Enterococcus faecium WEFA23-Derived Surface Layer Protein OTC Prevents Listeria monocytogenes Invasion by Strengthening Intestinal Barrier Function and Modulating Immune Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Cell Culture Conditions
2.3. Anti-Adhesion Assay
2.4. Anti-Invasion Assay
2.5. mRNA Level Determination of Cytokines, Tight Junction Proteins, and Virulence Factors
2.6. Protein Level Measurement of Tight Junction Protein
2.7. RNA Sequencing
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
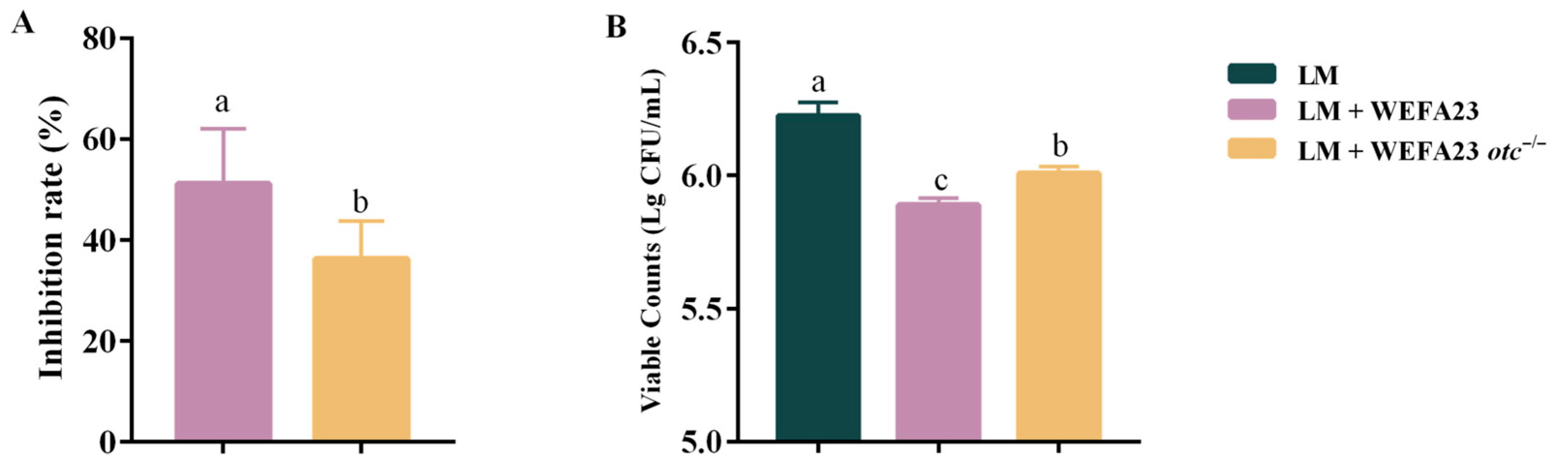
3.1. Effect of OTC on the Adhesive and Invasive Capacity of L. monocytogenes in Caco-2 Cells
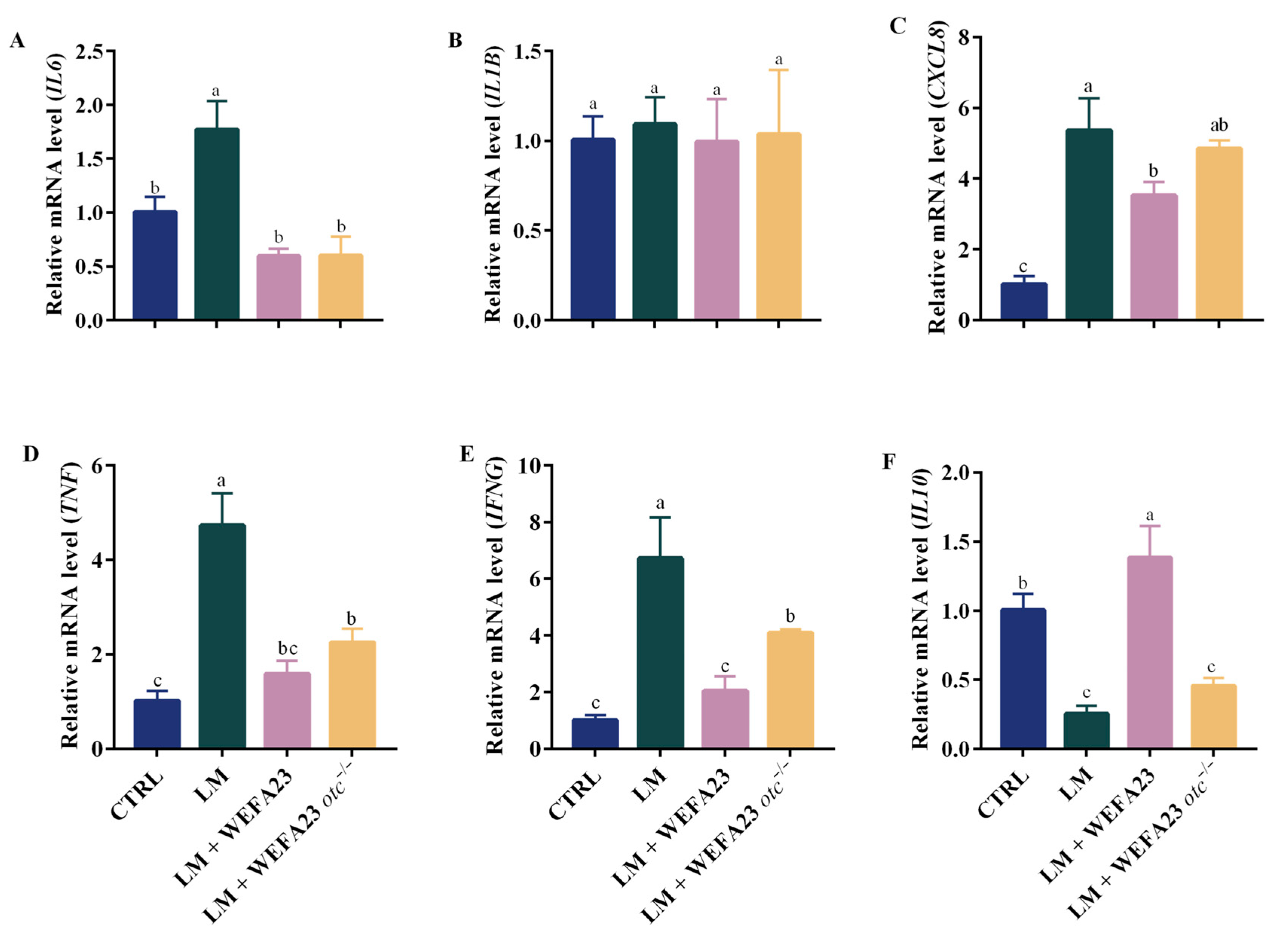
3.2. Effect of OTC on the mRNA Level of Cytokines in Caco-2 Cells
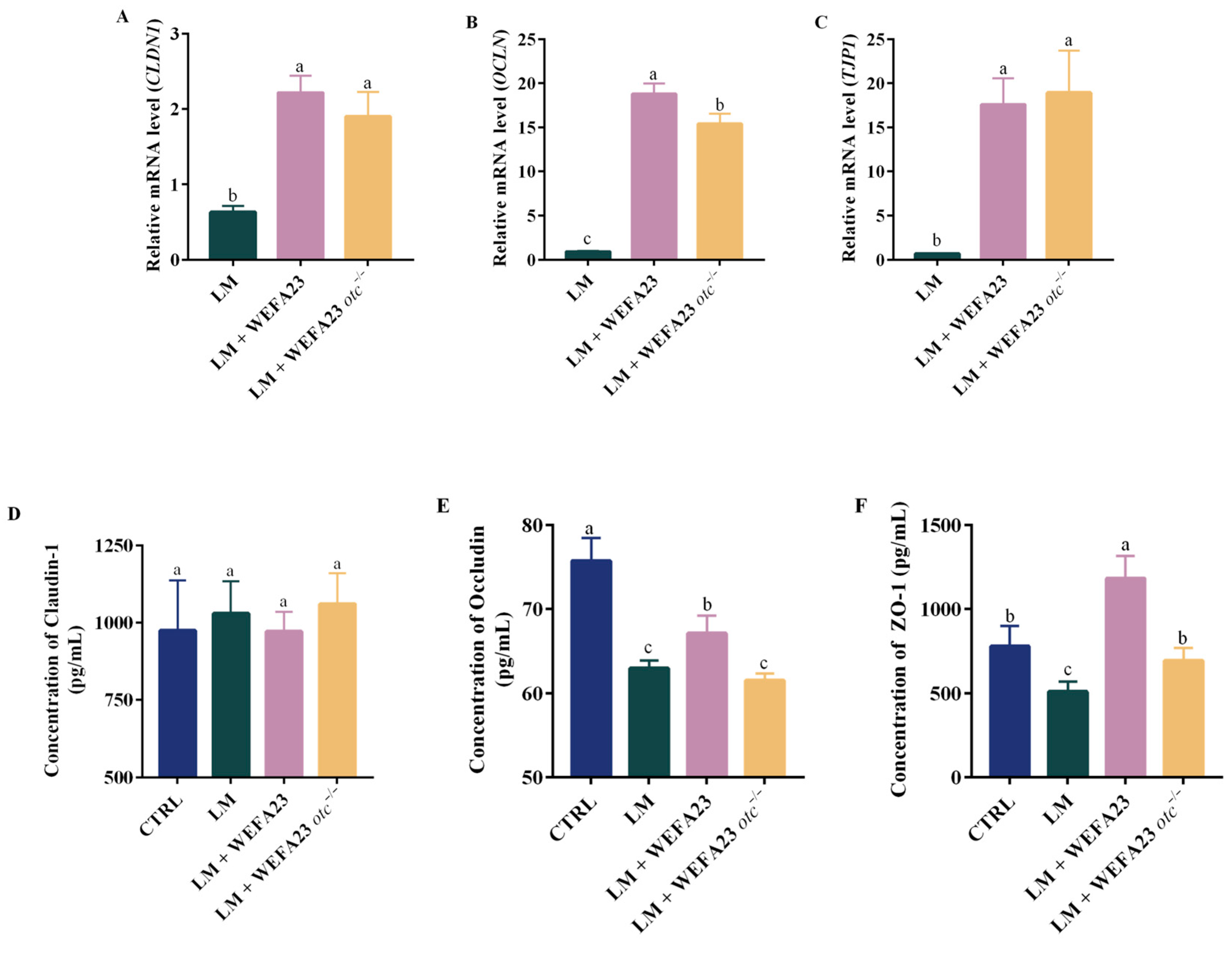
3.3. Effect of OTC on the Tight Junction Integrity in Caco-2 Cells
3.4. Effect of OTC on the mRNA Levels of Virulence Factors of L. monocytogenes
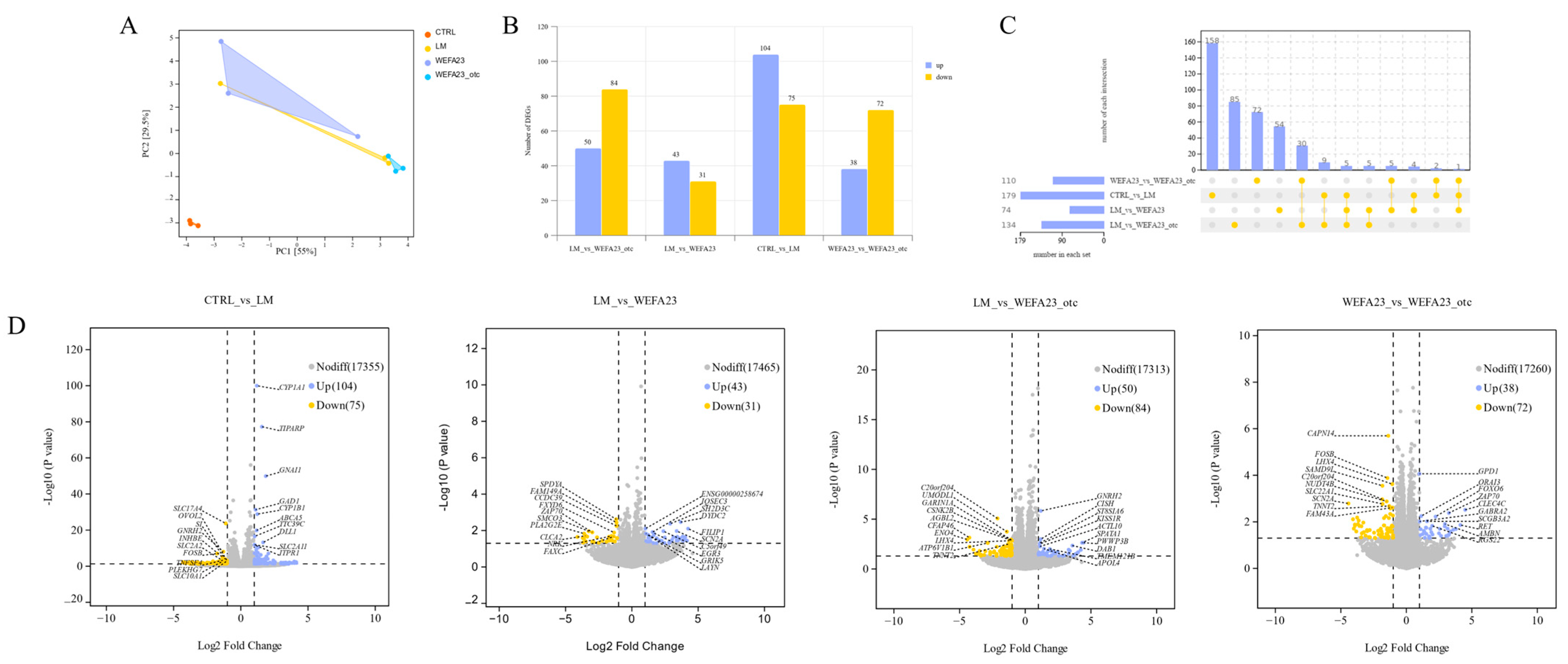
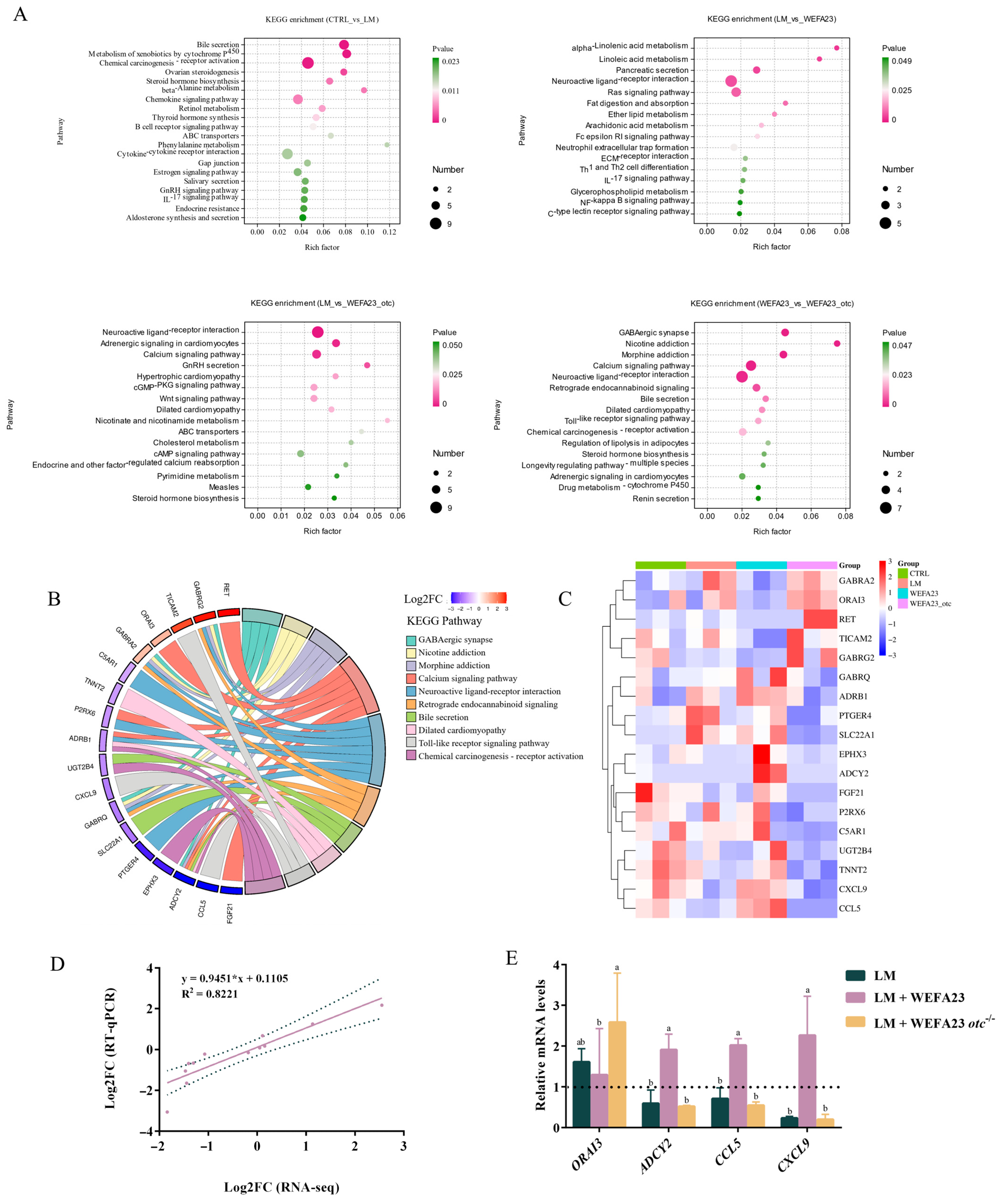
3.5. Effect of OTC on the Changes in Transcriptional Profile in Caco-2 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allaire, J.M.; Crowley, S.M.; Law, H.T.; Chang, S.Y.; Ko, H.J.; Vallance, B.A. The Intestinal Epithelium: Central Coordinator of Mucosal Immunity. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 677–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlech, W.F. Epidemiology and Clinical Manifestations of Listeria monocytogenes Infection. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osek, J.; Wieczorek, K. Listeria monocytogenes-How This Pathogen Uses Its Virulence Mechanisms to Infect the Hosts. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hou, X.; Yu, L. Contribution of Lactobacilli on Intestinal Mucosal Barrier and Diseases: Perspectives and Challenges of Lactobacillus casei. Life 2022, 12, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, Z.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Surface Components and Metabolites of Probiotics for Regulation of Intestinal Epithelial Barrier. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vimont, A.; Fernandez, B.; Hammami, R.; Ababsa, A.; Daba, H.; Fliss, I. Bacteriocin-Producing Enterococcus faecium LCW 44: A High Potential Probiotic Candidate from Raw Camel Milk. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popović, N.; Djokić, J.; Brdarić, E.; Dinić, M.; Terzić-Vidojević, A.; Golić, N.; Veljović, K. The Influence of Heat-Killed Enterococcus faecium BGPAS1-3 on The Tight Junction Protein Expression and Immune Function in Differentiated Caco-2 Cells Infected with Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 19111. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herranz, C.; Chen, Y.; Chung, H.J.; Cintas, L.M.; Hernández, P.E.; Montville, T.J.; Chikindas, M.L. Enterocin P Selectively Dissipates the Membrane Potential of Enterococcus faecium T136. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, F.; Xu, D.; Liu, Z.; Tao, X.; Wei, H. Anti-adhesion of Probiotic Enterococcus faecium WEFA23 against Five Pathogens and the Beneficial Effect of Its S-layer Proteins against Listeria monocytogenes. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yang, Q.; Tian, L.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, L.; Tao, X.; Wei, H. Protection of Surface Layer Protein from Enterococcus faecium WEFA23 Against Listeria monocytogenes CMCC54007 Infection by Modulating Intestinal Permeability and Immunity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 4269–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Long, X.; Dong, B.; Huang, Y.; Tao, X.; Wei, H. Surface-layer Proteins of Enterococcus faecium WEFA23 Inhibit Listeria monocytogenes-induced Inflammation via TLR2-mediated NF-κB and MAPK Signalling in RAW 264.7 cells. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 303, 128373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.I.; Bansod, S.; Kumar, R.B.; Sengupta, N.; Singh, L. Differential Proteomic Analysis of Clostridium perfringens ATCC13124; Identification of Dominant, Surface and Structure Associated Proteins. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yi, L.; Sun, L.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Wen, W.Y.; Li, X.K.; Mei, J.J.; Ding, K.; Wu, T.C.; Grenier, D. Identification and Characterization of a Streptococcus suis Immunogenic Ornithine Carbamoytransferase Involved in Bacterial Adherence. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, L.; Li, J.; Fan, Q.; Mao, C.; Jin, M.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Grenier, D.; Wang, Y. The otc Gene of Streptococcus suis Plays An Important Role in Biofilm Formation, Adhesion, and Virulence in A Murine Model. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 251, 108925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Tao, X.; Shah, N.P.; Wei, H. Antagonistics Against Pathogenic Bacillus cereus in Milk Fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum ZDY2013 and Its Anti-adhesion Effect on Caco-2 cells Against Pathogens. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 2666–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Zhong, C.; He, Y.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wei, H.; Tao, X. Preventive of Lacticaseibacillus casei WLCA02 Against Salmonella Typhimurium Infection via Strengthening the Intestinal Barrier and activating the Macrophages. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 104, 105507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quereda, J.J.; Morón-García, A.; Palacios-Gorba, C.; Dessaux, C.; García-Del Portillo, F.; Pucciarelli, M.G.; Ortega, A.D. Pathogenicity and Virulence of Listeria monocytogenes: A Trip from Environmental to Medical Microbiology. Virulence 2021, 12, 2509–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Belkum, A.; Almeida, C.; Bardiaux, B.; Barrass, S.V.; Butcher, S.J.; Çaykara, T.; Chowdhury, S.; Datar, R.; Eastwood, I.; Goldman, A.; et al. Host-Pathogen Adhesion as the Basis of Innovative Diagnostics for Emerging Pathogens. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, R.; Singh, K.S.; Bisht, S.; Kumar, S.; Mohanty, A.K.; Grover, S.; Kaushik, J.K. Host-microbe Interaction and Pathogen Exclusion Mediated by An Aggregation-prone Surface Layer Protein of Lactobacillus helveticus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drolia, R.; Amalaradjou, M.A.R.; Ryan, V.; Tenguria, S.; Liu, D.; Bai, X.; Xu, L.; Singh, A.K.; Cox, A.D.; Bernal-Crespo, V.; et al. Receptor-targeted Engineered Probiotics Mitigate Lethal Listeria Infection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Xu, P.; Wu, Z.; Pan, D. Anti-inflammatory Activity of Surface Layer Protein SlpA of Lactobacillus acidophilus CICC 6074 in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 Cells and DSS-induced Mice Colitis. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 51, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drolia, R.; Tenguria, S.; Durkes, A.C.; Turner, J.R.; Bhunia, A.K. Listeria Adhesion Protein Induces Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction for Bacterial Translocation. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 470–484.e477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, L.; Liang, W.; Li, C.; Wang, Z. Bacillus coagulans Restores Pathogen-induced Intestinal Dysfunction via Acetate-FFAR2-NF-κB-MLCK-MLC Axis in Apostichopus japonicus. mSystems 2024, 9, e0060224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Ren, L.F.; Li, Z.J.; Zhang, L. How Do Intestinal Probiotics Restore the Intestinal Barrier? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 929346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantel, M.; Durand, T.; Bessard, A.; Pernet, S.; Beaudeau, J.; Guimaraes-Laguna, J.; Maillard, M.B.; Guédon, E.; Neunlist, M.; Le Loir, Y.; et al. Propionibacterium freudenreichii CIRM-BIA 129 Mitigates Colitis through S Layer Protein B-dependent Epithelial Strengthening. Am. J. Physiology. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2024, 326, G163–G175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodovalho, V.R.; da Luz, B.S.R.; Rabah, H.; do Carmo, F.L.R.; Folador, E.L.; Nicolas, A.; Jardin, J.; Briard-Bion, V.; Blottière, H.; Lapaque, N.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Produced by the Probiotic Propionibacterium freudenreichii CIRM-BIA 129 Mitigate Inflammation by Modulating the NF-κB Pathway. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.; Yang, H.; Kang, H.S.; Ahn, C.; Hong, E.J.; An, B.S.; Jeung, E.B. Alteration of Tight Junction Gene Expression by Calcium- and Vitamin D-deficient Diet in the Duodenum of Calbindin-null Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 22997–23010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, C.; Nagidi, S.H.; Collett, K.; McKell, J.; Mizrachi, D. Calcium Regulates the Interplay Between the Tight Junction and Epithelial Adherens Junction at the Plasma Membrane. FEBS Lett. 2022, 596, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dramsi, S.; Cossart, P. Listeriolysin O-mediated Calcium Influx Potentiates Entry of Listeria monocytogenes Into the Human Hep-2 Epithelial Cell Line. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 3614–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, K.F.; LaVigne, J.E.; Brust, T.F.; Seifert, R.; Dessauer, C.W.; Watts, V.J.; Ostrom, R.S. Physiological Roles of Mammalian Transmembrane Adenylyl Cyclase Isoforms. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 815–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auteri, M.; Zizzo, M.G.; Serio, R. GABA and GABA Receptors in The Gastrointestinal Tract: From Motility to Inflammation. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 93, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambuy, Y.; De Angelis, I.; Ranaldi, G.; Scarino, M.L.; Stammati, A.; Zucco, F. The Caco-2 Cell Line as A Model of The Intestinal Barrier: Influence of Cell and Culture-related Factors on Caco-2 Cell Functional Characteristics. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2005, 21, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matereke, L.T.; Okoh, A.I. Listeria monocytogenes Virulence, Antimicrobial Resistance and Environmental Persistence: A Review. Pathogens 2020, 9, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ireton, K.; Mortuza, R.; Gyanwali, G.C.; Gianfelice, A.; Hussain, M. Role of Internalin Proteins in the Pathogenesis of Listeria monocytogenes. Mol. Microbiol. 2021, 116, 1407–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Kragh, M.L.; Aabo, S.; Jensen, A.N.; Olsen, J.E. Inhibition of Virulence Gene Expression in Salmonella Dublin, Escherichia coli F5 and Clostridium perfringens Associated with Neonatal Calf Diarrhea by Factors Produced by Lactic Acid Bacteria During Fermentation of Cow Milk. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 828013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, Q.; Shi, C.; Zhang, C.; Xia, X.; Wang, X. Effect of Coenzyme Q0 on Biofilm Formation and Attachment-invasion Efficiency of Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control 2018, 90, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| IL6 | AGCAAAGCAAAGAAACCGAT | CAGCTCTGAGATGGCTTCAG |
| IL1B | TACAGTGGCAATGAGGAT | ATGAAGGGAAAGAAGGTG |
| TNF | TTTGATCCCTGACATCTGGA | GGCCTAAGGTCCACTTGTGT |
| IFNG | AGGCTTTATCTCAGGGGCCA | AGCACTGGCTCAGATTGCAG |
| IL10 | AAGCCTGACCACGCTTTCTA | TCCGAGACACTGGAAGGTGA |
| CXCL8 | ACCCCAAGGAAAACTGGGTG | GTTTGCTGTGCTTCTCTTGGA |
| TJP1 | AGCCTTGCAAAGCCAGCTCA | AGTGGCCTGGATGGGTTCATAG |
| OCLN | AAGAGTTGACAGTCCCATGGCATAC | ATCCACAGGCCAAGTTAATGGAAG |
| CLDN1 | GCATGAAGTATATGAAGTGCTTGGA | CGATTCTATTGCCATACCATGCTG |
| ACTB | GGCTATCCAGCGTACTCCAAA | CGGCAGGCATACTCATCTTTTT |
| prfA | TGAGCAAGAATCTTACGCACTTTT | GCTAGGCTGTATGAAACTTGTTTTTG |
| actA | CGGGTAAATGGGTACGTGAT | TGGTCAATTAACCCTGCACTT |
| plcA | TCGGACCATTGTAGTCATCTTGA | CACAAATTCGGCATGCAGTT |
| plcB | CGCAGCTCCGCATGATATT | GATTATCCGCGGACCAACTAAG |
| inlA | AATGTAACAGACACGGTCTCACAAA | TCCCTAATCTATCCGCCTGAAG |
| 16 S rRNA | AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG | GGCTACCTTGTTACGACTT |
| ORAI3 | CATTTTGGGGGAAGATTTCG | GTAGAAACACCCAAATCCCT |
| ADCY2 | GCCGTGTTCAACATGTTTTT | CCACCTGATTATTTGAGGCT |
| CCL5 | ATGCTTGGTTGCTATTTTGG | CAGTAGCAATGAGGATGACA |
| CXCL9 | TGATTGGAGTGCAAGGAAC | GCTGAATCTGGGTTTAGACA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Y.; Dong, B.; Xie, K.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tao, X.; Wei, H. Enterococcus faecium WEFA23-Derived Surface Layer Protein OTC Prevents Listeria monocytogenes Invasion by Strengthening Intestinal Barrier Function and Modulating Immune Responses. Foods 2025, 14, 4110. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234110
He Y, Dong B, Xie K, Hu Y, Huang Y, Tao X, Wei H. Enterococcus faecium WEFA23-Derived Surface Layer Protein OTC Prevents Listeria monocytogenes Invasion by Strengthening Intestinal Barrier Function and Modulating Immune Responses. Foods. 2025; 14(23):4110. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234110
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Yao, Bing Dong, Ke Xie, Yingsheng Hu, Yina Huang, Xueying Tao, and Hua Wei. 2025. "Enterococcus faecium WEFA23-Derived Surface Layer Protein OTC Prevents Listeria monocytogenes Invasion by Strengthening Intestinal Barrier Function and Modulating Immune Responses" Foods 14, no. 23: 4110. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234110
APA StyleHe, Y., Dong, B., Xie, K., Hu, Y., Huang, Y., Tao, X., & Wei, H. (2025). Enterococcus faecium WEFA23-Derived Surface Layer Protein OTC Prevents Listeria monocytogenes Invasion by Strengthening Intestinal Barrier Function and Modulating Immune Responses. Foods, 14(23), 4110. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234110





