Matrix Interference of Vegetable on Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Parathion Residue Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
2.2. Analysis of Matrix Interference Mechanism
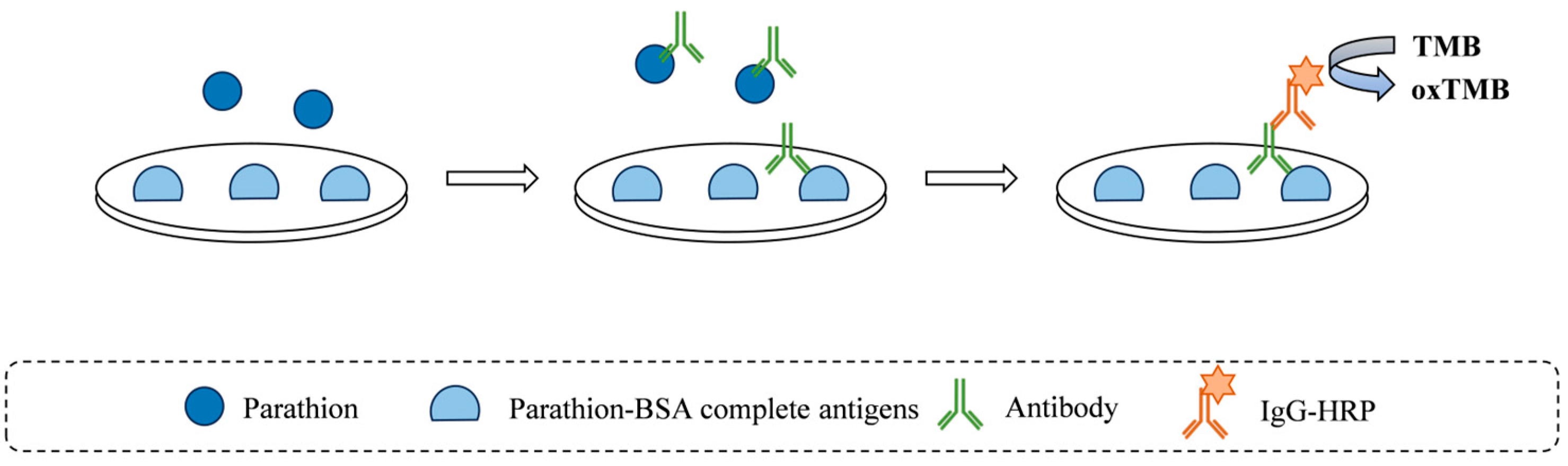
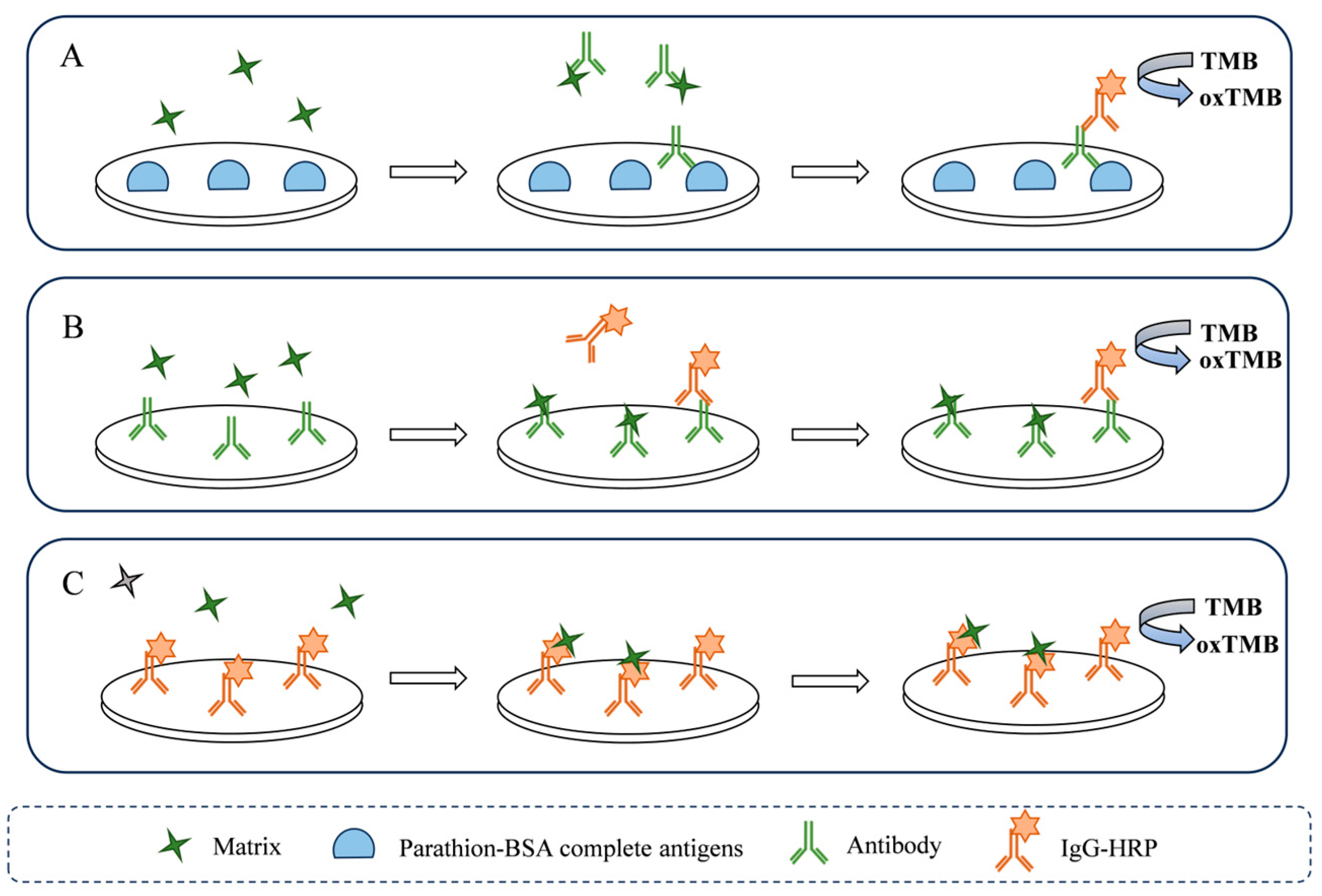
2.2.1. Analysis of Matrix Interference on Antigen–Antibody Binding
2.2.2. Analysis of Matrix Interference on Antibody–IgG-HRP Binding
2.2.3. Analysis of Matrix Interference on HRP
2.3. Elimination of Vegetable Matrix
2.3.1. Chlorophyll
2.3.2. Protein
2.4. Verification in Vegetable Samples
2.5. Establishment of an Immunoassay
2.6. Spike-and-Recovery Test for Vegetable Samples
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimal Concentrations of Parathion–BSA Complete Antigens and Antibody
3.2. Optimization of Competitive Step Time
3.3. Vegetable Matrix Interference on Antigen–Antibody Binding
3.4. Vegetable Matrix Interference on Antibody–IgG-HRP Binding
3.5. Vegetable Matrix Interference on HRP
3.6. Vegetable Matrix Interference on Residual Parathion ELISA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foong, S.Y.; Ma, N.L.; Lam, S.S.; Peng, W.; Low, F.; Lee, B.H.K.; Alstrup, A.K.O.; Sonne, C. A recent global review of hazardous chlorpyrifos pesticide in fruit and vegetables: Prevalence, remediation and actions needed. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonso, L.-F.; Germán, G.V.; María del Carmen, P.C.; Hossein, G. Adsorption of organophosphorus pesticides in tropical soils: The case of karst landscape of northwestern Yucatan. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, C.; Gowthaman, N.S.K.; Abraham John, S. Chain-like 2-amino-4-thiazoleacetic acid tethered AuNPs as colorimetric and spectrophotometric probe for organophosphate pesticide in water and fruit samples. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.-Y.; Liang, Y.-F.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-H.; Yang, J.-Y.; Shen, Y.-D.; Xu, Z.-L.; Hammock, B.; Hongsibsong, S.; et al. Engineering bioluminescent immunoassay for mix-to-measure parathion detection in foodstuffs. Microchem. J. 2025, 210, 112936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 2763-2021; National Food Safety Standard for Maximum Residue Limits of Pesticides in Food. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021. Available online: http://www.chinapesticide.org (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- European Commission. Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 February 2005 on maximum residue levels of pesticides in or on food and feed of plant and animal origin. Off. J. Eur. Union 2005, L70, 1–16. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2005/396/oj (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Khairy, M.; Ayoub, H.A.; Banks, C.E. Non-enzymatic electrochemical platform for parathion pesticide sensing based on nanometer-sized nickel oxide modified screen-printed electrodes. Food Chem. 2018, 255, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Tan, P.; Wang, R.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z. Advances in organophosphorus pesticides pollution: Current status and challenges in ecotoxicological, sustainable agriculture, and degradation strategies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nousiainen, M.; Peräkorpi, K.; Sillanpää, M. Determination of gas-phase produced ethyl parathion and toluene 2,4-diisocyanate by ion mobility spectrometry, gas chromatography and liquid chromatography. Talanta 2007, 72, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulgurcuoğlu, A.E.; Durak, B.Y.; Chormey, D.S.; Bakırdere, S. Development of a switchable solvent liquid phase extraction method for the determination of chlorthiamid, ethyl parathion, penconazole and fludioxonil pesticides in well, tap and lake water samples by gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, M.; He, M.; Liu, T.; Chen, F.; Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F. Magnetic solid phase extraction sorbents using methyl-parathion and quinalphos dual-template imprinted polymers coupled with GC-MS for class-selective extraction of twelve organophosphorus pesticides. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Hwang, H.-M. A Study of the Degradation of Organophosphorus Pesticides in River Waters and the Identification of Their Degradation Products by Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 56, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Xie, P.; Fan, L.; Cao, C.; Xi, T.; Zhou, P. Synthesis and characteristics of a novel artificial hapten using the copper mercaptide of penicillenic acid from penicillin G for immunoassay of heavy metal ions. Sci. China Life Sci. 2011, 54, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Yang, L.; Jin, M.; Du, P.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Shao, H.; Jin, F.; Zheng, L.; Wang, S.; et al. The Rapid Screening of Triazophos Residues in Agricultural Products by Chemiluminescent Enzyme Immunoassay. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Ding, Z. Evaluation of matrix effects for pesticide residue analysis by QuEChERs coupled with UHPLC-MS/MS in complex herbal matrix. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.H.; Kim, C.J.; Kim, S.-H.; Eun, H.-R.; Shin, Y.; Jeong, W.T. GC–MS/MS–based multiresidue pesticide analysis in mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) larvae: Optimization of standard QuEChERS-based method to minimize matrix effects. Food Chem. X 2025, 27, 102386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; He, Z.; Zeng, M.; Chen, J. Impact of Matrix Species and Mass Spectrometry on Matrix Effects in Multi-Residue Pesticide Analysis Based on QuEChERS-LC-MS. Foods 2023, 12, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damale, R.D.; Dutta, A.; Shaikh, N.; Pardeshi, A.; Shinde, R.; Babu, K.D.; Gaikwad, N.N.; Banerjee, K. Multiresidue analysis of pesticides in four different pomegranate cultivars: Investigating matrix effect variability by GC-MS/MS and LC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2023, 407, 135179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.F. Preparation of Fe3O4@BA-MOF magnetic solid-phase extraction material and its application to the detection of pesticide residues in tea. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2021, 39, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, J.; Yan, W.; Xia, Y. Facile synthesis disposable MOF membrane filter: Growth of NH2-MIL-125 (Ti) on filter paper for fast removal of organophosphorus pesticides in aqueous solution and vegetables. Food Chem. 2022, 389, 133056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zou, R.; Yi, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, H.; Qi, C.; Lai, W.; Guo, Y.; Xianyu, Y. “Four-In-One” Multifunctional Dandelion-Like Gold@platinum Nanoparticles-Driven Multimodal Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Small 2024, 20, 2310869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzi, E.; Piper, A.; Nastri, F.; Merkoçi, A.; Lombardi, A. An Artificial Miniaturized Peroxidase for Signal Amplification in Lateral Flow Immunoassays. Small 2023, 19, 2207949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanazzo, D.; Ricci, F.; Volpe, G.; Elliott, C.T.; Vesco, S.; Kroeger, K.; Moscone, D.; Stroka, J.; Van Egmond, H.; Vehniäinen, M.; et al. Development of a recombinant Fab-fragment based electrochemical immunosensor for deoxynivalenol detection in food samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2615–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edupuganti, S.R.; Edupuganti, O.P.; Hearty, S.; O’Kennedy, R. A highly stable, sensitive, regenerable and rapid immunoassay for detecting aflatoxin B1 in corn incorporating covalent AFB1 immobilization and a recombinant Fab antibody. Talanta 2013, 115, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Wang, K.; Vasylieva, N.; Zhou, H.; Xue, X.; Wang, B.; Li, Q.X.; Hammock, B.D.; Xu, T. Development of a nanobody-based ELISA for the detection of the insecticides cyantraniliprole and chlorantraniliprole in soil and the vegetable bok choy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 2503–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschemann-Witzel, J.; Gantriis, R.F.; Fraga, P.; Perez-Cueto, F.J.A. Plant-based food and protein trend from a business perspective: Markets, consumers, and the challenges and opportunities in the future. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Lin, H.; Gao, X.; Lin, H.; Li, Z. Insights into effects of processing and food matrices on structure and ELISA detection of sarcoplasmic calcium binding protein. Food Chem. 2025, 478, 143718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Sun, L.; Chen, G.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, H.; Li, Z. Influence of linoleic acid on the immunodetection of shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) tropomyosin and the mechanism investigation via multi-spectroscopic and molecular modeling techniques. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairoli, S.; Arnoldi, A.; Pagani, S. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for the Quantitation of the Fungicide Tetraconazole in Fruits and Fruit Juices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 3849–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, Y. Experiment Guidance of Postharvest Physiology and Biochemistry of Fruits and Vegetables; China Light Industry Press Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Parra, J.; Mercader, J.V.; Agulló, C.; Abad-Somovilla, A.; Abad-Fuentes, A. Generation of anti-azoxystrobin monoclonal antibodies from regioisomeric haptens functionalized at selected sites and development of indirect competitive immunoassays. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 715, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Huang, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, M.; Hua, X. Electrofusion preparation of anti-triazophos monoclonal antibodies for development of an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J. Immunol. Methods 2022, 500, 113184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland, A.V.; Dory, D.; Pons, L.; Chopin, C.; Rabesona, H.; Guéant, J.L.; Fleurence, J. Purification of a 41 kDa cod-allergenic protein. J. Chromatogr. B: Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1998, 706, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, H.; Cao, L.; Zhang, X.; Sui, J. The matrix interference to the immunoassay of food samples: The effect of some proteins in aquatic products. Food Agric. Immunol. 2016, 27, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyola, B.; Mendez, L.; Ramírez, J.; Sandoval Torres, S.; Aquino Gonzalez, L.; Barriada-Bernal, L. Techno-functional properties and antioxidant capacity of the concentrate and protein fractions of Leucaena spp. seeds. Arch. Latinoam. Nutr. 2022, 72, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuzhukin, V.I.; Gorbunov, V.S.; Bagdalova, A.Z. Study of biochemical composition of seeds and green beans of vegetable cowpea (Vigna Ung. ssp. Sesquipedalis). Russ. Agric. Sci. 2017, 43, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, H.; Sui, J.; Cao, L. The effect of fish matrix on the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of antibiotics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 93, 1603–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreen, K.; Ahamad, S.; Ahmad, F.; Hassan, M.I.; Islam, A. Macromolecular crowding induces molten globule state in the native myoglobin at physiological pH. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, J.; Mizoguchi, T.; Tsukatani, Y.; Yokono, M.; Tanaka, A.; Tamiaki, H. Chlorophyllide a Oxidoreductase Works as One of the Divinyl Reductases Specifically Involved in Bacteriochlorophyll a Biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 12716–12726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villari, V.; Mineo, P.; Scamporrino, E.; Micali, N. Amino acids recognition by water-soluble uncharged porphyrin tweezers: Spectroscopic evidences in high optical density solutions. Chem. Phys. 2012, 402, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, H.; Qu, X.; Zheng, H.; Sui, J.; Cao, L. The effect of fish matrix on colloidal gold immunochromatographic assay of antibiotics: The source of interference and removal method. Food Agric. Immunol. 2018, 29, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yan, T.; Liu, C.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Genetically encoded Nδ-vinyl histidine for the evolution of enzyme catalytic center. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karow, A.R.; Bahrenburg, S.; Garidel, P. Buffer capacity of biologics—From buffer salts to buffering by antibodies. Biotechnol. Prog. 2013, 29, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Cao, M.; Newell, K.; Afdahl, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.K.; Li, Y. Double-peak elution profile of a monoclonal antibody in cation exchange chromatography is caused by histidine-protonation-based charge variants. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1424, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostuni, E.; Chapman, R.G.; Holmlin, R.E.; Takayama, S.; Whitesides, G.M. A Survey of Structure−Property Relationships of Surfaces that Resist the Adsorption of Protein. Langmuir 2001, 17, 5605–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metelitza, D.I.; Karasyova, E.I.; Grintsevich, E.E.; Thorneley, R.N.F. Peroxidase-catalyzed co-oxidation of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine in the presence of substituted phenols and their polydisulfides. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2004, 98, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khramtsov, P.; Novokshonova, A.; Galaeva, Z.; Morozova, M.; Bezukladnikova, T.; Rayev, M. A Systematic Investigation of TMB Substrate Composition for Signal Enhancement in ELISA; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Estey, T.; Kang, J.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Carpenter, J.F. BSA degradation under acidic conditions: A model for protein instability during release from PLGA delivery systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 1626–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, N.; Karadeniz, F.; Burdurlu, H.S. Effect of pH on chlorophyll degradation and colour loss in blanched green peas. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Gong, N.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Sun, C.; Fang, W.; Men, Z. Effect of pH on fluorescence and absorption of aggregates of chlorophyll a and carotenoids. Dye. Pigment. 2020, 173, 107975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Long, M.; Huo, B. Competitive Binding to Cuprous Ions of Protein and BCA in the Bicinchoninic Acid Protein Assay. Open Biomed. Eng. J. 2010, 4, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wen, A.; Liu, J.; Wu, D.; Wu, Y. Facile extraction and determination of organophosphorus pesticides in vegetables via magnetic functionalized covalent organic framework nanocomposites. Food Chem. 2021, 337, 127974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraji, M.; Jafari, M.T.; Mossaddegh, M. Halloysite nanotubes-titanium dioxide as a solid-phase microextraction coating combined with negative corona discharge-ion mobility spectrometry for the determination of parathion. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 926, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.C.; Ma, J.K.; Feng, R.X.; Wei, S.L. Simultaneous determination of five organophosphorus pesticide residues in different food samples by solid-phase microextraction fibers coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 6998–7007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Antibody (mg·L−1) | Parathion-BSA Complete Antigens (mg·L−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.50 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 3.00 | |
| 0.25 | 0.44 | 0.67 | 0.53 | 0.56 |
| 0.50 | 0.62 | 0.66 | 0.69 | 0.65 |
| 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.09 | 1.06 | 1.05 |
| 2.00 | 1.62 | 1.76 | 1.76 | 1.68 |
| 4.00 | 2.40 | 2.56 | 2.60 | 2.57 |
| 8.00 | 2.81 | 3.04 | 3.14 | 2.97 |
| Method | Sample | Pre-Treatment | Average Recovery Rate/% | Im/% | RSD/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | Spinach | Non-acid treatment | 87–144 | 16 | 1–10 | This study |
| Perilla | 127–178 | 10 | 0–13 | |||
| Purple kale | 217–225 | 26 | 2–6 | |||
| Spinach | Acetic acid treatment | 84–113 | 14 | 1–7 | ||
| Perilla | 80–111 | 23 | 1–8 | |||
| Purple kale | 82–120 | 13 | 2–6 | |||
| Gas chromatography | Spinach | Magnetic solid-phase extraction | 97–98 | / | / | [52] |
| Lettuce | 101–121 | / | / | |||
| Cabbage | 102–114 | / | / | |||
| Negative corona discharge-ion mobility spectrometer | Celery | Solid-phase microextraction | 85–90 | / | 5–11 | [53] |
| High-performance liquid chromatography | Tomato | Solid-phase microextraction | 92–96 | / | 5–7 | [54] |
| Cabbage | 86–92 | / | 6–6 | |||
| Barley | 86–96 | / | 4–7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, G.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Qin, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Matrix Interference of Vegetable on Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Parathion Residue Detection. Foods 2025, 14, 3414. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193414
Chen L, Chen G, Zhang X, Wu Q, Liu G, Xu X, Zhang Y, Li L, Qin L, Wang J, et al. Matrix Interference of Vegetable on Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Parathion Residue Detection. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3414. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193414
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Linglong, Ge Chen, Xing Zhang, Qinghuan Wu, Guangyang Liu, Xiaomin Xu, Yanguo Zhang, Lingyun Li, Lin Qin, Jing Wang, and et al. 2025. "Matrix Interference of Vegetable on Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Parathion Residue Detection" Foods 14, no. 19: 3414. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193414
APA StyleChen, L., Chen, G., Zhang, X., Wu, Q., Liu, G., Xu, X., Zhang, Y., Li, L., Qin, L., Wang, J., Jin, M., & Xu, D. (2025). Matrix Interference of Vegetable on Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Parathion Residue Detection. Foods, 14(19), 3414. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193414









