Chlorogenic Acid Targets Cell Integrity and Virulence to Combat Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Cultivation
2.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration and Growth Curve Determination
2.3. Measurement of Extracellular Nucleic Acid and Protein Content
2.4. Measurement of Extracellular Potassium Ion and Glucose Content
2.5. Determination of Malondialdehyde (MDA) Content
2.6. Determination of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Content
2.7. Determination of Alkaline Phosphatase Content
2.8. Staining of Live and Dead Cells
2.9. Observation of Cell Morphology Using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.10. Determination of Hydrophobicity
2.11. Determination of Extracellular Polysaccharides
2.12. Determination of Biofilm
2.13. Motility Assay
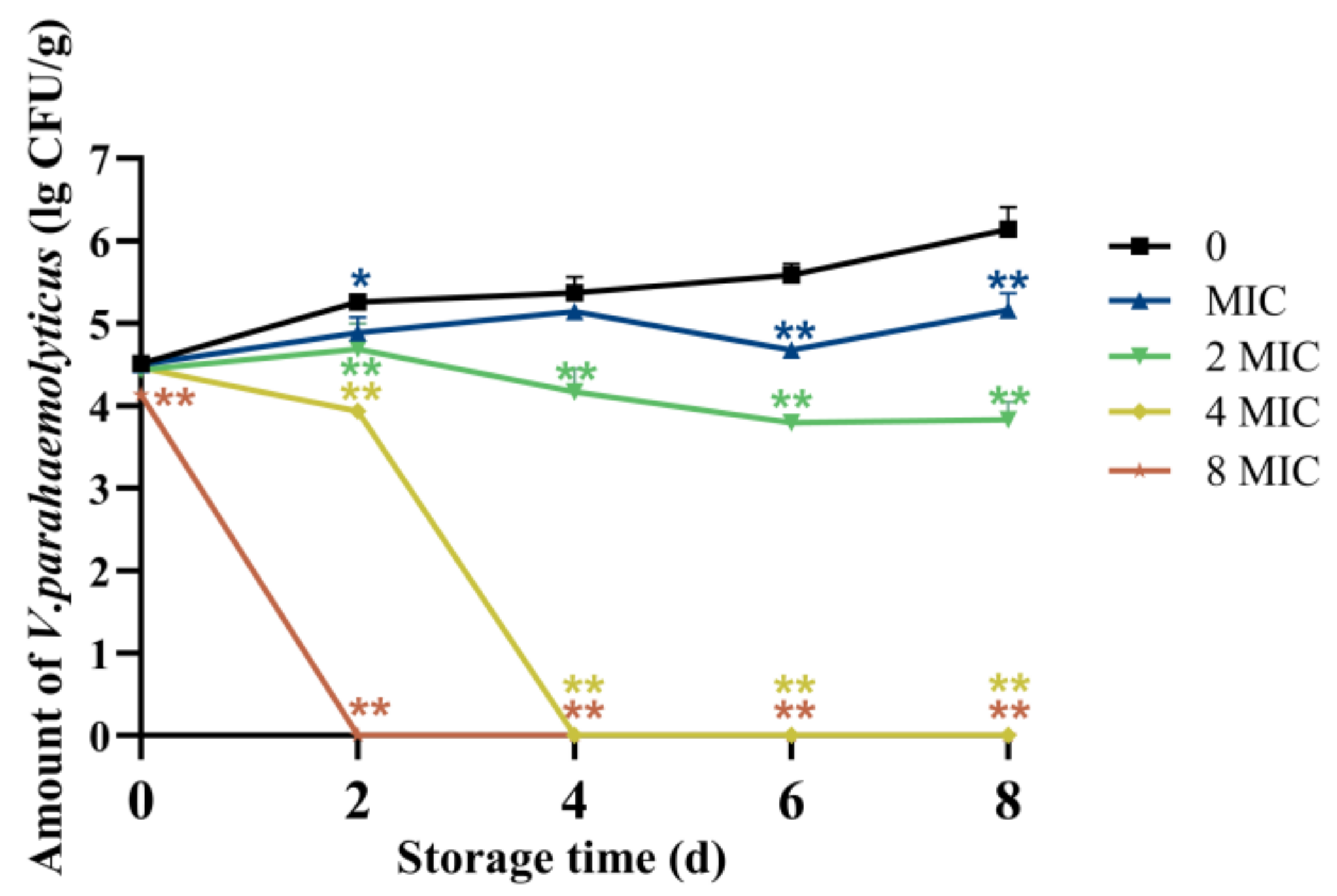
2.14. Application in Salmon Preservation
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
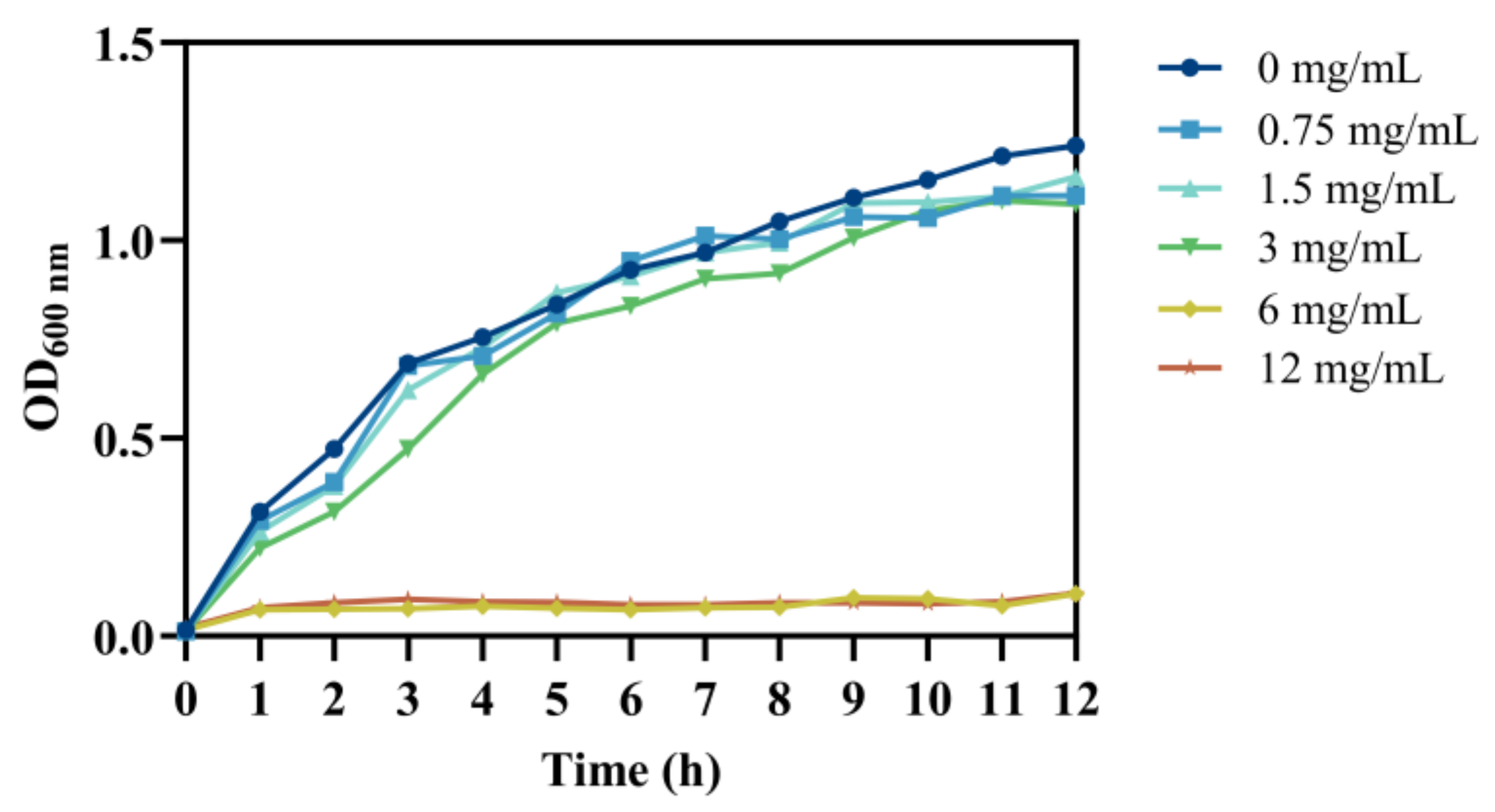
3.1. The Effect of Chlorogenic Acid on the Growth of V. parahaemolyticus
3.2. CA Targeted on the Cell Membrane and Cell Wall of V. parahaemolyticus
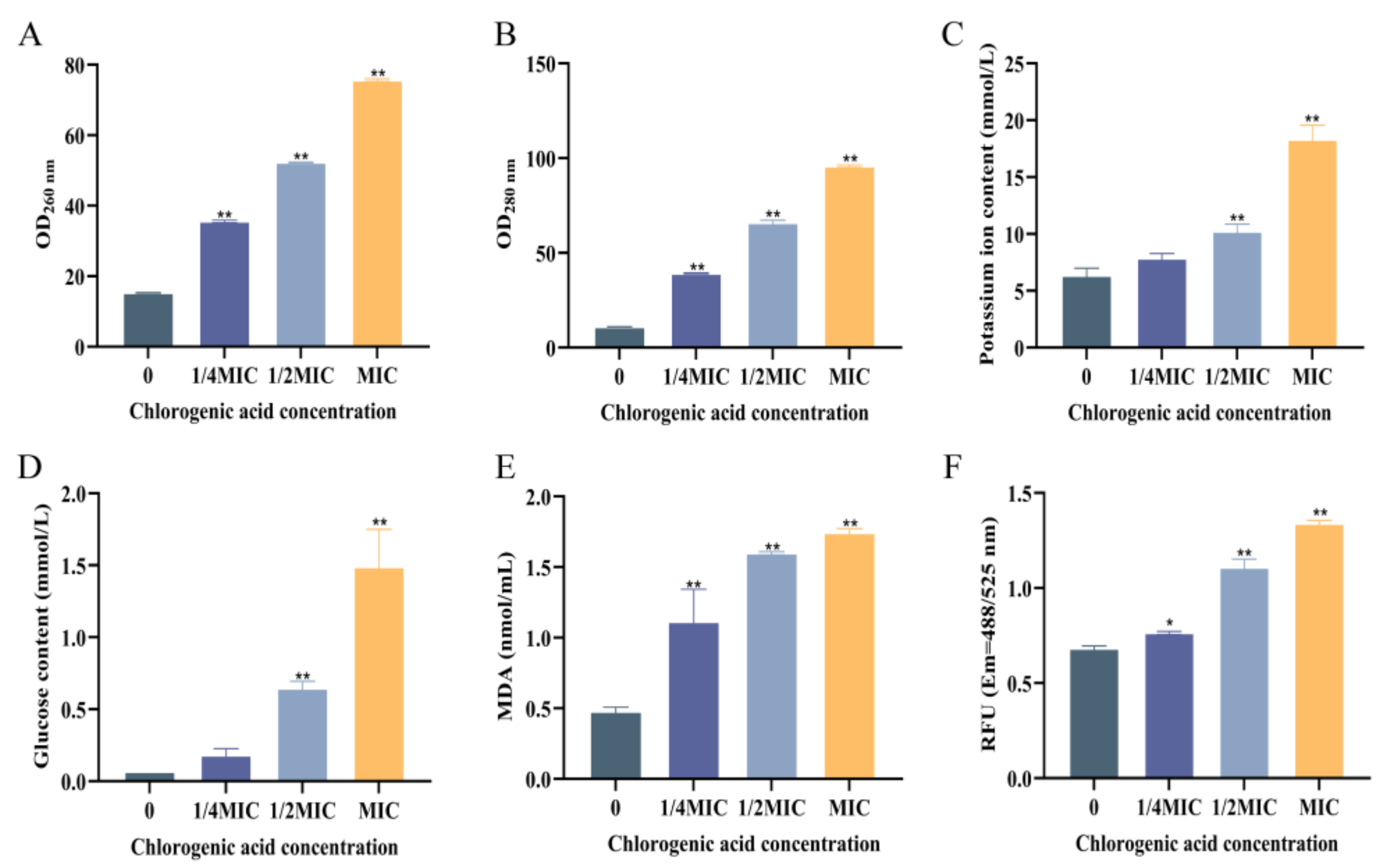
3.2.1. The Effect of CA on the Extracellular Nucleic Acid and Protein Content of V. parahaemolyticus
3.2.2. CA’s Action on the Extracellular Potassium Ion and Glucose Content of V. parahaemolyticus
3.2.3. The Effect of CA on Lipid Oxidation of V. parahaemolyticus
3.2.4. The Effect of CA on the Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Content of V. parahaemolyticus
3.2.5. The Effect of Chlorogenic Acid on Alkaline Phosphatase of V. parahaemolyticus
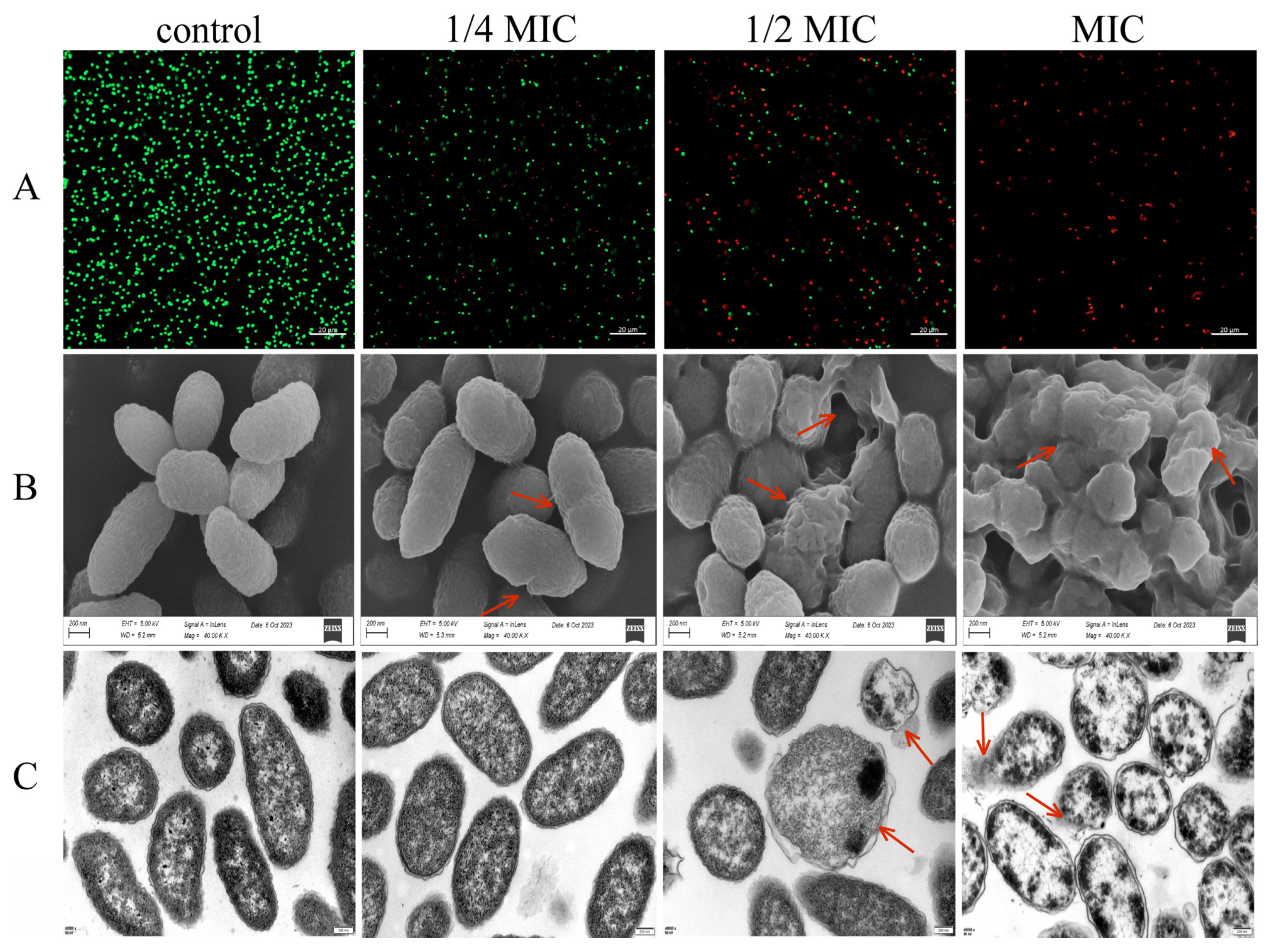
3.2.6. Staining of Live and Dead Cells
3.2.7. CA’s Effect on the Cell Morphology and Ultrastructure of V. parahaemolyticus
3.3. The Effect of Chlorogenic Acid on the Attenuation of V. parahaemolyticus
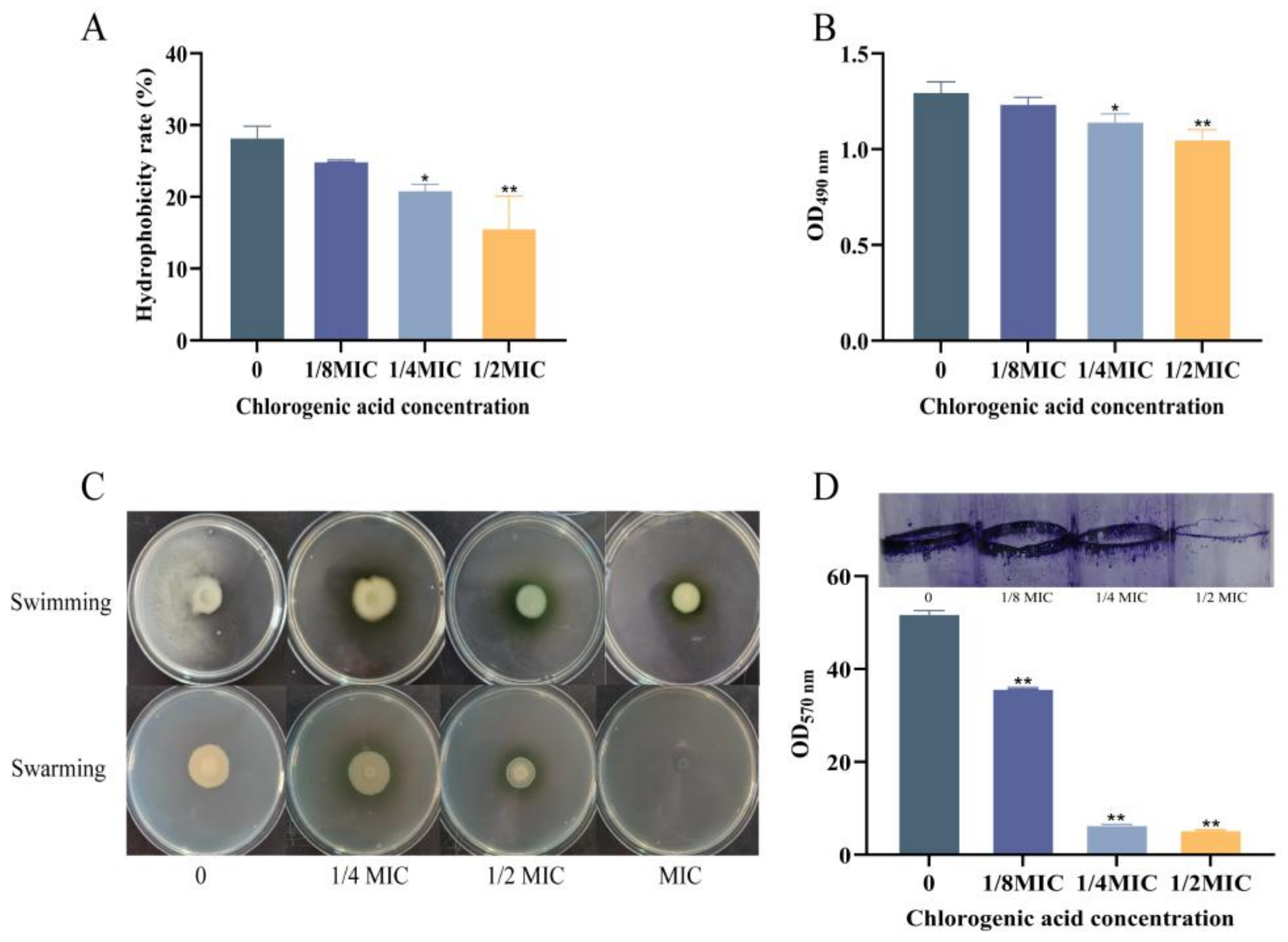
3.3.1. The Effect of Chlorogenic Acid on the Hydrophobicity of V. parahaemolyticus
3.3.2. The Effect of CA on the Extracellular Polysaccharide Content of V. parahaemolyticus
3.3.3. The Effect of CA on the Motility of V. parahaemolyticus
3.3.4. The Effect of CA on Biofilm Formation of V. parahaemolyticus
3.4. Changes in Bacterial Colonies of Salmon After Treatment with CA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, M.R.; Guo, Y.Y.; Wei, H.Z.; Zhu, Y.P.; Liu, R.R.; Ma, R.N.; Shi, F.K.; Guo, J.S.; Zhuang, J. The effectiveness of gliding arc discharge plasma in sterilizing artificial seawater contaminated with Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafudoulla, M.; Mizan, M.F.R.; Ha, A.J.W.; Park, S.H.; Ha, S.D. Antibacterial and antibiofilm mechanism of eugenol against antibiotic resistance Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Food Microbiol. 2020, 91, 103500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, F.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.X.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, H.M.; Zhang, M. Antimicrobial mechanism of linalool against Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its application in black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namadi, P.; Deng, Z.Q. Optimum environmental conditions controlling prevalence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in marine environment. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 183, 105828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Yang, Y.F.; Zhou, Y.J.; Zhang, R.H.; Liu, C.W.; Liu, H.; Li, X.G.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.N. Estimating the burden of foodborne gastroenteritis due to nontyphoidal Salmonella enterica, Shigella and Vibrio parahaemolyticus in China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0277203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearnley, E.; Leong, L.E.X.; Centofanti, A.; Dowsett, P.; Combs, B.; Draper, A.D.K.; Hocking, H.; Howden, B.; Horan, K.; Wilmot, M.; et al. Vibrio parahaemolyticus foodborne illness associated with oysters, Australia, 2021–2022. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 2271–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.K.; Roy, A.; Jeon, E.B.; DeWitt, C.A.M.; Park, J.W.; Park, S.Y. Comprehensive analysis of predominant pathogenic bacteria and viruses in seafood products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.P.; Zhou, S.X.; Wang, X.; Lu, Q.B.; Shi, L.S.; Ren, X.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Lin, S.H.; Zhang, C.H.; et al. Etiological, epidemiological, and clinical features of acute diarrhea in China. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, K.; Oshima, K.; Kurokawa, K.; Yokoyama, K.; Uda, T.; Tagomori, K.; Iijima, Y.; Najima, M.; Nakano, M.; Yamashita, A.; et al. Genome sequence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: A pathogenic mechanism distinct from that of V. cholerae. Lancet 2003, 361, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasu, H.; Iida, T.; Sugahara, T.; Yamaichi, Y.; Park, K.S.; Yokoyama, K.; Makino, K.; Shinagawa, H.; Honda, T. A filamentous phage associated with recent pandemic Vibrio parahaemolyticus O3:K6 strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 2156–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.L.; Yan, H.; Cui, Z.K.; Li, H.B.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Z.B.; Zhang, H.; Manoli, T.; Mo, H.Z.; Hu, L.B. Ultrasound-assisted blue light killing Vibrio parahaemolyticus to improve salmon preservation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 95, 106389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.M.; Sun, R.X.; Pan, C.G.; Sun, Y.; Mai, B.X.; Li, Q.X. Antibiotics and food safety in aquaculture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11908–11919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.P.; Zhang, S.; Chen, A.; Song, Z.G.; Shi, S.R. Comparison of the effects of chlorogenic acid isomers and their compounds on alleviating oxidative stress injury in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.X.; Li, F.; Zhe, T.T.; Sun, X.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wan, P.; Na, H.; Zhao, J.N.; Wang, L. Biopolymer films incorporated with chlorogenic acid nanoparticles for active food packaging application. Food Chem. 2024, 435, 137552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.Z.; Dang, M.Z.; Ge, Z.Z.; Huo, Y.Q.; Yu, B.; Tang, S.W. Interactions of chlorogenic acid and isochlorogenic acid A with model lipid bilayer membranes: Insights from molecular dynamics simulations. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2021, 240, 105136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.Y.; He, L.J. Synergistic improvement of antioxidant and antibacterial properties of carbon quantum complexes with zinc doping and chlorogenic acid for longan preservation. Food Chem. 2024, 439, 138169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Chen, S.; Fu, Q.; Zhu, S.Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Amelioration effects of chlorogenic acid on mice colitis: Anti-inflammatory and regulation of gut flora. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.H.; Piao, L.H.; Liu, X.D. Chlorogenic acid suppresses neutrophil recruitment to tumors by inducing apoptosis and reverse migration. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.L.; Yang, Y.H.; Mi, S.M.; Fan, Q.S.; Sun, X.M.; Deng, B.C.; Wu, G.Y.; Li, Y.F.; Zhou, Q.C.; Ruan, Z. Hepatoprotective effect of chlorogenic acid against chronic liver injury in inflammatory rats. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 62, 103540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Peng, C.T.; Chi, F.; Yu, C.D.; Yang, Q.L.; Li, Z.Z. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of chlorogenic acid against Yersinia enterocolitica. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 885092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Y.J.; He, L.Y.; Li, S.; Xiong, C.J.; Lu, C.H.; Yang, X.Y. Chlorogenic acid exerts antibacterial effects by affecting lipid metabolism and scavenging ROS in Streptococcus pyogenes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2022, 369, fnac061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.C.; Liu, N.Y.; Wang, C.J.; Luo, Y.; Liu, J.X. Lonicera japonica protects Pelodiscus sinensis by inhibiting the biofilm formation of Aeromonas hydrophila. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Wang, K.R.; Lu, T.Y.; Li, L.Z.; Jiao, X.A. Vibrio parahaemolyticus CadC regulates acid tolerance response to enhance bacterial motility and cytotoxicity. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; He, X.X.; Jiang, H.Y.; Yao, J.J.; Xia, F.; Zhao, Y.N.; Chen, X.F. Antimicrobial and antivirulence efficacies of citral against foodborne pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus RIMD2210633. Food Control 2021, 120, 107507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.J.; Zhang, Y.P.; Pan, X.H.; Zhu, F.Z.; Jiang, C.Y.; Liu, Q.Q.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Dai, G.; Wu, G.J.; Wang, L.Q.; et al. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1469–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebeloane, M.M.; Famuyide, I.M.; Dzoyem, J.P.; Adeyemo, R.O.; Makhubu, F.N.; Elgorashi, E.E.; Kgosana, K.G.; McGaw, L.J. Influence of selected plant extracts on bacterial motility, aggregation, hydrophobicity, exopolysaccharide production and quorum sensing during biofilm formation of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 167, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.Y.; Kang, S.N.; Guo, M.X.; Shen, C.Y.; Wang, L.H.; Xia, X.D.; Lü, X.; Shi, C. Evaluation of the antibacterial mechanism and biofilm removal effect of eugenol on Vibrio vulnificus and its application in fresh oysters. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Guan, L.; Yang, D.; Luo, H.L.; Zhang, H. Investigating the synergistic antibacterial effects of chlorogenic and p-coumaric acids on Shigella dysenteriae. Food Chem. 2025, 462, 141011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.M.; Liu, F.; Luo, Z.; Wu, H.H.; Zhang, X.X.; Wang, D.Y.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Sun, Z.L.; Xu, W.M.; Miao, Y. The antibacterial activity and mechanism of chlorogenic acid against foodborne pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhibar, H.; Laouani, A.; Touzout, S.N.; Alenazy, R.; Alqasmi, M.; Bokhari, Y.; Saguem, k.; Ben-Attia, M.; El-Bok, S.; Merghni, A. Chemical composition of Ailanthus altissima (Mill.) Swingle methanolic leaf extracts and assessment of their antibacterial activity through oxidative stress induction. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Koo, N.; Min, D.B. Reactive oxygen species, aging, and antioxidative nutraceuticals. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2004, 3, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kai, K.; Wang, R.; Bi, W.L.; Ma, Z.T.; Shi, W.; Ye, Y.W.; Zhang, D.F. Chlorogenic acid induces ROS-dependent apoptosis in Fusarium fujikuroi and decreases the postharvest rot of cherry tomato. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, C.L.; Su, Z.J.; Zhao, L.; Wu, J.X.; Sun, X.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Hu, X.Q. Inactivation of Salmonella typhimurium SL1344 by chlorogenic acid and the impairment of cellular integrity. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 887950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunthof Christine, J.; van Schalkwijk, S.; Meijer, W.; Abee, T.; Hugenholtz, J. Fluorescent method for monitoring cheese starter permeabilization and lysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 4264–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.H.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.F.; Zhang, B.G.; Xia, X.D. Antimicrobial effect and mode of action of chlorogenic acid on Staphylococcus aureus. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 238, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Wu, M.; Guo, W.Y.; Li, H.; Gai, Z.C.; Gong, G.L. Evaluation of the Membrane Damage Mechanism of Chlorogenic Acid against Yersinia enterocolitica and Enterobacter sakazakii and Its Application in the Preservation of Raw Pork and Skim Milk. Molecules 2021, 26, 6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.L.; Zhang, X.X.; Wu, H.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Bian, H.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Xu, W.M.; Liu, F.; Wang, D.Y.; Fu, L.Y. Antibacterial activity and action mode of chlorogenic acid against Salmonella enteritidis, a foodborne pathogen in chilled fresh chicken. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, G.; Regente, M.; Jacobi, S.; Del Rio, M.; Pinedo, M.; de la Canal, L. Chlorogenic acid is a fungicide active against phytopathogenic fungi. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 140, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.Y.; An, P.P.; Zhai, X.; Wang, S.; Kong, Q.J. The antibacterial mechanism of pterostilbene derived from xinjiang wine grape: A novel apoptosis inducer in Staphyloccocus aureus and Escherichia coli. LWT 2019, 101, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Lee, D.G. Depletion of reactive oxygen species induced by chlorogenic acid triggers apoptosis-like death in Escherichia coli. Free Radic. Res. 2018, 52, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.L.; Hao, L.R.; Lan, W.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.H. Blueberry extract inhibits quorum-sensing regulators and controls Vibrio parahaemolyticus biofilms and virulence. LWT 2023, 189, 115492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Y.; Li, Y.F.; Yang, X.; He, J.Z.; Tang, W.H.; Chai, Y.M.; Duan, Z.Y.; Li, W.J.; Zhao, D.; Wang, X.F.; et al. Chlorogenic acid: A promising strategy for milk preservation by inhibiting Staphylococcus aureus growth and biofilm formation. Foods 2024, 13, 4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Dey, P. Bacterial exopolysaccharides as emerging bioactive macromolecules: From fundamentals to applications. Res. Microbiol. 2023, 174, 104024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, F.H.; Visick, K.L. Vibrio biofilms: So much the same yet so different. Trends Microbiol. 2009, 17, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.Y.; Zhou, Y.N.; Zhang, M.M.; Li, X.; Zhang, N.; Luo, X.; Ni, B.; Wu, H.S.; Lu, R.F.; Zhang, Y.Q. CalR inhibits the swimming motility and polar flagellar gene expression in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Microbiol. 2024, 62, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafudoulla, M.; Mizan, M.F.R.; Park, H.; Byun, K.-H.; Lee, N.; Park, S.H.; Ha, S.-D. Genetic relationship, virulence factors, drug resistance profile and biofilm formation ability of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from mussel. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.Y.; Ma, Y.J.; Fu, J.J.; Zhao, A.J.; Guo, Z.R.; Malakar, P.K.; Pan, Y.J.; Zhao, Y. Effect of temperature on pathogenic and non-pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus biofilm formation. Food Control 2017, 73, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlan, R. Biofilms: Microbial life on surfaces. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. 2002, 8, 881. [Google Scholar]
- Abdallah, M.; Benoliel, C.; Drider, D.; Dhulster, P.; Chihib, N.-E. Biofilm formation and persistence on abiotic surfaces in the context of food and medical environments. Arch. Microbiol. 2014, 196, 453–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer, K. Should we stay or should we go? Local and national factionalism in the National Organization for Women. Qual. Sociol. 2017, 40, 403–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Flint, S.H.; Palmer, J.S.; Gagic, D.; Fletcher, G.C.; On, S.L.W. Global expansion of Vibrio parahaemolyticus threatens the seafood industry: Perspective on controlling its biofilm formation. LWT 2022, 158, 113182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, X.L.; Pei, H.R.; Liu, P.; Song, Y.; Wu, Y.L. Anti-biofilm activity of chlorogenic acid against Pseudomonas Using quorum sensing system. Foods 2023, 12, 3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroll, C.; Barken, K.B.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Struve, C. Role of type 1 and type 3 fimbriae in Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilm formation. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satish Kumar, R.; Samiraj, R.; Ann Susan, S. Antibiofilm and anti-β-lactamase activities of burdock root extract and chlorogenic acid against Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 542–551. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Zhao, J.; Shi, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhao, Y. Chlorogenic Acid Targets Cell Integrity and Virulence to Combat Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Foods 2025, 14, 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193416
Liu H, Zhao J, Shi Y, Cao J, Zhao Y. Chlorogenic Acid Targets Cell Integrity and Virulence to Combat Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193416
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Huan, Jie Zhao, Yile Shi, Juanjuan Cao, and Yanni Zhao. 2025. "Chlorogenic Acid Targets Cell Integrity and Virulence to Combat Vibrio parahaemolyticus" Foods 14, no. 19: 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193416
APA StyleLiu, H., Zhao, J., Shi, Y., Cao, J., & Zhao, Y. (2025). Chlorogenic Acid Targets Cell Integrity and Virulence to Combat Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Foods, 14(19), 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193416





