Effects of Polystyrene Diet on the Growth and Development of Tenebrio molitor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Treatments
2.2. Physical Representation of Excrement and Histology Observation of Intestinal Tract
2.3. Illumina Sequencing for Transcriptome Analysis
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Validation
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Vital Signs of Tenebrio molitor Larvae and Degradation Rate of PS
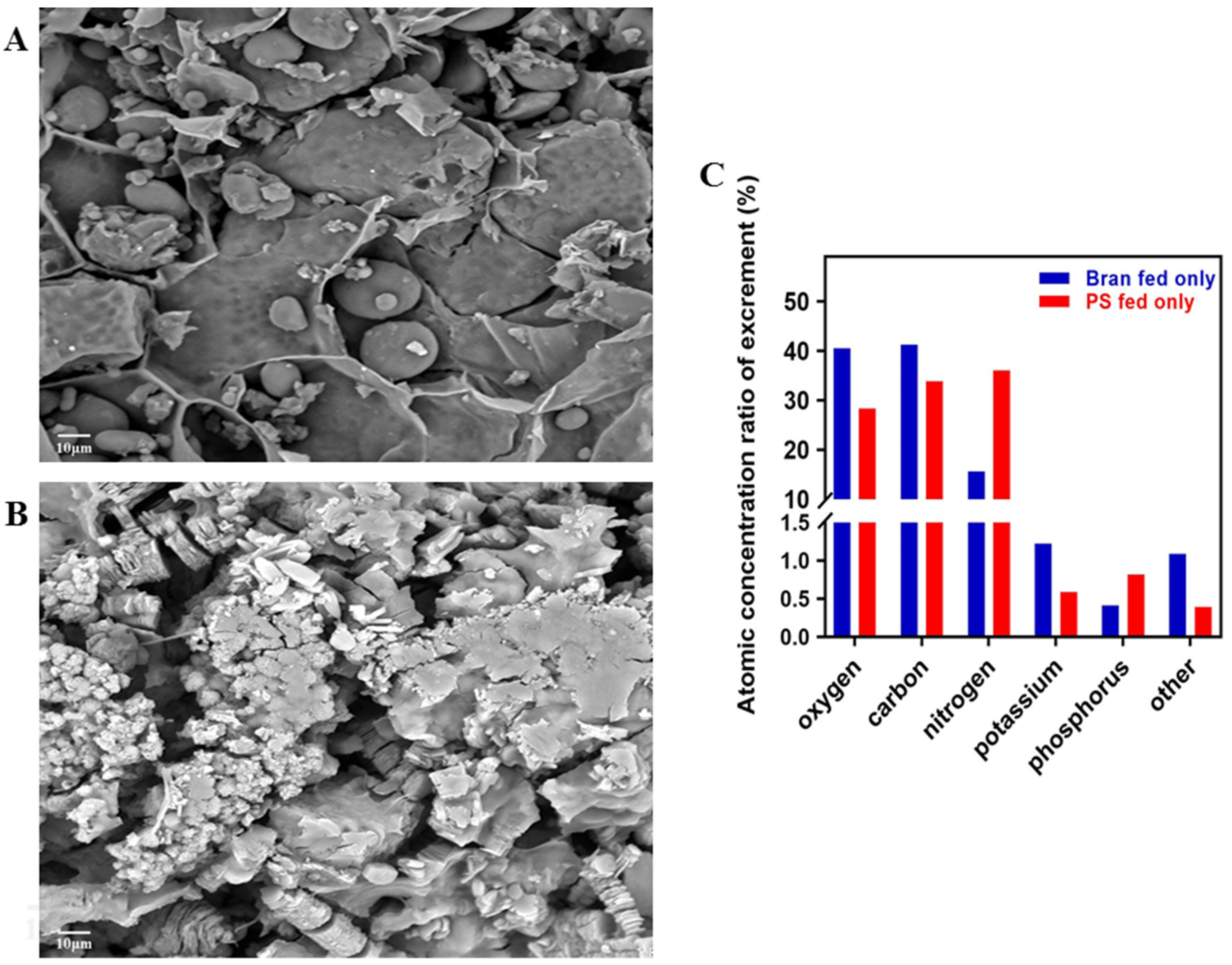
3.2. Physical and Chemical Representation of Excrement
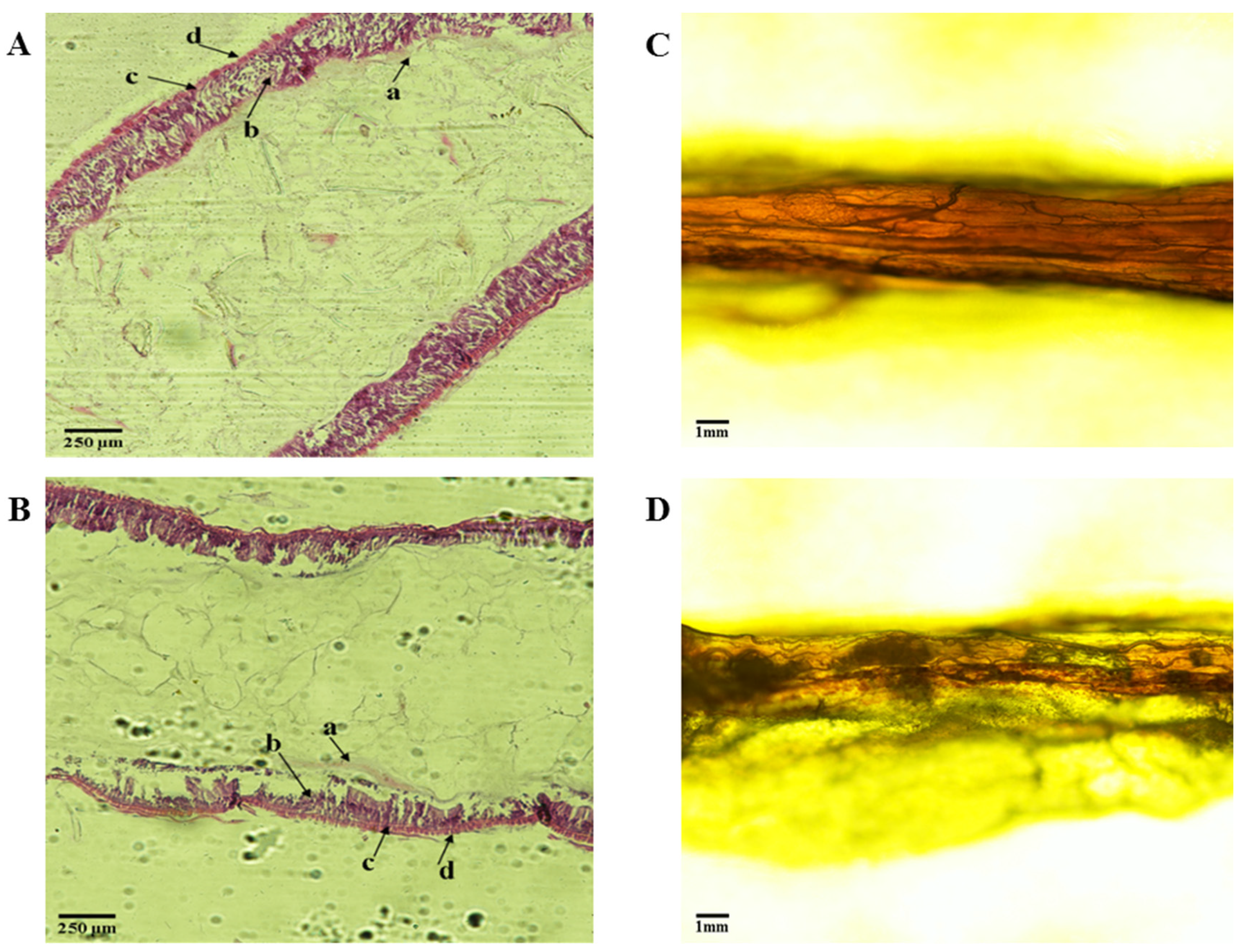
3.3. Midgut of Tenebrio molitor Larva
3.4. Transcriptome Analysis and qRT-PCR Verification
3.4.1. Statistics of Transcriptome Sequencing Yield
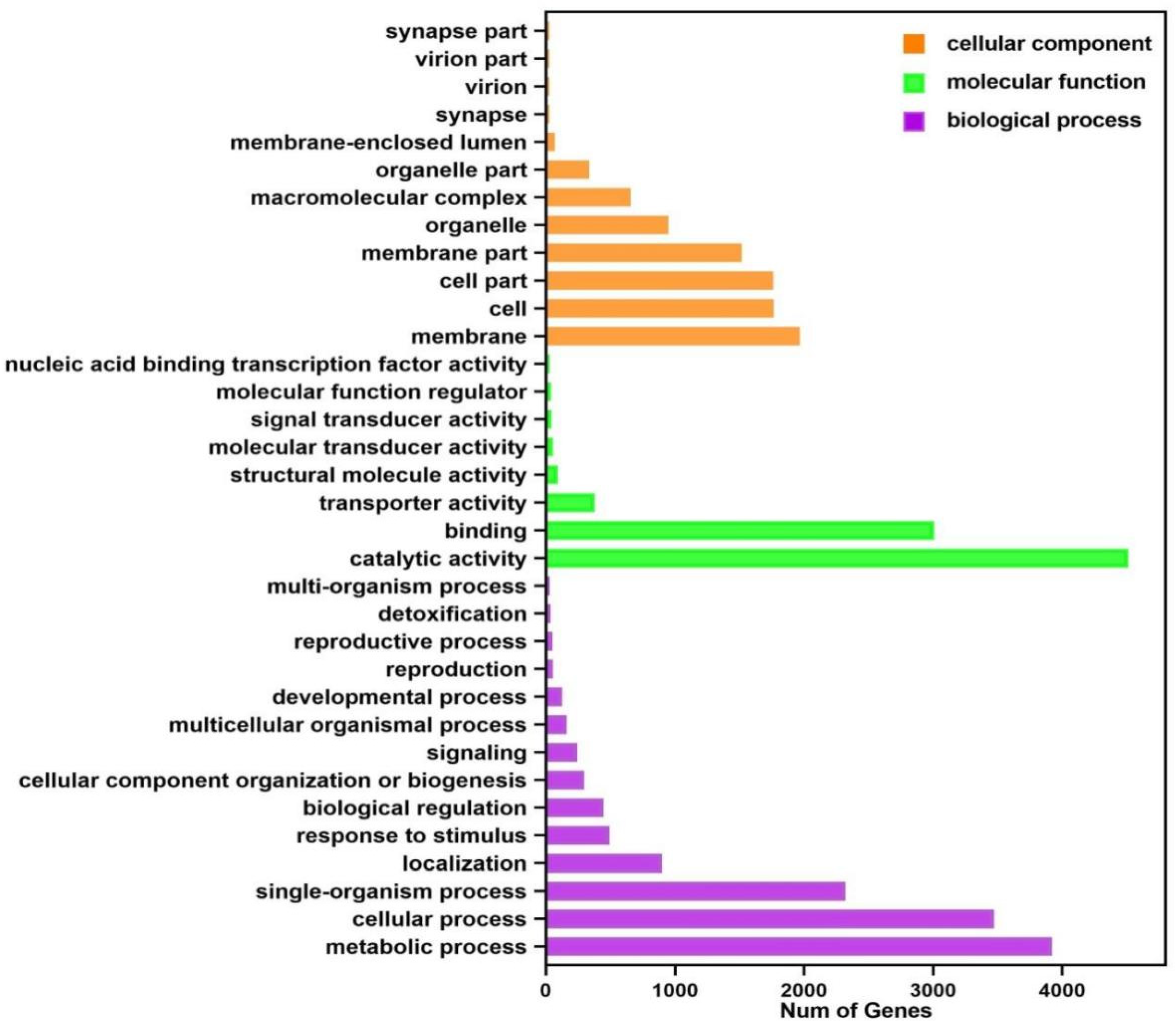
3.4.2. Gene Ontology (GO) Functional Classification of Transcriptome
3.4.3. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
3.4.4. Genetic Analysis and qRT-PCR Verification
4. Discussion
4.1. Vital Signs of Tenebrio molitor Larvae and Degradation Rate of PS
4.2. Physical and Chemical Characterization of Tenebrio molitor Excrement
4.3. Histological Observation on Intestinal Tract of Tenebrio molitor
4.4. Transcriptomic Analysis and qRT-PCR Test of Tenebrio molitor
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ho, B.T.; Roberts, T.K.; Lucas, S. An Overview on Biodegradation of Polystyrene and Modified Polystyrene: The Microbial Approach. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajendiran, A.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Abraham, J. Microbial Degradation of Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) by Aspergillus Clavatus Strain JASK1 Isolated from Landfill Soil. 3 Biotech. 2016, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, Use, and Fate of All Plastics Ever Made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Hernandez, J.C. A Toxicological Perspective of Plastic Biodegradation by Insect Larvae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 248, 109117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenti, C.C.; Binelli, A.; Caccia, S.; Della Torre, C.; Magni, S.; Pirovano, G.; Casartelli, M. Ingestion and Effects of Polystyrene Nanoparticles in the Silkworm Bombyx Mori. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, M. Biodegradation and Mineralization of Polystyrene by Plastic-Eating Superworms Zophobas Atratus. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandon, A.M.; Garcia, A.M.; Khlystov, N.A.; Wu, W.M.; Criddle, C.S. Enhanced Bioavailability and Microbial Biodegradation of Polystyrene in an Enrichment Derived from the Gut Microbiome of Tenebrio Molitor (Mealworm Larvae). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 2027–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xin, X.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y. A Polystyrene-Degrading Acinetobacter Bacterium Isolated from the Larvae of Tribolium Castaneum. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nukmal, N.; Umar, S.; Amanda, S.P.; Kanedi, M. Effect of Styrofoam Waste Feeds on the Growth, Development and Fecundity of Mealworms (Tenebrio Molitor). Online J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 18, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelkheir, M.G.; Visconte, L.Y.; Oliveira, G.E.; Toledo Filho, R.D.; Souza, F.G. The Biodegradative Effect of Tenebrio Molitor Linnaeus Larvae on Vulcanized SBR and Tire Crumb. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Su, T.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z. Biodegradation of Polystyrene by Tenebrio Molitor, Galleria Mellonella, and Zophobas Atratus Larvae and Comparison of Their Degradation Effects. Polymers 2021, 13, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, W.M.; Zhao, J.; Song, Y.; Gao, L.; Yang, R.; Jiang, L. Biodegradation and Mineralization of Polystyrene by Plastic-Eating Mealworms: Part 1. Chemical and Physical Characterization and Isotopic Tests. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12080–12086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, W.M.; Zhao, J.; Song, Y.; Gao, L.; Yang, R.; Jiang, L. Biodegradation and Mineralization of Polystyrene by Plastic-Eating Mealworms: Part 2. Role of Gut Microorganisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12087–12093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przemieniecki, S.W.; Kosewska, A.; Ciesielski, S.; Kosewska, O. Changes in the Gut Microbiome and Enzymatic Profile of Tenebrio Molitor Larvae Biodegrading Cellulose, Polyethylene and Polystyrene Waste. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandon, A.M.; Gao, S.H.; Tian, R.; Ning, D.; Yang, S.S.; Zhou, J.; Wu, W.-M.; Criddle, C.S. Biodegradation of Polyethylene and Plastic Mixtures in Mealworms (Larvae of Tenebrio Molitor) and Effects on the Gut Microbiome. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6526–6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.Q.; Luo, L.P.; Yang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.M.; Lu, Y.L.; Zhao, X.; Hu, X.M. Research progress on plastic degradation by worms. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2020, 26, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröncke, N.; Grebenteuch, S.; Keil, C.; Demtröder, S.; Kroh, L.; Thünemann, A.F.; Benning, R.; Haase, H. Effect of Different Drying Methods on Nutrient Quality of the Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio Molitor L.). Insects 2019, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.J.; Hwang, I.K.; Nho, C.W.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, S.H. Determination of Carbohydrate Composition in Mealworm (Tenebrio Molitor L.) Larvae and Characterization of Mealworm Chitin and Chitosan. Foods 2021, 10, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, E.; Zieliński, D.; Jakubczyk, A.; Karaś, M.; Pankiewicz, U.; Flasz, B.; Dziewięcka, M.; Lewicki, S. The Impact of Polystyrene Consumption by Edible Insects Tenebrio Molitor and Zophobas Morio on Their Nutritional Value, Cytotoxicity, and Oxidative Stress Parameters. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.J.; Yang, H.S.; Wang, D.F.; Cao, T.; Liu, S.M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhou, H.L. Advances in application of Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio Molitor) meal as protein sources in diets of pigs, broilers and fishes. Chin. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 57, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.S.; Cho, K.H.; Hong, J.S.; Jang, H.S.; Chung, Y.H.; Kwon, G.T.; Shin, D.G.; Kim, Y.Y. Nutrient Ileal Digestibility Evaluation of Dried Mealworm (Tenebrio Molitor) Larvae Compared to Three Animal Protein by-Products in Growing Pigs. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Han, T.; Kim, Y.Y. Mealworm (Tenebrio Molitor Larvae) as an Alternative Protein Source for Monogastric Animal: A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Nutrition; Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA); Turck, D.; Bohn, T.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; et al. Safety of Frozen and Dried Formulations from Whole Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio Molitor Larva) as a Novel Food Pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordiean, A.; Krzyżaniak, M.; Stolarski, M.J.; Czachorowski, S.; Peni, D. Will Yellow Mealworm Become a Source of Safe Proteins for Europe? Agriculture. 2020, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garino, C.; Mielke, H.; Knüppel, S.; Selhorst, T.; Broll, H.; Braeuning, A. Quantitative Allergenicity Risk Assessment of Food Products Containing Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio Molitor). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 142, 111460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałęcki, R.; Michalski, M.M.; Wierzchosławski, K.; Bakuła, T. Gastric Canthariasis Caused by Invasion of Mealworm Beetle Larvae in Weaned Pigs in Large-Scale Farming. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.M.; Criddle, C.S. Characterization of Biodegradation of Plastics in Insect Larvae. Methods Enzym. 2021, 648, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Ekaterina, P.; Yang, S.S.; Lu, B.; Liu, B.; Ren, N.; Corvini PF, X.; Xing, D. Biodegradation of Polyethylene and Polystyrene by Greater Wax Moth Larvae (Galleria Mellonella L.) and the Effect of Co-Diet Supplementation on the Core Gut Microbiome. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2821–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsochatzis, E.; Lopes, J.A.; Gika, H.; Theodoridis, G. Polystyrene Biodegradation by Tenebrio Molitor Larvae: Identification of Generated Substances Using a GC-MS Untargeted Screening Method. Polymers 2020, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Hwang, I.-K.; Nho, C.W.; Kim, S.H. Could Defatted Mealworm (Tenebrio Molitor) and Mealworm Oil Be Used as Food Ingredients? Foods 2020, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adámková, A.; Mlček, J.; Adámek, M.; Borkovcová, M.; Bednářová, M.; Hlobilová, V.; Knížková, I.; Juríková, T. Tenebrio Molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae)-Optimization of Rearing Conditions to Obtain Desired Nutritional Values. J. Insect Sci. 2020, 20, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, S.X.; Tian, Y.Z.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, H. Effects of temperature on development and humoral immune defense of Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) larvae. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2014, 57, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.S.; Wu, W.M.; Brandon, A.M.; Fan, H.Q.; Receveur, J.P.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Fan, R.; McClellan, R.L.; Gao, S.H.; et al. Ubiquity of Polystyrene Digestion and Biodegradation within Yellow Mealworms, Larvae of Tenebrio Molitor Linnaeus (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Chemosphere 2018, 212, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matyja, K.; Rybak, J.; Hanus-Lorenz, B.; Wróbel, M.; Rutkowski, R. Effects of Polystyrene Diet on Tenebrio Molitor Larval Growth, Development and Survival: Dynamic Energy Budget (DEB) Model Analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Tao, H.; Wong, M.H. Feeding and Metabolism Effects of Three Common Microplastics on Tenebrio Molitor L. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodschneider, R.; Crailsheim, K. Nutrition and health in honey bees. Apidologie 2010, 41, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, A.P. Protein and amino acid requirements of the honeybee (Apis mellifera). Physiol. Comp. Oecol. 1953, 3, 197–285. [Google Scholar]
- Renault, D.; Hervant, F.; Vernon, P. Comparative Study of the Metabolic Responses during Food Shortage and Subsequent Recovery at Different Temperatures in the Adult Lesser Mealworm, Alphitobius Diaperinus (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Physiol. Entomol. 2002, 27, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanek, A.K.; Rybak, J.; Wróbel, M.; Leluk, K.; Mirończuk, A.M. A Comprehensive Assessment of Microbiome Diversity in Tenebrio Molitor Fed with Polystyrene Waste. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, B.; Liu, Q.; Yang, S.-S.; Liu, B.; Ren, N.; Wu, W.-M.; Xing, D. Response of the Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio Molitor) Gut Microbiome to Diet Shifts during Polystyrene and Polyethylene Biodegradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, L.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, C.; Guo, H.; Han, T.; Zhou, A.; Zhao, X. Different Plastics Ingestion Preferences and Efficiencies of Superworm (Zophobas Atratus Fab.) and Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio Molitor Linn.) Associated with Distinct Gut Microbiome Changes. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Sharma, N. Mechanistic Implications of Plastic Degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 561–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S. Treholose Regulation, One Aspect of Metabolic Homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1978, 23, 389–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Tang, S.; Li, D.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, T. Transcriptional Response Provides Insights into the Effect of Chronic Polystyrene Nanoplastic Exposure on Daphnia Pulex. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, H.; Koshland, D.E. Trehalose Is a Versatile and Long-Lived Chaperone for Desiccation Tolerance. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 2758–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, M.; Shen, Q.; Liu, X.; Shi, Z.; Wang, S.; Tang, B. Functional Characterization of Three Trehalase Genes Regulating the Chitin Metabolism Pathway in Rice Brown Planthopper Using RNA Interference. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Qu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Q. Structural Analysis of Group II Chitinase (ChtII) Catalysis Completes the Puzzle of Chitin Hydrolysis in Insects. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 2652–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baia-da-Silva, D.C.; Alvarez LC, S.; Lizcano, O.V.; Costa, F.T.M.; Lopes, S.C.P.; Orfanó, A.S.; Pascoal, D.O.; Nacif-Pimenta, R.; Rodriguez, I.C.; Guerra, M.; et al. The Role of the Peritrophic Matrix and Red Blood Cell Concentration in Plasmodium Vivax Infection of Anopheles Aquasalis. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genta, F.A.; Blanes, L.; Cristofoletti, P.T.; do Lago, C.L.; Terra, W.R.; Ferreira, C. Purification, Characterization and Molecular Cloning of the Major Chitinase from Tenebrio Molitor Larval Midgut. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 36, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, S. 20-Hydroxyecdysone Enhances the Expression of the Chitinase 5 via Broad-Complex Zinc-Finger 4 during Metamorphosis in Silkworm, Bombyx Mori. Insect Mol. Biol. 2017, 26, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrashed, S.A.A.; Bakar, F.D.A.; Said, M.; Hassan, O.; Rabu, A.; Illias, R.M.; Murad, A.M.A. Expression and characterization of the recombinant Trichoderma virens endochitinase Cht2. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 4, 1758–1767. [Google Scholar]
- Werck-Reichhart, D.; Feyereisen, R. Cytochromes P450: A Success Story. Genome. Biol. 2000, 1, reviews3003.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feyereisen, R. Insect P450 Enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1999, 44, 507–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.H. Molecular mechanisms of cytochrome P450-mediated drug resistance in insects. J. Insectol. 2014, 57, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.S.; Peck, L.S. Triggers of the HSP70 Stress Response: Environmental Responses and Laboratory Manipulation in an Antarctic Marine Invertebrate (Nacella Concinna). Cell Stress Chaperones 2009, 14, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravaux, J.; Toullec, J.Y.; Léger, N.; Lopez, P.; Gaill, F.; Shillito, B. First Hsp70 from Two Hydrothermal Vent Shrimps, Mirocaris Fortunata and Rimicaris Exoculata: Characterization and Sequence Analysis. Gene 2007, 386, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Unigene Number | Primers | Protein (& Gene) Description |
|---|---|---|
| N/A | F 5′-GTGGTCGTTTCTGGCAAACT-3′ R 5′-CAACACTCCTTGCCTCAACA-3′ | Ribosomal protein S3(RpS3) |
| Unigene028165 | F 5′-CCTGGGCACGACCTACTC-3′ R 5′-GGGTGGTTCTGTTACCTTGG-3′ | Heat shock protein 70 (YHSP70) |
| Unigene040524 | F 5′-TGGGATGGGTTCTTGCTG-3′ R 5′-GACCTGGGTGGTGGGATG-3′ | Chitinase (chit5) |
| Unigene049660 | F 5′-CTTTACCTACCCACGGTTCC-3′ R 5′-AGCATTTACGAATACACACGG-3′ | Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase CYP4BN28(N/A) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Tang, T. Effects of Polystyrene Diet on the Growth and Development of Tenebrio molitor. Toxics 2022, 10, 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100608
Wang X, Tang T. Effects of Polystyrene Diet on the Growth and Development of Tenebrio molitor. Toxics. 2022; 10(10):608. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100608
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaosu, and Tianle Tang. 2022. "Effects of Polystyrene Diet on the Growth and Development of Tenebrio molitor" Toxics 10, no. 10: 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100608
APA StyleWang, X., & Tang, T. (2022). Effects of Polystyrene Diet on the Growth and Development of Tenebrio molitor. Toxics, 10(10), 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100608





