Simulation Experiment of Environmental Impact of Deep-Sea Mining: Response of Phytoplankton Community to Polymetallic Nodules and Sediment Enrichment in Surface Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
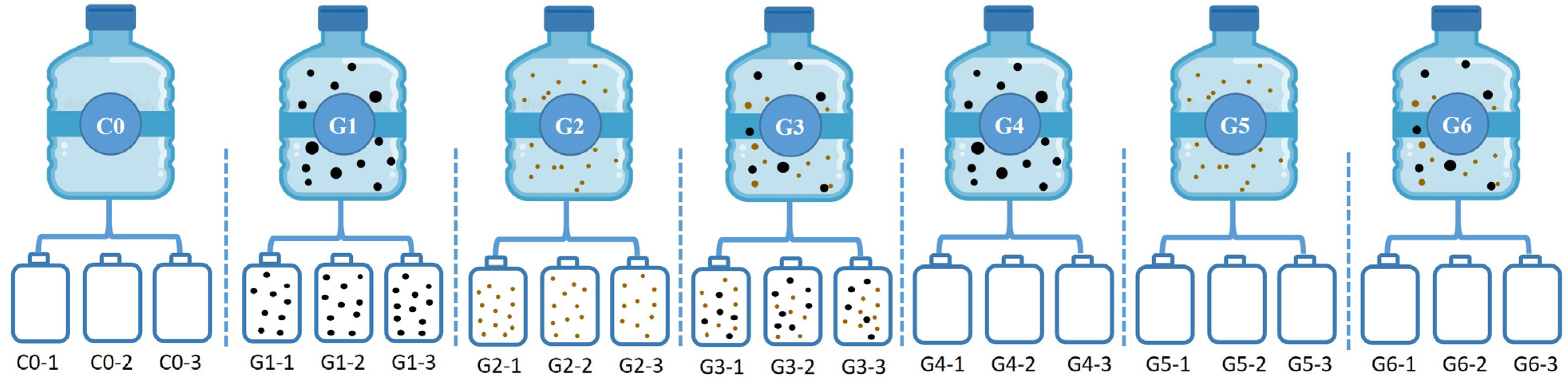
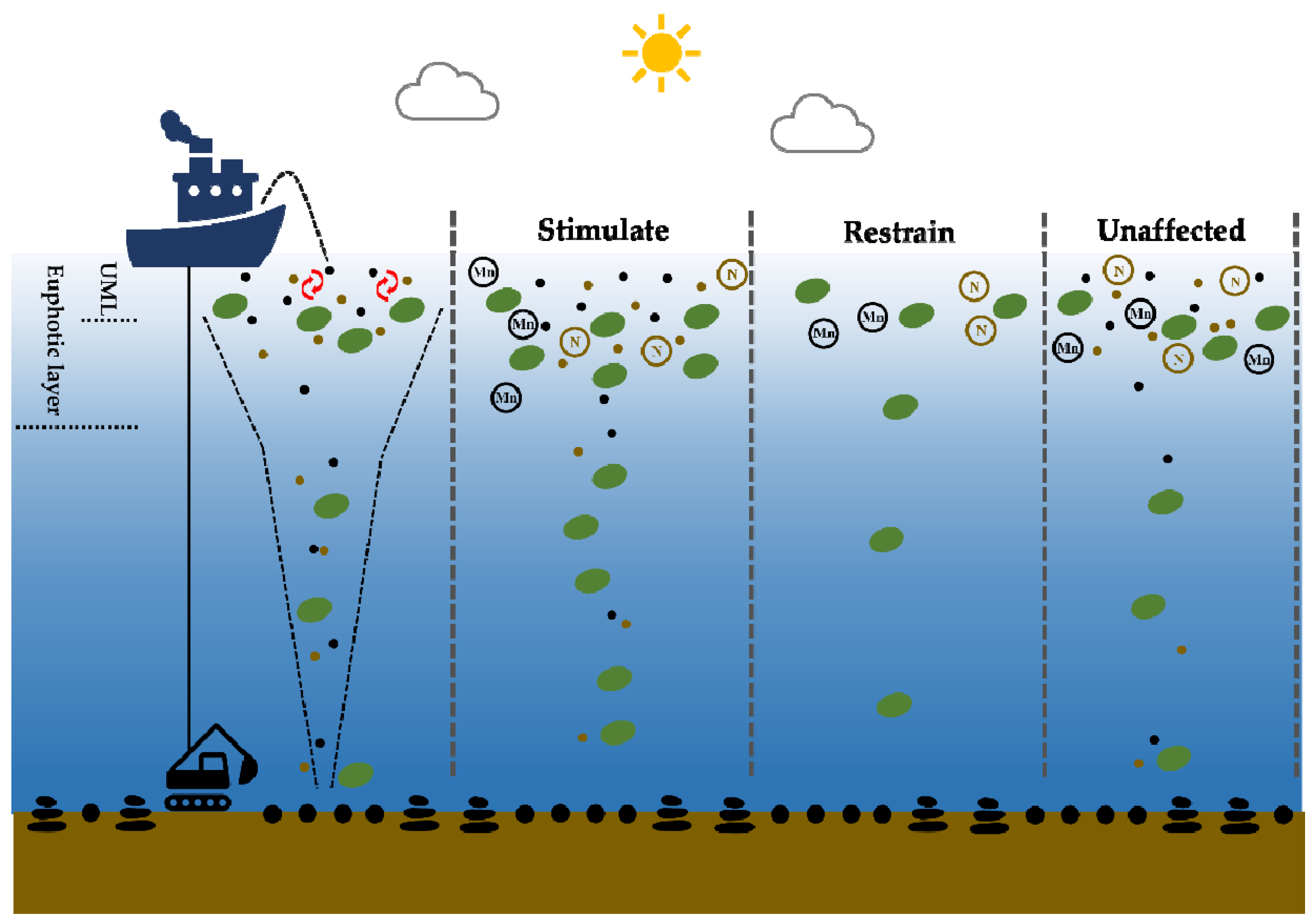
2.2. Culture Medium and Experimental Design
2.3. Sampling and Measurement
2.3.1. PMNs and Sediment
2.3.2. Chlorophyll a
2.3.3. Pico-Phytoplankton
2.3.4. Trace Metal
2.3.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
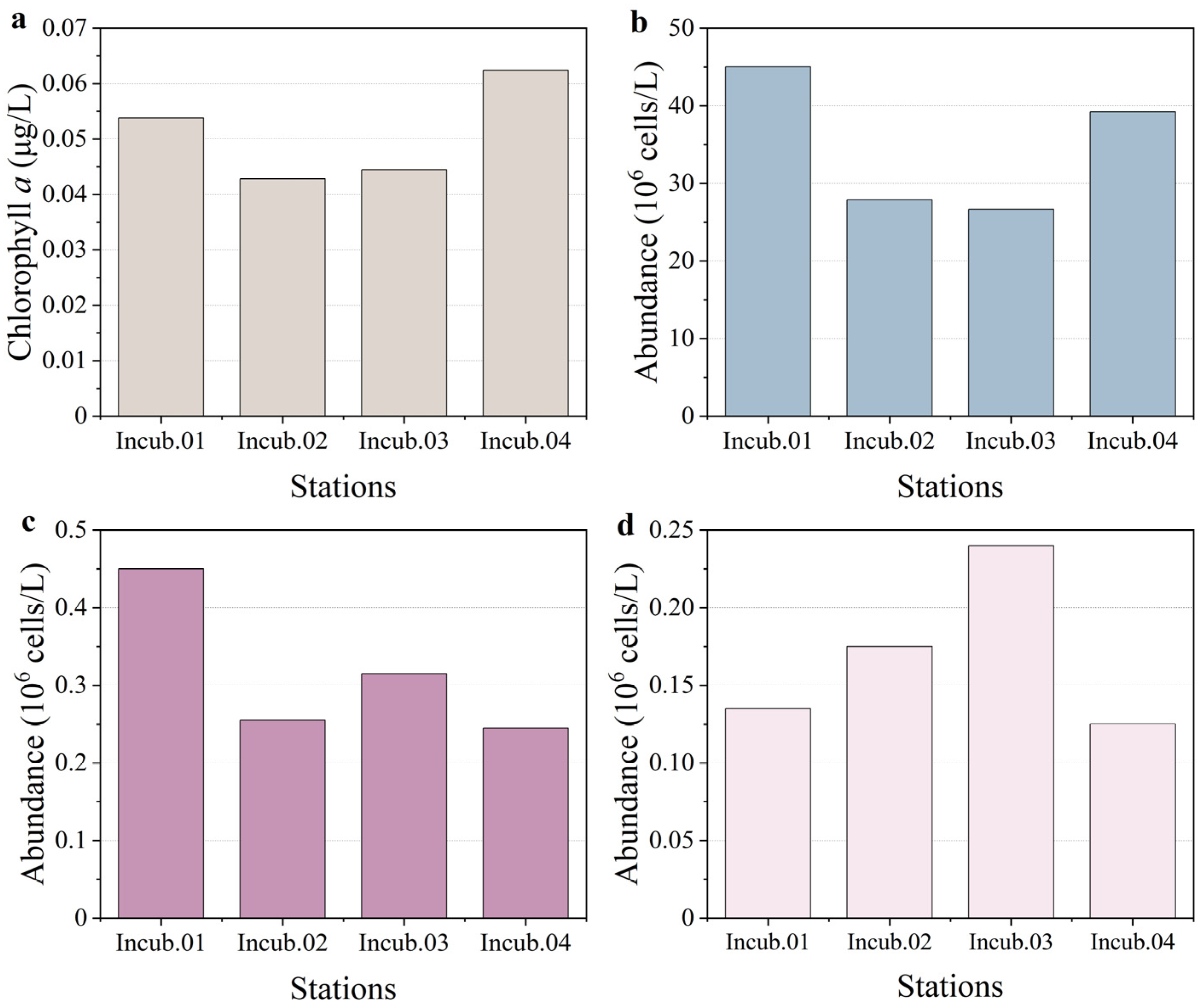
3.1. Phytoplankton Biomass and Community Composition Pre-Incubation, and Different Response Patterns to PMNs and Sediment Enrichment
3.2. Response of Pico-Phytoplankton Community
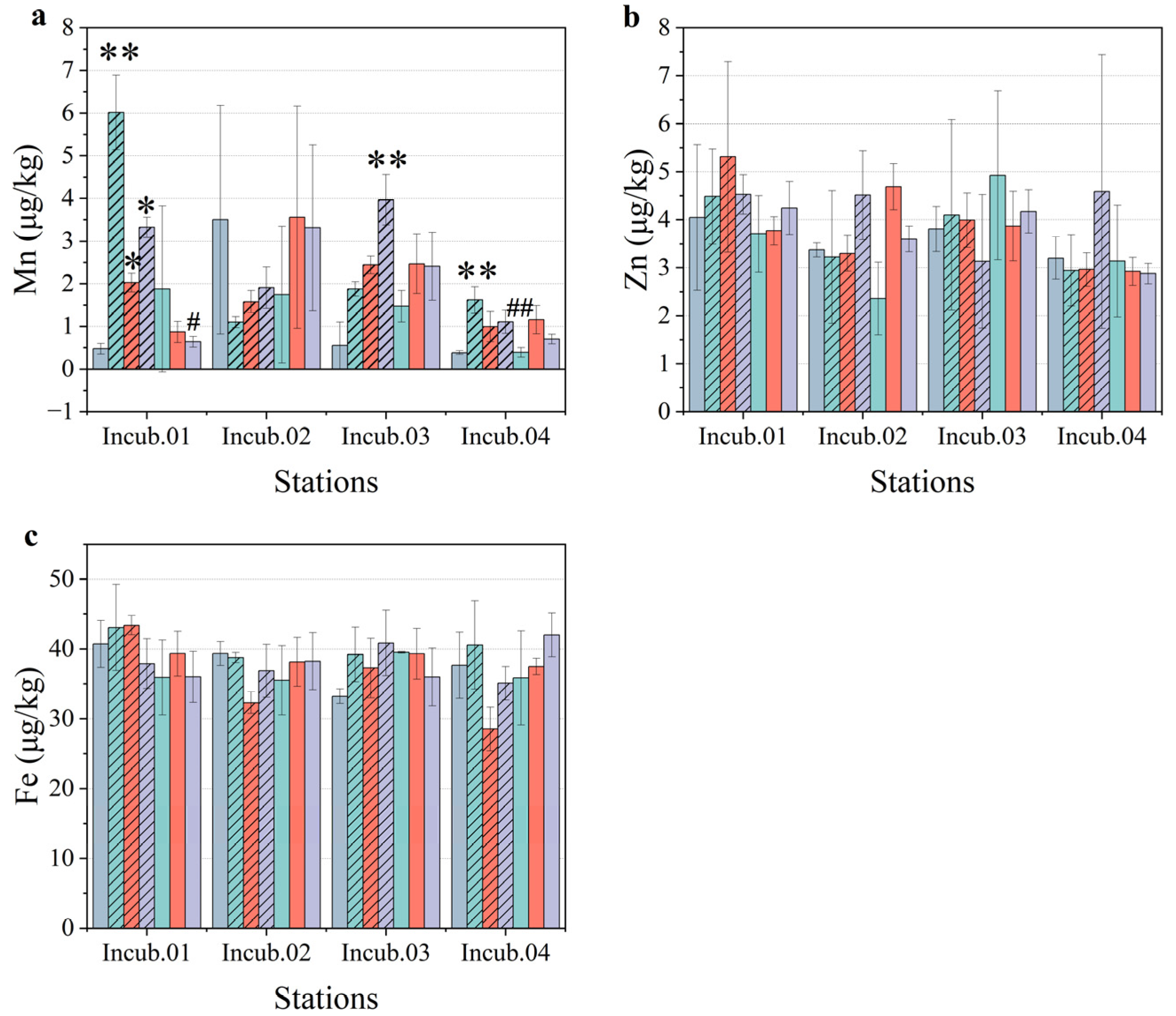
3.3. Metal Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- There were three different response patterns of phytoplankton to the addition of PMNs and sediments, namely, restrained, stimulated, and unaffected patterns. There was a significant variation in our results.
- The major factors that affected the response mechanism were complicated and acted in coordination. The phytoplankton biomass baseline determined the response, which indicated that a lower biomass was more likely to positively affect growth. Manganese assimilation was the most important physiological characteristic of pico-phytoplankton, especially for the dominant Prochlorococcus.
- The turbidity caused by the sediment was another important factor in the response of phytoplankton. As compared to the negative effect of reducing the available light, the unfiltered particles provided more available nutrients and metals for the growth of phytoplankton.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwerhoff, G.; Stuermer, M. Non-Renewable Resources, Extraction Technology and Endogenous Growth. Fed. Reserve Bank Dallas Work. Pap. 2019, 2015, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretariat of the Pacific Community. Deep Sea Minerals: Deep Sea Minerals and the Green Economy; Baker, E., Beaudoin, Y., Eds.; GRID-Arendal: Arendal, Norway, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 8–9. ISBN 978-82-7701-122-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hein, J.R.; Koschinsky, A.; Kuhn, T. Deep-ocean polymetallic nodules as a resource for critical materials. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, E.; Beaudoin, Y.; Secretariat of the Pacific Community. Deep Sea Minerals: Manganese Nodules, a Physical, Biological, Environmental, and Technical Review; Baker, E., Beaudoin, Y., Eds.; GRID-Arendal: Arendal, Norway, 2013; Volume 1B, pp. 10–11. ISBN 978-82-7701-120-2. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.R.; De Leo, F.C.; Bernardino, A.; Sweetman, A.K.; Martinez-Arbizu, P. Abyssal food limitation, ecosystem structure and climate change. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, E.; Beaudoin, Y.; Secretariat of the Pacific Community. Deep Sea Minerals: Cobalt-Rich Ferromanganese Crusts, a Physical, Biological, Environmental, and Technical Review; Baker, E., Beaudoin, Y., Eds.; GRID-Arendal: Arendal, Norway, 2013; Volume 1C, pp. 7–14. ISBN 78-82-7701-121-9. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.O.; Kaiser, S.; Sweetman, A.K.; Smith, C.R.; Menot, L.; Vink, A.; Trueblood, D.; Greinert, J.; Billett, D.S.M.; Arbizu, P.M.; et al. Biological responses to disturbance from simulated deep-sea polymetallic nodule mining. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jonge, D.S.; Stratmann, T.; Lins, L.; Vanreusel, A.; Purser, A.; Marcon, Y.; Rodrigues, C.F.; Ravara, A.; Esquete, P.; Cunha, M.R.; et al. Abyssal food-web model indicates faunal carbon flow recovery and impaired microbial loop 26 years after a sediment disturbance experiment. Prog. Oceanogr. 2020, 189, 102446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, R.; Londsdale, J. Risk assessment for deep sea mining: An overview of risk. Mar. Policy 2020, 114, 103485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, B.; Denda, A.; Christiansen, S. Potential effects of deep seabed mining on pelagic and benthopelagic biota. Mar. Policy 2019, 114, 103442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.A.; Thompson, K.F.; Johnston, P.; Santillo, D. An Overview of Seabed Mining Including the Current State of Development, Environmental Impacts, and Knowledge Gaps. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 4, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollner, S.; Kaiser, S.; Menzel, L.; Jones, D.O.; Brown, A.; Mestre, N.C.; van Oevelen, D.; Menot, L.; Colaço, A.; Canals, M.; et al. Resilience of benthic deep-sea fauna to mining activities. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 129, 76–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spearman, J.; Taylor, J.; Crossouard, N.; Cooper, A.; Turnbull, M.; Manning, A.; Lee, M.; Murton, B. Measurement and modelling of deep sea sediment plumes and implications for deep sea mining. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vare, L.L.; Baker, M.C.; Howe, J.A.; Levin, L.; Neira, C.; Ramirez-Llodra, E.Z.; Reichelt-Brushett, A.; Rowden, A.; Shimmield, T.M.; Simpson, S.; et al. Scientific Considerations for the Assessment and Management of Mine Tailings Disposal in the Deep Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Royo, C.; Peacock, T.; Alford, M.H.; Smith, J.A.; Le Boyer, A.; Kulkarni, C.S.; Lermusiaux, P.F.J.; Haley, P.J., Jr.; Mirabito, C.; Wang, D.; et al. Extent of impact of deep-sea nodule mining midwater plumes is influenced by sediment loading, turbulence and thresholds. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, P.P.E.; Billett, D.S.M.; Van Dover, C.L. Environmental Risks of Deep-sea Mining. In Handbook on Marine Environment Protection: Science, Impacts and Sustainable Management; Salomon, M., Markus, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 215–245. [Google Scholar]
- Hoagland, P.; Beaulieu, S.; Tivey, M.A.; Eggert, R.G.; German, C.; Glowka, L.; Lin, J. Deep-sea mining of seafloor massive sulfides. Mar. Policy 2010, 34, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, H. Evaluation of the environmental consequences of polymetallic nodule mining based on the results of the TUSCH Research Association. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2001, 48, 3433–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oebius, H.U.; Becker, H.J.; Rolinski, S.; A Jankowski, J. Parametrization and evaluation of marine environmental impacts produced by deep-sea manganese nodule mining. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2001, 48, 3453–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISA. Recommendations for the Guidance of Contractors for the Assessment of the Possible Environmental Impacts Arising from Exploration for Polymetallic Nodules in the Area; ISBA/16/LTC/7; ISA: Kingston, Jamaica, 2010; Available online: https://isa.org.jm/files/files/documents/isba-16ltc-7_0.pdf (accessed on 11 October 2022).
- ISA. Recommendations for the Guidance of Contractors for the Assessment of the Possible Environmental Impacts Arising from Exploration for Marine Minerals in the Area; ISBA/25/LTC/6/Rev.1; ISA: Kingston, Jamaica, 2020; Available online: https://isa.org.jm/files/files/documents/26ltc-6-rev1-en_0.pdf (accessed on 11 October 2022).
- Howard, P.; Jenner, N.; Parker, G. New report applies the mitigation hierarchy and deep-ocean science to determine risks and impacts of deep-seabed mining. Oryx 2020, 54, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-T.A.; Liu, K.-K.; Macdonald, R. Continental Margin Exchanges. In Ocean Biogeochemistry: The Role of the Ocean Carbon Cycle in Global Change; Fasham, M.J.R., Ed.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 53–97. [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm, S.; Olson, R.J.; Zettler, E.; Goericke, R.; Waterbury, J.B.; Welschmeyer, N.A. A novel free-living prochlorophyte abundant in the oceanic euphotic zone. Nature 1988, 334, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterbury, J.B.; Watson, S.W.; Guillard, R.R.L.; Brand, L.E. Widespread occurrence of a unicellular, marine, planktonic, cyanobacterium. Nature 1979, 277, 293–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon-van der Staay, S.Y.; De Wachter, R.; Vaulot, D. Oceanic 18S rDNA sequences from picoplankton reveal unsuspected eukaryotic diversity. Nature 2001, 409, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grob, C.; Ulloa, O.; Claustre, H.; Huot, Y.; Alarcón, G.; Marie, D. Contribution of picoplankton to the total particulate organic carbon concentration in the eastern South Pacific. Biogeosciences 2007, 4, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, C.B.; Behrenfeld, M.J.; Randerson, J.T.; Falkowski, P. Primary Production of the Biosphere: Integrating Terrestrial and Oceanic Components. Science 1998, 281, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twining, B.S.; Baines, S.B. The Trace Metal Composition of Marine Phytoplankton. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2013, 5, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, P.; Marigoudar, S.R.; Nagarjuna, A.; Sharma, K.V. Toxicity assessment of cobalt and selenium on marine diatoms and copepods. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2019, 1, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Wang, B.; Kang, R.; Huo, R.; Randhawa, V. Aureococcus anophagefferens growth potential affected by coastal water toxicants. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, E.R.; Scherfig, J.; Dixon, P.S. Effects of manganese, copper and lead on Selenastrum capricornutum and Chlorella stigmatophora. Water Res. 1979, 13, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowska, A.; Kamennaya, N.A.; Murton, B.J.; Zubkov, M.V. Impact of ferromanganese ore pollution on phytoplankton CO2 fixation in the surface ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, T.; Maita, Y.; Lalli, C.M. Amanual of chemical and biological methods for seawater analysis. In Biological Oceanographic Processes; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984; p. 173. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, R.J.; Zettler, E.R.; DuRand, M.D. Phytoplankton analysis using flow cytometry. In Handbook of Methods in Aquatic Microbial Ecology; Kemp, P.F., Sherr, B.F., Sherr, E.B., Cole, J.J., Eds.; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; pp. 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Irwin, A.J.; Finkel, Z.V. Mining a Sea of Data: Deducing the Environmental Controls of Ocean Chlorophyll. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessmann, D.; Fyson, A.; Nixdorf, B. Experimental eutrophication of a shallow acidic mining lake and effects on the phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugdale, R.C. Nutrient limitation in the sea dynamics, identification, and significance. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1967, 12, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunda, W.G. Feedback Interactions between Trace Metal Nutrients and Phytoplankton in the Ocean. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanan, S.; Hagar, L.; Yeala, S.; Nir, K. Iron–Nutrient Interactions within Phytoplankton. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1223. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.H. Glacial-interglacial CO2 change: The iron hypothesis. Paleoceanography 1990, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; McCain, J.S.P.; Rowland, E.; Middag, R.; Sandgren, M.; Allen, A.E.; Bertrand, E.M. Manganese and iron deficiency in Southern Ocean Phaeocystis antarctica populations revealed through taxon-specific protein indicators. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, J.H.; Kim, K.H.; Jung, H.S.; Lee, K.Y. Potential environmental impact of deep seabed manganese nodule mining on the synechococcus (cyanobacteria) in the northeast equatorial pacific: Effect of bottom water-sediment slurry. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 1998, 16, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, T.J.; Achterberg, E.P.; Engel, A.; Mawji, E. Manganese co-limitation of phytoplankton growth and major nutrient drawdown in the Southern Ocean. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunda, W.G.; Huntsman, S.A. Effect of sunlight on redox cycles of manganese in the southwestern Sargasso Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part A Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1998, 35, 1297–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, J.A.; Evans, M.C.W.; Korb, R.E. The role of trace metals in photosynthetic electron transport in O2-evolving organisms. Photosynth. Res. 1999, 60, 111–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturgut, E.; Lavelle, J.W.; Burns, R.E. Chapter 15 Impacts of Manganese Nodule Mining on the Environment: Results from Pilot-Scale Mining Tests in the North Equatorial Pacific. In Elsevier Oceanography Series; Geyer, R.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981; Volume 27, pp. 437–474. [Google Scholar]
- Schriever, G.; Thiel, H. Tailings and their Disposal in Deep-Sea Mining. In Proceedings of the Tenth ISOPE Ocean Mining and Gas Hydrates Symposium, Szczecin, Poland, 22–26 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, R.E. Assessment of environmental effects of deep ocean mining of manganese nodules. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, A.F.; Roels, O.A. Environmental aspects of manganese nodule mining. Mar. Policy 1977, 1, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
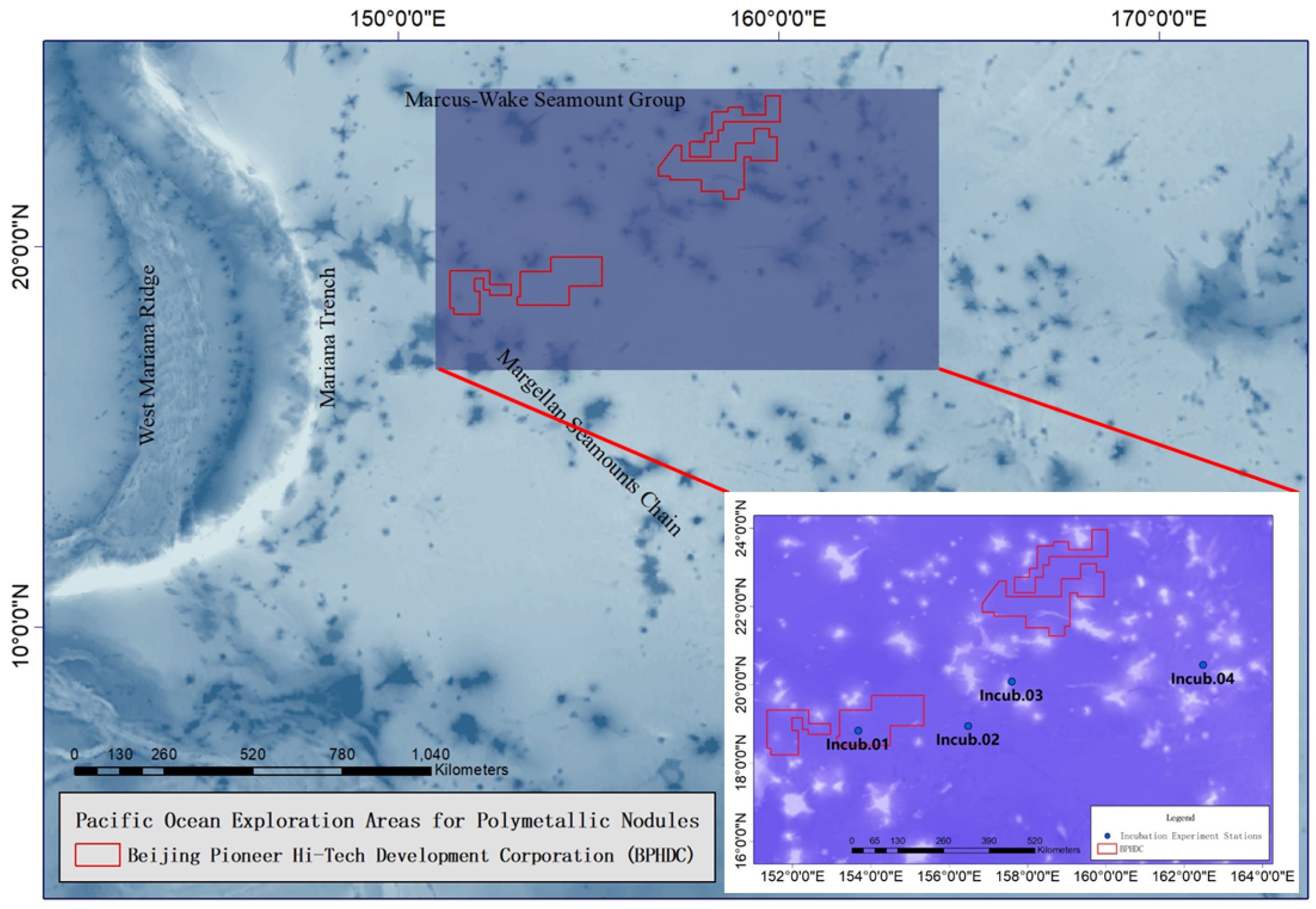



| Station | Date | Time | Latitude (N) | Longitude (E) | Depth (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incub.01 | 27 October 2021 | 09:41 | 18°49.8317′ | 152°53.3914′ | 5528 |
| Incub.02 | 28 October 2021 | 07:43 | 18°49.9030′ | 153°16.2637′ | 5668 |
| Incub.03 | 29 October 2021 | 04:43 | 18°49.6079′ | 153°40.4914′ | 5650 |
| Incub.04 | 30 October 2021 | 00:27 | 18°33.7015′ | 153°40.5757′ | 5645 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ou, R.; Cai, L.; Qiu, J.; Huang, H.; Ou, D.; Li, W.; Lin, F.; He, X.; Wang, L.; Wu, R. Simulation Experiment of Environmental Impact of Deep-Sea Mining: Response of Phytoplankton Community to Polymetallic Nodules and Sediment Enrichment in Surface Water. Toxics 2022, 10, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100610
Ou R, Cai L, Qiu J, Huang H, Ou D, Li W, Lin F, He X, Wang L, Wu R. Simulation Experiment of Environmental Impact of Deep-Sea Mining: Response of Phytoplankton Community to Polymetallic Nodules and Sediment Enrichment in Surface Water. Toxics. 2022; 10(10):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100610
Chicago/Turabian StyleOu, Rimei, Lei Cai, Jinli Qiu, Hao Huang, Danyun Ou, Weiwen Li, Fanyu Lin, Xuebao He, Lei Wang, and Risheng Wu. 2022. "Simulation Experiment of Environmental Impact of Deep-Sea Mining: Response of Phytoplankton Community to Polymetallic Nodules and Sediment Enrichment in Surface Water" Toxics 10, no. 10: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100610
APA StyleOu, R., Cai, L., Qiu, J., Huang, H., Ou, D., Li, W., Lin, F., He, X., Wang, L., & Wu, R. (2022). Simulation Experiment of Environmental Impact of Deep-Sea Mining: Response of Phytoplankton Community to Polymetallic Nodules and Sediment Enrichment in Surface Water. Toxics, 10(10), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100610






