Exploring Sensory Attributes in Spinach- and Offals-Filled Chicken Roulades: An Empirical Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
- i.
- Realization of chicken roulades containing iron-rich fillings from two different sources: plant-based (spinach) and animal-based (chicken offal—chicken hearts, gizzards, and liver), which could be a novel meat product;
- ii.
- Making chicken rolls with the same fillings from chicken meat from two different regions of the carcass: chicken breast and chicken thigh; in order to analyze their possible influence on the sensory profile of the products and the consumers’ perception;
- iii.
- Sensory analysis of the products using descriptive and affective sensory tests.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Chicken Roulades
2.3. Consumer Sensory Analysis
2.3.1. Hedonic Ranking of the Products
2.3.2. Check-All-That-Apply (CATA)
2.3.3. Multiple Correspondence Analysis (MCA)
2.3.4. Quantitative Descriptive Analysis (QDA)
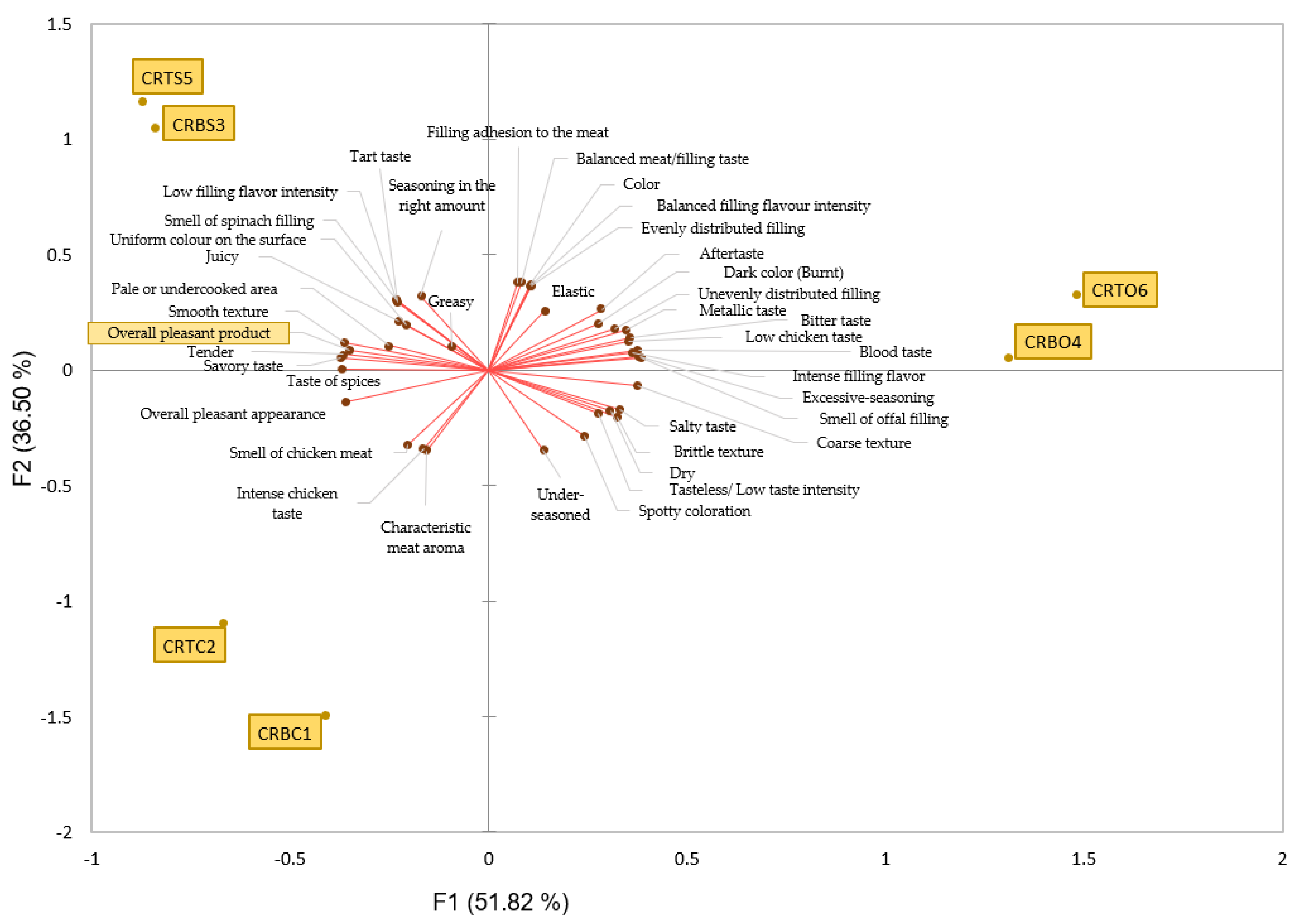
2.3.5. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
2.3.6. Preference Mapping (PrefMap)
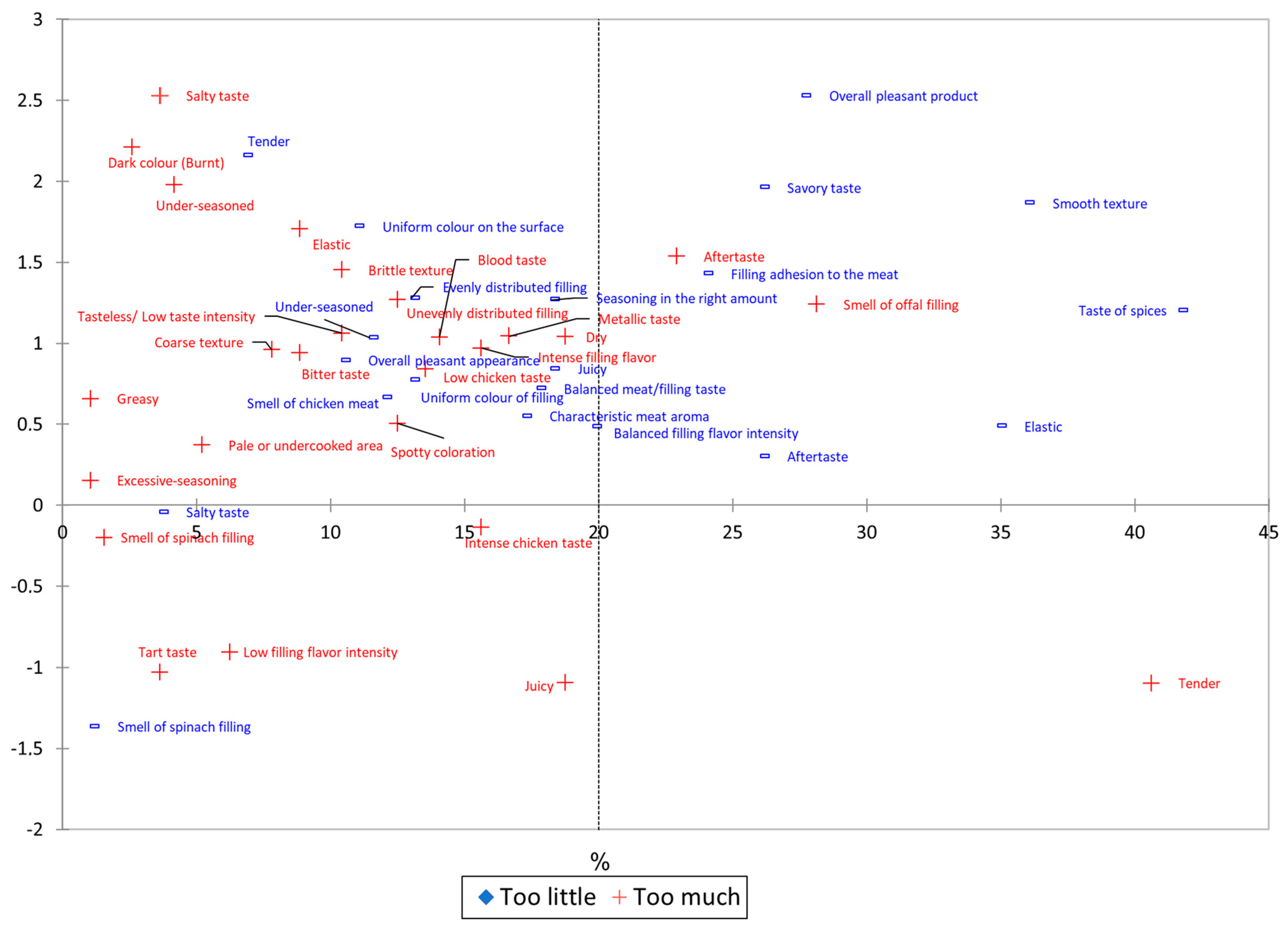
2.3.7. Penalty Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Consumer Sensory Analysis
3.1.1. Hedonic Ranking of the Chicken Roulades Samples
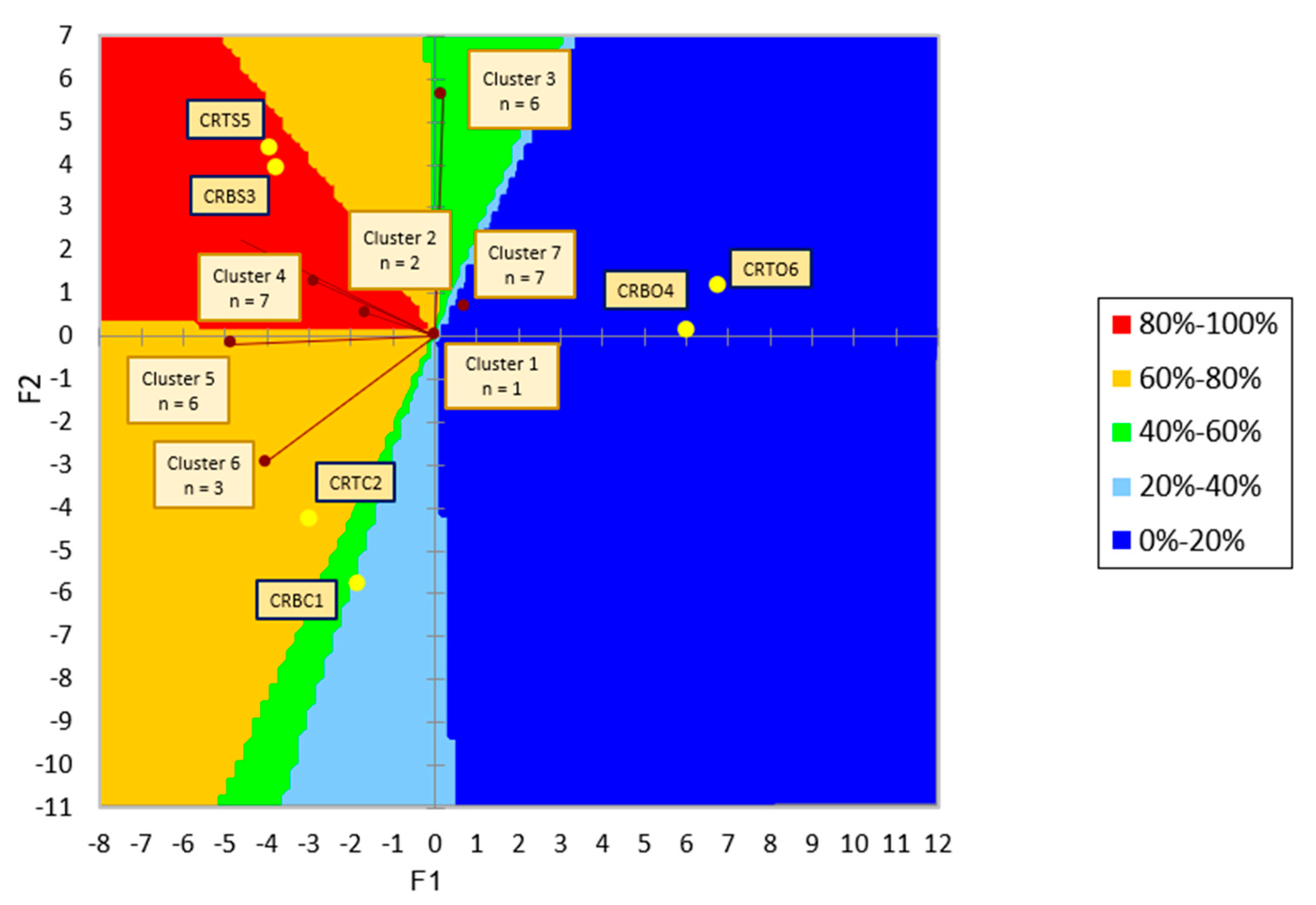
3.1.2. Check-All-That-Apply (CATA)
3.1.3. Quantitative Descriptive Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stone, H.; Bleibaum, R.N.; Thomas, H.A. Sensory Evaluation Practices, 5th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Barda, N. Análisis sensorial de los alimentos. In Fruticultura & Diversificación; Instituto Nacional de Tecnologia Agropecuaria (INTA), Estacion Experimental Agropecuaria Alto Valle: Rio Negro, Argentina, 2011; pp. 34–37. Available online: https://www.studocu.com/es-mx/document/universidad-juarez-del-estado-de-durango/nutricion/analisis-sensorial-de-los-alimentos-articulo/31640808 (accessed on 11 September 2024).
- Stone, H.; Sidel, J.L. Introduction to sensory evaluation. In Sensory Evaluation Practices, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2004; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ares, G. Methodological challenges in sensory characterization. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawless, H.T.; Heymann, H. Sensory Evaluation of Food: Principles and Practices; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Herrero, A.M.; Pintado, T.; Delgado-Pando, G. Sensory analysis and consumer research in new meat products development. Foods 2021, 10, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piggott, J.R.; Simpson, S.J.; Williams, S.A. Sensory analysis. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1998, 33, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Herrero, A.M. Sensory Analysis and Consumer Research in New Product Development. Foods 2021, 10, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD/FAO. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2021–2030; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokanović, M.R.; Tomović, V.M.; Jović, M.T.; Škaljac, S.B.; Šojić, B.V.; Ikonić, P.M.; Tasić, T.A. Proximate and mineral composition of chicken giblets from Vojvodina (Northern Serbia). Int. Sch. Sci. Res. Innov. 2014, 8, 982–985. [Google Scholar]
- Ockerman, H.W.; Basu, L. By-products. In Encyclopedia of Meat Sciences; Jensen, W.K., Devine, C., Dikeman, M., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2004; pp. 104–112. [Google Scholar]
- Seong, P.N.; Cho, S.H.; Park, K.M.; Kang, G.H.; Park, B.Y.; Moon, S.S.; Van Ba, H. Characterization of chicken by-products by mean of proximate and nutritional compositions. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2015, 35, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ockerman, H.W.; Hansen, C.L. Animal By-Product Processing; VCH: Weinheim, Germany; Horwood: Chichester, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Daros, F.G.; Masson, M.L.; Amico, S.C. The influence of the addition of mechanically deboned poultry meat on the rheological properties of sausage. J. Food Eng. 2005, 68, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.M.D.C.C.; Vicente, A.F.D.R.B. Meat nutritional composition and nutritive role in the human diet. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honikel, K.O. Composition and Calories. In Handbook of Analysis of Edible Animal By-Products; Nollet, L.M.L., Toldrá, F., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 105–121. [Google Scholar]
- Seong, P.N.; Park, K.M.; Cho, S.H.; Kang, G.H.; Kang, S.M.; Park, B.Y.; Moon, S.S.; Ba, H.V. Characterization of pork by-Products by Means of Yield, Physicochemical and Nutritional Composition. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2014, 34, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmicheva, M.B. Trends in the development of the Russian market of meat semi-finished products. Meat Ind. 2010, 7, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, D.K.; Kapri, M.; Billoria, S.; Mahato, D.K.; Prem, P.S. Effects of thermal processing on nutritional composition of green leafy vegetables: A review. In Engineering Interventions in Foods and Plants; As part of book series on “Innovations in Agricultural and Biological Engineering”; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, T.; Salauddin, M.; Roy, S.; Chakraborty, R.; Rebezov, M.; Shariati, M.A.; Rengasamy, K.R.R. Underutilized green leafy vegetables: Frontier in fortified food development and nutrition. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 63, 11679–11733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.K.; Thakur, M.; Srivastav, P.P.; Karizaki, V.M.; Suleria, H.A.R. Effects of drying technology on physiochemical and nutritional quality of fruits and vegetables. In Emerging Thermal and Nonthermal Technologies in Food Processing; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 69–116. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, D.K.; Thakur, M.; Singh, S.; Tripathy, S.; Sandhu, K.S.; Kaur, M.; Srivastav, P.P. The Emphasis of Effect of Cooking and Processing Methods on Antinutritional Phytochemical of Legumes and Their Significance in Human Health. In Phytochemicals in Food and Health; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 3–47. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Temimi, A.A.; Al-Hilifi, S.A.; Aum-El-bashar, A.M. An investigation on glutathione derived from spinach and red cabbage leaves and their effects of adding to meat patties. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 8586:2023; Sensory Analysis—Selection and Training of Sensory Assessors. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Singh-Ackbarali, D.; Maharaj, R. Sensory Evaluation as a Tool in Determining Acceptability of Innovative Products Developed by Undergraduate Students in Food Science and Technology at the University of Trinidad and Tobago. J. Curric. Teach. 2014, 3, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marina, T.; Marija, C.; Ida, R. Functional Foods and the Young. J. Food Prod. Mark. 2014, 20, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiangli, R.; Ma, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Tang, K.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y. Differences and Correlations between Industrial Experts and Semi-trained Assessors in the Sensory Evaluation of Strong-aroma Baijiu Using Rate-all-that-apply. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 5841–5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacalone, D.; Hedelund, P.I. Rate-All-That-Apply (RATA) with Semi-Trained Assessors: An Investigation of the Method Reproducibility at Assessor-, Attribute- and Panel-Level. Food Qual. Prefer. 2016, 51, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 13299:2016; Sensory Analysis—Methodology—General Guidance for Establishing a Sensory Profile. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Addinsoft. XLSTAT Statistical and Data Analysis Solution; Addinsoft: Paris, France, 2019; Available online: https://www.xlstat.com (accessed on 5 November 2024).
- Lim, J. Hedonic scaling: A review of methods and theory. Food Qual. Prefer. 2011, 22, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Nexticapa, M.; Angulo, O.; O’mahony, M. How well does the 9-point hedonic scale predict purchase frequency? J. Sens. Stud. 2005, 20, 313–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ares, G.; Jaeger, S.R. Check-all-that-apply questions: Influence of attribute order on sensory product characterization. Food Qual. Prefer. 2013, 28, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrique, N.A.; Deliza, R.; Rosenthal, A. Consumer sensory characterization of cooked ham using the Check-All-That-Apply (CATA) methodology. Food Eng. Rev. 2015, 7, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenacre, M.J. Biplots in correspondence analysis. J. Appl. Stat. 1993, 20, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Chattopadhyay, P. Application of principal component analysis (PCA) as a sensory assessment tool for fermented food products. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzolino, D.; Power, A.; Chapman, J.J.F.A.M. Interpreting and reporting principal component analysis in food science analysis and beyond. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 2469–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenket, R.; Chambers, E., IV; Adhikari, K. A comparison of seven preference mapping techniques using four software programs. J. Sens. Stud. 2011, 26, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagès, J.; Berthelo, S.; Brossier, M.; Gourret, D. Statistical penalty analysis. Food Qual. Prefer. 2014, 32, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldaña, E.; Saldarriaga, L.; Cabrera, J.; Behrens, J.H.; Selani, M.M.; Rios-Mera, J.; Contreras-Castillo, C.J. Descriptive and hedonic sensory perception of Brazilian consumers for smoked bacon. Meat Sci. 2019, 147, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bro, R.; Smilde, A.K. Principal component analysis. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 2812–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.A.L.; Pateiro, M.; Domínguez, R.; Barba-Orellana, S.; Mattar, J.; Rimac Brnčić, S.; Barba, F.J.; Lorenzo, J.M. Replacement of meat by spinach on physicochemical and nutritional properties of chicken burgers. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e13935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. Effect of Spinach on the Quality of Beef Hamburger Patties. Korean J. Community Living Sci. 2017, 28, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castenmiller, J.J.M.; Linssen, J.P.H.; Heinonen, I.M.; Hopia, A.I.; Schwarz, K.; Hollmann, P.C.H.; West, C.E. Antioxidant properties of differently processed spinach products. Food/Nahrung 2002, 46, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasyleva, N.S.; Slozhenkina, M.I.; Khramova, V.N.; Shinkareva, S.V.; Chekhova, E.A.; Knyazhechenko, O.A. Research of the effect of spinach on the quality indicators of chopped poultry semi-finished products. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 677, 032004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, A.A.; Morsy, H.A. Studies on quality attributes of chicken burger prepared with spinach, basil and radish. J. Food Dairy Sci. 2019, 10, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, D. The nutritional benefits of chicken meat compared with other meats. Role Poult. Hum. Nutr. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Llauger, M.; Claret, A.; Bou, R.; López-Mas, L.; Guerrero, L. Consumer attitudes toward consumption of meat products containing offal and offal extracts. Foods 2021, 10, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banu, D.; Şmatoc, V. Identificarea fraudei alimentare la fabricarea semipreparatelor din carne tocată. In Chimia Ecologică şi a Mediului; The Editorial-Polygraphic Center of the Moldova State University: Chișinău, Republic of Moldova, 2023; pp. 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Babicz, M.; Kropiwiec-Domańska, K.; Skrzypczak, E.; Szyndler-Nędza, M.; Szulc, K. Analysis of technological and consumption quality of offal and offal products obtained from pulawska and polish landrace pigs. Animals 2020, 10, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henchion, M.; McCarthy, M.; O’Callaghan, J. Transforming beef by-products into valuable ingredients: Which spell/recipe to use? Front. Nutr. 2016, 3, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample | Chicken Breast, % | Chicken Thigh, % | Filling, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRBC1 | 100 | - | - |
| CRTC2 | - | 100 | - |
| CRBS3 | 70 | - | 30 |
| CRBO4 | |||
| CRTS5 | - | 70 | |
| CRTO6 |
| Stage | Time (min.) | Temperature (°C) | The Temperature in the Center of the Product (°C) | Humidity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drying | 30–50 | 65 | 55 | 25 |
| Smoking | 30–60 | 65 | 55 | 25 |
| Boiling | 120 | 72 | 69 | 99 |
| Drying | 20 | 80 | 72 | 25 |
| Roasting | 10–20 | 80–95 | 72 | 22 |
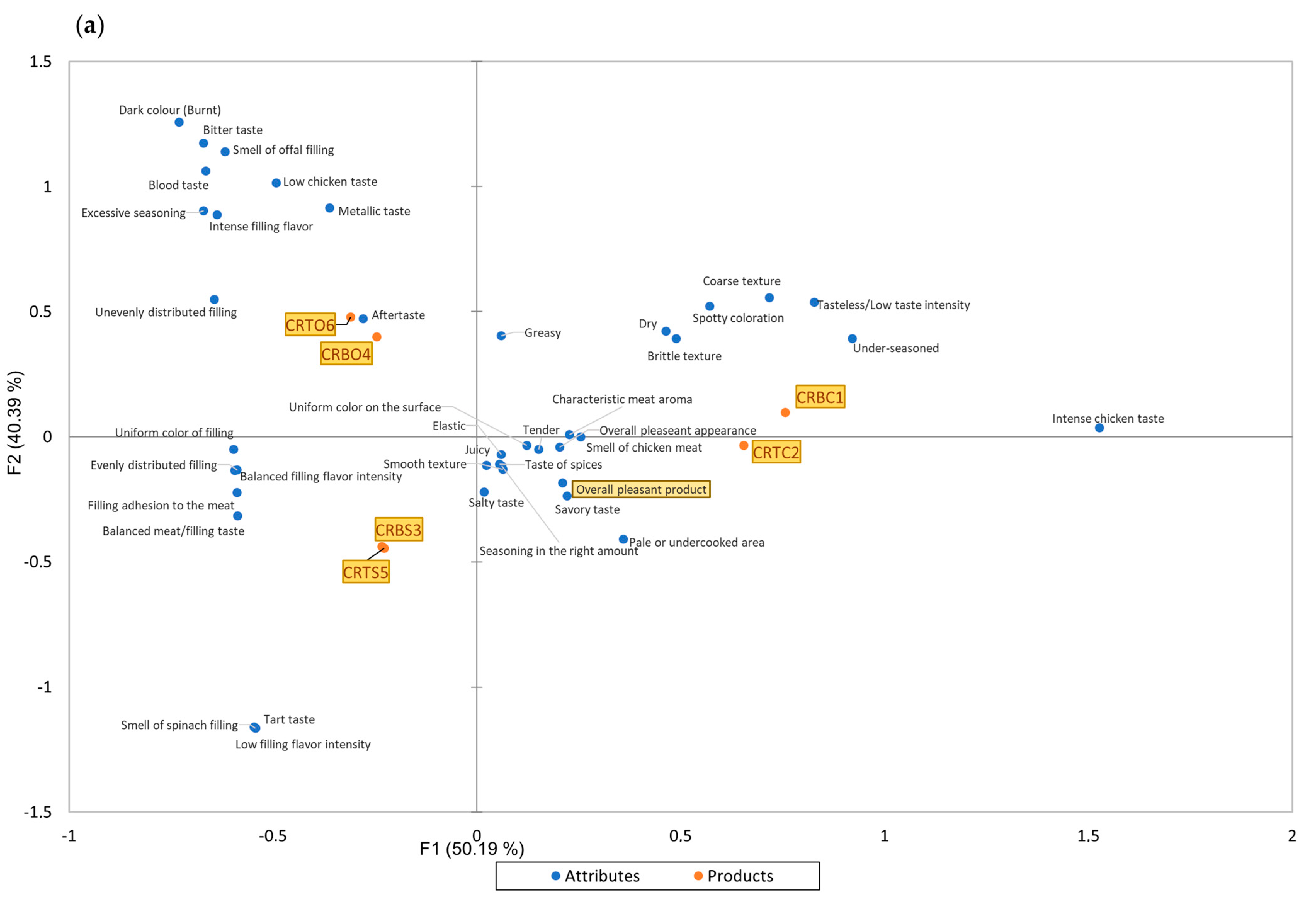
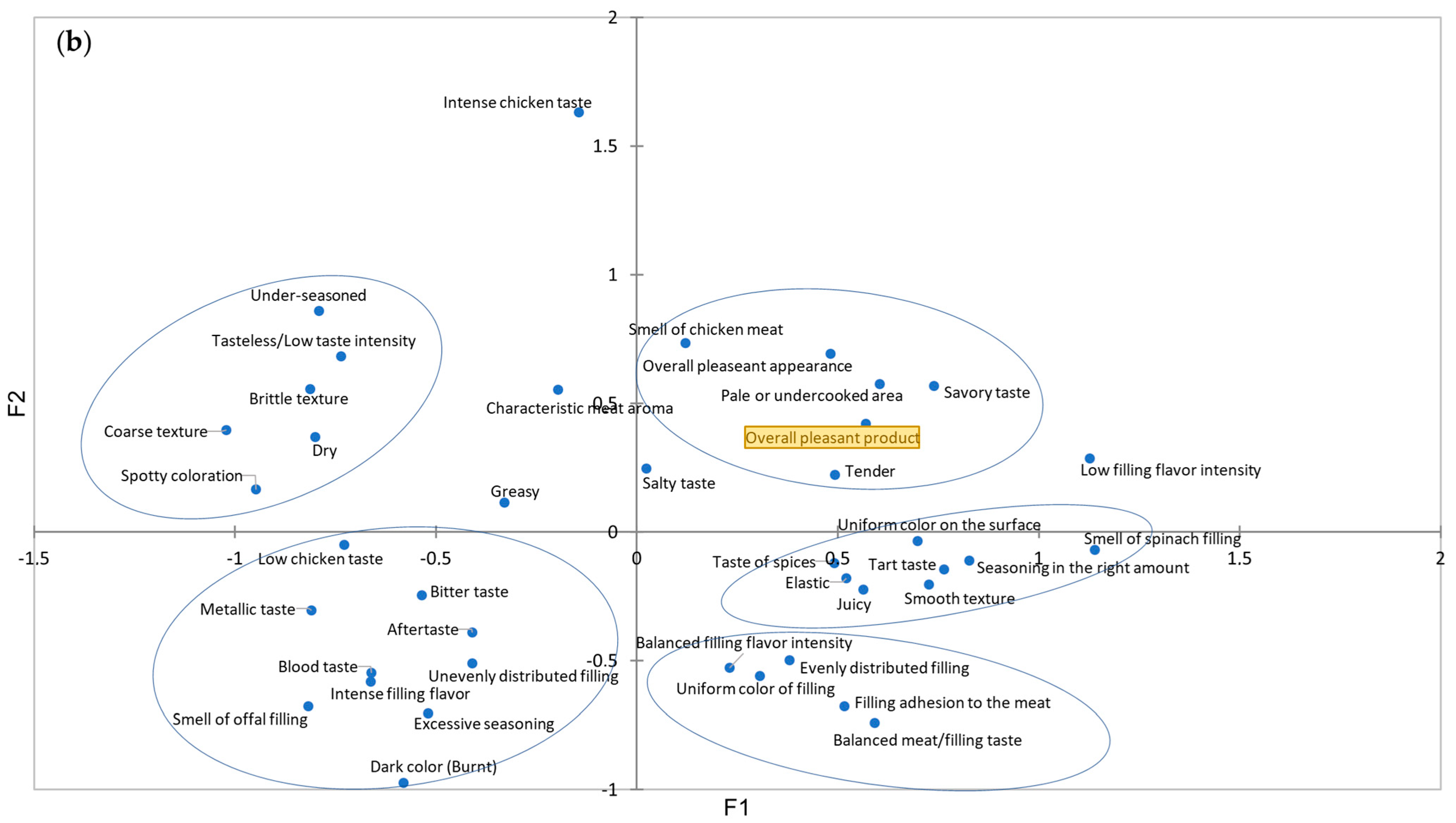
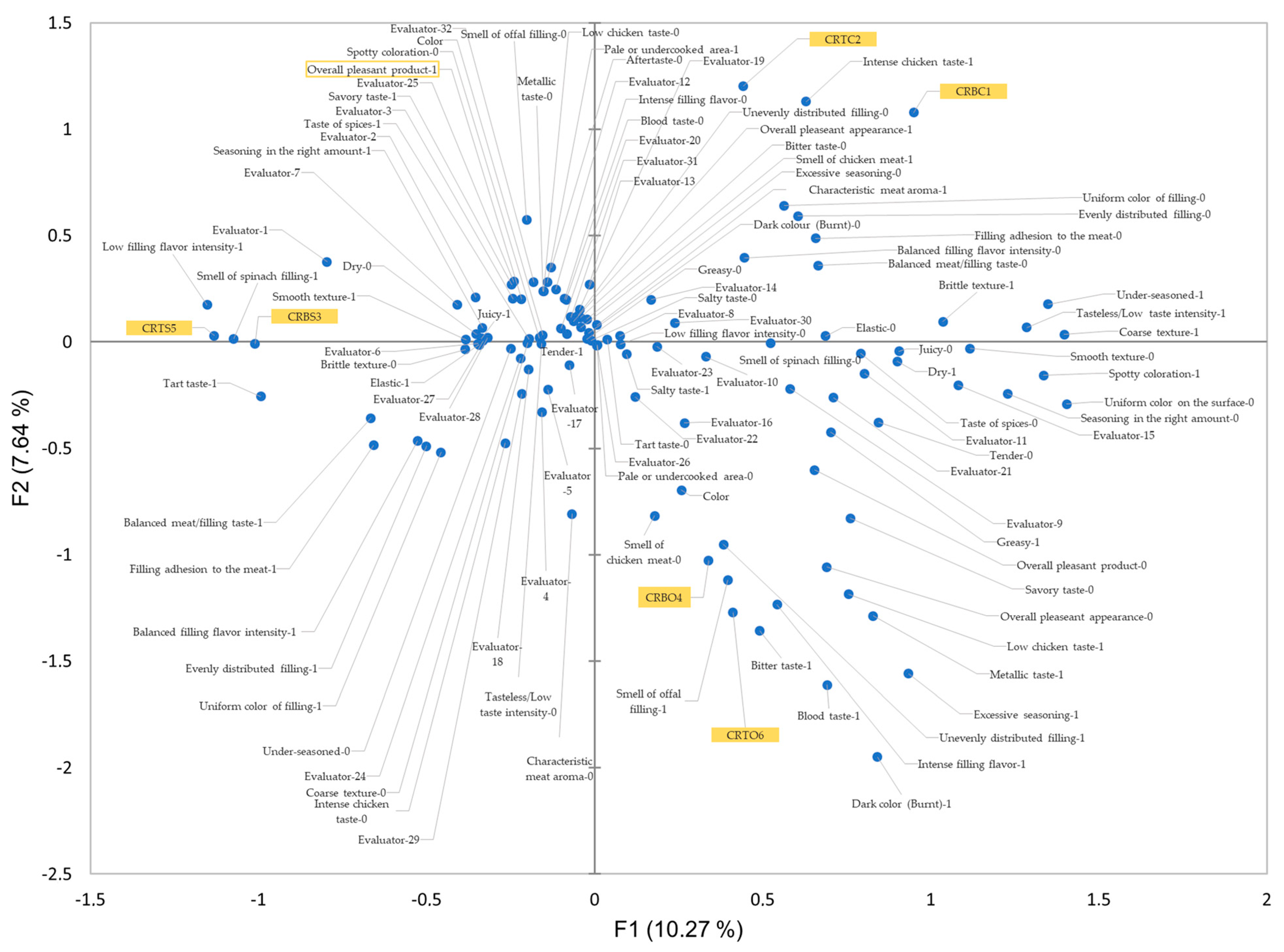
| Sensory Property | CATA Terms |
|---|---|
| Appearance | overall pleasant appearance, pale or undercooked area, dark color (burnt), uniform color on the surface, uniform color of filling, spotty coloration, evenly distributed filling, unevenly distributed filling; |
| Texture | dry, juicy, smooth texture, brittle texture, coarse texture, elastic, tender, greasy, filling adhesion to the meat; |
| Olfactive perception | the smell of chicken meat, the smell of spinach filling, the smell of offals filling; |
| Taste | characteristic meat aroma, low filling flavor intensity, balanced filling flavor intensity, intense filling flavor intensity, salty taste, under-seasoned, seasoning in the right amount, excessive seasoning, metallic taste, blood taste, tart taste, bitter taste, tasteless/low taste intensity, low chicken taste, balanced meat/filling taste, intense chicken taste, savory taste, a taste of spices, aftertaste; |
| Overall liking | overall pleasant product. |
| Sensory Attributes | Frequency of Presence | Cochran’s Q Test p-Value and Significance | Sensory Attributes | Frequency of Presence | Cochran’s Q Test p-Value and Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall pleasant appearance | 176 | 0.003 | Metallic taste | 30 | <0.0001 |
| Pale or undercooked area | 10 | 0.416 | Spotty coloration | 21 | 0.024 |
| Dark color (Burnt) | 4 | 0.001 | Uniform color on the surface | 173 | 0.035 |
| Uniform color of filling | 106 | <0.0001 | Elastic | 128 | <0.0001 |
| Evenly distributed filling | 105 | <0.0001 | Tender | 175 | 0.016 |
| Unevenly distributed filling | 22 | <0.0001 | Greasy | 6 | 0.053 |
| Characteristic meat aroma | 175 | 0.013 | Filling adhesion to the meat | 96 | <0.0001 |
| Balanced filling flavor intensity | 88 | <0.0001 | Low chicken taste | 32 | <0.0001 |
| Low filling flavor intensity | 12 | <0.0001 | Balanced meat/filling taste | 96 | <0.0001 |
| Intense filling flavor | 27 | <0.0001 | Intense chicken taste | 57 | <0.0001 |
| Salty taste | 19 | 0.691 | Tart taste | 7 | 0.001 |
| Tasteless/low taste intensity | 21 | 0.000 | Blood taste | 21 | <0.0001 |
| Under-seasoned | 30 | <0.0001 | Bitter taste | 15 | <0.0001 |
| Seasoning in the right amount | 151 | 0.000 | Savory taste | 145 | <0.0001 |
| Excessive seasoning | 8 | 0.007 | Smell of chicken meat | 170 | 0.015 |
| Dry | 54 | <0.0001 | Smell of spinach filling | 63 | <0.0001 |
| Juicy | 140 | <0.0001 | Smell of offals filling | 65 | <0.0001 |
| Smooth texture | 143 | <0.0001 | Taste of spices | 154 | <0.0001 |
| Brittle texture | 52 | 0.001 | Overall pleasant product | 144 | <0.0001 |
| Coarse texture | 24 | 0.003 | Aftertaste | 64 | <0.0001 |
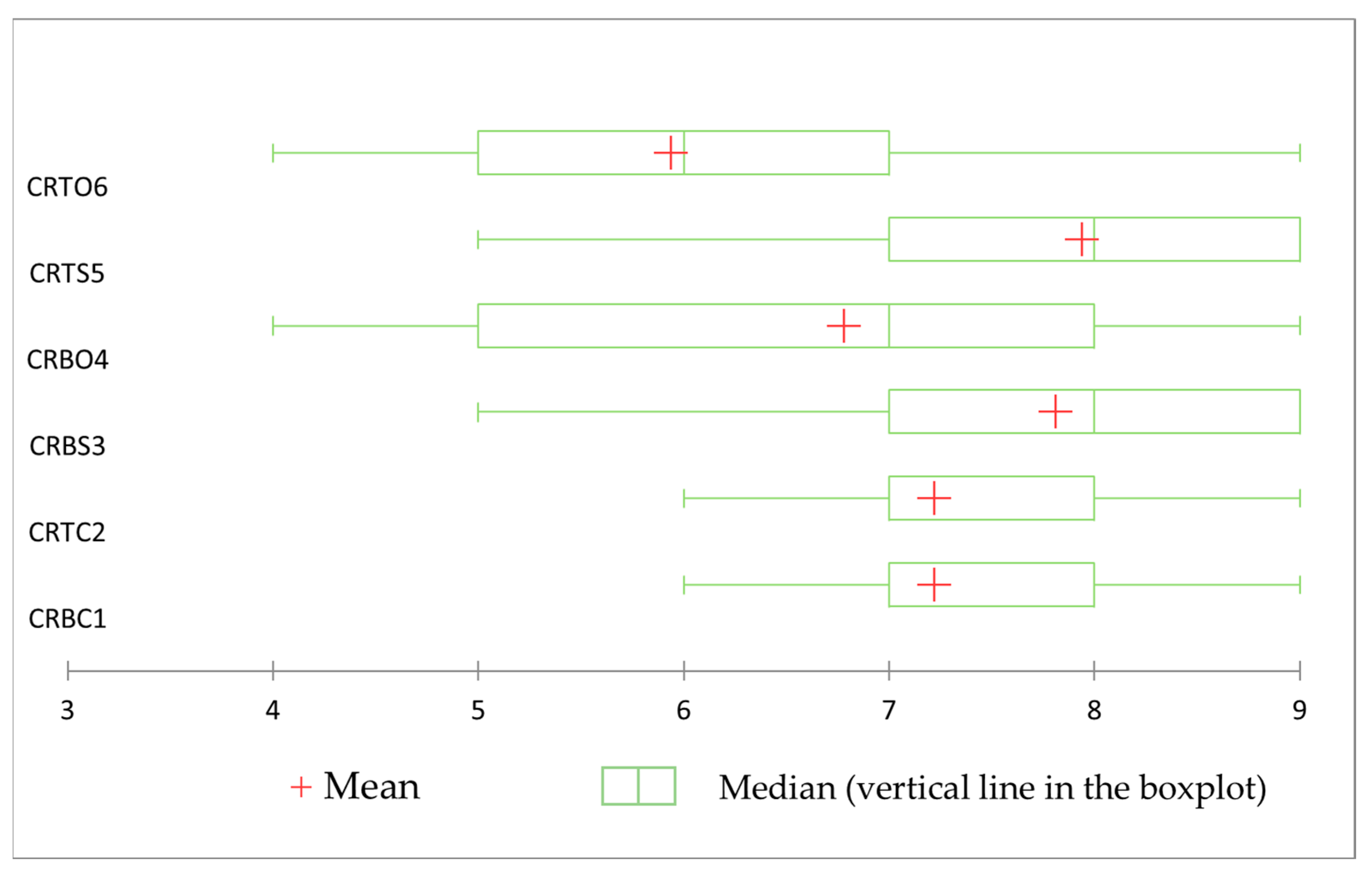
| Sensory Attributes | CRBC1 | CRTC2 | CRBS3 | CRBO4 | CRTS5 | CRTO6 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salty taste | 4.84 ± 0.13 | 5.03 ± 0.15 | 4.28 ± 0.13 | 5.53 ± 0.16 | 4.34 ± 0.12 | 5.28 ± 0.18 | <0.0001 |
| Tender | 7.22 ± 0.19 | 6.97 ± 0.21 | 7.44 ± 0.22 | 5.91 ± 0.30 | 8.00 ± 0.15 | 5.69 ± 0.29 | <0.0001 |
| Elastic | 3.41 ± 0.21 | 4.34 ± 0.18 | 4.28 ± 0.22 | 4.84 ± 0.17 | 6.25 ± 0.21 | 6.28 ± 0.17 | <0.0001 |
| Coarse texture | 1.72 ± 0.18 | 1.38 ± 0.16 | 1.28 ± 0.14 | 2.34 ± 0.22 | 1.29 ± 0.07 | 2.22 ± 0.20 | <0.0001 |
| Aftertaste | 2.00 ± 0.23 | 2.00 ± 0.21 | 3.97 ± 0.15 | 5.78 ± 0.18 | 4.41 ± 0.12 | 5.84 ± 0.14 | <0.0001 |
| Juicy | 4.41 ± 0.18 | 6.19 ± 0.25 | 6.88 ± 0.20 | 3.28 ± 0.30 | 7.53 ± 0.13 | 6.03 ± 0.33 | <0.0001 |
| Dry | 2.78 ± 0.15 | 2.13 ± 0.22 | 1.59 ± 0.19 | 3.78 ± 0.34 | 1.16 ± 0.08 | 2.72 ± 0.29 | <0.0001 |
| Greasy | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.56 ± 0.11 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.88 ± 0.14 | 1.44 ± 0.14 | <0.0001 |
| Brittle texture | 2.34 ± 0.23 | 1.81 ± 0.20 | 1.25 ± 0.08 | 2.56 ± 0.18 | 1.13 ± 0.06 | 2.59 ± 0.18 | <0.0001 |
| Uniform color on the surface | 7.53 ± 0.22 | 7.75 ± 0.22 | 8.69 ± 0.10 | 8.06 ± 0.17 | 8.13 ± 0.15 | 7.06 ± 0.22 | <0.0001 |
| Spotty coloration | 2.56 ± 0.25 | 2.47 ± 0.17 | 2.00 ± 0.13 | 2.47 ± 0.22 | 2.13 ± 0.17 | 2.59 ± 0.23 | 0.089 |
| Pale or undercooked area | 2.28 ± 0.17 | 1.06 ± 0.06 | 2.50 ± 0.18 | 1.38 ± 0.12 | 2.19 ± 0.16 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | <0.0001 |
| Dark color (Burnt) | 1.09 ± 0.09 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.34 ± 0.09 | 1.53 ± 0.12 | 1.56 ± 0.12 | 2.31 ± 0.23 | <0.0001 |
| Uniform color of filling | - | - | 7.91 ± 0.20 | 7.22 ± 0.20 | 7.84 ± 0.16 | 6.78 ± 0.21 | <0.0001 |
| Overall pleasant appearance | 8.66 ± 0.12 | 8.66 ± 0.12 | 8.41 ± 0.13 | 7.16 ± 0.18 | 8.19 ± 0.16 | 7.09 ± 0.20 | <0.0001 |
| Evenly distributed filling | - | - | 7.88 ± 0.26 | 7.53 ± 0.20 | 7.81 ± 0.24 | 6.56 ± 0.23 | <0.0001 |
| Unevenly distributed filling | - | - | 1.63 ± 0.24 | 2.09 ± 0.26 | 1.53 ± 0.21 | 3.16 ± 0.26 | <0.0001 |
| Characteristic meat aroma | 9.00 ± 0.00 | 9.00 ± 0.00 | 6.90 ± 0.23 | 6.88 ± 0.18 | 6.98 ± 0.18 | 6.88 ± 0.15 | <0.0001 |
| Low chicken taste | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.63 ± 0.21 | 2.75 ± 0.26 | 1.13 ± 0.07 | 2.53 ± 0.28 | <0.0001 |
| Balanced meat/filling taste | - | - | 8.06 ± 0.20 | 6.78 ± 0.21 | 8.06 ± 0.17 | 6.69 ± 0.22 | <0.0001 |
| Intense chicken taste | 7.59 ± 0.15 | 8.81 ± 0.10 | 1.19 ± 0.08 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.50 ± 0.16 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | <0.0001 |
| Savory taste | 7.31 ± 0.21 | 7.88 ± 0.14 | 7.84 ± 0.19 | 6.72 ± 0.26 | 8.09 ± 0.18 | 6.34 ± 0.23 | <0.0001 |
| Tasteless/Low taste intensity | 2.34 ± 0.25 | 1.19 ± 0.10 | 1.06 ± 0.04 | 2.34 ± 0.30 | 1.03 ± 0.03 | 2.00 ± 0.22 | <0.0001 |
| Tart taste | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.88 ± 0.23 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.63 ± 0.16 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | <0.0001 |
| Blood taste | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.13 ± 0.07 | 2.34 ± 0.28 | 1.13 ± 0.06 | 2.66 ± 0.28 | <0.0001 |
| Smooth texture | 6.90 ± 0.21 | 7.63 ± 0.25 | 8.09 ± 0.21 | 5.88 ± 0.30 | 8.31 ± 0.16 | 6.03 ± 0.23 | <0.0001 |
| Under-seasoned | 3.13 ± 0.34 | 2.31 ± 0.36 | 1.38 ± 0.12 | 2.50 ± 0.23 | 1.31 ± 0.10 | 2.16 ± 0.28 | 0.000 |
| Seasoning in the right amount | 6.38 ± 0.34 | 7.34 ± 0.38 | 8.06 ± 0.10 | 6.94 ± 0.19 | 8.06 ± 0.10 | 7.19 ± 0.26 | <0.0001 |
| Excessive seasoning | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.09 ± 0.09 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.13 ± 0.13 | 0.475 |
| Low filling flavor intensity | - | - | 1.75 ± 0.14 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.88 ± 0.24 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | <0.0001 |
| Balanced filling flavor intensity | - | - | 7.78 ± 0.19 | 6.72 ± 0.26 | 7.53 ± 0.25 | 6.97 ± 0.22 | <0.0001 |
| Intense filling flavor | - | - | 1.09 ± 0.09 | 2.88 ± 0.32 | 1.19 ± 0.14 | 2.25 ± 0.22 | <0.0001 |
| Bitter taste | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.25 ± 0.10 | 1.72 ± 0.18 | 1.16 ± 0.07 | 1.94 ± 0.21 | <0.0001 |
| Metallic taste | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.50 ± 0.12 | 2.56 ± 0.26 | 1.56 ± 0.12 | 2.69 ± 0.28 | <0.0001 |
| Smell of chicken meat | 9.00 ± 0.00 | 9.00 ± 0.00 | 7.69 ± 0.18 | 7.31 ± 0.16 | 7.44 ± 0.16 | 7.19 ± 0.16 | <0.0001 |
| Smell of spinach filling | - | - | 6.31 ± 0.10 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 6.69 ± 0.11 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | <0.0001 |
| Smell of offals filling | - | - | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 7.16 ± 0.14 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 7.13 ± 0.12 | <0.0001 |
| Filling adhesion to the meat | - | - | 7.78 ± 0.15 | 6.00 ± 0.20 | 7.22 ± 0.12 | 6.22 ± 0.22 | <0.0001 |
| Overall pleasant product | 7.22 ± 0.15 | 7.29 ± 0.18 | 7.75 ± 0.19 | 6.78 ± 0.28 | 7.94 ± 0.21 | 5.94 ± 0.27 | <0.0001 |
| Taste of spices | 4.59 ± 0.18 | 4.03 ± 0.19 | 4.75 ± 0.17 | 2.78 ± 0.12 | 4.53 ± 0.14 | 2.75 ± 0.12 | <0.0001 |
| Variable | Level | Frequencies | % | Mean Drops | Penalties | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not enough | 7 | 3.65% | −0.044 | |||
| Salty taste | JAR | 178 | 92.71% | 1.242 | 0.001 | |
| Too much | 7 | 3.65% | 2.527 | |||
| Not enough | 13 | 6.77% | 2.159 | |||
| Tender | JAR | 101 | 52.60% | −0.632 | 0.001 | |
| Too much | 78 | 40.63% | −1.097 | |||
| Not enough | 67 | 34.90% | 0.487 | |||
| Elastic | JAR | 108 | 56.25% | 0.734 | 0.000 | |
| Too much | 17 | 8.85% | 1.708 | |||
| Not enough | 50 | 26.04% | 0.302 | |||
| Aftertaste | JAR | 98 | 51.04% | 0.880 | <0.0001 | |
| Too much | 44 | 22.92% | 1.536 | |||
| Not enough | 35 | 18.23% | 0.842 | |||
| Juicy | JAR | 121 | 63.02% | −0.140 | 0.501 | |
| Too much | 36 | 18.75% | −1.095 | |||
| Not enough | 22 | 11.46% | 1.034 | |||
| Under-seasoned | JAR | 162 | 84.38% | 1.285 | <0.0001 | |
| Too much | 8 | 4.17% | 1.977 | |||
| Not enough | 2 | 1.04% | −1.366 | |||
| Smell of spinach filling | JAR | 187 | 97.40% | −0.666 | 0.291 | |
| Too much | 3 | 1.56% | −0.200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boișteanu, P.-C.; Anchidin, B.-G.; Ciobanu, M.-M. Exploring Sensory Attributes in Spinach- and Offals-Filled Chicken Roulades: An Empirical Analysis. Foods 2025, 14, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020303
Boișteanu P-C, Anchidin B-G, Ciobanu M-M. Exploring Sensory Attributes in Spinach- and Offals-Filled Chicken Roulades: An Empirical Analysis. Foods. 2025; 14(2):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020303
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoișteanu, Paul-Corneliu, Bianca-Georgiana Anchidin, and Marius-Mihai Ciobanu. 2025. "Exploring Sensory Attributes in Spinach- and Offals-Filled Chicken Roulades: An Empirical Analysis" Foods 14, no. 2: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020303
APA StyleBoișteanu, P.-C., Anchidin, B.-G., & Ciobanu, M.-M. (2025). Exploring Sensory Attributes in Spinach- and Offals-Filled Chicken Roulades: An Empirical Analysis. Foods, 14(2), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020303








