Application of Composite Soaking Solution in Fillet Storage and Caco-2 Cell Antioxidant Repair
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Fillets
2.3. Preparation of Simulated Digestive Juice In Vitro
2.4. Cell Experimental Groups
2.5. Single-Factor Experiment
2.6. Orthogonal Experiment
2.7. Physicochemical Properties of Fillets After Soaking in CSS
2.7.1. Thawing Loss
2.7.2. Cooking Loss
2.7.3. Water Holding Capacity
2.7.4. Moisture Distribution and MRI Imaging Analysis
2.7.5. pH
2.7.6. Thiobarbituric Acid
2.7.7. Sensory Evaluation
2.7.8. HE Staining
2.7.9. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.8. Determination of the Effect of the Digestive Fluid on the Caco-2 Injury Model In Vitro
2.8.1. Cell Proliferation Activity
2.8.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.8.3. Establishment of the Oxidative Damage Model
2.8.4. Determination of the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
2.8.5. Determination of Peroxy Radicals
2.8.6. Observation of Cell Morphology
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
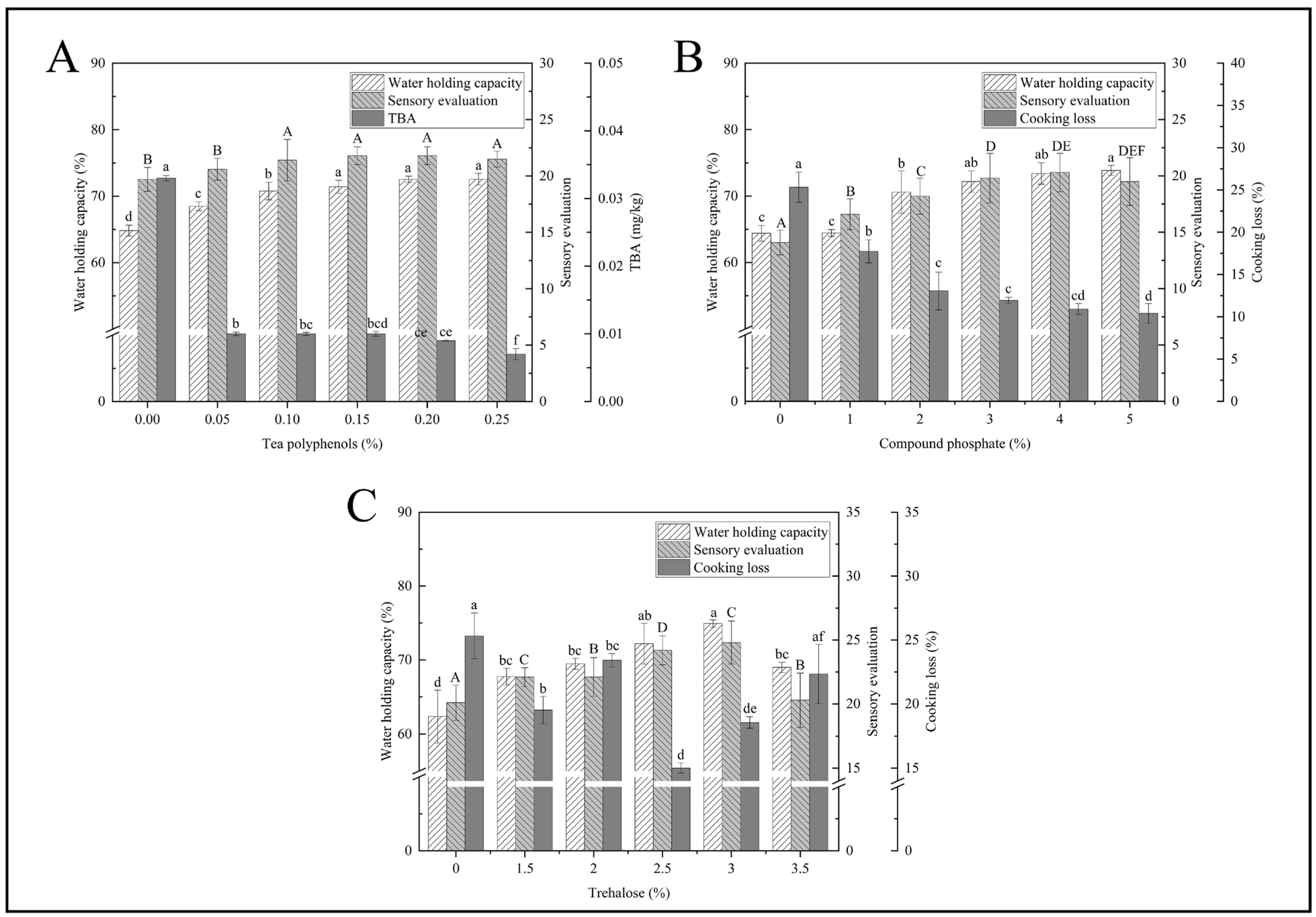
3.1. Single-Factor Experiment
3.1.1. TP Concentration
3.1.2. PC Concentration
3.1.3. TR Concentration
3.2. Orthogonal Test
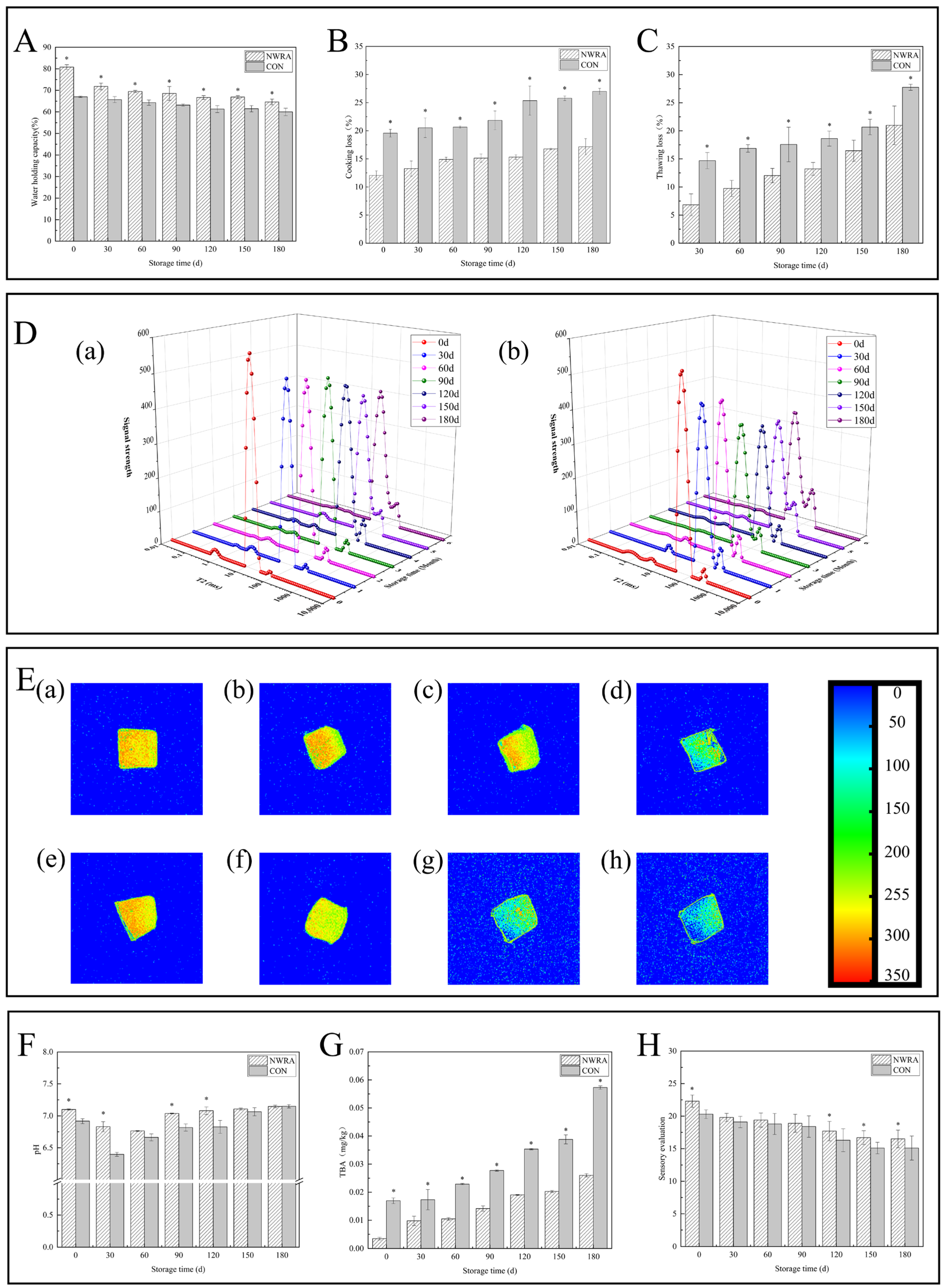
3.3. Effect of CSS on the Quality of Fillets During Storage
3.3.1. Water Holding Capacity, Cooking Loss, and Thawing Loss
3.3.2. Moisture Distribution and Migration
3.3.3. Nuclear Magnetic Imaging Pseudo-Colour Image
3.3.4. pH
3.3.5. TBA
3.3.6. Evaluation of Sensory Characteristics
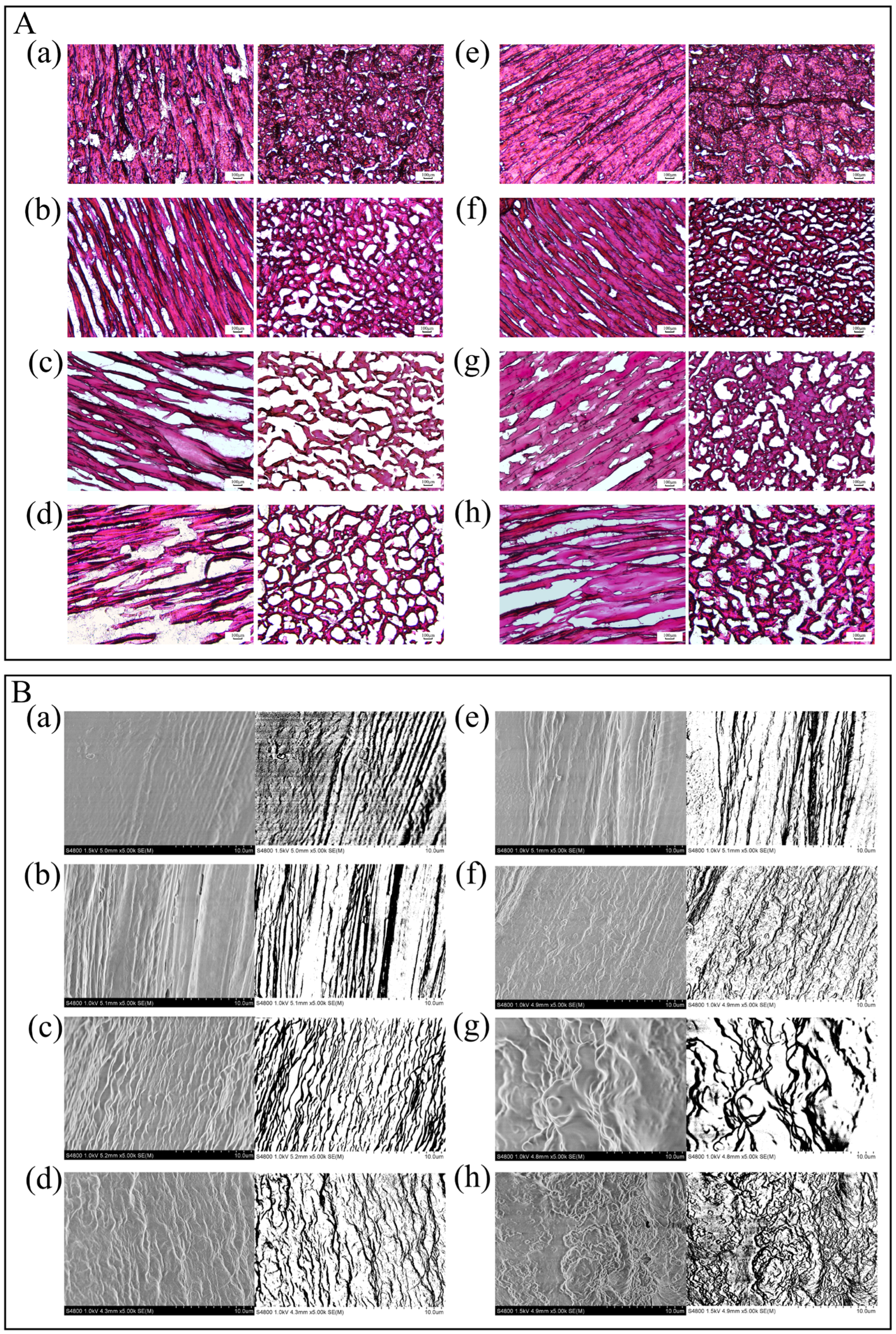
3.3.7. Microstructure
3.4. Effects of the Digestive Fluid of CSS-Treated Fillets on the Caco-2 Cell Injury Model In Vitro
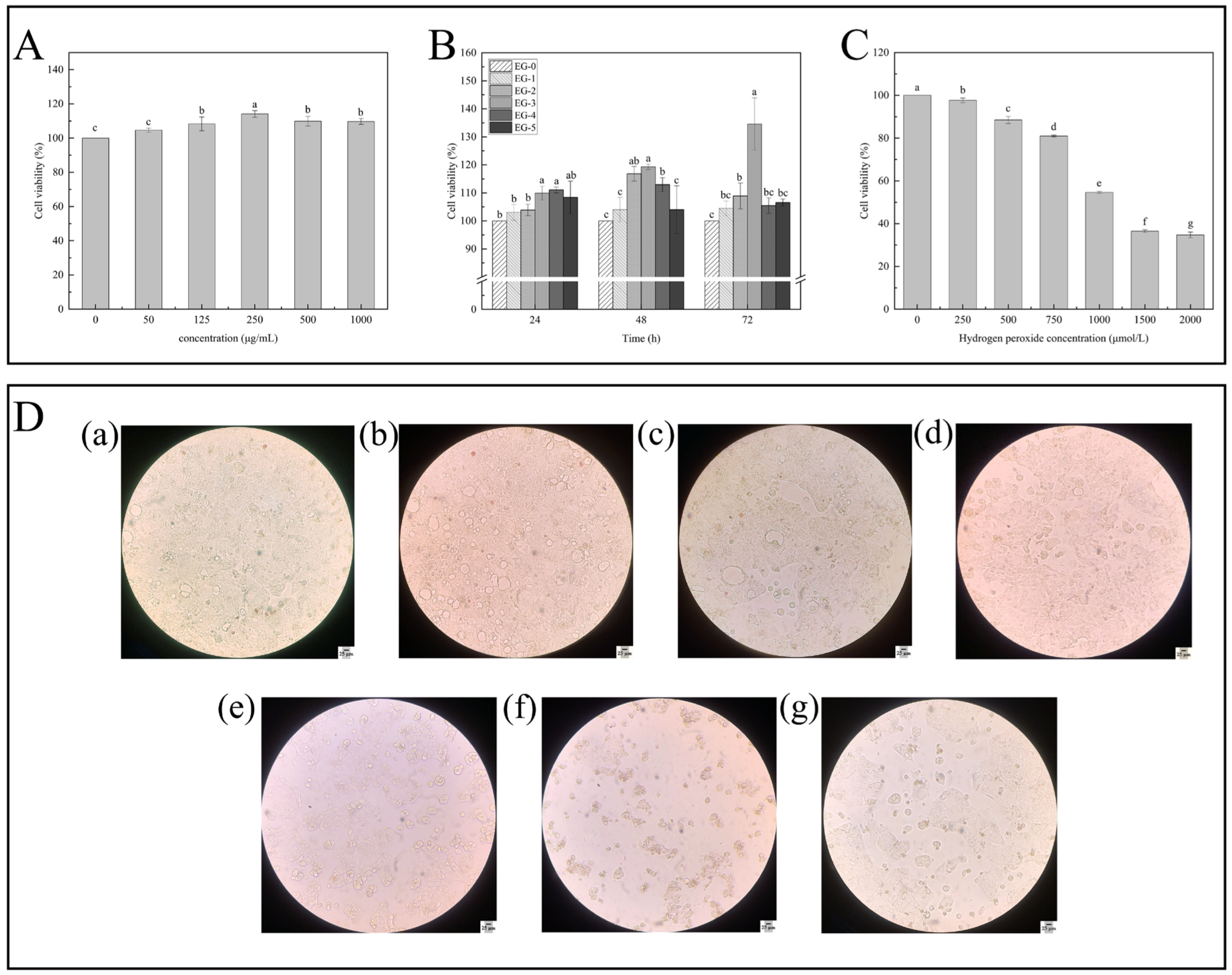
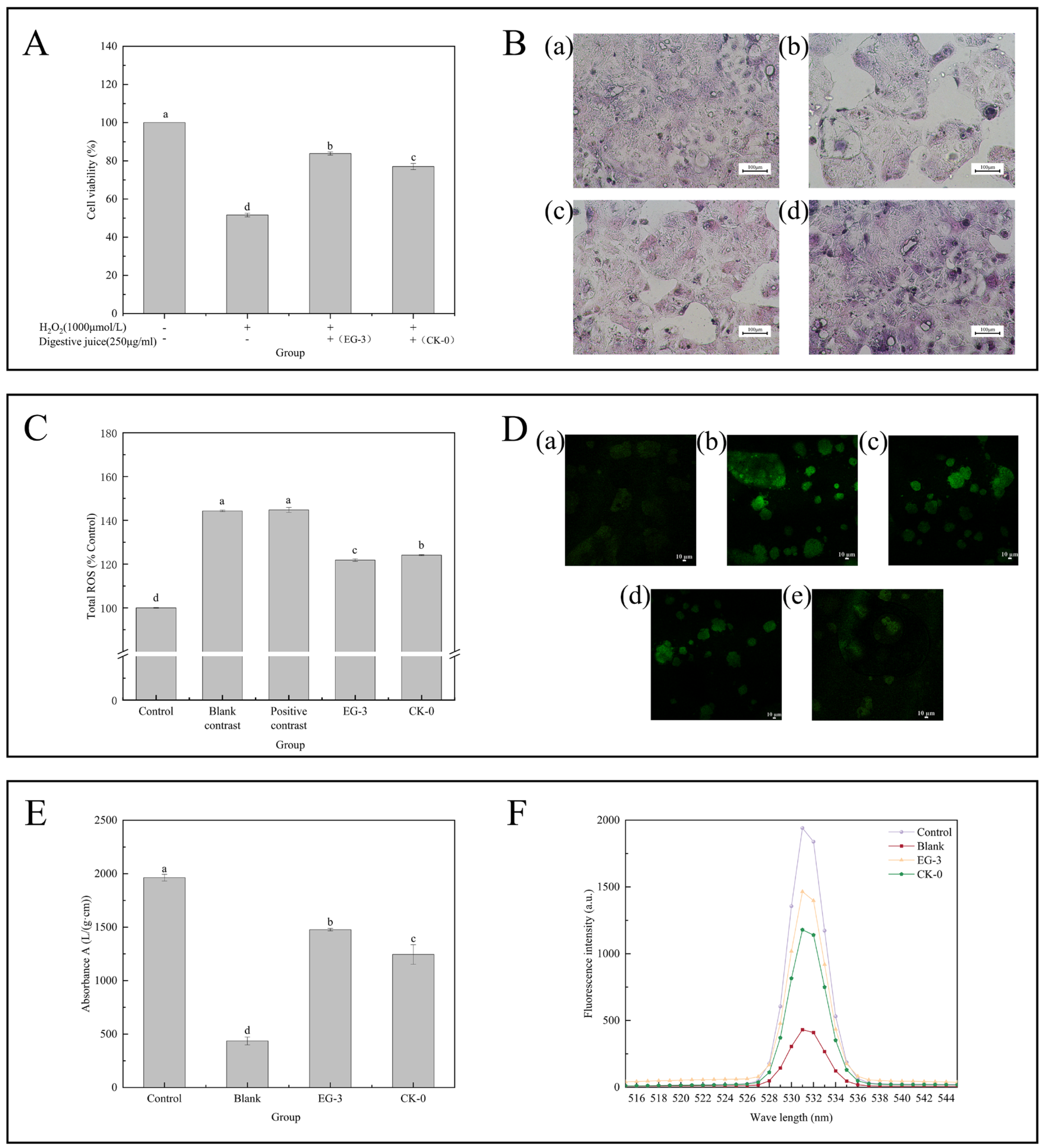
3.4.1. Detection of Cytotoxicity and Cell Proliferation
3.4.2. Determination of Effects of H2O2 Concentration on the Caco-2 Cell Oxidative Damage Model
3.4.3. Antioxidant Activity
3.4.4. Cell Morphology Observation
3.4.5. Analysis of Changes in the ROS Content
3.4.6. Measurement of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Electrolyte | Molar Concentration (mmol/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SSF | SGF | SIF | |
| K+ | 18.80 | 7.80 | 7.60 |
| H2PO4− | 3.70 | 0.90 | 0.80 |
| HCO3−, CO32− | 13.70 | 25.50 | 85.00 |
| Cl− | 19.50 | 70.20 | 55.50 |
| Mg2+ | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.33 |
| NH4+ | 0.12 | 1.00 | —— |
| Na+ | 13.60 | 72.20 | 123.40 |
| Ca2+ | 1.50 | 0.15 | 0.60 |
| Digestive Fluid | Electrolyte Stock Solution (mL) | CaCl2 (mL) | pH | Deionized Water (mL) | Other Substances and Final Concentrations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSF | 16.00 | 0.10 | 7.00 | 3.90 | α-amylase (0.81 mg) |
| SGF | 36.40 | 0.02 | 1.60 | 3.58 | Pepsin (10,000 U/mg) (16 mg) |
| SIF | 74.00 | 0.16 | 7.00 | 5.84 | Pancreatin (4000 U/g) (4 g); bile salts (0.65g) |
| Levels | Factors | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tea Polyphenol (%) | Composite Phosphate (%) | Trehalose (%) | ||
| Single-factor experiment | 1 | 0.05 | 1 | 1.5 |
| 2 | 0.1 | 2 | 2 | |
| 3 | 0.15 | 3 | 2.5 | |
| 4 | 0.2 | 4 | 3 | |
| 5 | 0.25 | 5 | 3.5 | |
| Orthogonal experiment | 1 | 2.50 | 0.10 | 1.00 |
| 2 | 3.00 | 0.15 | 3.00 | |
| 3 | 3.50 | 0.20 | 5.00 | |
| Item | 1–3 Points | 4–7 Points | 8–10 Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hue | The surface is dull and the colour is dim. | The surface is slightly shiny and the colour is dark. | Lustrous surface, bright colour. |
| flavour | No fragrance, there is a smell. The fishy smell is heavier. | Lighter aroma. There is a small amount of astringency and fishy smell. | The fragrance is fresh. The comprehensive taste is good. |
| Texture | Low hardness, poor elasticity, and the concave part is slow to appear or does not disappear after pressing. | It has more hardness and elasticity, and the concave part gradually disappears after pressing. | Hardness is high, elastic, the depression part immediately disappears after pressing. |
References
- Bao, Y.; Ertbjerg, P.; Estévez, M.; Yuan, L.; Gao, R. Freezing of meat and aquatic food: Underlying mechanisms and implications on protein oxidation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 5548–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Liu, L.; Monto, A.R.; Su, K.; Zhang, H.; Shi, T.; Xiong, Z.; Xu, G.; Luo, Y.; Bao, Y.; et al. Metabolomic profile of muscles from tilapia cultured in recirculating aquaculture systems and traditional aquaculture in ponds and protein stability during freeze-thaw cycles. Food Chem. 2024, 451, 139325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Walayat, N.; Ding, Y.; Liu, J. The role of trifunctional cryoprotectants in the frozen storage of aquatic foods: Recent developments and future recommendations. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 21, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Yi, S.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, G. Effect of compound phosphate on the water-holding capacity and nutritional quality of sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicus) fillets. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, W.; Wei, H.; Deng, S.; Yu, X.; Huang, T. The mechanisms and applications of cryoprotectants in aquatic products: An overview. Food Chem. 2022, 408, 135202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørkevoll, I.; Reboredo, R.G.; Fossen, I. Effect of polyphosphates on the quality of frozen light salted cod (Gadus morhua L.) fillets. Food Control. 2017, 78, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Yu, D.; Zhang, X. Stabilization effects of saccharides in protein formulations: A review of sucrose, trehalose, cyclodextrins and dextrans. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 192, 106625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Li, P.; Han, F.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, K.; Wang, Y.; Cai, K.; Li, C.; Xu, B. Myofibrillar protein interacting with trehalose elevated the quality of frozen meat. Foods 2022, 11, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Kong, B.; He, J.; Zhang, Q.; An, G.; Zhang, T.; Xia, X. Cryoprotective effect of water-tailored trehalose-based natural deep eutectic solvents on frozen-thawed mirror carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) surimi. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma L k Zhang, B.; Deng S, g.; Xie, C. Comparison of the cryoprotective effects of trehalose, alginate, and Its oligosaccharides on peeled shrimp (Litopenaeus Vannamei) during frozen storage. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, C540–C546. [Google Scholar]
- Nikoo, M.; Benjakul, S. Potential application of seafood-derived peptides as bifunctional ingredients, antioxidant–cryoprotectant: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Fang, C.; Qi, H.; Benjakul, S.; Aubourg, S.P.; Zhang, B. Low-temperature vacuum permeation of sodium tripolyphosphate and trehalose suppresses the denaturation of myofibrillar proteins in peeled shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) during frozen storage. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1012864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Cao, H.-J.; Lin, H.-M.; Deng, S.-G.; Wu, H. Insights into ice-growth inhibition by trehalose and alginate oligosaccharides in peeled Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) during frozen storage. Food Chem. 2018, 278, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Gu, S.; Xu, M.; Wang, W.; Yao, H.; Zhou, X.; Ding, Y. The effect of tea polyphenols on biogenic amines and free amino acids in bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) fillets during frozen storage. LWT 2021, 150, 111933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, S. The use of a tea polyphenol dip to extend the shelf life of silver carp (Hypophthalmicthys molitrix) during storage in ice. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, F.; Luo, Y.; Zeng, X.; Pei, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, D.; Yin, F. Effects of tea polyphenol and Its combination with other antioxidants added during the extraction process on oxidative stability of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) Oil. Foods 2022, 11, 3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Sun, J.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Sun, B. Effects of cooking methods on aroma formation in pork: A comprehensive review. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assunção, L.S.; Ribeiro, C.D.F.; de Souza, C.O.; Danielski, R.; Kumari, S.; Nunes, I.L.; Shahidi, F. Nanoencapsulation of hybrid crude palm oil Unaué HIE OxG with jackfruit by-products as encapsulants: A study of cellular antioxidant activity and cytotoxicity in Caco-2 cells. Food Chem. 2024, 448, 139009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Espindola, J.S.; Taccóla, M.F.; da Silva, V.S.N.; dos Santos, L.D.; Rossini, B.C.; Mendonça, B.C.; Pacheco, M.T.B.; Galland, F. Digestion-resistant whey peptides promote antioxidant effect on Caco-2 cells. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monto, A.R.; Yuan, L.; Xiong, Z.Y.; Shi, T.; Li, M.Z.; Wang, X.; Gao, R.C. Effect of α-tocopherol, soybean oil, and glyceryl monostearate oleogel on gel properties and the in-vitro digestion of low-salt silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) surimi. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Kuang, S.; Xiao, T.; Hu, L.; Nie, P.; Ramaswamy, H.S.; Yu, Y. The effect of pressure–shift freezing versus air freezing and liquid immersion on the quality of frozen fish during storage. Foods 2022, 11, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndazigaruye, G.; Kim, D.-H.; Kang, C.-W.; Kang, K.-R.; Joo, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-R.; Lee, K.-W. Effects of low-protein diets and exogenous protease on growth performance, carcass traits, intestinal morphology, cecal volatile fatty acids and serum parameters in broilers. Animals 2019, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Xiong, Z.; McClements, D.J.; Bao, Y.; Song, T.; Li, J.; Yuan, L.; Jin, W.; et al. Mechanism of low-salt surimi gelation induced by microwave heating combined with l-arginine and transglutaminase: On the basis of molecular docking between l-arginine and myosin heavy chain. Food Chem. 2022, 391, 133184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Lv, Y.; Li, X.; Yi, S.; Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Xu, Y. Improvement of gelation properties of silver carp surimi through ultrasound-assisted water bath heating. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2022, 83, 105942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siu, G.M.; Draper, H.H. A survey of the malonaldehyde content of retail meats and fish. J. Food Sci. 1978, 43, 1147–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dertli, E.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Tatlisu, N.B.; Toker, O.S.; Cankurt, H.; Sagdic, O. Effects of in situ exopolysaccharide production and fermentation conditions on physicochemical, microbiological, textural and microstructural properties of Turkish-type fermented sausage (sucuk). Meat Sci. 2016, 121, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zou, Y.; Zhou, A.; Xiao, J.; Benjakul, S. Insight into the effect of ice addition on the gel properties of nemipterus virgatus surimi gel combined with water migration. Foods 2021, 10, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Wang, A.; Wang, D.; Meng, X.; Ma, J.; Hong, L.; Qin, R.; Wang, A.; Dong, J.; Huang, Q.; et al. Establishment of malignantly transformed dendritic cell line SU3-ihDCTC induced by Glioma stem cells and study on Its sensitivity to resveratrol. BMC Immunol. 2018, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, R.; Jia, Z.; Lin, P.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, W.; Yi, S.; Li, X.; Li, J. Investigating on the influence mechanism of sausage of sea bass on calcium absorption and transport based on Caco-2 cell monolayer model. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1046945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Yang, C.; Li, Z.; Finn, P.W.; Perkins, D.L.; Sun, J.; Bai, Z.; Gao, L.; Zhang, M.; Ren, D. In vitro antioxidant activities of Rhodobacter sphaeroides and protective effect on Caco-2 cell line model. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 103, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Xiong, Y.L.; Kong, B.; Liu, Q.; Xia, X. Radical scavenging activity of black currant (Ribes nigrum L.) extract and Its inhibitory effect on gastric cancer cell proliferation via induction of apoptosis. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blattner, J.R.; He, L.; Lemasters, J.J. Screening assays for the mitochondrial permeability transition using a fluorescence multiwell plate reader. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 295, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Gao, Y.M.; Sun, X.; Guo, N.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Fu, Y.J. Hepatoprotective effect of 2′-O-galloylhyperin against oxidative stress-induced liver damage through induction of Nrf2/ARE-mediated antioxidant pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 102, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Xiong, Y.L. Chlorogenic acid-mediated gel formation of oxidatively stressed myofibrillar protein. Food Chem. 2015, 180, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Sameen, D.E.; Zeng, Y.; Li, S.; Qin, W.; Liu, Y. An overview of tea polyphenols as bioactive agents for food packaging applications. LWT 2022, 167, 113845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Regenstein, J. Water uptake, protein solubility, and protein changes of cod mince stored on ice as affected by polyphosphates. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Nakazawa, N.; Hu, Y.; Osako, K.; Okazaki, E. Changes in quality properties and tissue histology of lightly salted tuna meat subjected to multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Food Chem. 2019, 293, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Guan, Z.Q.; Ling, C.M. Effects of different phosphorus-free water-retaining agents on the quality of frozen tilapia fillets. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 10, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Jin, H.X.; Zhao, Q.L.; Liu, C.J.; Li, R.W.; Tang, Y.P. Collagen extracted from bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus) skin by isoelectric precipitation: Physicochemical properties, proliferation, and migration activities. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Z.; Yu, C.; Yuan, Y. Effect of slurry ice during storage on myofibrillar protein of Pseudosciaena crocea. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 3806–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Pi, R.; Mubango, E.; Tan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Hong, H. Inhibitive effect of cryoprotectants on the oxidative and structural changes in myofibrillar proteins of unwashed mince from silver carp during frozen storage. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Xie, J.; Yu, W.; Sun, Y. Effects of Frozen Storage Temperature on Water-Holding Capacity and Physicochemical Properties of Muscles in Different Parts of Bluefin Tuna. Foods 2022, 11, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Yang, W.; Shi, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Xia, G.; Wu, H. Effects of ferulic acid grafted-chitosan hydrocolloid on the quality preservation of golden pompano (Trachinotus blochii) fillets during refrigerated storage with emphasis on lable-free proteomics. LWT 2024, 210, 116853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Li, J. Effect of tea polyphenols on the physical and chemical characteristics of dried-seasoned squid (Dosidicus gigas) during storage. Food Control. 2013, 31, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-D.; Tao, Q.; Bai, L.-X.; Qin, Z.; Liu, X.-W.; Li, S.-H.; Yang, Y.-J.; Ge, W.-B.; Li, J.-Y. The transport and uptake of resveratrol mediated via glucose transporter 1 and Its antioxidant effect in Caco-2 cells. Molecules 2023, 28, 4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilla, A.; Rodrigo, M.J.; Zacarías, L.; De Ancos, B.; Sánchez-Moreno, C.; Barberá, R.; Alegría, A. Protective effect of bioaccessible fractions of citrus fruit pulps against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in Caco-2 cells. Food Res. Int. 2017, 103, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Fang, C.-D.; Hao, G.-J.; Zhang, Y.-Y. Effect of kappa-carrageenan oligosaccharides on myofibrillar protein oxidation in peeled shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) during long-term frozen storage. Food Chem. 2017, 245, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aredia, F.; Czaplinski, S.; Fulda, S.; Scovassi, A.I. Molecular features of the cytotoxicity of an NHE inhibitor: Evidence of mitochondrial alterations, ROS overproduction and DNA damage. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, S.; Yun, X.; Rao, W.; Xiao, C.; Xu, Z.; Lang, J.; Huang, Q. Emamectin benzoate induces ROS-mediated DNA damage and apoptosis in Trichoplusia Tn5B1-4 cells. Chem. Interactions 2017, 273, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; She, X.; Chen, Z.; Wei, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, X. Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum (L.) Gaertn) protein-derived antioxidant peptides: Mechanisms of action and structure-activity relationship in Caco-2 cell models. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group | Trehalose (A) (%) | Phosphate Compound (B) (%) | Tea Polyphenols (C) (%) | Water Holding Capacity (%) | TBA (μg/kg) | Sensory Evaluation (Score) | Cooking Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 77.479 | 12.630 | 20.200 | 21.660 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 77.875 | 5.530 | 21.100 | 16.678 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 81.391 | 5.370 | 22.300 | 12.406 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 80.87 | 2.370 | 22.500 | 18.979 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 80.891 | 2.230 | 22.500 | 12.151 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 80.147 | 8.530 | 21.200 | 12.476 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 70.434 | 3.770 | 19.800 | 22.956 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 77.529 | 11.700 | 20.300 | 14.932 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 81.928 | 5.770 | 22.500 | 12.402 |
| Water holding capacity | |||||||
| K1 | 236.745 | 228.783 | 235.155 | ||||
| K2 | 241.908 | 236.295 | 240.673 | ||||
| K3 | 229.891 | 243.466 | 232.716 | ||||
| R | 12.017 | 14.683 | 7.957 | ||||
| TBA | |||||||
| K1 | 23.530 | 18.770 | 32.860 | ||||
| K2 | 13.130 | 19.530 | 13.670 | ||||
| K3 | 21.240 | 19.830 | 11.370 | ||||
| R | 10.400 | 1.060 | 21.490 | ||||
| Sensory evaluation | |||||||
| K1 | 63.600 | 62.500 | 61.700 | ||||
| K2 | 66.200 | 63.900 | 66.100 | ||||
| K3 | 62.600 | 66.000 | 64.600 | ||||
| R | 3.600 | 3.500 | 4.400 | ||||
| Cooking loss | |||||||
| K1 | 50.744 | 63.595 | 49.068 | ||||
| K2 | 43.606 | 43.761 | 48.059 | ||||
| K3 | 50.290 | 37.284 | 47.513 | ||||
| R | 7.138 | 26.311 | 1.555 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yi, S. Application of Composite Soaking Solution in Fillet Storage and Caco-2 Cell Antioxidant Repair. Foods 2025, 14, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030442
Shao Q, Wang Z, Yi S. Application of Composite Soaking Solution in Fillet Storage and Caco-2 Cell Antioxidant Repair. Foods. 2025; 14(3):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030442
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Qing, Zhongqiang Wang, and Shumin Yi. 2025. "Application of Composite Soaking Solution in Fillet Storage and Caco-2 Cell Antioxidant Repair" Foods 14, no. 3: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030442
APA StyleShao, Q., Wang, Z., & Yi, S. (2025). Application of Composite Soaking Solution in Fillet Storage and Caco-2 Cell Antioxidant Repair. Foods, 14(3), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030442





