Towards the Development of Standardized Bioassays for Corals: Acute Toxicity of the UV Filter Benzophenone-3 to Scleractinian Coral Larvae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Coral Species and Acquisition of Larvae
2.3. Preparation of Test Media
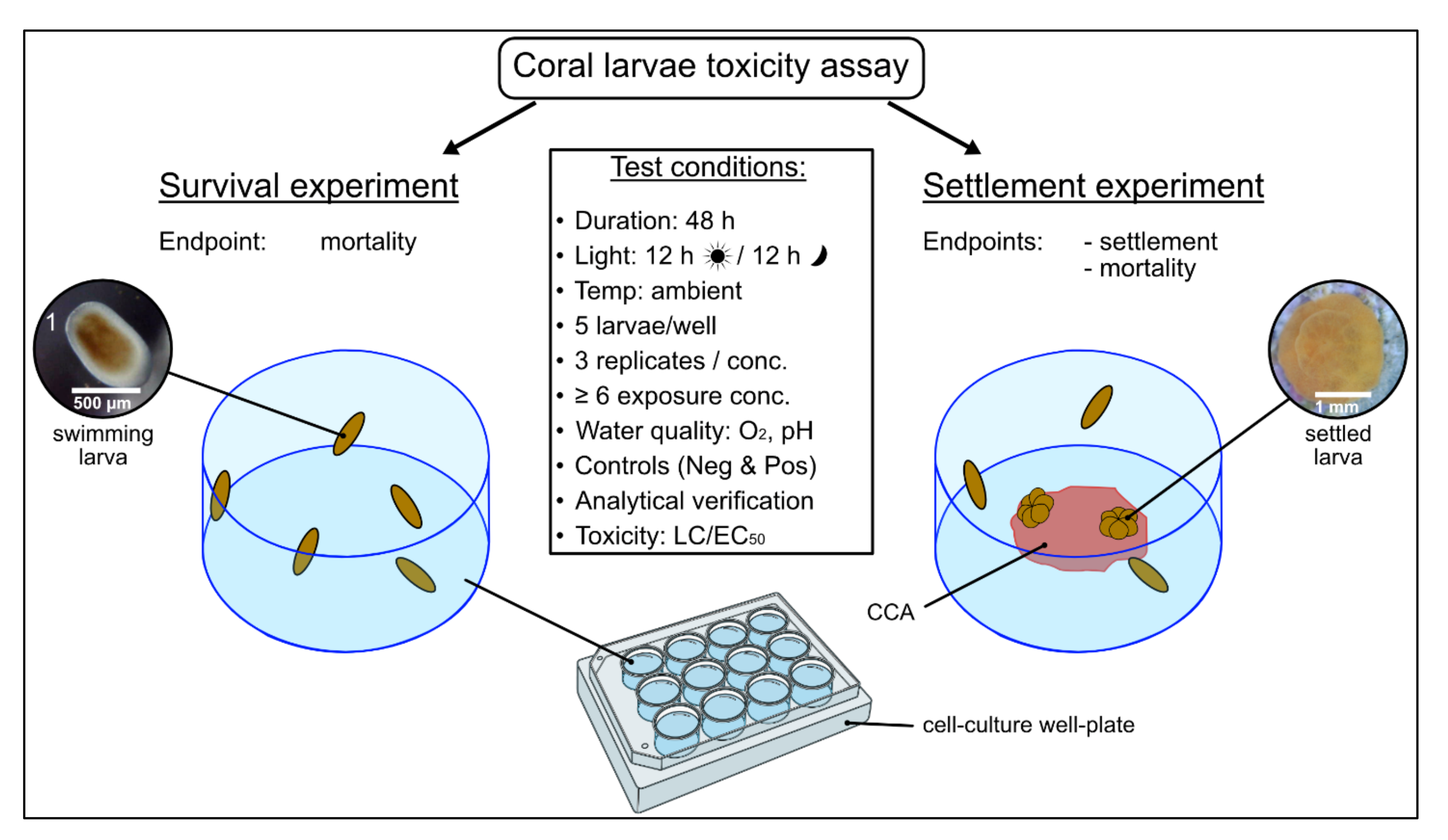
2.4. Acute Larvae Toxicity Assays
2.5. Water Quality
2.6. Chemical Analysis for Verification of Exposure Concentrations
2.6.1. Sampling and Sample Preparation
2.6.2. Analytical System
2.6.3. Identification and Quantification of BP3
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Verification of Exposure Concentrations
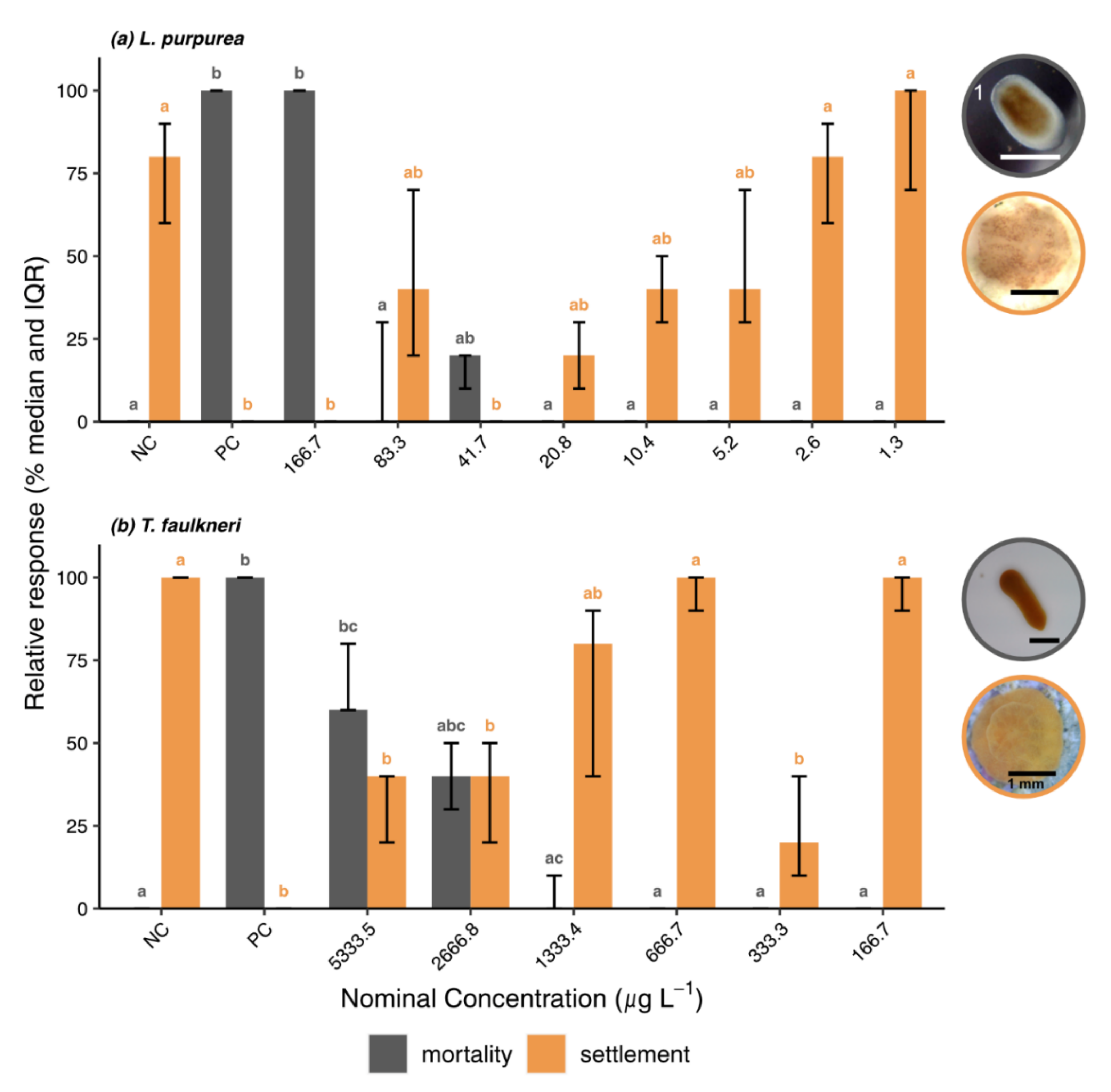
3.2. Bioassays
3.2.1. Survival Bioassays
3.2.2. Settlement Bioassays
3.3. Biological Endpoints
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations and Implications for the Development of a Standard Toxicity Test for Corals
4.1.1. Assay Performance and Choice of Toxicological Endpoints
4.1.2. Considerations for Settlement as an Endpoint
4.1.3. Coral Recruits as Another Possible Early Life Stage Endpoint
4.1.4. Analytical Challenges in Small Water Volumes
4.2. Toxicity Thresholds
4.3. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moberg, F.; Folke, C. Ecological goods and services of coral reef ecosystems. Ecol. Econ. 1999, 29, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, L.; Reytar, K.; Spalding, M.; Perry, A. Reefs at Risk Revisited; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; ISBN 9781569737620. [Google Scholar]
- Spalding, M.D.; Grenfell, A.M. New estimates of global and regional coral reef areas. Coral Reefs 1997, 16, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.; O’Leary, R.A.; Low-Choy, S.; Mengersen, K.; Knowlton, N.; Brainard, R.E.; Caley, M.J. Species richness on coral reefs and the pursuit of convergent global estimates. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Goeij, J.M.; Van Oevelen, D.; Vermeij, M.J.A.; Osinga, R.; Middelburg, J.J.; De Goeij, A.F.P.M.; Admiraal, W. Surviving in a marine desert: The sponge loop retains resources within coral reefs. Science 2013, 342, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rädecker, N.; Pogoreutz, C.; Voolstra, C.R.; Wiedenmann, J.; Wild, C. Nitrogen cycling in corals: The key to understanding holobiont functioning? Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rougerie, F.; Wauthy, B. The endo-upwelling concept: From geothermal convection to reef construction. Coral Reefs 1993, 12, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O. Climate change, coral bleaching and the future of the world’s coral reefs. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1999, 50, 839–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, T.P.; Kerry, J.T.; Álvarez-Noriega, M.; Álvarez-Romero, J.G.; Anderson, K.D.; Baird, A.H.; Babcock, R.C.; Beger, M.; Bellwood, D.R.; Berkelmans, R.; et al. Global warming and recurrent mass bleaching of corals. Nature 2017, 543, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellwood, D.R.; Hughes, T.P.; Folke, C.; Nyström, M. Confronting the coral reef crisis. Nature 2004, 429, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Poloczanska, E.S.; Skirving, W.; Dove, S. Coral reef ecosystems under climate change and ocean acidification. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roff, G.; Mumby, P.J. Global disparity in the resilience of coral reefs. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, T.P.; Linares, C.; Dakos, V.; van de Leemput, I.A.; van Nes, E.H. Living dangerously on borrowed time during slow, unrecognized regime shifts. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, T.P.; Barnes, M.L.; Bellwood, D.R.; Cinner, J.E.; Cumming, G.S.; Jackson, J.B.C.; Kleypas, J.; van de Leemput, I.A.; Lough, J.M.; Morrison, T.H.; et al. Coral reefs in the Anthropocene. Nature 2017, 546, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; The Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 9789291691432. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Heron, S.F.; Maynard, J.A.; Van Hooidonk, R.; Eakin, C.M. Warming Trends and Bleaching Stress of the World’s Coral Reefs 1985-2012. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, T.P.; Anderson, K.D.; Connolly, S.R.; Heron, S.F.; Kerry, J.T.; Lough, J.M.; Baird, A.H.; Baum, J.K.; Berumen, M.L.; Bridge, T.C.; et al. Spatial and temporal patterns of mass bleaching of corals in the Anthropocene. Science 2018, 359, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eakin, C.M.; Sweatman, H.P.A.; Brainard, R.E. The 2014–2017 global-scale coral bleaching event: Insights and impacts. Coral Reefs 2019, 38, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, T.P.; Kerry, J.T.; Baird, A.H.; Connolly, S.R.; Dietzel, A.; Eakin, C.M.; Heron, S.F.; Hoey, A.S.; Hoogenboom, M.O.; Liu, G.; et al. Global warming transforms coral reef assemblages. Nature 2018, 556, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hooidonk, R.; Maynard, J.; Tamelander, J.; Gove, J.; Ahmadia, G.; Raymundo, L.; Williams, G.; Heron, S.F.; Planes, S. Local-scale projections of coral reef futures and implications of the Paris Agreement. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.B.C.; Kirby, M.X.; Berger, W.H.; Bjorndal, K.A.; Botsford, L.W.; Bourque, B.J.; Bradbury, R.H.; Cooke, R.; Erlandson, J.; Estes, J.A.; et al. Historical overfishing and the recent collapse of coastal ecosystems. Science 2001, 293, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raymundo, L.J.; Halford, A.R.; Maypa, A.P.; Kerr, A.M. Functionally diverse reef-fish communities ameliorate coral disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17067–17070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, C.M. Effects of Fishing on the Ecosystem Structure of Coral Reefs. Conserv. Biol. 1995, 9, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, T.P.; Baird, A.H.; Bellwood, D.R.; Card, M.; Connolly, S.R.; Folke, C.; Grosberg, R.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Jackson, J.B.C.; Kleypas, J.; et al. Climate change, human impacts, and the resilience of coral reefs. Science 2003, 301, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellwood, D.R.; Hoey, A.S.; Choat, J.H. Limited functional redundancy in high diversity systems: Resilience and ecosystem function on coral reefs. Ecol. Lett. 2003, 6, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Graham, N.A.J.; Jackson, J.B.C.; Mumby, P.J.; Steneck, R.S. Rising to the challenge of sustaining coral reef resilience. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, N.A.J.; Jennings, S.; MacNeil, M.A.; Mouillot, D.; Wilson, S.K. Predicting climate-driven regime shifts versus rebound potential in coral reefs. Nature 2015, 518, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Barrett, S.; Carpenter, S.R.; Folke, C.; Green, A.J.; Holmgren, M.; Hughes, T.P.; Kosten, S.; Van De Leemput, I.A.; Nepstad, D.C.; et al. Creating a safe operating space for iconic ecosystems: Manage local stressors to promote resilience to global change. Science 2015, 347, 1317–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van de Leemput, I.A.; Hughes, T.P.; van Nes, E.H.; Scheffer, M. Multiple feedbacks and the prevalence of alternate stable states on coral reefs. Coral Reefs 2016, 35, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giokas, D.L.; Salvador, A.; Chisvert, A. UV filters: From sunscreens to human body and the environment. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisvert, A.; Salvador, A. UV Filters in Sunscreens and other Cosmetics. Regulatory Aspects and Analytical Methods. In Analysis of Cosmetic Products; Salvador, A., Chisvert, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 83–120. ISBN 978-0-444-52260-3. [Google Scholar]
- Osterwalder, U.; Sohn, M.; Herzog, B. Global state of sunscreens. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2014, 30, 62–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawlowski, S.; Petersen-Thiery, M. Sustainable Sunscreens: A Challenge Between Performance, Animal Testing Ban, and Human and Environmental Safety. In Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020; Volume 94, pp. 185–207. [Google Scholar]
- Downs, C.A.; Kramarsky-Winter, E.; Fauth, J.E.; Segal, R.; Bronstein, O.; Jeger, R.; Lichtenfeld, Y.; Woodley, C.M.; Pennington, P.; Kushmaro, A.; et al. Toxicological effects of the sunscreen UV filter, benzophenone-2, on planulae and in vitro cells of the coral, Stylophora pistillata. Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, C.A.; Kramarsky-Winter, E.; Segal, R.; Fauth, J.; Knutson, S.; Bronstein, O.; Ciner, F.R.; Jeger, R.; Lichtenfeld, Y.; Woodley, C.M.; et al. Toxicopathological Effects of the Sunscreen UV Filter, Oxybenzone (Benzophenone-3), on Coral Planulae and Cultured Primary Cells and Its Environmental Contamination in Hawaii and the U. S. Virgin Islands. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 70, 265–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Wang, W.H. Membrane lipid profiles of coral responded to zinc oxide nanoparticle-induced perturbations on the cellular membrane. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 187, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanović, B.; Guzmán, H.M. Effects of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles on caribbean reef-building coral (Montastraea faveolata). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifan, H. Alarming the impacts of the organic and inorganic UV blockers on endangered coral’s species in the Persian Gulf: A scientific concern for coral protection. Sustain. Future 2020, 2, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Tsui, M.M.P.; Tan, C.J.; Ng, K.Y.; Guo, F.W.; Wang, L.H.; Chen, T.H.; Fan, T.Y.; Lam, P.K.S.; Murphy, M.B. Comparative toxicities of four benzophenone ultraviolet filters to two life stages of two coral species. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2391–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Tsui, M.M.P.; Tan, C.J.; Ma, C.Y.; Yiu, S.K.F.; Wang, L.H.; Chen, T.H.; Fan, T.Y.; Lam, P.K.S.; Murphy, M.B. Toxicological effects of two organic ultraviolet filters and a related commercial sunscreen product in adult corals. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stien, D.; Clergeaud, F.; Rodrigues, A.M.S.; Lebaron, K.; Pillot, R.; Romans, P.; Fagervold, S.; Lebaron, P. Metabolomics Reveal That Octocrylene Accumulates in Pocillopora damicornis Tissues as Fatty Acid Conjugates and Triggers Coral Cell Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fel, J.-P.; Lacherez, C.; Bensetra, A.; Mezzache, S.; Béraud, E.; Léonard, M.; Allemand, D.; Ferrier-Pagès, C. Photochemical response of the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata to some sunscreen ingredients. Coral Reefs 2019, 38, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCoshum, S.M.; Schlarb, A.M.; Baum, K.A. Direct and indirect effects of sunscreen exposure for reef biota. Hydrobiologia 2016, 776, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corinaldesi, C.; Marcellini, F.; Nepote, E.; Damiani, E.; Danovaro, R. Impact of inorganic UV filters contained in sunscreen products on tropical stony corals (Acropora spp.). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijgerde, T.; van Ballegooijen, M.; Nijland, R.; van der Loos, L.; Kwadijk, C.; Osinga, R.; Murk, A.; Slijkerman, D. Adding insult to injury: Effects of chronic oxybenzone exposure and elevated temperature on two reef-building corals. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danovaro, R.; Bongiorni, L.; Corinaldesi, C.; Giovannelli, D.; Damiani, E.; Astolfi, P.; Greci, L.; Pusceddu, A. Sunscreens Cause Coral Bleaching by Promoting Viral Infections. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stien, D.; Suzuki, M.; Rodrigues, A.M.S.; Yvin, M.; Clergeaud, F.; Thorel, E.; Lebaron, P. A unique approach to monitor stress in coral exposed to emerging pollutants. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, M.; Pawlowski, S.; Petersen-Thiery, M.; Miller, I.B.; Nietzer, S.; Heisel-Sure, Y.; Kellermann, M.Y.; Schupp, P.J. Challenges in Current Coral Reef Protection – Possible Impacts of UV Filters Used in Sunscreens, a Critical Review. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchelmore, C.L.; Burns, E.E.; Conway, A.; Heyes, A.; Davies, I.A. A Critical Review of Organic Ultraviolet Filter Exposure, Hazard, and Risk to Corals. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 967–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, I.B.; Pawlowski, S.; Kellermann, M.Y.; Petersen-Thiery, M.; Moeller, M.; Nietzer, S.; Schupp, P.J. Toxic effects of UV filters from sunscreens on coral reefs revisited: Regulatory aspects for “reef safe” products. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 2021, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, E.E.; Davies, I.A. Coral Ecotoxicological Data Evaluation for the Environmental Safety Assessment of Ultraviolet Filters. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 3441–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, S.; Moeller, M.; Miller, I.B.; Kellermann, M.Y.; Schupp, P.J.; Petersen-Thiery, M. UV filters used in sunscreens—A lack in current coral protection? Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2021, 17, 926–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, R. Reproduction and Recruitment in Corals: Critical Links in the Persistence of Reefs. In Life and Death of Coral Reefs; Birkeland, C., Ed.; Springer: Jersey City, NJ, USA, 1997; pp. 174–197. ISBN 9781461559955. [Google Scholar]
- Richmond, R.H.; Tisthammer, K.H.; Spies, N.P. The Effects of Anthropogenic Stressors on Reproduction and Recruitment of Corals and Reef Organisms. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kushmaro, A.; Henning, G.; Hofmann, D.K.; Benayahu, Y. Metamorphosis of Heteroxenia fuscescens planulae (Cnidaria: Octocorallia) is inhibited by crude oil: A novel short term toxicity bioassay. Mar. Environ. Res. 1997, 43, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, M.; Nietzer, S.; Schils, T.; Schupp, P.J. Low sediment loads affect survival of coral recruits: The first weeks are crucial. Coral Reefs 2017, 36, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penin, L.; Michonneau, F.; Baird, A.H.; Connolly, S.R.; Pratchett, M.S.; Kayal, M.; Adjeroud, M. Early post-settlement mortality and the structure of coral assemblages. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 408, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adjeroud, M.; Kayal, M.; Penin, L. Importance of Recruitment Processes in the Dynamics and Resilience of Coral Reef Assemblages. In Marine Animal Forests: The Ecology of Benthic Biodiversity Hotspots; Rossi, S., Bramanti, L., Gori, A., Orejas, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–1366. ISBN 978-3-319-21011-7. [Google Scholar]
- Negri, A.; Vollhardt, C.; Humphrey, C.; Heyward, A.; Jones, R.; Eaglesham, G.; Fabricius, K. Effects of the herbicide diuron on the early life history stages of coral. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, A.P.; Smith, L.D.; Webster, N.S.; Heyward, A.J. Understanding ship-grounding impacts on a coral reef: Potential effects of anti-foulant paint contamination on coral recruitment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, S.; Downs, C.A.; Richmond, R.H. Concentrations of Irgarol in selected marinas of Oahu, Hawaii and effects on settlement of coral larval. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, N.; Bak, R.P.M.; Rinkevich, B. Toxicity of third generation dispersants and dispersed Egyptian crude oil on Red Sea coral larvae. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, A.; Harrison, P.L. Effects of oil contaminants on survivorship of larvae of the scleractinian reef corals Acropora tenuis, Goniastrea aspera and Platygyra sinensis from the Great Barrier Reef. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Coral Reef Symposium, Bali, Indonesia, 23–27 October 2000; Volume 1, pp. 6–408. [Google Scholar]
- Negri, A.P.; Heyward, A.J. Inhibition of Fertilization and Larval Metamorphosis of the Coral Acropora millepora (Ehrenberg, 1834) by Petroleum Products. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 41, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodbody-Gringley, G.; Wetzel, D.L.; Gillon, D.; Pulster, E.; Miller, A.; Ritchie, K.B. Toxicity of Deepwater Horizon Source Oil and the Chemical Dispersant, Corexit® 9500, to Coral Larvae. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e45574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordborg, F.M.; Flores, F.; Brinkman, D.L.; Agustí, S.; Negri, A.P. Phototoxic effects of two common marine fuels on the settlement success of the coral Acropora tenuis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, D.F.; Hofmann, D.K. Coral larvae: From gametes to recruits. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2011, 408, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ChemicalBook. Chemical Book. Available online: https://www.chemicalbook.com/productindex_en.aspx (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- ChemSpider. Search and Share Chemistry. Available online: http://www.chemspider.com/ (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- ECHA. The REACH registration dossier. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/registered-substances (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- Nietzer, S.; Moeller, M.; Kitamura, M.; Schupp, P.J. Coral Larvae Every Day: Leptastrea purpurea, a Brooding Species That Could Accelerate Coral Research. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moeller, M.; Nietzer, S.; Schupp, P.J. Neuroactive compounds induce larval settlement in the scleractinian coral Leptastrea purpurea. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craggs, J.; Guest, J.R.; Davis, M.; Simmons, J.; Dashti, E.; Sweet, M. Inducing broadcast coral spawning ex situ: Closed system mesocosm design and husbandry protocol. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 11066–11078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. OECD Guidance Document on Aquatic Toxicity Testing of Difficult Substances and Mixtures. In Series on Testing and Assessment No. 23, 2nd ed.; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2019; pp. 1–81. [Google Scholar]
- Heyward, A.J.; Negri, A.P. Natural inducers for coral larval metamorphosis. Coral Reefs 1999, 18, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, A.P.; Heyward, A.J. Inhibition of coral fertilisation and larval metamorphosis by tributyltin and copper. Mar. Environ. Res. 2001, 51, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lee, H.K. Determination of ultraviolet filters in water samples by vortex-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1249, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMEA ICH Q2 (R1) Validation of analytical procedures: Text and methodology—Step 5. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-q2-r1-validation-analytical-procedures-text-methodology (accessed on 6 May 2021).
- RStudio Team RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 21 December 2021).
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of Ranks in One-Criterion Variance Analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, O.J. Multiple Comparisons Using Rank Sums. Technometrics 1964, 6, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, S.C. LD50/LC50 (Lethal Dosage 50/Lethal Concentration 50). In Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 3rd ed.; Wexler, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; Volume 50, pp. 58–60. ISBN 978-0-12-386455-0. [Google Scholar]
- Savi, M.K.; Mangamana, E.T.; Deguenon, J.M.; Hounmenou, C.G.; Kakaï, R.G. Determination of Lethal Concentrations Using an R Software Function Integrating the Abbott Correction. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. A 2017, 7, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- OECD. OECD Current Approaches in the Statistical analysis of Ecotoxicity data: A Guidance to application. In OECD Environment Health and Safety Publications—Series on Testing and Assessment No. 54; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2006; pp. 1–147. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, M.W.; Park, R.M.; Bailer, A.J. Comparing median lethal concentration values using confidence interval overlap or ratio tests. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 1441–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, A.P.; Brinkman, D.L.; Flores, F.; Botte, E.S.; Jones, R.J.; Webster, N.S. Acute ecotoxicology of natural oil and gas condensate to coral reef larvae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overmans, S.; Nordborg, M.; Díaz-Rúa, R.; Brinkman, D.L.; Negri, A.P.; Agustí, S. Phototoxic effects of PAH and UVA exposure on molecular responses and developmental success in coral larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 198, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, L.-E.; Kellermann, M.Y.; Nietzer, S.; Schupp, P.J. Photosensitivity of the Bacterial Pigment Cycloprodigiosin Enables Settlement in Coral Larvae—Light as an Understudied Environmental Factor. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.E.; Moeller, M.; Versluis, D.; Nietzer, S.; Kellermann, M.Y.; Schupp, P.J. Mono- and multispecies biofilms from a crustose coralline alga induce settlement in the scleractinian coral Leptastrea purpurea. Coral Reefs 2021, 40, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, A.J.; Gonsior, M.; Clark, C.; Heyes, A.; Mitchelmore, C.L. Acute toxicity of the UV filter oxybenzone to the coral Galaxea fascicularis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. OECD Test No. 305: Bioaccumulation in Fish: Aqueous and Dietary Exposure. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 3; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2012; pp. 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- McCook, L.J.; Jompa, J.; Diaz-Pulido, G. Competition between corals and algae on coral reefs: A review of evidence and mechanisms. Coral Reefs 2001, 19, 400–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littler, M.M.; Littler, D.S. Epithallus sloughing: A self-cleaning mechanism for coralline algae. Coral Reefs 1999, 18, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, T.D.; Schellinger, J.L.; Strimaitis, A.M.; Reuter, K.E. Evolution of anthozoan polyp retraction mechanisms: Convergent functional morphology and evolutionary allometry of the marginal musculature in order Zoanthidea (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Hexacorallia). BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- May, L.A.; Burnett, A.R.; Miller, C.V.; Pisarski, E.; Webster, L.F.; Moffitt, Z.J.; Pennington, P.; Wirth, E.; Baker, G.; Ricker, R.; et al. Effect of Louisiana sweet crude oil on a Pacific coral, Pocillopora damicornis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 222, 105454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.D.; Negri, A.P.; Philipp, E.; Webster, N.S.; Heyward, A.J. The effects of antifoulant-paint-contaminated sediments on coral recruits and branchlets. Mar. Biol. 2003, 143, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, J.; Altenburger, R. Physicochemical substance properties as indicators for unreliable exposure in microplate-based bioassays. Chemos 2007, 67, 2210–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. OECD Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2: Effects on Biotic Systems; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013; pp. 1–22. ISBN 9789264203709. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber, R.; Altenburger, R.; Paschke, A.; Kluester, E. How to deal with lipophilic and volatile organic substances in microtiter plate assays. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1676–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlowski, S.; Lanzinger, A.C.; Dolich, T.; Füßl, S.; Salinas, E.R.; Zok, S.; Weiss, B.; Hefner, N.; Van Sloun, P.; Hombeck, H.; et al. Evaluation of the bioaccumulation of octocrylene after dietary and aqueous exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kais, B.; Schneider, K.E.; Keiter, S.; Henn, K.; Ackermann, C.; Braunbeck, T. DMSO modifies the permeability of the zebrafish (Danio rerio) chorion-Implications for the fish embryo test (FET). Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 140–141, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gironi, B.; Kahveci, Z.; McGill, B.; Lechner, B.D.; Pagliara, S.; Metz, J.; Morresi, A.; Palombo, F.; Sassi, P.; Petrov, P.G. Effect of DMSO on the Mechanical and Structural Properties of Model and Biological Membranes. Biophys. J. 2020, 119, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Mauro, V.; Kamyab, E.; Nietzer, S.; Kellermann, M.Y.; Miller, I.B.; Pawlowski, S.; Petersen-Thiery, M.; Schupp, P.J. Ecotoxicological Effects of Commonly Used Organic Solvents on the Coral Species Montipora digitata in a 16-days Exposure; Environmental Biochemistry Group; Institute for Chemsitry and Biology of the Marine Environment (ICBM); Carl von Ossietzky University Oldenburg: Wilhelmshaven, Germany, 2022; manuscript in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- National Health and Environmental Effects Research Laboratory (NHEERL); Mid-Continent Ecology Division (MED). EPA/600/R-01/067: A Short-term Test Method for Assessing the Reproductive Toxicity of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals Using the Fathead Minnow (Pimephales promelas); United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Duluth, MN, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Nordborg, F.M.; Brinkman, D.L.; Ricardo, G.F.; Agustí, S.; Negri, A.P. Comparative sensitivity of the early life stages of a coral to heavy fuel oil and UV radiation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.L.; Wallace, C.W. Reproduction, dispersal and recruitment of scleractinian corals. In Ecosystems of the World: Coral Reefs; Dubinsky, Z., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 133–207. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, A.M.; Baird, A.H.; Hughes, T.P. Correlated evolution of sex and reproductive mode in corals (Anthozoa: Scleractinia). Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 278, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, A.H.; Guest, J.R.; Willis, B.L. Systematic and Biogeographical Patterns in the Reproductive Biology of Scleractinian Corals. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 551–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Nominal Concentration 1 (µg L−1) | Measured Concentration (µg L−1) | Recovery 2 (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. purpurea | T. faulkneri | A. millepora | A. digitifera | ||||
| Survival | Settlement | Survival | Settlement | Survival | Survival | ||
| 6000 (Stock) | 8474.3 | 6475.5 | 6848.1 | 6848.1 | 6323.7 | n.a. | 105–141 |
| 5333.5 | n.t. | n.t. | 1040.0 | 1201.8 | 5219.4 | n.t. | 20–98 |
| 2668.8 | n.t. | n.t. | 684.4 | 684.4 | 2522.7 | n.t. | 26–95 |
| 1333.4 | n.t. | n.t. | 661.0 * | 284.2 * | 1289.8 | n.t. | 21–97 |
| 666.7 | n.t. | n.t. | 561.6 | 142.1 * | 631.9 | n.t. | 21–95 |
| 333.3 | n.t. | n.t. | 285.2 | 52.2 | 290.3 | n.t. | 16–87 |
| 166.7 | n.t. | 43.0 | 114.7 | 22.3 | 113.0 | n.t. | 13–69 |
| 83.3 | 43.5 | 21.5 * | 64.7 | n.t. | 65.5 | 2.5 | 3–79 |
| 41.7 | 21.6 * | 10.8 * | 24.9 * | n.t. | 28.4 | 1.2 * | 3–69 |
| 20.8 | 10.8 * | 5.4 * | 17.0 | n.t. | 14.0 | 0.6 * | 3–82 |
| 10.4 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 8.7* | n.t. | 10.7 | 0.067 | 0.6–103 |
| 5.2 | 2.7 * | 1.3* | 4.2 | n.t. | 4.8 | 0.150 * | 3–92 |
| 2.6 | 1.4 * | 0.7 * | 2.2 * | n.t. | 2.5 * | 0.080 * | 3–97 |
| 1.3 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 1.0 | n.t. | 1.2 | 0.074 | 6–92 |
| Recovery 3 (%) | 8–54 | 15–29 | 20–86 | 13–26 | 67–103 | 0.6–5.7 | 0.6–103 |
| Survival Assay | Settlement Assay | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Species | LC50 | LC50 | EC50 |
| L. purpurea | 13.47 [10.58, 17.14] | 23.35 [18.85, 28.93] | 1.84 [0.97, 3.47] |
| T. faulkneri | 2951.24 [813.63, 10,705] | 799.84 [603.80, 1059.54] | 298.92 [122.40, 730.00] |
| A. millepora | 1042.31 [543.82, 1997.75] | - | - |
| A. digitifera | 0.75 [0.66, 0.87] | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miller, I.B.; Moeller, M.; Kellermann, M.Y.; Nietzer, S.; Di Mauro, V.; Kamyab, E.; Pawlowski, S.; Petersen-Thiery, M.; Schupp, P.J. Towards the Development of Standardized Bioassays for Corals: Acute Toxicity of the UV Filter Benzophenone-3 to Scleractinian Coral Larvae. Toxics 2022, 10, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050244
Miller IB, Moeller M, Kellermann MY, Nietzer S, Di Mauro V, Kamyab E, Pawlowski S, Petersen-Thiery M, Schupp PJ. Towards the Development of Standardized Bioassays for Corals: Acute Toxicity of the UV Filter Benzophenone-3 to Scleractinian Coral Larvae. Toxics. 2022; 10(5):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050244
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiller, Ingo B., Mareen Moeller, Matthias Y. Kellermann, Samuel Nietzer, Valentina Di Mauro, Elham Kamyab, Sascha Pawlowski, Mechtild Petersen-Thiery, and Peter J. Schupp. 2022. "Towards the Development of Standardized Bioassays for Corals: Acute Toxicity of the UV Filter Benzophenone-3 to Scleractinian Coral Larvae" Toxics 10, no. 5: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050244
APA StyleMiller, I. B., Moeller, M., Kellermann, M. Y., Nietzer, S., Di Mauro, V., Kamyab, E., Pawlowski, S., Petersen-Thiery, M., & Schupp, P. J. (2022). Towards the Development of Standardized Bioassays for Corals: Acute Toxicity of the UV Filter Benzophenone-3 to Scleractinian Coral Larvae. Toxics, 10(5), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050244









