Modulation of Intestinal Smooth Muscle Cell Function by BL-99 Postbiotics in Functional Constipation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains Cultivation and Preparing CFS Samples
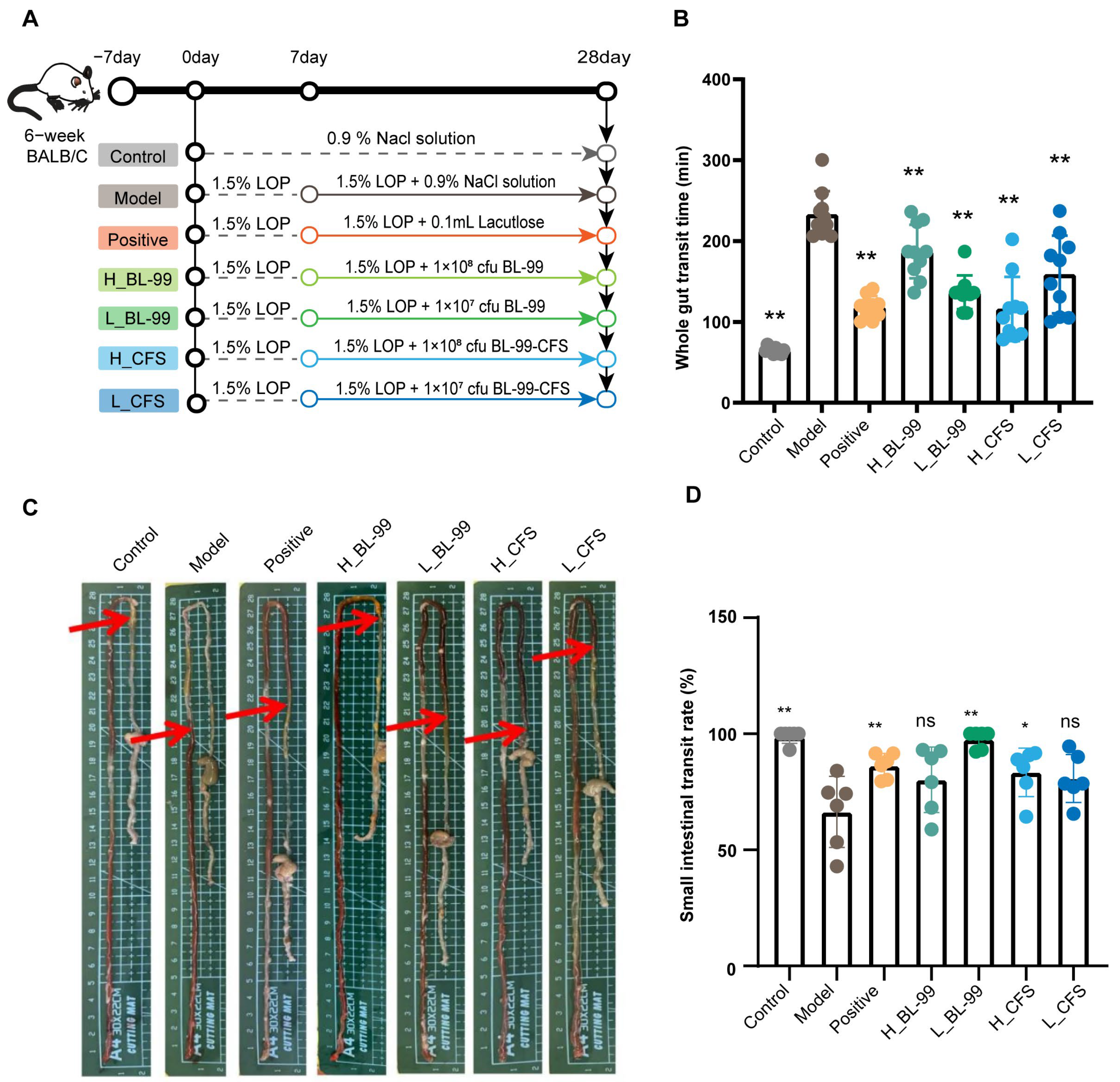
2.2. Experimental Animals and Design
2.3. Fecal Parameter Measurement
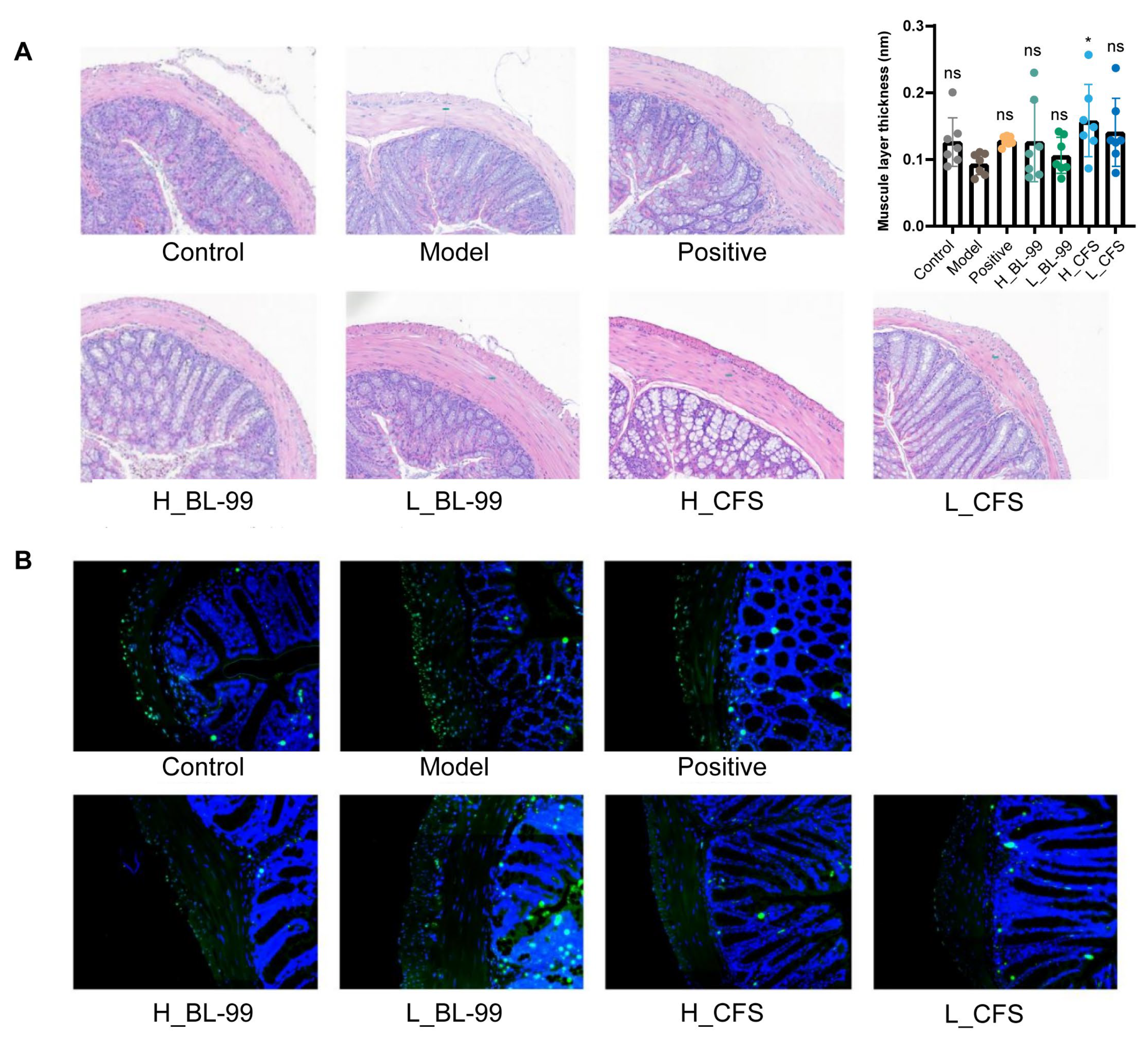
2.4. Colon Tissue TUNEL Staining
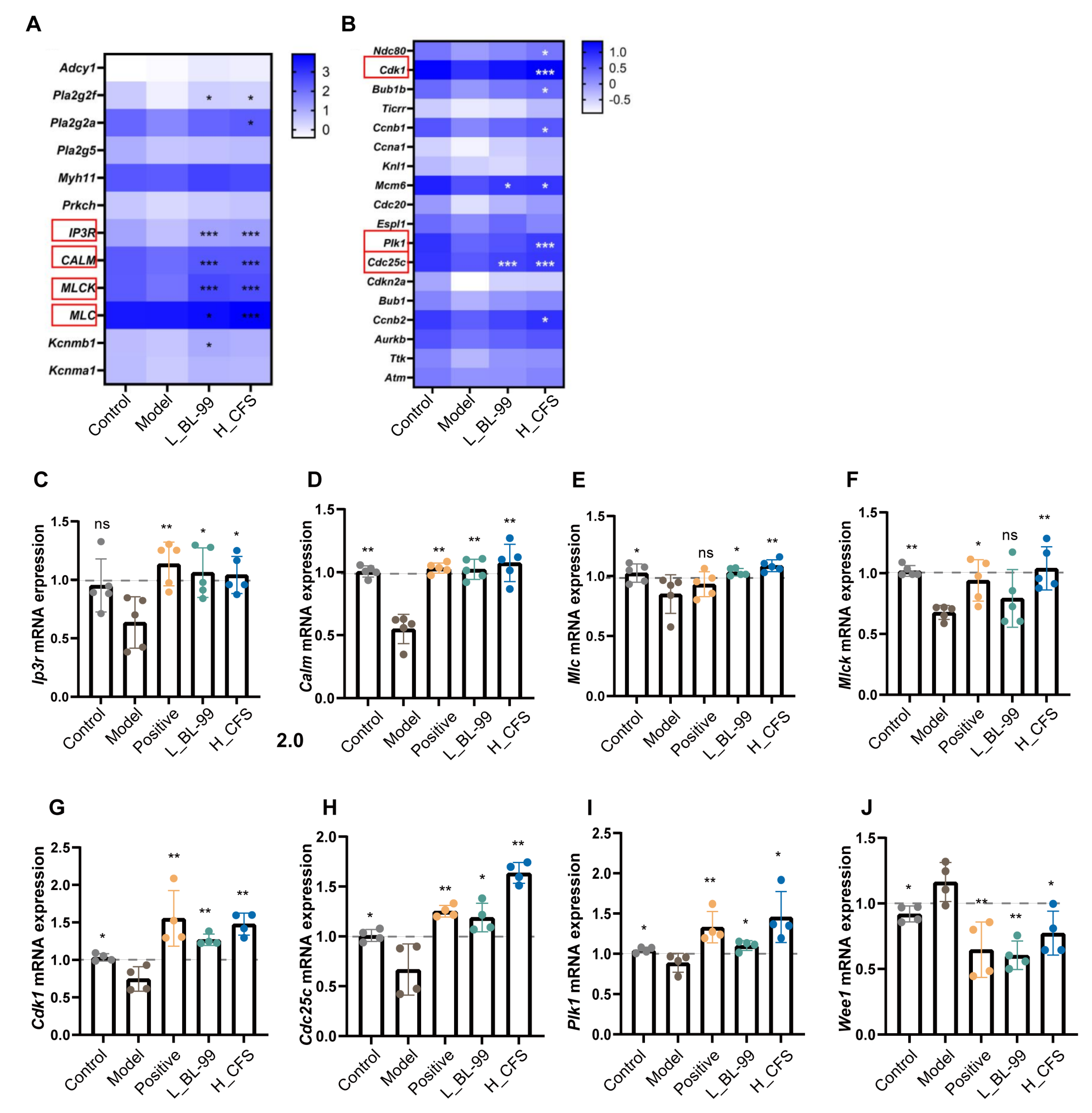
2.5. Transcriptomic Analysis
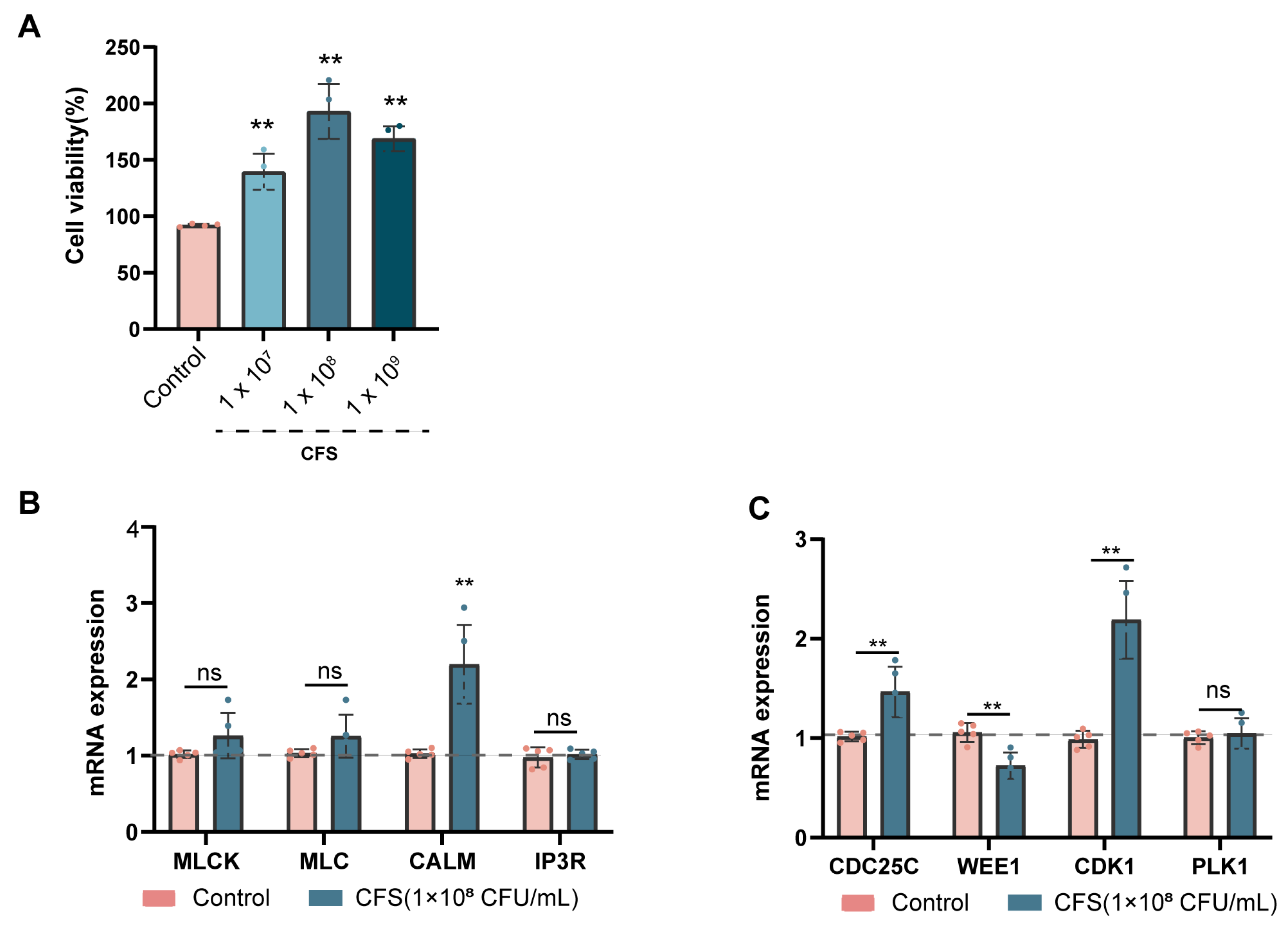
2.6. HAVSMC Culture
2.7. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis
2.8. Quantification of Gene Expression by Real-Time PCR
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. BL-99 and Its Postbiotics Enhanced the Intestinal Motility of Constipated Mice
3.2. BL-99 and Its Postbiotics Improved Constipation Related Symptoms in Mice
3.3. BL-99 and Its Postbiotics Promoted the Thickening of the Intestinal Muscle Layer in Constipated Mice
3.4. BL-99 and Its Postbiotics Enhanced the Contraction and Proliferation Functions of Intestinal SMCs
3.5. BL-99 Postbiotics Regulated the Contraction and Proliferation Functions of SMCs In Vitro
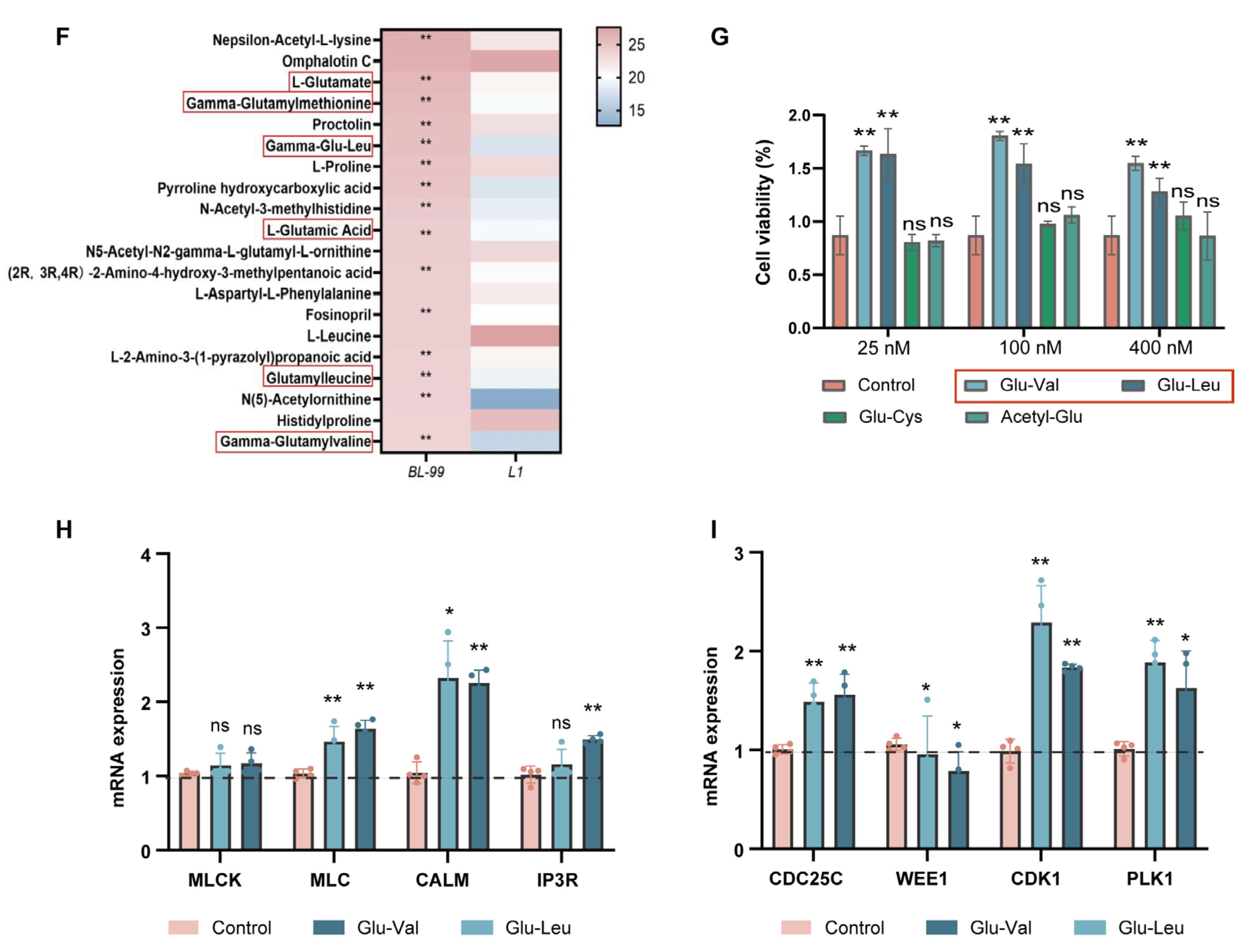
3.6. Glu-Val and Glu-Leu Are Key Bioactive Components of BL-99 Postbiotics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Black, C.J.; Ford, A.C. Chronic idiopathic constipation in adults: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis and clinical management. Med. J. Aust. 2018, 209, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberio, B.; Judge, C.; Savarino, E.V.; Ford, A.C. Global prevalence of functional constipation according to the Rome criteria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Liu, S.; Jia, P.; Wang, X.; Gan, J.; Hu, W.; Zhu, H.; Song, Y.; Niu, J.; Ji, Y. Epidemiology of Constipation in Elderly People in Parts of China: A Multicenter Study. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 823987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Wu, H.; Huang, F.; Li, X.Y.; Zhen, Y.H.; Zhang, B.F.; Li, H.Y. Causal association between constipation and risk of colorectal cancer: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1282066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staller, K.; Olén, O.; Söderling, J.; Roelstraete, B.; Törnblom, H.; Song, M.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Chronic Constipation as a Risk Factor for Colorectal Cancer: Results from a Nationwide, Case-Control Study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1867–1876.e1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, K.; Molnar, M.Z.; Potukuchi, P.K.; Thomas, F.; Lu, J.L.; Yamagata, K.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kovesdy, C.P. Constipation and risk of death and cardiovascular events. Atherosclerosis 2019, 281, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Lee, M.; Park, M.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Park, J.; Koyanagi, A.; Smith, L.; Nehs, C.J.; Yon, D.K.; et al. Slow gut transit increases the risk of Alzheimer’s disease: An integrated study of the bi-national cohort in South Korea and Japan and Alzheimer’s disease model mice. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 65, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimidi, E.; Christodoulides, S.; Scott, S.M.; Whelan, K. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics and the Gastrointestinal Microbiota on Gut Motility and Constipation. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimidi, E.; Mark Scott, S.; Whelan, K. Probiotics and constipation: Mechanisms of action, evidence for effectiveness and utilisation by patients and healthcare professionals. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassard, C.; Dapoigny, M.; Scott, K.P.; Crouzet, L.; Del’homme, C.; Marquet, P.; Martin, J.C.; Pickering, G.; Ardid, D.; Eschalier, A.; et al. Functional dysbiosis within the gut microbiota of patients with constipated-irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimidi, E.; Christodoulides, S.; Fragkos, K.C.; Scott, S.M.; Whelan, K. The effect of probiotics on functional constipation in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekharan, B.; Saeedi, B.J.; Alam, A.; Houser, M.; Srinivasan, S.; Tansey, M.; Jones, R.; Nusrat, A.; Neish, A.S. Interactions Between Commensal Bacteria and Enteric Neurons, via FPR1 Induction of ROS, Increase Gastrointestinal Motility in Mice. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 179–192.e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. Lactis A6 alleviates comorbid constipation and depression by rebalancing tryptophan metabolism. Sci. Bull. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, M.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Chen, W. Different Bifidobacterium bifidum strains change the intestinal flora composition of mice via different mechanisms to alleviate loperamide-induced constipation. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 6058–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Wang, Q.; Ullah, S.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, M.; Feng, F.; Zhong, H. Ligilactobacillus acidipiscis YJ5 modulates the gut microbiota and produces beneficial metabolites to relieve constipation by enhancing the mucosal barrier. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Nie, S.P.; Zhu, K.X.; Xiong, T.; Li, C.; Gong, J.; Xie, M.Y. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116 on loperamide-induced constipation in mice. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 66, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, D.; Gao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, T.; Jiang, L.; Tang, Y. Association between fecal short-chain fatty acid levels and constipation severity in subjects with slow transit constipation. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 36, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, L.; Ma, C.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Tian, F.; Xue, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. A key genetic factor governing arabinan utilization in the gut microbiome alleviates constipation. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 1989–2006.e1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Takami, D.; Makizaki, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Nakajima, S.; Ohno, H.; Sagami, T. Effects of Bifidobacterium longum CLA8013 on bowel movement improvement: A placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind study. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2023, 42, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Li, Y.; Yang, N.; Wang, H.; Shi, X.; Liu, Y.; Jin, H.; Kwok, L.Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H. Efficacy of a postbiotic and its components in promoting colonic transit and alleviating chronic constipation in humans and mice. Cell Rep. Med. 2025, 6, 102093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinderola, G.; Sanders, M.E.; Salminen, S. The Concept of Postbiotics. Foods 2022, 11, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahedi, S.; Pashangeh, S. Bioactivities of postbiotics in food applications: A review. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2025, 17, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Shamir, R.; Swann, J.R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Luo, J.; Shi, S.; Niu, X.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Fang, B.; et al. Synergistic defecation effects of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BL-99 and fructooligosaccharide by modulating gut microbiota. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1520296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Duan, S.; Liu, W.H.; Zhang, C.; Sun, S.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Hung, W.L.; et al. In vitro Study of Bifidobacterium lactis BL-99 With Fructooligosaccharide Synbiotics Effected on the Intestinal Microbiota. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 890316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur Clark, J.A.; Sun, D. Guidelines for the ethical review of laboratory animal welfare People’s Republic of China National Standard GB/T 35892-2018 [Issued 6 February 2018 Effective from 1 September 2018]. Animal Model. Exp. Med. 2020, 14, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, Z.; Fang, B.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Lan, H.; Zhao, W.; Hung, W.-L.; Zhang, M. Exploring the Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei Postbiotics: Mechanistic Insights and Functional Components. Food Biosci. 2025, 65, 106105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Feng, H.; He, J.; Guo, J.; Hung, W.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; et al. Oat β-Glucan and Lacticaseibacillus paracasei K56 synergistically ameliorate hypercholesterolemia in mice by modulating gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 315, 144420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ponti, F.; Giaroni, C.; Cosentino, M.; Lecchini, S.; Frigo, G. Calcium-channel blockers and gastrointestinal motility: Basic and clinical aspects. Pharmacol. Ther. 1993, 60, 121–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvanese, C.M.; Villani, F.; Ercolini, D.; De Filippis, F. Postbiotics versus probiotics: Possible new allies for human health. Food Res. Int. 2025, 217, 116869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W. Different microbial ecological agents change the composition of intestinal microbiota and the levels of SCFAs in mice to alleviate loperamide-induced constipation. Benef. Microbes 2024, 15, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanihiro, R.; Yuki, M.; Sakano, K.; Sasai, M.; Sawada, D.; Ebihara, S.; Hirota, T. Effects of Heat-Treated Lactobacillus helveticus CP790-Fermented Milk on Gastrointestinal Health in Healthy Adults: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharucha, A.E.; Lacy, B.E. Mechanisms, Evaluation, and Management of Chronic Constipation. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1232–1249.e1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Liu, S.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, X.; Hu, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Gao, J.; Zhu, M.-S.; et al. Heterotrimeric G Stimulatory Protein α Subunit Is Required for Intestinal Smooth Muscle Contraction in Mice. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, N.; Yu, Q.; Mei, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium bifidum CCFM1163 Alleviated Cathartic Colon by Regulating the Intestinal Barrier and Restoring Enteric Nerves. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yu, Q.; Xue, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Zhai, Q.; Zhao, J.; et al. Bifidobacterium bifidum CCFM1163 alleviates cathartic colon by activating the BDNF-TrkB-PLC/IP(3) pathway to reconstruct the intestinal nerve and barrier. Food Funct. 2025, 16, 2057–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimidi, E.; Zdanaviciene, A.; Christodoulides, S.; Taheri, S.; Louis, P.; Duncan, P.I.; Emami, N.; Crabbé, R.; De Castro, C.A.; McLean, P.; et al. Randomised clinical trial: Bifidobacterium lactis NCC2818 probiotic vs placebo, and impact on gut transit time, symptoms, and gut microbiology in chronic constipation. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Chen, Q.; Yang, B.; Qin, H.; Li, N. Analysis of Gut Microbiome and Metabolite Characteristics in Patients with Slow Transit Constipation. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 3026–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Sun, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, M.; Niu, T.; Kang, X.; Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Sun, E.; Li, Y. Effect of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis MN-Gup on constipation and the composition of gut microbiota. Benef. Microbes 2021, 12, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammoscato, F.; Scirocco, A.; Altomare, A.; Matarrese, P.; Petitta, C.; Ascione, B.; Caronna, R.; Guarino, M.; Marignani, M.; Cicala, M.; et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus protects human colonic muscle from pathogen lipopolysaccharide-induced damage. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, 984-e777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobol, C.V. Stimulatory Effect of Lactobacillus Metabolites on Colonic Contractions in Newborn Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.N.; Yan, J.K.; Xiao, Y.T.; Wen, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, K.J.; Wang, Y.; Cai, W. Butyrate stimulates the growth of human intestinal smooth muscle cells by activation of yes-associated protein. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.J.; Ganesan, R.; Jin, Y.J.; Park, H.J.; Min, B.H.; Jeong, M.K.; Yoon, S.J.; Choi, M.R.; Choi, J.; Moon, J.H.; et al. Multi-strain probiotics alleviate loperamide-induced constipation by adjusting the microbiome, serotonin, and short-chain fatty acids in rats. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1174968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitha, M.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Srinivasan, S. Gut microbial products regulate murine gastrointestinal motility via Toll-like receptor 4 signaling. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 1006–1016.e1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Field, C.J. New role of glutamate as an immunoregulator via glutamate receptors and transporters. Front. Biosci. (Schol. Ed.) 2011, 3, 1007–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.; Sarkar, K.; Nath, P.P.; Khatun, A.; Pal, S.; Paul, G. Monosodium glutamate impairs the contraction of uterine visceral smooth muscle ex vivo of rat through augmentation of acetylcholine and nitric oxide signaling pathways. Reprod. Biol. 2018, 18, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs-Nolan, J.; Zhang, H.; Ibuki, M.; Nakamori, T.; Yoshiura, K.; Turner, P.V.; Matsui, T.; Mine, Y. The PepT1-transportable soy tripeptide VPY reduces intestinal inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 1753–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.; Ibuki, M.; Nakamori, T.; Fan, M.; Mine, Y. Soy-derived di- and tripeptides alleviate colon and ileum inflammation in pigs with dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene Name | Primer Sequence/(5′-3′)(Mouse) | Primer Sequence/(5′-3′)(Human) |
|---|---|---|
| Gapdh | F: AAGCCCATCACCATCTTCCA R: CACCAGTAGACTCCACGACA | F: AGATCCCTCCAAAATCAAGTGG R: GGCAGAGATGATGACCCTTTT |
| Ip3r | F: TGGCAGAGATGATCAGGGAAA R: GCTCGTTCTGTTCCCCTTCAG | F: GTGACAGGAAACATGCAGACTCG R: CAGCAGTTGCACAAAGACAGGC |
| Calm | F: ACTGGGTCAGAACCCAACAG R: GTTCTGCCGCACTGATGTAA | F: CCAACAGAAGCTGAATTGCAGGA R: CAAAGACTCGGAATGCCTCACG |
| Mlc | F: GAGGGCTACGTCCAATGTCT R: GTCGTGCAGGTCCTCCTTAT | F: GAGGGCAAAGGACCCATTAAC R: CTTCTGGGTCCGTTCCATTAAG |
| Mlck | F: GTTCATCAGCAAGCCTCGTT R: TTCTGGAGCAGCTCAAAGTG | F: GAGGTGCTTCAGAATGAGGACG R: GCATCAGTGACACCTGGCAACT |
| Cdk1 | F: GTCCGTCGTAACCTGTTGAG R: TGACTATATTTGGATGTCGAAG | F: GGAAACCAGGAAGCCTAGCATC R: GGATGATTCAGTGCCATTTTGCC |
| Cdc25c | F: CATTCAGATGGAGGAGGAAGAG R: CACTGTGTCTGGGCTGATATAC | F: AGAAGCCCATCGTCCCTTTGGA R: GCAGGATACTGGTTCAGAGACC |
| Plk1 | F: TGGGTGGACTATTCGGACAAG R: ACCCCCACACTGTTGTCACA | F: GCACAGTGTCAATGCCTCCAAG R: GCCGTACTTGTCCGAATAGTCC |
| Wee1 | F: GAAACAAGACCTGCCAAAAGAA R: GCATCCATCTAACCTCTTCACAC | F: GATGTGCGACAGACTCCTCAAG R: CTGGCTTCCATGTCTTCACCAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, W.; Liu, M.; Lan, H.; Wang, R.; Hung, W.-L.; He, J.; Fang, B. Modulation of Intestinal Smooth Muscle Cell Function by BL-99 Postbiotics in Functional Constipation. Foods 2025, 14, 3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193441
Zhao W, Liu M, Lan H, Wang R, Hung W-L, He J, Fang B. Modulation of Intestinal Smooth Muscle Cell Function by BL-99 Postbiotics in Functional Constipation. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193441
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Wen, Mingkun Liu, Hanglian Lan, Ran Wang, Wei-Lian Hung, Jian He, and Bing Fang. 2025. "Modulation of Intestinal Smooth Muscle Cell Function by BL-99 Postbiotics in Functional Constipation" Foods 14, no. 19: 3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193441
APA StyleZhao, W., Liu, M., Lan, H., Wang, R., Hung, W.-L., He, J., & Fang, B. (2025). Modulation of Intestinal Smooth Muscle Cell Function by BL-99 Postbiotics in Functional Constipation. Foods, 14(19), 3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193441






