Relationship between Pesticide Standards for Classification of Water Bodies and Ecotoxicity: A Case Study of the Brazilian Directive
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
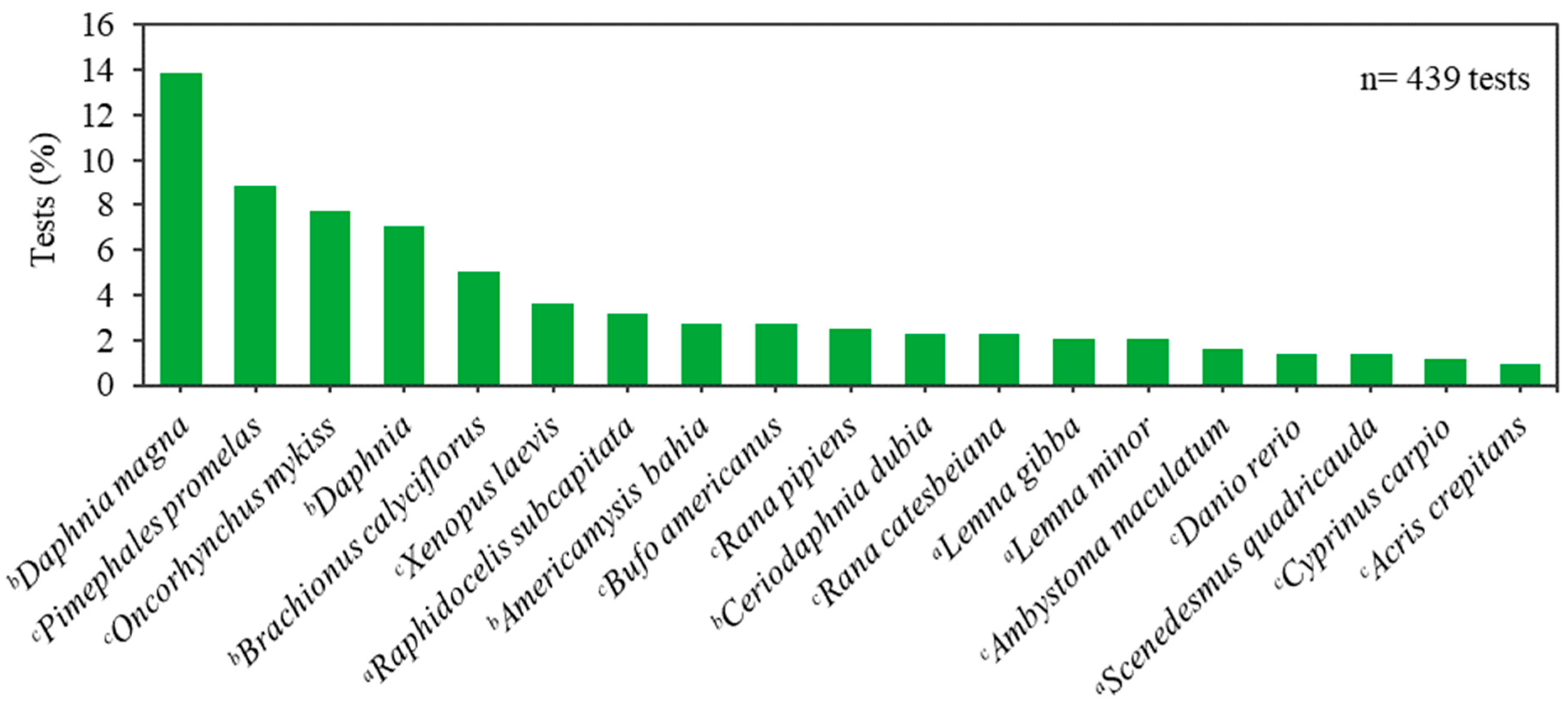
3. Results and Discussion
| Pesticide | Risk Quotient Class 1,2/3 (µg/L) | Endpoint: Concentration (µg/L) | Tested Organism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alachlor | 3/- | EC50 (72 h): 6.69 | Raphidocelis subcapitata a | [26] |
| 2/- | EC50 (96 h): 10 | Raphidocelis subcapitata a | [27] | |
| 2/- | EC50 (7 d)-biomass: 10 | Lemna minor a | [20] | |
| 12.2/- | EC50 (<10 d): 1.64 | Nonvascular plants a | [7] | |
| 8.7/- | EC50 (<10 d): 2.3 | Vascular plants a | [7] | |
| Aldrin | -/3 | NOEC-ratio of ovigerous to non-ovigerous females: 0.01 | Brachionus calyciflorus b | [31] |
| -/1.8 | LC50 (96 h): 0.017 | Pimephales promelas c | [21] | |
| Dieldrin | 5/30 | LOEC-population growth rate: 0.001 | Brachionus calyciflorus b | [31] |
| 5/30 | NOEC-ratio of ovigerous to non-ovigerous females: 0.001 | Brachionus calyciflorus b | [31] | |
| -/3 | LOEC-ratio of ovigerous to non-ovigerous females: 0.01 | Brachionus calyciflorus b | [31] | |
| Atrazine | 2/2 | EC50 (<10 d): <1 | Nonvascular plants a | [7] |
| Carbaryl | -/1.2 | NOEC-resting egg production: 60 | Brachionus calyciflorus b | [37] |
| -/3.5 | NOEC-resting egg hatching rate: 20 | Brachionus calyciflorus b | [37] | |
| -/1.2 | LOEC-resting egg hatching rate: 60 | Brachionus calyciflorus b | [37] | |
| -/41.2 | EC50 or LC50 (48 or 96 h): 1.7 | Invertebrates b | [7] | |
| -/140 | NOAEC: 0.5 | Invertebrates b | [7] | |
| -/10.9 | EC50 (48 h): 6.4 | Daphnia pulex b | [20] | |
| -/12.3 | LC50 (96 h): 5.7 | Americamysis bahia b | [20] | |
| -/11.7 | NOAEC: 6 | Fish c | [7] | |
| Chlordane | -/2.4 | LC50 (96 h): 0.127 | Neocaridina denticulate b | [43] |
| -/1.7 | NOEC (14 d)-survival: 0.18 | Ceriodaphnia dubia b | [44] | |
| -/1.7 | NOEC (14 d)- number of offspring per female: 0.18 | Ceriodaphnia dubia b | [44] | |
| -/1.7 | NOEC (21 d)- number of offspring per female: 0.18 | Daphnia magna b | [44] | |
| -/4.3 | LC50 (48 h)-trans: 0.07 | Daphnia b | [21] | |
| -/7.5 | LC50 (96 h)-trans: 0.04 | Pimephales promelas c | [21] | |
| 2,4-D | -/1 | LOEC: 29 | Hyalella meinerti b | [48] |
| -/1 | NOEC: <29 | Hyalella meinerti b | [48] | |
| 1.2/9.3 | LC50 (48 h): 3.22 | Daphnia b | [21] | |
| 1.5/11.6 | LC50 (96 h): 2.59 | Pimephales promelas c | [21] | |
| Demeton | -/1.3 | EC50 (48 h) d: 10.4 | Daphnia pulex b | [20] |
| -/1.6 | LC50 (48 h) d1: 8.62 | Daphnia b | [21] | |
| -/3.2 | LC50 (96 h) d1: 4.43 | Pimephales promelas c | [21] | |
| -/3.2 | LC50 (48 h) d2: 4.44 | Daphnia b | [21] | |
| DDT | -/1 | EC50 (48 h) e: 1 | Bosmina longirostris b | [20] |
| Endosulfan | 5.6/22 | NOAEC: 0.01 | Invertebrates b | [7] |
| 0.6/2.2 | LC50 (96 h): 0.1 | Fish c | [7] | |
| 2.4/9.6 | NOAEC: 0.023 | Fish c | [7] | |
| 155.6/611.1 | LC50 (96 h): 0.00036 | Chironomus ramosus b | [52] | |
| 112/440 | NOEC (28 d): 0.0005 | Cyprinodon variegatus c | [20] | |
| Endrin | -/1.1 | LC50 (48 h): 0.19 | Daphnia b | [21] |
| 2/100 | LC50 (96 h): 0.002 | Pimephales promelas c | [21] | |
| -/1.7 | NOEC (21 d): 0.12 | Cyprinodon variegatus c | [20] | |
| Lindane | -/2 | EC50 or LC50 (48 or 96 h): 1 | Invertebrates b | [7] |
| -/1.2 | LC50 (96 h): 1.7 | Fish c | [7] | |
| -/0.7 | LC50 (96 h): 2.9 | Oncorhynchus mykiss c | [20] | |
| Malathion | 1/1020.4 | EC50 or LC50 (48 or 96 h): 0.098 | Invertebrates b | [7] |
| 1.7/1666.7 | NOAEC: 0.06 | Invertebrates b | [7] | |
| -/111.1 | LC50 (48 h): 0.9 | Daphnia magna b | [57] | |
| -/4.9 | LC50 (48 h): 20.32 | Daphnia b | [21] | |
| -/142.9 | EC50 (48 h): 0.7 | Daphnia magna b | [20] | |
| 1.7/1666.7 | NOEC (21 d): 0.06 | Daphnia magna b | [20] | |
| -/66.7 | LC50 (96 h): 1.5 | Americamysis bahia b | [20] | |
| -/24.4 | LC50 (96 h): 4.1 | Fish c | [7] | |
| -/11.6 | NOAEC: 8.6 | Fish c | [7] | |
| 3125/3,125,000 | LC50 (96 h): 0.000032 | Chironomus ramosus b | [52] | |
| -/22.3 | LC50 (96 h): 4.48 | Pimephales promelas c | [21] | |
| -/5.6 | LC50 (96 h): 18 | Oncorhynchus mykiss c | [20] | |
| -/1.1 | NOEC (21 d): 91 | Oncorhynchus mykiss c | [20] | |
| Metolachlor | 1.3/- | EC50 (<10 d): 8 | Nonvascular Plants a | [7] |
| 10/- | NOAEC: 1 | Invertebrates b | [7] | |
| Metoxichlor | -/0.7 | LC50 (48 h): 30 | Daphnia b | [21] |
| -/14.3 | EC50 or LC50 (48 or 96 h): 1.4 | Invertebrates b | [7] | |
| -/25.6 | EC50 (48 h): 0.78 | Daphnia magna b | [20] | |
| -/20 | NOEC (21 d): 1 | Daphnia magna b | [20] | |
| -/1.3 | LC50 (96 h): 15 | Fish c | [7] | |
| Parathion | -/92.1 | LC50 (48 h): 0.38 | Daphnia magna b | [57] |
| -/46.7 | LC50 (48 h): 0.75 | Daphnia b | [21] | |
| -/14 | EC50 (48 h): 2.5 | Daphnia magna b | [20] | |
| -/350 | NOEC (21 d): 0.1 | Daphnia magna b | [20] | |
| -/318.2 | LC50 (96 h): 0.11 | Americamysis bahia b | [20] |
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliver, D.P.; Kookana, R.S.; Anderson, J.S.; Cox, J.W.; Waller, N.; Smith, L.H. Off-Site Transport of Pesticides in Dissolved and Particulate Forms from Two Land Uses in the Mt. Lofty Ranges, South Australia. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 106, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, E.D. Toxicological Aspects of Pesticides. In Sustainable Agrochemistry: A Compendium of Technologies; Vaz, S., Jr., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 197–230. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, K.R.; Brock, T.C.M.; Zwart, D.; Dyer, S.D.; Posthuma, L.; Richards, S.M.; Sanderson, H.; Sibley, P.K.; van den Brink, P.J. Extrapolation in the Context of Criteria Setting and Risk Assessment. In Extrapolation Practice for Ecotoxicological Effect Characterization; Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry: Dublin, Ireland, 2008; pp. 1–410. ISBN 8504691500. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Jennings, A.A. Ranking System for National Regulatory Jurisdictions Based on Pesticide Standard Values in Major Exposures. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2017, 4, 540–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, E.P.; Caldas, E.D.; Oliveira-Filho, E.C. Pesticides in Surface Freshwater: A Critical Review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directive 2013/39/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 August 2013 Amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as Regards Priority Substances in the Field of Water Policy Text with EEA Relevance; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2013; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Aquatic Life Benchmarks and Ecological Risk Assessments for Registered Pesticides. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pesticide-science-and-assessing-pesticide-risks/aquatic-life-benchmarks-and-ecological-risk#ref_1 (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- MMA Ministério do Meio Ambiente. Brasil Resolução CONAMA N° 357 de 18 de Março de 2005. Dispõe Sobre a Classificação Dos Corpos de Água e Diretrizes Ambientais Para o Seu Enquadramento, Bem Como Estabelece as Condições e Padrões de Lançamento de Efluentes, e Dá Outras Providências; MMA Ministério do Meio Ambiente: Brasília, Brasil, 2005; pp. 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- ANA (Agência Nacional de Águas e Saneamento Básico). Conjuntura Dos Recursos Hídricos No Brasil. 2021. Available online: https://relatorio-conjuntura-ana-2021.webflow.io/ (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Brasil Instituto Brasileiro Do Meio Ambiente e Dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis. Portaria No 84, de 15 de Outubro de 1996. Estabelece Procedimentos a Serem Adotados Junto Ao Ibama, Para Efeito de Registro e Avaliação Do Potencial de Periculosidade Ambiental—(PPA) de Agrotóxicos, Seus Componentes e Afins, e Institui o Sistema Permanente Da Avaliação e Controle Dos Agrotóxicos, Segundo Disposições Do Decreto No 98.816 Em Seu Art. 2o; Brasil Instituto Brasileiro Do Meio Ambiente e Dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis: Brasília, Brasil, 1996; pp. 21358–21366.
- Oliveira-Filho, E.C. Capítulo 8: Avaliação Da Toxicidade. In Princípios de Toxicologia Ambiental; Sisinno, C.L.S., Oliveira-Filho, E.C., Eds.; Interciência: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2013; pp. 1–216. [Google Scholar]
- Rebelo, R.M.; Caldas, E.D. Avaliação de Risco Ambiental de Ambientes Aquáticos Afetados Pelo Uso de Agrotóxicos. Quim. Nova 2014, 37, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.R.; Olivi, P.; Botta, C.M.R.; Espindola, E.L.G. A Toxicidade Em Ambientes Aquáticos: Discussão e Métodos de Avaliação. Quim. Nova 2008, 31, 1820–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, A.; Báez, M.C.D.; Granados, Y.P. Conceptos Generales. In Ensayos Toxicológicos y Métodos de Evaluación de Calidad de Aguas; Castillo, G.M., Ed.; IMTA: Progreso, Mexico; IDCR: Ottawa, Canada, 2004; pp. 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Umbuzeiro, G.A.; Kummrow, F.; Rei, F.F.C. Toxicologia, Padrões de Qualidade de Água e a Legislação. INTERFACEHS—Rev. Gestão Integr. Em Saúde Trab. Meio Ambiente 2010, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque, A.F.; Ribeiro, J.S.; Kummrow, F.; Nogueira, A.J.A.; Montagner, C.C.; Umbuzeiro, G.A. Pesticides in Brazilian Freshwaters: A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2016, 18, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). Pesticides Use Statistical Databases. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/RP/visualize (accessed on 9 January 2020).
- IBAMA (Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis). Consolidação de Dados Fornecidos Pelas Empresas Registrantes de Produtos Técnicos, Agrotóxicos e Afins, Conforme Art. 41 Do Decreto 4.074/2002. Available online: http://www.ibama.gov.br/phocadownload/qualidadeambiental/relatorios/2019/grafico_do_historico_de_comercializacao_2000-2019.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- MAPA (Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento). Sistema de Agrotóxicos Fitossanitários—Agrofit. Available online: https://agrofit.agricultura.gov.br/agrofit_cons/principal_agrofit_cons (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- PPDB (Pesticide Properties DataBase). Pesticide Properties DataBase. Available online: http://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/en/index.htm (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- NORMAN (Network of Reference Laboratories, ReseArch. Centres and Related Organisations for Monitoring of Emerging Environmental Substances). NORMAN Ecotoxicology Database. Available online: https://www.norman-network.com/nds/susdat/ (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, P.; Lu, S.; Liu, X.; Zhai, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Wan, Z. Occurrence and Risk Evaluation of Organophosphorus Pesticides in Typical Water Bodies of Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.V.; Peris, A.; Postigo, C.; Moya-Garcés, A.; Monllor-Alcaraz, L.S.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Eljarrat, E.; López de Alda, M. Evaluation of the Occurrence and Fate of Pesticides in a Typical Mediterranean Delta Ecosystem (Ebro River Delta) and Risk Assessment for Aquatic Organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 115813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANVISA (Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária. Monografias de Agrotóxicos Em Vigência). Monografias de Agrotóxicos Em Vigência. Available online: https://www.gov.br/anvisa/pt-br/acessoainformacao/dadosabertos/informacoes-analiticas/monografias-de-agrotoxicos (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Technical Overview of Ecological Risk Assessment: Risk Characterization. Available online: https://epa.gov/pesticide-science-and-assessing-pesticide-risks/forms/contact-us-about-pesticide-science-and (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Souissi, Y.; Bouchonnet, S.; Bourcier, S.; Kusk, K.O.; Sablier, M.; Andersen, H.R. Identification and Ecotoxicity of Degradation Products of Chloroacetamide Herbicides from UV-Treatment of Water. Sci. Total. Environ. 2013, 458, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairchild, J.F.; Ruessler, D.S.; Carlson, A.R. Comparative Sensitivity of Five Species of Macrophytes and Six Species of Algae to Atrazine, Metribuzin, Alachlor, and Metolachlor. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998, 17, 1830–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivey, C.D.; Besser, J.M.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Wang, N.; Rogers, D.C.; Raimondo, S.; Bauer, C.R.; Hammer, E.J. Acute Sensitivity of the Vernal Pool Fairy Shrimp, Branchinecta Lynchi (Anostraca; Branchinectidae), and Surrogate Species to 10 Chemicals. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, G.E.; Gillis, R.; Mowbray, R.C. Effect of Chemical Synergy and Larval Stage on the Toxicity of Atrazine and Alchlor to Amphibian Larvae. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998, 17, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peebua, P.; Kruatrachue, M.; Pokethitiyook, P.; Singhakaew, S. Histopathological Alterations of Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis Niloticus in Acute and Subchronic Alachlor Exposure. J Environ. Biol. 2008, 29, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Xi, Y.; Zha, C.; Wen, X. Responses in the Population Growth and Reproduction of Freshwater Rotifer Brachionus Calyciflorus to Four Organochlorine Pesticides. Ann. Limnol. 2013, 49, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Campagna, A.F.; Eler, M.N.; Fracácio, R.; Rodrigues, B.K.; Verani, N.F. The Toxic Potential of Aldrin and Heptachlor on Danio Rerio Juveniles (Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae). Ecotoxicology 2007, 16, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyanarayan, S.; Bejankiwar, R.S.; Chaudhari, P.R.; Kotangale, J.P.; Satyanarayan, A. Impact of Some Chlorinated Pesticides Onthe Haematology of the Cyprinus Carpio and Puntius Ticto. J. Environ. Scien. 2004, 16, 631–634. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, I.; Nagel, R. Stress Proteins HSP60 and HSP70 in Three Species of Amphipods Exposed to Cadmium, Diazinon, Dieldrin and Fluoranthene. Environ. Toxicol. Chem 1997, 16, 2393–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuytema, G.S.; Nebeker, A.V.; Griffis, W.L.; Wilson, K.N. Teratogenesis, Toxicity, and Bioconcentration in Frogs Exposed to Dieldrin. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1991, 21, 332–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Vechia, J.F.; Cruz, C.; Silva, A.F.; Cerveira, W.R.; Garlich, N. Macrophyte Bioassay Applications for Monitoring Pesticides in the Aquatic Environment. Planta Daninha. 2016, 34, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhao, B.; Yang, J.; Snell, T.W. Effects of Atrazine and Carbaryl on Growth and Reproduction of the Rotifer Brachionus Calyciflorus Pallas. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2012, 27, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Yu, J.; Chen, G.; Li, W.; He, J.; Li, H. Acute Toxicity of Butachlor and Atrazine to Freshwater Green Alga Scenedesmus Obliquus and Cladoceran Daphnia Carinata. EcoToxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 80, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phyu, Y.L.; Warne, M.S.J.; Lim, R.P. Toxicity and Bioavailability of Atrazine and Molinate to the Freshwater Shrimp (Paratya Australiensis) under Laboratory and Simulated Field Conditions. EcoToxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 60, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velisek, J.; Kouba, A.; Stara, A. Acute Toxicity of Triazine Pesticides to Juvenile Signal Crayfish (Pacifastacus Leniusculus). Neuroendocrinol. Lett. 2013, 34, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Saka, M.; Tada, N.; Kamata, Y. Chronic Toxicity of 1,3,5-Triazine Herbicides in the Postembryonic Development of the Western Clawed Frog Silurana Tropicalis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KreutzI, L.C.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; Silva, T.O.; Anziliero, D.; Martins, D.; Lorenson, M.; Marteninghe, A.; Silva, L.B. Acute Toxicity Test of Agricultural Pesticides on Silver Catfish (Rhamdia Quelen) Fingerlings. Ciência Rural. 2008, 38, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.J.; Chen, H.C. Effects of Chlordane and Lindane on Testosterone and Vitellogenin Levels in Green Neon Shrimp (Neocaridina Denticulata). Int. J. Toxicol. 2004, 23, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manar, R.; Vasseur, P.; Bessi, H. Chronic Toxicity of Chlordane to Daphnia Magna and Ceriodaphnia Dubia: A Comparative Study. Environ. Toxicol. 2012, 27, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manar, R.; Bessi, H.; Vasseur, P. Reproductive Effects and Bioaccumulation of Chlordane in Daphnia Magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2150–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.F.; Cruz, C.; Neto, A.N.; Pitelli, R.A. Ecotoxicidade de Herbicidas Para a Macrófita Aquática (Azolla Caroliniana). Planta Daninha. 2012, 30, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sanford, M.; Washuck, N.; Carr, K.; Prosser, R.S. Pulsed Exposure of the Macrophyte Lemna Minor to Herbicides and the Mayfly Neocloeon Triangulifer to Diamide Insecticides. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 128582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Pinto, T.J.; Moreira, R.A.; Silva, L.C.M.; Yoshii, M.P.C.; Goulart, B.V.; Fraga, P.D.; Rolim, V.L.S.; Montagner, C.C.; Daam, M.A.; Espindola, E.L.G. Toxicity of Fipronil and 2,4-D Formulations (Alone and in a Mixture) to the Tropical Amphipod Hyalella Meinerti. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 38308–38321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farah, M.A.; Ateeq, B.; Ali, M.N.; Sabir, R.; Ahmad, W. Studies on Lethal Concentrations and Toxicity Stress of Some Xenobiotics on Aquatic Organisms. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holcombe, G.W.; Phipps, G.L.; Fiandt, J.T. Effects of Phenol, 2,4-Dimethylphenol, 2,4-Dichlorophenol, and Pentachlorophenol on Embryo, Larval, and Early-Juvenile Fathead Minnows (Pimephales Promelas). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1982, 11, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, G.L.; Holcombe, G.W.; Fiandt, J.T. Acute Toxicity of Phenol and Substituted Phenols to the Fathead Minnow. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1981, 26, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, T.N.; Gupta, A. Acute Toxicity of Endosulfan and Malathion on Chironomus Ramosus (Insecta: Diptera: Chironomidae) from North Cachar Hills, Assam, India. J. Environ. Biol. 2009, 30, 469–470. [Google Scholar]
- Carriger, J.F.; Hoang, T.C.; Rand, G.M.; Gardinali, P.R.; Castro, J. Acute Toxicity and Effects Analysis of Endosulfan Sulfate to Freshwater Fish Species. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 60, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.J.; Swineford, D.M. Acute Toxicities of Toxaphene and Endrin to Larvae of Seven Species of Amphibians. Toxicol. Lett. 1981, 8, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuytema, G.S.; Nebeker, A.V.; Griffis, W.L. Toxicity of Guthion® and Guthion® 2S to Xenopus Laevis Embryos. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1994, 27, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebeker, A.V.; Schuytema, G.S.; Griffis, W.L.; Cataldo, A. Impact of Guthion on Survival and Growth of the Frog Pseudacris Regilla and the Salamanders Ambystoma Gracile and Ambystoma Maculatum. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1998, 35, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Zha, J.; Ma, M.; Wang, Z.; Gerhardt, A. The Early Warning of Aquatic Organophosphorus Pesticide Contamination by On-Line Monitoring Behavioral Changes of Daphnia Magna. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 134, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.; Venturino, A.; D’Angelo, A.M.P. Time Course of Brain Cholinesterase Inhibition and Recovery Following Acute and Subacute Azinphosmethyl, Parathion and Carbaryl Exposure in the Goldfish (Carassius Auratus). EcoToxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 57, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzmayer, K.M.; Geiger, J.G.; Avyle, M.J. van den Effects of Chronic Exposure to Simazine on the Cladoceran, Daphnia Pulex. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1982, 11, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayim, F. Toxicity of Trifluralin on the Embryos and Larvae of the Red-Bellied Toad, Bombina Bombina. Turk. J. Zool. 2010, 34, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poleksic, V.; Karan, V. Effects of Trifluralin on Carp: Biochemical and Histological Evaluation. EcoToxicol. Environ. Saf. 1999, 43, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, S.M.; Yu, S.; Salice, C.J. Acute Toxicity of Herbicide Formulations and Chronic Toxicity of Technical-Grade Trifluralin to Larval Green Frogs (Lithobates Clamitans). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 2029–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Guidance on Information Requirements and Chemical Safety Assessment Chapter R.10: Characterisation of Dose [Concentration]-Response for Environment Guidance for the Implementation of REACH; European Commission: Brussels, Brazil, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- REFLORA.(Resgate Histórico e Herbário Virtual para o Conhecimento e Conservação da Flora Brasileira) Flora e Funga Do Brasil. Available online: http://floradobrasil.jbrj.gov.br/ (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- Forzza, R.C.; Leitman, P.M.; Costa, A.; de Carvalho, A.A., Jr.; Peixoto, A.L.; Walter, B.M.T.; Bicudo, C.; Zappi, D.; da Costa, D.P.; Lleras, E.; et al. Catálogo de Plantas e Fungos Do Brasil; Instituto de Pesquisa Jardim Botânico do Rio de Janeiro: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2010; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- TCBF. (Taxonomic Catalog of the Brazilian Fauna). Available online: http://fauna.jbrj.gov.br/fauna/listaBrasil/PrincipalUC/PrincipalUC.do?lingua=en (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility). Available online: https://www.gbif.org/ (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- Bundschuh, R.; Bundschuh, M.; Otto, M.; Schulz, R. Food-Related Exposure to Systemic Pesticides and Pesticides from Transgenic Plants: Evaluation of Aquatic Test Strategies. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBAMA (Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis). Os 10 Ingredientes Ativos Mais Vendidos-2020. Available online: http://www.ibama.gov.br/agrotoxicos/relatorios-de-comercializacao-de-agrotoxicos#hist-comercializacao (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- ANVISA (Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária). Resolução—RE N 1967, de 18 de Julho de 2019; Diário Oficial da União: Brasília, Brasil, 2019.
- UN Environment Programme. Stockholm Convention Stockholm Convention: On Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs); UN Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on Environmental Quality Standards in the Field of Water Policy, Amending and Subsequently Repealing Council Directives 82/176/EEC, 83/513/EEC, 84/156/EEC, 84/491/EEC, 86/280/EEC and Amending Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. 2008; 84–97.
- Pires, N.L.; Passos, C.J.S.; Morgado, M.G.A.; Mello, D.C.; Infante, C.M.C.; Caldas, E.D. Determination of Glyphosate, AMPA and Glufosinate by High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection in Waters of the Santarém Plateau, Brazilian Amazon. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2020, 55, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severo, E.S.; Marins, A.T.; Cerezer, C.; Costa, D.; Nunes, M.; Prestes, O.D.; Zanella, R.; Loro, V.L. Ecological Risk of Pesticide Contamination in a Brazilian River Located near a Rural Area: A Study of Biomarkers Using Zebrafish Embryos. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, L.F.C.B.; Montagner, C.C.; Almeida, M.B.; Kuroda, E.K.; Vidal, C.; Freire, R.L. Determination of Pesticides in the Source and Drinking Waters in Londrina, Paraná, Brazil. Semin. Cienc. Agrar. 2019, 40, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.G.; Steinke, G.; Arias, J.L.O.; Primel, E.G.; Cabrera, L.C. Evaluation of Pesticide Contamination in the Water Sources of Southwest Parana Cities. Rev. Virtual Química 2017, 9, 1800–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, C.S.; Alves, R.I.S.; Fregonesi, B.M.; Tonani, K.A.A.; Martinis, B.S.; Sierra, J.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J.L.; Segura-Muñoz, S. Chemical Contamination of Water and Sediments in the Pardo River, São Paulo, Brazil. Procedia. Eng. 2016, 162, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovini, E.M.; Deus, B.C.T.; Vilas-Boas, J.A.; Quadra, G.R.; Carvalho, L.; Mendonça, R.F.; de Pereira, R.O.; Cardoso, S.J. Three-Bestseller Pesticides in Brazil: Freshwater Concentrations and Potential Environmental Risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Pesticide a | Current Situation b,c | Maximum Value, µg/L a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1/2 | Class 3 | ||
| Alachlor | Registered: Environmental class II c | 20 | - |
| Atrazine | Registered: Environmental class I–III c | 2 | 2 |
| Carbaryl | Registered: Environmental class II c | 0.02 | 70 |
| 2,4-D | Registered: Environmental class I–III c | 4 | 30 |
| Glyphosate | Registered: Environmental class I–III c | 65 | 280 |
| Malathion | Registered: Environmental class I–IV c | 0.1 | 100 |
| Simazine | Registered: Environmental class II–III c | 2 | - |
| Trifuraline | Registered: Environmental class I–II c | 0.2 | - |
| 2,4,5-TP (fenoprop) | Not registered | 10 | 10 |
| Metolachlor | Not registered | 10 | - |
| Methoxychlor | Not registered | 0.03 | 20 |
| Demeton (demeton-O, demeton-S) | Not registered | 0.1 | 14 |
| Gution (azinphos methyl) | Not registered | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| Parathion | Not registered | 0.04 | 35 |
| 2,4,5–T | Not registered | 2 | 2 |
| Aldrin | POP | 0.005 | 0.03 |
| Chlordane (cis, trans) | POP | 0.04 | 0.3 |
| DDT (p,p’-DDT, p,p’-DDE, p,p’-DDD) | POP | 0.002 | 1 |
| 2,4-Dichlorophenol | POP | 0.3 | - |
| Dieldrin | POP | 0.005 | 0.03 |
| Endosulfan (I, II, sulphate) | POP | 0.056 | 0.22 |
| Endrin | POP | 0.004 | 0.2 |
| Heptachlor +heptachlor epoxide | POP | 0.000039/0.01 | 0.03 |
| Hexachlorobenzene | POP | 0.00029/0.0065 | - |
| Lindane (γ-HCH) | POP | 0.02 | 2 |
| Pentachlorophenol | POP | 3/9 | 9 |
| Toxaphene | POP | 0.00028/0.01 | 0.21 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Araújo, E.P.; Caldas, E.D.; Oliveira-Filho, E.C. Relationship between Pesticide Standards for Classification of Water Bodies and Ecotoxicity: A Case Study of the Brazilian Directive. Toxics 2022, 10, 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120767
de Araújo EP, Caldas ED, Oliveira-Filho EC. Relationship between Pesticide Standards for Classification of Water Bodies and Ecotoxicity: A Case Study of the Brazilian Directive. Toxics. 2022; 10(12):767. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120767
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Araújo, Esmeralda Pereira, Eloisa Dutra Caldas, and Eduardo Cyrino Oliveira-Filho. 2022. "Relationship between Pesticide Standards for Classification of Water Bodies and Ecotoxicity: A Case Study of the Brazilian Directive" Toxics 10, no. 12: 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120767
APA Stylede Araújo, E. P., Caldas, E. D., & Oliveira-Filho, E. C. (2022). Relationship between Pesticide Standards for Classification of Water Bodies and Ecotoxicity: A Case Study of the Brazilian Directive. Toxics, 10(12), 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120767









