Purification and Characterization of Immunomodulatory Peptides from Hydrolysates of Thunnus albacares Dark Muscle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Thunnus Albacares Protein Hydrolysate (TAPH)
2.3. Peptide Fractionation by Gel Filtration Chromatography
2.4. Reversed-Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
2.5. Peptide Sequence Identification by Using Liquid Chromatograph/Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC–MS/MS)
2.6. Molecular Docking of Peptides with TLR2 and TLR4/MD2
2.7. Peptide Synthesis
2.8. RAW 264.7 Cellular Immunomodulatory Activity Assays
2.8.1. Cell Culture
2.8.2. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.8.3. Phagocytosis Assay
2.8.4. Griess Assay
2.8.5. Cytokine Assays
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of TAPHs
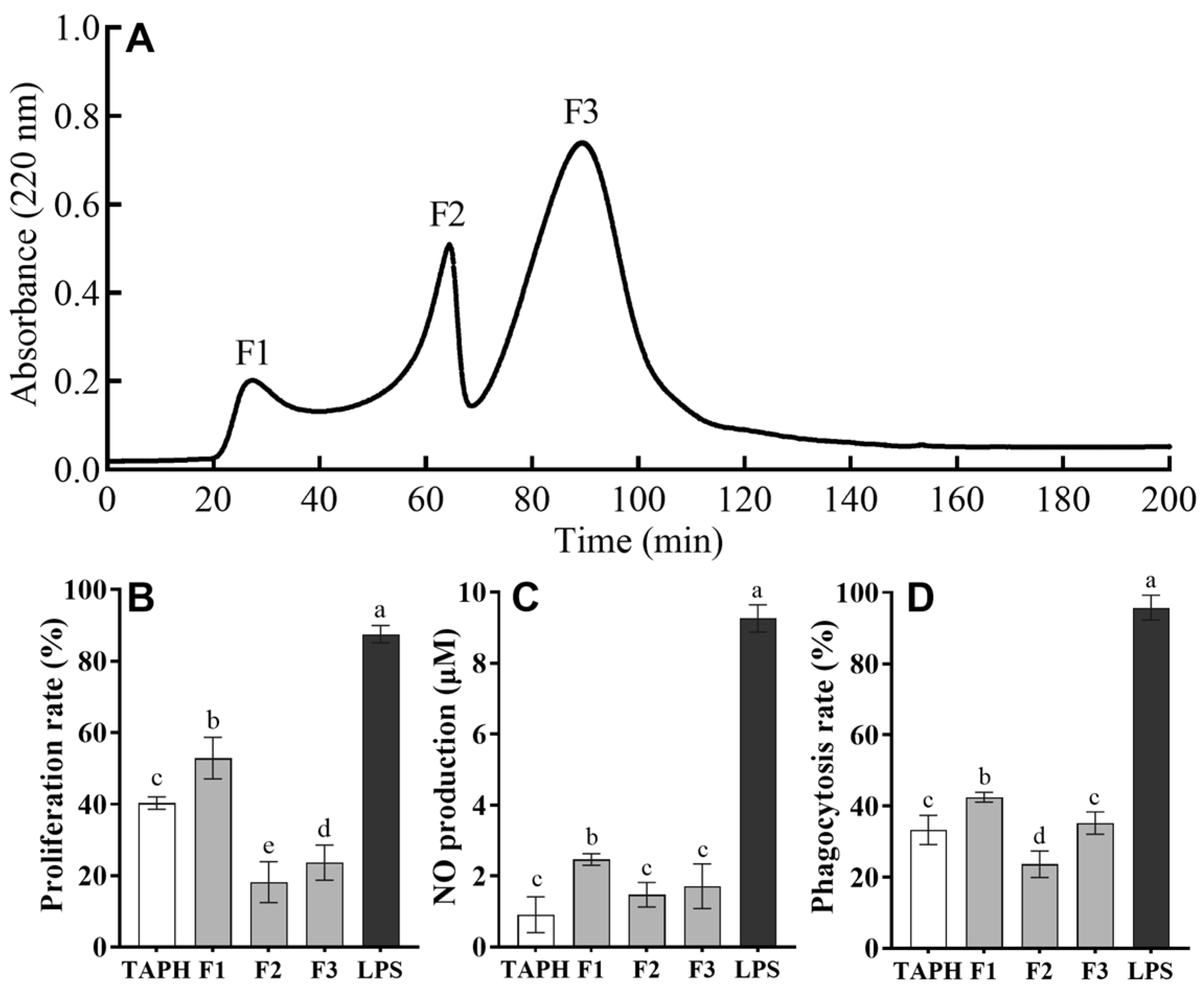
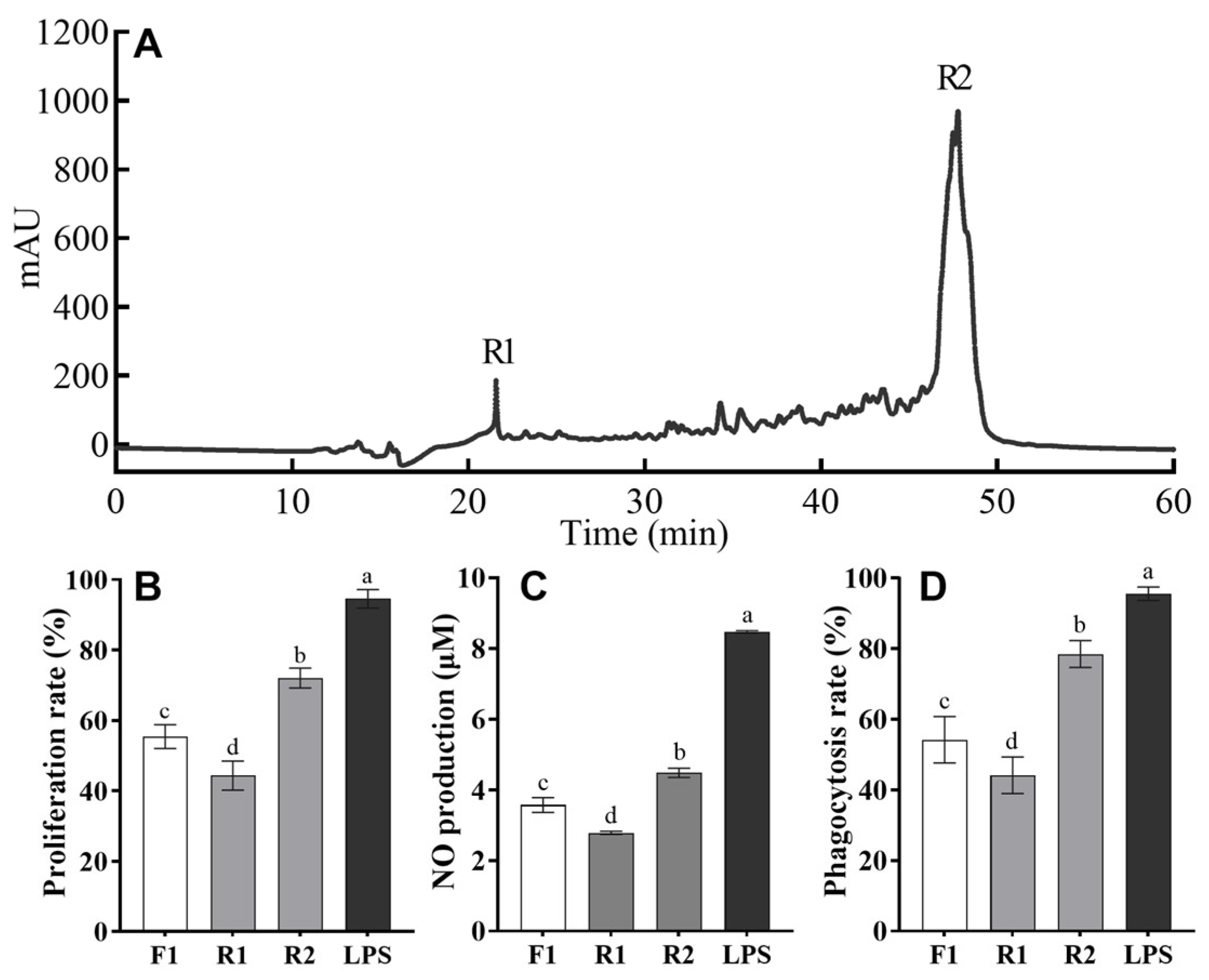
3.2. Purification of Immunomodulatory Peptides from Trypsin Hydrolysates of T. albacares Dark Muscle
3.3. Identification of Peptides
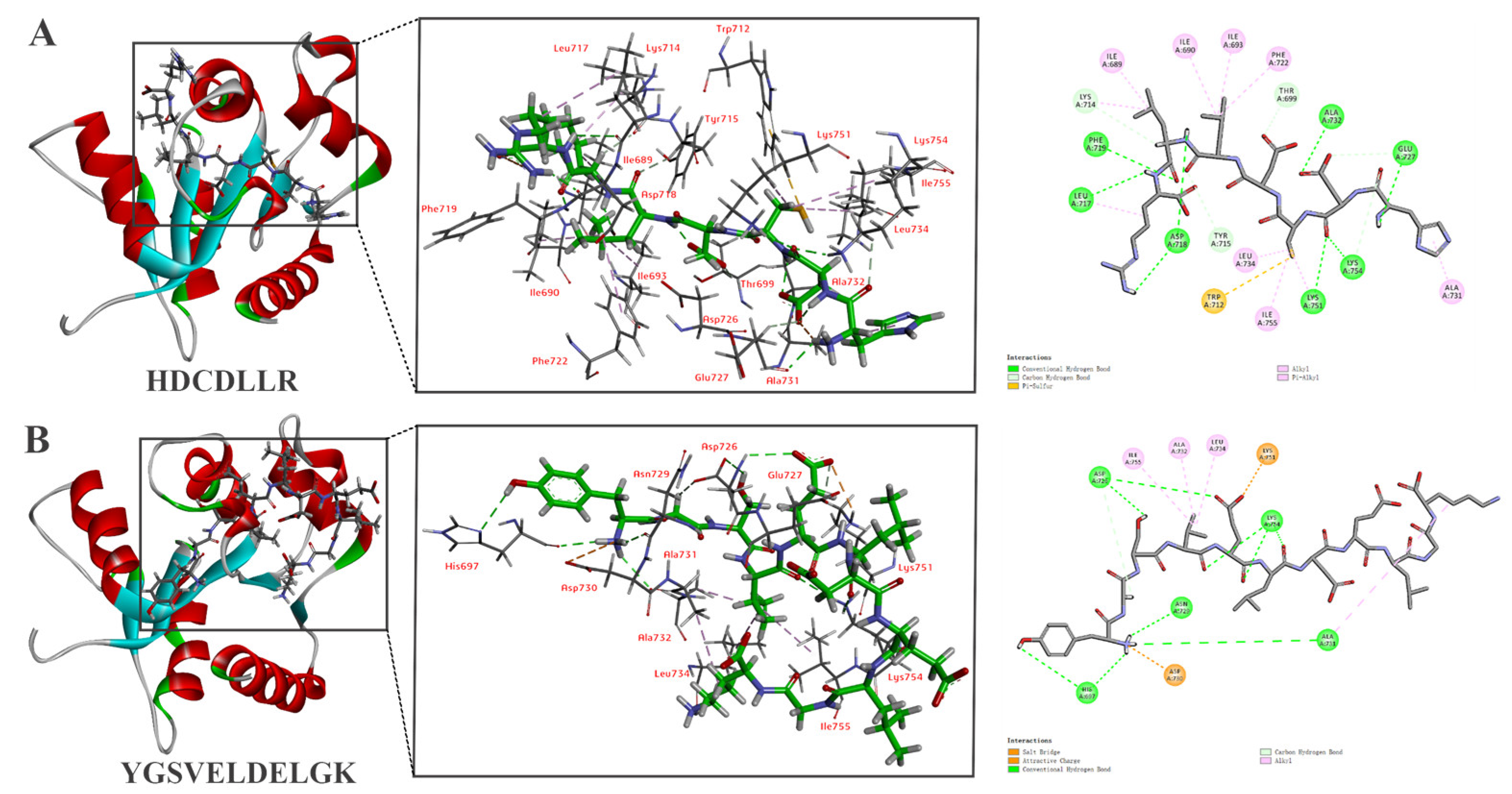
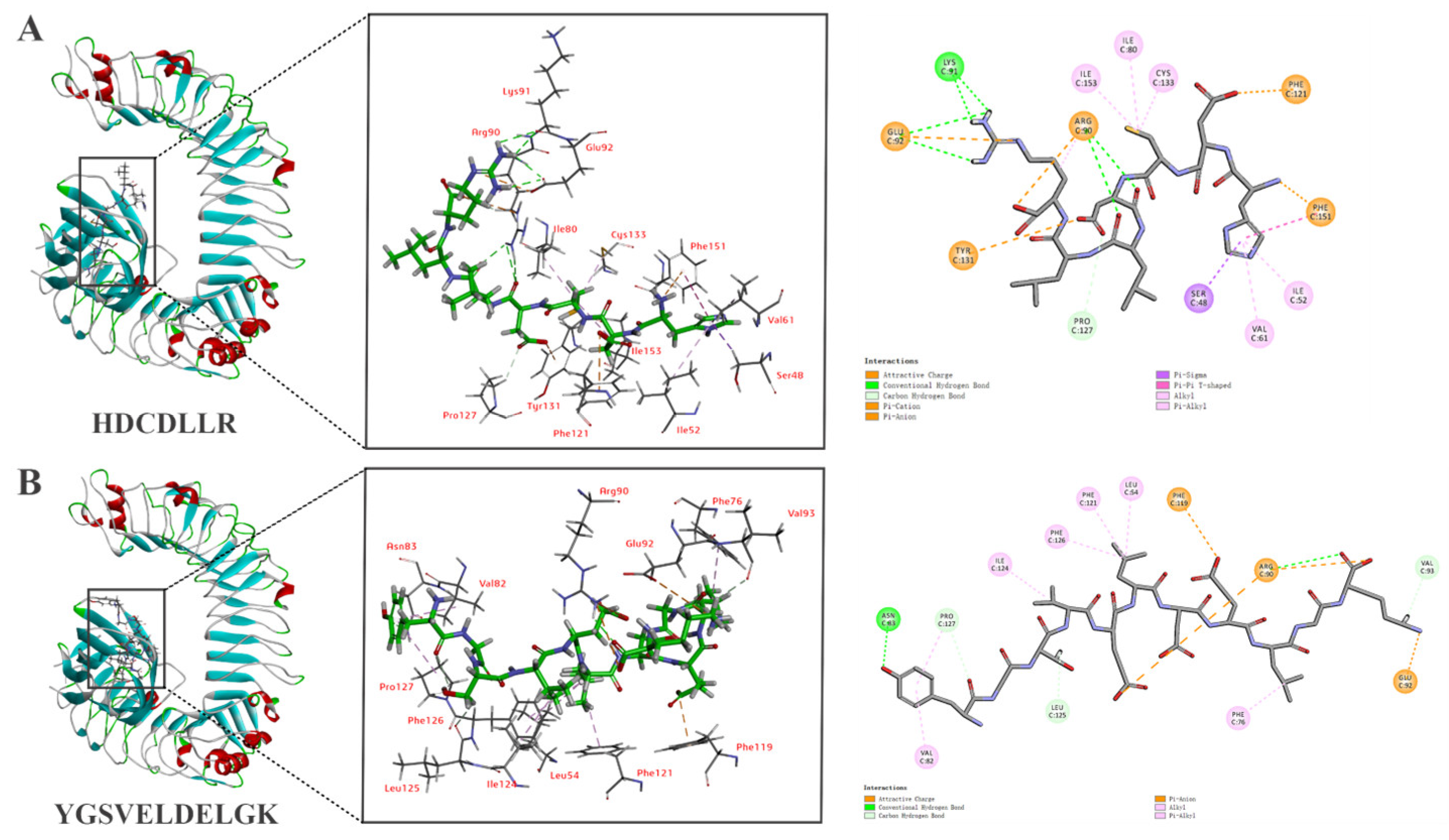
3.4. Screening of Peptides via Molecular Docking
3.5. Immunomodulatory Activity of Synthetic Peptides
3.6. In Silico Molecular Docking of HDCDLLR and YGSVELDELGK
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tecklenborg, J.; Clayton, D.; Siebert, S.; Coley, S.M. The Role of the Immune System in Kidney Disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 192, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daliri, E.B.-M.; Oh, D.H.; Lee, B.H. Bioactive Peptides. Foods 2017, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihlanto-Leppälä, A. Bioactive Peptides Derived from Bovine Whey Proteins: Opioid and Ace-Inhibitory Peptides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-López, L.; Hernández-Mendoza, A.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; Mata-Haro, V.; González-Córdova, A.F. Food-Derived Immunomodulatory Peptides. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 3631–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Z.F.; Kumar, S.; Bhat, H.F. Bioactive Peptides of Animal Origin: A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 5377–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestri, E.; Marmiroli, M.; Marmiroli, N. Bioactive Peptides in Plant-Derived Foodstuffs. J. Proteom. 2016, 147, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.; Malik, M.I.; Umar, T.; Ashraf, S.; Ahmad, A. A Comprehensive Review About Bioactive Peptides: Sources to Future Perspective. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2022, 28, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Liang, Y.; Lin, Q. Bioactive Peptides from Foods: Production, Function, and Application. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 7108–7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyei, D.; Danquah, M.K. Rethinking Food-Derived Bioactive Peptides for Antimicrobial and Immunomodulatory Activities. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 23, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurewicz, M.M.; Stern, L.J. Class II MHC Antigen Processing in Immune Tolerance and Inflammation. Immunogenetics 2019, 71, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, M.; Min, Q.; Gao, Y.; Sun, W. The Dual Regulatory Function of Lienal Peptide on Immune System. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 55, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, M. Bioactive Peptides Derived from Natural Proteins with Respect to Diversity of Their Receptors and Physiological Effects. Peptides 2015, 72, 208–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yathisha, U.G.; Bhat, I.; Karunasagar, I.; Mamatha, B.S. Antihypertensive Activity of Fish Protein Hydrolysates and Its Peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2363–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, S.; Saoudi, M.; Ben Amar, R. Valorisation of Tuna Processing Waste Biomass: Isolation, Purification and Characterisation of Four Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Tuna by-Product Hydrolysate. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 17383–17392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, C.; Hardy, R.W.; Contreras-Rojas, D.; López-Molina, B.; González-Rodríguez, B.; Domínguez-Jimenez, P. Evaluation of Tuna By-Product Meal as a Protein Source in Feeds for Juvenile Spotted Rose Snapper Utjanus Guttatus. Aquac. Nutr. 2014, 20, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, A.; Rustad, T.; Cusimano, G.M. Tuna Sidestream Valorization: A Circular Blue Bioeconomy Approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 62230–62248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, V.C.; Islam, M.R.; Sadia, S.; Yeasmin, M.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Chun, B.-S. Trash to Treasure: An Up-to-Date Understanding of the Valorization of Seafood By-Products, Targeting the Major Bioactive Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrato, A.; Capriotti, A.L.; Capuano, F.; Cavaliere, C.; Montone, A.M.I.; Montone, C.M.; Piovesana, S.; Zenezini Chiozzi, R.; Laganà, A. Identification and Antimicrobial Activity of Medium-Sized and Short Peptides from Yellowfin Tuna (Thunnus albacares) Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion. Foods 2020, 9, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurilmala, M.; Pertiwi, R.M.; Nurhayati, T.; Fauzi, S.; Batubara, I.; Ochiai, Y. Characterization of Collagen and Its Hydrolysate from Yellowfin Tuna Thunnus albacares Skin and Their Potencies as Antioxidant and Antiglycation Agents. Fish. Sci. 2019, 85, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.; Bernardi, D.; Drummond, F.; Dieterich, F.; Boscolo, W.; Leivas, C.; Kiatkoski, E.; Waszczynskyj, N. Potential Use of Tuna (Thunnus albacares) by-Product: Production of Antioxidant Peptides and Recovery of Unsaturated Fatty Acids from Tuna Head. Int. J. Food Eng. 2017, 13, 20150365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Du, T.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Shen, C. Optimization of Ultrasound-Assisted Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Immune Peptides from Thunnus albacores. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2024, 45, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.Q.; Cao, W.H.; Pan, G.K.; Yang, L.; Zhang, C.H. Enzymatic Hydrolysis Optimization of Paphia Undulata and Lymphocyte Proliferation Activity of the Isolated Peptide Fractions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 1544–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiyama, M.; Miyazono, Y.; Shiga, M.; Sasamoto, K. Water-Soluble Tetrazolium Salt Compounds. U.S. Patent No 6,063,587, 16 May 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Repetto, G.; del Peso, A.; Zurita, J.L. Neutral Red Uptake Assay for the Estimation of Cell Viability/Cytotoxicity. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griess, P. Bemerkungen Zu Der Abhandlung Der HH. Weselsky Und Benedikt “Ueber Einige Azoverbindungen”. Berichte Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1879, 12, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mant, C.T.; Chen, Y.; Yan, Z.; Popa, T.V.; Kovacs, J.M.; Mills, J.B.; Tripet, B.P.; Hodges, R.S. HPLC Analysis and Purification of Peptides. In Peptide Characterization and Application Protocols; Fields, G.B., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 3–55. ISBN 978-1-59745-430-8. [Google Scholar]
- Chalamaiah, M.; Yu, W.; Wu, J. Immunomodulatory and Anticancer Protein Hydrolysates (Peptides) from Food Proteins: A Review. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ye, S.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, J.; Jin, H.; Huang, F.; Yang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ding, G.; et al. Purification and Characterization of a Novel Pentadecapeptide from Protein Hydrolysates of Cyclina sinensis and Its Immunomodulatory Effects on RAW264.7 Cells. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkiewicz, P.; Iwaniak, A.; Darewicz, M. BIOPEP-UWM Database of Bioactive Peptides: Current Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lear, S.; Cobb, S.L. Pep-Calc.Com: A Set of Web Utilities for the Calculation of Peptide and Peptoid Properties and Automatic Mass Spectral Peak Assignment. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2016, 30, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, C.; Zhang, C.; Cao, W.; Qin, X.; Gao, J.; Zheng, H. The Purification and Identification of Immunoregulatory Peptides from Oyster (Crassostrea hongkongensis) Enzymatic Hydrolysate. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 32854–32863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, A.; Gauthier, S.F.; Fliss, I. Immunomodulating Effects of Whey Proteins and Their Enzymatic Digests. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, J.; Su, A.; Xu, H.; Li, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Mariga, A.M.; Yang, W. Isolation, Purification and Identification of Immunologically Active Peptides from Hericium erinaceus. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 151, 112111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhasmana, A.; Raza, S.; Jahan, R.; Lohani, M.; Arif, J.M. Chapter 19—High-Throughput Virtual Screening (HTVS) of Natural Compounds and Exploration of Their Biomolecular Mechanisms: An In Silico Approach. In New Look to Phytomedicine; Ahmad Khan, M.S., Ahmad, I., Chattopadhyay, D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 523–548. ISBN 978-0-12-814619-4. [Google Scholar]
- He, P.; Wang, Q.; Zhan, Q.; Pan, L.; Xin, X.; Wu, H.; Zhang, M. Purification and Characterization of Immunomodulatory Peptides from Enzymatic Hydrolysates of Duck Egg Ovalbumin. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, M.; Ren, Y.; Cai, X.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Min, T.; Wu, H. Characterization and Immunomodulatory Activity of a Novel Peptide, ECFSTA, from Wheat Germ Globulin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5561–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. TLR Signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Karmakar, S.; Babu, S.P.S. TLR2 and TLR4 Mediated Host Immune Responses in Major Infectious Diseases: A Review. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 20, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenken, J.A.; Poschenrieder, A.J. Bioanalytical Chemistry of Cytokines—A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 853, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, T. IL-6: From Its Discovery to Clinical Applications. Int. Immunol. 2010, 22, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patronov, A.; Salamanova, E.; Dimitrov, I.; Flower, D.R.; Doytchinova, I. Histidine Hydrogen Bonding in MHC at pH 5 and pH 7 Modeled by Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Curr. Comput. Aided Drug Des. 2014, 10, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Sequence | Score | Molecular Mass (Da) | Hydrophobicity (%) | pI | Bind Score (kcal/mol) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLR2 | TLR4/MD-2 | ||||||
| 1 | HDCDLLR | 99 | 870.98 | 28.57 | 5.21 | −9.47 | −9.45 |
| 2 | FVNDEAFLR | 99 | 1109.55 | 55.56 | 4.19 | −8.02 | −7.95 |
| 3 | LGEDFLR | 99 | 848.44 | 42.86 | 4.19 | −7.71 | −7.98 |
| 4 | QYGDLSTPEALK | 98 | 1320.66 | 33.33 | 4.19 | −9.21 | −8.87 |
| 5 | CDLDLR | 98 | 733.34 | 33.33 | 4.12 | −7.93 | −7.69 |
| 6 | LEAER | 97 | 616.32 | 40.00 | 4.25 | −9.33 | −8.19 |
| 7 | LGGGEFLELR | 97 | 1089.58 | 40.00 | 4.25 | −7.76 | −9.04 |
| 8 | YGSVELDELGK | 96 | 1208.59 | 27.27 | 3.92 | −12.21 | −10.22 |
| 9 | EDPHLVPCLGTK | 96 | 1307.65 | 41.67 | 5.23 | −8.28 | −9.4 |
| 10 | LVYPNDNFFEGK | 95 | 1441.69 | 41.67 | 4.19 | −8.86 | −8.7 |
| 11 | ACGAEEFLKR | 94 | 1122.55 | 40.00 | 6.17 | −9.61 | −8.01 |
| 12 | APCEFNLK | 94 | 920.44 | 50.00 | 6.05 | −9.27 | −9.16 |
| 13 | DRLDTPLPDRPF | 94 | 1440.74 | 50.00 | 4.32 | −8.86 | −8.56 |
| 14 | FPPDYLDDALR | 94 | 1320.64 | 54.55 | 3.84 | −8.30 | −10.22 |
| 15 | QDPEDVLLSAFK | 94 | 1360.69 | 50.00 | 3.88 | −8.17 | −8.54 |
| 16 | AFDDAFAEFQR | 93 | 1315.58 | 54.55 | 3.88 | −7.91 | −9.10 |
| 17 | YGPNDNFFEGK | 91 | 1286.56 | 27.27 | 4.19 | −10.10 | −11.19 |
| Treatment | Peptide Sequences | Proliferation Rate (%) | NO (μM) | Phagocytosis Rate (%) | IL-6 (pg/mL) | TNF-α (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 21.64 ± 2.05 e | 129.02 ± 11.89 f |
| No. 1 | HDCDLLR | 68.81 ± 8.48 b | 7.02 ± 0.20 b | 88.61 ± 3.52 a | 74.27 ± 1.09 c | 511.86 ± 15.49 c |
| No. 4 | QYGDLSTPEALK | 51.04 ± 3.60 d | 2.51 ± 0.32 e | 71.67 ± 2.74 c | 49.88 ± 2.19 d | 363.82 ± 8.47 e |
| No. 8 | YGSVELDELGK | 51.58 ± 3.96 cd | 5.93 ± 0.30 c | 84.21 ± 3.76 b | 93.26 ± 0.62 b | 643.95 ± 9.05 b |
| No. 12 | APCEFNLK | 54.00 ± 4.62 c | 2.57 ± 0.53 e | 28.83 ± 5.05 f | 49.03 ± 0.40 d | 384.85 ± 45.96 e |
| No. 14 | FPPDYLDDALR | 45.51 ± 2.42 e | 5.00 ± 0.35 d | 49.94 ± 6.23 d | 54.11 ± 0.32 d | 401.13 ± 30.50 de |
| No. 17 | YGPNDNFFEGK | 45.15 ± 6.83 de | 2.60 ± 0.70 e | 39.92 ± 7.64 e | 50.41 ± 0.64 d | 435.38 ± 4.66 d |
| LPS | N/A | 95.90 ± 0.37 a | 9.50 ± 0.41 a | 92.08 ± 1.82 a | 158.36 ± 7.34 a | 916.40 ± 24.16 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, C.; Xu, Y.; Yan, J.; Qi, X.; Cao, S.; Yang, H. Purification and Characterization of Immunomodulatory Peptides from Hydrolysates of Thunnus albacares Dark Muscle. Foods 2025, 14, 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061068
Shen C, Xu Y, Yan J, Qi X, Cao S, Yang H. Purification and Characterization of Immunomodulatory Peptides from Hydrolysates of Thunnus albacares Dark Muscle. Foods. 2025; 14(6):1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061068
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Cunkuan, Yuanfang Xu, Jinxin Yan, Xiangyang Qi, Shaoqian Cao, and Hua Yang. 2025. "Purification and Characterization of Immunomodulatory Peptides from Hydrolysates of Thunnus albacares Dark Muscle" Foods 14, no. 6: 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061068
APA StyleShen, C., Xu, Y., Yan, J., Qi, X., Cao, S., & Yang, H. (2025). Purification and Characterization of Immunomodulatory Peptides from Hydrolysates of Thunnus albacares Dark Muscle. Foods, 14(6), 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061068





