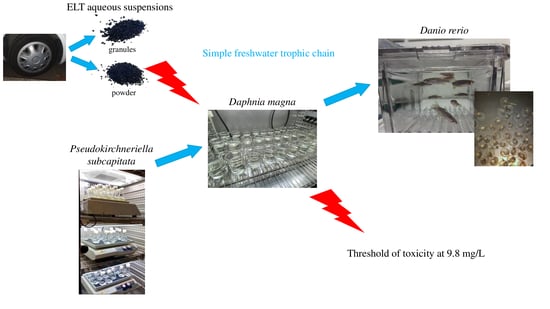
Ecological Impact of End-of-Life-Tire (ELT)-Derived Rubbers: Acute and Chronic Effects at Organism and Population Levels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ELT-dg and ELT-dp Collection
2.2. ELT Characterization and Preparation of Aqueous Suspensions
2.3. Characterization of ELT Suspensions
2.4. Toxicity Studies
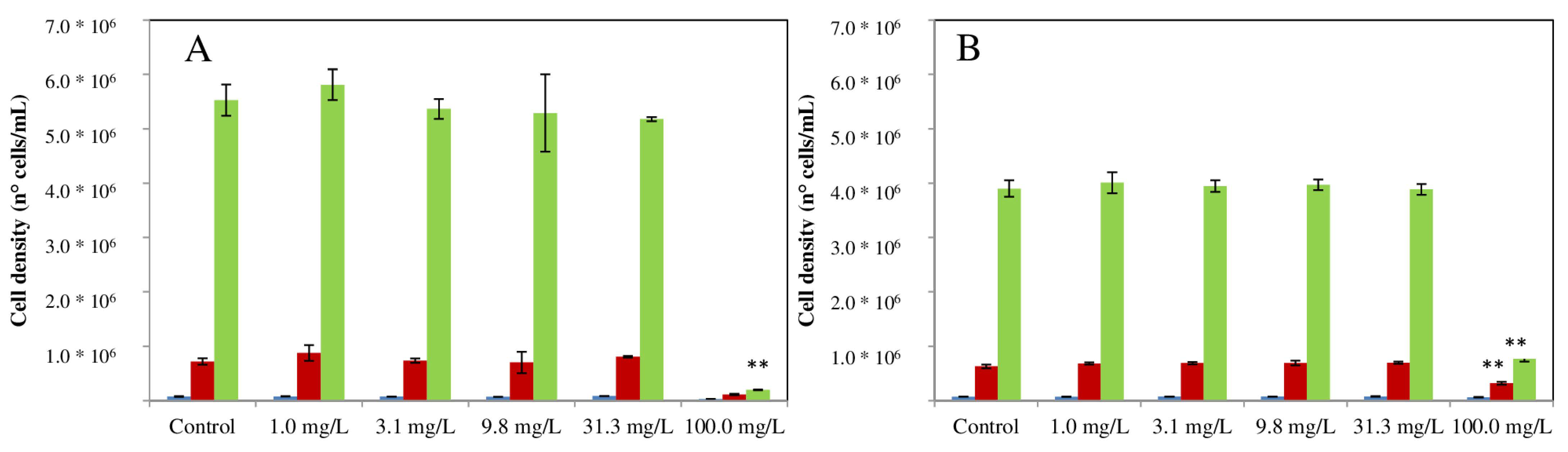
2.4.1. Growth Inhibition Test on P. subcapitata
2.4.2. Acute and Chronic Tests on D. magna
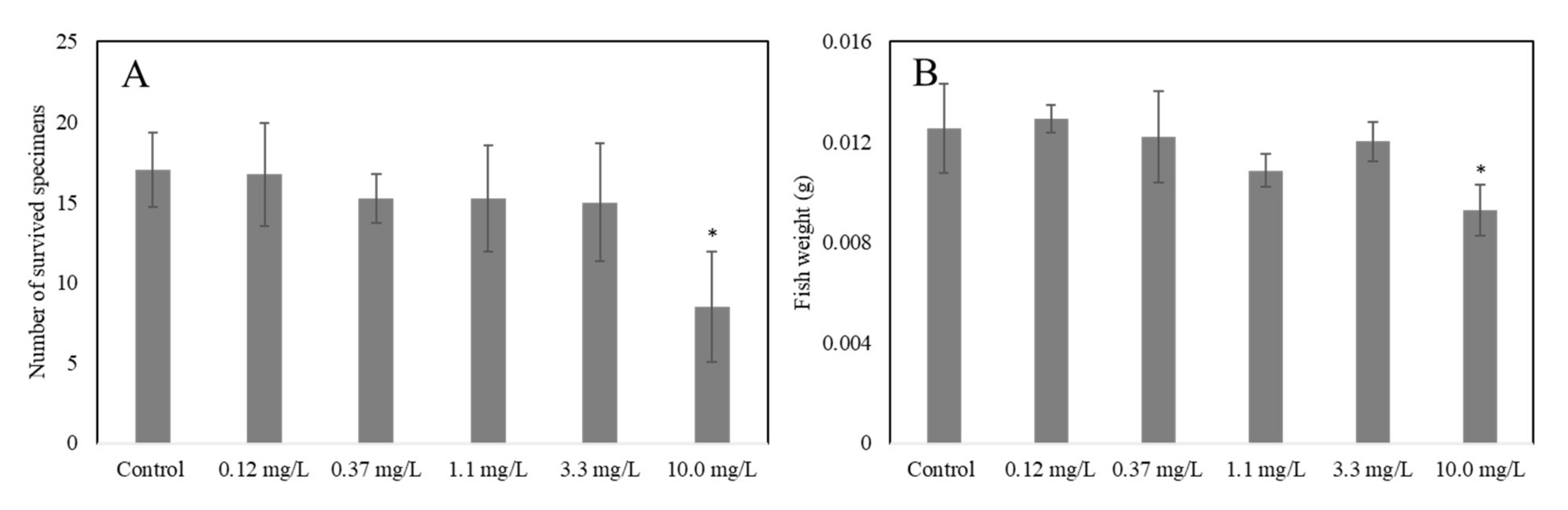
2.4.3. Acute and Chronic Tests on D. rerio
2.5. Statistical Analyses and Data Elaboration
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Zn and ELT Particle Detection in the Exposure Media
3.2. Acute and Chronic Effects of ELT-dg and ELT-dp Suspensions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crawford, C.B.; Quinn, B. Microplastic Pollutants, 1st ed.; Elsevier Limited: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; p. 330. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 472; Plastics—Vocabulary. 4th ed. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; p. 406.
- Lassen, C.; Foss Hansen, S.; Magnusson, K.; Norén, F.; Bloch Hartmann, N.I.; Rehne Jensen, P.; Torkel, G.N.; Brinch, A. Microplastics—Occurrence, Effects and Sources of Releases to the Environment in Denmark. Environmental Project No. 1793; Danish Environmental Protection Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015; p. 205. [Google Scholar]
- Eunomia. Plastics in the Marine Environment; Eunomia: Bristol, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Verschoor, A.; De Poorter, L.; Dröge, R.; Kuenen, J.; de Valk, E. Emission of Microplastics and Potential Mitigation Measures—Abrasive Cleaning Agents, Paints and Tyre Wear; National Institute for Public Health and the Environment: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2016; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, N.B.; Huffer, T.; Thompson, R.C.; Hasselov, M.; Verschoor, A.; Daugaard, A.E.; Rist, S.; Karlsson, T.; Brennholt, N.; Cole, M.; et al. Are we speaking the same language? Recommendations for a definition and categorization framework for plastic debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balbay, S. Effects of recycled carbon-based materials on tyre. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 22, 1768–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, E.P.; Ren, Z.; Mays, D.C. Zinc leaching from tire crumb rubber. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12856–12863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kole, P.J.; Löhr, A.J.; Van Belleghem, F.G.A.J.; Ragas, A.M.J. Wear and tear of tyres: A stealthy source of microplastics in the environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Hüffer, T.; Klöckner, P.; Wehrhahn, M.; Hofmann, T.; Reemtsma, T. Tire wear particles in the aquatic environment-a review on generation, analysis, occurrence, fate and effects. Water Res. 2018, 139, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hüffer, T.; Wagner, S.; Reemtsma, T.; Hofmann, T. Sorption of organic substances to tire wear materials: Similarities and differences with other types of microplastic. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziajahromi, S.; Drapper, D.; Hornbuckle, A.; Rintoul, L.; Leusch, F.D. Microplastic pollution in a stormwater floating treatment wetland: Detection of tyre particles in sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koski, M.; Søndergaard, J.; Christensen, A.M.; Nielsen, T.G. Effect of environmentally relevant concentrations of potentially toxic microplastic on coastal copepods. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 230, 105713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halle, L.L.; Palmqvist, A.; Kampmann, K.; Khan, F.R. Ecotoxicology of micronized tire rubber: Past, present and future considerations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundt, P.; Schulze, P.-E.; Syversen, F. Sources of Microplastics-pollution to the Marine Environment. Nor. Environ. Agency Miljødirektoaret 2014, 86, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Bertling, J.; Bertling, R.; Hamann, L. Kunststoffe in der Umwelt. Mikro- und Makroplastik. In Ursachen, Mengen, Umweltschicksale, Wirkungen, Lösungsansätze, Empfehlungen. Kurzfassung der Konsortialstudie; Fraunhofer-Institut für Umwelt Oberhausen: Oberhausen, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Leads, R.R.; Weinstein, J.E. Occurrence of tire wear particles and other microplastics within the tributaries of the Charleston Harbor Estuary, South Carolina, USA. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unice, K.M.; Weeber, M.P.; Abramson, M.M.; Reid, R.C.D.; van Gils, J.A.G.; Markus, A.A.; Vethaak, A.D.; Panko, J.M. Characterizing export of land-based microplastics to the estuary—Part I: Application of integrated geospatial microplastic transport models to assess tire and road wear particles in the Seine watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, L.J.; Parker-Jurd, F.N.; Al-Sid-Cheikh, M.; Thompson, R.C. Tyre wear particles: An abundant yet widely unreported microplastic? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18345–18354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelsang, C.; Lusher, A.; Dadkhah, M.E.; Sundvor, I.; Umar, M.; Ranneklev, S.B.; Eidsvoll, D.; Meland, S. Microplastics in Road Dust-Characteristics, Pathways and Measures; NIVA-Rapport: Oslo, Norway, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Magni, S.; Binelli, A.; Pittura, L.; Avio, C.G.; Della Torre, C.; Parenti, C.C.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. The fate of microplastics in an Italian Wastewater Treatment Plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binelli, A.; Pietrelli, L.; Di Vito, S.; Coscia, L.; Sighicelli, M.; Della Torre, C.; Parenti, C.C.; Magni, S. Hazard evaluation of plastic mixtures from four Italian subalpine great lakes on the basis of laboratory exposures of zebra mussels. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magni, S.; Nigro, L.; Della Torre, C.; Binelli, A. Characterization of plastics and their ecotoxicological effects in the Lambro River (N. Italy). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binelli, A.; Della Torre, C.; Nigro, L.; Riccardi, N.; Magni, S. A realistic approach for the assessment of plastic contamination and its ecotoxicological consequences: A case study in the metropolitan city of Milan (N. Italy). Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 806, 150574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Olesen, K.B.; Borregaard, A.R.; Vollertsen, J. Microplastics in urban and highway stormwater retention ponds. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baensch-Baltruschat, B.; Kocher, B.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. Tyre and road wear particles (TRWP)-A review of generation, properties, emissions, human health risk, ecotoxicity, and fate in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 137823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EASME. Recycling Rubber to Reduce Noise. 2015. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/easme/en/news/recycling-rubber-reduce-noise (accessed on 3 February 2017).
- Depaolini, A.R.; Bianchi, G.; Fornai, D.; Cardelli, A.; Badalassi, M.; Cardelli, C.; Davoli, E. Physical and chemical characterization of representative samples of recycled rubber from end-of-life tires. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammelis, P.; Margaritis, N.; Dallas, P.; Rakopoulos, D.; Mavrias, G. Review on management of end of life tires (ELTs) and alternative uses of textile fibers. Energies 2021, 14, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global ELT Management. A Global State of Knowledge on Regulation, Management Systems, Impacts of Recovery and Technologies; Global ELT Management, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, F.R.; Halle, L.L.; Palmqvist, A. Acute and long-term toxicity of micronized car tire wear particles to Hyalella azteca. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 213, 105216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.E.; de Ruijter, V.N.; Mintenig, S.M.; Verschoor, A.; Koelmans, A.A. Ingestion and chronic effects of car tire tread particles on freshwater benthic macroinvertebrates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13986–13994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, K.E.; Holtze, K.E.; Metcalfe-Smith, J.L.; Bishop, C.T.; Dutka, B.J. Toxicity of leachate from automobile tires to aquatic biota. Chemosphere 1993, 27, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephensen, E.; Adolfsson-Erici, M.; Celander, M.; Hulander, M.; Parkkonen, J.; Hegelund, T.; Sturve, J.; Hasselberg, L.; Bengtsson, M.; Förlin, L. Biomarker responses and chemical analyses in fish indicate leakage of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and other compounds from car tire rubber. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 2926–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wik, A.; Dave, G. Environmental labeling of car tires—Toxicity to Daphnia magna can be used as a screening method. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wik, A.; Dave, G. Acute toxicity of leachates of tire wearmaterial to Daphnia magna—Variability and toxic components. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wik, A.; Nilsson, E.; Källqvist, T.; Tobiesen, A.; Dave, G. Toxicity assessment of sequential leachates of tire powder using a battery of toxicity tests and toxicity identification evaluations. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panko, J.M.; Kreider, M.L.; McAtee, B.L.; Marwood, C. Chronic toxicity of tire and road wear particles to water- and sediment-dwelling organisms. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwood, C.; McAtee, B.; Kreider, M.; Ogle, R.S.; Finley, B.; Sweet, L.; Panko, J. Acute aquatic toxicity of tire and road wear particles to alga, daphnid, and fish. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 2079–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, B.; Harper, B.; Brander, S.; Harper, S. Toxicity of Micro and Nano Tire Particles and Leachate for Model Freshwater Organisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNI ISO 2859–1; Procedimenti di Campionamento Nell’ispezione per Attributi—Parte 1: Schemi di Campionamento Indicizzati Secondo il Limite di Qualità Accettabile (AQL) Nelle Ispezioni Lotto per Lotto. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- UNI EN 14243–2; Materiali da Recupero di Pneumatici Fuori Uso—Parte 2: Granuli e Polverini—Metodi per Determinare la Distribuzione Delle Dimensioni Delle Particelle e Delle Impurità, Compresi il Contenuto di Ferro Libero e di Tessile Libero. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- UNI ISO 11648–1; Aspetti Statistici del Campionamento da Materiali Sfusi—Parte 1: Principi Generali. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- UNI EN 15442; Combustibili Solidi Secondari—Metodi di Campionamento. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- ISO 3165; Sampling of Chemical Products for Industrial Use—Safety in Sampling. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1976.
- Magni, S.; Bonasoro, F.; Della Torre, C.; Parenti, C.C.; Maggioni, D.; Binelli, A. Plastics and biodegradable plastics: Ecotoxicity comparison between polyvinylchloride and Mater-Bi® micro-debris in a freshwater biological model. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD 201; Freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria, Growth Inhibition Test. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2. OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2011.
- OECD 202; Daphnia sp. Acute Immobilization Test. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2. OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2004.
- OECD 203; Fish, Acute Toxicity Test. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2. OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2019.
- OECD 211; Daphnia magna Reproduction Test. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2. OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2012.
- OECD 23; Guidance Document on Aquatic Toxicity Testing of Difficult Substances and Mixtures. OECD Series on Testing and Assessment. OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2019.
- OECD 210; Fish, Early-Life Stage Toxicity Test. OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 1992.
- Banasiak, L.; Chiaro, G.; Palermo, A.; Granello, G. Environmental implications of the recycling of End-of-Life Tires in seismic isolation foundation systems. In Advances in Sustainable Construction and Resource Management; Springer: Singapore, 2021; Volume 144, pp. 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Degaffe, F.S.; Turner, A. Leaching of zinc from tire wear particles under simulated estuarine conditions. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capolupo, M.; Sørensen, L.; Jayasena, K.D.R.; Booth, A.M.; Fabbri, E. Chemical composition and ecotoxicity of plastic and car tire rubber leachates to aquatic organisms. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Zhou, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, R.; Zhou, S.; Xu, E.G.; Xing, B. Environmental occurrence, fate, impact, and potential solution of tire microplastics: Similarities and differences with tire wear particles. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Zhao, H.; Peter, K.T.; Gonzalez, M.; Wetzel, J.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; Prat, J.; Mudrock, E.; Hettinger, R.; et al. A ubiquitous tire rubber-derived chemical induces acute mortality in coho salmon. Science 2021, 371, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halsband, C.; Sørensen, L.; Booth, A.M.; Herzke, D. Car tire crumb rubber: Does leaching produce a toxic chemical cocktail in coastal marine systems? Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwell, S.I.; Jordahl, D.M.; Dawson, C.E.O. The effect of salinity on tire leachate toxicity. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2000, 121, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, M.; Andrioletti, M.; Vismara, C.; Milani, M.; Camatini, M. Toxicity of tire debris leachates. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Suspension from ELT-dg | Suspension from ELT-dp | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC50 | NOEC (mg/L) | LOEC (mg/L) | EC50 | NOEC (mg/L) | LOEC (mg/L) | ||
| P. subcapitata chronic test | Growth rate | 93.7 (0–72 h) | 31.3 (0–72 h) | 100.0 (0–72 h) | >100.0 (0–72 h) | 31.3 (0–72 h) | 100.0 (0–72 h) |
| Yeld | 54.2 (0–72 h) | 31.3 (0–72 h) | 100.0 (0–72 h) | 73.6 (0–72 h) | 31.3 (0–72 h) | 100.0 (0–72 h) | |
| D. magna acute test | Immobilization | >100.0 (24 and 48 h) | 100.0 (24 and 48 h) | >100.0 (24 and 48 h) | 100.0 (24 and 48 h) | ||
| D. rerio acute test | Mortality | >100.0 (24, 48, 72 and 96 h) | 100.0 (24, 48, 72 and 96 h) | >100.0 (24, 48, 72 and 96 h) | 100.0 (24, 48, 72 and 96 h) | ||
| D. magna chronic test | Reproduction | >100.0 (21 d) | 3.1 (21 d) | 9.8 (21 d) | >100.0 (21 d) | 100.0 (21 d) | >100.0 (21 d) |
| Parental mortality | 100.0 (21 d) | >100.0 (21 d) | 100.0 (21 d) | >100.0 (21 d) | |||
| D. rerio chronic test | Hatching | 10.0 (96 hpf) | >10.0 (96 hpf) | 10.0 (96 hpf) | >10.0 (96 hpf) | ||
| Juvenile survival | 3.3 (30 d) | 10.0 (30 d) | 3.3 (30 d) | 10.0 (30 d) | |||
| Juvenile weight | 3.3 (30 d) | 10.0 (30 d) | 10.0 (30 d) | >10.0 (30 d) | |||
| Juvenile lenght | 10.0 (30 d) | >10.0 (30 d) | 10.0 (30 d) | >10.0 (30 d) | |||
| Abnormal behaviour | 3.3 (30 d) | 10.0 (30 d) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magni, S.; Tediosi, E.; Maggioni, D.; Sbarberi, R.; Noé, F.; Rossetti, F.; Fornai, D.; Persici, V.; Neri, M.C. Ecological Impact of End-of-Life-Tire (ELT)-Derived Rubbers: Acute and Chronic Effects at Organism and Population Levels. Toxics 2022, 10, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050201
Magni S, Tediosi E, Maggioni D, Sbarberi R, Noé F, Rossetti F, Fornai D, Persici V, Neri MC. Ecological Impact of End-of-Life-Tire (ELT)-Derived Rubbers: Acute and Chronic Effects at Organism and Population Levels. Toxics. 2022; 10(5):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050201
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagni, Stefano, Erica Tediosi, Daniela Maggioni, Riccardo Sbarberi, Francesca Noé, Fabio Rossetti, Daniele Fornai, Valentina Persici, and Maria Chiara Neri. 2022. "Ecological Impact of End-of-Life-Tire (ELT)-Derived Rubbers: Acute and Chronic Effects at Organism and Population Levels" Toxics 10, no. 5: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050201
APA StyleMagni, S., Tediosi, E., Maggioni, D., Sbarberi, R., Noé, F., Rossetti, F., Fornai, D., Persici, V., & Neri, M. C. (2022). Ecological Impact of End-of-Life-Tire (ELT)-Derived Rubbers: Acute and Chronic Effects at Organism and Population Levels. Toxics, 10(5), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050201