Contamination and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil and Ditch Sediments in Long-Term Mine Wastes Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
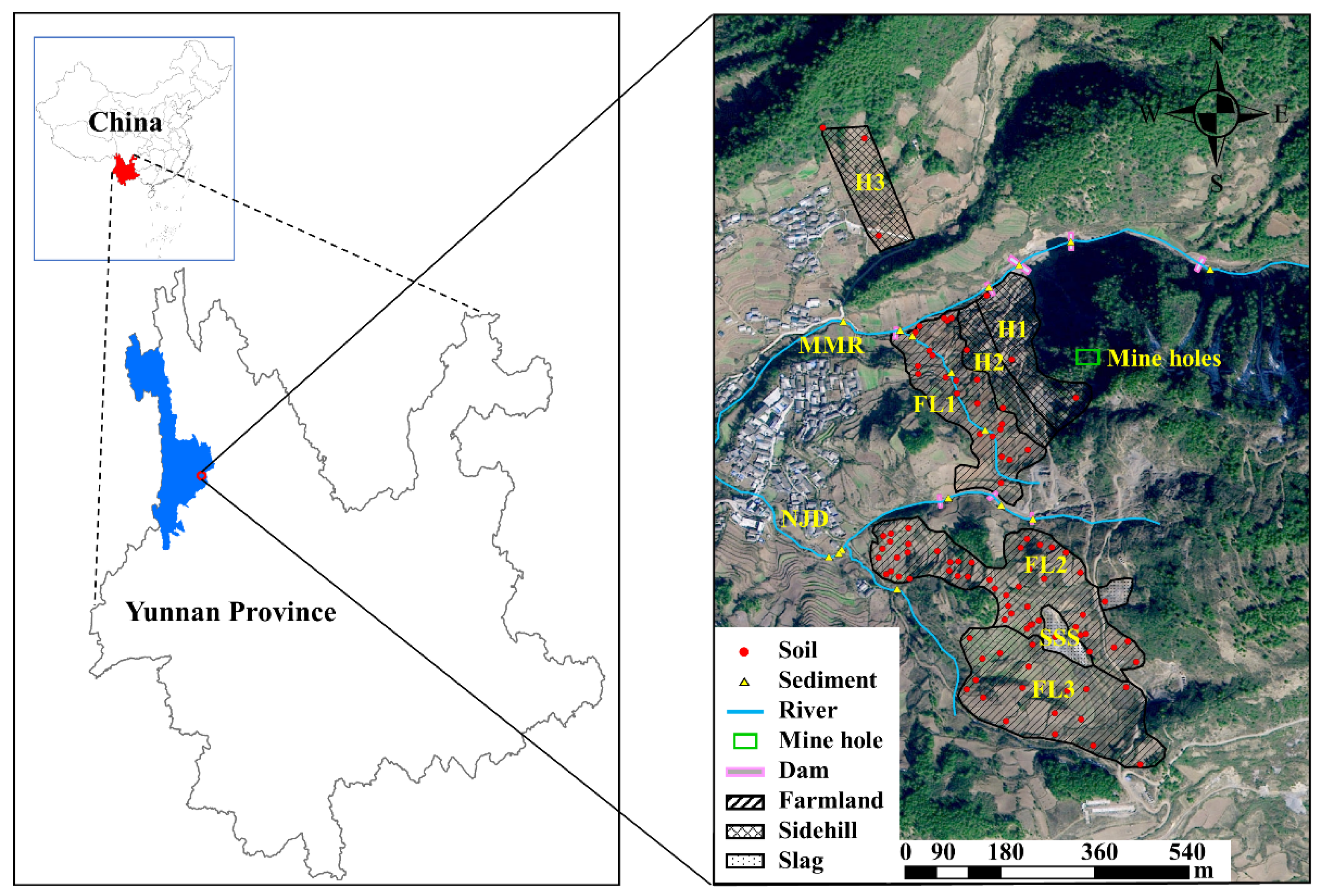
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.4. Semivariance Analysis
2.5. Pollution Assessment
2.6. Exposure Assessment
2.7. Data Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. pH and OM Contents
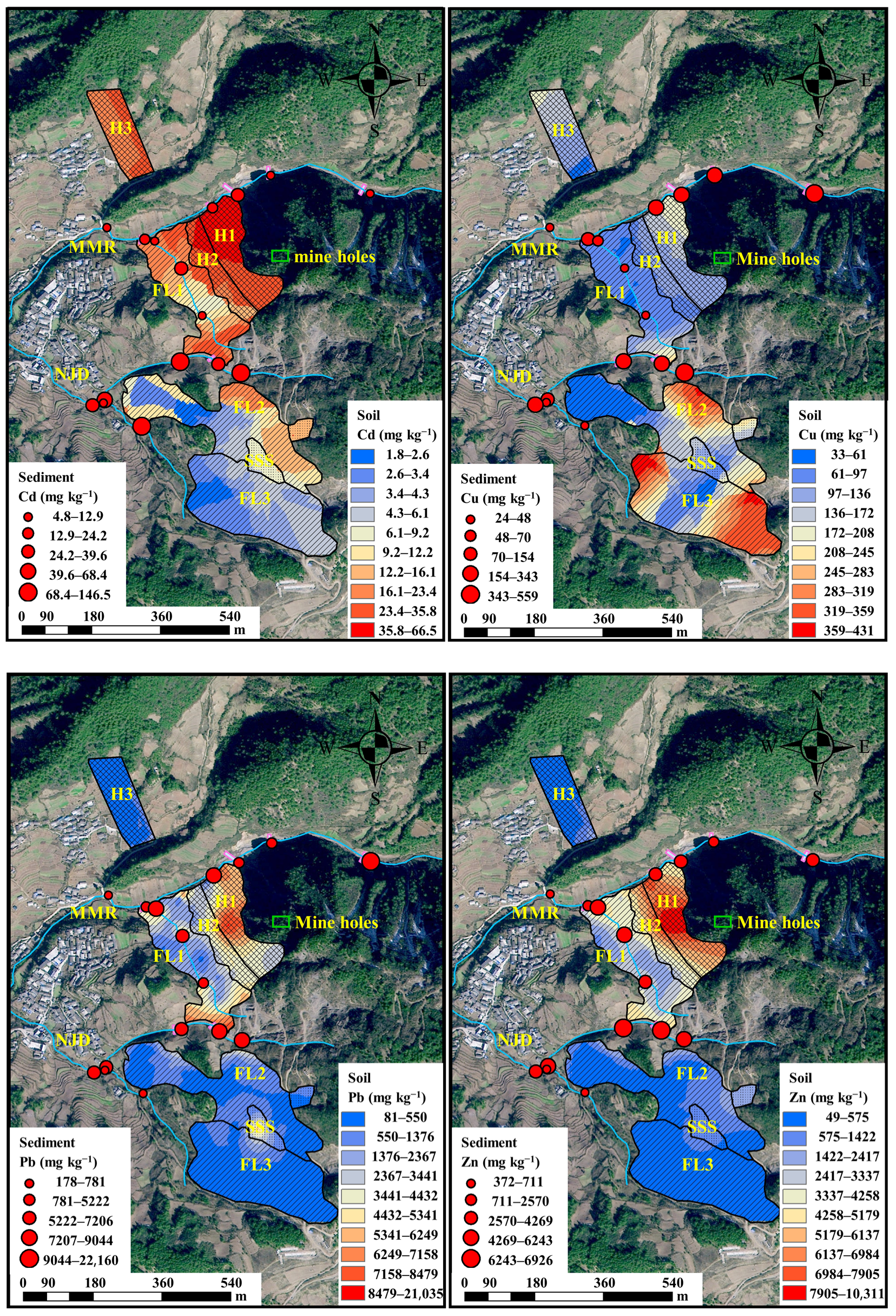
3.2. Heavy Metal Contents
3.3. Heavy Metal Contents in Surface Water
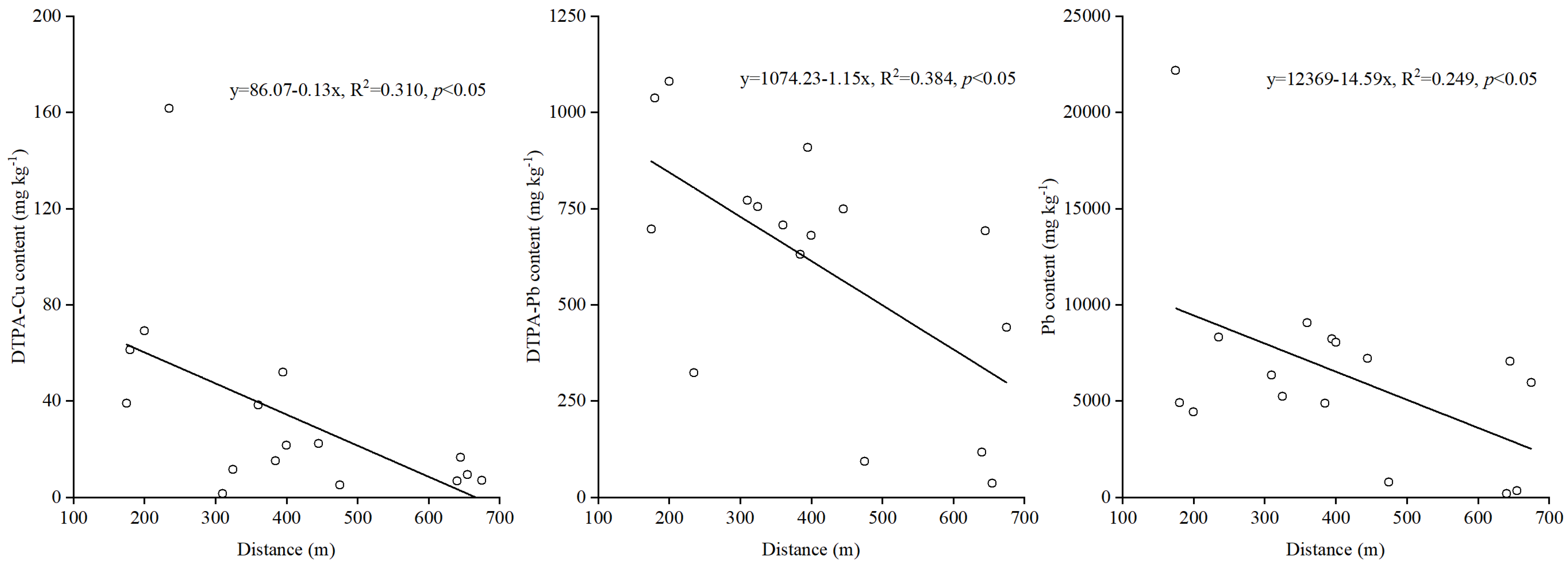
3.4. Relationships between Soil Chemical Properties, Altitude and Distance
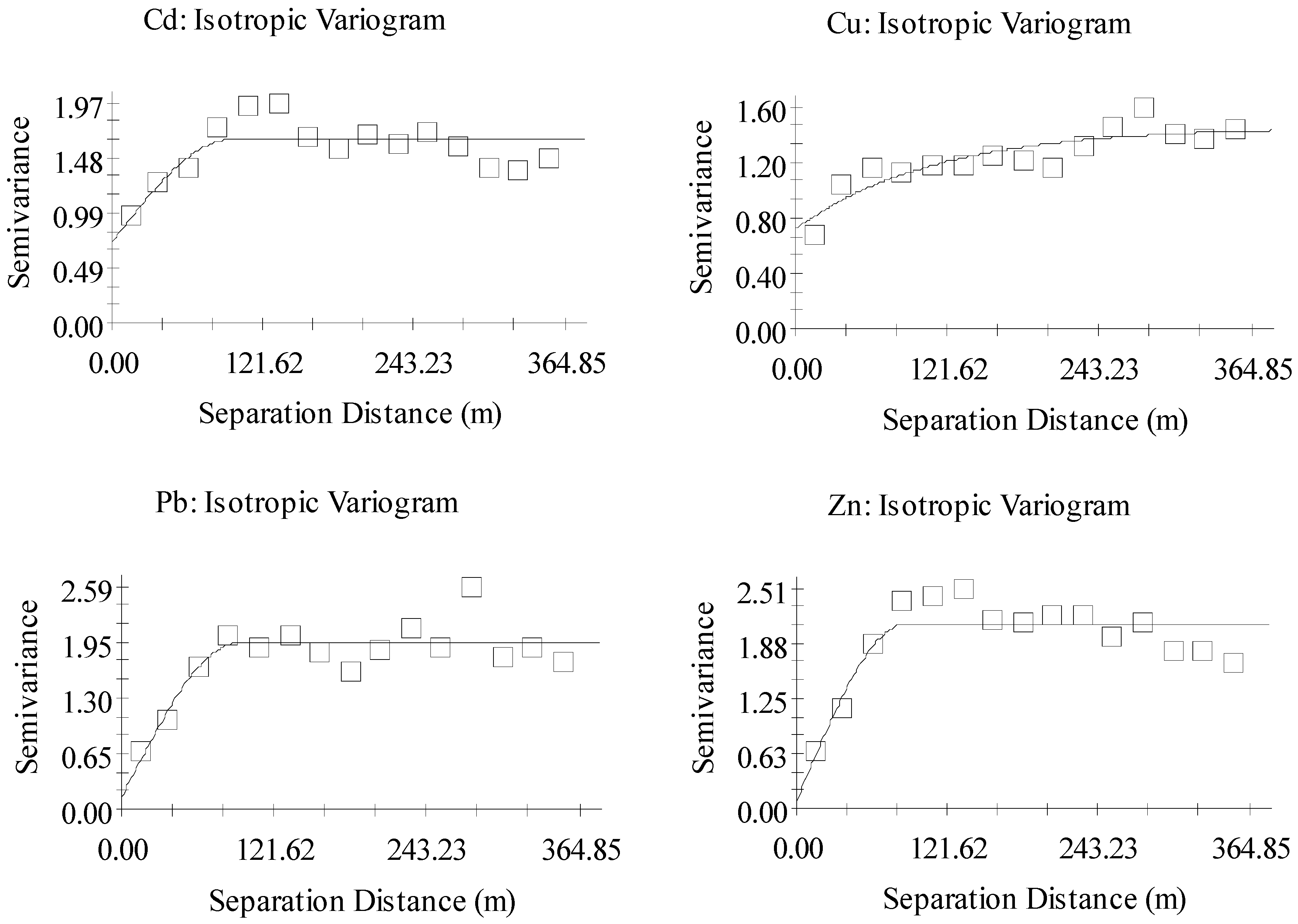
3.5. Semi-Variogram Analysis of Heavy Metals in Soil and Sediment
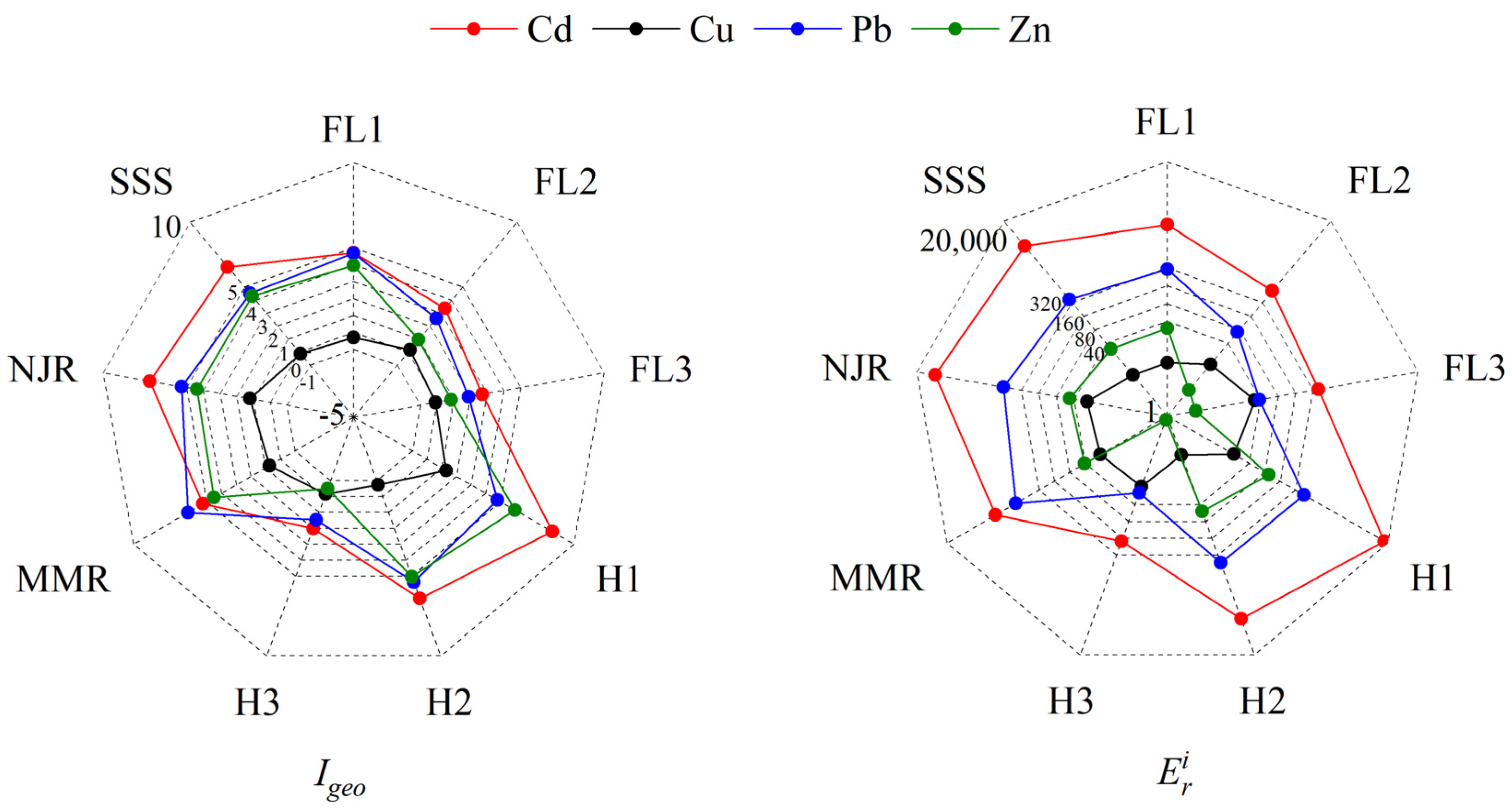
3.6. Assessment of Environmental Risks
3.7. Potential Ecological Risk Index
3.8. Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Duan, Q.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Pinedo-Hernandez, J.; Diez, S. Assessment of heavy metal pollution, spatial distribution and origin in agricultural soils along the Sinu River Basin, Colombia. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Liao, R.; Ali, A.; Mahar, A.; Guo, D.; Li, R.; Xining, S.; Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil near a Pb/Zn smelter in Feng County, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 139, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y.; Ma, Z.W.; van der Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.W.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Deng, M.; Japenga, J.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; He, Z. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of agricultural soils in a typical peri-urban area in southeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.Q.; Yang, N.; Li, Y.Z.; Ren, B.; Ding, X.H.; Bian, H.L.; Yao, X. Total concentrations and sources of heavy metal pollution in global river and lake water bodies from 1972 to 2017. Global Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Teng, Y.G.; Lu, S.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, J.S. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, X.; Dong, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhou, M.; Hou, H. Contamination and health risk assessment of heavy metals in China’s lead-zinc mine tailings: A meta-analysis. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Li, T.; He, Z.; Yang, X. Current status of agricultural soil pollution by heavy metals in China: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 3034–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornberger, M.I.; Luoma, S.N.; Johnson, M.L.; Holyoak, M. Influence of remediation in a mine-impacted river: Metal trends over large spatial and temporal scales. Ecol. Appl. 2009, 19, 1522–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Cheng, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, D. Effects of natural factors on the spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils surrounding mining regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Žibret, G.; Gosar, M.; Miler, M.; Alijagić, J. Impacts of mining and smelting activities on environment and landscape degradation—Slovenian case studies. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 4457–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.-W.; Baveye, P.C.; Kim, K.-B.; Kang, D.-H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Son, J.; Kim, D.-H.; Yoon, Y.-C.; Yu, C. Effect of postmining land use on the spatial distribution of metal(loid)s and their transport in agricultural soils: Analysis of a case study of Chungyang, South Korea. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 170, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, J. Spatial variability of heavy metals in soils across a valley plain in Southeastern China. Environ. Geol. 2007, 55, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciszewski, D.; Kubsik, U.; Aleksander-Kwaterczak, U. Long-term dispersal of heavy metals in a catchment affected by historic lead and zinc mining. J. Soils Sediments 2012, 12, 1445–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolo, M.T.; Khandaker, M.U.; Amin, Y.M.; Abdullah, W.H.B.; Bradley, D.A.; Alzimami, K.S. Assessment of health risk due to the exposure of heavy metals in soil around mega coal-fired cement factory in Nigeria. Results Phys. 2018, 11, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Niu, Z.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Xiang, P. Soil heavy metal pollution and food safety in China: Effects, sources and removing technology. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, J.B.; Mazurek, R.; Gasiorek, M.; Zaleski, T. Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination-A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2395–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Chu, C.; Shao, C.; Ju, M.; Dai, E. Study of integrated risk regionalisation method for soil contamination in industrial and mining area. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Moorman, T.B.; Novak, J.M.; Parkin, T.B.; Karlen, D.L.; Turco, R.F.; Konopka, A.E. Field-Scale Variability of Soil Properties in Central Iowa Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, M. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Surface Soil of Xilinguole Coal Mining Area Based on Semivariogram. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CNEMC. Background Values of Soil Elements in China; China Environment Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, G. Index of Geoaccumulation in Sediments of the Rhine River. Geo J. 1969, 2, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.R.; Deblon, J.; Zu, Y.Q.; Colinet, G.; Li, B.; He, Y.M. Geochemical Baseline Values Determination and Evaluation of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soils of Lanping Mining Valley (Yunnan Province, China). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2019, 4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahim, G.M.; Parker, R.J. Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liang, Q.F.; Gao, Y. Spatial Distribution and Pollution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Plant Leaves in Baoji City. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 4504–4513. [Google Scholar]
- EPA Human Health Risk Assessment Guidance. Available online: www.epa.gov (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Integrated Risk In-Formation System (IRIS). Available online: www.epa.gov/iris (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- MEE. Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, L.; Li, B.; Li, Z.R.; He, Y.M.; Hu, W.Y.; Zu, Y.Q.; Zhan, F.D. Pollution and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Farmlands and Vegetables Surrounding a Lead-Zinc Mine in Yunnan Province, China. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2021, 31, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, P.; Yang, S.; Lei, M.; Chen, T.; Dong, N. Quantitative analysis of the factors influencing spatial distribution of soil heavy metals based on geographical detector. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 392–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, G.S.; Shit, P.K.; Chattopadhyay, R. Assessment of spatial variability of soil properties using geostatistical approach of lateritic soil (West Bengal, India). Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2018, 16, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Ji, B.; Khoso, S.A.; Tang, H.H.; Liu, R.Q.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.H. An extensive review on restoration technologies for mining tailings. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 33911–33925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinitchenko, V.P.; Glinushkin, A.P.; Minkina, T.M.; Mandzhieva, S.S.; Sushkova, S.N.; Sukovatov, V.A.; Il’ina, L.P.; Makarenkov, D.A. Chemical Soil-Biological Engineering Theoretical Foundations, Technical Means, and Technology for Safe Intrasoil Waste Recycling and Long-Term Higher Soil Productivity. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 17553–17564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Zhang, G.; Rong, L.; Fang, H.; He, D.; Feng, D. Spatial distribution and environmental factors of catchment-scale soil heavy metal contamination in the dry-hot valley of Upper Red River in southwestern China. CATENA 2015, 135, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, F.; Zeng, W.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; He, Y.; Li, Y. Inhibition of native arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi induced increases in cadmium loss via surface runoff and interflow from farmland. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, E.; Wang, W.; Sun, M. Mineral composition and particle size distribution of river sediment and loess in the middle and lower Yellow River. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2021, 36, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, X.P.; Cai, Y.; Ai, Y.W.; Sun, X.M.; Yu, H.T. Geochemical behavior and risk of heavy metals in different size lead-polluted soil particles. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 4212–4221. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Sheng, Y.; Meng, Y.; Sun, J. Multistage remediation of heavy metal contaminated river sediments in a mining region based on particle size. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Ai, Y.; Chen, J.; Luo, X.; Chen, J.; Zhong, S. Effects and mechanisms of revegetation modes on cadmium and lead pollution in artificial soil on railway rock-cut slopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.K.; Wang, J.F.; Liao, P.; Sun, Q.Q.; Yang, X.H.; Jin, Z.; Chen, J.A. Effects of cascade dam on the distribution of heavy metals and biogenic elements in sediments at the watershed scale, Southwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 8970–8979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Chang, Q. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils and identification of main influencing factors in a typical industrial park in northwest China. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Investigated Area | pH | OM(g kg−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | CV | Mean ± SD | CV | |
| FL1 | 8.19±0.73 a | 8.97% | 36.09±19.88 ab | 55.08% |
| FL2 | 6.76±0.65 b | 9.65% | 41.91±13.05 a | 31.14% |
| FL3 | 6.79±1.13 b | 16.65% | 36.81±11.66 ab | 31.68% |
| H1 | 7.71±0.25 ab | 3.26% | 13.70±10.10 c | 73.69% |
| H2 | 8.77±0.97 a | 11.03% | 39.23±24.75 a | 63.09% |
| H3 | 8.18±1.20 a | 14.64% | 11.50±5.42 c | 47.18% |
| MMR | 8.70±0.99 a | 11.41% | 18.92±8.19 bc | 43.30% |
| NJD | 7.93±0.50 a | 6.34% | 9.13±2.87 c | 31.42% |
| SSS | 7.83±0.04 ab | 0.45% | 12.27±15.98 c | 130.20% |
| Investigated Area | Cd | Cu | Pb | Zn | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | Percentage | Content | Percentage | Content | Percentage | Content | Percentage | |
| FL1 | 2.16 ± 2.00 b | 1–86% | 8.93 ± 7.06 b | 2–30% | 496.9 ± 401.1 ab | 1–51% | 254.4 ± 222.0 ab | 0–24% |
| FL2 | 1.32 ± 1.05 b | 1–76% | 10.57 ± 10.09 b | 1–68% | 162.8 ± 143.6 c | 7–72% | 25.18 ± 38.93 cd | 0–25% |
| FL3 | 0.44 ± 0.33 b | 3–62% | 9.17 ± 10.99 b | 0–53% | 82.37 ± 59.77 c | 9–72% | 26.48 ± 23.03 cd | 0–29% |
| H1 | 6.14 ± 3.38 a | 3–6% | 10.75 ± 5.99 b | 3–11% | 260.2 ± 125.8 bc | 2–56% | 456.6 ± 195.5 a | 3–11% |
| H2 | 2.23 ± 0.24 b | 4–15% | 9.00 ± 4.07 b | 12–40% | 672.4 ± 335.7 a | 13–29% | 361.5 ± 363.4 ab | 1–10% |
| H3 | 0.24 ± 0.27 b | 2–33% | 7.53 ± 3.78 b | 2–24% | 32.79 ± 15.43 c | 8–22% | 6.05 ± 4.83 d | 1–23% |
| MMR | 1.62 ± 0.67 c | 3–35% | 44.71 ± 50.04 a | 4–62% | 676.8 ± 311.5 a | 3–24% | 345.8 ± 300.2 ab | 0–23% |
| NJD | 4.24 ± 3.40 a | 0–13% | 19.35 ± 15.79 b | 3–25% | 517.5 ± 332.2 ab | 7–66% | 227.5 ± 275.4 bc | 0–17% |
| SSS | 1.64 ± 0.22 b | 3–10% | 4.48 ± 2.29 b | 5–8% | 615.8 ± 591.4 a | 18–45% | 143.1 ± 80.8 bc | 3–8% |
| Investigated Sites | Dissolved | Total | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cu | Pb | Zn | Cd | Cu | Pb | Zn | pH | |
| MMR | 0.31 ± 0.19 b | 2.98 ± 1.56 a | 1.35 ± 0.96 a | 321.9 ± 473.4 a | 0.47 ± 0.25 b | 5.85 ± 3.53 a | 5.06 ± 3.05 a | 406.0 ± 475.7 a | 8.33 ± 0.05 b |
| NJD | 0.68 ± 0.31 a | 4.42 ± 2.29 a | 1.57 ± 0.73 a | 245.5 ± 169.3 a | 0.99 ± 0.24 a | 8.28 ± 2.86 a | 9.07 ± 3.46 a | 421.3 ± 187.9 a | 8.50 ± 0.11 a |
| Altitude | pH | OM | DTPA-Cd | DTPA-Cu | DTPA-Pb | DTPA-Zn | Cd | Cu | Pb | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altitude | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| pH | −0.316 ** | 1.000 | |||||||||
| OM | −0.001 | −0.360 ** | 1.000 | ||||||||
| DTPA-Cd | −0.179 | 0.294 ** | −0.165 | 1.000 | |||||||
| DTPA-Cu | 0.004 | 0.248 ** | −0.128 | 0.132 | 1.000 | ||||||
| DTPA-Pb | −0.199 * | 0.416 ** | −0.155 | 0.417 ** | 0.316 ** | 1.000 | |||||
| DTPA-Zn | −0.261 ** | 0.437 ** | −0.134 | 0.329 ** | 0.484 ** | 0.576 ** | 1.000 | ||||
| Cd | −0.123 | 0.205 * | −0.351 ** | 0.642 ** | 0.138 | 0.280 ** | 0.494 ** | 1.000 | |||
| Cu | 0.249 ** | −0.064 | −0.109 | 0.021 | 0.286 ** | 0.030 | 0.006 | 0.049 | 1.000 | ||
| Pb | −0.210 * | 0.488 ** | −0.271 ** | 0.398 ** | 0.415 ** | 0.638 ** | 0.529 ** | 0.400 ** | 0.147 | 1.000 | |
| Zn | −0.319 ** | 0.515 ** | −0.300 ** | 0.719 ** | 0.233 * | 0.636 ** | 0.711 ** | 0.741 ** | 0.024 | 0.681 ** | 1.000 |
| Parameters | Best-Fit Model | Nugget (C0) | Sill (C + C0) | Range (m) | N:S (C0/(C + C0)) | Spatial Dependence | R2 | RSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LogCd | Spherical | 0.715 | 1.64 | 96 | 0.436 | Moderate | 0.565 | 0.418 |
| LogCu | Exponential | 0.717 | 1.45 | 338 | 0.494 | Moderate | 0.772 | 0.149 |
| LogPb | Spherical | 0.132 | 1.93 | 94 | 0.068 | Strong | 0.746 | 0.703 |
| LogZn | Spherical | 0.091 | 2.10 | 89 | 0.043 | Strong | 0.766 | 0.783 |
| Investigated Area | Pi | IN | PLI | mCd | IIN | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cu | Pb | Zn | |||||
| FL1 | 57.83 | 1.61 | 60.46 | 30.49 | 61.04 | 18.17 | 37.60 | 4.37 |
| FL2 | 19.33 | 2.75 | 14.20 | 3.75 | 17.24 | 6.49 | 10.01 | 2.82 |
| FL3 | 13.10 | 6.38 | 7.62 | 3.12 | 12.92 | 4.93 | 7.55 | 2.37 |
| H1 | 577.6 | 3.99 | 94.34 | 96.98 | 430.7 | 61.91 | 193.2 | 7.04 |
| H2 | 150.7 | 1.02 | 88.70 | 52.43 | 118.5 | 27.34 | 73.21 | 5.34 |
| H3 | 6.05 | 3.73 | 4.85 | 1.17 | 6.13 | 2.75 | 3.95 | 1.74 |
| MMR | 75.29 | 4.09 | 180.8 | 41.32 | 141.4 | 33.04 | 75.38 | 5.43 |
| NJD | 325.4 | 4.78 | 130.1 | 47.37 | 249.8 | 51.44 | 126.9 | 6.06 |
| SSS | 188.2 | 1.62 | 75.75 | 30.05 | 168.6 | 22.49 | 73.91 | 5.67 |
| Non-Carcinogenic Risk | Direct Ingestion | Dermal Contact | Inhalation Absorption | HI | ||||
| Adults | Children | Adults | Children | Adults | Children | Adults | Children | |
| HQCd | 2.34 × 10−2 | 1.01 × 10−1 | 9.32 × 10−3 | 2.84 × 10−3 | 3.43 × 10−4 | 1.18 × 10−3 | 3.30 × 10−2 | 1.06 × 10−1 |
| HQCu | 5.86 × 10−3 | 2.55 × 10−2 | 7.79 × 10−5 | 7.13 × 10−5 | 8.58 × 10−7 | 1.12 × 10−4 | 5.94 × 10−3 | 2.56 × 10−2 |
| HQPb | 8.34 × 10−1 | 3.63 | 2.22 × 10−2 | 6.77 × 10−2 | 1.22 × 10−4 | 1.01 × 10−4 | 8.57 × 10−1 | 3.69 |
| HQZn | 8.46 × 10−3 | 3.67 × 10−2 | 1.69 × 10−4 | 5.14 × 10−4 | 1.24 × 10−6 | 1.03 × 10−6 | 8.63 × 10−3 | 3.73 × 10−2 |
| HIHMs | 8.72 × 10−1 | 3.79 | 3.18 × 10−2 | 7.11 × 10−2 | 4.68 × 10−4 | 1.39 × 10−3 | 9.04 × 10−1 | 3.86 |
| Carcinogenic Risk | Direct Ingestion | Dermal Contact | Inhalation Absorption | CRI | ||||
| Adults | Children | Adults | Children | Adults | Children | Adults | Children | |
| CRCd | 4.46 × 10−5 | 4.85 × 10−5 | 1.78 × 10−7 | 1.36 × 10−7 | 6.78 × 10−9 | 5.60 × 10−9 | 4.48 × 10−5 | 4.86 × 10−5 |
| CRPb | 7.78 × 10−6 | 8.45 × 10−6 | 6.21 × 10−8 | 4.73 × 10−8 | 5.65 × 10−9 | 4.67 × 10−9 | 7.85 × 10−6 | 8.50 × 10−6 |
| CRIHMs | 5.24 × 10−5 | 5.69 × 10−5 | 2.40 × 10−7 | 1.83 × 10−7 | 1.24 × 10−8 | 1.03 × 10−8 | 5.27 × 10−5 | 5.71 × 10−5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Deng, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhan, F.; He, Y.; He, L.; Li, Y. Contamination and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil and Ditch Sediments in Long-Term Mine Wastes Area. Toxics 2022, 10, 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100607
Li B, Deng J, Li Z, Chen J, Zhan F, He Y, He L, Li Y. Contamination and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil and Ditch Sediments in Long-Term Mine Wastes Area. Toxics. 2022; 10(10):607. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100607
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bo, Jiangdi Deng, Zuran Li, Jianjun Chen, Fangdong Zhan, Yongmei He, Lu He, and Yuan Li. 2022. "Contamination and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil and Ditch Sediments in Long-Term Mine Wastes Area" Toxics 10, no. 10: 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100607
APA StyleLi, B., Deng, J., Li, Z., Chen, J., Zhan, F., He, Y., He, L., & Li, Y. (2022). Contamination and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil and Ditch Sediments in Long-Term Mine Wastes Area. Toxics, 10(10), 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100607






