Laboratory-Induced Bifenthrin, Flonicamid, and Thiamethoxam Resistance and Fitness Costs in Rhopalosiphum padi
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing and Insecticides
2.2. Laboratory Bioassays
2.3. Establishment of Resistant Strain Populations
2.4. Evaluating the Fitness Cost
2.5. Life Table Data Analysis
2.6. Population Projection
3. Results
3.1. Selection-Induced Insecticide Resistance Development
3.2. Impact of Insecticide Resistance on Different Developmental Stages of R. padi
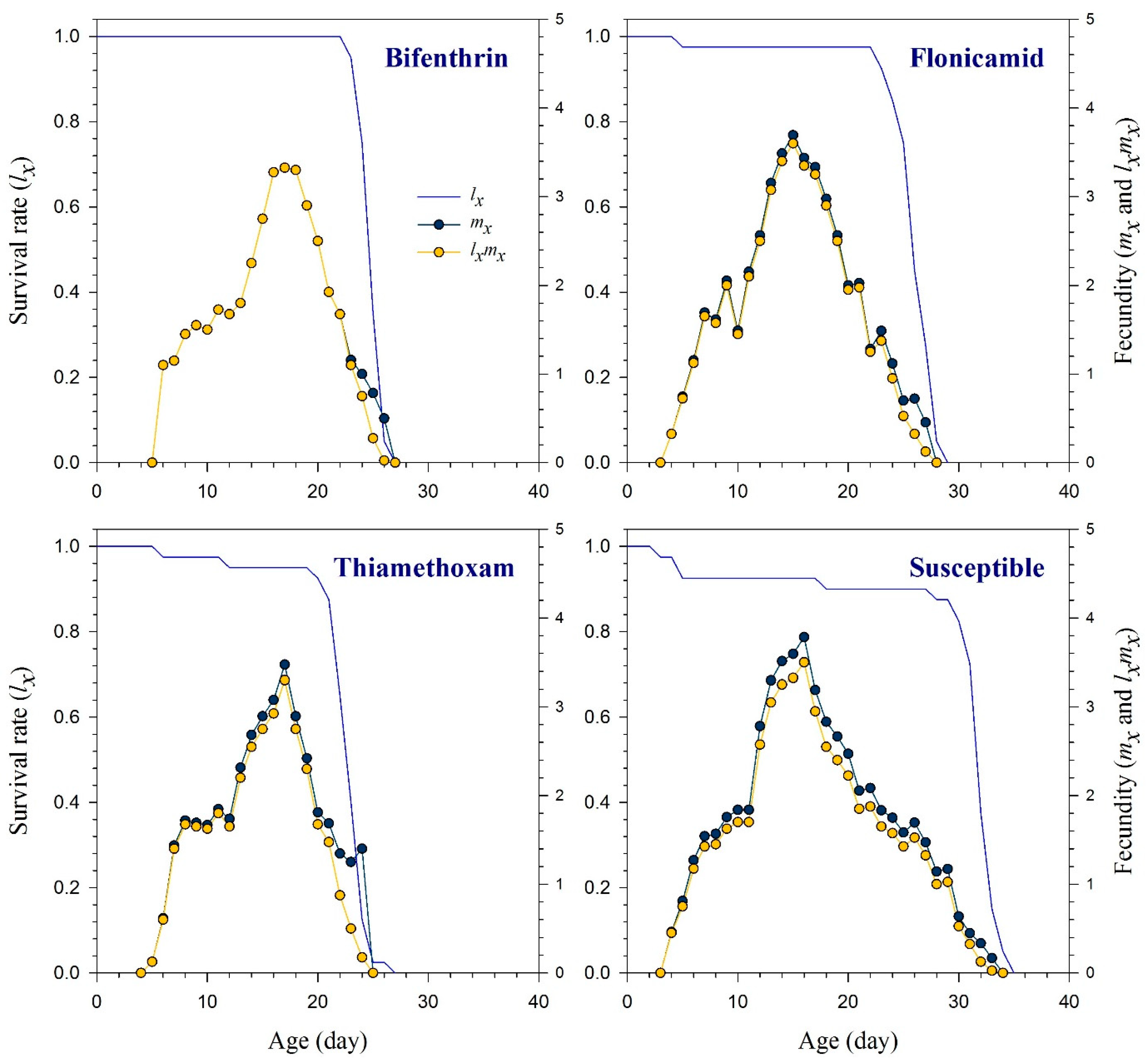
3.3. Reproduction and Life Table Parameters of the Insecticide-Resistant Strain of R. padi
3.4. Population Projection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hullé, M.; Chaubet, B.; Turpeau, E.; Simon, J.-C. Encyclop’Aphid: A website on aphids and their natural enemies. Entomol. Gen. 2020, 40, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.-C.; Du, W.-M.; Zang, L.-S.; Ruan, C.-C.; Zhang, J.-J.; Zou, Z.; Monticelli, L.S.; Harwood, J.D.; Desneux, N. Multi-parasitism: A promising approach to simultaneously produce Trichogramma chilonis and T. dendrolimi on eggs of Antheraea pernyi. Entomol. Gen. 2021, 41, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieri, R.; Anfora, G.; Mazzoni, V.; Stacconi, R. Semiochemicals, semiophysicals and their integration for the development of innovative multi-modal systems for agricultural pests’ monitoring and control. Entomol. Gen. 2022, 42, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheggen, F.; Barrès, B.; Bonafos, R.; Desneux, N.; Escobar-Gutiérrez, A.J.; Gachet, E.; Laville, J.; Siegwart, M.; Thiéry, D.; Jactel, H. Producing sugar beets without neonicotinoids: An evaluation of alternatives for the management of viruses-transmitting aphids. Entomol. Gen. 2022, 42, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.-S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Desneux, N. Biological control with Trichogramma in China: History, present status and perspectives. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2021, 66, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticelli, L.S.; Desneux, N.; Biondi, A.; Mohl, E.; Heimpel, G.E. Post-introduction changes of host specificity traits in the aphid parasitoid Lysiphlebus testaceipes. Entomol. Gen. 2022, 42, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Bai, J.; Zhao, J.; Su, S.; Liu, L.; Han, Z.; Chen, M. Super-kdr mutation M918L and multiple cytochrome P450s associated with the resistance of Rhopalosiphum padi to pyrethroid. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2809–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Gao, H.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, E.; Zhu, X. Field evolved resistance to pyrethroids, neonicotinoids, organophosphates and macrolides in Rhopalosiphum padi (Linnaeus) and Sitobion avenae (Fabricius) from China. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.-N.; An, J.-J.; Park, S.-E.; Kim, J.-I.; Kim, G.-H. Regional susceptibilities to 12 insecticides of melon and cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and a point mutation associated with imidacloprid resistance. Crop. Prot. 2014, 55, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, H.; Ullah, F.; Biondi, A.; Desneux, N.; Qian, D.; Gao, X.; Song, D. Resistance against clothianidin and associated fitness costs in the chive maggot, Bradysia odoriphaga. Entomol. Gen. 2019, 39, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Cheng, S.; Desneux, N.; Gao, X.; Xiu, X.; Wang, F.; Hou, M. Transgenerational hormesis effects of nitenpyram on fitness and insecticide tolerance/resistance of Nilaparvata lugens. J. Pest Sci. 2023, 96, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Ullah, F.; Ding, Q.; Gao, X.; Desneux, N.; Song, D. Comparison of full-length transcriptomes of different imidacloprid-resistant strains of Rhopalosiphum padi (L.). Entomol. Gen. 2021, 41, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Cao, C.-W.; Gao, X.-W. The effect of pretreatment with S, S, S-tributyl phosphorotrithioate on deltamethrin resistance and carboxylesterase activity in Aphis gossypii (Glover) (Homoptera: Aphididae). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 98, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassmann, A.J.; Carrière, Y.; Tabashnik, B.E. Fitness costs of insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2009, 54, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyed, A.H.; Ahmad, M.; Crickmore, N. Fitness costs limit the development of resistance to indoxacarb and deltamethrin in Heliothis virescens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 1927–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriere, Y.; Tabashnik, B. Reversing insect adaptation to transgenic insecticidal plants. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 268, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliot, A.; Ghanim, M. Fitness costs associated with insecticide resistance. Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; You, M.; Atlıhan, R.; Smith, C.L.; Kavousi, A.; Özgökçe, M.S.; Güncan, A.; Tuan, S.-J.; Fu, J.-W.; Xu, Y.-Y.; et al. Age-Stage, two-sex life table: An introduction to theory, data analysis, and application. Entomol. Gen. 2020, 40, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, N.; Shah, R.M.; Shad, S.A.; Azher, F. Dominant fitness costs of resistance to fipronil in Musca domestica Linnaeus (Diptera: Muscidae). Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 226, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Li, Q.; Qiu, H.; Tang, L.; Zeng, D.; Liu, K.; Gao, Y. Resistance development, stability, cross-resistance potential, biological fitness and biochemical mechanisms of spinetoram resistance in Thrips hawaiiensis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1564–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, D.; Moritz, G.; Nauen, R. Fitness costs and life table parameters of highly insecticide-resistant strains of Plutella xylostella (L.)(Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) at different temperatures. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Mao, K.; Liao, X.; He, B.; Jin, R.; Tang, T.; Wan, H.; Li, J. Fitness cost of nitenpyram resistance in the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Gul, H.; Tariq, K.; Desneux, N.; Gao, X.; Song, D. Acetamiprid resistance and fitness costs of melon aphid, Aphis gossypii: An age-stage, two-sex life table study. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 171, 104729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Tang, Q.; Xia, J.; Lv, N.; Gao, X. Fitness costs of sulfoxaflor resistance in the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 158, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-H.; Gong, Y.-J.; Chen, J.-C.; Su, X.-C.; Cao, L.-J.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Wei, S.-J. Laboratory selection for resistance to sulfoxaflor and fitness costs in the green peach aphid Myzus persicae. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2018, 21, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.R.; Rodrigues, A.R.S.; Silva, W.M.; Silva, T.B.M.; Silva, V.R.F.; Guedes, R.N.C.; Siqueira, H.A.A. Spinosad and the tomato borer Tuta absoluta: A bioinsecticide, an invasive pest threat, and high insecticide resistance. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, L. The intrinsic rate of natural increase of an insect population. J. Anim. Ecol. 1948, 17, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H. Life-table analysis incorporating both sexes and variable development rates among individuals. Environ. Entomol. 1988, 17, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Liu, H. Two new methods for the study of insect population ecology. Bull. Inst. Zool. Acad. Sin. 1985, 24, 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, H.; Güncan, A.; Kavousi, A.; Gharakhani, G.; Atlihan, R.; Özgökçe, M.S.; Shirazi, J.; Amir-Maafi, M.; Maroufpoor, M.; Taghizadeh, R. TWOSEX-MSChart: The key tool for life table research and education. Entomol. Gen. 2022, 42, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H. TWOSEX-MSChart: A Computer Program for the Age-Stage, Two-Sex Life Table Analysis; National Chung Hsing University in Taiwan. 2023. Available online: http://140.120.197.173/Ecology/prod02.htm (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Chen, G.-M.; Chi, H.; Wang, R.-C.; Wang, Y.-P.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Li, X.-D.; Yin, P.; Zheng, F.-Q. Demography and uncertainty of population growth of Conogethes punctiferalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) reared on five host plants with discussion on some life history statistics. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 2143–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, D. Optimal life histories, optimal notation, and the value of reproductive value. Am. Nat. 1982, 119, 803–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Su, H.-Y. Age-stage, two-sex life tables of Aphidius gifuensis (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and its host Myzus persicae (Sulzer)(Homoptera: Aphididae) with mathematical proof of the relationship between female fecundity and the net reproductive rate. Environ. Entomol. 2006, 35, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, S.J.; Lee, C.C.; Chi, H. Population and damage projection of Spodoptera litura (F.) on peanuts (Arachis hypogaea L.) under different conditions using the age-stage, two-sex life table. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.B.; Chi, H. Age-stage, two-sex life tables of Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett) (Diptera: Tephritidae) with a discussion on the problem of applying female age-specific life tables to insect populations. Insect Sci. 2012, 19, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akca, I.; Ayvaz, T.; Yazici, E.; Smith, C.L.; Chi, H. Demography and population projection of Aphis fabae (Hemiptera: Aphididae): With additional comments on life table research criteria. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Chi, H.; Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Ma, R. Demography of Cacopsylla chinensis (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) reared on four cultivars of Pyrus bretschneideri (Rosales: Rosaceae) and P. communis pears with estimations of confidence intervals of specific life table statistics. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 2343–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H. TIMING-MSChart: A Computer Program for the Population Projection Based on Age-Stage, Two-Sex Life Table; National Chung Hsing University in Taiwan. 2023. Available online: http://140.120.197.173/Ecology/prod02.htm (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Chi, H. Timing of control based on the stage structure of pest populations: A simulation approach. J. Econ. Entomol. 1990, 83, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-W.; Chi, H.; Smith, C.L. Linking demography and consumption of Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) fed on Solanum photeinocarpum (Solanales: Solanaceae): With a new method to project the uncertainty of population growth and consumption. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, W.; Brown, J.M.; Knowles, C.O. Insecticide resistance in field and laboratory strains of western flower thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 1995, 88, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafius, E.; Bishop, B. Resistance to imidacloprid in Colorado potato beetles from Michigan. Res. Pest Manag. 1996, 8, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Elbert, A.; Nauen, R. Resistance of Bemisia tabaci (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) to insecticides in southern Spain with special reference to neonicotinoids. Pest Manag. Sci. 2000, 56, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, M.; Gorman, K.; Day, S.; Denholm, I.; Elbert, A.; Nauen, R. Baseline determination and detection of resistance to imidacloprid in Bemisia tabaci (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 1996, 86, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Gul, H.; Desneux, N.; Said, F.; Gao, X.; Song, D. Fitness costs in chlorfenapyr-resistant populations of the chive maggot, Bradysia odoriphaga. Ecotoxicology 2020, 29, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafeez, M.; Liu, S.; Jan, S.; Ali, B.; Shahid, M.; Fernández-Grandon, G.M.; Nawaz, M.; Ahmad, A.; Wang, M. Gossypol-induced fitness gain and increased resistance to deltamethrin in beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Hübner). Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, M.; Afzal, M.B.S.; Shabbir, G.; Serrão, J.E.; Shad, S.A.; Muhammad, W. Laboratory selection of chlorpyrifos resistance in an Invasive Pest, Phenacoccus solenopsis (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae): Cross-resistance, stability and fitness cost. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 137, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.G.; Georghiou, G.P. Rapid development of high-level permethrin resistance in a field-collected strain of the house fly (Diptera: Muscidae) under laboratory selection. J. Econ. Entomol. 1985, 78, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Han, Z. Fitness costs of laboratory-selected imidacloprid resistance in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stål. Pest Manag. Sci. 2006, 62, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewen, L.; Zhaojun, H.; Yinchang, W.; Lingchun, Z.; Hongwei, Z.; Chengjun, L. Selection for imidacloprid resistance in Nilaparvata lugens: Cross-resistance patterns and possible mechanisms. Pest Manag. Sci. 2003, 59, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Xu, X.; Gul, H.; Güncan, A.; Hafeez, M.; Gao, X.; Song, D. Impact of imidacloprid resistance on the demographic traits and expressions of associated genes in Aphis gossypii Glover. Toxics 2022, 10, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, A.; Shan, T.; Dong, W.; Shi, X.; Gao, X. Cross-resistance and fitness cost analysis of resistance to thiamethoxam in Melon and Cotton Aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 1946–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, N.; Khan, H.; Shad, S.A. Cross-resistance, stability, and fitness cost of resistance to imidacloprid in Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae). Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Wang, Q.; Qi, H.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, H.; Rui, C. Resistance selection of indoxacarb in Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): Cross-resistance, biochemical mechanisms and associated fitness costs. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, F.; Gul, H.; Tariq, K.; Desneux, N.; Gao, X.; Song, D. Fitness costs in clothianidin-resistant population of the melon aphid, Aphis gossypii. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Sanada-Morimura, S.; Matsukura, K.; Van Chien, H.; Cuong, L.Q.; Loc, P.M.; Estoy, G.F., Jr.; Matsumura, M. Energy reserve compensating for trade-off between metabolic resistance and life history traits in the brown planthopper (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, A.; Magaud, A.; Nicot, A.; Vézilier, J. Energetic cost of insecticide resistance in Culex pipiens mosquitoes. J. Med. Entomol. 2011, 48, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Generations | Insecticides | LC50 (95%CI) a ppm | Slope ± SE b | χ2 | p-Value | RR c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 | Thiamethoxam | 11.458 (9.766–13.416) | 2.718 ± 0.283 | 5.458 | 0.964 | - |
| Flonicamid | 5.710 (4.869–6.746) | 2.453 ± 0.238 | 6.147 | 0.940 | - | |
| Bifenthrin | 18.863 (16.230–21.958) | 2.719 ± 0.256 | 11.039 | 0.607 | - | |
| F1 | Thiamethoxam | 12.504 (10.608–14.755) | 2.581 ± 0.275 | 4.914 | 0.977 | 1.09 |
| Flonicamid | 5.956 (5.072–7.039) | 2.442 ± 0.239 | 3.393 | 0.996 | 1.04 | |
| Bifenthrin | 24.621 (21.057–28.616) | 2.987 ± 0.341 | 9.519 | 0.732 | 1.31 | |
| F2 | Thiamethoxam | 17.656 (14.602–22.031) | 2.030 ± 0.224 | 3.735 | 0.994 | 1.54 |
| Flonicamid | 6.800 (5.594–8.428) | 1.882 ± 0.209 | 3.366 | 0.996 | 1.19 | |
| Bifenthrin | 36.702 (31.064–44.364) | 2.433 ± 0.255 | 6.840 | 0.910 | 1.94 | |
| F3 | Thiamethoxam | 21.052 (17.013–27.463) | 1.852 ± 0.220 | 3.846 | 0.993 | 1.83 |
| Flonicamid | 12.232 (9.572–17.022) | 1.691 ± 0.236 | 3.206 | 0.997 | 2.14 | |
| Bifenthrin | 53.151 (43.078–69.989) | 2.063 ± 0.253 | 3.854 | 0.992 | 2.81 | |
| F4 | Thiamethoxam | 39.996 (31.959–53.067) | 1.716 ± 0.211 | 8.047 | 0.841 | 3.49 |
| Flonicamid | 19.423 (15.319–26.205) | 1.623 ± 0.217 | 4.248 | 0.988 | 3.40 | |
| Bifenthrin | 73.771 (56.240–110.790) | 1.822 ± 0.258 | 6.710 | 0.916 | 3.91 | |
| F5 | Thiamethoxam | 60.509 (50.436–74.271) | 2.088 ± 0.223 | 12.067 | 0.522 | 5.28 |
| Flonicamid | 35.908 (30.070–43.689) | 2.367 ± 0.289 | 4.520 | 0.984 | 6.28 | |
| Bifenthrin | 99.397 (79.869–132.243) | 1.920 ± 0.235 | 7.830 | 0.854 | 5.26 | |
| F6 | Thiamethoxam | 102.398 (86.485–122.681) | 2.271 ± 0.231 | 12.708 | 0.470 | 8.93 |
| Flonicamid | 47.424 (40.097–56.463) | 2.298 ± 0.229 | 3.436 | 0.995 | 8.31 | |
| Bifenthrin | 141.104 (110.687–200.683) | 2.039 ± 0.279 | 4.320 | 0.987 | 7.48 | |
| F7 | Thiamethoxam | 170.830 (139.511–219.495) | 1.986 ± 0.230 | 7.188 | 0.892 | 14.90 |
| Flonicamid | 73.741 (59.665–94.896) | 1.833 ± 0.228 | 4.652 | 0.982 | 12.91 | |
| Bifenthrin | 219.672 (179.875–284.911) | 2.294 ± 0.304 | 7.717 | 0.861 | 11.64 | |
| F8 | Thiamethoxam | 258.040 (207.098–350.288) | 2.176 ± 0.284 | 4.432 | 0.985 | 22.52 |
| Flonicamid | 84.169 (69.397–106.080) | 2.167 ± 0.275 | 3.114 | 0.997 | 14.74 | |
| Bifenthrin | 326.191 (244.979–508.106) | 1.838 ± 0.268 | 6.442 | 0.928 | 17.29 | |
| F9 | Thiamethoxam | 335.723 (287.430–391.916) | 3.385 ± 0.498 | 4.913 | 0.977 | 29.30 |
| Flonicamid | 109.285 (93.127–128.223) | 2.754 ± 0.305 | 3.814 | 0.993 | 19.13 | |
| Bifenthrin | 442.158 (352.672–599.054) | 1.939 ± 0.243 | 7.605 | 0.868 | 23.44 | |
| F10 | Thiamethoxam | 394.846 (324.190–506.346) | 2.171 ± 0.253 | 7.709 | 0.862 | 34.46 |
| Flonicamid | 151.141 (120.502–200.341) | 1.659 ± 0.207 | 3.145 | 0.997 | 26.46 | |
| Bifenthrin | 603.210 (480.636–842.423) | 2.315 ± 0.326 | 3.398 | 0.996 | 31.97 |
| Stage | Susceptible | Bifenthrin | Flonicamid | Thiamethoxam | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean ± SE | n | Mean ± SE | n | Mean ± SE | n | Mean ± SE | |
| First-instar nymph | 40 | 1.43 ± 0.08 b | 40 | 1.65 ± 0.10 ab | 40 | 1.48 ± 0.09 b | 40 | 1.85 ± 0.08 a |
| Second-instar nymph | 40 | 1.05 ± 0.03 a | 40 | 1.13 ± 0.05 a | 40 | 1.13 ± 0.05 a | 40 | 1.15 ± 0.06 a |
| Third-instar nymph | 38 | 1.21 ± 0.07 b | 40 | 1.43 ± 0.08 a | 40 | 1.20 ± 0.06 b | 40 | 1.50 ± 0.08 a |
| Fourth-instar nymph | 37 | 1.11 ± 0.05 b | 40 | 1.80 ± 0.06 a | 39 | 1.26 ± 0.07 b | 39 | 1.77 ± 0.08 a |
| Total pre-adult stages | 37 | 4.78 ± 0.13 c | 40 | 6.01 ± 0.01 b | 39 | 5.05 ± 0.14 c | 39 | 6.28 ± 0.14 a |
| Adult longevity | 37 | 27.14 ± 0.44 a | 40 | 19.10 ± 0.15 c | 39 | 21.33 ± 0.17 b | 39 | 16.62 ± 0.34 d |
| Total longevity | 37 | 31.92 ± 0.44 a | 40 | 25.10 ± 0.15 c | 39 | 26.38 ± 0.24 b | 39 | 22.90 ± 0.35 d |
| Parameters a | Susceptible | Bifenthrin | Flonicamid | Thiamethoxam |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SE | Mean ± SE | Mean ± SE | Mean ± SE | |
| R0 (offspring/individual) | 50.35 ± 2.65 a | 38.00 ± 0.65 c | 44.00 ± 1.42 b | 34.00 ± 1.28 d |
| r (day−1) | 0.3008 ± 0.0069 a | 0.2657 ± 0.0027 b | 0.3021 ± 0.0062 a | 0.2667 ± 0.0047 b |
| λ (day−1) | 1.3510 ± 0.0093 a | 1.3044 ± 0.0035 b | 1.3527 ± 0.0084 a | 1.3056 ± 0.0062 b |
| T (days) | 13.03 ± 0.21 bc | 13.69 ± 0.11 a | 12.53 ± 0.22 c | 13.22 ± 0.19 b |
| F (nymphs/female) | 54.43 ± 1.50 a | 38.00 ± 0.65 c | 45.13 ± 0.91 b | 34.87 ± 0.96 d |
| RPd (days) | 24.22 ± 0.59 a | 18.00 ± 0.17 c | 19.28 ± 0.23 b | 15.69 ± 0.35 d |
| APRP (days) | 0.35 ± 0.11 a | 0.20 ± 0.08 a | 0.41 ± 0.11 a | 0.28 ± 0.08 a |
| TPRP (days) | 5.14 ± 0.17 c | 6.20 ± 0.08 b | 5.46 ± 0.19 c | 6.56 ± 0.12 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gul, H.; Haq, I.u.; Güncan, A.; Ullah, F.; Desneux, N.; Liu, X. Laboratory-Induced Bifenthrin, Flonicamid, and Thiamethoxam Resistance and Fitness Costs in Rhopalosiphum padi. Toxics 2023, 11, 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100806
Gul H, Haq Iu, Güncan A, Ullah F, Desneux N, Liu X. Laboratory-Induced Bifenthrin, Flonicamid, and Thiamethoxam Resistance and Fitness Costs in Rhopalosiphum padi. Toxics. 2023; 11(10):806. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100806
Chicago/Turabian StyleGul, Hina, Ihsan ul Haq, Ali Güncan, Farman Ullah, Nicolas Desneux, and Xiaoxia Liu. 2023. "Laboratory-Induced Bifenthrin, Flonicamid, and Thiamethoxam Resistance and Fitness Costs in Rhopalosiphum padi" Toxics 11, no. 10: 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100806
APA StyleGul, H., Haq, I. u., Güncan, A., Ullah, F., Desneux, N., & Liu, X. (2023). Laboratory-Induced Bifenthrin, Flonicamid, and Thiamethoxam Resistance and Fitness Costs in Rhopalosiphum padi. Toxics, 11(10), 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100806







