Investigation of Global Trends of Pollutants in Marine Ecosystems around Barrang Caddi Island, Spermonde Archipelago Cluster: An Ecological Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Equipment
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Sample Measurement
- The analysis of microplastic components, especially the total abundance of microplastics was completed using 30% H2O2 solvent. Measurement of the total abundance of microplastics was carried out in triplicate. The polymer structure was analyzed as the main characteristic of each microplastic, using FTIR combined with GC/MS chromatogram data [26,76,77];
- The types and abundance of the PAH contaminants were analyzed based on GC/MS chromatogram data. Information on the pesticide residue contaminants and media waste can also be obtained from the GC/MS chromatogram [24,76,77]. However, the determination of components was more specific, because in general, pesticide residues and several types of medical waste have chemical structures with reactive groups that should be identified using a combination of pyrolysis-GC/MS [54,78,79];
- Determination of the concentration of heavy metal contaminants, particularly exposure to Lead (Pb) and Copper (Cu) ions, was conducted for each sample according to AAS absorption at the maximum wavelength (Pb: λmax. 228.9 nm and Cu: λmax. 324.7 nm) [33,34,80]. The method for determining the pollutant concentrations of Pb+2 and Cu+2 first makes a calibration curve to make ten series of Pb+2 and Cu+2 standard solutions whose estimated sample concentrations fall within the range of the standard solution, then the absorption of each concentration is measured. Then, the standard deviation and slope determination calculations are carried out. The concentration of each sample (Pb+2 and Cu+2) was calculated based on the absorption obtained from AAS after being plotted into the regression equation [22,33,80]. Determination of pollutant concentrations of Pb+2 and Cu+2 carried out measurements of three replications for each type of sample obtained at three different sampling points. The data from the measurement results were calculated on average and summarized in a table. The quality of seawater according to the quality standard for pollutants Pb+2 and Cu+2 is a maximum of 0.05 mg/L. The quality standard for fish and other non-spongy biota is a maximum of 0.008 mg/L [55,76,80,81,82]. The maximum limit is not specified for sponges because they are included in the category of biota that are not eaten. The maximum limit of Pb+2 and Cu+2 for sediment is 0.10 µg/g. The quality of seawater and fish in BCI is determined by comparing the average pollutant concentration calculated compared to the standard for seawater and fish [4,10,59,83].
2.5. Data Presentation and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Microplastic Pollutant Analysis
3.2. PAH Pollutant Analysis
3.3. Pesticide Residue Pollutant Analysis and Medical Waste
3.4. Heavy Metal Pollutant Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergmann, M.; Gutow, L.; Klages, M. Marine anthropogenic litter. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del-Mondo, G.; Peng, P.; Gensel, J.; Claramunt, C.; Lu, F. Leveraging spatio-temporal graphs and knowledge graphs: Perspectives in the field of maritime transportation. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, A.I.; Sakti, A.D.; Robbani, B.F.; Ristiyani, M.; Agustin, R.T.; Yati, E.; Nuha, M.U.; Anika, N.; Putra, R.; Siregar, D.I.; et al. Assessing potential climatic and human pressures in Indonesian coastal ecosystems using a spatial data-driven approach. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garba, F.; Ogidiaka, E.; Akamagwuna, F.C.; Nwaka, K.H.; Edegbene, A.O. Deteriorating water quality state on the structural assemblage of aquatic insects in a North-Western NigerianRiver. Water Sci. 2022, 36, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Paena, M.; Athirah, A.; Ratnawati, E.; Asaf, R.; Suwoyo, H.S.; Sahabuddin, S.; Hendrajat, E.A.; Kamaruddin, K.; Septiningsih, E.; et al. Temporal and Spatial Analysis of Coastal Water Quality to Support Application of Whiteleg Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Intensive Pond Technology. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakib, M.R.J.; Jolly, Y.N.; Dioses-Salinas, D.C.; Pizarro-Ortega, C.I.; De-la-Torre, G.E.; Khandaker, M.U.; Alsubaie, A.; Almalki, A.S.A.; Bradley, D.A. Macroalgae in biomonitoring of metal pollution in the Bay of Bengal coastal waters of Cox’s Bazar and surrounding areas. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busuricu, F.; Schroder, V.; Margaritti, D.; Anghel, A.H.; Tomos, S. Nutritional quality of some non-alcoholic beverages from the Romanian market. Tech. Biochem. 2022, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Islam, M.N.; Billah, M.M.; Sarker, A. COVID-19 pandemic and healthcare solid waste management strategy–A mini-review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, C.J.; Easson, C.G.; Fiore, C.L.; Thacker, R.W. Sponge–Microbe Interactions on Coral Reefs: Multiple Evolutionary Solutions to a Complex Environment. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 705053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuki, I.; Gusty, S.; Armus, R.; Sapar, A.; Asaf, R.; Athirah, A.; Jaya, J. Secondary Metabolite Analysis and Anti-Bacteria and Fungal Activities of Marine Sponge Methanol Extract Based on Coral Cover. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Basic Sciences, Maluku, Indonesia, 4–5 November 2020; Volume 2360, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvin, J.; Shanmugha, P.S.; Seghal, K.G.; Thangavelu, T.; Sapna, B.N. Sponge-associated marine bacteria as indicators of heavy metal pollution. Microbiol. Res. 2009, 164, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kui, M.; Wu, L.; Fam, H. Heavy metal ions affecting the removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by fungi with heavy-metal resistance. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9817–9827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuki, I. The Bio-adsorption Pattern Bacteria Symbiont Sponge Marine Against Contaminants Chromium and Manganese in The Waste Modification of Laboratory Scale. Indones. Chim. Acta 2020, 13, 1–9. Available online: http://journal.unhas.ac.id/index.php/ica/article/view/9972 (accessed on 1 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Xu, M.; Sun, K.; Cao, L.H.; Dai, C.; Jia, Y. Biodegradation of phenanthrene by endophytic fungus Phomopsis liquidambari in vitro and in vivo. Chemosphere 2018, 203, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imachi, H.; Aoi, K.; Tasum, E.; Saito, Y.; Yamanaka, Y.; Saito, Y.; Takashi, Y.; Tomaru, H.; Takeuchi, R.; Morono, Y.; et al. Cultivation of methanogenic community from subseafloor sediments using a continuous-flow bioreactor. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1913–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wu, L.; Song, J.; Qian, W.; Christie, P.; Chen, S. Distribution patterns of polychlorinated biphenyls in soils collected from Zhejiang province, east China. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2006, 28, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essumang, D.K.; Togoh, G.K.; Chokky, L. Pesticide residues in the water and Fish (lagoon tilapia) samples from lagoons in Ghana. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2009, 23, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alava, J.J.; Tirapé, A.; Mc-Mullen, K.; Uyaguari, M.; Domínguez, G.A. Microplastics and Macroplastic Debris as Potential Physical Vectors of SARS-CoV-2: A Hypothetical Overview with Implications for Public Health. Microplastics 2022, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baalkhuyur, F.M.; Bin- Dohaish, E.-J.A.; Elhalwagy, M.E.A.; Alikunhi, N.M.; AlSuwailem, A.M.; Rostad, A.; Coker, D.J.; Berumen, M.L.; Duarte, C.M. Microplastic in the gastrointestinal tract of fishes along the Saudi Arabian Red Sea coast. Mar. Pol. Bull. 2018, 131, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuki, I.; Ahmad, R.; Kamaruddin, M.; Asaf, R.; Armus, R.; Siswanty, I. Performance of cultured marine sponges-symbiotic bacteria as a heavy metal bio-adsorption. Biodiversitas 2021, 22, 5536–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, O.K.; Zhuo, M.; Zhang, K. Concomitant degradation of complex organics and metals recovery from fracking wastewater: Roles of nano zerovalent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobota, M.; Swi, M. Marine Waste—Sources, Fate, Risks, Challenges and Research Needs. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2021, 18, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chulalaksananukul, S.; Gadd, G.M.; Sangvanich, P.; Sihanonth, P.; Piapukiew, J.; Vangnai, A.S. Biodegradation of benzo(a)pyrene by a newly isolated Fusarium sp. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 262, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoto, O.; Azuure, A.A.; Adotey, K.D. Pesticide residues in water, sediment and fish from Tono Reservoir and their health risk implications. Springer Plus 2016, 5, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghazeer, R.; Azwai, S.; Garbaj, A.M.; Amr, A.; Elghmasi, S.; Sidati, M.; Yudiati, E.; Kubbat, M.G.; Eskandrani, A.A.; Shamlan, G.; et al. Alkaloids Rich Extracts from Brown Algae Against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria by Distinctive Mode of Action. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelluccio, S.; Alvim, C.B.; Bes-Piá, M.A.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A.; Fiore, S. Assessment of Microplastics Distribution in a Biological Wastewater Treatment. Microplastics 2022, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitri, S.; Patria, M.P. Microplastic contamination on Anadara granosa Linnaeus 1758 in Pangkal Babu mangrove forest area, Tanjung Jabung Barat district, Jambi. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1282, 012109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, A.; Øysæd, K.B.; Agustsson, T.; van Hoytema, N.; van Thiel, T.; Grati, F. First record of characterization, concentration and distribution of microplastics in coastal sediments of an urban fjord in south west Norway using a thermal degradation method. Chemosphere 2019, 227, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, N.A.; Moawad, M.N.; Ahmed, E.F. Toxic phenolic compounds in the Egyptian coastal waters of Alexandria: Spatial distribution, source identification, and ecological risk assessment. Water Sci. 2022, 36, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medaura, M.C.; Guivernau, M.; Moreno-Ventas, X.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F.X.; Viñas, M. Bioaugmentation of Native Fungi, an Efficient Strategy for the Bioremediation of an Aged Industrially Polluted Soil With Heavy Hydrocarbons. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Tian, J.; Yu, Y.; Chand, A.; Zhang, S.; Meng, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, S. Multifunctional graphene-based composite sponge. Sensors 2020, 20, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, C.T.; Jousset, A.; Van, O.L.; Van, E.J.D.; Costa, R. The freshwater sponge Ephydatia fluviatilis harbours diverse Pseudomonas species (Gammaproteobacteria, Pseudomonadales) with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dural, M.; Göksu, M.Z.L.; Özak, A.A. Investigation of heavy metal levels in economically important fish species captured from the Tuzla lagoon. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratiwi, N.T.M.; Wulandari, D.Y.; Iswantari, A. Horizontal Distribution of Zooplankton in Tangerang Coastal Waters, Indonesia. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 33, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bart, M.C.; Hudspith, M.; Rapp, H.T.; Verdonschot, P.F.M.; de Goeij, M.J. A Deep-Sea Sponge Loop? Sponges Transfer Dissolved and Particulate Organic Carbon and Nitrogen to Associated Fauna. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepe, Y.; Türkmen, M.; Türkmen, A. Assessment of heavy metals in two commercial fish species of four Turkish seas. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 146, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, Y. Assessment of medical waste generation, associated environmental impact, and management issues after the outbreak of COVID-19: A case study of the Hubei Province in China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0259207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anbumani, S.; Kakkar, P. Ecotoxicological effects of microplastics on biota: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14373–14396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, A.K.; Midway, S.R. Relationship of Microplastics to Body Size for Two Estuarine Fishes. Microplastics 2022, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, J.; Landos, M. Pesticides in Queensland and Great Barrier Reef Waterways-Potential Impacts on Aquatic Ecosystems and The Failure of National Management. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 230, 106447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotinagu, K.; Krishnaiah, N. Organochlorine and Organophosphorus Pesticide Residues in Todder and Milk Samples Along Musi River Belt, India. Vet. World 2015, 8, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, A.; Polat, S.; Simsek, A.; Kurt, T.T.; Ozyurt, G. Pesticide residues in muscles of some marine fish species and seaweeds of Iskenderun Bay (Northeastern Mediterranean), Turkey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 3756–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Jia, W.; Sun, H. Enzyme activities during Benzo[a]pyrene degradation by the fungus Lasiodiplodia theobromae isolated from a polluted soil. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gran, S.A.; Ramos, Z.J.; Fuentes, E.; Bravo, D.; Pérez, D.J.M. Effect of co-contamination by PAHs and heavy metals on bacterial communities of diesel contaminated soils of south shetland islands, antarctica. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaimee, M.Z.A.; Sarjadi, M.S.; Rahman, M.L. Heavy metals removal from water by efficient adsorbents. Water 2021, 13, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuki, I.; Sinardi, S.; Pratama, I.; Chaerul, M.; Paserangi, I.; Kamaruddin, M.; Asaf, R. Performance of sea sponges micro symbionts as a biomaterial in biodegradation naphthalene waste of modified. In Proceedings of the 5th International Seminar on Sustainable Urban Development, Jakarta, Indonesia, 10–11 October 2021; p. 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curchod, L.; Christelle, O.; Marion, J.; Christian, S.; Mohamed, A.D.; Martin, R.; Samuel, F. Temporal Variation of Pesticide Mixtures in Rivers of Three Agricultural Watersheds During a Major Drought in The Western Cape, South Africa. Water Res. 2020, 10, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topal, T.; Onac, C. Determination of Heavy Metals and Pesticides in Different Types of Fish Samples Collected from Four Different Locations of Aegean and Marmara Sea. J. Food Qual. 2020, 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaboudi, A.A.; Ahmed, B.; Brodie, G. Annals of Agricultural Sciences Phytoremediation of Pb and Cd contaminated soils by using sun fl ower (Helianthus annuus) plant. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2018, 63, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuki, I.; Alwi, R.S.; Erniati; Mudyawati; Sinardi; Iryani, A.S. Chitosan Performance of Shrimp Shells in The Biosorption Ion Metal of Cadmium, Lead and Nickel Based on Variations pH Interaction; Proceeding in Advances in Engineering Research; Atlantik Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, X.; Cao, Y.; Jing, W.P.; Yu, H.J.; Guo, P.; Huang, L. Biodegradation of Phenanthrene and Heavy Metal Removal by Acid-Tolerant Burkholderia fungorum FM-2. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baburam, C.; Feto, N.A. Mining of two novel aldehyde dehydrogenases (DHY-SC-VUT5 and DHY-G-VUT7) from metagenome of hydrocarbon contaminated soils. BMC Biotechnol. 2021, 21, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruddin, M.; Marzuki, I.; Burhan, A.; Ahmad, R. Screening acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from marine-derived actinomycetes by simple chromatography. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Biotechnology and Food Sciences, Surabaya, Indonesia, 11 September 2020; p. 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuki, I.; Ali, M.Y.; Syarif, H.U.; Gusty, S.; Daris, L.; Nisaa, K. Investigation of Biodegradable Bacteria as Bio indicators of the Presence of PAHs Contaminants in Marine Waters in the Marine Tourism Area of Makassar City. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Tropical Coastal Region Eco-Development 2020, Indonesia, 27–28 October 2020; p. 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuki, I.; Daris, L.; Nisaa, K.; Emelda, A. The power of biodegradation and bio-adsorption of bacteria symbiont sponges sea on waste contaminated of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Env. Sci. 2020, 584, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Greaves, A.K.; Teclechiel, D.; Letcher, R.J. In Vitro Metabolism of Photolytic Breakdown Products of Tetradecabromo-1,4-diphenoxybenzene Flame Retardant in Herring Gull and Rat Liver Microsomal Assays. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8335–8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuki, I.; Kamaruddin, M.; Ahmad, R. Identification of marine sponges-symbiotic bacteria and their application in degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Biodiversitas 2021, 22, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoni, V.T.; Lag-Brotons, A.J.; Ibeto, C.N.; Semple, K.T. Effects of biological pre-treatment of lignocellulosic waste with white-rot fungi on the stimulation of 14C-phenanthrene catabolism in soils. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 165, 105324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orani, A.M.; Barats, A.; Vassileva, E.; Thomas, O.P. Marine sponges as a powerful tool for trace elements biomonitoring studies in coastal environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rua, C.P.J.; Oliveira, L.S.; De-Froes, A.; Tschoeke, D.A.; Soares, A.C.; Leomil, L.; Gregoracci, G.B.; Coutinho, R.; Hajdu, E.; Thompson, C.C.; et al. Microbial and Functional Biodiversity Patterns in Sponges that Accumulate Bromopyrrole Alkaloids Suggest Horizontal Gene Transfer of Halogenase Genes. Microb. Ecol. J. 2018, 76, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzuki, I.; Daris, L.; Yunus, S.; Riana, A.D. Selection and characterization of potential bacteria for polycyclic aromatic biodegradation of hydrocarbons in sea sponges from Spermonde Islands, Indonesia. AACL Bioflux. 2020, 13, 3493–3506. [Google Scholar]
- Ziarati, P.; Ziarati, N.N.; Nazeri, S.; Saber, G.M. Phytoextraction of heavy metals by two sorghum spices in treated soil using black tea residue for cleaning-uo the contaminated soil. Orient. J. Chem. 2015, 31, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, F.; Faheem, M.; Azhar, E.I.; Yasir, M.; Alvi, S.A.; Kamal, M.A.; Ikram, U.; Naseer, M.I. Bacteria From Marine Sponges: A Source of New Drugs. Curr. Drug Metab. 2016, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Y.S.; Rathnam, R.; Anuar, S.T.; Khalik, W.M.A.W.M. Separation and characterization of microplastics in the Lates calcarifer from the soils of setiu Malaysia. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2017, 21, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuki, I.; Asaf, R.; Paena, M.; Athirah, A.; Nisaa, K.; Ahmad, R.; Kamaruddin, M. Anthracene and Pyrene Biodegradation Performance of Marine Sponge Symbiont Bacteria Consortium. Molecules 2021, 26, 6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Cho, S.-H.; Kim, K.-H.; Kwon, E.E. Progress in quantitative analysis of microplastics in the environment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 422, 130154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löder, M.G.J.; Kuczera, M.; Mintenig, S.; Lorenz, C.; Gerdts, G. Focal plane array detector-based micro-Fourier-transform infrared imaging for the analysis of microplastics in environmental samples. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 563–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roebroek, C.T.J.; Harrigan, S.; Van-Emmerik, T.H.M.; Baugh, C.; Eilander, D.; Prudhomme, C.; Pappenberger, F. Plastic in global rivers: Are floods making it worse? Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwinghammer, L.; Krause, S.; Schaum, C. Determination of large microplastics: Wet-sieving of dewatered digested sludge, co-substrates, and compost. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onyena, A.P.; Aniche, D.C.; Ogbolu, B.O.; Rakib, M.R.J.; Uddin, J.; Walker, T.R. Governance Strategies for Mitigating Microplastic Pollution in the Marine Environment: A Review. Microplastics 2021, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, N.; Verma, P.; Shahi, S.K. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (phenanthrene and pyrene) by the ligninolytic fungi Ganoderma lucidum isolated from the hardwood stump. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2018, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Wang, P.; Li, J.L.; Wang, R.; Duan, L.; Luo, X.; Irfan, M.; Peng, Z.; Yin, L.; Li, W.-J. Impacts of bio-stimulants on pyrene degradation, prokaryotic community compositions, and functions. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atagana, H.I. Biodegradation of PAHs by fungi in contaminated-soil containing cadmium and nickel ions. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 5780–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, S.; Pandey, P.; Bhargava, B.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, V.; Krishan, D. Bioremediation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) using rhizosphere technology. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotsenko, I.V.; Mikhailenko, A.V. Phytoplankton and Its Role in Accumulation of Microelements in Bottom Deposits of Azov Sea. Sci. World J. 2019, 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, S.; Jesuraja, K.; Venkatramanan, S.; Roy, P.D.; Kumari, P.J. Hazardous microplastic characteristics and its role as a vector of heavy metal in groundwater and surface water of coastal south India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, N.; Kratofil Krehula, L.; Ptiček Siročić, A.; Hrnjak-Murgić, Z. Analysis of recycled PET bottles products by pyrolysis-gas chromatography. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leila, M.; Moscariello, A. Depositional and petrophysical controls on the volumes of hydrocarbons trapped in the Messinian reservoirs, onshore Nile Delta. Egypt Petroleum. 2018, 4, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Zeng, G.M.; Niu, Q.Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, L.H.; Tan, X.-F.; Xu, P.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, M. Bioremediation mechanisms of combined pollution of PAHs and heavy metals by bacteria and fungi: A mini review. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoog, D.A.; Holler, F.J.; Crouch, S.R. Principles of Instrumental Analysis, 7th ed.; Brooks/Cole, Ed.; Cengage Learning: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, J.J.; Davy, S.K.; Jones, T.; Taylor, M.W.; Webster, N.S. Could some coral reefs become sponge reefs as our climate changes? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2613–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawad, A.S.S. Acute toxicity of some heavy metals to the fresh water snail, Theodoxus niloticus (Reeve, 1856). Egypt J. Aquat. Res. 2018, 44, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igiri, B.E.; Okoduwa, S.I.R.; Idoko, G.O.; Akabuogu, E.P.; Adeyi, A.O.; Ejiogu, I.K. Toxicity and Bioremediation of Heavy Metals Contaminated Ecosystem from Tannery Wastewater: A Review. J. Toxicol. 2018, 2018, 2568038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armus, R.; Selry, C.; Marzuki, I.; Hasan, H.; Syamsia; Sapar, A. Investigation of Potential Marine Bacterial Isolates in Biodegradation Methods on Hydrocarbon Contamination. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Engineering, Makassar, Indonesia, 5 October 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melawaty, L.; Noor, A.; Harlim, H.; de Voogd, N. Essential metal Zn in sponge Callyspongia aerizusa from Spermonde Archipelago. Adv. Biol. Chem. 2014, 4, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Çoban-Yıldız, Y.; Chiavari, G.; Fabbri, D.; Gaines, A.F.; Galletti, G.; Tuğrul, S. The chemical composition of Black Sea suspended particulate organic matter: Pyrolysis-GC/MS as a complementary tool to traditional oceanographic analyses. Mar. Chem. 2000, 69, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermabessiere, L.; Himber, C.; Boricaud, B.; Kazour, M.; Amara, R.; Cassone, A.-L.; Laurentie, M.; Paul-Pont, I.; Soudant, P.; Dehaut, A.; et al. Optimization, performance, and application of a pyrolysis-GC/MS method for the identification of microplastics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 6663–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Guan, W. Fungal degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) by Scopulariopsis brevicaulis and its application in bioremediation of PAH-contaminated soil. Acta Agric. Scand Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2016, 66, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhamfar, M.; Abtahi, H.; Godini, K.; Saeedi, R.; Sartaj, M.; Villaseñor, J.; Coulon, F.; Kumar, V.; Soltanighias, T.; Ghaznavi-Rad, E.; et al. Biodegradation of heavy oily sludge by a two-step inoculation composting process using synergistic effect of indigenous isolated bacteria. Process Biochem. 2020, 91, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Sar, P.; Sarkar, J.; Dutta, A.; Gupta, A.; Mohapatra, B.; Pal, S.; Kazy, S.K. Petroleum hydrocarbon rich oil refinery sludge of North-East India harbours anaerobic, fermentative, sulfate-reducing, syntrophic and methanogenic microbial populations. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraswath, A.; Hallberg, R. Degradation of pyrene by indigenous fungi from a former gasworks site. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 210, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehu, U.; Ahmad, F.A.; Yusuf, F.; Muhammad, F.; Yakasai, H.M. Isolation and Identification of Anthracene Utilizing Proteus vulgaris from Oil Spill Contaminated Soil at NNPC Depot Kano State Nigeria. J. Adv. Biol. Biotechnol. 2021, 24, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, H.M.; de L-Barreto, L.R.; da Mota, A.J.; de Oliveira, L.A.; Barroso, H.; Zanotto, S.S.P. Tolerance to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) by filamentous fungi isolated from contaminated sediment in the Amazon region. Acta. Sci.-Biol. Sci. 2017, 39, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govarthanan, M.; Fuzisawa, S.; Hosogai, T.; Chang, Y.C. Biodegradation of aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons using the filamentous fungus Penicillium sp. CHY-2 and characterization of its manganese peroxidase activity. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 20716–20723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfa’I, M.; Arifin, A.; Kriswandana, F.; Thohari, I. The Design of Medical Waste Treatment in Public Health Center (MWT-P) for Reducing Total Bacteria Count in Banjarbaru. J. Kesehat. Lingkung 2020, 12, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mormede, S.; Davies, I.M. Polychlorobiphenyl and pesticide residues in monkfish Lophius piscatorius and black scabbard Aphanopus carbo from the Rockall Trough. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2001, 58, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Busch, K.; Wurz, E.; Rapp, H.T.; Bayer, K.; Franke, A.; Hentschel, U. Chloroflexi Dominate the Deep-Sea Golf Ball Sponges Craniella zetlandica and Craniella infrequens Throughout Different Life Stages. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, G.; Violi, B.; Bavestrello, G.; Pansini, M.; Bertolino, M. Aplysina aerophoba (Nardo, 1833) (Porifera, Demospongiae): An unexpected miniaturised growth form from the tidal zone of Mediterranean caves: Morphology and DNA barcoding. Eur. Zool. J. 2020, 87, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Stegeman, J.J.; Fleming, L.E.; Allemand, D.; Anderson, D.M.; Backer, L.C.; Brucker-Davis, F.; Chevalier, N.; Corra, L.; Czerucka, D.; et al. Human health and ocean pollution. Ann. Glob. Health 2020, 86, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafidi, M.; Shirkhan, F.; Zahedi, M.T.; Ziarati, P.; Hochwimmer, B. Risk Assessment of the Heavy Metals Contents in Ready-to-eat Vegetables in Distributed Brands at the Supply Level of Sales Centers in Tehran, Iran. Res. Line (IJCSREM) 2019, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziss, E.; Friesl-Hanl, W.; Noller, C.; Watzinger, A.; Hood-Nowotny, R. Heavy Metal City-Zen. Exploring the potential risk of heavy metal contamination of food crop plants in urban gardening contexts using a citizen science approach. EGU Gen. Assem. Conf. Abstr. 2020, 15, 8626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xia, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Hermanowicz, S.W. Associated Adsorption Characteristics of Pb (II) and Zn (II) by a Novel Biosorbent Extracted from Waste-Activated Sludge. Environ. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, L. Developing a new spectral index for detecting cadmium-induced stress in rice on a regional scale. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2019, 16, 4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, H. Facial synthesis of adsorbent from hemicelluloses for Cr(VI) adsorption. Molecules 2021, 26, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenea, A.G.; Vasile, G.G.; Dinu, C.; Gheorgh, S.; Pascu, L.F.; Mureseanu, M.; Ene, C. Behavior of Cd accumulation in sinapis alba L. In the presence of essential elements (Ca, Mg, Fe, Zn, Mn, Cu, Ni). Rev. Chim. 2020, 71, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Han, G.; Liu, M.; Li, X. The mercury behavior and contamination in soil profiles in mun river basin, Northeast Thailand. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Liu, M.; Zhang, B. A framework for rice heavy metal stress monitoring based on phenological phase space and temporal profile analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korytár, P.; Covaci, A.; De Boer, J.; Gelbin, A.; Brinkman, U.A.T. Retention-time database of 126 polybrominated diphenyl ether congeners and two Bromkal technical mixtures on seven capillary gas chromatographic columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1065, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, A.; Øysæd, K.B.; Palmas, L.; Skogerbø, G. Application of GC/MS-pyrolysis to estimate the levels of microplastics in a drinking water supply system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, N.-C. Organochlorine Pesticide Residues in Plankton, Rangsit Agricultural Area, Central Thailand W. Bull. Env. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 81, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Han, G.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Liang, B. Distribution and contamination assessment of soil heavy metals in the jiulongjiang river catchment, southeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomina, M.; Charnock, J.M.; Hillier, S.; Alvarez, R.; Livens, F.; Gadd, G.M. Role of fungi in the biogeochemical fate of depleted uranium. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohowa, B.; Kiteresi, L.I.; Wanjeri, V.W.; Mwamburi, S.M.; Tunje, S.L. Sponges as simple biomonitoring tools for trace element pollution in marine environments: Insights from a Kenyan study focused on the leaf sponge Phyllospongia foliascens. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 43, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Vries, I.; Schreiber, S.; Boßmann, D.; Hellmann, Z.; Kopatz, J.; Neumann, H.; Beutel, S. Single-use membrane adsorbers for endotoxin removal and purification of endogenous polysialic acid from Escherichia coli K1. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 17, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Franco, C.M.M.; Lin, H.W.; Zhang, W. Untapped sponge microbiomes: Structure specificity at host order and family levels. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käppler, A.; Fischer, M.; Scholz-Böttcher, B.M.; Oberbeckmann, S.; Labrenz, M.; Fischer, D.; Eichhorn, K.-J.; Voit, B. Comparison of μ-ATR-FTIR spectroscopy and py-GCMS as identification tools for microplastic particles and fibers isolated from river sediments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5313–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaboula, A.; Papadakis, E.; Vryzas, Z.; Kotopoulou, A.; Kintzikoglou, K.; Papadopoulou, M.E. Assessment and Management of Pesticide Pollution at a River Basin Level Part II: Optimization of Pesticide Monitoring Networks on Surface Aquatic Ecosystems by Data Analysis Methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 1597–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Love, D.C.; Rochman, C.M.; Neff, R.A. Microplastics in Seafood and the Implications for Human Health. Curr. Environ. Heal Rep. 2018, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Gadd, G.M. Fungal bioremediation of soil co-contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons and toxic metals. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 8999–9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galitskaya, P.; Biktasheva, L.; Blagodatsky, S.; Selivanovskaya, S. Response of bacterial and fungal communities to high petroleum pollution in different soils. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuki, I.; Pratama, I.; Ismail, H.E.; Paserangi, I.; Kamaruddin, M.; Chaerul, M.; Ahmad, R. The Identification and Distribution Components of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Contaminants at the Port of Paotere, Makassar, South Sulawesi. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Biotech. and Food Sciences, Surabaya, Indonesia, 11 September 2020; p. 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawad, A.S.S. Concentrations of heavy metals in water, sediment and mollusk gastropod, Lanistes carinatus from Lake Manzala, Egypt. Egypt J. Aquat. Res. 2018, 44, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, T.; Suryati, E.; Ahmad, T. Evaluation in a Shrimp Aquaculture System Using Mangroves, Oysters, and Seaweed as Biofilters Based on the Concentrations of Nutrients and Chlorophyll. JARQ 2006, 40, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bayan, I.E.; Yulianda, F.; Setyobudiandi, I. Degradation analysis of mangrove ecological function as macrozoobenthos habitat and its management in the Angke Kapuk Coastal Area, Jakarta. Biodiversitas (Bonorowo Wetl.) 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
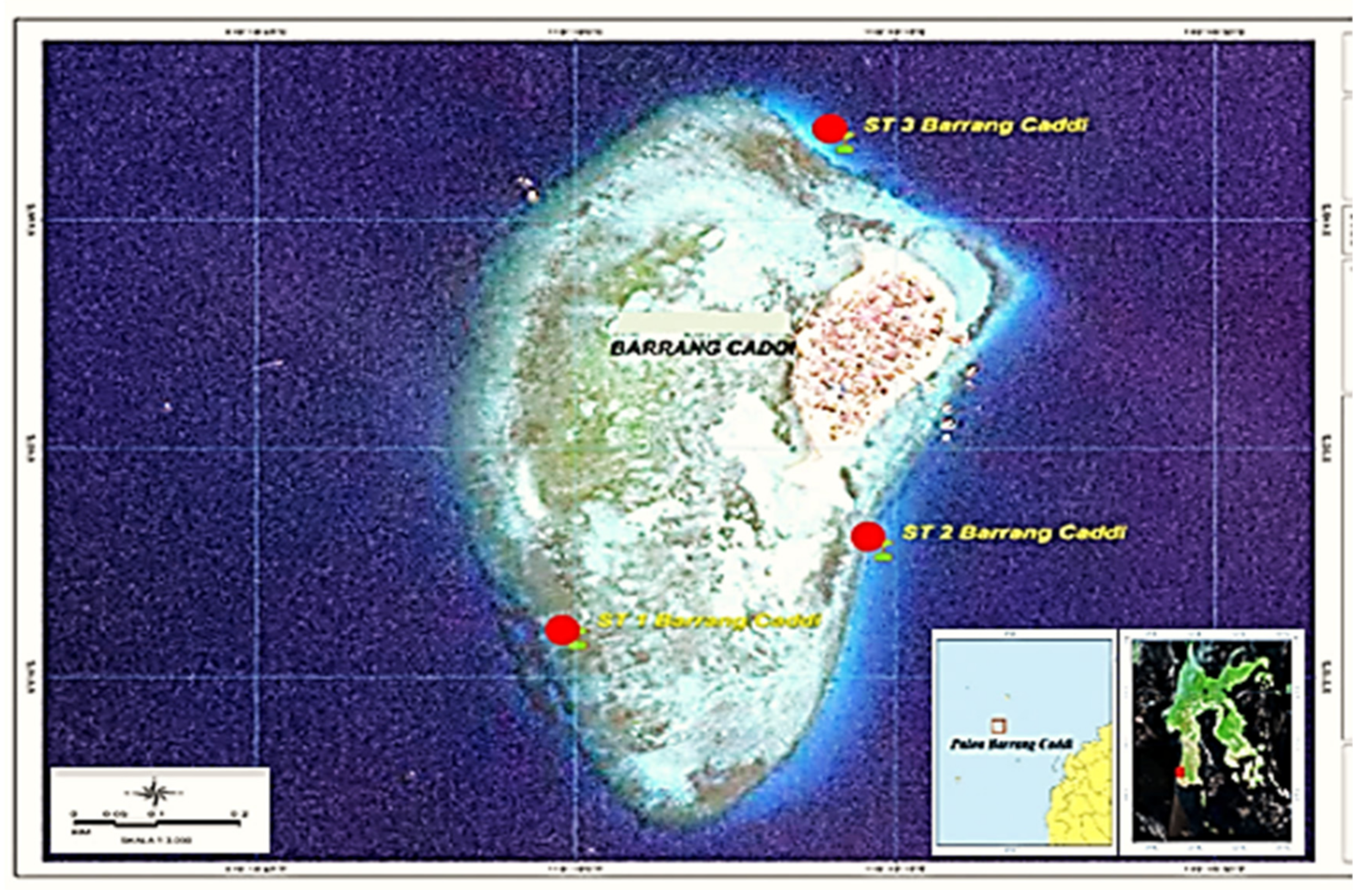
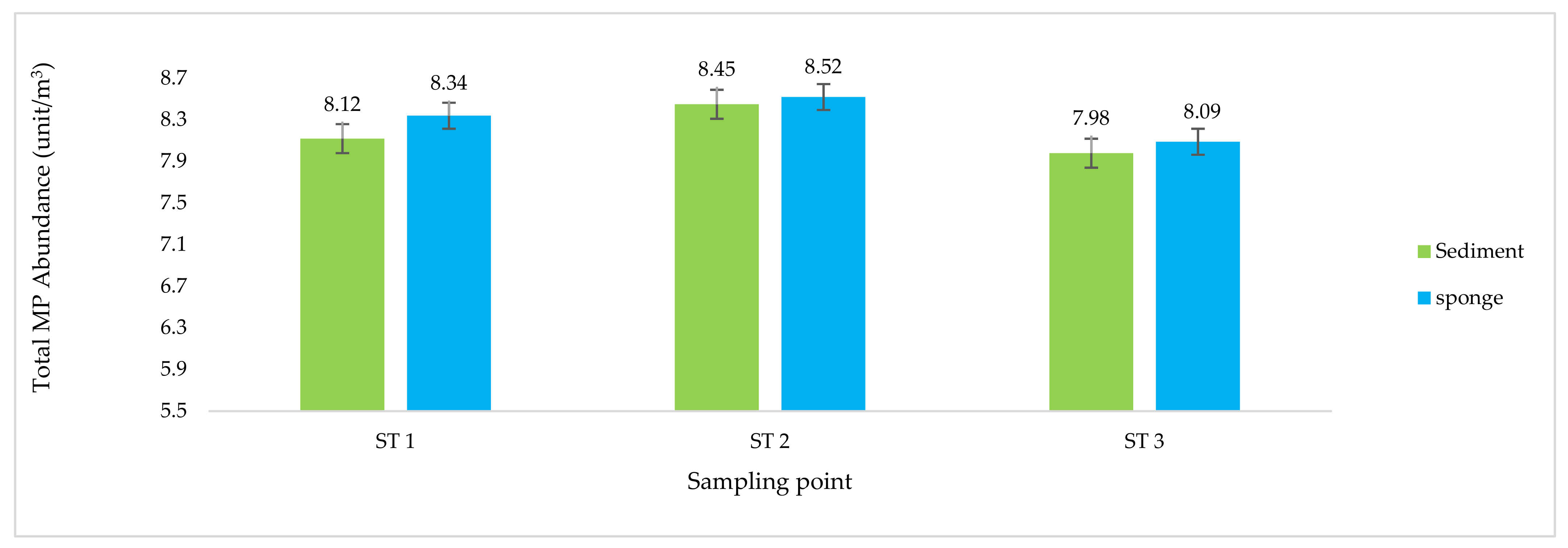

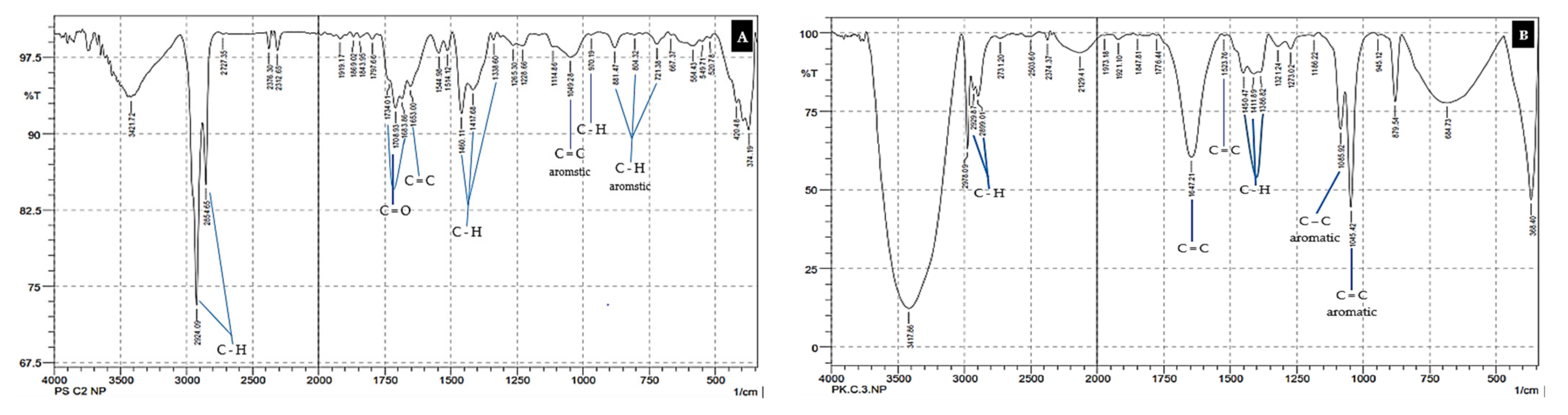
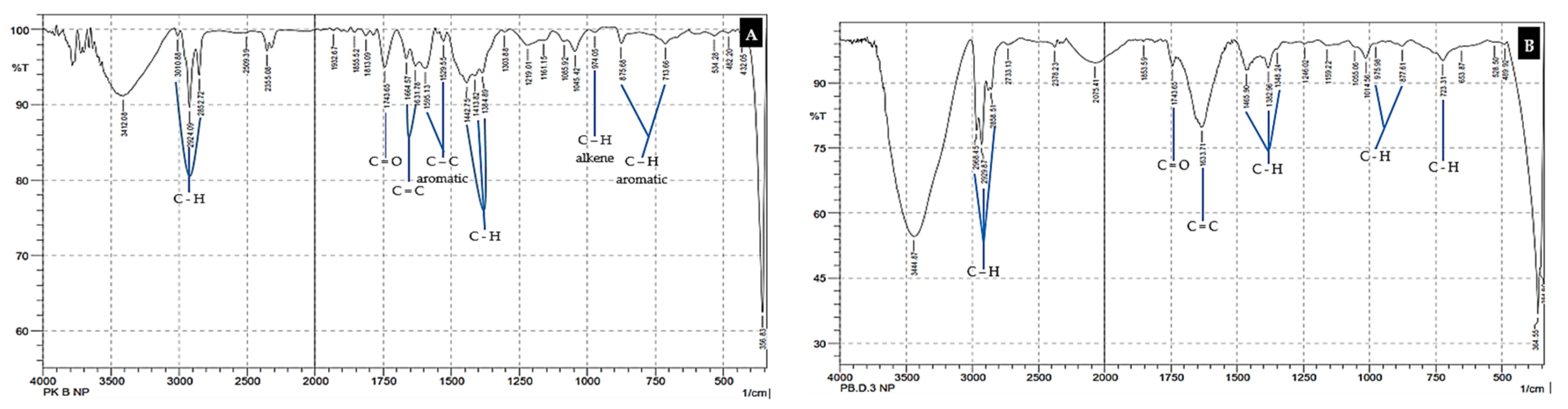
| Station Sampling | Coordinate | Depth MSL (m) | Distance from the Beach (m) | pH | Temperature (°C) | EC (ds/m) | TDS (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST 1 | 5°5′12.48216″ S 119°19′0.16536″ E | 5 | ±300 | 7.32 | 29.8 | 14.91 | 7.56 |
| ST 2 | 5°5′70.1664″ S 119°19′14.20716″ E | 6 | ±350 | 7.30 | 30.4 | 16.69 | 8.12 |
| ST 3 | 4°46′01664″ S 119°19′12.58932″ E | 8 | ±370 | 7.31 | 29.9 | 16.33 | 8.22 |
| Station Sampling | Sponges | Fishes |
|---|---|---|
| ST 1 | Cribrochalina olemda | Chrysiptera Unimaculata |
| ST 2 | Clathria Reinwardtii | Ambhygphidodon Curacao |
| ST 3 | Clathria sp. | Scolopsis Brenatus |
| Station Sampling | Sample Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sediment | Sponges | Marine Water | Fishes | |
| ST 1 | PA, PC, PE, PP PS, ABS | PA, PE, PP, PS, ABS | PC, PE, PP, PS, PVC, ABS | PA, PE, PC, PP, PS |
| ST 2 | PA, PC, PE, PP, PS | PA, PC, PE, PP, PS | PC, PE, PP, PS, ABS | PA, PC, PE, PP, PS |
| ST 3 | PA, PC, PE, PP, PS, PVC | PA, PC, PE, PS, PVC | PA, PC, PP, PS, PVC | PA, PC, PE, PS, PVC |
| Sample Type | Peak Number | Retention Time | Peak Height | Quality (%) | Abundance (%) | Compound Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sediment | 4 | 9.167 | 2,027,937 | 91 | 66,386 | NL |
| 6 | 15.550 | 68,138 | 90 | 2.324 | AZ | |
| 9 | 17.788 | 26,924 | 85 | 0.786 | PH | |
| 12 | 19.023 | 31,894 | 87 | 1.278 | PN | |
| Sponge | 2 | 9.168 | 2,565,156 | 91 | 76.539 | NL |
| 6 | 19.023 | 28,386 | 93 | 2.410 | PN | |
| 7 | 26.736 | 62,698 | 87 | 11.672 | BZ | |
| Sea water | 1 | 9.168 | 1,581,333 | 91 | 78.456 | NL |
| 3 | 15.550 | 87,843 | 91 | 3.045 | AZ | |
| Fish | 2 | 9.167 | 2,134,672 | 91 | 74.456 | NL |
| 6 | 26.736 | 54,789 | 88 | 8.192 | BZ |
| Sample Type | Peak Number | Retention Time | Peak Height | Quality (%) | Abundance (%) | Compound Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sediment | 1 | 9.168 | 1,125,323 | 91 | 84.221 | NL |
| 2 | 13.205 | 20,184 | 96 | 1.186 | PD | |
| Sediment | 3 | 15.549 | 54,212 | 85 | 3.643 | AZ |
| 4 | 17.788 | 18,406 | 85 | 1.369 | PH | |
| 6 | 19.023 | 62,311 | 89 | 3.409 | PN | |
| 8 | 26.735 | 71,925 | 86 | 5.357 | BZ | |
| Sponge | 3 | 9.167 | 3,219,575 | 91 | 86.046 | NL |
| 4 | 13.206 | 44,603 | 97 | 0.978 | PD | |
| 6 | 16.283 | 14,355 | 86 | 0.696 | PT | |
| 8 | 19.023 | 31,674 | 87 | 1.312 | PN | |
| Sea water | 3 | 9.168 | 860,498 | 91 | 63.945 | NL |
| 4 | 13.205 | 20,327 | 96 | 1.204 | PD | |
| 9 | 19.023 | 138,767 | 96 | 10.165 | PN | |
| Fish | 2 | 9.168 | 4,322,267 | 87 | 89.859 | NL |
| 4 | 19.023 | 12,458 | 92 | 3.146 | PN |
| Sample Type | Peak Number | Retention Time | Peak Height | Quality (%) | Abundance (%) | Compound Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sediment | 2 | 9.168 | 1,222,751 | 91 | 82.356 | NL |
| 4 | 15.549 | 88,566 | 90 | 3.087 | AZ | |
| 5 | 16.283 | 22,123 | 86 | 1.126 | PT | |
| 7 | 19.023 | 99,864 | 88 | 4.106 | PN | |
| 9 | 26.734 | 67,854 | 86 | 2.123 | BZ | |
| Sponge | 2 | 9.167 | 2,423,789 | 91 | 78.127 | NL |
| 4 | 15.550 | 65,832 | 85 | 3.983 | AZ | |
| 6 | 16.283 | 16,732 | 86 | 0.883 | PT | |
| 8 | 19.023 | 34,376 | 87 | 1.515 | PN | |
| Sea water | 2 | 9.168 | 1,222,751 | 91 | 82.356 | NL |
| 4 | 16.283 | 21,874 | 86 | 1.083 | PT | |
| 6 | 19.023 | 64,357 | 88 | 2.982 | PN | |
| Fish | 3 | 9.168 | 1,111,244 | 91 | 64.362 | NL |
| 5 | 19.023 | 13,318 | 87 | 0.734 | PN |
| Type of Pollutant | Sampling Station | Average Concentration of Pollutants Replication (n = 3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sediment (µg/g) | Sponge (µg/g) | Sea Water (mg/L) | Fish (µg/kg) | ||
| Lead ion (Pb+2) | ST 1 | 4.041 ± 0.0004 | 3.871 ± 0.0003 | 0.104 ± 0.0002 | 2.452 ± 0.0003 |
| ST 2 | 4.676 ± 0.0003 | 3.725 ± 0.0002 | 0.251 ± 0.0002 | 1.656 ± 0.0001 | |
| ST 3 | 4.643 ± 0.0005 | 3.813 ± 0.0004 | 0.137 ± 0.0005 | 1.326 ± 0.0004 | |
| Average: | 4.453 ± 0.0003 | 3.803 ± 0.0003 | 0.164 ± 0.0001 | 1.811 ± 0.0002 | |
| Copper ion (Cu+2) | ST 1 | 9.279 ± 0.0001 | 6.166 ± 0.0002 | 0.319 ± 0.0002 | 4.822 ± 0.0001 |
| ST 2 | 8.843 ± 0.0001 | 5.567 ± 0.0003 | 0.286 ± 0.0003 | 4.474 ± 0.0002 | |
| ST 3 | 7.920 ± 0.0002 | 5.474 ± 0.0002 | 0.275 ± 0.0004 | 3.821 ± 0.0004 | |
| Average: | 8.681 ± 0.0004 | 5.735 ± 0.0007 | 0.293 ± 0.0007 | 4.372 ± 0.0003 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marzuki, I.; Septiningsih, E.; Kaseng, E.S.; Herlinah, H.; Sahrijanna, A.; Sahabuddin, S.; Asaf, R.; Athirah, A.; Isnawan, B.H.; Samidjo, G.S.; et al. Investigation of Global Trends of Pollutants in Marine Ecosystems around Barrang Caddi Island, Spermonde Archipelago Cluster: An Ecological Approach. Toxics 2022, 10, 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10060301
Marzuki I, Septiningsih E, Kaseng ES, Herlinah H, Sahrijanna A, Sahabuddin S, Asaf R, Athirah A, Isnawan BH, Samidjo GS, et al. Investigation of Global Trends of Pollutants in Marine Ecosystems around Barrang Caddi Island, Spermonde Archipelago Cluster: An Ecological Approach. Toxics. 2022; 10(6):301. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10060301
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarzuki, Ismail, Early Septiningsih, Ernawati Syahruddin Kaseng, Herlinah Herlinah, Andi Sahrijanna, Sahabuddin Sahabuddin, Ruzkiah Asaf, Admi Athirah, Bambang Heri Isnawan, Gatot Supangkat Samidjo, and et al. 2022. "Investigation of Global Trends of Pollutants in Marine Ecosystems around Barrang Caddi Island, Spermonde Archipelago Cluster: An Ecological Approach" Toxics 10, no. 6: 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10060301
APA StyleMarzuki, I., Septiningsih, E., Kaseng, E. S., Herlinah, H., Sahrijanna, A., Sahabuddin, S., Asaf, R., Athirah, A., Isnawan, B. H., Samidjo, G. S., Rumagia, F., Hamidah, E., Santi, I. S., & Nisaa, K. (2022). Investigation of Global Trends of Pollutants in Marine Ecosystems around Barrang Caddi Island, Spermonde Archipelago Cluster: An Ecological Approach. Toxics, 10(6), 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10060301
















