Hydroxytyrosol Ameliorates Colon Inflammation: Mechanistic Insights into Anti-Inflammatory Effects, Inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway, Gut Microbiota Modulation, and Liver Protection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animals and Experimental Treatments
2.3. Quantitative Analysis of Inflammatory Cytokines and Antioxidant Indices in Colon, Liver, and Serum
2.4. Histological Analysis
2.5. Evaluation of the Pyroptosis Pathway
2.6. Measurement of Liver Biomarkers
2.7. Total RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR
2.8. Protein Immunoblotting of Mouse Colon and Liver Tissues
2.9. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.10. Correlation Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
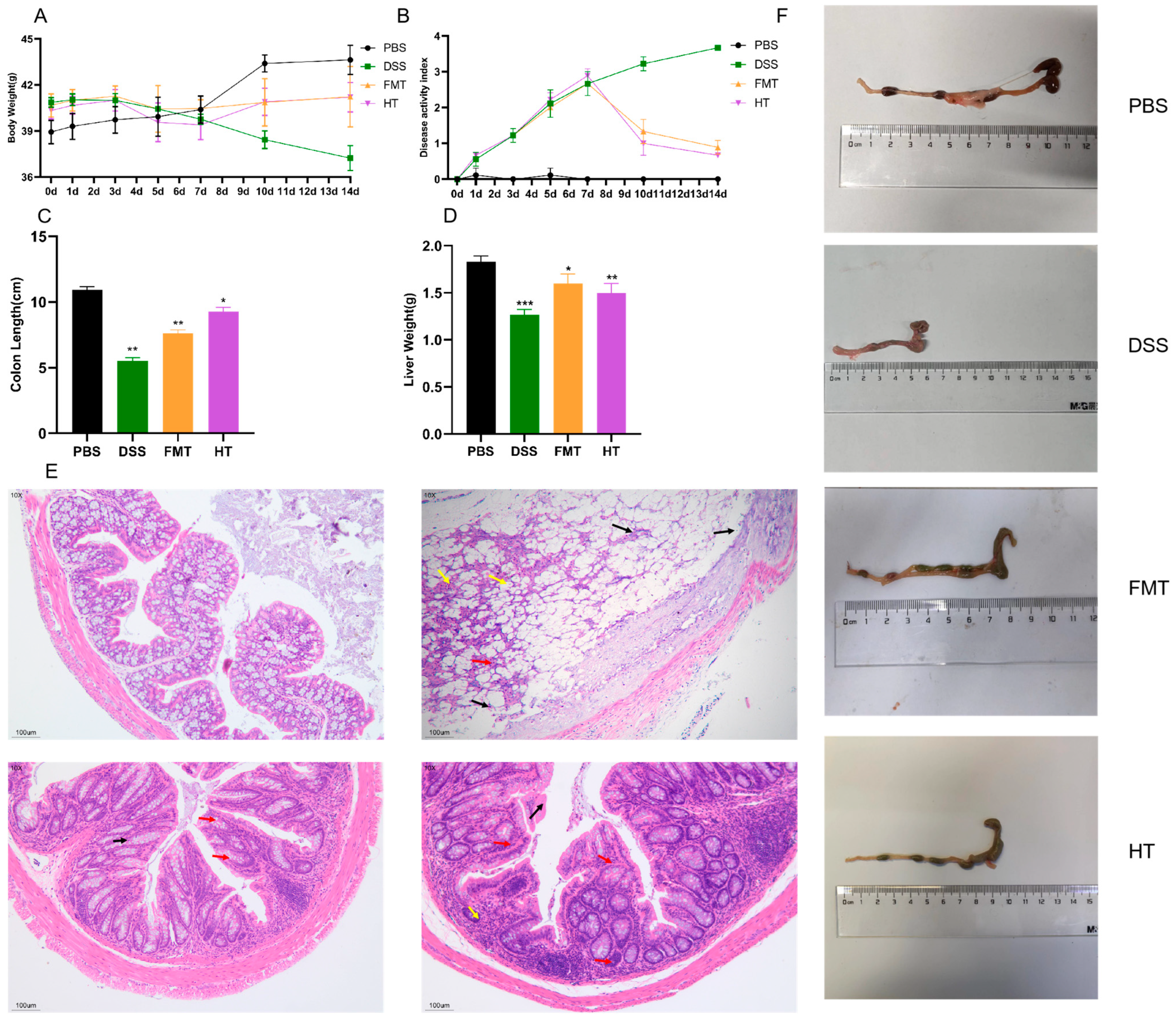
3.1. Effects of HT on Disease Symptoms and Histopathological Features in Mice
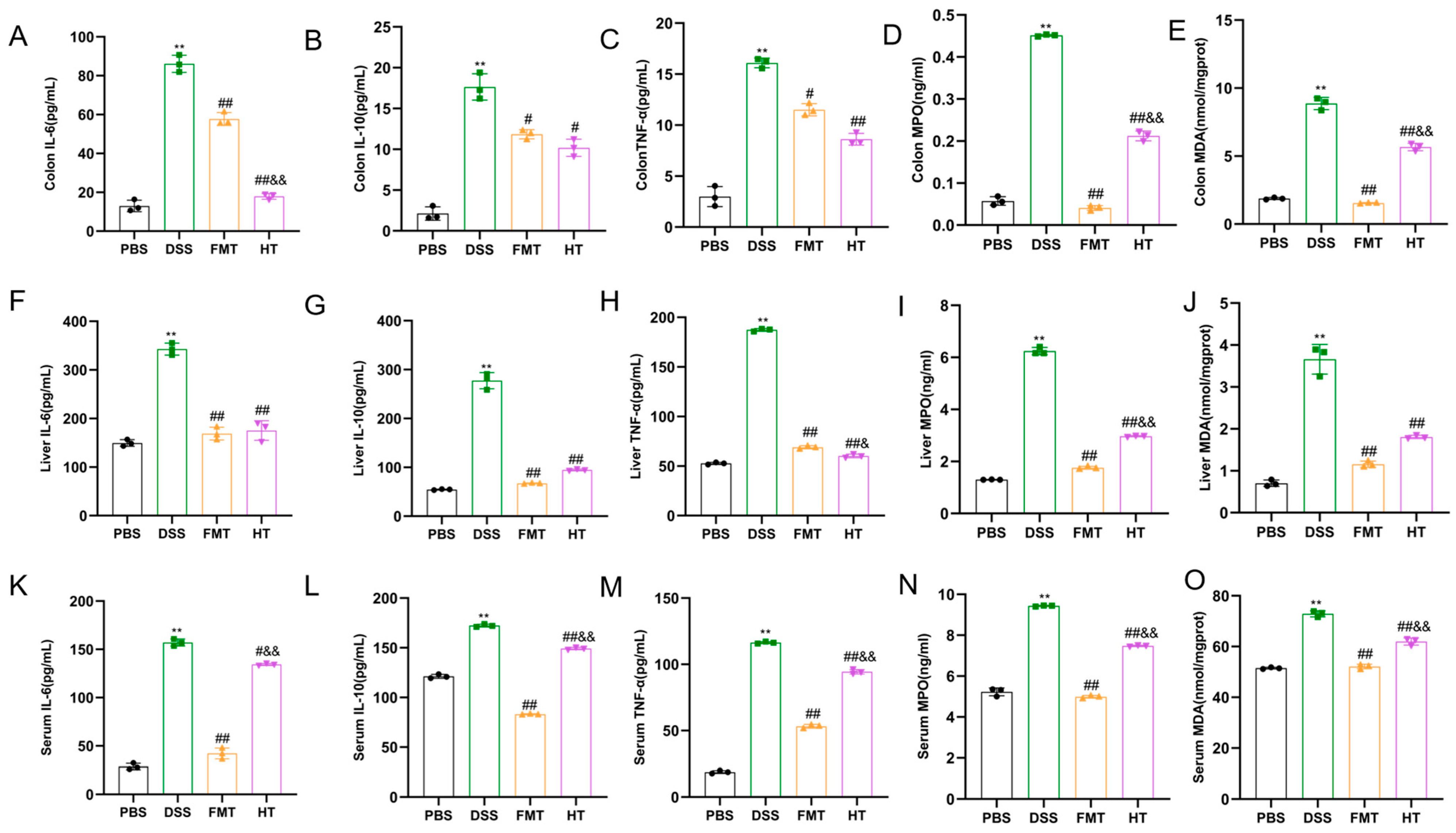
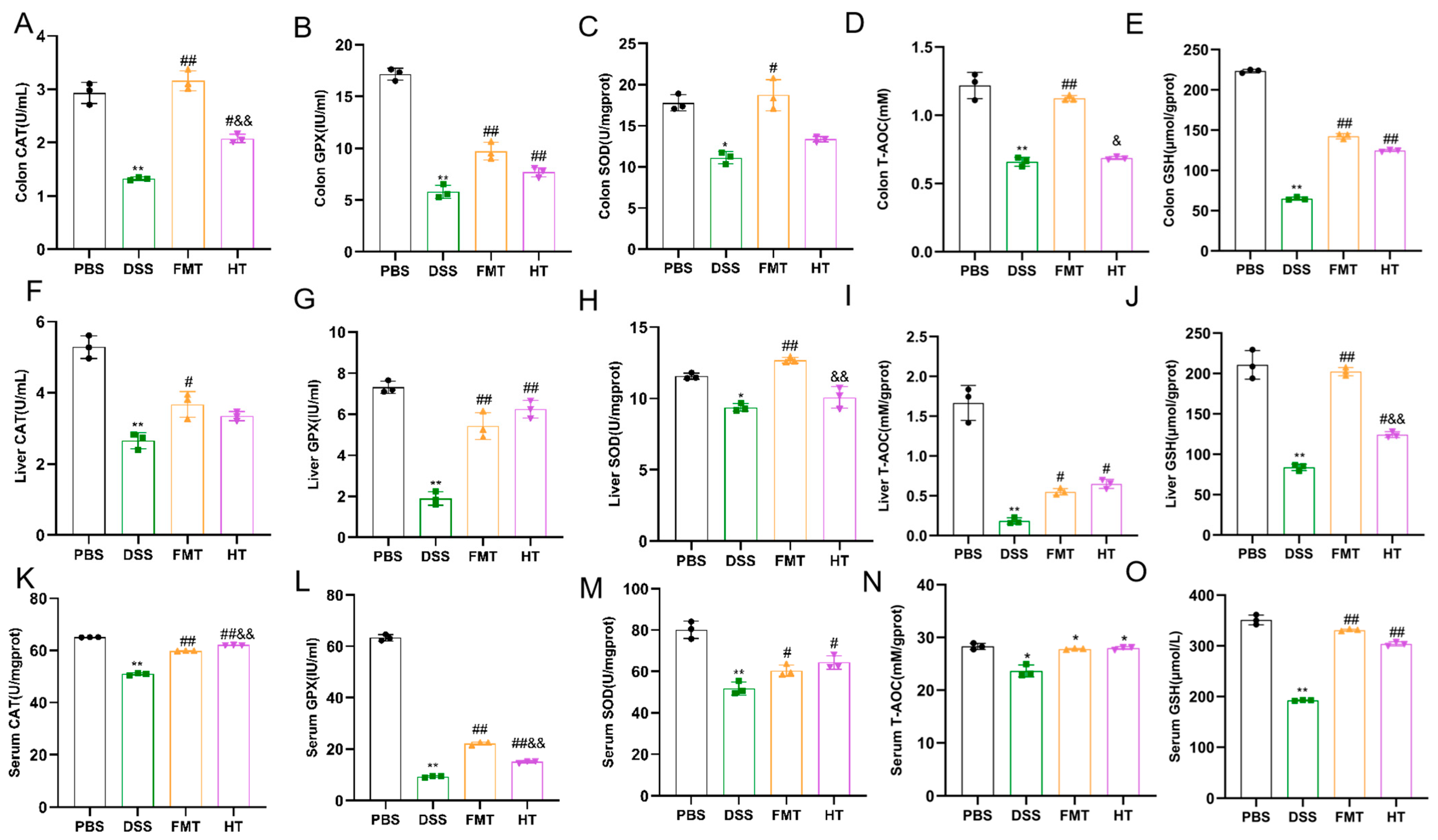
3.2. Effects of HT on Inflammatory Factors and Antioxidant Indices in Mice
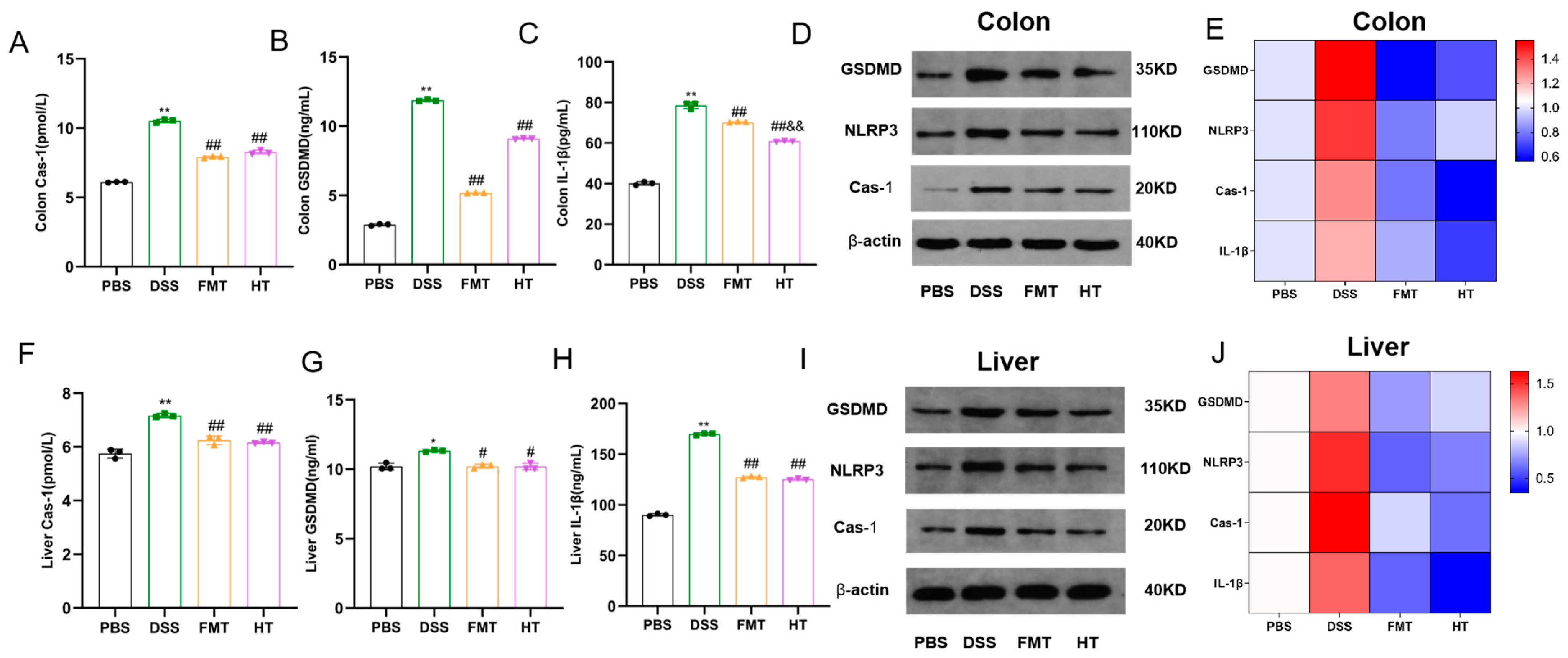
3.3. Effects of HT on Colonic and Hepatic Pyroptosis in Mice
3.4. Effects of HT on Gut Inflammatory Markers, Inflammatory Gene Expression, and Gut Barrier and Hepatic Injury in Mice
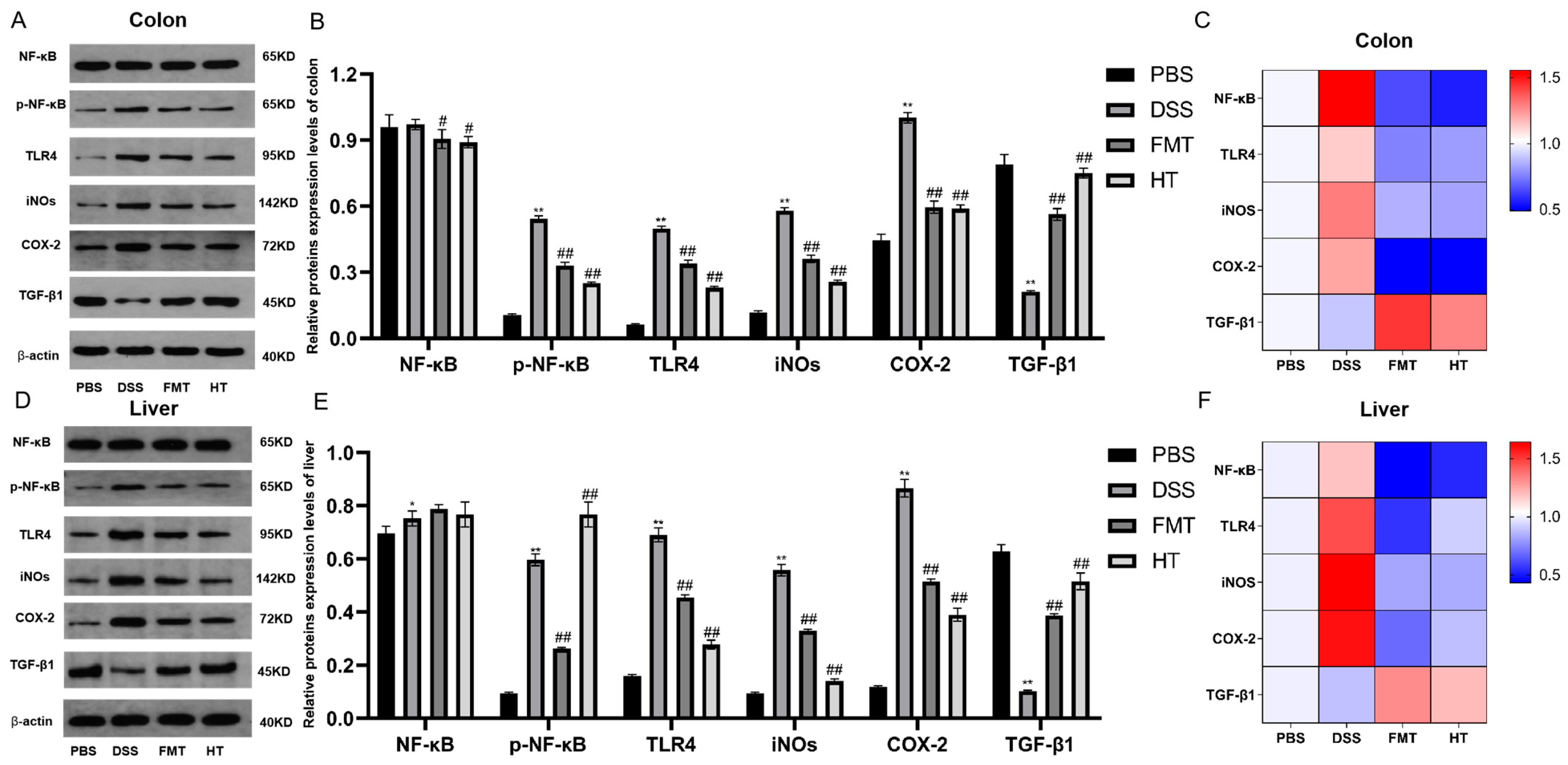
3.5. Effects of HT on the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice, and iNOS, COX-2, and TGF-β1 Expression Levels
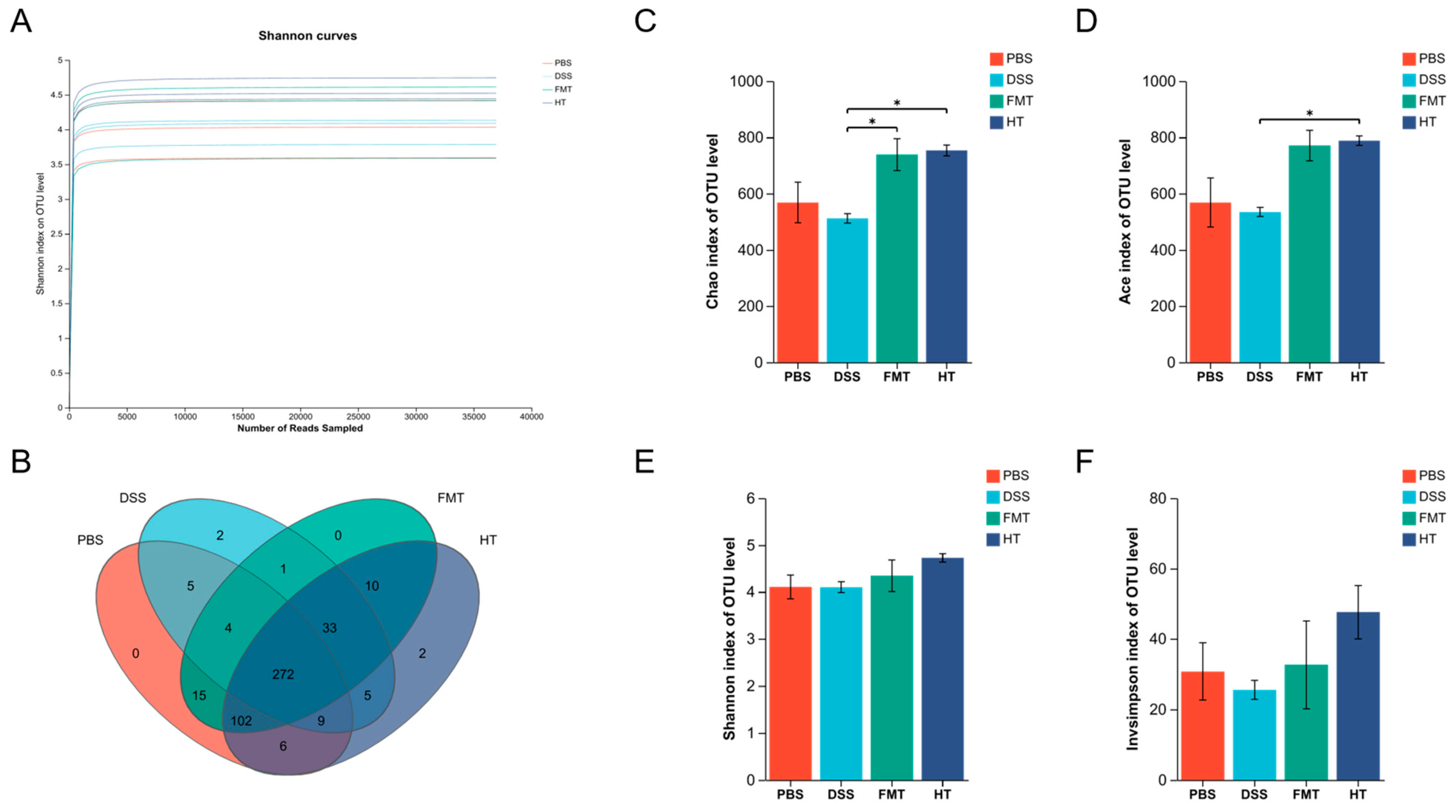
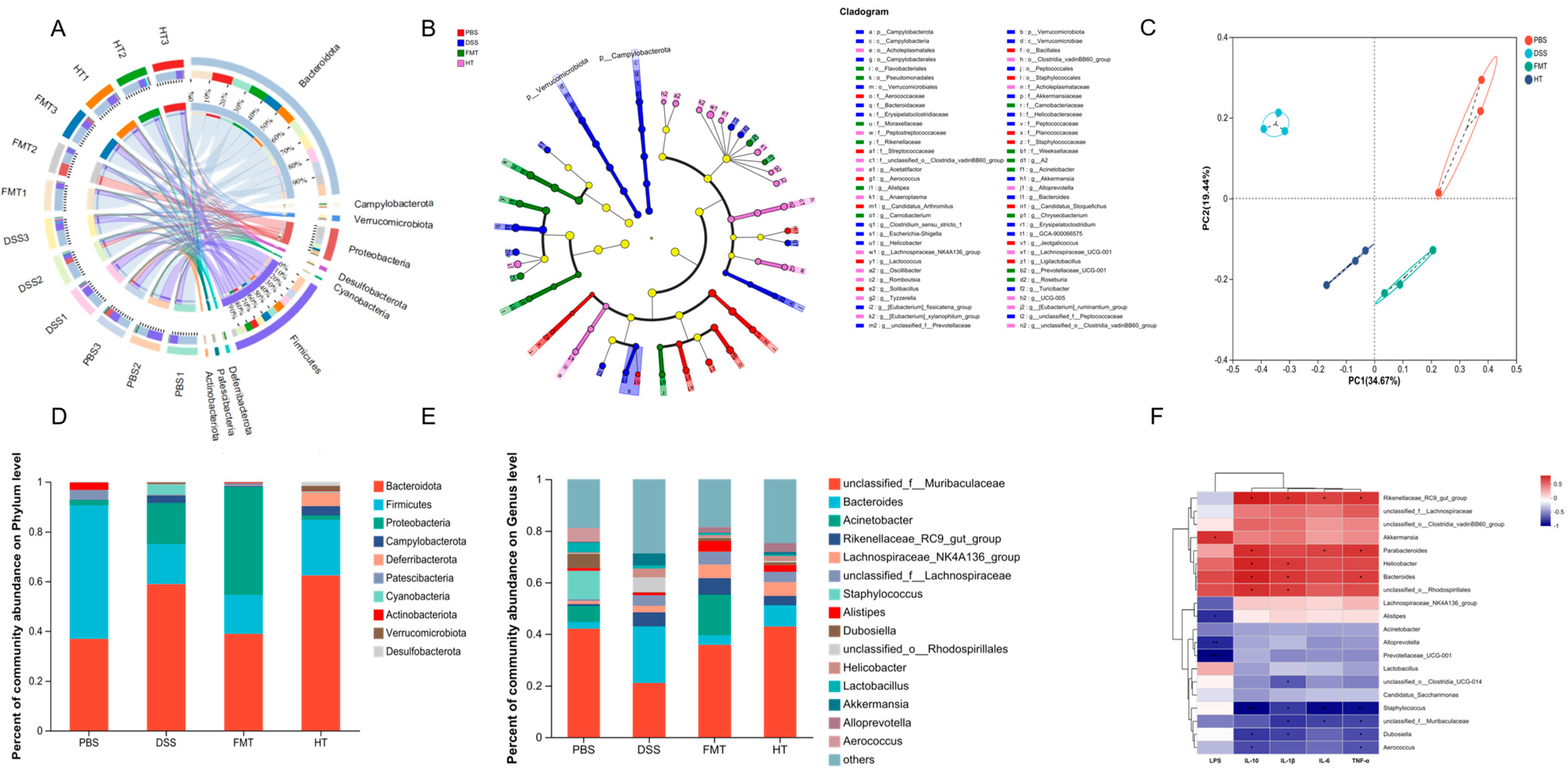
3.6. Effects of FCD on the Gut Microbiota of Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Nakano, H.; Ruiz, H.H.; Becker, S.; Bai, Y.; Cortes-Burgos, L.A.; Eckersdorff, M.M.; Macdonald, L.E.; Croll, S.D. Pharmacological inhibition of NPY receptors illustrates dissociable features of experimental colitis in the mouse DSS model: Implications for preclinical evaluation of efficacy in an inflammatory bowel disease model. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittayanon, R.; Lau, J.T.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Tse, F.; Yuan, Y.; Surette, M.; Moayyedi, P. Differences in Gut Microbiota in Patients With vs Without Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 930–946.e931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, C.N. Treatment of IBD: Where We Are and Where We Are Going. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, G.G.; Windsor, J.W. The four epidemiological stages in the global evolution of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhao, P.; Li, X.; Guo, L.; Gao, W. The potential roles of natural plant polysaccharides in inflammatory bowel disease: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, L.; Maugeri, A.; Cirmi, S.; Lombardo, G.E.; Russo, C.; Gangemi, S.; Calapai, G.; Navarra, M. Citrusfruits and their flavonoids in inflammatory bowel disease: An overview. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 34, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.P.d.F.; Geraldi, M.V.; do Nascimento, R.d.P.; Moya, A.M.T.M.; Vezza, T.; Diez-Echave, P.; Gálvez, J.J.; Cazarin, C.B.B.; Maróstica Júnior, M.R. Polyphenols from food by-products: An alternative or complementary therapy to IBD conventional treatments. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, J.; Gong, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Qi, C.; Chen, G.; Wang, C.; Chen, W. Biosynthesis and Biotechnological Synthesis of Hydroxytyrosol. Foods 2024, 13, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Bolanos, J.; Rodriguez, G.; Rodriguez, R.; Heredia, A.; Guillen, R.; Jimenez, A. Production in large quantities of highly purified hydroxytyrosol from liquid-solid waste of two-phase olive oil processing or “Alperujo”. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 6804–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olajide, T.M.; Liu, T.; Liu, H.; Weng, X. Antioxidant properties of two novel lipophilic derivatives of hydroxytyrosol. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigagli, E.; Cinci, L.; Paccosi, S.; Parenti, A.; D’Ambrosio, M.; Luceri, C. Nutritionally relevant concentrations of resveratrol and hydroxytyrosol mitigate oxidative burst of human granulocytes and monocytes and the production of pro-inflammatory mediators in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 43, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karković Marković, A.; Torić, J.; Barbarić, M.; Jakobušić Brala, C. Hydroxytyrosol, Tyrosol and Derivatives and Their Potential Effects on Human Health. Molecules 2019, 24, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayram, B.; Ozcelik, B.; Grimm, S.; Roeder, T.; Schrader, C.; Ernst, I.M.A.; Wagner, A.E.; Grune, T.; Frank, J.; Rimbach, G. A Diet Rich in Olive Oil Phenolics Reduces Oxidative Stress in the Heart of SAMP8 Mice by Induction of Nrf2-Dependent Gene Expression. Rejuvenation Res. 2012, 15, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulotta, S.; Celano, M.; Lepore, S.M.; Montalcini, T.; Pujia, A.; Russo, D. Beneficial effects of the olive oil phenolic components oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol: Focus on protection against cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Wu, G.D.; Albenberg, L.; Tomov, V.T. Gut microbiota and IBD: Causation or correlation? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Xiao, H. Whole Food–Based Approaches to Modulating Gut Microbiota and Associated Diseases. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 11, 119–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Xiong, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Yan, R. Gut microbiome, metabolome, host immunity associated with inflammatory bowel disease and intervention of fecal microbiota transplantation. J. Autoimmun. 2023, 141, 103062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natividad, J.M.M.; Verdu, E.F. Modulation of intestinal barrier by intestinal microbiota: Pathological and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, Ú.; López de las Hazas, M.-C.; Piñol, C.; Rubió, L.; Motilva, M.-J.; Fernandez-Castillejo, S.; Solà, R. Hydroxytyrosol and its main plasma circulating metabolites attenuate the initial steps of atherosclerosis through inhibition of the MAPK pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula do Nascimento, R.; Lima, A.V.; Oyama, L.M.; Paiotti, A.P.R.; Cardili, L.; Martinez, C.A.R.; Pereira, J.A.; Silva, M.F.; Garofolo, I.C.; Silveira, V.L.F.; et al. Extra virgin olive oil and flaxseed oil have no preventive effects on DSS-induced acute ulcerative colitis. Nutrition 2020, 74, 110731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhraei, N.; Abdolghaffari, A.H.; Delfan, B.; Abbasi, A.; Rahimi, N.; Khansari, A.; Rahimian, R.; Dehpour, A.R. Protective Effect of Hydroalcoholic Olive Leaf Extract on Experimental Model of Colitis in Rat: Involvement of Nitrergic and Opioidergic Systems. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuccelli, R.; Fabiani, R.; Rosignoli, P. Hydroxytyrosol Exerts Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidant Activities in a Mouse Model of Systemic Inflammation. Molecules 2018, 23, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morvaridi, M.; Jafarirad, S.; Seyedian, S.S.; Alavinejad, P.; Cheraghian, B. The effects of extra virgin olive oil and canola oil on inflammatory markers and gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with ulcerative colitis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Fidalgo, S.; Sánchez de Ibargüen, L.; Cárdeno, A.; Alarcón de la Lastra, C. Influence of extra virgin olive oil diet enriched with hydroxytyrosol in a chronic DSS colitis model. Eur. J. Nutr. 2011, 51, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoditti, E.; Nestola, A.; Massaro, M.; Calabriso, N.; Storelli, C.; De Caterina, R.; Carluccio, M.A. Hydroxytyrosol suppresses MMP-9 and COX-2 activity and expression in activated human monocytes via PKCα and PKCβ1 inhibition. Atherosclerosis 2014, 232, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilman, J.; Anyangwe, N.; Tran, N.; Edwards, J.; Beilstein, P.; López, J. Toxicological evaluation of an olive extract, H35: Subchronic toxicity in the rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 84, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, J.R.; Lee, H.-I.; Choi, R.-Y.; Sim, M.-O.; Seo, K.-I.; Lee, M.-K. Anti-steatotic and anti-inflammatory roles of syringic acid in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J. Characterization, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammation Capacities of Fermented Flammulina velutipes Polyphenols. Molecules 2021, 26, 6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of rRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, E.; Nguyen, D.; Low, D. Animal models of ulcerative colitis and their application in drug research. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 1341–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Gong, P.; Shi, R.; Chen, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Z. Syringic Acid Alleviates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice by Modulating Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 8458–8470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurath, M.F. Current and emerging therapeutic targets for IBD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Li, Y.R. Oxidative stress and redox signaling mechanisms of inflammatory bowel disease: Updated experimental and clinical evidence. Exp. Biol. Med. 2012, 237, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. IL-6 pathway in the liver: From physiopathology to therapy. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, C. Therapeutic Potential of Fucoidan in Alleviating Histamine-Induced Liver Injury: Insights from Mice Studies. Foods 2024, 13, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Several lines of antioxidant defense against oxidative stress: Antioxidant enzymes, nanomaterials with multiple enzyme-mimicking activities, and low-molecular-weight antioxidants. Arch. Toxicol. 2024, 98, 1323–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keitelman, I.A.; Shiromizu, C.M.; Zgajnar, N.R.; Danielián, S.; Jancic, C.C.; Martí, M.A.; Fuentes, F.; Yancoski, J.; Vera Aguilar, D.; Rosso, D.A.; et al. The interplay between serine proteases and caspase-1 regulates the autophagy-mediated secretion of Interleukin-1 beta in human neutrophils. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 832306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Hsu, J.-M.; Hung, M.-C. Molecular mechanisms and functions of pyroptosis in inflammation and antitumor immunity. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 4579–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domitrović, R.; Rashed, K.; Cvijanović, O.; Vladimir-Knežević, S.; Škoda, M.; Višnić, A. Myricitrin exhibits antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic activity in carbon tetrachloride-intoxicated mice. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2015, 230, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypczak-Wiercioch, A.; Sałat, K. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Model of Neuroinflammation: Mechanisms of Action, Research Application and Future Directions for Its Use. Molecules 2022, 27, 5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Bechara, R.; Zhao, J.; McGeachy, M.J.; Gaffen, S.L. IL-17 receptor–based signaling and implications for disease. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wen, K.; Wu, B.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y. Huangkui Lianchang Decoction Ameliorates DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice by Inhibiting the NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 1040847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, K.; Zhang, G.; Sun, M.; He, S.; Kong, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, F.; Zha, X.; Wang, Y. Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis through intestinal barrier improvement, oxidative stress reduction, and inflammatory cytokines and gut microbiota modulation. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 7817–7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassarella, M.; Blaak, E.E.; Penders, J.; Nauta, A.; Smidt, H.; Zoetendal, E.G. Gut microbiome stability and resilience: Elucidating the response to perturbations in order to modulate gut health. Gut 2021, 70, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-M.; Kim, D.-H. Bifidobacterium adolescentis IM38 ameliorates high-fat diet-induced colitis in mice by inhibiting NF-κB activation and lipopolysaccharide production by gut microbiota. Nutr. Res. 2017, 41, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-Q.; Wei, S.-Y.; Cheng, N.; Zhong, Y.-B.; Yu, F.-H.; Li, M.-D.; Liu, D.-Y.; Li, S.-S.; Zhao, H.-M. Chimonanthus nitens Oliv. Leaf Granule Ameliorates DSS-Induced Acute Colitis Through Treg Cell Improvement, Oxidative Stress Reduction, and Gut Microflora Modulation. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 907813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; He, Y.-J.; Li, Y.; Gong, M.-X. Actions of four organic acids in radix isatidis on endotoxin-neutralization investigated by kinetic turbidimetric assay. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2012, 32, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Liu, H.; Yu, H.; Chen, M.; Yang, T.; Zeng, X.; Qiao, S. Core Altered Microorganisms in Colitis Mouse Model: A Comprehensive Time-Point and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Analysis. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (3′-5′) |
|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | ATGAGCACAGAAAGCATGA | AGTAGACAGAAGAGCGTGGT |
| IL-1β | TCCAGGATGAGGACATGAGCAC | GAACGTCACACACCAGCAGGTTA |
| COX-2 | CCCCATTAGCAGCCAGTT | CATTCCCCACGGTTTTGA |
| iNOS | GTTCTCAGCCCAACAATACAA | GTGGACGGGTCGATGTCACGA |
| IL-10 | ATAACTGCACCCACTTCCCA | GGGCATCACTTCTACCAGGT |
| TGF-β1 | CCTGCAAGACCATCGACATG | TGTTGTACAAAGCGAGCACC |
| NF-kB | GTGGTGCCTCACTGCTAACT | GGATGCACTTCAGCTTCTGT |
| IL-17A | GGAAAGGACGGACTGGTGTA | TGCCACTGGTCTGTAATCCA |
| TRAF6 | GTATCCGCATTGAGAAGC | GCAGTGAACCATCCGTGT |
| Occludin | GAGGAGAGTGAAGAGTACATGGGCTG | GTCTGTCATAATCTCCCACCATCCT |
| ZO-1 | TCATCCCAAATAAGAACAGAGC | GAAGAACAACCCTTTCATAAGC |
| Claudin-I | TCCTTGCTGAATCTGAACA | AGCCATCCACATCTTCTG |
| Caspase-1 | TGCCCAGAGCACAAGACTTC | TCCTTGTTTCTCTCCACGGC |
| GSDMD | ATGGCATGGCTTACACCACC | ATGGCATGGCTTACACCACC |
| NLRP3 | TCTGCACCCGGACTGTAAAC | CACCCAACTGTAGGCTCTGC |
| β-actin | AAGTCCCTCACCCTCCCAAAAG | AGCAATGCTGTCACCTTCCC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, W. Hydroxytyrosol Ameliorates Colon Inflammation: Mechanistic Insights into Anti-Inflammatory Effects, Inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway, Gut Microbiota Modulation, and Liver Protection. Foods 2025, 14, 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071270
Tang J, Zhang M, Wang J, Zhang H, Wang Z, Lei Z, Wang C, Chen W. Hydroxytyrosol Ameliorates Colon Inflammation: Mechanistic Insights into Anti-Inflammatory Effects, Inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway, Gut Microbiota Modulation, and Liver Protection. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071270
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Jiali, Mengyao Zhang, Jiaying Wang, Haijing Zhang, Zhong Wang, Ziteng Lei, Chengtao Wang, and Wei Chen. 2025. "Hydroxytyrosol Ameliorates Colon Inflammation: Mechanistic Insights into Anti-Inflammatory Effects, Inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway, Gut Microbiota Modulation, and Liver Protection" Foods 14, no. 7: 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071270
APA StyleTang, J., Zhang, M., Wang, J., Zhang, H., Wang, Z., Lei, Z., Wang, C., & Chen, W. (2025). Hydroxytyrosol Ameliorates Colon Inflammation: Mechanistic Insights into Anti-Inflammatory Effects, Inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway, Gut Microbiota Modulation, and Liver Protection. Foods, 14(7), 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071270








