Synthesis, Optimization, and Evaluation of a New Sustained-Release Food Formulation for Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Main Instruments and Equipment
2.3. Synthetic Process of PsP-HAP
2.4. Single-Factor Experiments
2.5. Response Surface Method (RSM) [1]
2.6. Physicochemical Characterization of HAP
2.7. Determination of Encapsulation Rate and PsP-Loading Capacity
2.7.1. Encapsulation Rate
2.7.2. Loading Capacity
2.8. Release Profile
2.9. DPPH Radical Scavenging Rate of PsP-HAP Sustained-Release System
2.10. Cytotoxicity Evaluation for PsP-HAP Sustained-Release System
2.11. Total Antioxidative Capacity of PsP-HAP Sustained-Release System
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
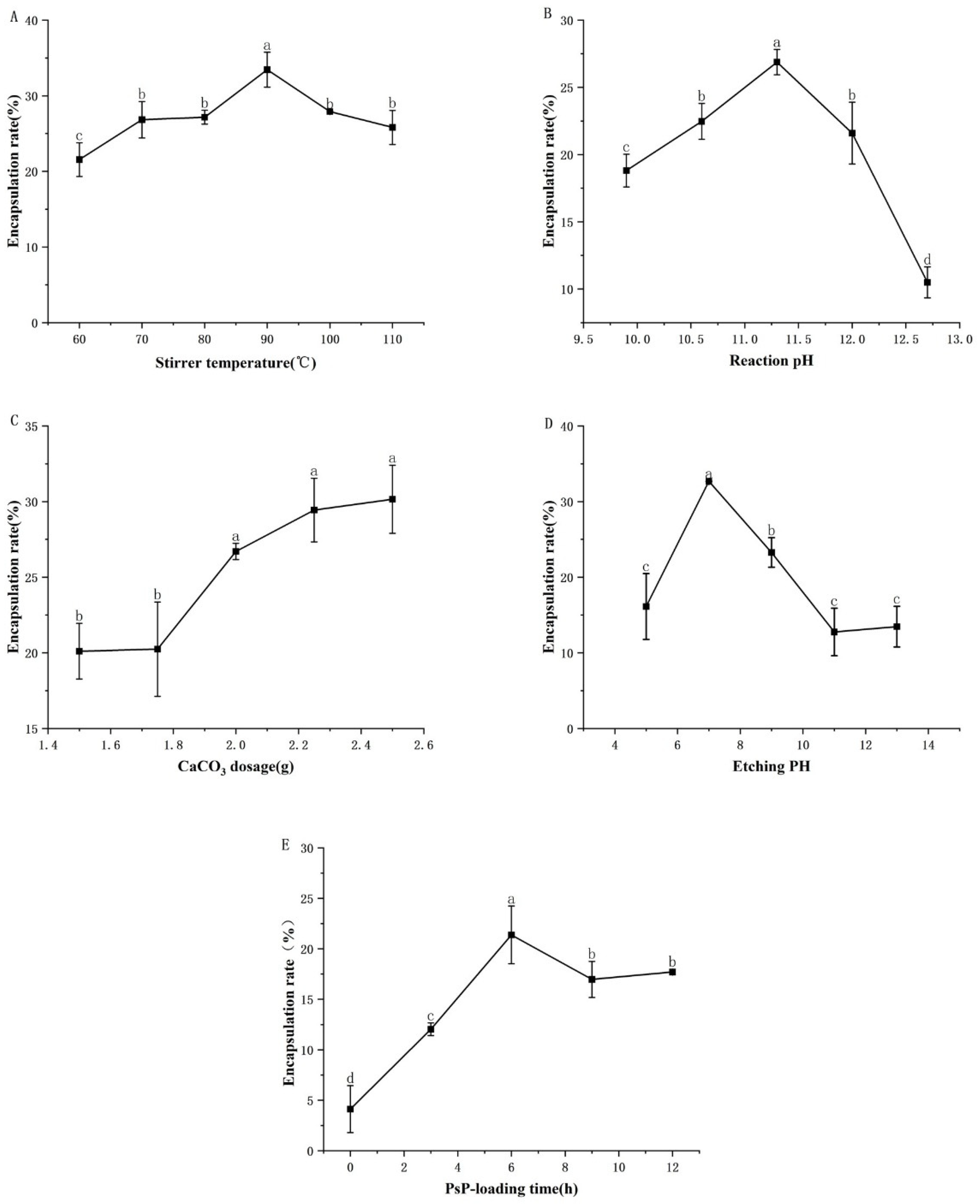
3.1. Single-Factor Experimental Results
3.2. Results of RSM Experiments
3.2.1. Model Establishment and Data Fitting [1]
3.2.2. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
3.2.3. Analysis of Contour Plots and 3D Plots
3.2.4. Verification of Optimal Process Conditions
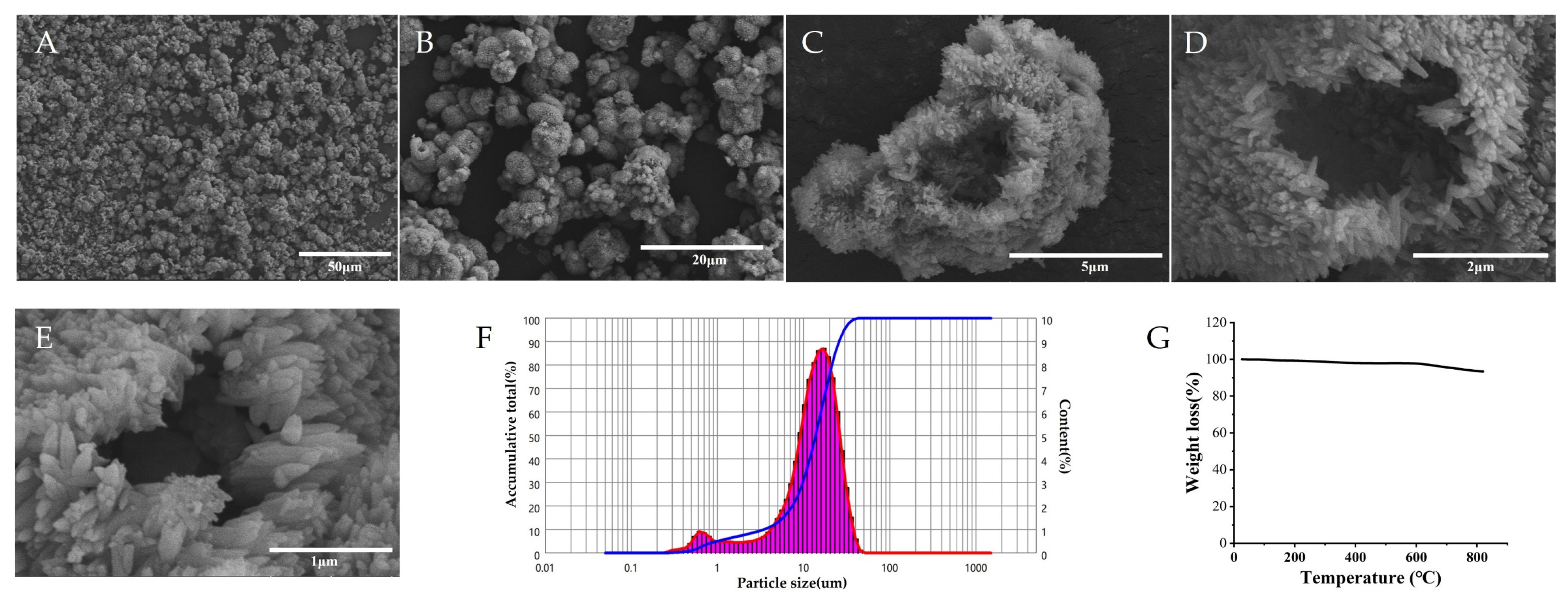
3.3. Physicochemical Characterization of HAP
3.4. Evaluation of PsP-HAP
3.4.1. PsP-Loading Capacity and Cumulative Release Rate of PsP-HAP Sustained-Release System
3.4.2. DPPH Radical Scavenging Rate of PsP-HAP Sustained-Release System
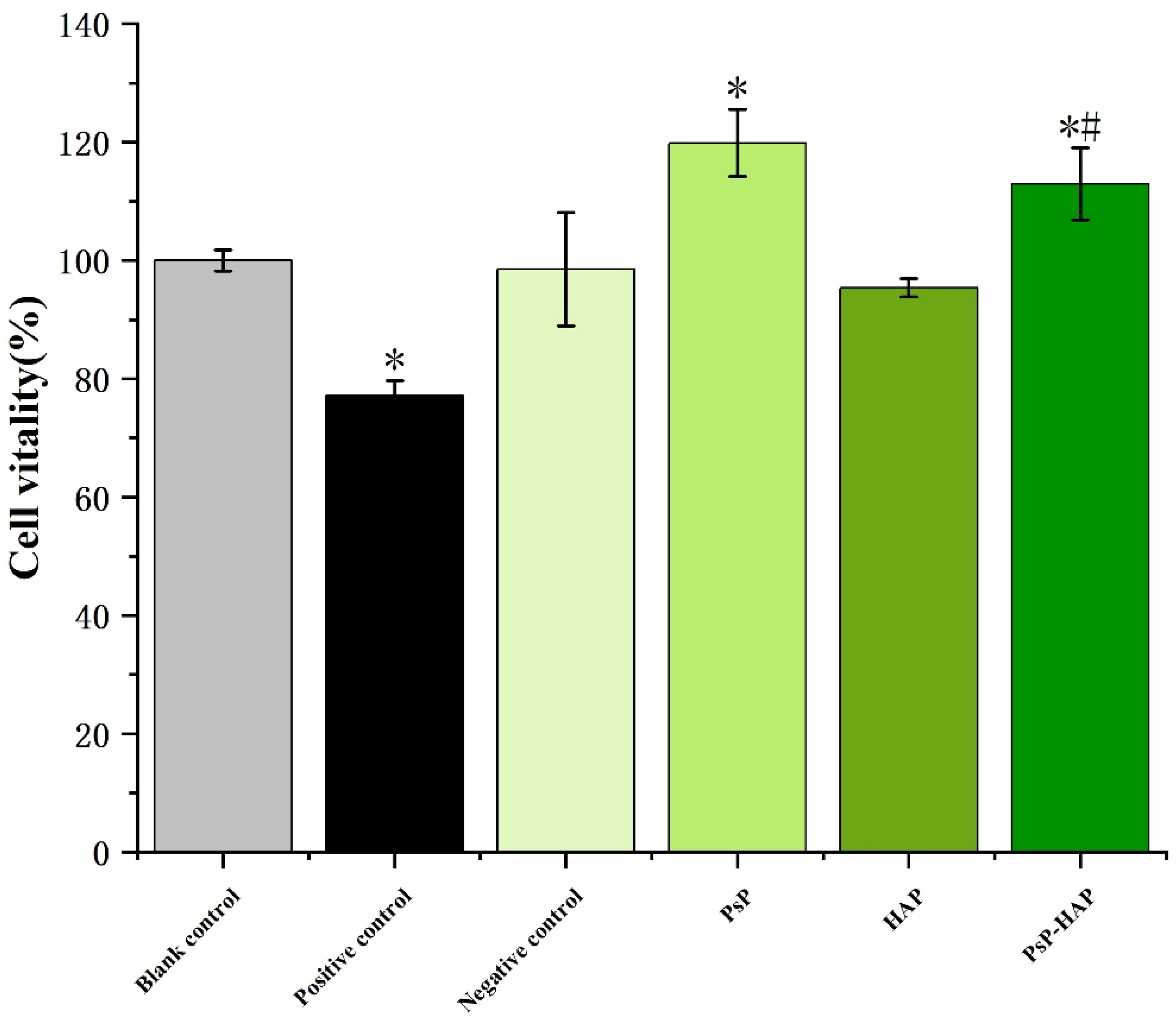
3.4.3. Cytotoxicity of PsP-HAP Sustained-Release System
3.4.4. Total Antioxidative Capacity of PsP-HAP Sustained-Release System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PsP | Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide |
| HAP | Hydroxyapatite |
| PsP-HAP | Sustained-release system of Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide |
| RSM | Response surface method |
| DPPH | 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| FRAP | Ferric reducing antioxidant power |
| UAE-DES | Ultrasound-assisted extraction with deep eutectic solvents |
| PLGA | Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer solution |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| BCA | Bicinchoninic acid |
References
- Sun, C.Q.; Wang, G.D.; Sun, J.; Yin, J.Y.; Huang, J.; Li, Z.Z.; Mu, D.; He, M.L.; Liu, T.T.; Cheng, J.L.; et al. A New Method of Extracting Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharide with Antioxidant Function: Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction-Deep Eutectic Solvents Method. Foods 2023, 12, 3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cheng, J.; Sun, Y.; He, L.; Li, R. Protective Effects of Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharides Against Type 2 Diabetic Mice Induced by High-Fat Diet and Low-Dose Streptozotocin. Toxics 2025, 13, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Tang, Y.; Song, Z.Y.; Ge, J.W. Polygonatum sibiricum F. Delaroche polysaccharide ameliorates HFD induced mouse obesity via regulation of lipid metabolism and inflammatory response. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, F.R.; Yuan, L.X.; Ruan, H.S.; Zhu, Z.B.; Fan, X.; Zhu, L.Y.; Peng, X. Blood-Enriching Effects and Immune-Regulation Mechanism of Steam-Processed Polygonatum Sibiricum Polysaccharide in Blood Deficiency Syndrome Mice. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 813676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.P.; Lu, X.; Yan, L.; Liu, T.; Niu, Y.; Yu, J. Polygonatum sibiricum (Huang Jing) polysaccharide reduces diabetic cardiomyopathy through increasing cyclic guanosine monophosphate-protein kinase G signaling in diabetic mice. J. Diabetes Investig. 2024, 15, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.Y.; Zhao, Y.H.; Zhu, J.F.; Zhang, Z.J.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Z.X. Synergistic Effect of Polydatin and Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharides in Combating Atherosclerosis via Suppressing TLR4-Mediated NF-κB Activation in ApoE-Deficient Mice. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 3885153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.P.; Li, N.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, L.; Wang, K.; Chen, S.J.; Gu, Q.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhai, K.F.; Xu, S.W. Pharmacology and metabolomic reveal Polysaccharides from polygonatum sibiricum ameliorate the diabetic osteoporosis in zebrafish. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2025, 25, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.K.; Guo, Y.; Lu, C.Y.; Yu, L.L.; Fang, C.; Li, C.T. Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide inhibited liver cancer in a simulated tumor microenvironment by eliminating TLR4/STAT3 pathway. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2023, 46, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Sun, C.; Qu, W.; Du, H.; He, M.; Huo, J.; Sun, J.; Huang, J.; et al. Comparison of Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharides Found in Young and Mature Rhizomes. Foods 2024, 13, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Du, H.C.; Qu, W.J.; Sun, C.Q.; Chen, Q.; Du, Y.P.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Guo, Y.R.; Wang, C.L.; Huang, J.; et al. Comparison of Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharides from Different Extraction Methods. Foods 2025, 14, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.Q.; Xu, Y.F.; Du, H.C.; Chen, Y.; Qu, W.J.; He, M.L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Huang, J.; Huo, J.S.; Yin, J.Y. Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharides Extracted with Ultrasound-Assisted Deep Eutectic Solvents Protect L6 Cells Against Oxidative Stress in a Cellular Model of Sarcopenic Obesity. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.X.; Chen, X.F.; Gong, P.; Chen, F.X.; Cui, D.D.; Wang, M.R. Advances in the in vitro digestion and fer-mentation of polysaccharides. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 4970–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, L. Driving forces for drug loading in drug carriers. J. Microencapsul. 2015, 32, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.; Turiel, S.; Sousa Gomes, P.; Costa, E.; Santos-Silva, A.; Quadros, P.; Duarte, J.; Battistuzzo, S.; Helena Fernandes, M. Vascular biosafety of commercial hydroxyapatite particles: Discrepancy between blood compatibility assays and endothelial cell behavior. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, S.; Zaheri Khosroshahi, A.; Maleki Dizaj, S.; Rezaei, Y. Preparation, physicochemical assessment and the antimicrobial action of hydroxyapatite–gelatin/curcumin nanofibrous composites as a dental biomaterial. Biomimetics 2021, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behbahani, E.S.; Ghaedi, M.; Abbaspour, M.; Rostamizadeh, K.; Dashtian, K. Curcumin loaded nanostructured lipid carriers: In vitro digestion and release studies. Polyhedron 2019, 164, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, A.P.S.; Venkatasubbu, G.D. Sustained release of amoxicillin from hydroxyapatite nanocomposite for bone infections. Prog. Biomater. 2018, 7, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güncüm, E.; Bakırel, T.; Anlaş, C.; Ekici, H.; Işıklan, N. Novel amoxicillin nanoparticles formulated as sustained release delivery system for poultry use. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 4, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Stephen Sipaut Mohd Nasri, C.; Bin Arshad, S.E. Hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite powders using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Prakash, K.H.; Cheang, P.; Khor, K.A. Temperature driven morphological changes of chemically precipitated hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Langmuir 2004, 20, 5196–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ning, F.; Guo, D.; Xu, Z. Synthesis and cellular biocompatibility of two kinds of HAP with different nanocrystal morphology. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 83, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.W.; Fang, C.H.; Liang, Y.J.; Yang, C.Y.; Kuo, W.T.; Lin, F.H. Controlled release of Clenbuterol from a hydroxyapatite carrier for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Bio-Mater. Res. 2023, 27, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geuli, O.; Metoki, N.; Zada, T.; Reches, M.; Eliaz, N.; Mandler, D. Synthesis, coating, and drug-release of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles loaded with antibiotics. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 7819–7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, D.; Zhang, D.; Huang, B.; Yi, P.; Yan, C. Structural characterization and DPPH· radical scavenging activity of a polysaccharide from Guara fruits. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.J.; Hong, J.Y.; Yang, I.H.; Zhou, X.R.; Lin, Y.W.; Lin, T.C.; Hou, C.H.; Lin, F.H. To Synthesize Hydroxyapatite by Modified Low Temperature Method Loaded with Bletilla striata Polysaccharide as Antioxidant for the Prevention of Sarcopenia by Intramuscular Administration. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oni, O.P.; Hu, Y.; Tang, S.J.; Yan, H.H.; Zeng, H.; Wang, H.M.; Ma, L.Y.; Yang, C.Y.; Ran, J.B. Syntheses and ap-plications of mesoporous hydroxyapatite: A review. Mater. Chem. Front. 2023, 7, 9–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu’ad, N.M.; Haq, R.A.; Noh, H.M.; Abdullah, H.Z.; Idris, M.I.; Lee, T.C. Synthesis method of hydroxyapatite: A review. Mater. Today: Proc. 2020, 29, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, Y.; Shen, W.; Cui, J. Kinetics of hydroxyapatite precipitation at pH 10 to 11. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Tan, C.Y.; Hamdi, M.; Sopyan, I.; Teng, W.D. The influence of Ca/P ratio on the properties of hydroxyapatite bioceramics. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Materials and Nanotechnology in Engineering, Harbin, China, 1–4 July 2007; Volume 6423, pp. 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Li, L.; Cao, S.W. Nanostructured porous hollow ellipsoidal capsules of hydroxyapatite and calcium silicate: Preparation and application in drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 2722–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.U.; Ihsan, A.; Sarwar, Y.; Bajwa, S.Z.; Bano, K.; Tehseen, B.; Zeb, N.; Hussain, I.; Ansari, M.T.; Saeed, M.; et al. Hollow mesoporous hydroxyapatite nanostructures; smart nanocarriers with high drug loading and controlled releasing features. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 544, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chen, T.; Wei, Y.T.; Chu, L.F.; Guo, Y.P. Hollow carbonated hydroxyapatite microspheres with mesoporous structure: Hydrothermal fabrication and drug delivery property. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 3166–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slósarczyk, A.; Szymura-Oleksiak, J.; Mycek, B. The kinetics of pentoxifylline release from drug-loaded hydroxyapatite implants. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhou, K.; Chen, C.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, H.; Zhang, D. Hollow and porous hydroxyapatite microspheres prepared with an O/W emulsion by spray freezing method. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 69, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, M.; Panduranga Rao, K. Preparation, characterization and in vitro release of gentamicin from coralline hydroxyapatite-gelatin composite microspheres. Biomaterials 2022, 23, 3175–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.Z.; Ge, J.C.; Li, F.; Yang, J.; Pan, L.H.; Zha, X.Q.; Li, Q.M.; Duan, J.; Luo, J.P. Digestive behavior of Dendrobium huoshanense polysaccharides in the gastrointestinal tracts of mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efentakis, M.; Dressman, J.B. Gastric juice as a dissolution medium: Surface tension and pH. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 1998, 23, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.F.; Pye, G.; Bramley, R.; Clark, A.G.; Dyson, T.J.; Hardcastle, J.D. Measurement of gastrointestinal pH profiles in normal ambulant human subjects. Gut 1988, 29, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Liu, C.H.; Liang, Y.H.; Lin, F.H.; Wu, K.C. Hollow mesoporous hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (hmHANPs) with enhanced drug loading and pH-responsive release properties for intracellular drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2447–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Grandfield, K.; Schwenke, A.; Engqvist, H. Synthesis and release of trace elements from hollow and porous hydroxyapatite spheres. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.H.; Liu, C.H.; Liao, S.H.; Lin, Y.Y.; Tang, H.W.; Liu, S.Y.; Lai, I.R.; Wu, K.C. Cosynthesis of cargo-loaded hydroxyapatite/alginate core-shell nanoparticles (HAP@Alg) as pH-responsive nanovehicles by a pre-gel method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6720–6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallingborg, J. Intraluminal pH of the human gastrointestinal tract. Dan. Med. Bull. 1999, 46, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nandhra, G.K.; Chaichanavichkij, P.; Birch, M.; Scott, S.M. Gastrointestinal Transit Times in Health as Deter-mined Using Ingestible Capsule Systems: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Erdogan, A.; Rao, S.S. How to assess regional and whole gut transit time with wireless motility capsule. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 20, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.H.; Jenkins, D.J.; Wiggins, H.S. Measurement of the mean transit time of dietary residue through the human gut. Gut 1976, 17, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirait, M.; Sinulingga, K.; Siregar, N.; Doloksaribu, M.E. Characterization of hydroxyapatite by cytotoxicity test and bending test. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2193, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Bardhan, R.; Mondal, B.; Dey, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.S.; Roy, S.; Guha, R.; Roy, K. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro cytotoxicity assessment of hydroxyapatite from different bioresources for tissue engineering application. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2012, 35, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, J.; Ding, Y.; Sun, L. Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Longzhua mushroom Polysaccharide Hydrogel and Slow-Release Behavior of Encapsulated Rambutan Peel Polyphenols. Foods 2024, 13, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; You, J.; Yan, X.; Ji, H.; Ji, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, P.; Yue, P.; Ullah, Z.; et al. Okra Flower Polysaccharide–Pea Protein Conjugates Stabilized Pickering Emulsion Enhances Apigenin Stability, Bioaccessibility, and Intestinal Absorption In Vitro. Foods 2025, 14, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ding, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, S.; Meng, D.; Gu, C.; Yang, R. Construction of a Yeast Protein-Chitooligosaccharide W/O/W Emulsion System for Carrying and Stabilization of Betacyanins. Foods 2025, 14, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.N.; Wang, Y.Y.; Khan, M.F.; Zhu, L.N.; Chen, Z.L.; Wang, Z.; Song, B.B.; Zhao, Q.L.; Zhong, S.Y.; Li, R. Supramolecular Co-Assembled Fmoc-FRGDF/Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel for Quercetin Delivery: Multifunctional Bioactive Platform. Foods 2025, 14, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Name of Product | Product Code | Company (City, State, Country) |
|---|---|---|
| Na2HPO4 | D7292 | Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) |
| CaCO3 | 239232 | Sigma Co., Ltd. (Louis, MO, USA) |
| NaOH | 240515D1 | Xilong Scientific Co., Ltd. (Shantou, China) |
| Anthrone | A140968 | Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) [10,11] |
| Phosphate buffer solution (PBS) | P1020 | Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) [10,11] |
| DMEM culture medium | SH30243.01 | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. (Waltham, MA, USA) [10,11] |
| Fetal bovine serum | 10091148 | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. (Waltham, MA, USA) [10,11] |
| Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide | 2025060503 | Shanxi Nanba Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Taiyuan, China) |
| CCK-8 cell activity detection kit | C0037 | Beyotime, Inc. (Shanghai, China) [10,11] |
| Total Antioxidant Capacity Assay Kit with FRAP method | S0116 | Beyotime, Inc. (Shanghai, China) [10,11] |
| BCA Protein Assay Kit | P0012 | Beyotime, Inc. (Shanghai, China) [10,11] |
| Citrate | C108869 | Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| DPPH | Y0303 | Hefei BASF Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Hefei, China) [10,11] |
| Levels | Factors | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) Stirrer Temperature (°C) | (B) Reaction pH | (C) Etching pH | (D) PsP-Loading Time (h) | |
| −1 | 60.00 | 10.60 | 5.00 | 3.00 |
| 0 | 85.00 | 11.30 | 7.00 | 6.00 |
| 1 | 110.00 | 12.00 | 9.00 | 9.00 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 1608.38 | 14 | 114.88 | 35.49 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A—Stirrer temperature | 0.8216 | 1 | 0.8216 | 0.2538 | 0.6222 | |
| B—Reaction pH | 28.55 | 1 | 28.55 | 8.82 | 0.0101 | |
| C—Etching pH | 455.96 | 1 | 455.96 | 140.87 | <0.0001 | |
| D—PsP-loading time | 5.63 | 1 | 5.63 | 1.74 | 0.2084 | |
| AB | 5.62 | 1 | 5.62 | 1.74 | 0.2089 | |
| AC | 2.79 | 1 | 2.79 | 0.8616 | 0.3690 | |
| AD | 4.45 | 1 | 4.45 | 1.38 | 0.2604 | |
| BC | 13.47 | 1 | 13.47 | 4.16 | 0.0607 | |
| BD | 32.66 | 1 | 32.66 | 10.09 | 0.0067 | |
| CD | 0.2070 | 1 | 0.2070 | 0.0640 | 0.8040 | |
| A2 | 374.02 | 1 | 374.02 | 115.55 | <0.0001 | |
| B2 | 210.54 | 1 | 210.54 | 65.05 | <0.0001 | |
| C2 | 699.86 | 1 | 699.86 | 216.22 | <0.0001 | |
| D2 | 301.79 | 1 | 301.79 | 93.24 | <0.0001 | |
| Residual | 45.32 | 14 | 3.24 | |||
| Lack of fit | 41.54 | 10 | 4.15 | 4.40 | 0.0830 | not significant |
| Pure error | 3.78 | 4 | 0.9438 | |||
| Cor total | 1653.69 | 28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Qu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, J.; Yin, J. Synthesis, Optimization, and Evaluation of a New Sustained-Release Food Formulation for Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharide. Foods 2026, 15, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010147
Qu W, Zhang Z, Guo Y, Chen Y, Wang L, Huang J, Yin J. Synthesis, Optimization, and Evaluation of a New Sustained-Release Food Formulation for Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharide. Foods. 2026; 15(1):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010147
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Wenjie, Zhuoyuan Zhang, Yiran Guo, Yan Chen, Linpeng Wang, Jian Huang, and Jiyong Yin. 2026. "Synthesis, Optimization, and Evaluation of a New Sustained-Release Food Formulation for Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharide" Foods 15, no. 1: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010147
APA StyleQu, W., Zhang, Z., Guo, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, L., Huang, J., & Yin, J. (2026). Synthesis, Optimization, and Evaluation of a New Sustained-Release Food Formulation for Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharide. Foods, 15(1), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010147






