Climate Change and Its Impact on the Yield of Major Food Crops: Evidence from Pakistan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Review of Literature
2. Methodology
2.1. Climatic Features of Major Food Crops in Pakistan
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Model Specification
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
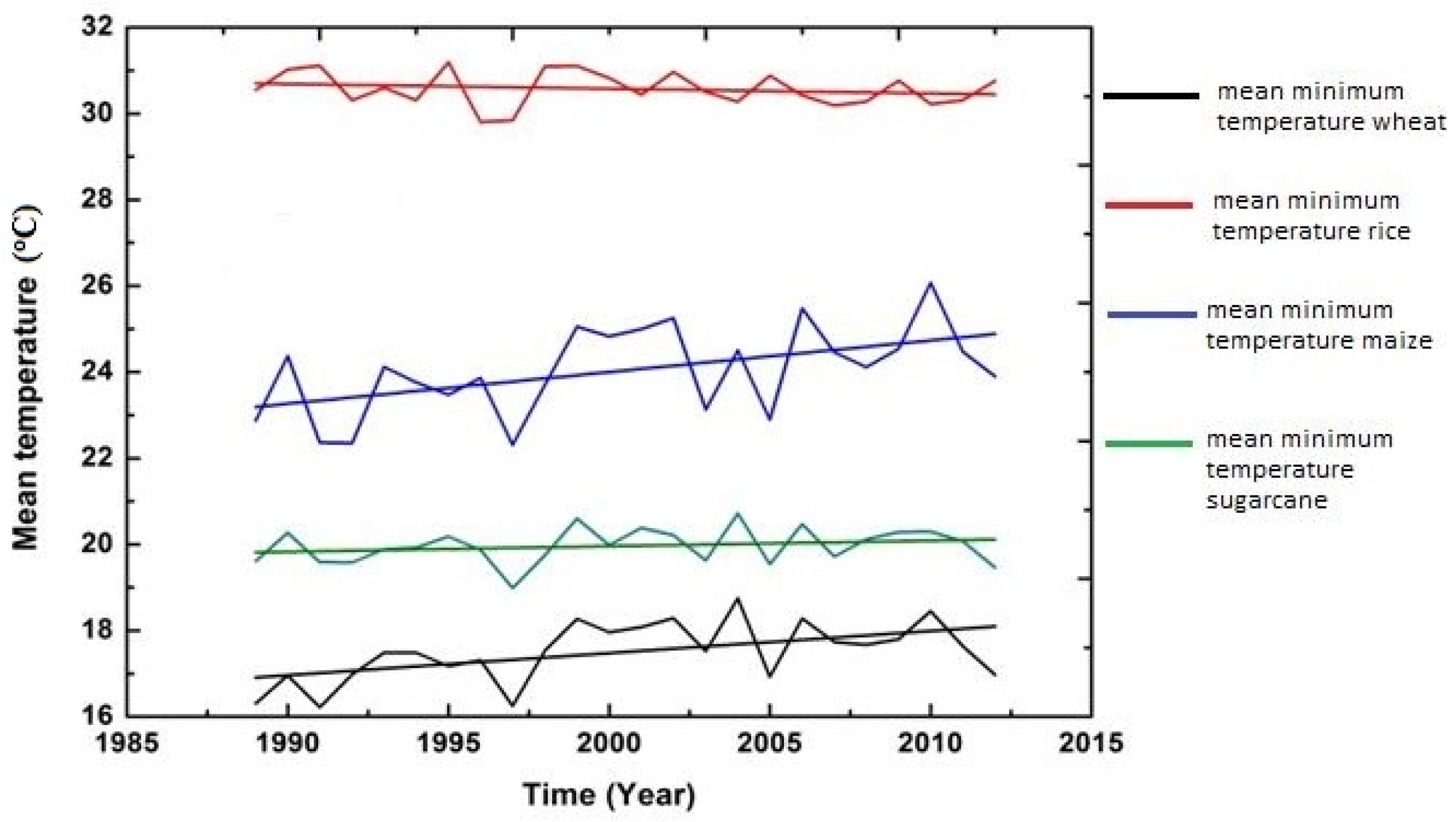
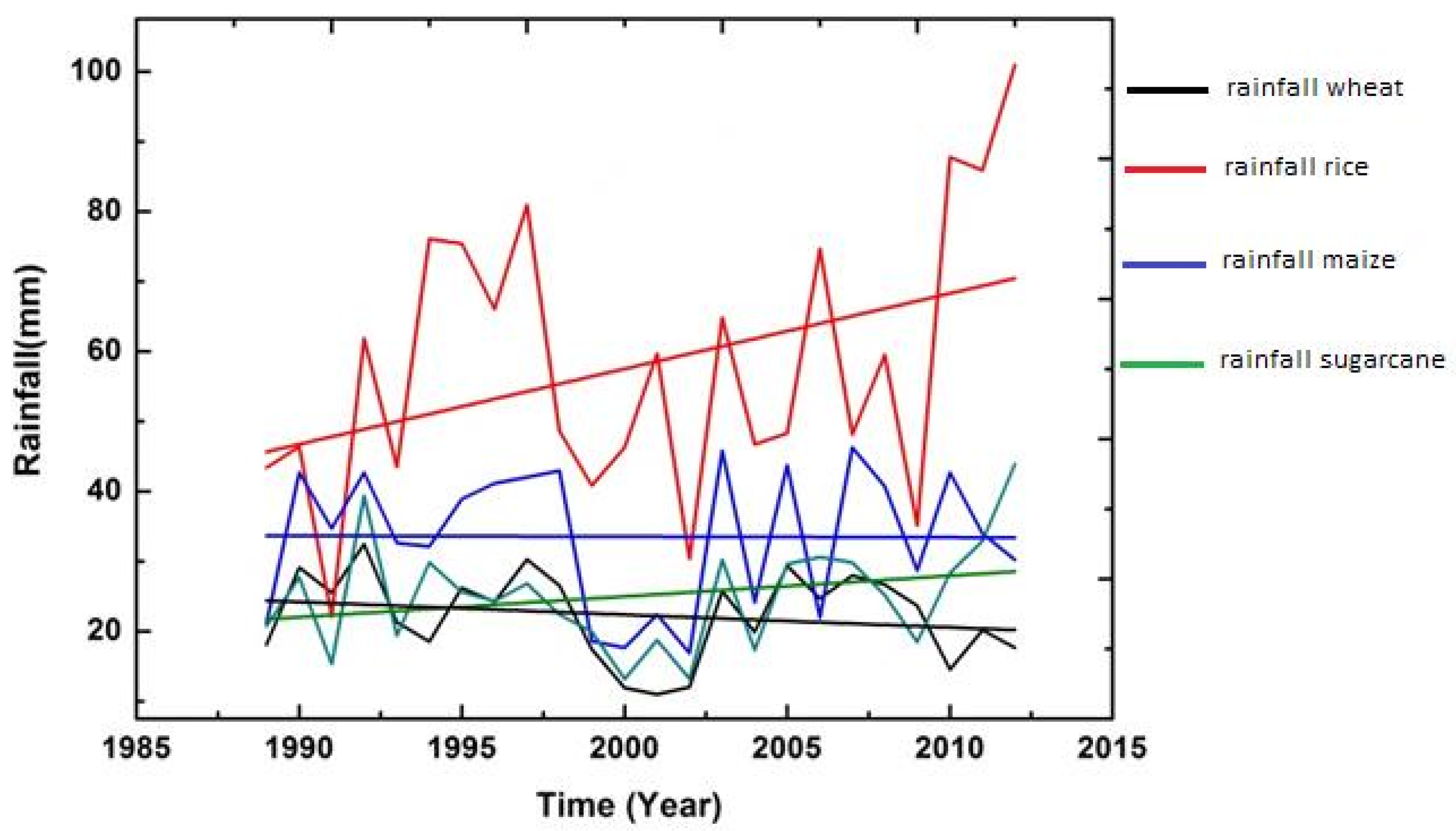
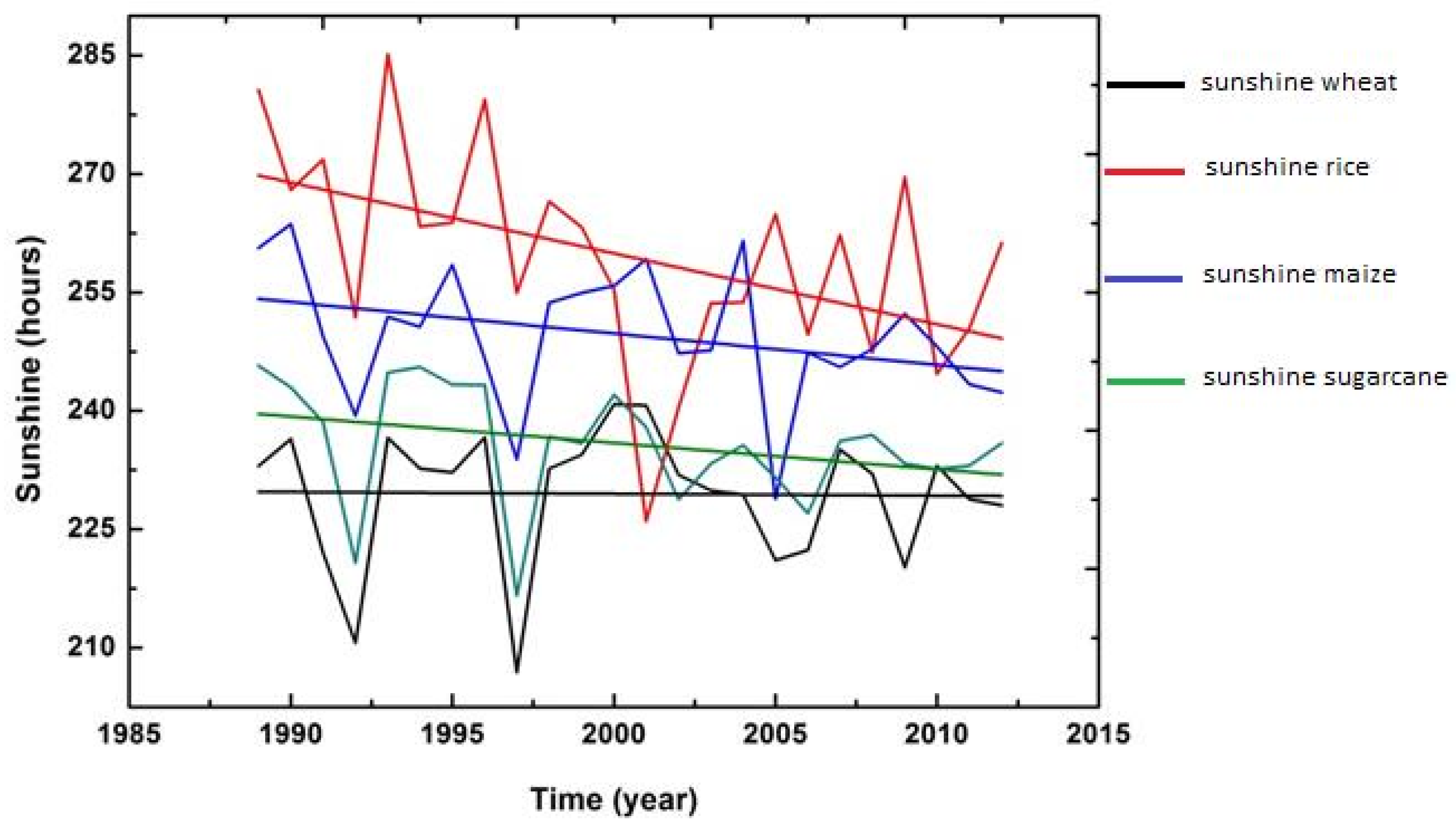
3.2. Trend Graph
3.2.1. Climate and Wheat Crop
3.2.2. Climate and Rice Crop
3.2.3. Climate and Maize Crop
3.2.4. Climate and Sugarcane Crop
4. Conclusions
5. Limitations and Future Research Direction
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurukulasuriya, P.; Mendelsohn, R.; Hassan, R.; Benin, J.; Deressa, T.; Diop, M.; Eid, H.M.; Fosu, K.Y.; Gbetibuo, G.; Jain, S.; et al. Will African agriculture survive climate change? World Bank Econ. Rev. 2006, 20, 367–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, R. The impact of climate change on agriculture in Asia. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.M.Q. Modeling the Effects of Climate Change on Flooding in Bangladesh. Ph.D. Thesis, International Global Change Institute (IGCI), University of Waikato, Hamilton, New Zealand, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Government of Bangladesh (GOB); United Nations Development Program (UNDP). The Probable Impacts of Climate Change on Poverty and Economic Growth and Options of Coping with Adverse Effects of Climate Change in Bangladesh; Policy Study: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2009.
- Misra, A.K. Climate change and challenges of water and food security. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2014, 3, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spash, C.L. Climate change: Need for new economic thought. Econ. Political Wkly. 2007, 42, 483–490. [Google Scholar]
- Spash, C.L. The economics of climate change impacts à la Stern: Novel and nuanced or rhetorically restricted? Ecol. Econ. 2007, 63, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, J.M.; Mainuddin, M.; Mpelasoka, F.; Ahmad, M.D.; Palash, W.; Quadir, M.E.; Shah-Newaz, S.M.; Hossain, M.M. The impact of climate change on regional water balances in Bangladesh. Clim. Chang. 2016, 135, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droogers, P.; Aerts, J. Adaptation strategies to climate change and climate variability: A comparative study between seven contrasting river basins. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2005, 30, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, T.; Von Braun, J. Climate change impacts on global food security. Science 2013, 341, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Climate Change. Available online: www.fao.org/clim/index_en.htm (accessed on 20 May 2017).
- Vermeulen, S.J.; Aggrawal, P.K.; Ainslie, A.; Angelone, C.; Campbell, B.M.; Challinor, A.A.; Hansen, J.W.; Ingram, J.S.I.; Jarvis, A.; Kristjanson, P.; et al. Options for support to agriculture and food security under climate change. Environ. Sci. Policy 2012, 15, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, J.S.; Cai, Y. The impact of climate change on food crop productivity, food prices and food security in South Asia. Econ. Anal. Policy 2014, 44, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank (WB). World Bank Health Nutrition and Population Statistics. 2012. Available online: http://databank.worldbank.org/data/home.aspx (accessed on 20 May 2017).
- Janjua, P.Z.; Samad, G.; Khan, N.U.; Nasir, M. Impact of Climate Change on Wheat Production: A Case Study of Pakistan. Pak. Dev. Rev. 2010, 49, 799–822. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, N.; Ahmad, B.; Hassen, S.; Baskh, K. Impact of temperature adn precipitation on rice productivity in rice-wheat cropping system of punjab province. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2012, 22, 993–997. [Google Scholar]
- Facing Climate Change by Securing Water for Food, Livelihoods and Ecosystems. Available online: http://www.iwmi.cgiar.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/02/sp11.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2017).
- Cline, W.R. Global Warming and Agriculture: Impact Estimates by Country; Peterson Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Alcamo, J.; Dronin, N.; Endejan, M.; Golubev, G.; Kirilenko, A. A new assessment of climate change impacts on food production shortfalls and water availability in Russia. Global Environ. Chang. 2007, 17, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, T.P.; Adam, J.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions. Nature 2005, 438, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döll, P.; Siebert, S. Global modeling of irrigation water requirements. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnell, N.W.; Livermore, M.J.L.; Kovats, S.; Levy, P.E.; Nicholls, R.; Parry, M.L.; Gaffin, S.R. Climate and socio-economic scenarios for global-scale climate change impacts assessments: Characterising the SRES storylines. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2004, 14, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, C.; Parry, M.L. Potential impact of climate change on world food supply. Nature 1994, 367, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandlikar, M.; Risbey, J. Agricultural impacts of climate change: if adaptation is the answer, what is the question? Clim. Change 2000, 45, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Available online: http://ipcc.ch/publications_and_data/publications_and_data_reports.shtml (accessed on 20 April 2016).
- Stern, N. What is the economics of climate change? World Econ. 2006, 7, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Maskrey, A.; Beuscher, G.; Pedduzi, P.; Schaerapf, C. Disaster Risk Reduction: 2007 Global Review. Consultation Edition. In Proceedings of the Prepared for the Global Platform for Disaster Risk Reduction First Session, Geneva, Switzerland, June 2007; pp. 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.N.; Schmitz, M. Economic assessment of the impact of climate change on the agriculture of Pakistan. Bus. Econ. Horiz. 2011, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, R.; Dinar, A. Climate change, agriculture, and developing countries: Does adaptation matter? World Bank Res. Obs. 1999, 14, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, R. Global Warming and the American Economy. In New Horizons in Environmental Economics; Oates, W.E., Folmer, H., Eds.; Edward Elga: Broadheath, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ji-kun, H. Climate change and agriculture: Impact and adaptation. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 4, 001. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, R.; Shivakoti, G.P.; Kamran, A.; Zulfiqar, F. Farmers versus nature: Managing disaster risks at farm level. Nat. Hazards 2016, 82, 1931–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.A.; Ping, Q.; Abid, M.; Kazmi, S.M.M.; Rizwan, M. Assessing risk perceptions and attitude among cotton farmers: A case of Punjab province, Pakistan. Int. J. Dis. Risk Reduct. 2016, 16, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musser, W.N.; Patrick, G.F. How Much Does Risk Really Matter to Farmers? In A Comprehensive Assessment of the Role of Risk in US Agriculture; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002; pp. 537–556. [Google Scholar]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobell, D.B.; Field, C.B. Global scale climate–crop yield relationships and the impacts of recent warming. Environ. Res. Lett. 2007, 2, 014002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Schlenker, W.; Costa-Roberts, J. Climate trends and global crop production since 1980. Science 2011, 333, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde, C; Liverman, D.; Flores, M.; Ferror, R.; Araujao, R.; Betancourt, E.; Villarreal, G.; Gay, C. Vulnerability of rainfed maize crops in Mexico to climate change. Clim. Res. 1998, 9, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, K.; Nicola, R.; Swenja, S.; Margaret, A.; Joanne, L.-B.; Erwan, M.-K.; Paul, K.; Celine, H. Adaptation to climate change: Linking Disaster Risk Reduction and Insurance; United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, J. Paying the Price of Climate Change Adaptation: Compensation for Climate Change Impacts; Federation Press: Leichhardt, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Drollette, S.A. Managing Production Risk in Agriculture; Department of Applied Economics Utah State University: Logan, UT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Deen, S. Pakistan 2010 floods. Policy gaps in disaster preparedness and response. Int. J. Dis. Risk Reduct. 2015, 12, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.N.; Khan, S.N.; Ali, A. Analysis of damages caused by flood-2010 in district Peshawar. J. Sc. Tech. Univ. Peshawar 2010, 36, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, M.P.; Pabuayon, I.M. Risk perceptions, attitudes, and influential factors of rainfed lowland rice farmers in Ilocos Norte, Philippines. Asian J. Agri. Dev. 2011, 8, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Kitonyoh, K.C. A Farm Level Analysis of Risk Attitude, Sources and Risk Measurement Strategies Among Farmers in Trans Nzoia County, Kenya; Moi University: Eldoret, Kenya, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dadzie, S.K.N.; Acquah, H. Attitudes toward risk and coping responses: The case of food crop farmers at Agona Duakwa in Agona East District of Ghana. Int. J. Agri. Forest. 2012, 2, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkholz, S.; Muro, M.; Jeffrey, P.; Smith, H.M. Rethinking the relationship between flood risk perception and flood management. Sci.Total Environ. 2014, 478, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Saqib, S.; Ahmad, M.M.; Panezai, S. Factors Affecting the Risk Attitude of Farmers in Flood Risk Prone Areas of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa: The Case of Mardan District, Pakistan; Institute of Development Administration: Bangkok, Thailand, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, G.; Tubiello, F.N.; Velthuizen, H.V.; Wiberg, D.A. Climate change impacts on irrigation water requirements: Effects of mitigation, 1990–2080. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2007, 74, 1083–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, M.; Nige, A.; Tony, M.; Robert, N.; Pim, M.; Sari, K.; Mattew, L.; Cynthia, R.; Ana, L.; Gunther, F. Millions at risk: Defining critical climate threats and targets. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2001, 11, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, I.; Ghumman, A.R.; Hashmi, H.N.; Kamal, M.A. Carbon emissions from power sector in Pakistan and opportunities to mitigate those. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Erenstein, O. Assessing farmer use of climate change adaptation practices and impacts on food security and poverty in Pakistan. Clim. Risk Manag. 2017, 16, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Food Programme (WFP). Pakistan Flood Impact Assessment; WFP: Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA). Flood Rapid Response Plan; NDMA: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2011.
- Government of Pakistan (GOP). Ministry of Pakistan. Available online: http://www.finance.gov.pk/ (accessed on 20 May 2017).
- National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA). Recovery Needs Assessment and Action Framework 2014–2016; NDMA: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2014.
- Fu, X.; Tang, Z.; Wu, J.; McMillan, K. Drought planning research in the United States: An overview and outlook. Int. J. Dis. Risk Sci. 2013, 4, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M.; Siwar, C.; Toriman, B.E.; Molla, R.I.; Talib, B. Climate change induced adaptation by paddy farmers in Malaysia. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2012, 17, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deressa, T.T.; Hassan, R.M.; Ringler, C.; Alemu, T.; Yesuf, M. Determinants of farmers’ choice of adaptation methods to climate change in the Nile Basin of Ethiopia. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2009, 19, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, E.; Derresa, T.T.; Gbetibouo, G.A.; Ringler, C. Adaptation to climate change in Ethiopia and South Africa: Options and constraints. Environ. Sci. Policy 2009, 12, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Turvey, C.G. Climate change, adaptation and China’s grain production. China Econ. Rev. 2014, 28, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walthall, C.L.; Hatfield, J.; Backlund, P.; Lengnick, L.; Marshal, E.; Walsh, M.; Adkins, S.; Aillery, M.; Ainsworth, E.A.; Ammann, C.; et al. Climate Change and Agriculture in the United States: Effects and Adaptation; USDA Technical Bulletin 1935; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 186.
- Wandel, J.; Smit, B. Agricultural Risk Management in Light of Climate Variability and Change. In Agricultural and Environmental Sustainability in the New Countryside; Rural Research Centre, Nova Scotia Agricultural College: Truro, NS, Canada, 2000; pp. 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Adger, W.N.; Huq, S.; Brown, K.; Convay, D.; Hulme, M. Adaptation to climate change in the developing world. Prog. Dev. Stud. 2003, 3, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddison, D. The Perception of and Adaptation to Climate Change in Africa; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; Volume 4308. [Google Scholar]
- Kreft, S.; Eckstein, D.; Junghans, L.; Kerestan, C.; Hagen, U. Global Climate Risk Index 2015: Who Suffers Most From Extreme Weather Events? Weather-Related Loss Events in 2013 and 1994 to 2013; Germanwatch: Bonn, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nomman, A.M.; Schmitz, M. Economic assessment of the impact of climate change on the agriculture of Pakistan. Bus. Econ. Horiz. 2011, 04, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Ashfaq, M.; Khalid, I.; Ishaq, U. An economic evaluation of impact of soil quality on Bt (Bacillus thuringiensis) cotton productivity. Soil Environ. 2011, 30, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, J.J. Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability: Contribution of Working Group II to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Smit, B.; Skinner, M.W. Adaptation options in agriculture to climate change: A typology. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2002, 7, 85–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.A.; Fee, L. Cities and Climate Change Initiative-Abridged Report: Islamabad Pakistan, Climate Change Vulnerability Assessment. United Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-Habitat). Available online: http://www.fukuoka.unhabitat.org/programmes/ccci/pdf/Islamabad(Pakistan)_23_February_2015_FINAL (5th_ revision).pdf (accessed on 7 March 2016).
- Asif, M. Climatic Change, Irrigation Water Crisis and Food Security in Pakistan; Uppsala Universitet: Uppsala, Sweden, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abid, M.; Scheffran, J.; Schneider, U.; Ashfaq, M. Farmers’ perceptions of and adaptation strategies to climate change and their determinants: The case of Punjab province, Pakistan. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2015, 6, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goverment of Pakistan (GOP). Pakistan Economic Survey; Ministry of Finance, GOP: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2016.
- Food and Agriculture Organizaitonof the United Nations (FAO). The State of Food Insecurity in the World the Multiple Dimensions of Food Security; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organizaitonof the United Nations (FAO). The State of Food Insecurity in the World: Strengthening the Enabling Environment for Food Security and Nutrition; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gera, N. Food security under structural adjustment in Pakistan. Asian Surv. 2004, 44, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A. The Looming Food Security. In Economics and Bussiness Reviews; The Daily Dawn: Karachi, Pakistan, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, G.C.; Rosegrant, M.W.; Koo, J.; Robertson, R.; Sulser, T.; Zhu, T.; Ringler, C.; Msangi, S.; Palazoo, A.; Batka, M.; et al. Climate Change: Impact on Agriculture and Costs of Adaptation; International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; Volume 21. [Google Scholar]
- Pakistan Bureau of Statistics (PBS). Agricultural Statistics. Available online: http://www.pbs.gov.pk/content/agriculture-statistics (accessed on 5 May 2016).
- Pakistan Meteroloigcal Department (PMD). Available online: http://www.pmd.gov.pk/ (accessed on 1 March 2016).
- Sombroek, W.G. The Climate Change Agriculture Conundrum: Global Climate Change and Agricultural Production. Direct and Indirect Effects. 2016. Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/W5183E/w5183e03.htm (accessed on 15 April 2016).
- Mathur, S.; Jajoo, A. Effects of Heat Stress on Growth and Crop Yield of Wheat (Triticum aestivum). In Physiological Mechanisms and Adaptation Strategies in Plants under Changing Environment; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 163–191. [Google Scholar]
- Bhandari, K.; Nayyar, H. Low Temperature Stress in Plants: An Overview of Roles of Cryoprotectants in Defense. In Physiological Mechanisms and Adaptation Strategies in Plants Under Changing Environment; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 193–265. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein, D. The Effects of the Rainy Season on Farmers. 2016. Available online: http://www.ehow.com/info_7996601_effects-rainy-season-farmers.html (accessed on 20 April 2016).
- TNAU. Agrometeorology: Relative Humidity and Plant Growth. 2016. Available online: http://www.agritech.tnau.ac.in/agriculture/agri_agrometeorology_relativehumidity.html (accessed on 10 April 2016).
- Smestad, A. The Effect of Light on Plant Growth. 2016. Available online: http://www.ehow.com/about_5251025_effect-light-plant-growth.html (accessed on 12 April 2016).
- Wooldridge, J.M. Introductory Econometrics: A Modern Approach; Nelson Education: Scarborough, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Government of Pakistan (GOP). Pakistan Economic Survey, 2014–2015; Ministry of Finance: New Delhi, India, 2015.
- Janjua, P.Z.; Samad, G.; Khan, N. Climate change and wheat production in Pakistan: An autoregressive distributed lag approach. NJAS-Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2014, 68, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Tabasam, N.; Bakhsh, K.; Ashfaq, M.; Hassen, S. Food security in the context of climate change in Pakistan. Pak. J. Commer. Soc. Sci. 2014, 8, 540–550. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, M.A.R.; Alam, K.; Gow, J. Exploring the relationship between climate change and rice yield in Bangladesh: An analysis of time series data. Agric. Syst. 2012, 112, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, U.; Saboor, A.; Baig, I.; Afzal, A.; Rahman, A. Climate variability impacts on rice crop production in Pakistan. Pak. J. Agri. Res. 2015, 28, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Awal, M.; Siddique, M. Rice production in Bangladesh employing by ARIMA model. Bangladesh J. Agri. Res. 2011, 36, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Huang, J.; Sheehy, J.E.; Laza, R.C.; Visperas, R.M.; Zhong, X.; Centenso, G.S.; Khush, G.S.; Cassman, K.G. Rice yields decline with higher night temperature from global warming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9971–9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saseendran, S.; Singh, K.; Rathor, L.; Singh, S.; Sinha, S. Effects of climate change on rice production in the tropical humid climate of Kerala, India. Clim. Chang. 2000, 44, 495–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | Major Crops | Statistics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std. Dev. | Min. | Max. | Skewness | Kurtosis | ||
| Wheat | 93.74 | 80.16 | 2.10 | 324.50 | 1.13 | 3.30 | |
| Cropping Area (hectare) | Rice | 10.63 | 12.04 | 0.00 | 43.70 | 1.07 | 2.87 |
| Maize | 15.89 | 16.70 | 0.90 | 52.20 | 0.99 | 2.48 | |
| Sugarcane | 20.63 | 34.18 | 0.00 | 126.40 | 1.78 | 4.74 | |
| Wheat | 210.21 | 209.57 | 2.90 | 901.70 | 1.53 | 4.58 | |
| Production (tons) | Rice | 17.21 | 18.13 | 0.00 | 83.40 | 1.06 | 3.41 |
| Maize | 27.44 | 27.07 | 0.80 | 137.10 | 1.54 | 5.67 | |
| Sugarcane | 1018.16 | 1707.40 | 0.00 | 6403.80 | 1.75 | 4.64 | |
| Wheat | 879.91 | 262.46 | 252.53 | 1912.22 | 0.53 | 3.82 | |
| Yield (kg/acre) | Rice | 737.29 | 237.73 | 303.52 | 1315.23 | 0.40 | 2.27 |
| Maize | 949.31 | 1038.17 | 287.11 | 9307.80 | 5.71 | 42.95 | |
| Sugarcane | 18,284.91 | 3603.22 | 8498.42 | 29,454.20 | 0.11 | 3.14 | |
| Wheat | 25.50 | 3.44 | 14.47 | 29.96 | −1.90 | 5.93 | |
| Maximum | Rice | 36.91 | 2.00 | 32.40 | 42.90 | 0.36 | 2.93 |
| temperature (°C) | Maize | 32.39 | 3.46 | 24.95 | 38.67 | 0.04 | 2.12 |
| Sugarcane | 28.86 | 3.25 | 22.70 | 35.15 | 0.28 | 1.84 | |
| Wheat | 10.85 | 3.11 | 1.37 | 15.64 | −1.62 | 5.10 | |
| Minimum | Rice | 24.84 | 1.71 | 19.68 | 29.16 | −0.34 | 3.38 |
| temperature (°C) | Maize | 18.29 | 3.87 | 9.93 | 28.42 | 0.34 | 2.14 |
| Sugarcane | 14.81 | 3.17 | 8.86 | 21.48 | 0.09 | 2.10 | |
| Wheat | 22.28 | 17.58 | 0.00 | 71.18 | 0.79 | 2.75 | |
| Rainfall (mm/year) | Rice | 70.89 | 60.02 | 0.00 | 322.58 | 1.31 | 4.58 |
| Maize | 33.56 | 21.80 | 3.58 | 112.98 | 1.08 | 3.76 | |
| Sugarcane | 28.76 | 20.24 | 0.25 | 132.16 | 1.26 | 5.91 | |
| Wheat | 57.43 | 6.71 | 36.17 | 70.20 | −0.74 | 3.40 | |
| Humidity (%) | Rice | 58.57 | 5.90 | 44.80 | 74.00 | 0.09 | 2.82 |
| Maize | 51.34 | 5.80 | 37.25 | 64.25 | −0.21 | 2.36 | |
| Sugarcane | 60.35 | 5.87 | 43.55 | 73.43 | −0.52 | 2.89 | |
| Wheat | 229.33 | 21.91 | 160.96 | 280.80 | −0.24 | 3.33 | |
| Sunshine (h/day) | Rice | 259.49 | 23.06 | 175.14 | 381.00 | 0.15 | 7.15 |
| Maize | 249.24 | 18.37 | 190.35 | 290.35 | −0.13 | 3.26 | |
| Sugarcane | 233.13 | 24.12 | 176.38 | 290.11 | 0.37 | 2.47 | |
| Variables | Major Crops | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | Rice | Maize | Sugarcane | |
| Max Temp | −1.7991 * | 3.9200 * | 0.1174 | 0.4743 * |
| Min Temp | 0.6216 * | −0.7041 * | 0.5458 | 0.2578 * |
| Rainfall | −0.1195 * | −0.0126 | −0.703 | −0.0094 |
| R.Humidity | −0.1107 | 0.183 | −1.3219 * | 0.3135 * |
| Sunshine | 0.2169 | −0.2114 | −0.8761 | −0.1253 |
| Trend | 0.0135 * | 0.01447 * | 0.0391 * | 0.009 * |
| constant | 4.5121 * | −11.0511 * | 8.4222 | 0.8063 |
| F | 18.68 * | 18.26 * | 25.19 * | 10.69 * |
| Wald chi2 | 96.53 * | 87.75 * | 101.09 * | 60.69 * |
| R2 | 0.2993 | 0.3302 | 0.3932 | 0.2501 |
| n | 226 | 178 | 156 | 182 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, S.; Liu, Y.; Ishaq, M.; Shah, T.; Abdullah; Ilyas, A.; Din, I.U. Climate Change and Its Impact on the Yield of Major Food Crops: Evidence from Pakistan. Foods 2017, 6, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods6060039
Ali S, Liu Y, Ishaq M, Shah T, Abdullah, Ilyas A, Din IU. Climate Change and Its Impact on the Yield of Major Food Crops: Evidence from Pakistan. Foods. 2017; 6(6):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods6060039
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Sajjad, Ying Liu, Muhammad Ishaq, Tariq Shah, Abdullah, Aasir Ilyas, and Izhar Ud Din. 2017. "Climate Change and Its Impact on the Yield of Major Food Crops: Evidence from Pakistan" Foods 6, no. 6: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods6060039
APA StyleAli, S., Liu, Y., Ishaq, M., Shah, T., Abdullah, Ilyas, A., & Din, I. U. (2017). Climate Change and Its Impact on the Yield of Major Food Crops: Evidence from Pakistan. Foods, 6(6), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods6060039





