pH-Responsive Bacterial Nanocellulose Smart Labels Derived from Acid Whey for Estimating Beef Mince Quality Alterations During Storage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of BNC Material via Static Fermentation
2.3. Anthocyanin Extraction from Clitoria ternatea
2.4. Determination of Total Anthocyanin Content (TAC)
2.5. Preparation of pH-Responsive Labels
2.6. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Assessment
2.7. Indicator Implementation and Food Storage Evaluation
2.8. Color Response Assessment
2.9. Measurement of Mince pH
2.10. Determination of Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVBN) Content
2.11. Microbiological Assessment
2.12. Statistical Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Nanocellulose Synthesis
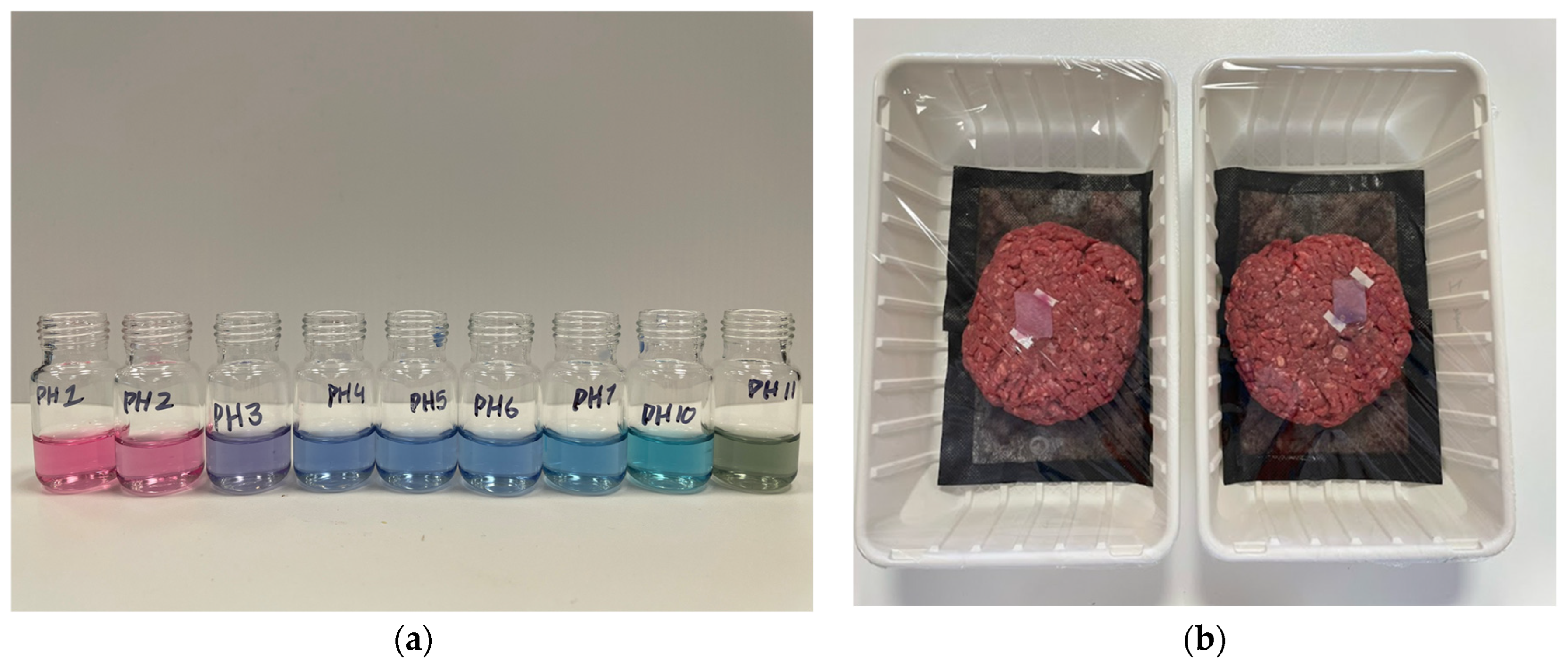
3.2. pH-Responsive Behavior of Anthocyanin and Label Integration in Packaging
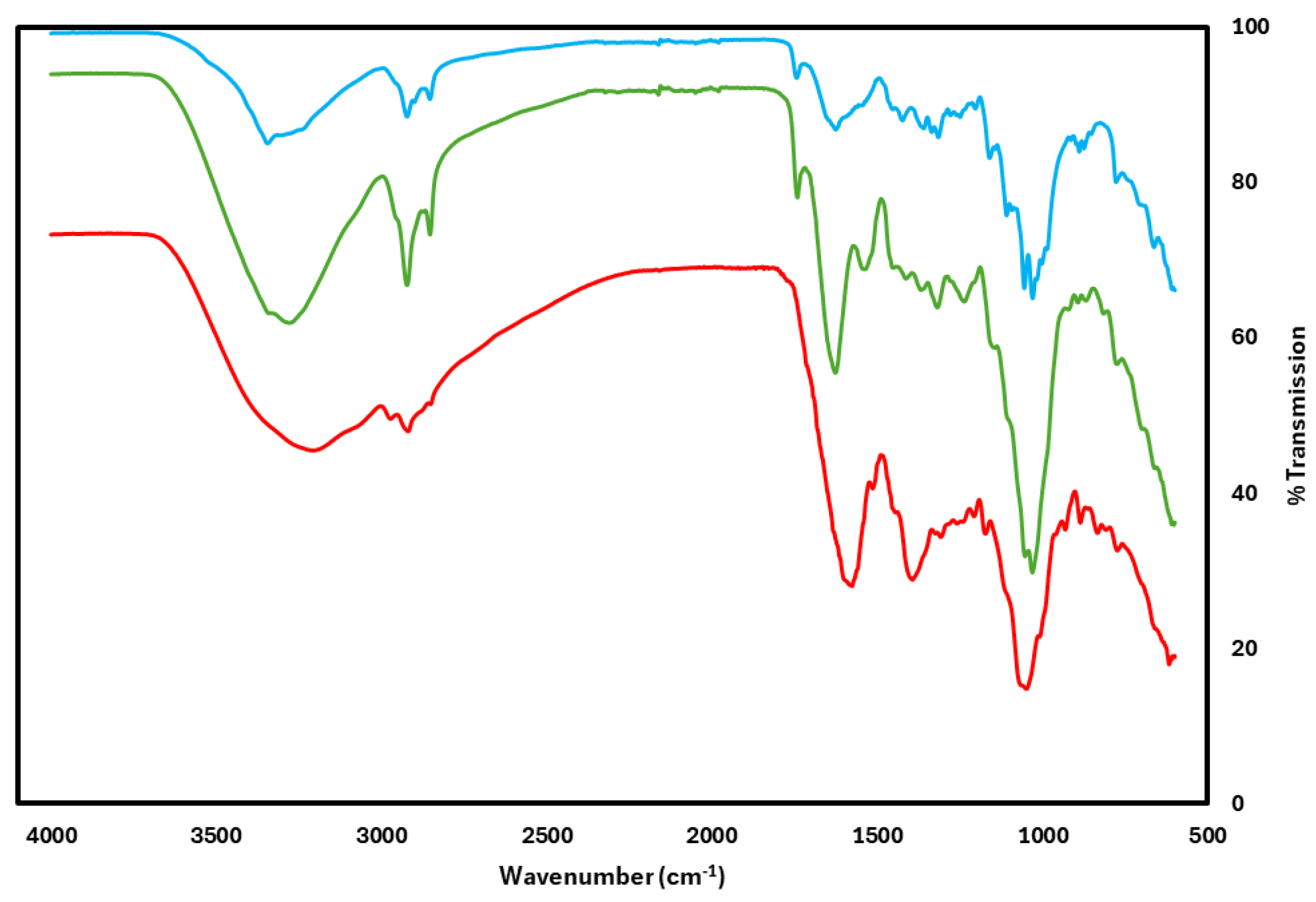
3.3. FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis of BNC, and Anthocyanin Incorporation
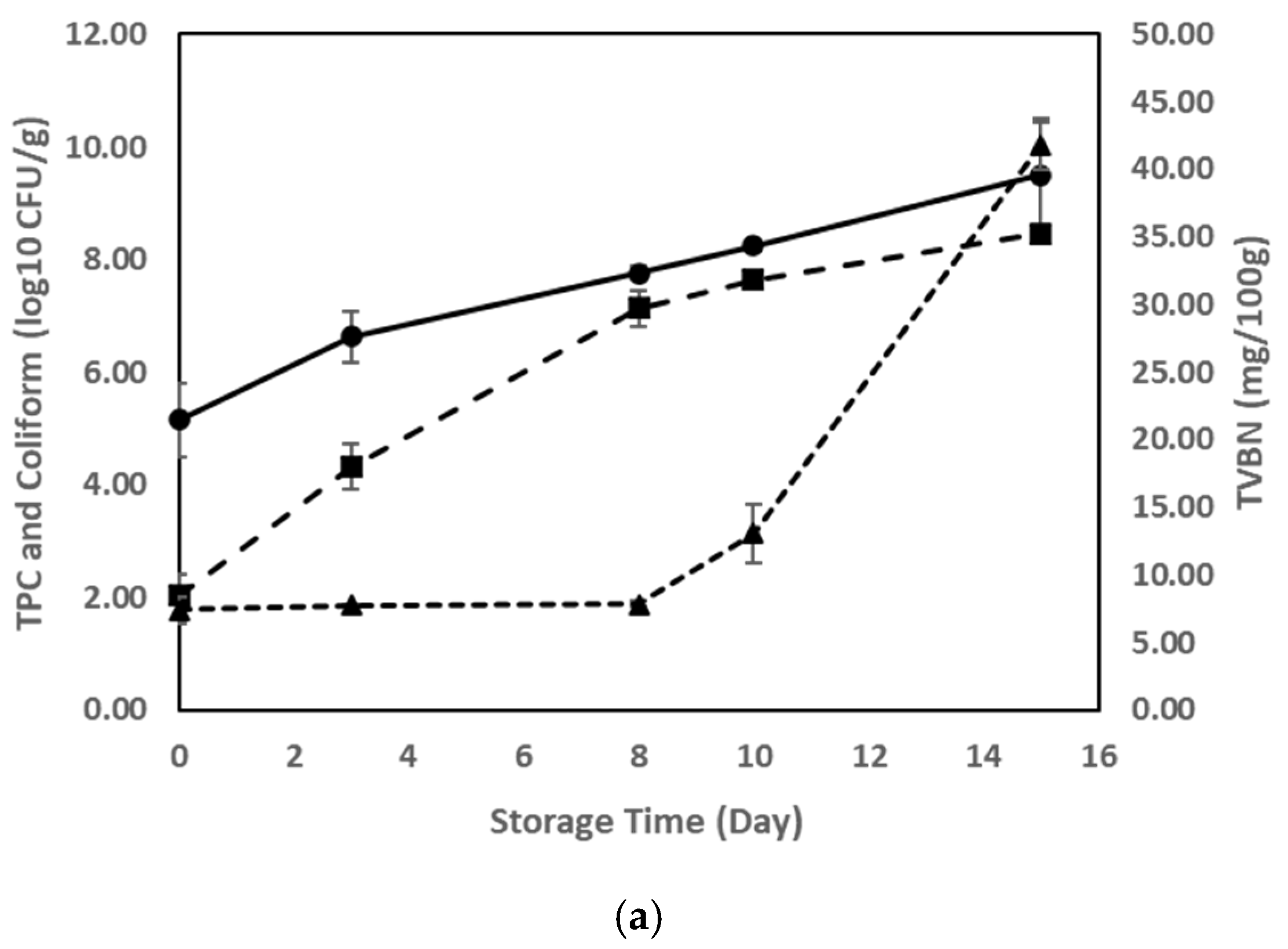
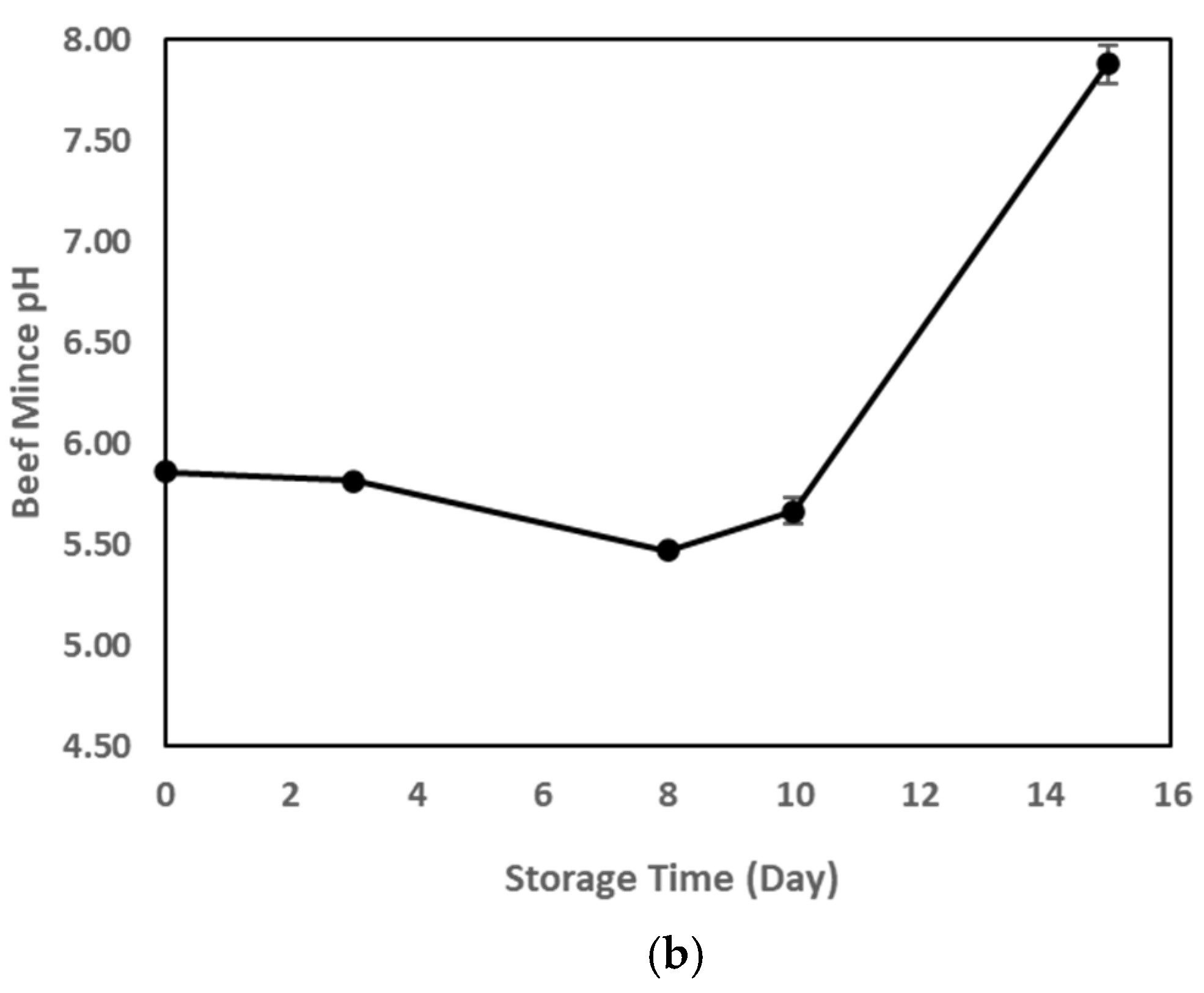
3.4. TVBN, pH, and Microbial Growth as Indicators of Meat Spoilage
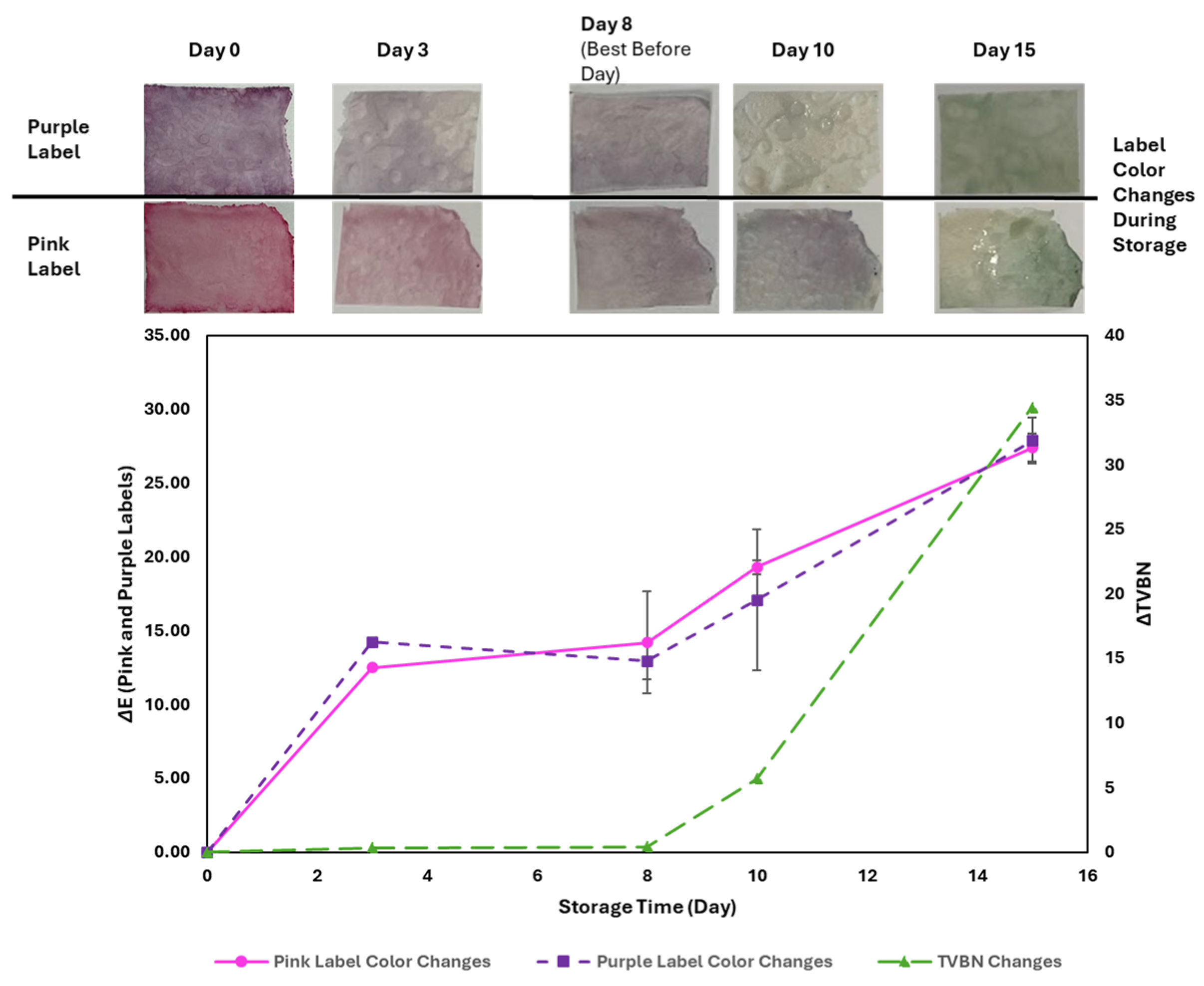
3.5. TVBN Accumulation and Its Impact on pH-Responsive Label Color Changes
3.6. Correlation Between ∆TVBN, TPC, Coliforms, and ∆E
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BNC | Bacterial Nanocellulose |
| FTIR | Fourier-Transform Infrared |
| RO | Reverse Osmosis |
| SCOBY | Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeast |
| TAC | Total Anthocyanin Content |
| TPC | Total Plate Counts |
| TVBN | Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen |
References
- Müller, P.; Schmid, M. Intelligent Packaging in the Food Sector: A Brief Overview. Foods 2019, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, M.; Tajik, H.; Almasi, H.; Forough, M.; Ezati, P. A Novel PH-Sensing Indicator Based on Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers and Black Carrot Anthocyanins for Monitoring Fish Freshness. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 115030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koosha, M.; Hamedi, S. Intelligent Chitosan/PVA Nanocomposite Films Containing Black Carrot Anthocyanin and Bentonite Nanoclays with Improved Mechanical, Thermal and Antibacterial Properties. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 127, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yong, H.; Qin, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, J. Development of Multifunctional Food Packaging Films Based on Chitosan, TiO2 Nanoparticles and Anthocyanin-Rich Black Plum Peel Extract. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahankari, S.S.; Subhedar, A.R.; Bhadauria, S.S.; Dufresne, A. Nanocellulose in Food Packaging: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 255, 117479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, A.; Pal, L.; Hubbe, M. Nanocellulose in Packaging: Advances in Barrier Layer Technologies. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 95, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, K.; Browne, C. Nanocellulose and Its Composite Films: Applications, Properties, Fabrication Methods, and Their Limitations. In Nanoscale Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 247–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilarinho, F.; Sanches Silva, A.; Fátima Vaz, M.; Paulo Farinha, J.; Vaz, M.F.; Paulo Farinha, J.; Jorge, R. Nanocellulose in Green Food Packaging. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1526–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherkhani, E.; Moradi, M.; Tajik, H.; Molaei, R.; Ezati, P. Preparation of On-Package Halochromic Freshness/Spoilage Nanocellulose Label for the Visual Shelf Life Estimation of Meat. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 2632–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullo, M.; China, S.L.; Massimiliano Falcone, P.; Giudici, P. Biotechnological Production of Cellulose by Acetic Acid Bacteria: Current State and Perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 6885–6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez Tapias, Y.A.; Di Monte, M.V.; Peltzer, M.A.; Salvay, A.G. Bacterial Cellulose Films Production by Kombucha Symbiotic Community Cultured on Different Herbal Infusions. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, D.A.; Maghrawy, H.H.; Abdel Kareem, H. Biosynthesis of Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibrils in Black Tea Media by a Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeast Isolated from Commercial Kombucha Beverage. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, N.E.A.; El-Malkey, S.E.; Abu-Saied, M.A.; Mohammed, A.B.A. Exploration of a Novel and Efficient Source for Production of Bacterial Nanocellulose, Bioprocess Optimization and Characterization. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Labas, A.; Long, B.; McKnight, S.; Xu, C.; Tian, J.; Xu, Y. Bacterial Nanocellulose Production Using Cost-Effective, Environmentally Friendly, Acid Whey Based Approach. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2023, 24, 101629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.H.; Almeida, A.d.R.; Maciel, M.V.d.O.B.; Vitorino, V.B.; Bazzo, G.C.; da Rosa, C.G.; Sganzerla, W.G.; Mendes, C.; Barreto, P.L.M. Microencapsulation by Spray Drying of Red Cabbage Anthocyanin-Rich Extract for the Production of a Natural Food Colorant. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022, 39, 102287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Wahab, H.M.F.A.; Moram, G.S.E.D. Toxic Effects of Some Synthetic Food Colorants and/or Flavor Additives on Male Rats. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2013, 29, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobylewski, S.; Jacobson, M.F. Toxicology of Food Dyes. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2012, 18, 220–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Sinha, R.; Roy, D. Toxicological Effects of Malachite Green. Aquatic. Toxicol. 2004, 66, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, C.; Pu, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, L.; Cui, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, C.; Pu, Y.; et al. Recent Advances in PH-Responsive Freshness Indicators Using Natural Food Colorants to Monitor Food Freshness. Foods 2022, 11, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chi, J.; Ye, X.; Wang, S.; Liang, J.; Yue, P.; Xiao, H.; Gao, X. Nanoliposomes as Delivery System for Anthocyanins: Physicochemical Characterization, Cellular Uptake, and Antioxidant Properties. LWT 2021, 139, 110554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ma, X.; Gao, X.; Wu, W.; Zhou, B. Light Induced Regulation Pathway of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadalinejhad, S.; Almasi, H.; Moradi, M. Immobilization of Echium Amoenum Anthocyanins into Bacterial Cellulose Film: A Novel Colorimetric PH Indicator for Freshness/Spoilage Monitoring of Shrimp. Food Control 2020, 113, 107169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rhim, J.W. Anthocyanin Food Colorant and Its Application in PH-Responsive Color Change Indicator Films. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2297–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wen, L.; Liu, J.; Du, P.; Liu, Y.; Hu, P.; Cao, J.; Wang, W. Enhanced PH-Sensitive Anthocyanin Film Based on Chitosan Quaternary Ammonium Salt: A Promising Colorimetric Indicator for Visual Pork Freshness Monitoring. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidana Gamage, G.C.; Lim, Y.Y.; Choo, W.S. Anthocyanins From Clitoria Ternatea Flower: Biosynthesis, Extraction, Stability, Antioxidant Activity, and Applications. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 792303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemat, F.; Abert-Vian, M.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Strube, J.; Uhlenbrock, L.; Gunjevic, V.; Cravotto, G. Green Extraction of Natural Products. Origins, Current Status, and Future Challenges. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Vian, M.A.; Ravi, H.K.; Khadhraoui, B.; Hilali, S.; Perino, S.; Tixier, A.S.F. Review of Alternative Solvents for Green Extraction of Food and Natural Products: Panorama, Principles, Applications and Prospects. Molecules 2019, 24, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belwal, T.; Huang, H.; Li, L.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Aalim, H.; Luo, Z. Optimization Model for Ultrasonic-Assisted and Scale-up Extraction of Anthocyanins from Pyrus Communis ‘Starkrimson’ Fruit Peel. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhai, W. Identification and Antioxidant Activity of Anthocyanins Extracted from the Seed and Cob of Purple Corn (Zea mays L.). Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Durst, R.W.; Wrolstad, R.E. Determination of Total Monomeric Anthocyanin Pigment Content of Fruit Juices, Beverages, Natural Colorants, and Wines by the PH Differential Method: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, S.; Saleh, E.; Hussein, M.; Sadek, K.; Shukry, M.; Ghamry, H.I.; Fericean, L.M.; Ali, E. Improving the Shelf Life and Quality of Minced Beef by Cassia Glauca Leaf Extracts during Cold Storage. Processes 2023, 11, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yang, H.; Yang, C.; Lu, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, D. Prediction of Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVB-N) and 2-Thiobarbituric Acid (TBA) of Smoked Chicken Thighs Using Computer Vision during Storage at 4 °C. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 199, 107170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulas, A.E.; Kontominas, M.G. Effect of Salting and Smoking-Method on the Keeping Quality of Chub Mackerel (Scomber japonicus): Biochemical and Sensory Attributes. Food Chem. 2005, 93, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriplai, N.; Pinitsoontorn, S. Bacterial Cellulose-Based Magnetic Nanocomposites: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abol-Fotouh, D.; Hassan, M.A.; Shokry, H.; Roig, A.; Azab, M.S.; Kashyout, A.E.H.B. Bacterial Nanocellulose from Agro-Industrial Wastes: Low-Cost and Enhanced Production by Komagataeibacter Saccharivorans MD1. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handayani, L.; Aprilia, S.; Arahman, N.; Bilad, M.R. Anthocyanin Extraction and PH-Modulated Color Alterations in Butterfly Pea Flower (Clitoria ternatea L.). Proc. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1359, 012087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Nobile, M.A.; Conte, A.; Cannarsi, M.; Sinigaglia, M. Strategies for Prolonging the Shelf Life of Minced Beef Patties. J. Food Saf. 2009, 29, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammor, M.S.; Argyri, A.; Nychas, G.J.E. Rapid Monitoring of the Spoilage of Minced Beef Stored under Conventionally and Active Packaging Conditions Using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy in Tandem with Chemometrics. Meat. Sci. 2009, 81, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Mendoza, D.; Kosmerl, E.; Krentz, A.; Zhang, L.; Badiger, S.; Miyagusuku-Cruzado, G.; Mayta-Apaza, A.; Giusti, M.; Jiménez-Flores, R.; García-Cano, I. Invited Review: Acid Whey Trends and Health Benefits. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 1262–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotta, T.; Solieri, L.; Iacumin, L.; Picozzi, C.; Gullo, M. Valorization of Cheese Whey Using Microbial Fermentations. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 2749–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesovs, S.; Semjonovs, P. Production of Bacterial Cellulose from Whey—Current State and Prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 7723–7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikmanis, P.; Kolesovs, S.; Semjonovs, P. Production of Biodegradable Microbial Polymers from Whey. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2020, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laavanya, D.; Shirkole, S.; Balasubramanian, P. Current Challenges, Applications and Future Perspectives of SCOBY Cellulose of Kombucha Fermentation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgieva, S.; Trček, J. Bacterial Cellulose: Production, Modification and Perspectives in Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oladzadabbasabadi, N.; Mohammadi Nafchi, A.; Ghasemlou, M.; Ariffin, F.; Singh, Z.; Al-Hassan, A.A. Natural Anthocyanins: Sources, Extraction, Characterization, and Suitability for Smart Packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 33, 100872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruprasath, N.; Sankarganesh, P.; Adeyeye, S.A.O.; Babu, A.S.; Parthasarathy, V. Review on Emerging Applications of Nanobiosensor in Food Safety. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 3950–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelliah, R.; Park, Y.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Barathikannan, K.; Yeon, S.-J.; Lim, M.; Kim, D.-G.; Oh, D.-H. Revolutionizing Smart Food Packaging: The Promise and Challenges of Biosensors and Biopolymer-Based Nanocomposites. J. Food Hyg. Saf. 2024, 39, 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, Q.; Mujumdar, A.S. Intelligent System/Equipment for Quality Deterioration Detection of Fresh Food: Recent Advances and Application. Foods 2024, 13, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Value (Mean ± SD) |
|---|---|
| Wet weight (g BNC/media L) | 31.27 ± 9.60 |
| Dry weight (g BNC/media L) | 1.14 ± 0.39 |
| Wet film thickness (mm) | 2.75 ± 0.35 |
| Beef Mince Freshness Indicators | Pink Label ∆E | Purple Label ∆E |
|---|---|---|
| ∆TVBN | 0.956 | 0.993 |
| Coliform Counts (Log10 CFU/g) | 0.933 | 0.875 |
| Total Plate Count (Log10 CFU/g) | 0.982 | 0.950 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.Z.; Hassan, S.; Long, B.M.; Labas, A.; Amamcharla, J.K.; Yoo, M.J.Y.; Hu, X.; Bean, D.C. pH-Responsive Bacterial Nanocellulose Smart Labels Derived from Acid Whey for Estimating Beef Mince Quality Alterations During Storage. Foods 2025, 14, 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091544
Liu DZ, Hassan S, Long BM, Labas A, Amamcharla JK, Yoo MJY, Hu X, Bean DC. pH-Responsive Bacterial Nanocellulose Smart Labels Derived from Acid Whey for Estimating Beef Mince Quality Alterations During Storage. Foods. 2025; 14(9):1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091544
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Dylan Zhe, Sabeen Hassan, Benjamin M. Long, Alan Labas, Jayendra K. Amamcharla, Michelle J. Y. Yoo, Xiaojie Hu, and David C. Bean. 2025. "pH-Responsive Bacterial Nanocellulose Smart Labels Derived from Acid Whey for Estimating Beef Mince Quality Alterations During Storage" Foods 14, no. 9: 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091544
APA StyleLiu, D. Z., Hassan, S., Long, B. M., Labas, A., Amamcharla, J. K., Yoo, M. J. Y., Hu, X., & Bean, D. C. (2025). pH-Responsive Bacterial Nanocellulose Smart Labels Derived from Acid Whey for Estimating Beef Mince Quality Alterations During Storage. Foods, 14(9), 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091544






