Smart Warehousing as a Wave of the Future
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology
- What elements (components) are essential for a smart warehouse system?
- How are those elements interconnected with each other, and how can they be synchronized and integrated to make warehousing operations more intelligent and successful?
- What are the key drivers for a smart warehouse system, and how do they affect the smart warehouse architecture?
- What are a smart warehouse system’s key value propositions or managerial benefits?
- How do we keep a smart warehouse project on track? What meaningful performance metrics can monitor a smart warehousing project and assess smart warehousing outcomes?
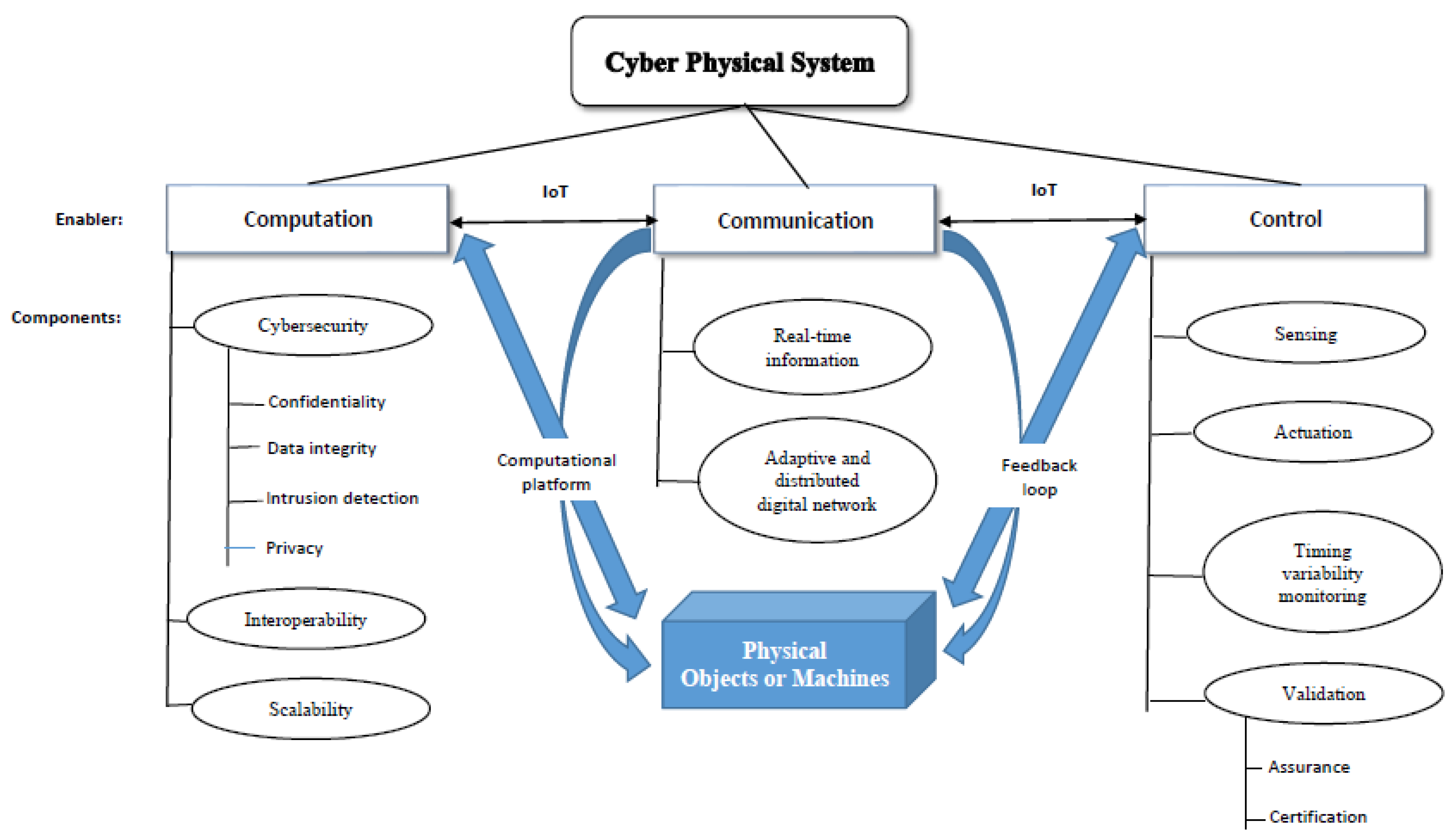
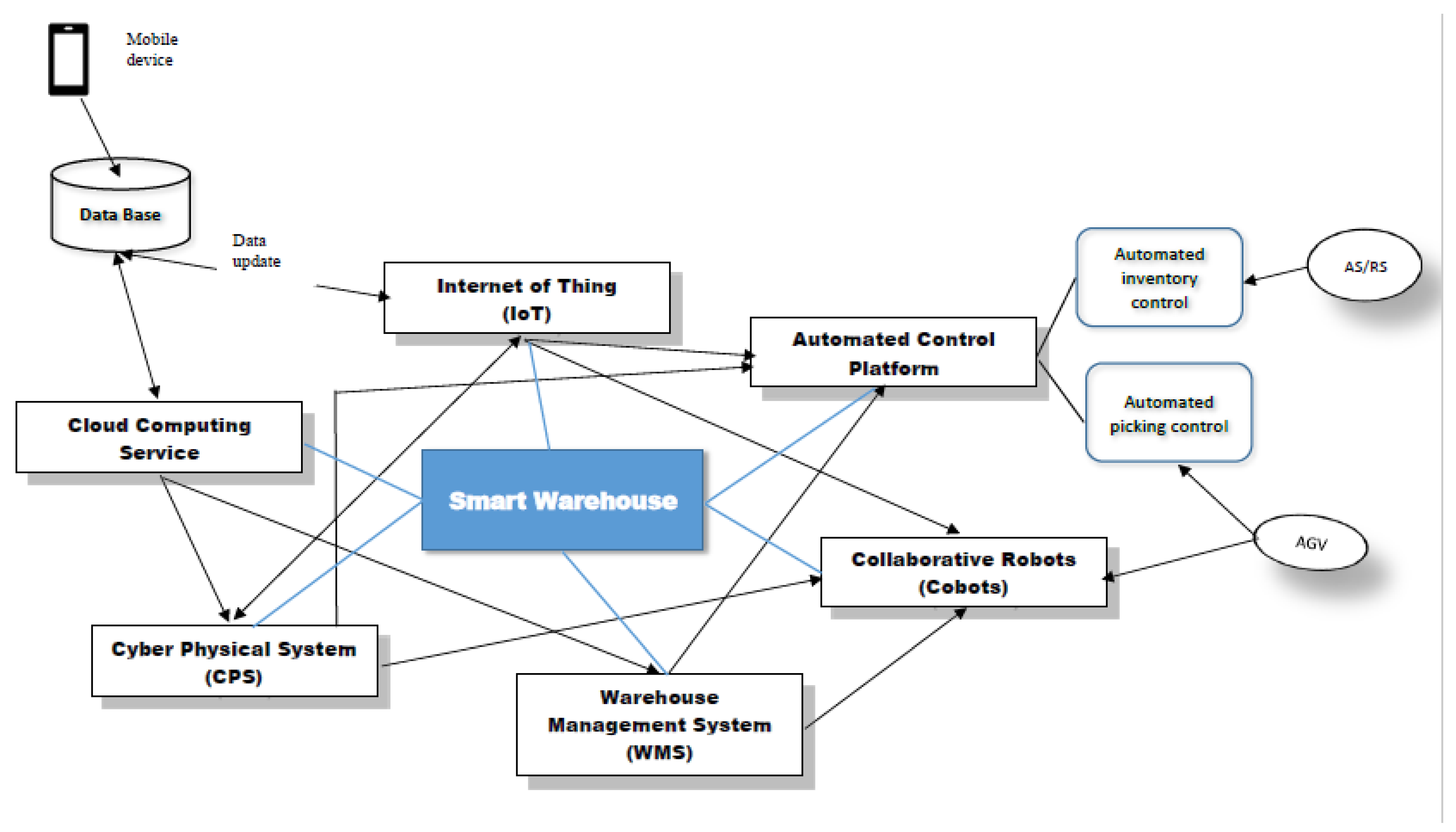
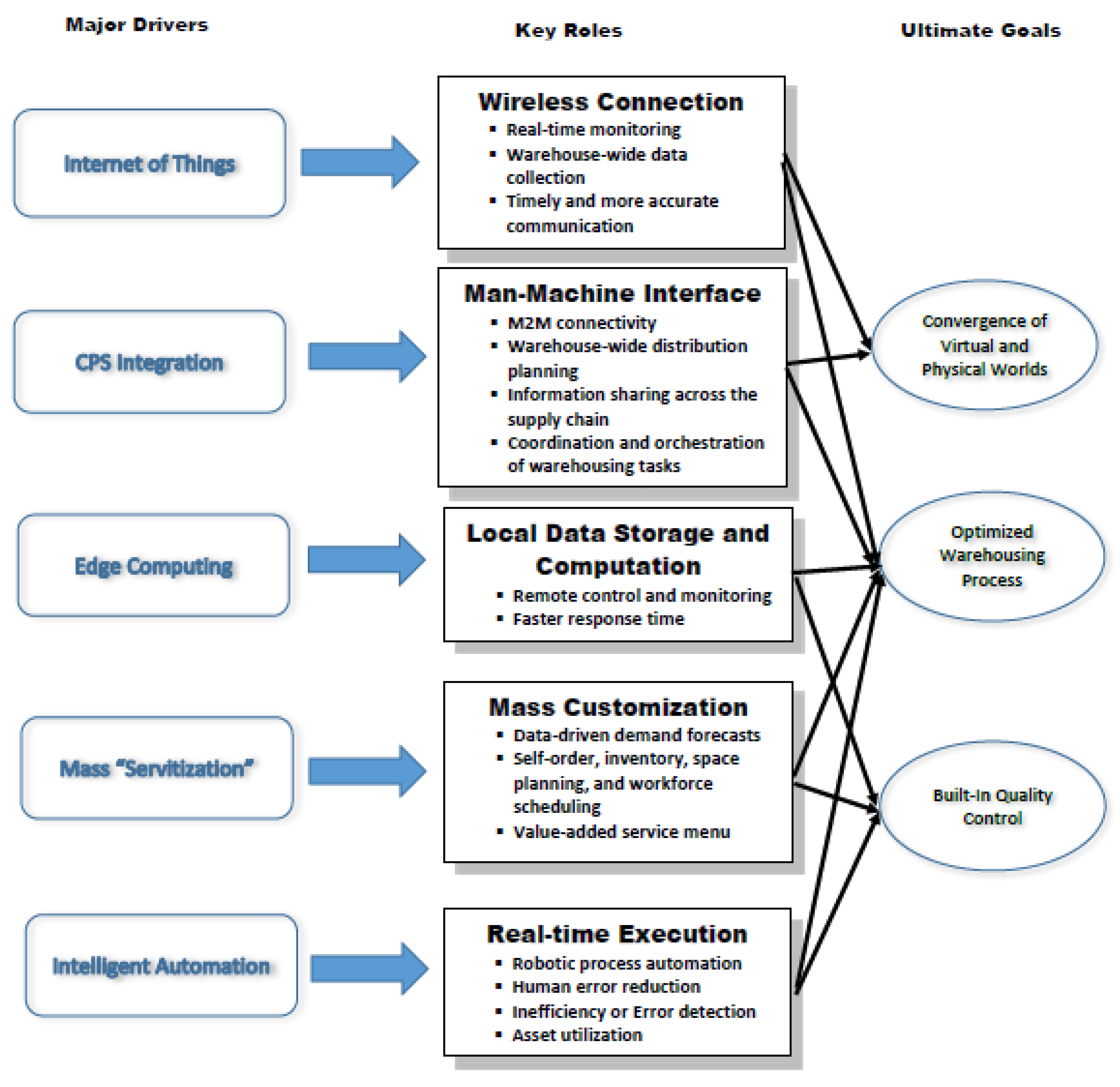
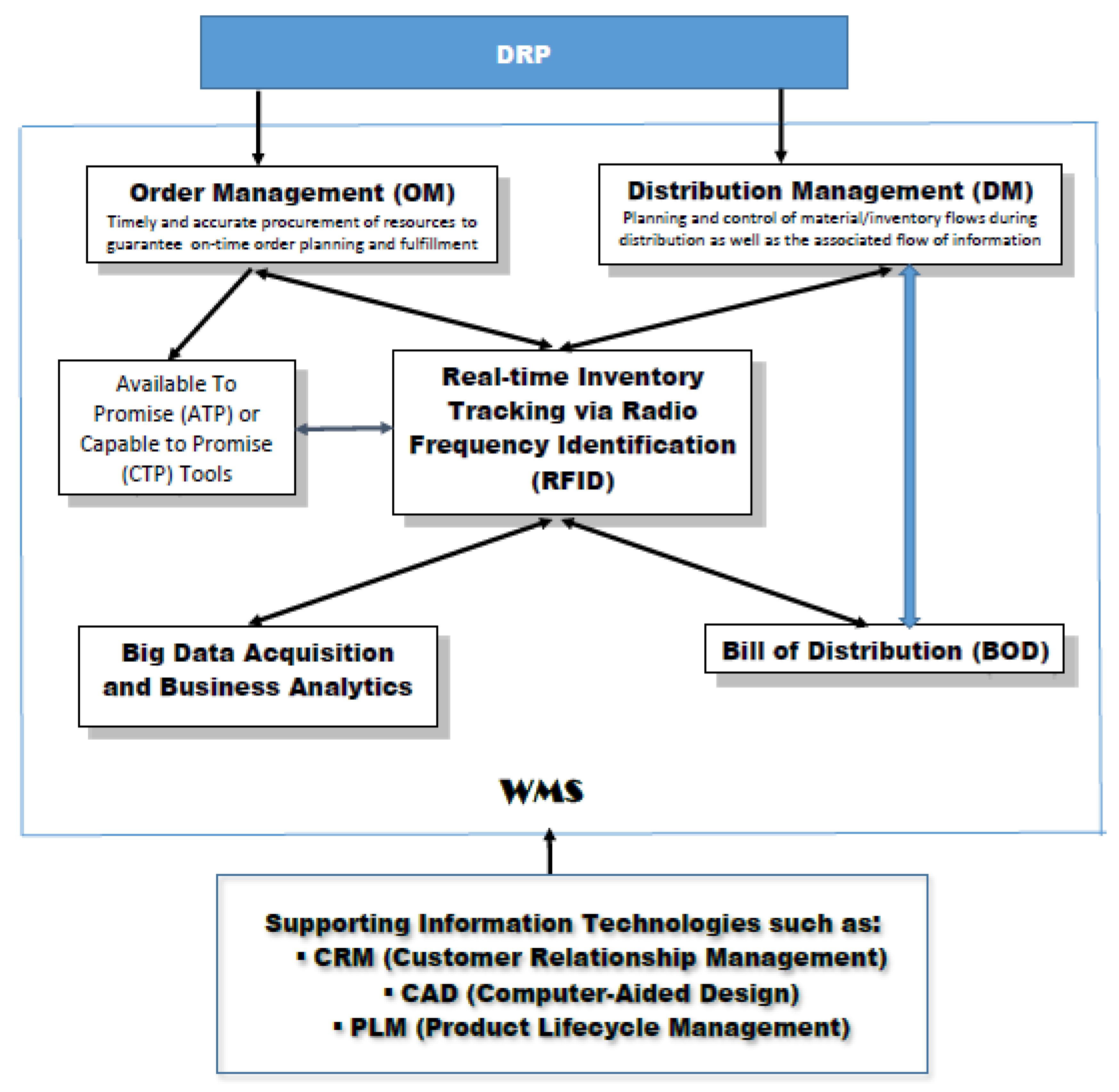
3. Architecture of the Smart Warehouse System
4. Managerial Benefits of the Smart Warehouse
- Reduced inventory levels via improved supply chain visibility. The rationale is that enhanced visibility of warehousing operations through the embedment of DRP within WMS increases real-time information availability. Such visibility allows warehousing workers to see all the potential bottlenecks and problematic areas well in advance and take corrective action. In addition, the enhanced warehousing visibility gives warehousing workers a bird’s eye view of the entire warehouse and how its various pieces function. For example, suppose inventory errors or delayed order picks are detected. In that case, warehousing workers can immediately figure out where they originated, and thus, can act before the problems become worse.
- Improved warehousing agility and faster customer response time are created due to the embedded sensor technology as it quickly recognizes fulfillment errors through automation. In addition, a smart warehouse system equipped with software as a service (Saas) can save time by nullifying the need for time-consuming on-premises warehousing software updates by completing these necessary updates on the fly.
- Enhanced labor productivity through increased automation and human–robotics cooperation, without minimal human involvement, in the entire warehousing process. Warehousing automation limits the need for on-site human staff and helps companies better prepare for the busiest times of the year, such as the Thanksgiving and Christmas holidays. It also reduces the time needed for warehousing workers to complete tasks such as order picking, packing, and shipping.
- Higher return on assets (ROA) through fully utilizing warehousing equipment.
- Better service quality control through earlier detection of anomalies and performance monitoring with embedded sensors. For example, vibration sensing can give the warehouse manager an early warning alert when warehousing equipment, the AS/RS, and AGVs need immediate maintenance or repair.
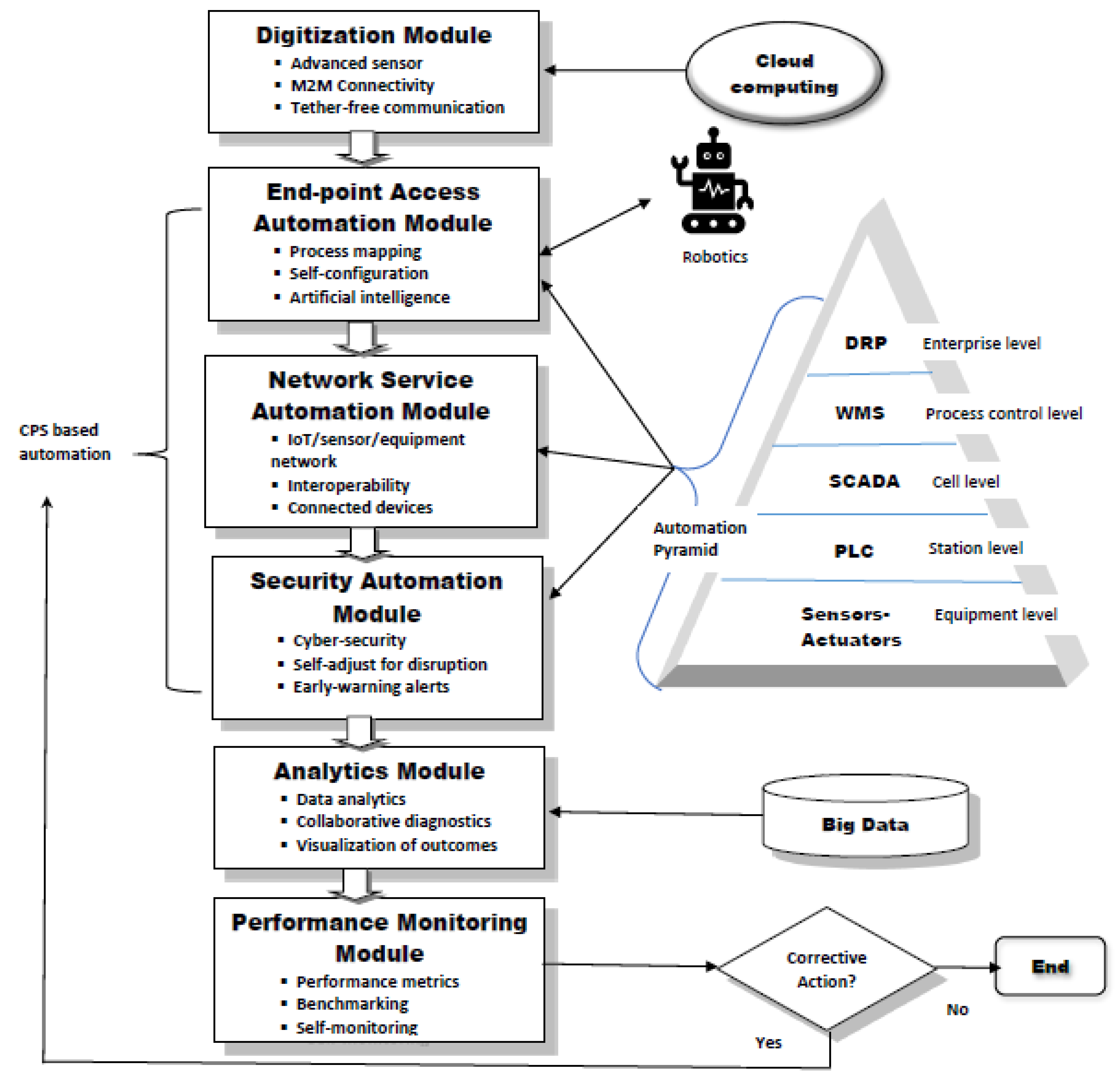
5. Smart Warehouse Implementation Plan
6. Conclusions and Future Outlooks on Smart Warehousing
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Accenture. Supply Chain Disruption: Supply Chain Networks of the Future Must Have Resilience and Sustainability at Their Heart. Unpublished Report. 2021. Available online: https://www.accenture.com/us-en/insights/consulting/supply-chain-disruption (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Alicke, K.; Barriball, E.; Trautwein, V. How COVID-19 Is Reshaping Supply Chains; Unpublished McKinsey Report; McKinsey & Company: Washington, DC, USA, November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden, A.B.; Crittenden, V.L.; Crittenden, W.F. The digitalization triumvirate: How incumbents survive. Bus. Horiz. 2019, 62, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ThSisinni, E.; Saifullah, A.; Han, S.; Jennehag, U.; Gidlund, M. Industrial Internet of Things: Challenges, opportunities, and directions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 4724–4734. [Google Scholar]
- Min, H. Developing a smart port architecture and essential elements in the ear of Industry 4.0. Marit. Econ. Logist. 2022, 24, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caggiano, A.; Teti, R. Digital manufacturing cell design for performance increase. Procedia CIRP 2012, 2, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H. Smart factory: A game changer or another fad in the era of the fourth industrial revolution. Int. J. Technol. Manag. 2022, 89, 26–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSF. Cyber-Physical Systems: Enabling a Smart and Connected World. 2018. Available online: https://www.nsf.gov/news/special_reports/cyber-physical/ (accessed on 11 January 2022).
- Chen, H. Applications of cyber-physical system: A literature review. J. Ind. Integr. Manag. 2017, 2, 1750012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.A. The past, present and future of cyber-physical systems: A focus on models. Sensors 2015, 15, 4837–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersey, A.D. A review of recent developments in fiber optic sensor technology. Opt. Fiber Technol. 1996, 2, 291–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.S. Sensor Technology Handbook; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, F.; Yang, L.T.; Wang, L.; Vinel, A. Internet of things. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2012, 25, 1101–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS. A Non-Geek’s A-to-Z Guide to the Internet of Things; Unpublished White Paper; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Faulds, D.J.; Raju, P.S. An interview with Chuck Martin on the Internet of Things. Bus. Horiz. 2019, 62, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, F.; Sadr, R. The Internet of Things (IoT) in retail: Bridging supply and demand. Bus. Horiz. 2019, 62, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KaaIoT Technologies. What Is an IoT Platform? 2019. Available online: https://www.kaaproject.org/what-is-iot-platform (accessed on 11 January 2022).
- Kahn, M. What’s an IoT Platform, and What Role Does It Play? 2019. Available online: https://www.business.att.com/learn/research-reports/whats-an-iot-platform-and-what-role-does-it-play.html (accessed on 11 January 2022).
- Andres, M. Automated Warehouse Systems: What Is ASRS and How Can It Help? 2021. Available online: https://www.tmhnc.com/blog/automated-warehouse-systems-asrs-how-it-can-help (accessed on 12 January 2022).
- Min, H. The Essentials of Supply Chain Management: Theory and Applications; Amazon Direct Publishing: Seattle, WA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Min, H. The applications of warehouse management systems: An exploratory study. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2006, 9, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloss, R. Collaborative robots are rapidly providing major improvements in productivity, safety, programming ease, portability, and cost while addressing many new applications. Ind. Robot. 2016, 43, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicentini, F. Collaborative robotics: A survey. J. Mech. Des. 2021, 143, 040802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Geest, M.; Tekinerdogan, B.; Catal, C. Smart warehouses: Rationale, challenges and solution directions. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett-Page, E.; Thomas, J. Methods for the synthesis of qualitative research: A critical review. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2009, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basias, N.; Pollalis, Y. Quantitative and qualitative research in business & technology: Justifying a suitable research methodology. Rev. Integr. Bus. Econ. Res. 2018, 7, 91–105. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, M.D. Qualitative Research in Business and Management; Sage Publications Limited: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Flick, U.; von Cardorff, E.; Steinke, I. A Companion to Qualitative Research; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mehtre, A. Edge Computing—Key Drivers and Benefits for Smart Manufacturing. 2017. Available online: https://iiot-world.com/smart-manufacturing/edge-computing-key-drivers-and-benefits-for-smart-manufacturing/ (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Xu, B.; Zhang, L. Multi-dimensional architecture modeling for cyber-physical systems. In Advances in Computer Science and Its Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, A.J. Distribution Resource Planning: The Gateway to True Quick Response and Continual Improvement, Revised Edition; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Stouffer, K.; Falco, J. Guide to Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) and Industrial Control Systems Security; Special Publication 800-82, National Institute of Standards and Technology; US Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- Boyer, S.A. SCADA: Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition; International Society of Automation: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Inductive Automation. What Is SCADA? 2018. Available online: https://inductiveautomation.com/resources/article/what-is-scada (accessed on 13 March 2022).
- Groover, M.P. Automation, Production Systems, and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall Press: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hackworth, J.R.; Hackworth, F.D. Programmable Logic Controllers: Programming Methods and Applications; Pearson Education: Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bright, J.R. Automation and Management; Division of Research, Graduate School of Business Administration, Harvard University: Boston, MA, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, Y.; Yang, G. Smart supply chain management in Industry 4.0: The review, research agenda and strategies in North America. Ann. Oper. Res. 2023, 322, 1075–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Raut, R.D.; Priyadarshinee, P.; Narkhede, B.E. Exploring warehouse management practices for adoption of IoT-blockchain. Supply Chain. Forum Int. J. 2023, 24, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Maturity Stage | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capability Level | Groundbreaking | Automation | Digitization | Connectivity Expansion and Orchestration | Knowledge Creation |
| Key action plans |
|
|
|
|
|
| Measurement attributes (including key performance indicators)—examples |
|
|
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, H. Smart Warehousing as a Wave of the Future. Logistics 2023, 7, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics7020030
Min H. Smart Warehousing as a Wave of the Future. Logistics. 2023; 7(2):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics7020030
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Hokey. 2023. "Smart Warehousing as a Wave of the Future" Logistics 7, no. 2: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics7020030
APA StyleMin, H. (2023). Smart Warehousing as a Wave of the Future. Logistics, 7(2), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics7020030





