Metagenomic Analysis of Raw Milk and the Inactivation of Foodborne Pathogens Using Ultraviolet-C
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Library Construction
2.3. Sequencing Data Processing and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Isolation and Identification of the Microorganisms in Raw Milk
2.5. Bacterial Cell Preparation
2.6. UV-C Treatment
2.7. Microbial Colony Count via the Standard Plate Method
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
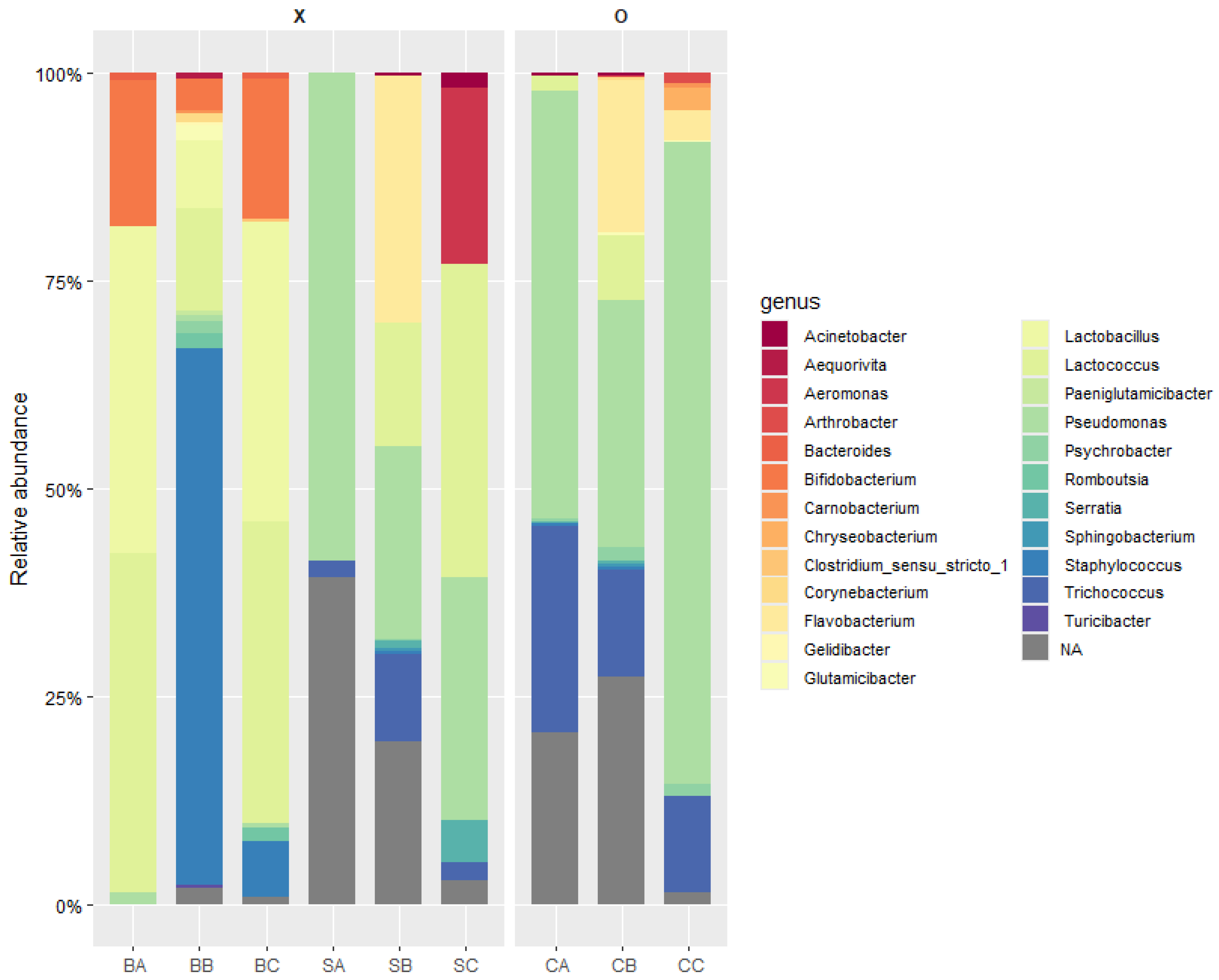
3.1. Metagenomic Analysis Following UV-C Treatment
3.2. Isolation and Identification of Microorganisms in Raw Milk
3.3. UV-C Resistance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, L.; Hu, S.; Pang, X.; Zhang, S.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, G. Community diversity of psychrophilic bacteria in dairy farm raw milk and its characteristic enzyme production at different temperature. Food Biosci. 2023, 54, 102921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeie, S.B.; Håland, M.; Thorsen, I.M.; Narvhus, J.; Porcellato, D. Bulk tank raw milk microbiota differs within and between farms: A moving goalpost challenging quality control. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1959–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Cheng, J.; Qi, X.; Guan, N.; Chen, Q.; Pei, X.; Man, C. Effect of thermostable enzymes produced by psychrotrophic bacteria in raw milk on the quality of ultra-high temperature sterilized milk. Foods 2023, 12, 3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jonghe, V.; Coorevits, A.; Van Hoorde, K.; Messens, W.; Van Landschoot, A.; De Vos, P.; Heyndrickx, M. Influence of storage conditions on the growth of Pseudomonas species in refrigerated raw milk. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scatamburlo, T.M.; Yamazi, A.K.; Cavicchioli, V.Q.; Pieri, F.A.; Nero, L.A. Spoilage potential of Pseudomonas species isolated from goat milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Park, W.S.; Yun, B.; Shin, M.; Go, G.W.; Kim, J.N.; Kim, Y. Diversity and characteristics of raw milk microbiota from Korean dairy farms using metagenomic and culturomic analysis. Food Control 2021, 127, 108160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Sadiq, F.A.; Burmølle, M.; Wang, N.I.; He, G. Insights into psychrotrophic bacteria in raw milk: A review. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, J.R.; De Oliveira, A.M.; Silva, F.D.G.; Tamanini, R.; De Oliveira, A.L.M.; Beloti, V. The main spoilage-related psychrotrophic bacteria in refrigerated raw milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Liu, S.; Fan, L.; Zheng, X.; Jiao, X. Microbial biodiversity of raw milk collected from Yangzhou and the heterogeneous biofilm-forming ability of Pseudomo-nas. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2023, 76, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, L.; O’Sullivan, O.; Stanton, C.; Beresford, T.P.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Cotter, P.D. The complex microbiota of raw milk. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 664–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchonkouang, R.D.; Lima, A.R.; Quintino, A.C.; Cristofoli, N.L.; Vieira, M.C. UV-C light: A promising preservation technology for vegetable-based nonsolid food products. Foods 2023, 12, 3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarapong, D.; Tantayanon, S.; Gowanit, C.; Inchaisri, C. Development of an innovative apparatus using UV-C for controlling the number of microorganisms in raw milk after milking. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2020, 73, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Zhu, Y.; Koutchma, T.; Gong, J. Inactivation and potential reactivation of pathogenic Escherichia coli O157: H7 in bovine milk exposed to three monochromatic ultraviolet UVC lights. Food Microbiol. 2015, 49, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engin, B.; Karagul Yuceer, Y. Effects of ultraviolet light and ultrasound on microbial quality and aroma-active components of milk. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, J.A.; Rossitto, P.V.; Parko, J.; Koutchma, T.; Cullor, J.S. Efficacy of ultraviolet (UV-C) light in a thin-film turbulent flow for the reduction of milkborne pathogens. Foodborne Path-Ogens Dis. 2015, 12, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Chitnis, N.; Monos, D.; Dinh, A. Next-generation sequencing technologies: An overview. Hum. Immunol. 2021, 82, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzy, M.F.; Murru, N.; Yu, Z.; Cnockaert, M.; Joossens, M.; Proroga, Y.T.R.; Houf, K. De-termination of the microbiological contamination in minced pork by culture dependent and 16S amplicon sequencing analysis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 290, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, H.; Hawley, E.; Kopf, S.; DeScenzo, R.; Sealock, S.; Henick-Kling, T.; Hess, M. Insights into the bacterial community and its temporal succession during the fermentation of wine grapes. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Gilbert, J.; Meyer, F. Metagenomics-a guide from sampling to data analysis. Microb. Inform. Exp. 2012, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poretsky, R.; Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Luo, C.; Tsementzi, D.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Strengths and limitations of 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing in revealing temporal microbial community dynamics. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, Y.; Qian, P.Y. Sensitivity and correlation of hypervariable regions in 16S rRNA genes in phylogenetic analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, D.L.; Cerutti, L.; Gürtler, A.; Griener, T.; Zelazny, A.; Emler, S. Performance and application of 16S rRNA gene cycle sequencing for routine identification of bacteria in the clinical microbiology laboratory. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, Y.; Bhatt, A.S. Sequencing-based analysis of microbiomes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2024, 25, 829–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.A.; François, R.; Yutani, H. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, G.H.; Lee, J.I.; Kang, D.H. Effects of storage temperature on microbiota shifts in raw milk biofilm developed on stainless steel. Food Microbiol. 2023, 110, 104163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.A.; Marquez, G.G.F. Inactivation behaviors of selected bacteria in ultraviolet-C-treated human breast milk. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 41, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| P. aeruginosa | S. aureus | L. lactis | L. curvatus | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (min) | Log10(N) | Time (min) | Log10(N) | Time (min) | Log10(N) | Time (min) | Log10(N) |
| 0 | 6.15 ± 0.03 a | 0 | 6.55 ± 0.03 a | 0 | 6.54 ± 0.12 a | 0 | 6.75 ± 0.29 a |
| 3 | 4.32 ± 0.13 b | 2 | 5.65 ± 0.22 a | 2 | 4.54 ± 0.20 b | 2 | 6.22 ± 0.12 ab |
| 6 | 3.72 ± 0.38 c | 4 | 4.52 ± 0.43 b | 4 | 3.28 ± 0.07 c | 4 | 5.63 ± 0.47 b |
| 9 | 3.86 ± 0.06 bc | 6 | 3.00 ± 0.71 c | 6 | 2.12 ± 0.10 d | 6 | 4.41 ± 0.51 c |
| 12 | 3.90 ± 0.11 bc | 8 | 1.97 ± 0.69 de | 8 | 1.97 ± 0.18 d | 8 | 2.23 ± 0.56 d |
| 15 | 3.92 ± 0.24 bc | 10 | 1.82 ± 0.69 de | 10 | ND | 10 | 2.11 ± 0.42 d |
| 12 | 1.52 ± 0.23 e | 12 | ND | 12 | 1.59 ± 0.20 d | ||
| 14 | 2.60 ± 0.35 cd | 14 | ND | 14 | 2.12 ± 0.52 d | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-H.; Moon, H.; Park, H.-R.; Noh, J.-I.; Kim, S.-S. Metagenomic Analysis of Raw Milk and the Inactivation of Foodborne Pathogens Using Ultraviolet-C. Foods 2025, 14, 1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081414
Lee J-H, Moon H, Park H-R, Noh J-I, Kim S-S. Metagenomic Analysis of Raw Milk and the Inactivation of Foodborne Pathogens Using Ultraviolet-C. Foods. 2025; 14(8):1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081414
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ju-Hui, Hyeonjun Moon, Hye-Rim Park, Ji-In Noh, and Sang-Soon Kim. 2025. "Metagenomic Analysis of Raw Milk and the Inactivation of Foodborne Pathogens Using Ultraviolet-C" Foods 14, no. 8: 1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081414
APA StyleLee, J.-H., Moon, H., Park, H.-R., Noh, J.-I., & Kim, S.-S. (2025). Metagenomic Analysis of Raw Milk and the Inactivation of Foodborne Pathogens Using Ultraviolet-C. Foods, 14(8), 1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081414





