Highly Sensitive Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Clenbuterol and Structurally Similar Beta2-Agonists in Meat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of CLE Immunogen
2.3. Preparation of CLE Coating Antigen
2.4. Animal Immunization and Antibody Production
2.5. ELISA of CLE
2.6. Preparation and Characterization of Gold Nanoparticles
2.7. Immobilization of Antibodies on GNPs
2.8. Production of Immunochromatographic Test Strips
2.9. Preparation of Spiked Meat Samples
2.10. LFIA of CLE
2.11. Registration and Processing of ELISA and LFIA Data
2.12. Study of LFIA Cross-Reactivity and Recovery
3. Results and Discussion
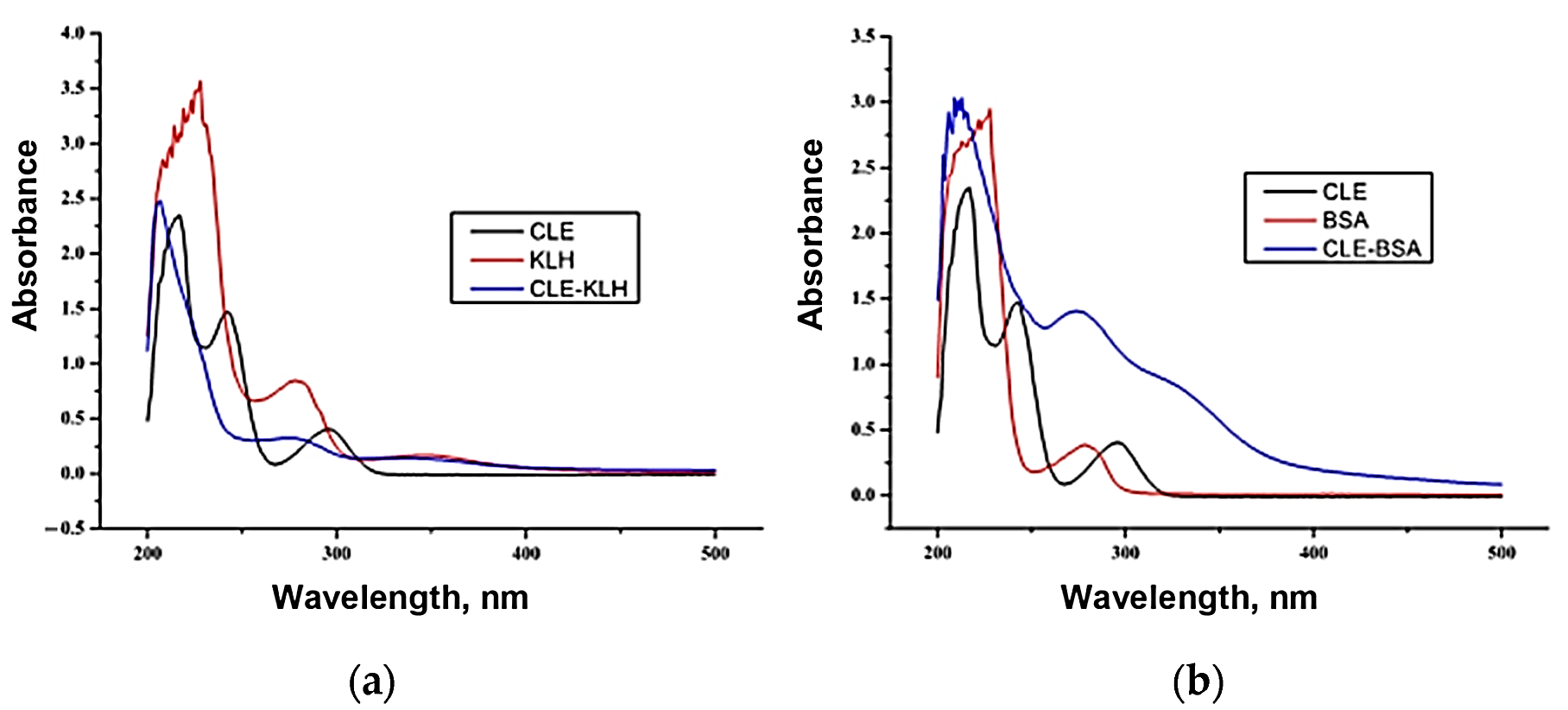
3.1. Immunoreactants Characterization
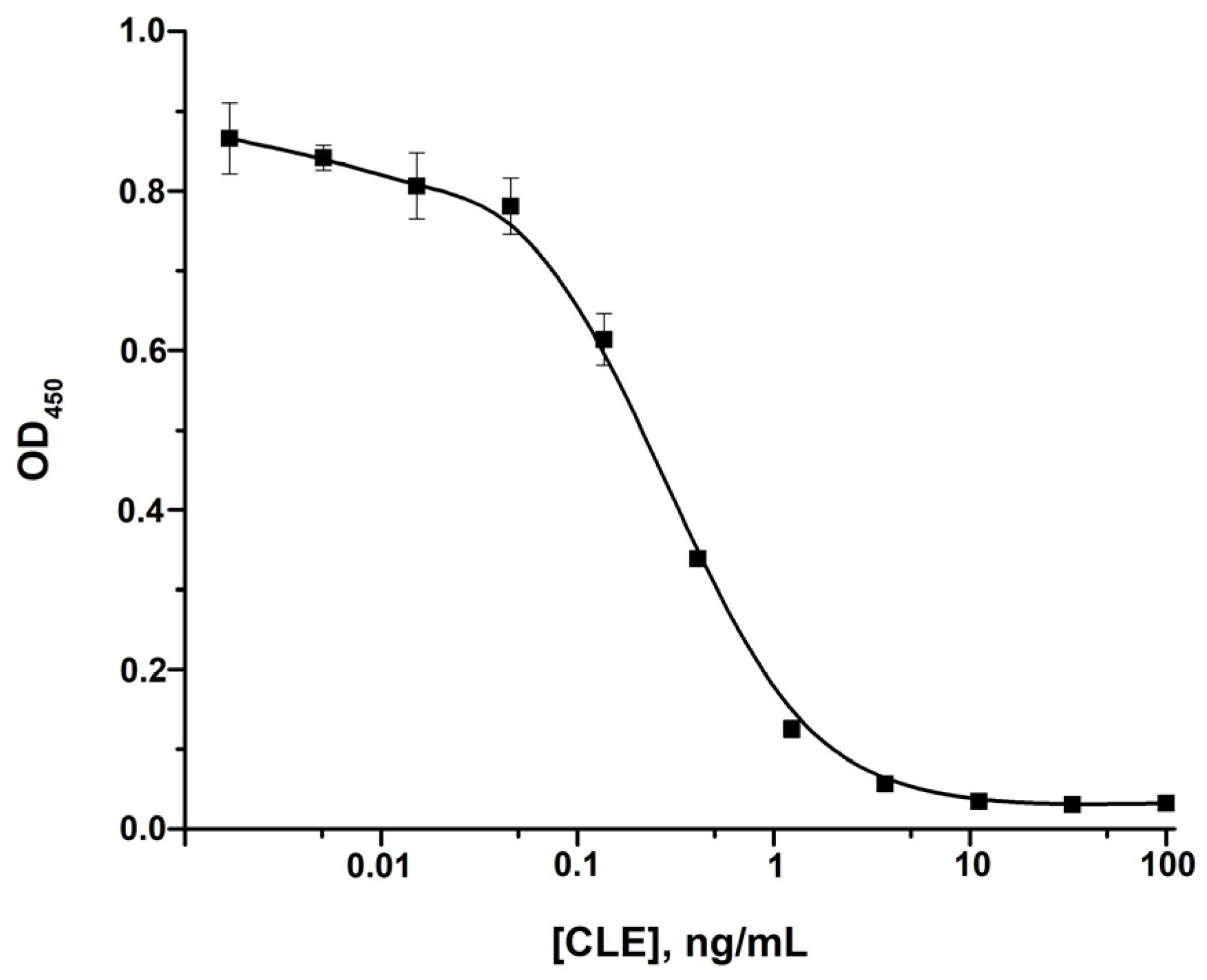
3.2. ELISA of CLE
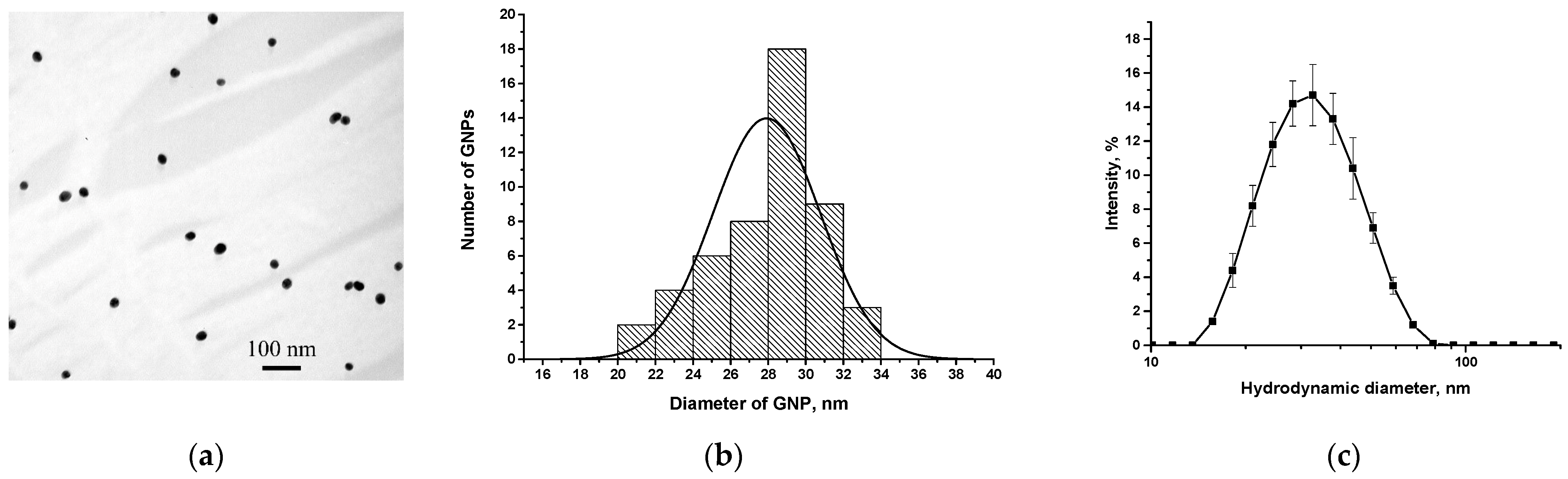
3.3. Synthesis and Characterization of GNPs and Their Conjugation with Antibodies
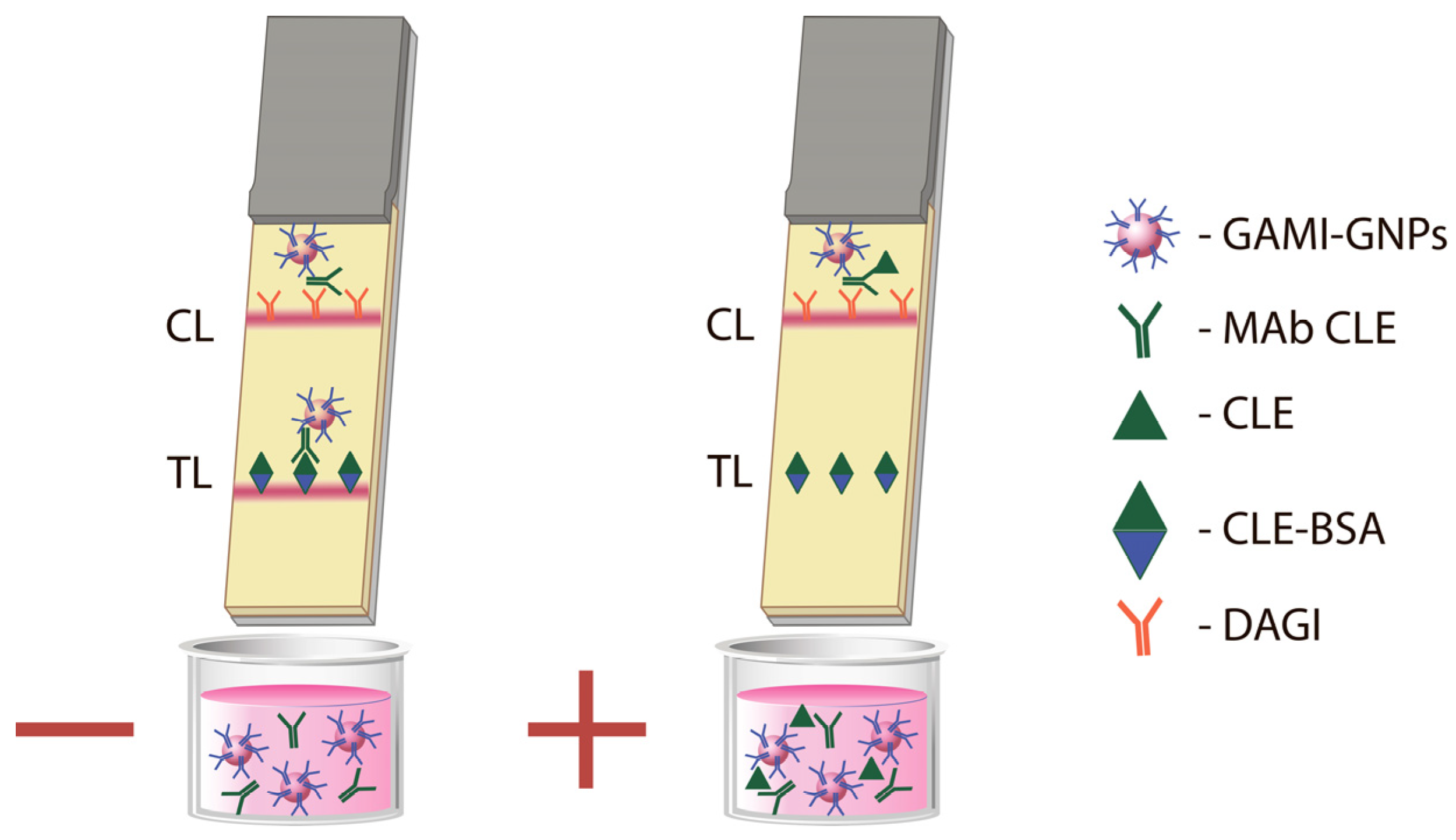
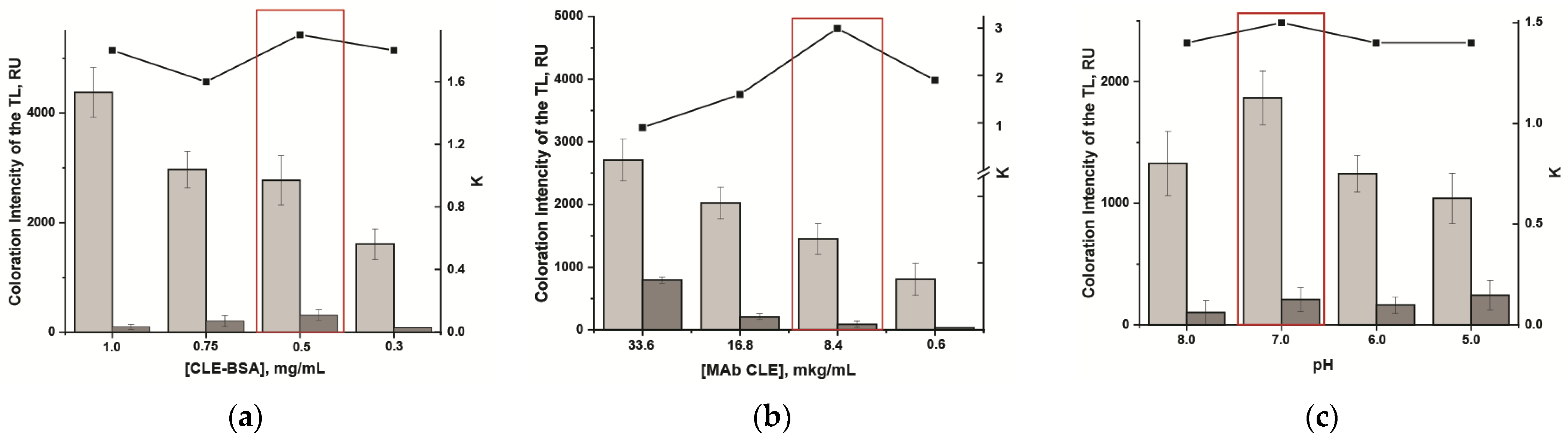
3.4. Development of the LFIA
3.5. Specificity of the Developed LFIA
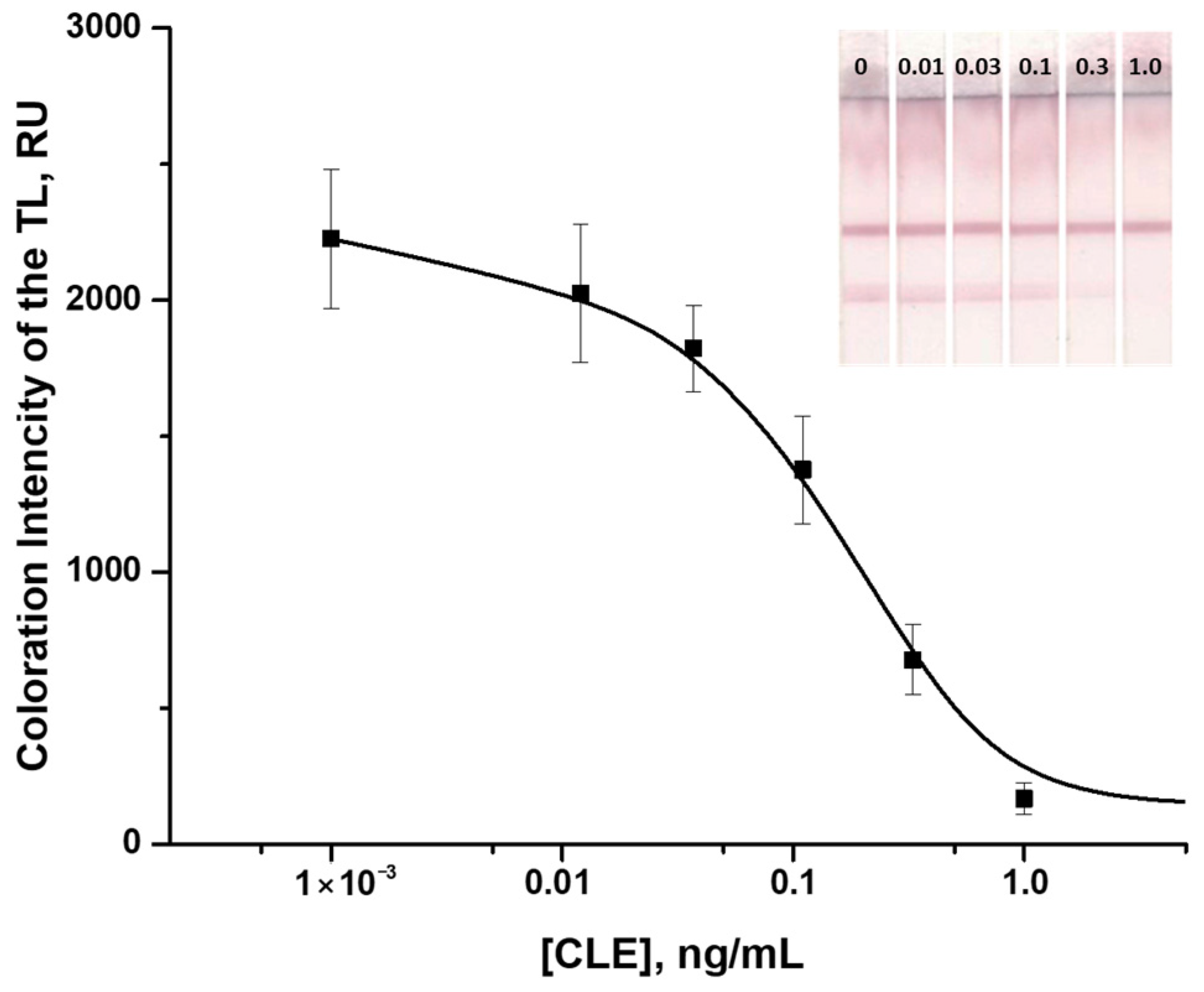
3.6. Determination of CLE in Meat Samples
3.7. Comparison of the Developed LFIA with Other LFIAs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, L.; Pan, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. Current progress in the detection of adrenergic receptor agonist residues in animal-derived foods. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 158, 116875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, P.; Su, X. Current advancement in analysis of β-agonists. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85 Pt C, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephany, R.W. Hormonal growth promoting agents in food producing animals. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2010, 195, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.J.; Wu, Y.F.; Ye, F.; Zha, Y.; Sun, J.; Shentu, X.; Yu, X.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.F. A clenbuterol detection method based on magnetic separation up-conversion fluorescent probe. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centner, T.J.; Petetin, L. Divergent approaches regulating beta agonists and cloning of animals for food: USA and European Union. Soc. Anim. 2020, 28, 613–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilger, A.C.; Johnson, B.J.; Brent, P.; Ellis, R.L. Comparison of beta-ligands used in cattle production: Structures, safety, and biological effects. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Gao, H.; Liu, X.; Gao, S.; Zhou, L.; Wang, F.; Chen, M. Electromembrane extraction of clenbuterol from swine urine for monitoring illegal use in livestock. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 3966–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śniegocki, T.; Sell, B.; Posyniak, A. Analysis of β-agonists in different biological matrices by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Vet. Res. 2021, 65, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S.; Yu, S.; Le, Y. Current advances in immunoassays for the detection of β2-agonists. Foods 2022, 11, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jigyasa; Rajput, J.K. Nanosensors: A smart remedy for early detection of clenbuterol contamination in food. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, Q.A.; Vu, T.H.H.; Ngo, V.K.T.; Kennedy, I.R.; Lee, N.A.; Allan, R. Development of an ELISA to detect clenbuterol in swine products using a new approach for hapten design. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 6045–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, N.A.A.; Salam, F.; Sulaiman, Y. Development of polyclonal antibody against clenbuterol for immunoassay application. Molecules 2018, 23, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Z.; Liu, C.; Xu, J.; Jia, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D.; et al. Chemical staining enhanced enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for sensitive determination of clenbuterol in food. Food Chem. 2023, 400, 134012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, G.; Sun, X.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Wu, T.; Wang, F. New advances in lateral flow immunoassay (LFI) technology for food safety detection. Molecules 2022, 27, 6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, W.; Wang, P.; Su, X. A paper-based competitive lateral flow immunoassay for multi β-agonist residues by using a single monoclonal antibody labelled with red fluorescent nanoparticles. Mikrochim. Acta 2018, 185, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Hu, S.; Zhang, G.; Peng, J.; Xia, J.; Lai, W. Integrated immunochromatographic assay for qualitative and quantitative detection of clenbuterol. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 577, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Dou, L.; Yao, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, M.; Yin, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J. Nanozyme amplification mediated on-demand multiplex lateral flow immunoassay with dual-readout and broadened detection range. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Hu, H.; Tian, Y.; Jia, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D. Highly sensitive colorimetric/surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy immunoassay relying on a metallic core–shell Au/Au nanostar with clenbuterol as a target analyte. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 8362–8369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Shu, R.; Nie, C.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.; Ji, Y.; Yin, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J. Bioresource-derived tannic acid-supported immuno-network in lateral flow immunoassay for sensitive clenbuterol monitoring. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Shi, L.; Li, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Liao, X.; Wu, H.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; et al. “Potential scalpel”: A bioassisted ultrafast staining lateral flow immunoassay from de novo to results. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 4095–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Tian, Y.; Yin, X.; Ren, J.; Su, L.; Xu, J.; Jia, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D. A lateral flow immunoassay based on chemisorbed probes in virtue of hydrogen bond receptors on the Bi2S3 NPs. Food Chem. 2023, 401, 134133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, R.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, S.; Sun, J.; Dou, L.; Zhu, M.; Bu, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, J. “From food waste to food supervision”—Cuttlefish ink natural nanoparticles-driven dual-mode lateral flow immunoassay for advancing point-of-care tests. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 219, 114807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Liu, Z.; Xie, H.; Fang, Y.; Quan, Q.; Shen, X.; Lei, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, X. Ultrasensitive magnetic assisted lateral flow immunoassay based on chiral monoclonal antibody against R-(−)-salbutamol of broad-specificity for 38 β-agonists detection in swine urine and pork. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 4112–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C. Recent advances in molecular recognition and ultrasensitive detection of growth-promoting drug residues in meat and meat products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 153, 104709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codex Alimentarius. Maximum Residue Limits (MRLs) and Risk Management Recommendations (RMRs) for Residues of Veterinary Drugs in Foods. 2024, CXM 2-2024. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/sh-proxy/hu/?lnk=1&url=https%253A%252F%252Fworkspace.fao.org%252Fsites%252Fcodex%252FStandards%252FCXM%2B2%252FMRL2e.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2025).
- Veterinary Medicines Directorate. Maximum Residue Limits in Great Britain. 2025. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/69148057db01ecfcf96fc845/Maximum_Residue_Limits_in_Great_Britain.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2025).
- The Japan Food Chemical Research Foundation. Maximum Residue Limits (MRLs) List of Agricultural Chemicals in Foods. Available online: https://db.ffcr.or.jp/front/pesticide_detail?id=19200 (accessed on 24 October 2025).
- Urusov, A.E.; Petrakova, A.V.; Zherdev, A.V.; Zvereva, E.A. Indirect labeling of antibodies as a universal approach to increase sensitivity of lateral flow tests: A case study for mycotoxins detection. Open Biotechnol. J. 2019, 13 (Suppl. 1, M2), 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolo, C.; Sena-Torralba, A.; Bergua, J.F.; Calucho, E.; Fuentes-Chust, C.; Hu, L.; Rivas, L.; Álvarez-Diduk, R.; Nguyen, E.P.; Cintim, S.; et al. Tutorial: Design and fabrication of nanoparticle-based lateral-flow immunoassays. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 3788–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, L.; Liu, L.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C.; Xu, X. Rapid determination of amygdalin in almonds and almond-based products using lateral flow immunoassay based on gold nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2025, 493, 145671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frens, G. Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvereva, E.A.; Hendrickson, O.D.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Immunochromatographic tests for the detection of microcystin-LR toxin in water and fish samples. Anal. Meth. 2020, 12, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RIDASCREEN® Clenbuterol. Enzyme Immunoassay for the Quantitative Determination of Clenbuterol. 2019. Available online: https://food.r-biopharm.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/R1711-Clenbuterol-16-12-19.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2025).
- Uhrovčík, J. Strategy for determination of LOD and LOQ values—Some basic aspects. Talanta 2014, 119, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvereva, E.A.; Hendrickson, O.D.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Zherdev, A.V. Double lateral flow immunosensing of undeclared pork and chicken components of meat products. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 61, 1148–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Xu, X.; Wu, A.; Song, S.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. An ultrasensitive colloidal gold immunosensor to simultaneously detect 12 beta (2)-adrenergic agonists. J. Chromatogr. B 2022, 1191, 123119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmitrienko, S.G.; Apyari, V.V.; Tolmacheva, V.V.; Gorbunova, M.V.; Furletov, A.A.; Zolotov, Y.A. Methods for the extraction of organic compounds from solid samples: 1. Solvent extraction. Review of reviews. J. Anal. Chem. 2024, 79, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Yao, X.; Wang, Z.; Dou, L.; Su, L.; Zhao, M.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J. Developing a simple immunochromatography assay for clenbuterol with sensitivity by one-step staining. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 15509–15515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shu, R.; Zhao, C.; Sun, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Dou, L.; Ji, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Precise spectral overlap-based donor−acceptor pair for a sensitive traffic light-typed bimodal multiplexed lateral flow immunoassay. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 5046–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Ding, J.; Sun, C.; Liu, D.; Gao, H.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Gao, X. Simultaneous detection of clenbuterol and higenamine in urine samples using interference-free SERS tags combined with magnetic separation. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 5394–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Compound | Molecular Structure and Charge Distribution * | Cross-Reactivity, % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clenbuterol | 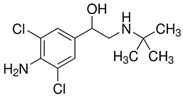 | 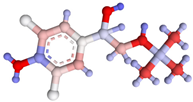 | 100 |
| Salbutamol | 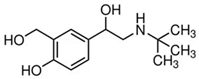 |  | 65 |
| Mabuterol |  | 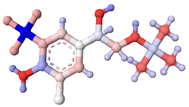 | 36 |
| Terbutaline | 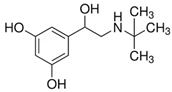 | 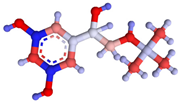 | 0.5 |
| Orciprenaline |  |  | <0.01 |
| Ractopamine | 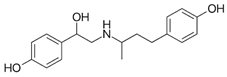 | 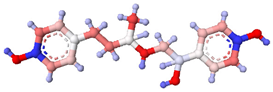 | <0.01 |
| Fenoterol | 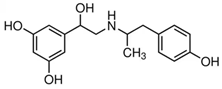 | 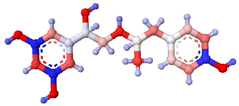 | <0.01 |
 | |||
| Added Content (ng/g) | Revealed Content | Recovery, % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Value, ng/g | Standard Deviation, ng/g | Relative Standard Deviation, % | ||
| 0.25 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 19 | 104 |
| 0.5 | 0.43 | 0.06 | 14 | 86 |
| 1.0 | 0.97 | 0.06 | 6 | 96 |
| Detection and Additional Techniques | Labels | Limits of Detection | Cross-Reacting Compounds | Real Samples | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorimetry | GNPs | 5 ng/mL | Not found | Pork, chicken, sausage | [18] |
| Colorimetry | Coomassie brilliant blue | 2 ng/mL | Not found | Milk, swine liver, pork tenderloin | [38] |
| Colorimetry | GNPs | 0.59 ng/mL | Not found | Beef and pork liver | [19] |
| Colorimetry | Prussian blue nanoparticles on GNPs | 0.27 ng/mL | Not found | Pork | [39] |
| Colorimetry | Magnetic Prussian blue nanozyme | 0.2 ng/mL | Not found | Pork, mutton | [17] |
| Colorimetry | Natural cuttlefish ink nanoparticles | 0.179 ng/mL | Not found | Pork, beef | [22] |
| Colorimetry | Tannic acid nanospheres | 0.13 ng/mL | Not found | Beef and pork liver | [19] |
| Colorimetry | Bi2S3 nanoparticles | 0.1 ng/mL | Not found | Pork, beef, milk | [21] |
| Colorimetry | GNPs | 0.02 ng/mL | Salbutamol, mabuterol | Pork | This work |
| Fluorimetry | Prussian blue nanoparticles on GNPs | 0.152 ng/mL | Not found | Pork | [39] |
| Fluorimetry | GNPs and time-resolved fluorescent nanobeads | 0.04 ng/mL | Not found | Pork | [16] |
| Fluorimetry | Fluorescent latex nanoparticles | 0.025 ng/mL | Mabuterol, banbuterol, brombuterol, bromchlorbuterol, cimaterol, cimbuterol | Pork | [15] |
| Photothermal measurements | Natural cuttlefish ink nanoparticles | 0.076 ng/mL | Not found | Pork, beef | [22] |
| Magnetic enrichment + photometry | Magnetic nanoparticles | 0.007 ng/mL | 37 other β-agonists | Pork, swine urine | [23] |
| Surface-enhanced Raman scattering | Au/Au core/shell nanostars | 0.05 ng/mL | Not found | Pork, chicken, sausage | [18] |
| Magnetic enrichment + surface-enhanced Raman scattering | Zero-background SERS tags and magnetic nanoparticles | 0.00087 ng/mL | Not found | Urine | [40] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zvereva, E.A.; Hendrickson, O.D.; Sotnikov, D.V.; Zherdev, A.V.; Xu, X.; Xu, C.; Dzantiev, B.B. Highly Sensitive Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Clenbuterol and Structurally Similar Beta2-Agonists in Meat. Foods 2025, 14, 3982. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14233982
Zvereva EA, Hendrickson OD, Sotnikov DV, Zherdev AV, Xu X, Xu C, Dzantiev BB. Highly Sensitive Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Clenbuterol and Structurally Similar Beta2-Agonists in Meat. Foods. 2025; 14(23):3982. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14233982
Chicago/Turabian StyleZvereva, Elena A., Olga D. Hendrickson, Dmitriy V. Sotnikov, Anatoly V. Zherdev, Xinxin Xu, Chuanlai Xu, and Boris B. Dzantiev. 2025. "Highly Sensitive Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Clenbuterol and Structurally Similar Beta2-Agonists in Meat" Foods 14, no. 23: 3982. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14233982
APA StyleZvereva, E. A., Hendrickson, O. D., Sotnikov, D. V., Zherdev, A. V., Xu, X., Xu, C., & Dzantiev, B. B. (2025). Highly Sensitive Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Clenbuterol and Structurally Similar Beta2-Agonists in Meat. Foods, 14(23), 3982. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14233982









