling the Nexus between Carbon Emissions, Urbanization, Population Growth, Energy Consumption, and Economic Development in Asia: Evidence from Grey Relational Analysis. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 5430–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Nautiyal, R.; Kumar, P.; Chandra, G.; Pal Panwar, V. A Grey Relational Model for Soil Erosion Vulnerability Assessment in Subwatershed of Lesser Himalayan Region. Catena 2022, 210, 105928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Zeng, R.J.; Sheng, G.-P.; Yu, H.-Q. An Integrated Approach to Identify the Influential Priority of the Factors Governing Anaerobic H2 Production by Mixed Cultures. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3234–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Li, W.-W.; Yu, H.-Q.; Harada, H. A Novel Integrated Approach to Quantitatively Evaluate the Efficiency of Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) Extraction Process. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Rizwan, M.; Li, M.; Song, F.; Zhou, S.; He, X.; Ding, R.; Dai, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Cao, M.; et al. Comparative Efficacy of Organic and Inorganic Silicon Fertilizers on Antioxidant Response, Cd/Pb Accumulation and Health Risk Assessment in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiqin, J.; Fuliang, Y.; Yong, Z. An Analysis of Vulnerability to Agricultural Drought in China Using the Expand Grey Relation Analysis Method. Procedia Eng. 2012, 28, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, Y.; Tang, L.; Hussain, B.; Usman, M.; Lin, Q.; Rashid, M.S.; He, Z.; Yang, X. Organic Soil Additives for the Remediation of Cadmium Contaminated Soils and Their Impact on the Soil-Plant System: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 136121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, G.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Chen, H. Enhanced Stabilization of Pb, Zn, and Cd in Contaminated Soils Using Oxalic Acid-Activated Phosphate Rocks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 2861–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maliki, S.; Al-Shamary, A. Vital Evidence for Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi, Bacteria and Cattail Plant to Remove Pb-Cd Heavy Metals from Contaminated Soils. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, M.; Panhwar, S.K.; Zafar, F.H.S. Ecosystem Based Approach to Delineate Coastal Degradation of Hawks Bay, Karachi, Pakistan. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Nino-Savala, A.G.; Mi, Z.; Wan, Y.; Su, D.; Li, H.; Fangmeier, A. Cadmium Accumulation in Wheat and Maize Grains from China: Interaction of Soil Properties, Novel Enrichment Models and Soil Thresholds. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 116623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Wang, P.; Guo, L.; Li, M.; Cui, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. The Remediation Effects of Microbial Organic Fertilizer on Soil Microorganisms after Chloropicrin Fumigation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Sheng, L. Effects of Long-Term Application of Organic Fertilizer on Improving Organic Matter Content and Retarding Acidity in Red Soil from China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Peng, H.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Bi, X.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, J. Effects of Exogenous Dissolved Organic Matter on the Adsorption–Desorption Behaviors and Bioavailabilities of Cd and Hg in a Plant–Soil System. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvin, A.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Hossain, M.K.; Saha, B.; Parvin, A.; Suchi, P.D.; Hoque, S. Chemical Speciation and Potential Mobility of Heavy Metals in Organic Matter Amended Soil. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2022, 2022, e2028860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Yu, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, X. Influence of Cadmium Stress on Root Exudates of High Cadmium Accumulating Rice Line (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinova, S. Distribution and Forms of Heavy Metals in Some Agricultural Soils. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2003, 12, 629–633. [Google Scholar]
- Amoakwah, E.; Van Slycken, S.; Tack, F.; Essumang, D. Assessing the Extraction Efficiency of CaCl2 and Rhizon Extraction Methods after the Application of Organic Matter and CaCl2 as Soil Amendments to Enhance the Mobility of Cd and Zn. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2013, 3, 1000167. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, R.; Hao, J.; Li, D.; Wei, Z.; Teng, R.; Sun, B. Protein and Carbohydrate Drive Microbial Responses in Diverse Ways during Different Animal Manures Composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, C.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Wei, Z. Assessment Contributions of Physicochemical Properties and Bacterial Community to Mitigate the Bioavailability of Heavy Metals during Composting Based on Structural Equation Models. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Camps-Arbestain, M.; Shen, Q.; Lehmann, J.; Singh, B.; Sabir, M. Biochar Effects on Crop Yields with and without Fertilizer: A Meta-Analysis of Field Studies Using Separate Controls. Soil Use Manag. 2020, 36, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Q.; Tan, Z. Development of a Carbon-Based Slow Release Fertilizer Treated by Bio-Oil Coating and Study on Its Feedback Effect on Farmland Application. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 118085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agegnehu, G.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bird, M.I. The Role of Biochar and Biochar-Compost in Improving Soil Quality and Crop Performance: A Review. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 119, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Gulshan, A.B.; Iqbal, J.; Husain, A.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Alkahtani, J.; Dwiningsih, Y.; Bakhsh, A.; Ahmed, N.; Khan, M.J.; et al. Comparative Role of Animal Manure and Vegetable Waste Induced Compost for Polluted Soil Restoration and Maize Growth. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 2534–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirecki, N.; Agič, R.; Šunić, L.; Milenković, L.; Ilić, Z.S. Transfer Factor as Indicator of Heavy Metals Content in Plants. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2015, 24, 4212–4219. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, G.; Xu, Y.; Liu, W.; Liang, X.; Wang, L. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Sepiolite, Bentonite, and Phosphate Amendments on the Stabilization Remediation of Cadmium-Contaminated Soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, F.U.; Liqun, C.; Coulter, J.A.; Cheema, S.A.; Wu, J.; Zhang, R.; Wenjun, M.; Farooq, M. Cadmium Toxicity in Plants: Impacts and Remediation Strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 211, 111887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandara, T.; Franks, A.; Xu, J.; Bolan, N.; Wang, H.; Tang, C. Chemical and Biological Immobilization Mechanisms of Potentially Toxic Elements in Biochar-Amended Soils. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 903–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; He, H.-Z.; Chen, G.-K.; Li, H.-S. Effects of Biochar and Crop Straws on the Bioavailability of Cadmium in Contaminated Soil. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahzadeh, H.; Kaczala, F.; Bhatnagar, A.; Hogland, W. Speciation of Metals in Contaminated Sediments from Oskarshamn Harbor, Oskarshamn, Sweden. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 2455–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matong, J.M.; Nyaba, L.; Nomngongo, P.N. Fractionation of Trace Elements in Agricultural Soils Using Ultrasound Assisted Sequential Extraction Prior to Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometric Determination. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Dai, Z.; Tang, C.; Xu, J. The Immobilization, Plant Uptake and Translocation of Cadmium in a Soil-Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) System Amended with Various Sugarcane Bagasse-Based Materials. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Malik, Z.; Parveen, A.; Zong, Y.; Abbasi, G.H.; Rafiq, M.T.; Shaaban, M.; Mustafa, A.; Bashir, S.; Rafay, M.; et al. Biochar Alleviates Cd Phytotoxicity by Minimizing Bioavailability and Oxidative Stress in Pak Choi (Brassica chinensis L.) Cultivated in Cd-Polluted Soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Hou, D.; Mao, Q.; Zhi, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Luo, L. Effect of RM-Based-Passivator for the Remediation of Two Kinds of Cd Polluted Paddy Soils and Mechanism of Cd(II) Adsorption. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Xu, J.; Brookes, P.C. Effects of Inorganic and Organic Amendments on the Uptake of Lead and Trace Elements by Brassica chinensis Grown in an Acidic Red Soil. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Xu, R.; Jiang, T.; Li, Z. Immobilization of Cu(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) by the Addition of Rice Straw Derived Biochar to a Simulated Polluted Ultisol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 229, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahori, A.H.; Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Rashid, M.; Kalhoro, S.A.; Memon, M.; Naheed, Z.; Ahmed, M.; Zhang, Z. Residual Effects of Tobacco Biochar along with Different Fixing Agents on Stabilization of Trace Elements in Multi-Metal Contaminated Soils. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 87, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yari, M.; Rahimi, G.; Ebrahimi, E.; Sadeghi, S.; Fallah, M.; Ghesmatpoor, E. Effect of Three Types of Organic Fertilizers on the Heavy Metals Transfer Factor and Maize Biomass. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 8, 2681–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Qiu, W.; Lian, F.; Yu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Song, Z. Field Evaluation of in Situ Remediation of Cd-Contaminated Soil Using Four Additives, Two Foliar Fertilisers and Two Varieties of Pakchoi. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 124, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Guo, J.; Xu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Feng, R. Evaluation of Silkworm Excrement and Mushroom Dreg for the Remediation of Multiple Heavy Metal/Metalloid Contaminated Soil Using Pakchoi. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 124, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Cai, H.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Chen, Z.; Yao, L. Heavy Metal-Immobilizing Bacteria Increase the Biomass and Reduce the Cd and Pb Uptake by Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) in Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 195, 110375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Zheng, N.; Tang, L.; Ji, X. Effects of Cadmium and Copper Mixtures to Carrot and Pakchoi under Greenhouse Cultivation Condition. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cai, S.; Mo, C.; Chu, B.; Peng, L.; Yang, F. Toxic Effects of Heavy Metals and Their Accumulation in Vegetables Grown in a Saline Soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; He, L.; Lu, K.; Sarmah, A.; Li, J.; Bolan, N.S.; Pei, J.; Huang, H. Using Biochar for Remediation of Soils Contaminated with Heavy Metals and Organic Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8472–8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basta, N.T.; Gradwohl, R.; Snethen, K.L.; Schroder, J.L. Chemical Immobilization of Lead, Zinc, and Cadmium in Smelter-Contaminated Soils Using Biosolids and Rock Phosphate. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Zhou, W.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, J. Influence of Green Waste Compost on Pb-Polluted Soil Remediation, Soil Quality Improvement, and Uptake by Pakchoi Cabbage (Brassica campestris L. Ssp). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7693–7701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azeem, M.; Ali, A.; Arockiam Jeyasundar, P.G.S.; Li, Y.; Abdelrahman, H.; Latif, A.; Li, R.; Basta, N.; Li, G.; Shaheen, S.M.; et al. Bone-Derived Biochar Improved Soil Quality and Reduced Cd and Zn Phytoavailability in a Multi-Metal Contaminated Mining Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Adeel, M.; Gulshan, A.B.; Iqbal, J.; Khan, S.; Rehman, M.; Azeem, M. Effects of Organic and Inorganic Passivators on the Immobilization of Cadmium in Contaminated Soils: A Review. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 36, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Huang, T.; Shi, J.; Chen, J.; Zhong, F.; Wu, L.; Xu, J. Decreasing Cadmium Uptake of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) in the Cadmium-Contaminated Paddy Field through Different Cultivars Coupling with Appropriate Soil Amendments. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1788–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, T.; Franks, A.; Xu, J.; Chathurika, J.B.A.J.; Tang, C. Biochar Aging Alters the Bioavailability of Cadmium and Microbial Activity in Acid Contaminated Soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Materials | Basic Characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Total Cd (mg kg−1) | CEC (cmol kg−1) | Organic Matter (g kg−1) | |
| Soil | 5.88 | 1.17 | 8.71 | 21.2 |
| Organic fertilizer | 8.04 | 0.46 | - | 485 |
| Biochar | 9.37 | 0.47 | 118.64 | 129.6 |
| Phosphate rock powder | 8.42 | 0.07 | - | 4.4 |
| Fish bone meal | 7.91 | 0.66 | 8.05 | 345 |
| Treatments | BAF | AF | TF | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 d | 30 d | 45 d | 15 d | 30 d | 45 d | 15 d | 30 d | 45 d | |
| CK | 0.186 Aa | 0.179 Aa | 0.186 Aa | 0.332 Ab | 0.345 Ad | 0.331 Ac | 0.563 Aa | 0.521 Aa | 0.564 Aa |
| PM | 0.184 Aa | 0.136 Bb | 0.122 Bbc | 0.455 Ba | 0.632 Aa | 0.567 Aa | 0.406 Ab | 0.217 Bb | 0.215 Bc |
| CBP | 0.168 Aa | 0.116 Bb | 0.109 Bc | 0.404 Aa | 0.455 Ac | 0.391 Ab | 0.417 Ab | 0.254 Bb | 0.277 Bb |
| PRP | 0.169 Aa | 0.144 Ab | 0.132 Bbc | 0.445 Ba | 0.534 Ab | 0.519 Aa | 0.381 Ab | 0.268 Bb | 0.254 Bbc |
| FBP | 0.181 Aa | 0.130 Bb | 0.139 Bb | 0.467 Ba | 0.562 Aab | 0.518 ABa | 0.387 Ab | 0.232 Bb | 0.269 Bb |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, W.; Li, Z.; Li, R.; Guo, J.; Hou, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F. In Situ Toxicity Reduction and Food Safety Assessment of Pak Choi (Brassica campestris L.) in Cadmium-Contaminated Soil by Jointly Using Alkaline Passivators and Organic Fertilizer. Toxics 2023, 11, 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100824
Jiao W, Li Z, Li R, Guo J, Hou X, Zhang X, Wang F. In Situ Toxicity Reduction and Food Safety Assessment of Pak Choi (Brassica campestris L.) in Cadmium-Contaminated Soil by Jointly Using Alkaline Passivators and Organic Fertilizer. Toxics. 2023; 11(10):824. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100824
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Wei, Zhi Li, Ruiping Li, Jiafeng Guo, Xiaoshu Hou, Xi Zhang, and Fangli Wang. 2023. "In Situ Toxicity Reduction and Food Safety Assessment of Pak Choi (Brassica campestris L.) in Cadmium-Contaminated Soil by Jointly Using Alkaline Passivators and Organic Fertilizer" Toxics 11, no. 10: 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100824
APA StyleJiao, W., Li, Z., Li, R., Guo, J., Hou, X., Zhang, X., & Wang, F. (2023). In Situ Toxicity Reduction and Food Safety Assessment of Pak Choi (Brassica campestris L.) in Cadmium-Contaminated Soil by Jointly Using Alkaline Passivators and Organic Fertilizer. Toxics, 11(10), 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100824





