The Effects of Single and Combined Stressors on Daphnids—Enzyme Markers of Physiology and Metabolomics Validate the Impact of Pollution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culturing of Daphnids and Toxicity Exposures
2.2. Sample Homogenization and Biochemical Assays
2.3. Metabolomic Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Toxicity of Individual Chemicals and Their Mixture
3.2. Enzyme Responses to Single Chemicals and Their Mixture
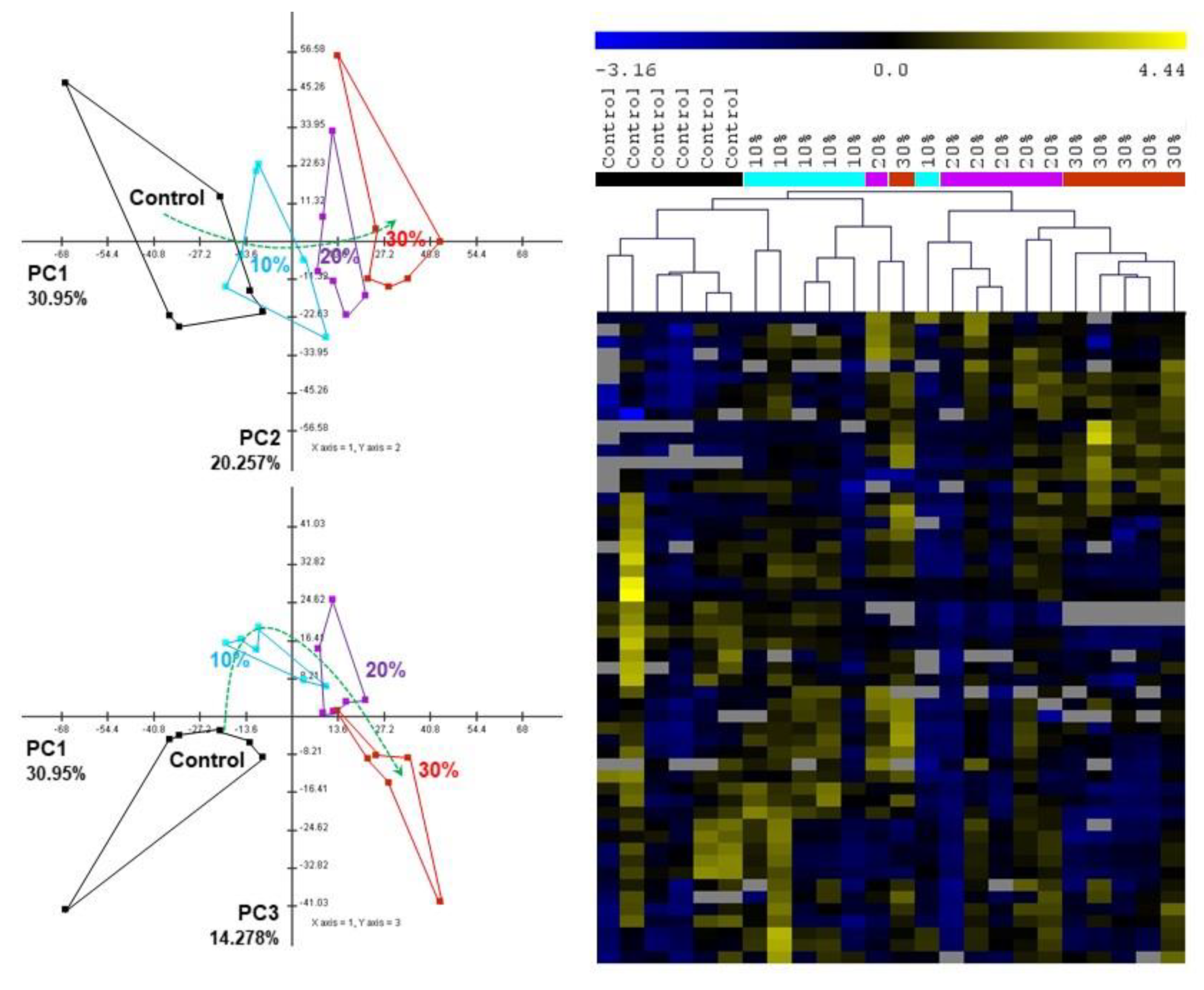
3.3. The Metabolic Responses to Mixture Exposure
4. Discussion
4.1. The Effects of Individual Stressors
4.2. Mixture Effects and Omics in Toxicology
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, U.; Mumtaz, R.; Anwar, H.; Mumtaz, S.; Qamar, A.M. Water quality monitoring: From conventional to emerging technologies. Water Supply 2019, 20, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardrid, Y.; Zayas, Z.P. Water sampling: Traditional methods and new approaches in water sampling strategy. Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brack, W.; Aissa, S.A.; Backhaus, T.; Dulio, V.; Escher, B.I.; Faust, M.; Hilscherova, K.; Hollender, J.; Hollert, H.; Müller, C.; et al. Effect-based methods are key. The European Collaborative Project SOLUTIONS recommends integrating effect-based methods for diagnosis and monitoring of water quality. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenburger, R.; Brack, W.; Burgess, R.M.; Busch, W.; Escher, B.I.; Focks, A.; Mark Hewitt, L.; Jacobsen, B.N.; de Alda, M.L.; Ait-Aissa, S.; et al. Future water quality monitoring: Improving the balance between exposure and toxicity assessments of real-world pollutant mixtures. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, K.J.; Carvalho, R.N.; Chipman, J.K.; Denslow, N.D.; Halder, M.; Murphy, C.A.; Roelofs, D.; Rolaki, A.; Schirmer, K.; Watanabe, K.H. Development and application of the adverse outcome pathway framework for understanding and predicting chronic toxicity: I. Challenges and research needs in ecotoxicology. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 764–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escher, B.I.; Stapleton, H.M.; Schymanski, E.L. Tracking complex mixtures of chemicals in our changing environment. Science 2020, 367, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grintzalis, K.; Dai, W.; Panagiotidis, K.; Belavgeni, A.; Viant, M.R. Miniaturising acute toxicity and feeding rate measurements in Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 139, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traudt, E.M.; Ranville, J.F.; Meyer, J.S. Effect of age on acute toxicity of cadmium, copper, nickel, and zinc in individual-metal exposures to Daphnia magna neonates. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 202: Daphnia sp. Acute Immobilisation Test; OECD: Paris, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Worthington, K.; Worthington, V. Worthington Enzyme Manual. Available online: https://www.worthington-biochem.com/index/manual.html (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Tang, S.S.; Lin, C.C.; Chang, G.G. Metal-catalyzed oxidation and cleavage of octopus glutathione transferase by the Cu(II)-ascorbate system. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 21, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warholm, M.; Guthenberg, C.; Mannervik, B.; Pacifici, G.M.; Rane, A. Glutathione S-transferases in human fetal liver. Acta Chem. Scandinavica. Ser. B: Org. Chem. Biochem. 1981, 35, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grintzalis, K.; Papapostolou, I.; Zisimopoulos, D.; Stamatiou, I.; Georgiou, C.D. Multiparametric protocol for the determination of thiol redox state in living matter. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 74, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grintzalis, K.; Georgiou, C.D.; Schneider, Y.J. An accurate and sensitive Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250-based assay for protein determination. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 480, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.I.; Sharov, V.; White, J.; Li, J.; Liang, W.; Bhagabati, N.; Braisted, J.; Klapa, M.; Currier, T.; Thiagarajan, M.; et al. TM4: A free, open-source system for microarray data management and analysis. BioTechniques 2003, 34, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diercks, D.B.; Owen, K.P.; Kline, J.A.; Sutter, M.E. Urine metabolomic analysis to detect metabolites associated with the development of contrast induced nephropathy. Clin. Exp. Emerg. Med. 2016, 3, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kszos, L.A.; Beauchamp, J.J.; Stewart, A.J. Toxicity of Lithium to Three Freshwater Organisms and the Antagonistic Effect of Sodium. Ecotoxicology 2003, 12, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, N.R.; Fields, P.D.; Horsfield, S.; Mirbahai, L.; Ebert, D.; Colbourne, J.K.; Fent, K. Mixtures of Aluminum and Indium Induce More than Additive Phenotypic and Toxicogenomic Responses in Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Yang, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kin, Y.J.; Seo, Y.R. Exploring potential biomarker responses to lithium in Daphnia magna from the perspectives of function and signaling networks. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagato, E.G.; D’Eon, J.C.; Lankadurai, B.P.; Poirier, D.G.; Reiner, E.J.; Simpson, A.J.; Simpson, M.J. (1)H NMR-based metabolomics investigation of Daphnia magna responses to sub-lethal exposure to arsenic, copper and lithium. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Trivedi, P.K. Glutathione S-Transferases: Role in Combating Abiotic Stresses Including Arsenic Detoxification in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, K.; Gu, L.; Li, B.; Lu, Y.; Wu, C.; Guan, H.; Yang, Z. Stress-responsive expression of a glutathione S-transferase (delta) gene in waterflea Daphnia magna challenged by microcystin-producing and microcystin-free Microcystis aeruginosa. Harmful Algae 2016, 56, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.R.; Abrantes, N.; Goncalves, F. Life-history traits of standard and autochthonous cladocerans: II. Acute and chronic effects of acetylsalicylic acid metabolites. Environ. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Olivan, L.M.; Galar-Martinez, M.; Islas-Flores, H.; Garcia-Medina, S.; SanJuan-Reyes, N. DNA damage and oxidative stress induced by acetylsalicylic acid in Daphnia magna. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. CBP 2014, 164, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, S.H.; Hong, N.H.; Ahn, J.Y.; Sekhon, S.S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Min, J. Proteomic analysis of Daphnia magna exposed to caffeine, ibuprofen, aspirin and tetracycline. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2015, 7, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, M.H. Effectiveness of diltiazem for chronic stable angina pectoris. Acta Pharmacol. Et Toxicol. 1985, 57 (Suppl. 2), 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinkey, D.; Lari, E.; Woodman, S.G.; Steinkey, R.; Luong, K.H.; Wong, C.S.; Pyle, G.G. The effects of diltiazem on growth, reproduction, energy reserves, and calcium-dependent physiology in Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2019, 232, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterhuis, M.; Sacher, F.; Ter Laak, T.L. Prediction of concentration levels of metformin and other high consumption pharmaceuticals in wastewater and regional surface water based on sales data. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 442, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosio-Albuquerque, E.P.; Cusioli, L.F.; Bergamasco, R.; Sinopolis Gigliolli, A.A.; Lupepsa, L.; Paupitz, B.R.; Barbieri, P.A.; Borin-Carvalho, L.A.; de Brito Portela-Castro, A.L. Metformin environmental exposure: A systematic review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 83, 103588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alla, L.N.R.; Monshi, M.; Siddiqua, Z.; Shields, J.; Alame, K.; Wahls, A.; Akemann, C.; Meyer, D.; Crofts, E.J.; Saad, F.; et al. Detection of endocrine disrupting chemicals in Danio rerio and Daphnia pulex: Step-one, behavioral screen. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemuth, N.J.; Jordan, R.; Crago, J.; Blanksma, C.; Johnson, R.; Klaper, R.D. Metformin exposure at environmentally relevant concentrations causes potential endocrine disruption in adult male fish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizalde-Velazquez, G.A.; Gomez-Olivan, L.M. Occurrence, toxic effects and removal of metformin in the aquatic environments in the world: Recent trends and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, B.; Liu, J.; Li, G.H. Metformin preconditioning protects Daphnia pulex from lethal hypoxic insult involving AMPK, HIF and mTOR signaling. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 163, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloner, R.A.; Fishbein, M.C.; Cotran, R.S.; Braunwald, E.; Maroko, P.R. The effect of propranolol on microvascular injury in acute myocardial ischemia. Circulation 1977, 55, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, T.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, S.D. Bioaccumulation and biotransformation of the beta-blocker propranolol in multigenerational exposure to Daphnia magna. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleuvers, M. Aquatic ecotoxicity of pharmaceuticals including the assessment of combination effects. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 142, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, T.Y.; Yoon, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, S.D. Mode of action characterization for adverse effect of propranolol in Daphnia magna based on behavior and physiology monitoring and metabolite profiling. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzialowski, E.M.; Turner, P.K.; Brooks, B.W. Physiological and reproductive effects of beta adrenergic receptor antagonists in Daphnia magna. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 50, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, T.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, S.D. Multi-generational effects of propranolol on Daphnia magna at different environmental concentrations. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.L.; Antunes, S.C.; Goncalves, F.; Rocha, O.; Nunes, B. Evaluation of ecotoxicological effects of drugs on Daphnia magna using different enzymatic biomarkers. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 119, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, J.S.; Dimaki, M.; Mortensen, J.; Svendsen, W.E. Detection of Glyphosate in Drinking Water: A Fast and Direct Detection Method without Sample Pretreatment. Sensors 2018, 18, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustinasari, K.; Slugocki, L.; Czerniawski, R.; Pandebesie, E.S.; Hermana, J. Acute toxicity and morphology alterations of glyphosate-based herbicides to Daphnia magna and Cyclops vicinus. Toxicol. Res. 2021, 37, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppa, A.; Kvist, J.; Li, X.; Dhandapani, V.; Almulla, H.; Tian, A.Y.; Kissane, S.; Zhou, J.; Perotti, A.; Mangelson, H.; et al. Roundup causes embryonic development failure and alters metabolic pathways and gut microbiota functionality in non-target species. Microbiome 2020, 8, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.R.; Kish, A.; Kish, L.; Faletra, P.; Salmon, K.M. The Impact of Glyphosate-Based Herbicides and Their Components on Daphnia Magna. bioRxiv 2019, 794156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palas, S.; Sandipan, P.; Kumar, A.k.; Apurba Ratan, G. Biochemical effects of glyphosate based herbicide, Excel Mera 71 on enzyme activities of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), lipid peroxidation (LPO), catalase (CAT), glutathione-S-transferase (GST) and protein content on teleostean fishes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 107, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.C.; Yang, Y.J.; Ma, K.X.; Shi, C.Y.; Chen, G.W.; Liu, D.Z. A novel sigma class glutathione S-transferase gene in freshwater planarian Dugesia japonica: Cloning, characterization and protective effects in herbicide glyphosate stress. Ecotoxicology 2020, 29, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocchi, M.; Sommaruga, R. Microplastics modify the toxicity of glyphosate on Daphnia magna. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oropesa, A.L.; Floro, A.M.; Palma, P. Toxic potential of the emerging contaminant nicotine to the aquatic ecosystem. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 16605–16616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-F.; Huang, S.-Y.; Chung, Y.-T.; Wang, K.-S.; Wang, C.-K.; Chang, S.-H. Detoxification of nicotine solution using Fe0-based processes: Toxicity evaluation by Daphnia magna neonate and embryo assays. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenburger, R.; Scholze, M.; Busch, W.; Escher, B.I.; Jakobs, G.; Krauss, M.; Krüger, J.; Neale, P.A.; Ait-Aissa, S.; Almeida, A.C.; et al. Mixture effects in samples of multiple contaminants—An inter-laboratory study with manifold bioassays. Environ. Int. 2018, 114, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.R.R.; Gonçalves, S.F.; Pavlaki, M.D.; Morgado, R.G.; Soares, A.; Loureiro, S. Mixture toxicity prediction of substances from different origin sources in Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrill, J.A.; Viant, M.R.; Yauk, C.L.; Sachana, M.; Gant, T.W.; Auerbach, S.S.; Beger, R.D.; Bouhifd, M.; O’Brien, J.; Burgoon, L.; et al. Progress towards an OECD reporting framework for transcriptomics and metabolomics in regulatory toxicology. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. RTP 2021, 125, 105020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessner, U.; Bowne, J. What is metabolomics all about? BioTechniques 2009, 46, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labine, L.M.; Simpson, M.J. Targeted Metabolomic Assessment of the Sub-Lethal Toxicity of Halogenated Acetic Acids (HAAs) to Daphnia magna. Metabolites 2021, 11, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.J.; Weber, R.J.M.; Viant, M.R. Spatially Mapping the Baseline and Bisphenol-A Exposed Daphnia magna Lipidome Using Desorption Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites 2022, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemuth, N.J.; Curtis, B.J.; Laudadio, E.D.; Sostare, E.; Bennett, E.A.; Neureuther, N.J.; Mohaimani, A.A.; Schmoldt, A.; Ostovich, E.D.; Viant, M.R.; et al. Energy Starvation in Daphnia magna from Exposure to a Lithium Cobalt Oxide Nanomaterial. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 2287–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, T.-Y.; Simpson, M.J. Daphnia magna metabolic profiling as a promising water quality parameter for the biological early warning system. Water Res. 2019, 166, 115033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.S.; Gavin, A.; Viant, M.R. Metabolomics Discovers Early-Response Metabolic Biomarkers that Can Predict Chronic Reproductive Fitness in Individual Daphnia magna. Metabolites 2018, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


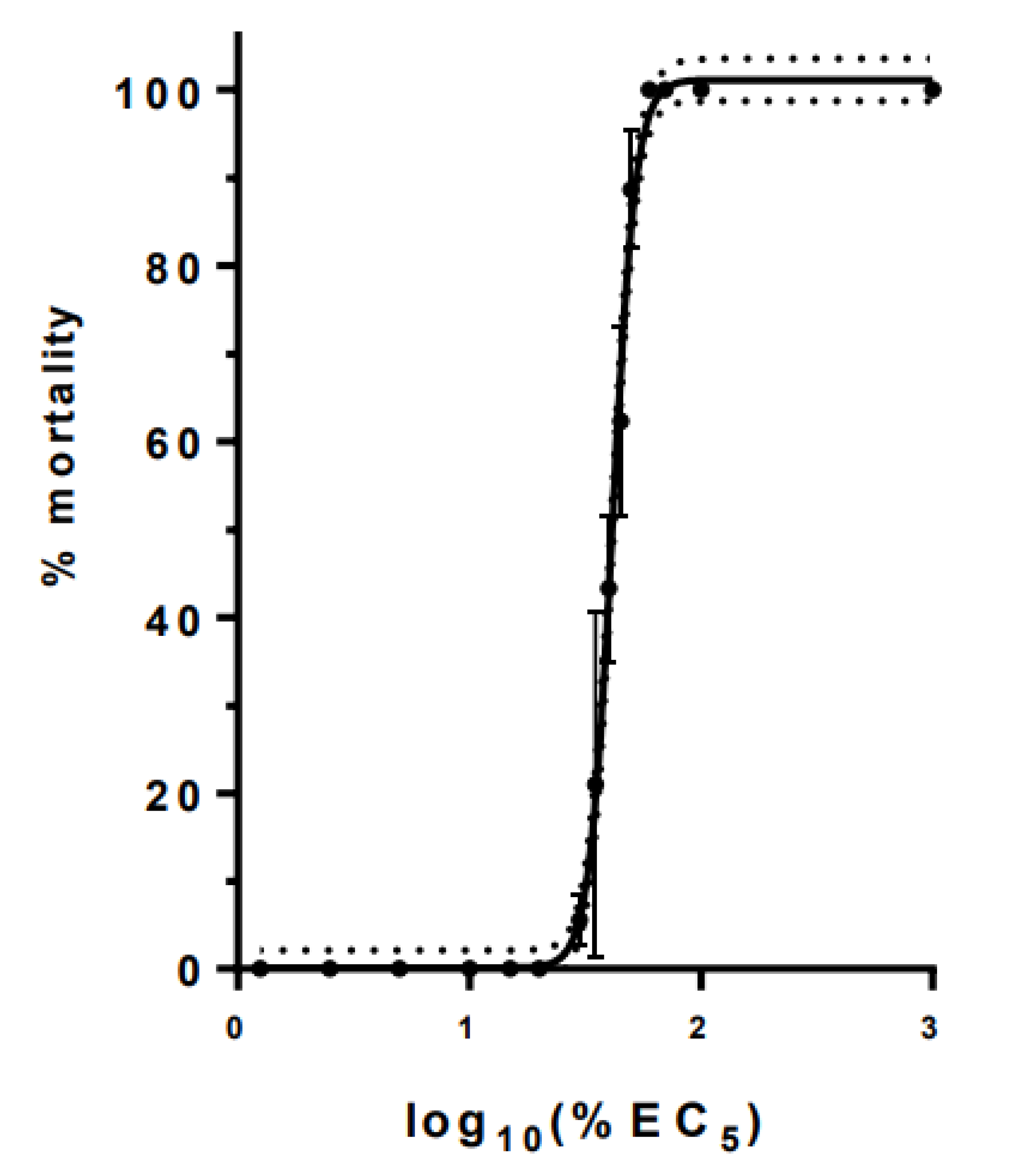

| Chemical | EC50 | Hill Slope | EC5 | % in Mixture |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminium sulfate hexadecahydrate | 59.4 | 5.282 | 34 | 4.53 |
| Lithium chloride | 93.7 | 9.354 | 68.4 | 9.11 |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | 75.8 | 13.03 | 60.5 | 8.06 |
| Diltiazem hydrochloride | 80.8 | 16.37 | 67.5 | 8.99 |
| Metformin | 145 | 9.534 | 106.5 | 14.19 |
| Propranolol | 83.6 | 3.864 | 39 | 5.19 |
| Glyphosate | 61.3 | 56.17 | 1.69 | 0.225 |
| Nicotine | 455 | 14.76 | 373 | 49.69 |
| Control | Li | Al | Acetyl Salicylic Acid | Propranolol | Diltiazem | Glyphosate | Nicotine | Metformin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALP | 7.53 ± 0.88 | 2.2 ± 0.21 (−71%) | 8.8 ± 0.31 | 8.13 ± 0.68 | 13.98 ± 1.19 (+84%) | 10.6 ± 0.34 (+41%) | 5.42 ± 0.53 (−28%) | 7.77 ± 0.79 | 4.7 ± 1.18 (−38%) |
| ACP | 5 ± 0.69 | 1.8 ± 0.07 (−64%) | 3.4 ± 0.13 (−32%) | 5.73 ± 0.09 | 7.44 ± 0.46 (+49%) | 5.7 ± 0.24 | 5 ± 0.21 | 4.38 ± 0.3 | 3.17 ± 0.71 (−37%) |
| βGAL | 11.63 ± 0.2 | 1.85 ± 0.1 (−84%) | 3.13 ± 0.05 (−73%) | 12.36 ± 0.87 | 9.96 ± 1.14 | 11.7 ± 1.02 | 11.7 ± 0.42 | 11.1 ± 1.25 | 4.72 ± 0.71 (−59%) |
| Lipase | 165 ± 10.1 | 50.2 ± 2.3 (−70%) | 104.6 ± 13.5 (−37%) | 181.64 ± 3.7 | 153 ± 16.4 | 190 ± 12.5 (+15%) | 187.8 ± 9.6 (+14%) | 169.4 ± 11.8 | 84.2 ± 16.7 (−49%) |
| Peptidase | 286 ± 21.8 | 53 ± 10.7 (−82%) | 158 ± 11.8 (−45%) | 240 ± 17.6 (−16%) | 387 ± 41.5 (+35%) | 291 ± 41.8 | 340 ± 8.9 (+19%) | 217 ± 27.5 (−24%) | 138 ± 27.8 (−52%) |
| LDH | 80.32 ± 6.52 | 63.8 ± 5.33 (−21%) | 83 ± 5.22 | 84.6 ± 4.33 | 77.7 ± 2.51 | 86.42 ± 7.88 | 72.59 ± 6.85 | 65.5 ± 3.15 (−18%) | 67.4 ± 4.91 (−16%) |
| GST | 212 ± 21.7 | 34.3 ± 19.7 (−84%) | 274 ± 7.6 (+29%) | 198.6 ± 6.6 | 215.6 ± 24.5 | 151.4 ± 6 (−29%) | 134.7 ± 7.2 (−37%) | 155.6 ± 4.8 (−27%) | 254.8 ± 9.2 |
| Reduced thiols | 64.9 ± 3.5 | 36.7 ± 1.2 (−43%) | 51.9 ± 1.7 (−20%) | 79.9 ± 2 (+23%) | 74.1 ± 2.5 (+14%) | 70.5 ± 2.2 (+8.6%) | 73.6 ± 3.9 (+13.5%) | 50.7 ± 1.3 (−22%) | 57.7 ± 3.2 (−11%) |
| Control | 10% | 20% | 30% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALP | 8.28 ± 0.19 | 11.67 ± 1.01 (+41%) | 11.64 ± 0.32 (+41%) | 11.22 ± 1.19 (+36%) |
| ACP | 3.08 ± 0.14 | 3.62 ± 0.44 (+18%) | 4.05 ± 0.27 (+31%) | 4.29 ± 0.45 (+37%) |
| βGAL | 3.62 ± 0.06 | 3.19 ± 0.09 (−12%) | 2.6 ± 0.13 (−28%) | 2.11 ± 0.09 (−42%) |
| Lipase | 17.73 ± 0.59 | 15.34 ± 1.31 (−13%) | 10.43 ± 1.18 (−41%) | 10.85 ± 1.24 (−39%) |
| Peptidase | 95.65 ± 4.44 | 93.09 ± 12.29 | 73.8 ± 6.81 (−23%) | 77.18 ± 6.58 (−20%) |
| LDH | 54.79 ± 2.32 | 50.44 ± 7.07 | 32.9 ± 10.11 (−40%) | 18.41 ± 4.3 (−67%) |
| GST | 149.52 ± 3.36 | 169.14 ± 13.02 | 193.41 ± 7.56 (+29%) | 227.61 ± 23.68 (+52%) |
| Reduced thiols | 201.44 ± 31.76 | 158.82 ± 12.12 (−21%) | 115.69 ± 17.18 (−43%) | 88.69 ± 35.97 (−56%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Michalaki, A.; McGivern, A.R.; Poschet, G.; Büttner, M.; Altenburger, R.; Grintzalis, K. The Effects of Single and Combined Stressors on Daphnids—Enzyme Markers of Physiology and Metabolomics Validate the Impact of Pollution. Toxics 2022, 10, 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100604
Michalaki A, McGivern AR, Poschet G, Büttner M, Altenburger R, Grintzalis K. The Effects of Single and Combined Stressors on Daphnids—Enzyme Markers of Physiology and Metabolomics Validate the Impact of Pollution. Toxics. 2022; 10(10):604. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100604
Chicago/Turabian StyleMichalaki, Anna, Allan Robert McGivern, Gernot Poschet, Michael Büttner, Rolf Altenburger, and Konstantinos Grintzalis. 2022. "The Effects of Single and Combined Stressors on Daphnids—Enzyme Markers of Physiology and Metabolomics Validate the Impact of Pollution" Toxics 10, no. 10: 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100604
APA StyleMichalaki, A., McGivern, A. R., Poschet, G., Büttner, M., Altenburger, R., & Grintzalis, K. (2022). The Effects of Single and Combined Stressors on Daphnids—Enzyme Markers of Physiology and Metabolomics Validate the Impact of Pollution. Toxics, 10(10), 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100604







