Insights into Physicochemical Characteristics, Flavor Development, and Microbial Succession During the Natural Fermentation of Sichuan-Style Black Soybean Soy Sauce
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soy Sauce Samples Collection
2.2. Physicochemical Characteristic Analysis
2.3. Organic Acid and Free Amino Acids
2.4. Volatile Compounds
2.5. High-Throughput Sequencing Analysis
2.6. Metabolic Pathway Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
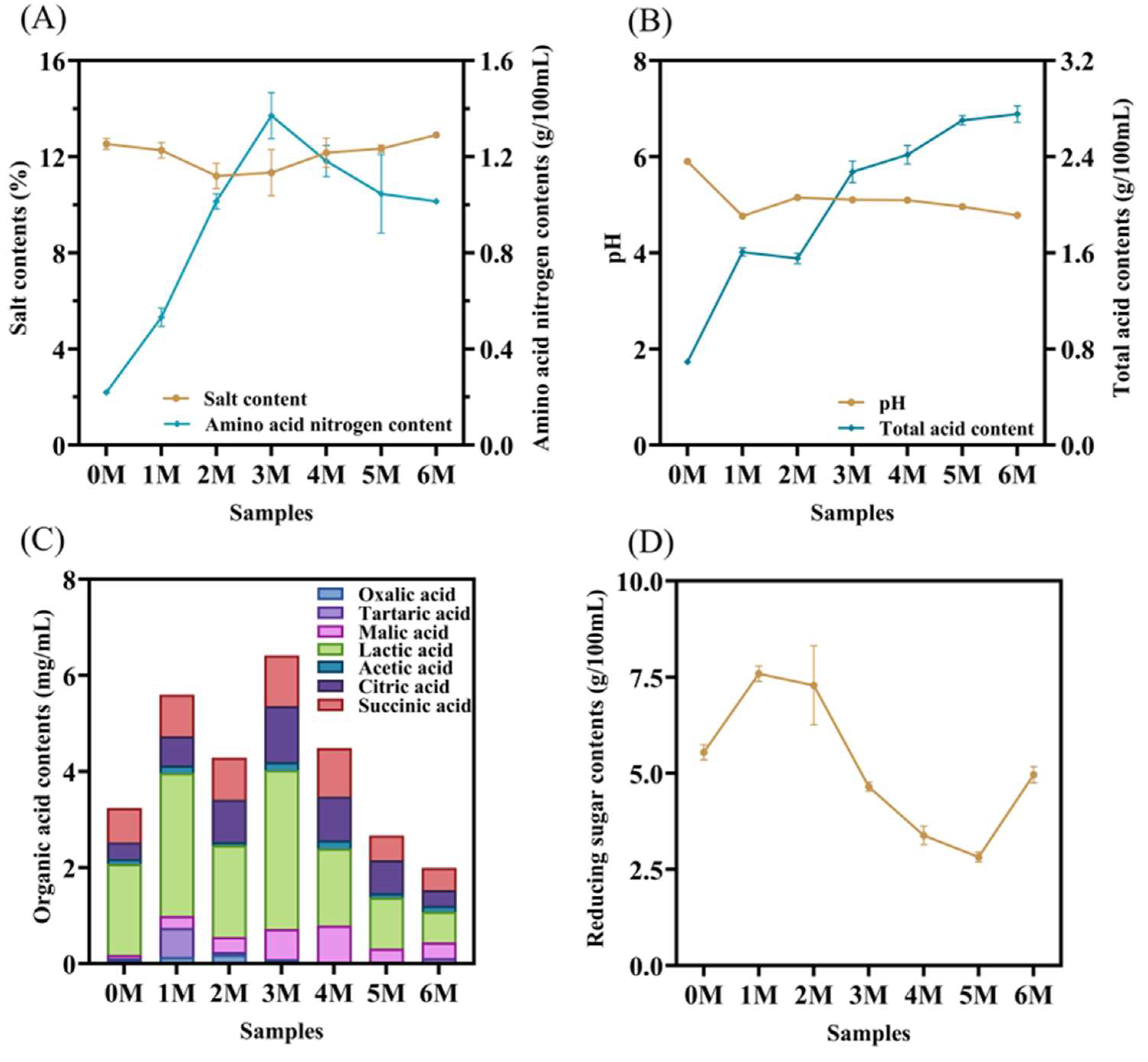
3.1. Dynamic Changes in Physicochemical Properties and Organic Acids
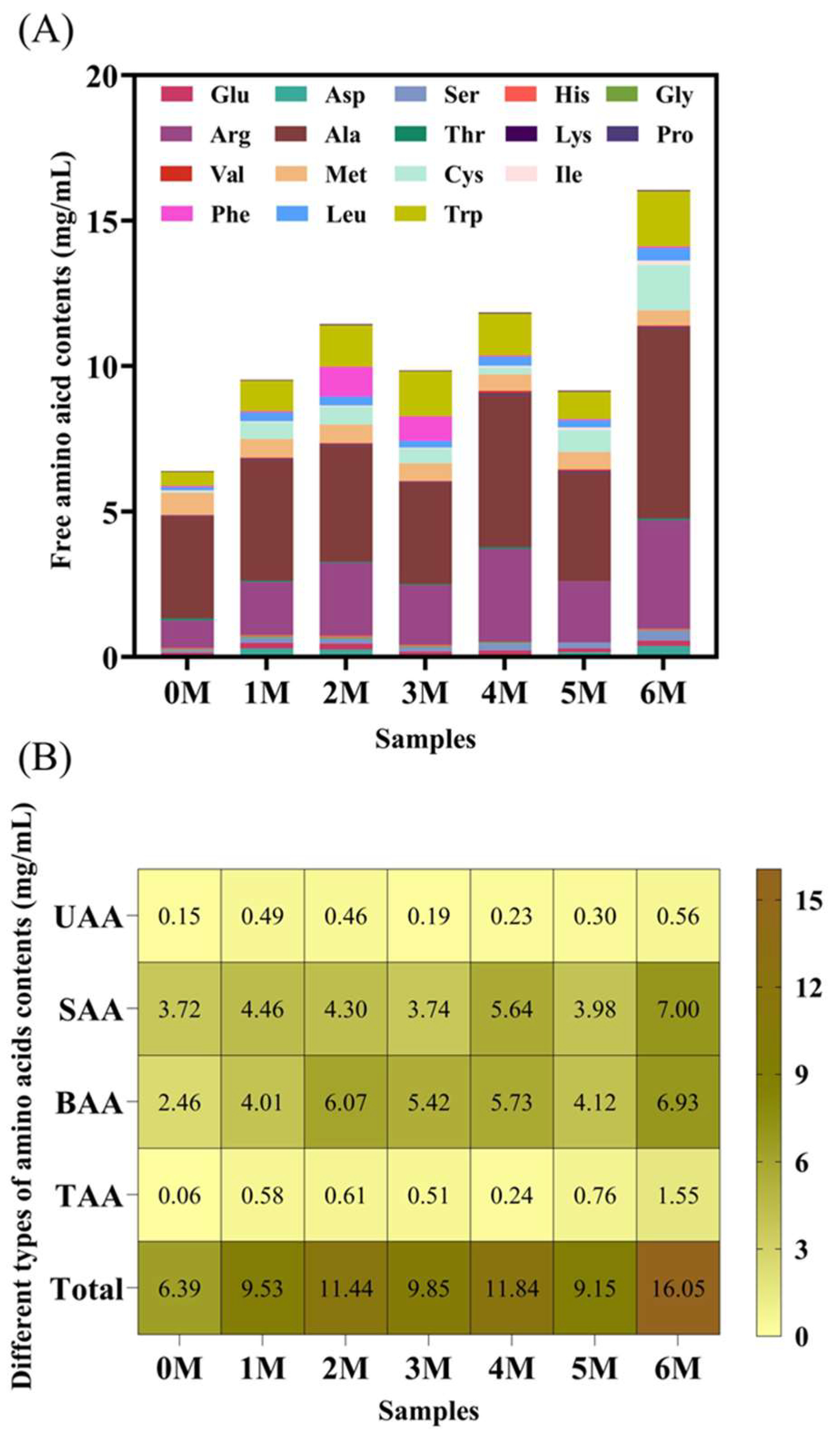
3.2. Changes in Free Amino Acids During Fermentation
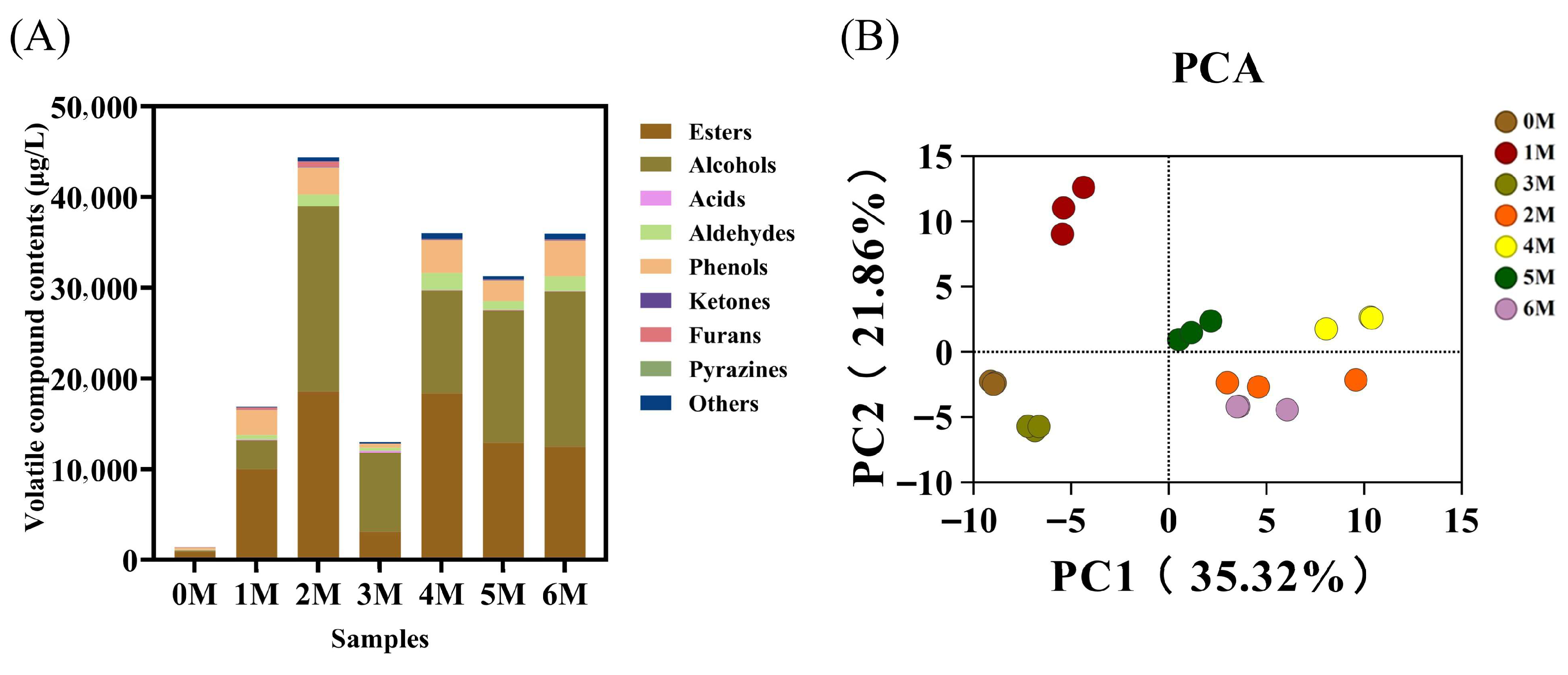
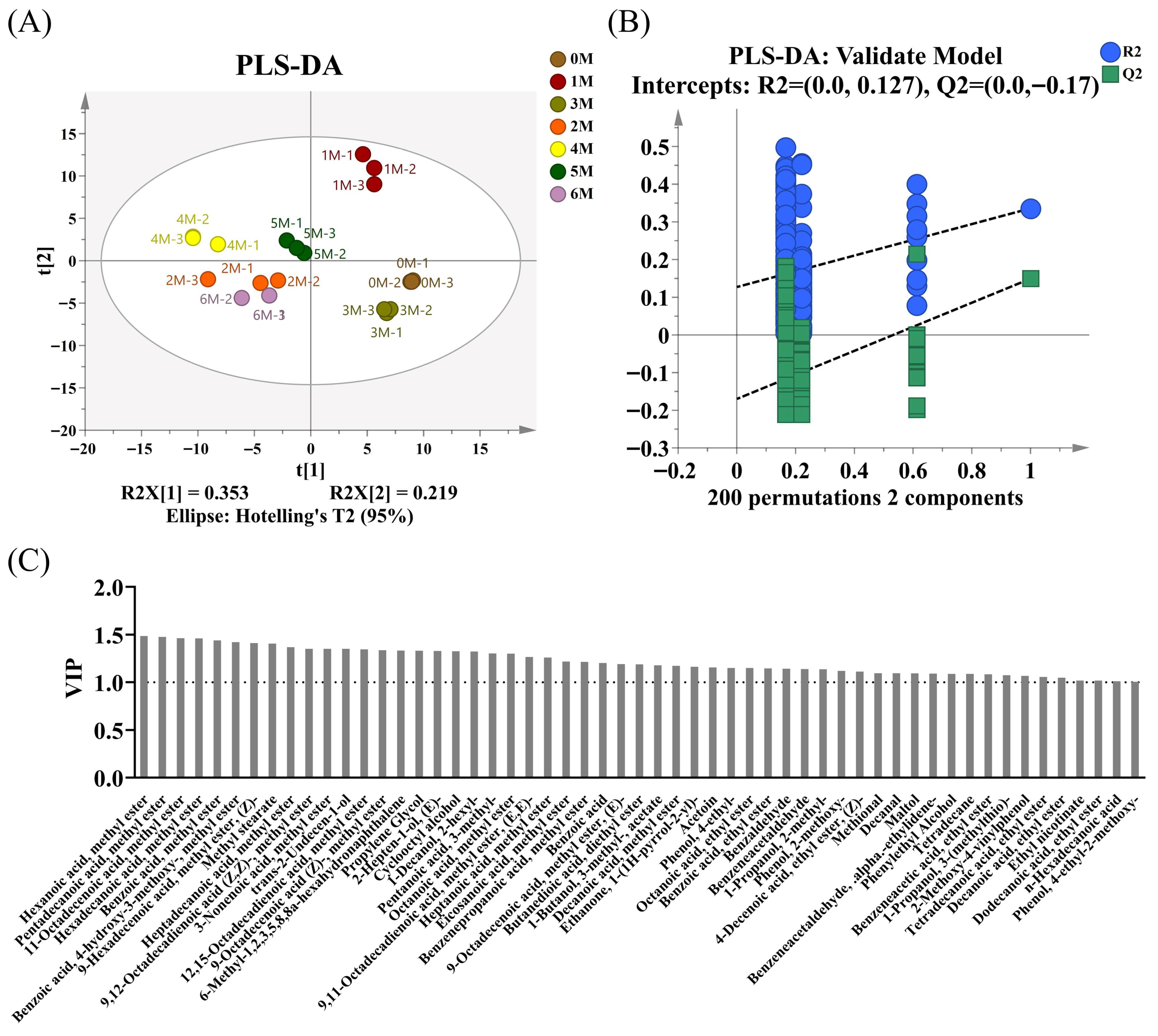
3.3. Changes in Volatile Flavor Compounds During Fermentation
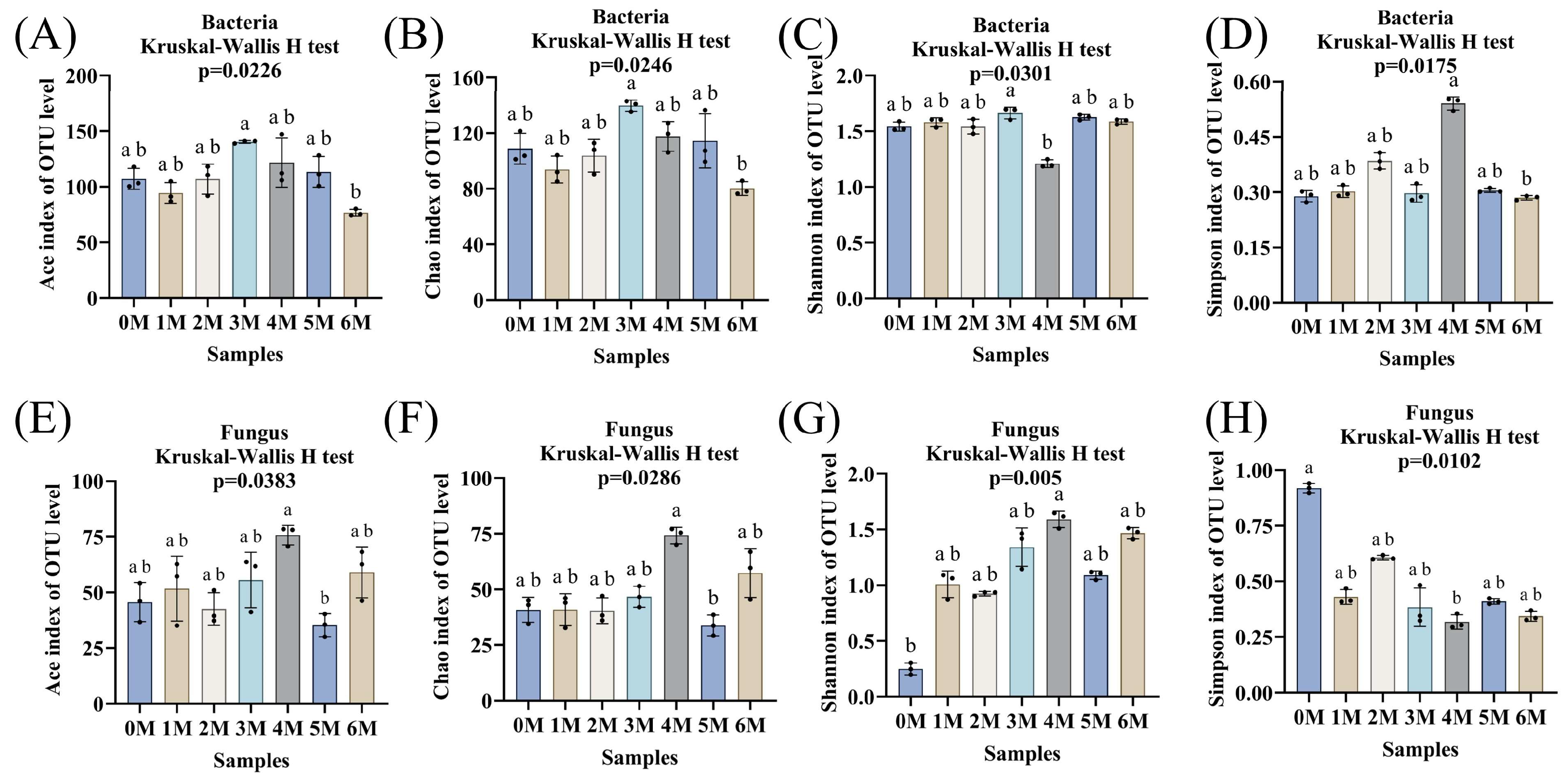
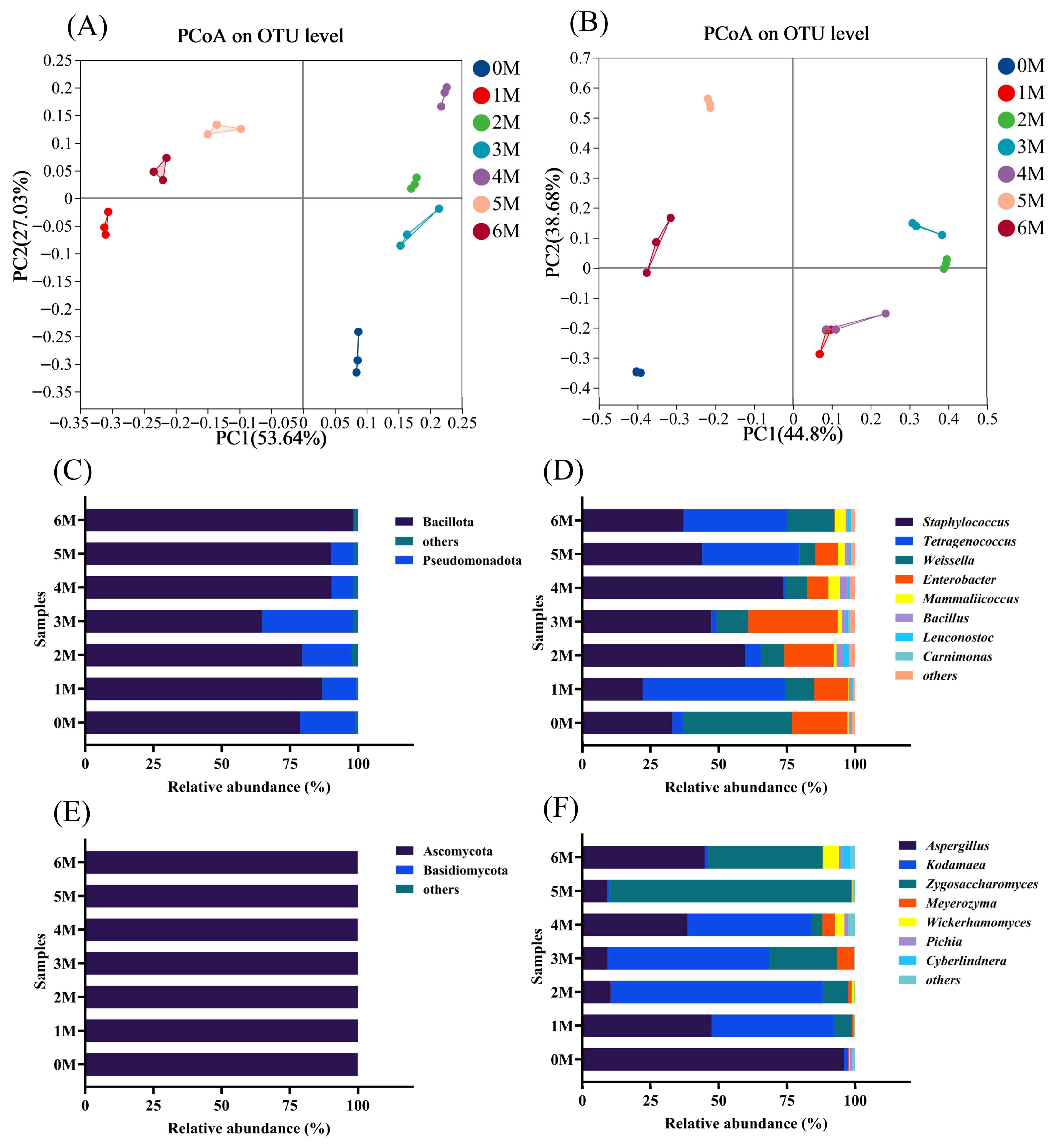
3.4. Succession of Microorganisms During Fermentation
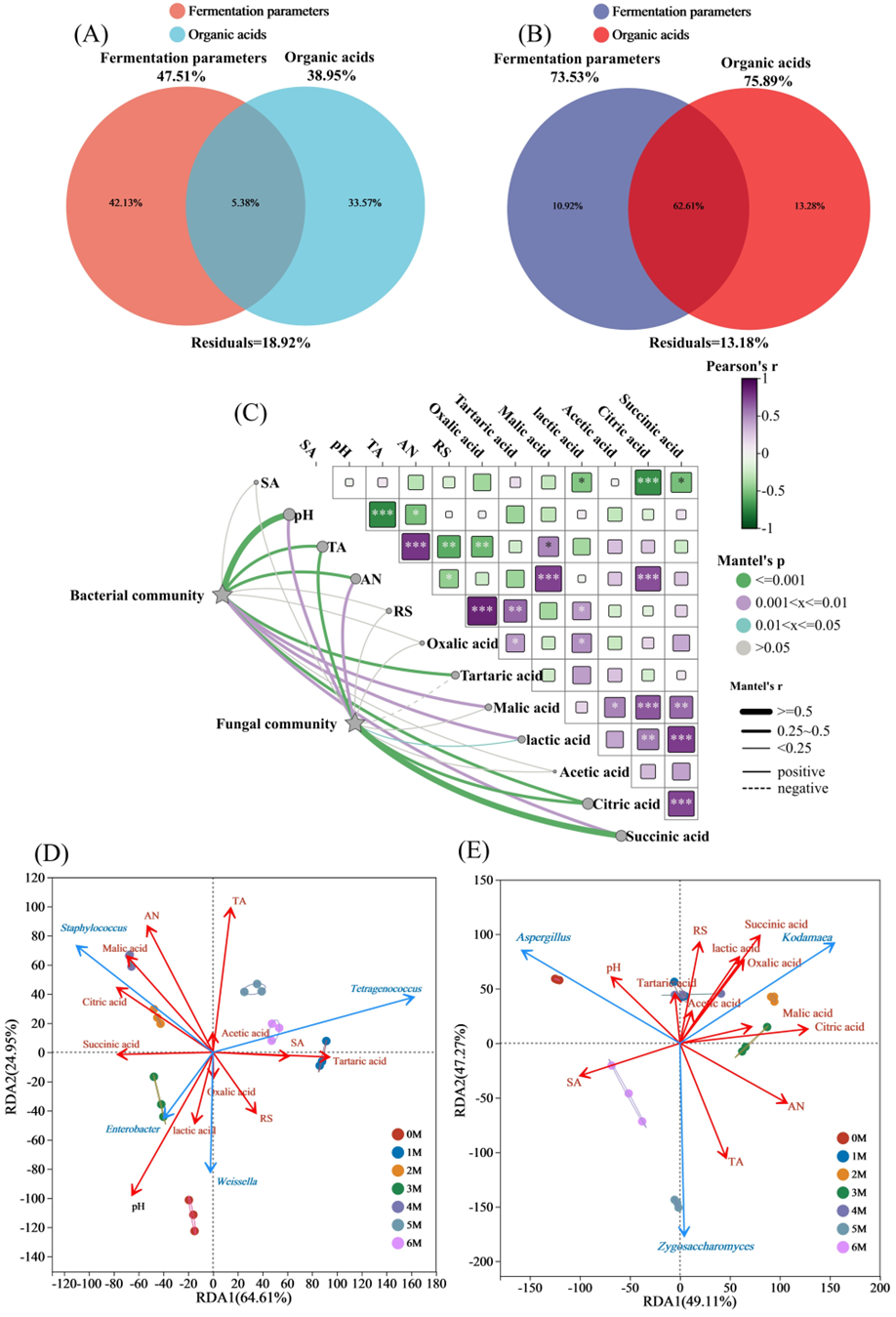
3.5. Drivers of Microbial Succession During Soy Sauce Fermentations
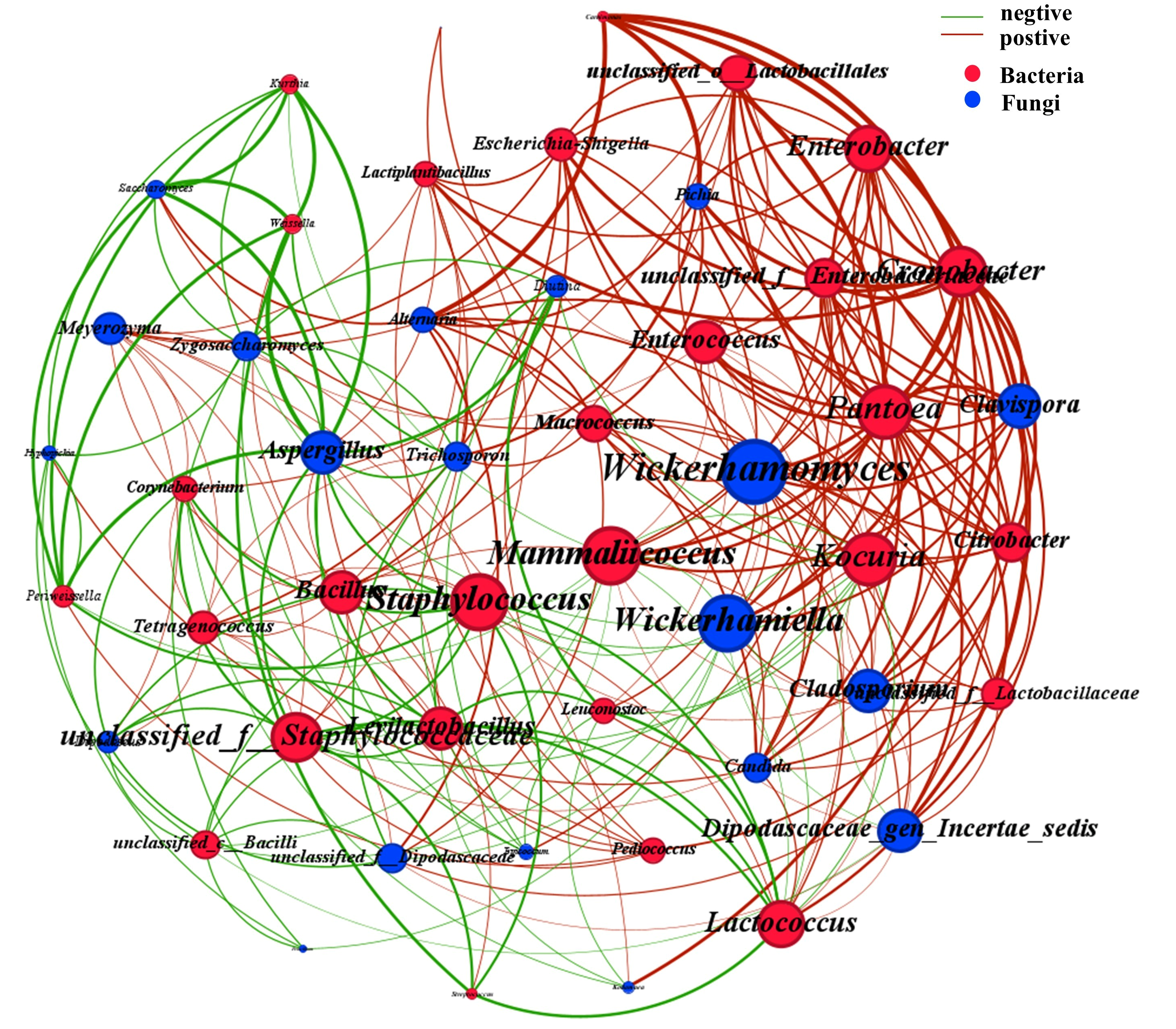
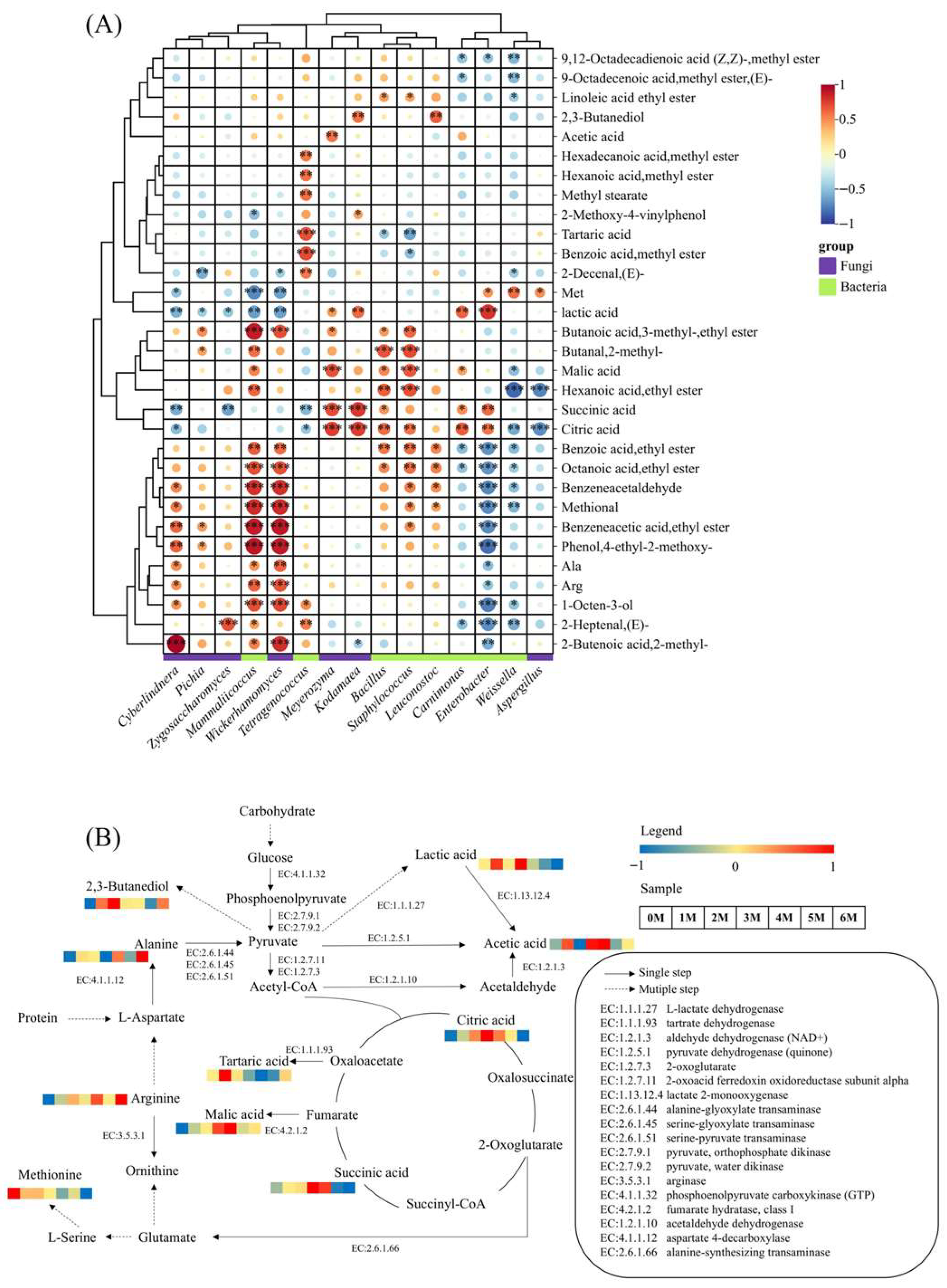
3.6. The Association Between Microorganisms and Specific Volatile Flavor and Taste Substances
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Y.; Tramper, J. Koji—Where East meets West in fermentation. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Imamura, M.; Fukusaki, E. Metabolomics-based investigation of the differences between traditional and modern soy sauce. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2025, 140, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Cui, C.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, M.; Yang, L.; Ren, J. Changes in volatile aroma compounds of traditional Chinese-type soy sauce during moromi fermentation and heat treatment. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Bai, L.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Nie, Y.; Sun, B.; Sun, Y.; Li, T.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, G. Flavor profile and peptide formation in soy sauce fermented from soybean meal by Aspergillus oryzae and Aspergillus niger. Food Chem. 2025, 495, 146631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Q.; Cao, L.; He, L.; Wang, P.; Deng, G.; Li, J.; Fu, J.; Huang, Q.; Ho, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Tracing the change of the volatile compounds of soy sauce at different fermentation times by PTR-TOF-MS, E-nose and GC–MS. Food Chem. X 2025, 25, 102002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Su, G.; Zhao, H.; Cai, Y.; Cui, C.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Zhao, M. Characterisation of aroma profiles of commercial soy sauce by odour activity value and omission test. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R.; Yang, M.; Zhang, L.; Peng, C.; Jin, Y.; Wu, C. Characterizing microbial community and metabolites of Cantonese soy sauce. Food Biosci. 2021, 40, 100872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Sun, M.; Huo, R.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Dong, T.; Zhang, M. Metagenomics and volatile metabolomics reveal microbial succession and flavor formation mechanisms during fermentation of Novel Pasture-style Laozao. Food Chem. X 2025, 28, 102598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Pan, Z.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Zheng, Z. Comparative evaluation of the microbial diversity and metabolite profiles of Japanese-style and Cantonese-style soy sauce fermentation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 976206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Lu, J.; Chen, X. Metagenomic analysis of the relationship between microorganisms and flavor development during soy sauce fermentation. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Meng, F.; Peng, Q.; Lin, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, Y. Elucidating metabolic and flavor evolution in traditional Chinese soy sauce during industrial-scale fermentation: A multi-omics approach. Food Chem. X 2025, 29, 102638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wu, W.; Chen, T.; Huang, M.; Zhao, M. Exploring the core functional microbiota related with flavor compounds in fermented soy sauce from different sources. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.; Lin, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Deng, W.; He, Q.; Chi, Y.; Xu, Z. Salt reduction-driven biogenic amine accumulation in broad bean paste: Insights into physicochemical properties, key enzyme activity, and microbial community dynamics. Food Biosci. 2025, 71, 107138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; He, J.; Dong, B.; Zhao, G. Influence of spatial and temporal diversity and succession of microbial communities on physicochemical properties and flavor substances of soy sauce. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xiong, S.; Du, T.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Wei, T.; Xiong, T.; Xie, M. Elucidating microbial succession dynamics and flavor metabolite formation in korean style spicy cabbage fermentation: Integration of flavoromics, amplicon sequencing, and metagenomics. Food Chem. 2025, 492, 145464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.; Su, H.; Li, W.; Lin, L.; Lin, W.; Luo, L. Effects of microbial community structure and its co-occurrence on the dynamic changes of physicochemical properties and free amino acids in the Cantonese soy sauce fermentation process. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 18186-2025; General Rule for the Quality of Soy Sauce. China General Chamber of Commerce: Beijing, China, 2026.
- Zhang, L.; Xiong, S.; Du, T.; Xu, Y.; Madjirebaye, P.; Huang, G.; Guan, Q.; Xiong, T. Effect of microbiota succession on the dynamics of characteristic flavors and physicochemical properties during the soy sauce fermentation. Food Biosci. 2023, 54, 102883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Simon, C.; Eichelsheim, C.; Mumm, R.; Hall, R.D. Chemical and Sensory Characteristics of Soy Sauce: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11612–11630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chu, M.; Yuan, B.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Mao, J.; et al. The dynamic of physicochemical properties, volatile compounds and microbial community during the fermentation of Chinese rice wine with diverse cereals. Food Res. Int. 2024, 198, 115319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yang, G.; Wang, Z.; Liao, S.; Du, M.; Song, J.; Kan, J. Comparative evaluation of commercial Douchi by different molds: Biogenic amines, non-volatile and volatile compounds. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, Z.; Xu, T.; Lin, H.; Hu, F.; Yu, Y.; Huang, G.; Lei, H.; Xu, Z. Comparison of flavor profiles of Cantonese soy sauces obtained at different fermentation stages. Process Biochem. 2023, 130, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wen, R.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Role of lactic acid bacteria in flavor development in traditional Chinese fermented foods: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 2741–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotzoll, N.; Dunkel, A.; Hofmann, T. Quantitative studies, taste reconstitution, and omission experiments on the key taste compounds in morel mushrooms (Morchella deliciosa Fr.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2705–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Xia, W.; Li, X.; Liu, S. Use of Wine and Dairy Yeasts as Single Starter Cultures for Flavor Compound Modification in Fish Sauce Fermentation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zeng, J.; Lei, H.; Zhao, M. Effect of fermentation containers on the taste characteristics and microbiota succession of soy sauce. Food Chem. 2024, 448, 139066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Han, X.; Tang, Y.; Song, H.; Meng, Q.; Chen, R.; Yu, J.; Yang, P.; Yu, Z. Exploring changes in key aroma-active compounds of soy sauce due to different fermentation processes. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 133, 106393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, M.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Qin, L.; Li, Z.; Yao, J.; Liang, X. Mixed culture of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Acetobacter pasteurianus for acetic acid production. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 79, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Tang, H.; Chen, X.; Guo, L.; Lin, J. Insights into volatile flavor compound variations and characteristic fingerprints in Longpai soy sauce moromi fermentation via HS-GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC× GC-ToF-MS. LWT 2023, 176, 114490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Yi, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yang, R.; Qu, L.; Lu, J.; Zhao, C. A critical review on research status and future prospects of fermented soybean products in China. J. Future Foods 2026, 6, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Feng, X.; Yang, G.; Peng, X.; Du, M.; Song, J.; Kan, J. Impact of aroma-enhancing microorganisms on aroma attributes of industrial Douchi: An integrated analysis using E-nose, GC-IMS, GC-MS, and descriptive sensory evaluation. Food Res. Int. 2024, 182, 114181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Jin, J.; Li, H.; Chen, F.; Fei, Y.; Wang, Y. Characterization of the flavor profile and dynamic changes in Chinese traditional fish sauce (Yu-lu) based on electronic nose, SPME-GC-MS and HS-GC-IMS. Food Res. Int. 2024, 192, 114772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Kan, Q.; Yang, L.; Huang, W.; Wen, L.; Fu, J.; Liu, Z.; Lan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Ho, C.; et al. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in soy sauce by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry-olfactometry, headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry, odor activity value, and aroma recombination and omission analysis. Food Chem. 2023, 419, 135995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, D.; Shi, Y.; Meng, R.; Yong, Q.; Shi, Z.; Shao, D.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y. Decoding the Different Aroma-Active Compounds in Soy Sauce for Cold Dishes via a Multiple Sensory Evaluation and Instrumental Analysis. Foods 2023, 12, 3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devanthi, P.V.P.; Gkatzionis, K. Soy sauce fermentation: Microorganisms, aroma formation, and process modification. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, H. Research progress on volatile compounds and microbial metabolism of traditional fermented soybean products in China. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, Q.; Yan, D.; Cai, L. Analysis of microbial Diversity in Soy Sauce fermented grains by Illumina High-throughput sequencing technique. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 440, 22044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Lei, J.; Yang, L.; Kan, Q.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Chen, C.; He, L.; Fu, J.; Ho, C.; et al. Metagenomics and untargeted metabolomics analyses to unravel the formation mechanism of characteristic metabolites in Cantonese soy sauce during different fermentation stages. Food Res. Int. 2024, 181, 114116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Xiao, Z.; Tang, J.; Wu, C.; Luo, X.; Zhou, S. Characteristics of microbial community, taste, aroma of high-salt liquid-state secondary fortified fermented soy sauce. LWT 2023, 182, 114792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xie, Z.; Huang, M.; Tong, X.; Hou, S.; Tin, H.; Zhao, M. Decoding temperature-driven microbial community changes and flavor regulation mechanism during winter fermentation of soy sauce. Food Res. Int. 2024, 177, 113756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Sun, Z.; Guo, J.; Li, D.; Lin, X.; Zhang, S.; Ji, C. Improving soy sauce quality via co-fermentation with indigenous Tetragenococcus: Reducing biogenic amines and enhancing flavor. Food Res. Int. 2025, 217, 116776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wang, C. Effect of Tetragenococcus halophilus, Zygosaccharomyces rouxii, and Torulopsis versatilis addition sequence on soy sauce fermentation. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 69, 102662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chen, T.; Zhao, M.; Feng, Y. Effect of co-inoculation of different halophilic bacteria and yeast on the flavor of fermented soy sauce. Food Biosci. 2023, 51, 102292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Lu, J.; Nie, Y.; Li, C.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Amino Acids Drive the Deterministic Assembly Process of Fungal Community and Affect the Flavor Metabolites in Baijiu Fermentation. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0264022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Ma, Z.; Huang, H.; Zheng, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhong, Q. Microbial succession and organic acid metabolism during spontaneous calamondin fermentation: The vital role of Pichia. Food Res. Int. 2025, 209, 116200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, C.; Ilham, Z.; Samsudin, N.; Sassi, S.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q. Microbial consortia and up-to-date technologies in global soy sauce production: A review. Int. Food Res. J. 2023, 30, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Fang, B.; Manzoor, A.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Mohamad, O.A.A.; Shu, W.; Li, W. Revealing the salinity adaptation mechanism in halotolerant bacterium Egicoccus halophilus EGI 80432(T) by physiological analysis and comparative transcriptomics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 2497–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Lu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, Q. Comprehensive investigation on volatile and non-volatile metabolites in low-salt doubanjiang with different fermentation methods. Food Chem. 2023, 413, 135588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Ding, L.; Yao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Pan, Z.; Kong, D. Extracellular Proteome Analysis and Flavor Formation During Soy Sauce Fermentation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Qian, Y.; Ji, F.; Chen, J.; Han, B. Microbial composition during Chinese soy sauce koji-making based on culture dependent and independent methods. Food Microbiol. 2013, 34, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, G.; Tang, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, R.; Ye, M.; Ming, J.; Wu, Y.; Xu, F.; Lai, X.; et al. Correlation between autochthonous microbial communities and flavor profiles during the fermentation of mustard green paocai (Brassica juncea Coss.), a typical industrial-scaled salted fermented vegetable. LWT 2022, 172, 114212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Lu, Z.; Peng, M.; Liu, Z.; Chai, L.; Zhang, X.; Shi, J.; Li, Q.; Xu, Z. Combined effects of fermentation starters and environmental factors on the microbial community assembly and flavor formation of Zhenjiang aromatic vinegar. Food Res. Int. 2022, 152, 110900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Peng, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, F.; Mu, H.; Huang, S.; Wu, K.; Sheng, J.; Tian, Y.; et al. Microbiomics and flavoromics insights into the effect of high temperature steam pretreatment on the flavor of walnut meal-based soy sauce. Food Chem. X 2025, 31, 103092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, W.; Lu, J.; Wu, D.; Ge, F. Construction of a synthetic microbial community and its application in salt-reduced soy sauce fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2025, 128, 104738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Lu, X.; Xing, L.; Ho, S.W.A.; Kwan, H.S. Genomic and transcriptomic comparison of Aspergillus oryzae strains: A case study in soy sauce koji fermentation. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 45, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, F.; Jin, Z.; Xia, X. Ecological succession and functional characteristics of lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 5841–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Peng, D.; Zhang, W.; Duan, M.; Ruan, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhou, S.; Fang, Q. Effect of aroma-producing yeasts in high-salt liquid-state fermentation soy sauce and the biosynthesis pathways of the dominant esters. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, Y.; Yoshimura, T.; Sawada, K.; Tsuge, K.; Nagano, Y.; Yoshizaki, Y.; Goto, M.; Kobayashi, G. Crucial role of early addition of Wickerhamiella versatilis in enhancing aroma formation during soy sauce fermentation. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2025, 139, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Sun, C.; Shen, Z.; Tian, Y.; Mo, F.; Wang, B.; Liu, B.; Wang, C. Untargeted metabolomic profiling of Aspergillus sojae 3.495 and Aspergillus oryzae 3.042 fermented soy sauce koji and effect on moromi fermentation flavor. LWT 2023, 184, 115027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Park, S.; Pak, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Whon, T.W.; Cho, K.; Kwak, S.; Son, H.; Roh, S.W. Effects of total microbiota-containing backslop from 450-day-fermented kimchi on microbe and metabolite dynamics. Food Chem. 2025, 468, 142420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Z.; Thakur, K.; Hu, F.; Khan, M.R.; Wei, Z. Metabolomics and HS-SPME-GC-MS-based analysis of quality succession patterns and flavor characteristics changes during the fermentation of Lycium barbarum and Polygonatum cyrtonema compound wine. Food Res. Int. 2024, 184, 114270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compounds | Taste Attributes | Threshold (mg/mL) 1 | Content (mg/mL) | TAV 2 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 M | 1 M | 2 M | 3 M | 4 M | 5 M | 6 M | 0 M | 1 M | 2 M | 3 M | 4 M | 5 M | 6 M | |||
| Oxalic acid | Sour | 0.504 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.19 ± 0.05 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Tartaric acid | Sour | 0.3 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.60 ± 0.11 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | <1 | 2.01 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Malic acid | Sour | 0.495 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.25 ± 0.05 | 0.31 ± 0.00 | 0.63 ± 0.00 | 0.76 ± 0.21 | 0.27 ± 0.04 | 0.32 ± 0.04 | <1 | <1 | <1 | 1.27 | 1.53 | <1 | <1 |
| Lactic acid | Sour | 1.26 | 1.89 ± 0.03 | 2.97 ± 0.16 | 1.91 ± 0.06 | 3.30 ± 0.09 | 1.60 ± 0.12 | 1.06 ± 0.06 | 0.64 ± 0.06 | 1.50 | 2.36 | 1.52 | 2.62 | 1.27 | <1 | <1 |
| Acetic acid | Sour | 0.0768 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 1.32 | 2.04 | <1 | 2.21 | 2.25 | 1.26 | 1.65 |
| Citric acid | Sour | 0.45 | 0.34 ± 0.09 | 0.61 ± 0.02 | 0.88 ± 0.01 | 1.16 ± 0.02 | 0.91 ± 0.09 | 0.68 ± 0.03 | 0.32 ± 0.03 | <1 | 1.35 | 1.96 | 2.58 | 2.01 | 1.52 | <1 |
| Succinic acid | Sour | 0.106 | 0.72 ± 0.00 | 0.87 ± 0.03 | 0.88 ± 0.02 | 1.06 ± 0.02 | 1.01 ± 0.16 | 0.51 ± 0.03 | 0.46 ± 0.03 | 6.77 | 8.19 | 8.29 | 9.95 | 9.54 | 4.85 | 4.37 |
| Aspartate | Umami | 1 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.29 ± 0.07 | 0.26 ± 0.04 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 0.37 ± 0.03 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Glutamine | Umami | 0.3 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.20 ± 0.04 | 0.20 ± 0.02 | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.20 ± 0.10 | 0.13 ± 0.08 | 0.19 ± 0.08 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Serine | Sweet | 1.5 | 0.09 ± 0.00 | 0.18 ± 0.04 | 0.18 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 0.24 ± 0.10 | 0.20 ± 0.10 | 0.34 ± 0.10 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Glycine | Sweet | 1.3 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | - | 0.03 ± 0.00 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | - | <1 |
| Histidine | Bitter | 0.9 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | - | - | 0.04 ± 0.00 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | - | - | <1 |
| Arginine | Bitter | 0.5 | 0.95 ± 0.08 | 1.82 ± 0.42 | 2.51 ± 0.28 | 2.05 ± 0.50 | 3.19 ± 1.60 | 2.11 ± 1.47 | 3.74 ± 1.47 | 1.89 | 3.64 | 5.02 | 4.10 | 6.39 | 4.21 | 7.48 |
| Threonine | Sweet | 2.6 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | - | <1 |
| Alanine | Sweet | 0.6 | 3.50 ± 0.25 | 4.14 ± 0.97 | 4.00 ± 0.46 | 3.47 ± 0.84 | 5.23 ± 2.60 | 3.73 ± 2.57 | 6.53 ± 2.57 | 5.83 | 6.90 | 6.67 | 5.79 | 8.71 | 6.21 | 10.89 |
| Proline | Sweet | 3 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Valine | Bitter | 0.4 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.04 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 0.05 ± 0.04 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Methionine | Bitter | 0.3 | 0.76 ± 0.03 | 0.64 ± 0.04 | 0.65 ± 0.06 | 0.61 ± 0.02 | 0.57 ± 0.06 | 0.60 ± 0.06 | 0.53 ± 0.06 | 2.53 | 2.14 | 2.15 | 2.04 | 1.90 | 2.01 | 1.76 |
| Cysteine | Tasteless | / | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.58 ± 0.19 | 0.61 ± 0.16 | 0.51 ± 0.13 | 0.24 ± 0.05 | 0.76 ± 0.55 | 1.55 ± 0.55 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| Isoleucine | Bitter | 0.9 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.09 ± 0.08 | 0.15 ± 0.08 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Leucine | Bitter | 1.9 | 0.11 ± 0.07 | 0.30 ± 0.09 | 0.31 ± 0.03 | 0.23 ± 0.05 | 0.30 ± 0.15 | 0.24 ± 0.17 | 0.42 ± 0.17 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Phenylalanine | Bitter | 0.2 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 1.02 ± 0.11 | 0.84 ± 0.19 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Tryptophan | Bitter | / | 0.47 ± 0.09 | 1.05 ± 0.31 | 1.44 ± 1.23 | 1.55 ± 0.38 | 1.44 ± 0.72 | 0.94 ± 0.65 | 1.91 ± 0.65 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| Compounds | Odor Threshold (μg/L) 1 | Odor Description 2 | ROAV 3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 M | 1 M | 2 M | 3 M | 4 M | 5 M | 6 M | |||
| Phenol, 4-ethyl-2-methoxy- | 89.3 | spicy and clove-like with medicinal | <1 | 4.70 | 13.11 | 2.75 | 29.78 | 19.15 | 36.36 |
| 2-Methoxy-4-vinylphenol | 12.02 | dry, woody, fresh | 21.63 | 181.11 | 111.63 | 3.55 | 25.28 | 15.63 | 14.10 |
| Butanal, 2-methyl- | 16 | musty, chocolate, nutty | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | 26.76 | <1 | <1 |
| 2-Heptenal, (E)- | 40 | green, fatty, oily, fruity | <1 | 1.21 | 1.04 | <1 | 1.35 | 2.60 | 1.34 |
| Methional | 0.45 | musty, tomato, potato | 4.77 | 53.20 | 79.61 | 37.04 | 114.66 | 66.67 | 119.05 |
| Benzeneacetaldehyde | 235.3 | honey, floral rose, sweet | <1 | <1 | 2.32 | <1 | 2.89 | 1.80 | 3.11 |
| 2-Decenal, (E)- | 10 | waxy, fatty, earthy | <1 | 1.48 | 1.15 | <1 | <1 | 1.28 | <1 |
| 2-Butenoic acid, 2-methyl- | 5.8 | sour | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | 1.32 |
| 1-Octen-3-ol | 1.5 | mushroom, earthy | 40.68 | 125.87 | 74.01 | 68.01 | 144.23 | 101.95 | 149.35 |
| 2,3-Butanediol | 100 | fruity, creamy, oily | <1 | <1 | 1.17 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Butanoic acid, 3-methyl-, ethyl ester | 6.89 | sweet, diffusive, estry | <1 | <1 | <1 | 3.12 | 8.85 | 1.82 | 4.81 |
| Hexanoic acid, methyl ester | 14 | ethereal, fruity, pineapple, | <1 | 5.94 | <1 | <1 | 2.74 | 1.86 | <1 |
| Hexanoic acid, ethyl ester | 5 | fruity, winey, waxy | <1 | 17.52 | 30.87 | 23.47 | 41.98 | 38.04 | 23.44 |
| Octanoic acid, ethyl ester | 12.9 | waxy, sweet, musty | <1 | 16.33 | 73.03 | <1 | 80.26 | 45.91 | 76.13 |
| Benzoic acid, methyl ester | 73 | floral, fruity | <1 | 7.56 | <1 | <1 | 1.59 | 1.82 | 0.73 |
| Benzoic acid, ethyl ester | 1430 | sweet, wintergreen, fruity | <1 | <1 | 1.75 | <1 | 1.87 | 1.38 | 1.58 |
| Benzeneacetic acid, ethyl ester | 407 | honey | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | 1.54 | <1 | 1.85 |
| Hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester | 2 | oily, waxy, fatty | 234.31 | 1648.23 | 448.54 | 95.39 | 836.49 | 716.20 | 207.97 |
| Methyl stearate | 3 | oily, waxy | 3.26 | 33.35 | 11.77 | 1.21 | 13.23 | 18.14 | 2.38 |
| 9-Octadecenoic acid, methyl ester, (E)- | 40 | oily | 1.64 | 11.02 | 9.95 | 1.02 | 8.88 | 8.80 | 2.48 |
| 9,12-Octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z)-, methyl ester | 35 | oily, fatty, woody | 4.45 | 28.53 | 15.81 | 3.39 | 27.54 | 23.29 | 9.20 |
| Linoleic acid ethyl ester | 4.5 | fatty, fruity, oily | 1.44 | 24.19 | 48.65 | 1.40 | 37.22 | 22.48 | 25.40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Y.; Liao, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Fu, Q.; He, Q.; Chi, Y.; Xu, Z. Insights into Physicochemical Characteristics, Flavor Development, and Microbial Succession During the Natural Fermentation of Sichuan-Style Black Soybean Soy Sauce. Foods 2025, 14, 4049. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234049
Xie Y, Liao S, Li Y, Wang X, Lu Y, Fu Q, He Q, Chi Y, Xu Z. Insights into Physicochemical Characteristics, Flavor Development, and Microbial Succession During the Natural Fermentation of Sichuan-Style Black Soybean Soy Sauce. Foods. 2025; 14(23):4049. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234049
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Yutian, Shenglan Liao, Youming Li, Xianbin Wang, Yunhao Lu, Qixu Fu, Qiang He, Yuanlong Chi, and Zhenghong Xu. 2025. "Insights into Physicochemical Characteristics, Flavor Development, and Microbial Succession During the Natural Fermentation of Sichuan-Style Black Soybean Soy Sauce" Foods 14, no. 23: 4049. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234049
APA StyleXie, Y., Liao, S., Li, Y., Wang, X., Lu, Y., Fu, Q., He, Q., Chi, Y., & Xu, Z. (2025). Insights into Physicochemical Characteristics, Flavor Development, and Microbial Succession During the Natural Fermentation of Sichuan-Style Black Soybean Soy Sauce. Foods, 14(23), 4049. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234049






