Wheat Bran-Derived Zinc Phytate Mitigates Hepatic Inflammation and Metabolic Disorders Associated with Gut Microbiota-FXR–PGC-1α Signaling in High-Fat Diet-Fed C57BL/6J Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Extraction of Zinc Phytate (ZnPA) from WHB
2.3. Animal Experiments
2.4. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) and Insulin Tolerance Test (ITT)
2.5. Biochemical Index Analysis of Serum and Liver
2.6. Histological Analysis
2.7. 16S rDNA Gene Amplification and MiSeq Sequencing
2.8. Analysis for Inositol Phosphates in Feces Samples
2.9. Assay for Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) in Colon Feces
2.10. Metabolomics Analysis of Feces
2.11. Quantitative RT-PCR Assay for HDAC3
2.12. Western Blot Analysis
2.13. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. ZnPA Decreases Body Weight and Alleviates Glucolipid Metabolism and Hepatic Steatosis in HFD-Fed Mice
3.2. ZnPA Restores Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in HFD-Fed Obese Mice
3.3. ZnPA Regulates Metabolites of ZnPA and SCFAs Profiles in Obese Mice
3.4. ZnPA Regulates Colonic Metabolites Related to Bile Acid Metabolism in HFD-Fed Obese Mice
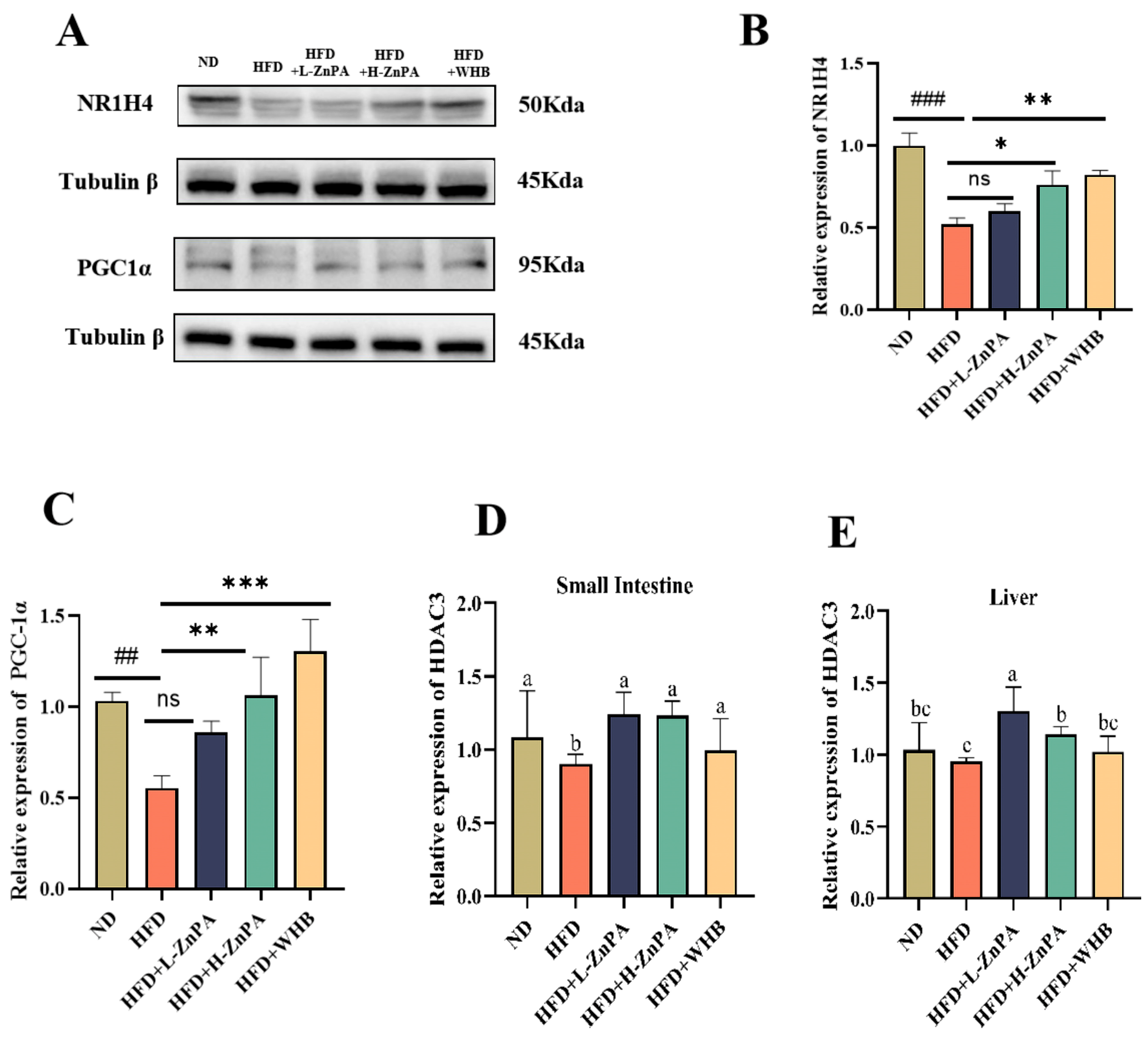
3.5. ZnPA Regulates HDAC3 and FXR–PGC-1α Signaling in the Liver of Obese Mice
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, F.C.; Butsch, W.S. Metabolically Healthy Obesity and Development of Chronic Kidney Disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 165, 742–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, J.; Li, X.; Chen, P.; Chen, F.; Pan, Y.; Deng, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, R.; Luo, T. Tyrosol Regulates Hepatic Lipid Metabolism in High-Fat Diet-Induced NAFLD Mice. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 3752–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Jin, X.; Li, Y. Current Strategies for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Treatment (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2024, 54, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Song, H.; Su, X.; Li, J.; Ye, Y.B.; Wang, C.L.; Xu, X.; Pang, G.L.; Liu, W.X.; Li, Z.H.; et al. Prophylactic Effects of Nutrition, Dietary Strategies, Exercise, Lifestyle and Environment on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Ann. Med. 2025, 57, 2464223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdomo, C.M.; Frühbeck, G.; Escalada, J. Impact of Nutritional Changes on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caussy, C.; Tripathi, A.; Humphrey, G.; Bassirian, S.; Singh, S.; Faulkner, C.; Bettencourt, R.; Rizo, E.; Richards, L.; Xu, Z.Z.; et al. A Gut Microbiome Signature for Cirrhosis Due to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kootte, R.S.; Vrieze, A.; Holleman, F.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M.; Zoetendal, E.G.; de Vos, W.M.; Groen, A.K.; Hoekstra, J.B.L.; Stroes, E.S.; Nieuwdorp, M. The Therapeutic Potential of Manipulating Gut Microbiota in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.Y.; Zhao, C.N.; Xu, X.Y.; Tang, G.Y.; Corke, H.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, H.B. Dietary Plants, Gut Microbiota, and Obesity: Effects and Mechanisms. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leão, G.O.C.; Galvão, F.C.; Gonçalves, C.D.R.A. Dietary Fat and Gut Microbiota: Mechanisms Involved in Obesity Control. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3045–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, R.W.; Arhire, L.; Covasa, M. Gut Microbiota: From Microorganisms to Metabolic Organ Influencing Obesity. Obesity 2018, 26, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.H.; Wang, M.L.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, L.Q.; Chai, X.J.; Zheng, W.; Chen, S.L.; Zhu, X.Y.; Zhao, S.T. High-fat Diet-disturbed Gut Microbiota-colonocyte Interactions Contribute to Dysregulating Peripheral Tryptophan-kynurenine Metabolism. Microbiome 2023, 11, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Whon, T.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Jeon, C.O.; Bae, J.W. Gut Microbiome Therapy: Fecal Microbiota Transplantation vs Live Biotherapeutic Products. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2412376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Liang, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, A.; Tang, P.; et al. Gut Microbiota Induces DNA Methylation via SCFAs Predisposing Obesity-Prone Individuals to Diabetes. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 182, 106355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Wu, J.; Li, Z. Vegetable Oil Intake: The Distinctive Trilateral Relationship of Bile Acid, Gut Microbiota and Health. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 160, 105001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Li, P.; Luo, X.; Lei, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Xu, W.; Liu, X. Dietary Patterns Interfere with Gut Microbiota to Combat Obesity. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1387394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, A.; Uchino, G.; Akabane, T.; Aiseki, A.; Perera, I.; Hirotsu, N. Phytic Acid in Brown Rice Can Be Reduced by Increasing Soaking Temperature. Foods 2021, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, A.G., Jr. Structure Studies of Phytate-Zinc Ion Complexes: X-Ray Diffraction and Thermal Analysis. Inorganica Chim. Acta 1985, 106, L9–L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Skibsted, L.H. Zinc Bioavailability from Phytate-Rich Foods and Zinc Supplements. Modeling the Effects of Food Components with Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Sulfur Donor Ligands. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8727–8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.R.; Ellis, R. Bioavailability to Rats of Iron and Zinc in Wheat Bran: Response to Low-Phytate Bran and Effect of the Phytate/Zinc Molar Ratio. J. Nutr. 1980, 110, 2000–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, N.K.; Scholey, D.V.; Burton, E.J. Use of Zn Concentration in the Gastrointestinal Tract as a Measure of Phytate Susceptibility to the Effect of Phytase Supplementation in Broilers. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Liu, J.; Fu, S.; He, F.; Li, K.; Hu, G.; Guo, W. Phytic Acid Maintains the Integrity of the Blood–Milk Barrier by Regulating Inflammatory Response and Intestinal Flora Structure. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, X.; Hu, G.; He, F.; Li, K.; Li, F.; Xu, D.; Liu, J.; Fu, S. Phytic Acid Improves Hepatic Steatosis, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress in High-Fat Diet (HFD)-Fed Mice by Modulating the Gut-Liver Axis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 11401–11411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Hashimoto-Hill, S.; Woo, V.; Eshleman, E.M.; Whitt, J.; Engleman, L.; Karns, R.; Denson, L.A.; Haslam, D.B.; Alenghat, T. Microbiota-Derived Metabolite Promotes HDAC3 Activity in the Gut. Nature 2020, 586, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Pasha, I.; Saeed, M.; Asgher, M. Antioxidant Profiling of Native and Modified Cereal Brans. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Ahmad, F.; Pasha, I.; Nasir, M.A.; Subtain, M.; Ahmad, S. Characterization and End-Use Perspectives of Modified Cereal Brans: A Step towards Waste Valorization. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 15, 17727–17737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadni, M.; Haudrechy, A.; Couvreur, J.; Allais, F. Investigation of Ferulic Acid Recovery from Enzymatic Hydrolysate of Wheat Bran Using Various Solvents and Liquid-Liquid Extraction Assisted by Membrane Contactor. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 400, 124538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Sun, J.; Zhao, W.T.; Wang, D.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhao, X.Y. Tomato Pectin Ameliorated Hepatic Steato sis in High-Fat-Diet Mice by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Bile Acid Metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 13700–13716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.T.; Yang, C.Y.; Peng, L.; Li, L.; Chen, N.T.; Feng, X.; Xie, J.; Wu, T.C.; Xu, T.; Chen, Y.Z. QiShenYiQi Pill Inhibits Ath erosclerosis by Promoting TTC39B-LXR Mediated Reverse Cholesterol Transport in Liver. Phytomedicine 2024, 123, 155192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Ren, D.; Li, T.; Niu, P.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Xiao, J. Fu Brick Tea Manages HFD/STZ-Induced Type 2 Diabetes by Regu lating the Gut Microbiota and Activating the IRS1/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8274–8287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzack, F.; Hubel, F.; Zhang, W.; Hansen, P.E.; Rasmussen, S.K. Inositol Phosphates from Barley Low-Phytate Grain Mutants Analysed by Metal-Dye Detection HPLC and NMR. Biochem. J. 2001, 354, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grases, F.; Simonet, B.M.; Prieto, R.M.; March, J.G. Phytate Levels in Diverse Rat Tissues: Influence of Dietary Phytate. Br. J. Nutr. 2001, 86, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.C.; Du, Y.; Zhao, A.Q.; Liu, L.; Ren, D.Y.; Niu, P.F.; Zhang, X.N.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.B. Dietary Turmeric Consumption Alleviates Ulcerative Colitis via Restoring Tryptophan Metabolism and Alleviating Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 15213–15224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, J.; Ning, Y.; Ren, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zong, X.; Shi, H. Enhancement of PPARα-Inhibited Leucine Metabolism-Stimulated β-Casein Synthesis and Fatty Acid Synthesis in Primary Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 16184–16193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, B.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, D.; Qin, X.; Wang, N.; Yang, X. Fu Brick Tea Alleviates Constipation via Regulating the Aquaporins-Mediated Water Transport System in Association with Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 3862–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, L.; Lin, J.D. Reprogramming of Hepatic Metabolism and Microenvironment in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2022, 42, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.X.; He, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, C.L.; Wu, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.; Qin, L.-Q.; Li, Y.-H. Protective Effect and Mechanism of Lactoferrin Combined with Hypoxia against High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 227, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.M.; Zhou, T.Y.; Zhang, S.Q.; Leng, J.C.; Li, L.; Zhao, W. β-Glucan-Based Superabsorbent Hydrogel Ameliorates Obesity-Associated Metabolic Disorders via Delaying Gastric Emptying, Improving Intestinal Barrier Function, and Modulating Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 304, 140846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.J.; Lao, X.Q.; Wu, Y.Z.; Zhang, J.; Liang, M.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Gao, X.W. Insights into Effects of Sodium Phytate on Gut Microbiome of Mice by High-Throughput Sequencing. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2023, 37, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Gao, W.; Liu, Z.; Fang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Lu, W.; Chen, W. Specific Strains of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii Ameliorate Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice in Association with Gut Microbiota Regulation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, A.S.; Andersson, H.; Carlsson, N.G.; Sandström, B. Degradation Products of Bran Phytate Formed during Digestion in the Human Small Intestine: Effect of Extrusion Cooking on Digestibility. J. Nutr. 1987, 117, 2061–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ann-Sofie, S.; Henrik, A. Effect of Dietary Phytase on the Digestion of Phytate in the Stomach and Small Intestine of Humans. J. Nutr. 1988, 118, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Zhang, S.; Dong, L.; Huang, F.; Jia, X.; Su, D.; Chi, J.; Muhammad, Z.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, D.; et al. Shatianyu (Citrus grandis L. Osbeck) Flavonoids and Dietary Fiber in Combination Are More Effective Than Individually in Alleviating High-Fat-Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemia in Mice by Altering Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 14654–14664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ablimit, N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Miao, T.; Wu, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. Novel β-Mannanase/GLP-1 Fusion Peptide High Effectively Ameliorates Obesity in a Mouse Model by Modifying Balance of Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Li, D.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, M.; Jia, L.; Yang, F. Cordyceps Militaris Polysaccharide Alleviates Di abetic Symptoms by Regulating Gut Microbiota against TLR4/NF-κB Pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ai, C.; Lin, X.; Guo, X.; Song, S.; Zhu, B. Sea Cucumber Sulfated Polysaccharides and Lactobacillus Gasseri Synergistically Ameliorate the Overweight Induced by Altered Gut Microbiota in Mice. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 4106–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- House, W.A.; Welch, R.M.; Van Campen, D.R. Effect of Phytic Acid on the Absorption, Distribution, and Endogenous Excretion of Zinc in Rats. J. Nutr. 1982, 112, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Sang, Y.; Dong, L. The Improved Effect and Its Mechanism of Phytic Acid on DSS-Induced UC Mice. Life Sci. 2022, 311, 121139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilworth, L.; Stennett, D.; Omoruyi, F. Cellular and Molecular Activities of IP6 in Disease Prevention and Therapy. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazyan, R.; Sun, Z.; Kim, Y.H.; Titchenell, P.M.; Hill, D.A.; Lu, W.Y.; Damle, M.; Wan, M.; Zhang, Y.X.; Briggs, E.R.; et al. Physiological Suppression of Lipotoxic Liver Damage by Complementary Actions of HDAC3 and SCAP/SREBP. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Yan, S.; Sun, W.; Yan, J.; Teng, M.; Jia, M.; Tian, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, W. Chlorothalonil Induces Obesity in Mice by Regulating Host Gut Microbiota and Bile Acids Metabolism via FXR Pathways. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Andreu-Sánchez, S.; Kuipers, F.; Fu, J. Gut Microbiome and Bile Acids in Obesity-Related Diseases. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 35, 101493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adorini, L.; Trauner, M. FXR Agonists in NASH Treatment. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1317–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, W.; Liu, P.; Shen, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Li, T.; et al. PGC1α Protects against Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance via Enhancing IL10-Mediated Anti-Inflammatory Response. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 10751–10761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.C.; Dou, J.Y.; Xuan, M.Y.; Gao, C.; Li, Z.X.; Lian, L.H.; Cui, Z.Y.; Nan, J.X.; Wu, Y.L. Raspberry Ketone Attenuates Hepatic Fibrogenesis and Inflammation via Regulating the Crosstalk of FXR and PGC-1α Signaling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 15740–15754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadaleta, R.M.; van Erpecum, K.J.; Oldenburg, B.; Willemsen, E.C.L.; Renooij, W.; Murzilli, S.; Klomp, L.W.J.; Siersema, P.D.; Schipper, M.E.I.; Danese, S.; et al. Farnesoid X Receptor Activation Inhibits Inflammation and Preserves the Intestinal Barrier in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gut 2011, 60, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farup, P.G.; Valeur, J. Changes in Faecal Short-Chain Fatty Acids after Weight-Loss Interventions in Subjects with Morbid Obesity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Bi, J.; Yi, J.; Peng, J.; Ma, Q. Dose-Dependent Effects of Apple Pectin on Alleviating High Fat-Induced Obesity Modulated by Gut Microbiota and SCFAs. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeger, D.; O’Mahony, L.; Murphy, E.F.; Bourke, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Kiely, B.; Shanahan, F.; Quigley, E.M.M. Bifidobacterium Infantis 35624 Modulates Host Inflammatory Processes beyond the Gut. Gut Microbes 2013, 4, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
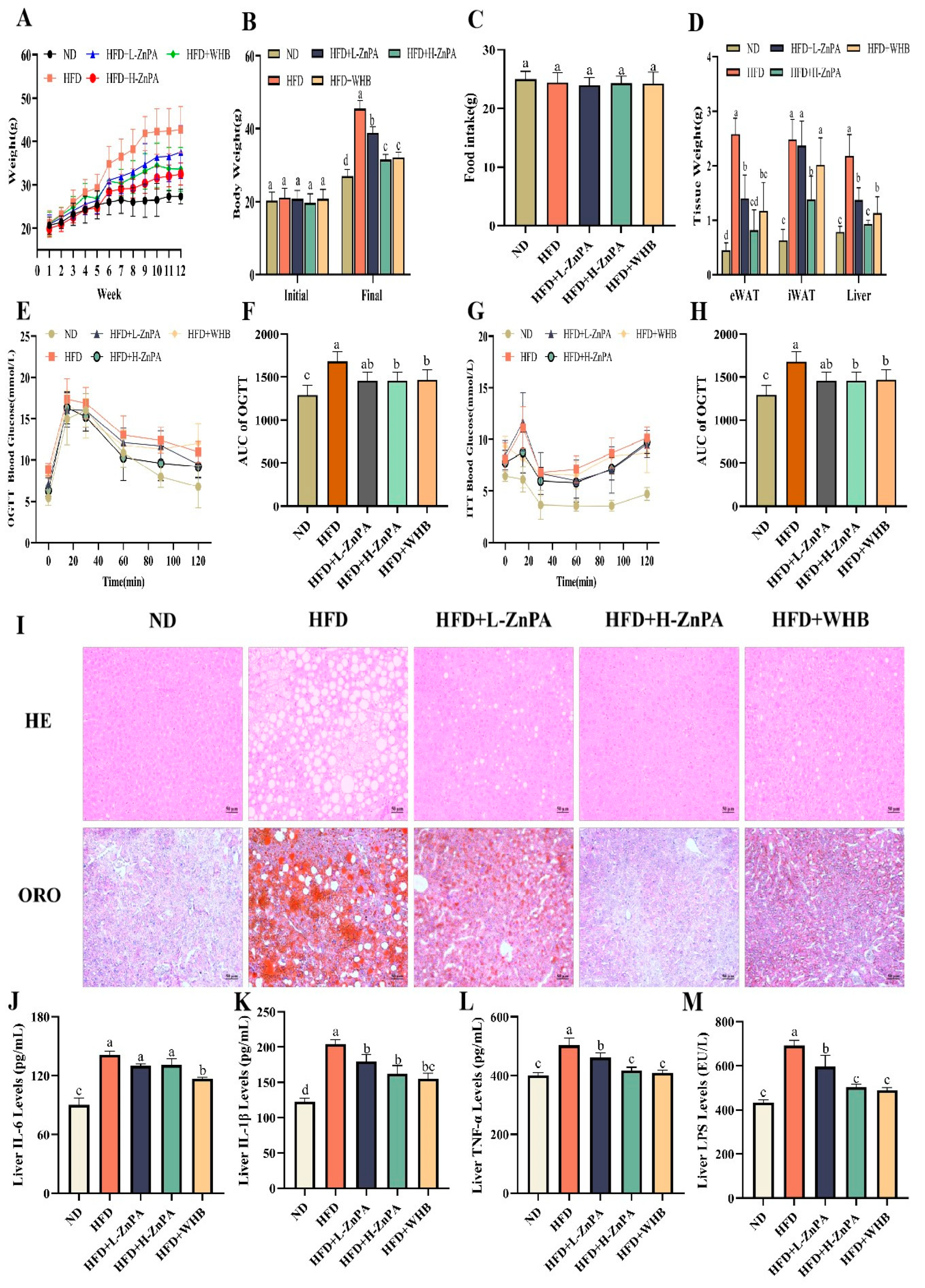
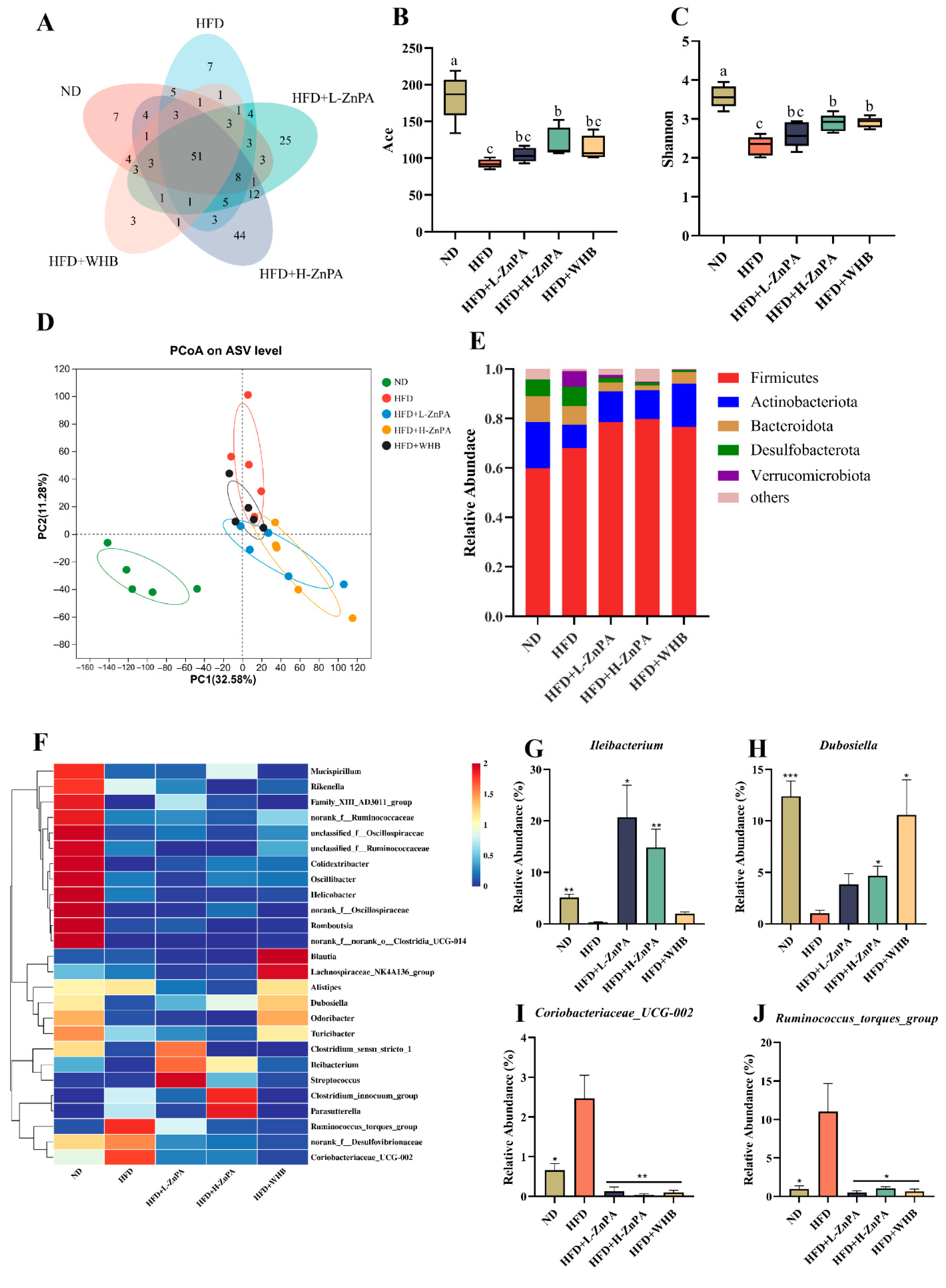
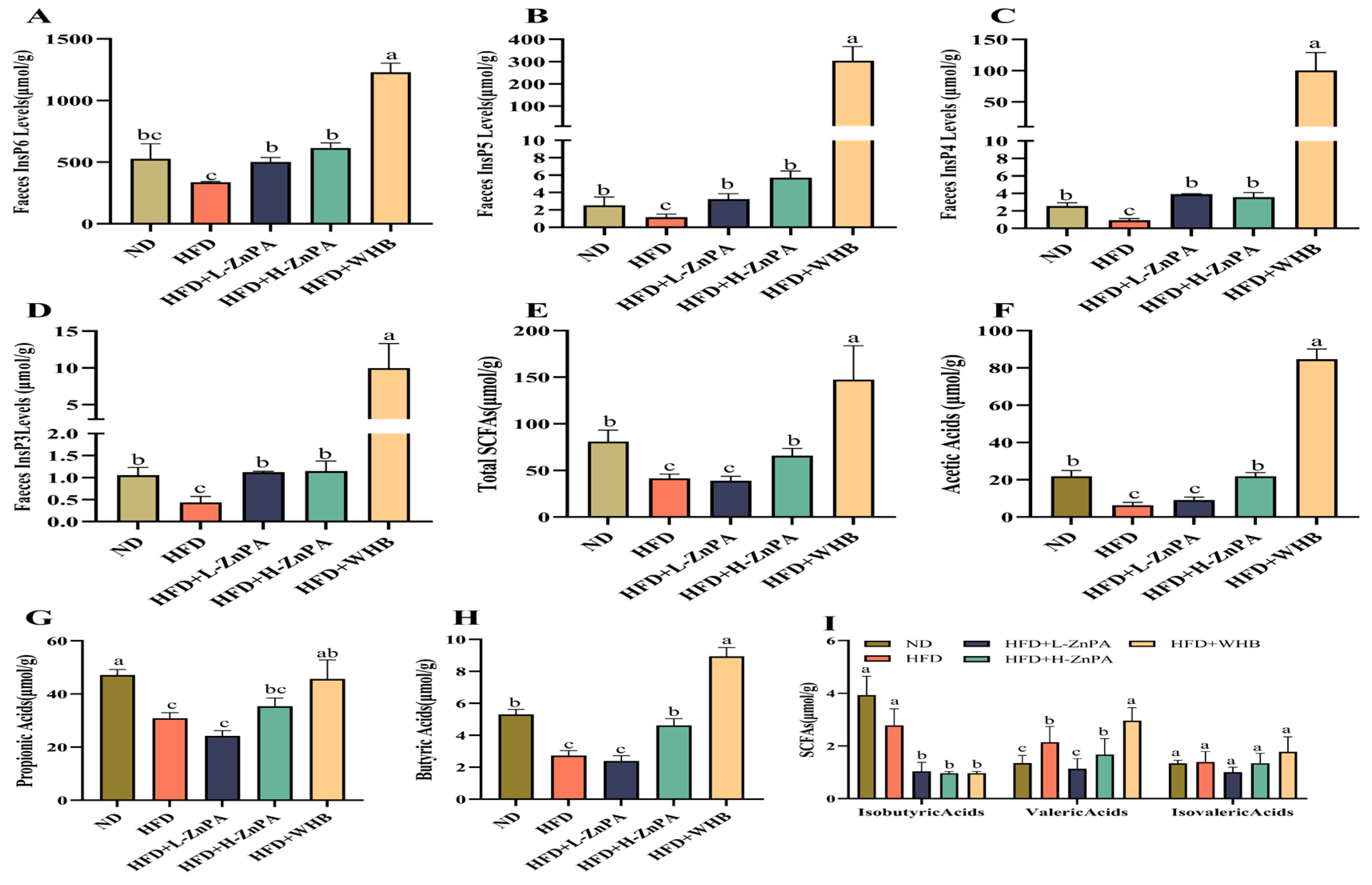
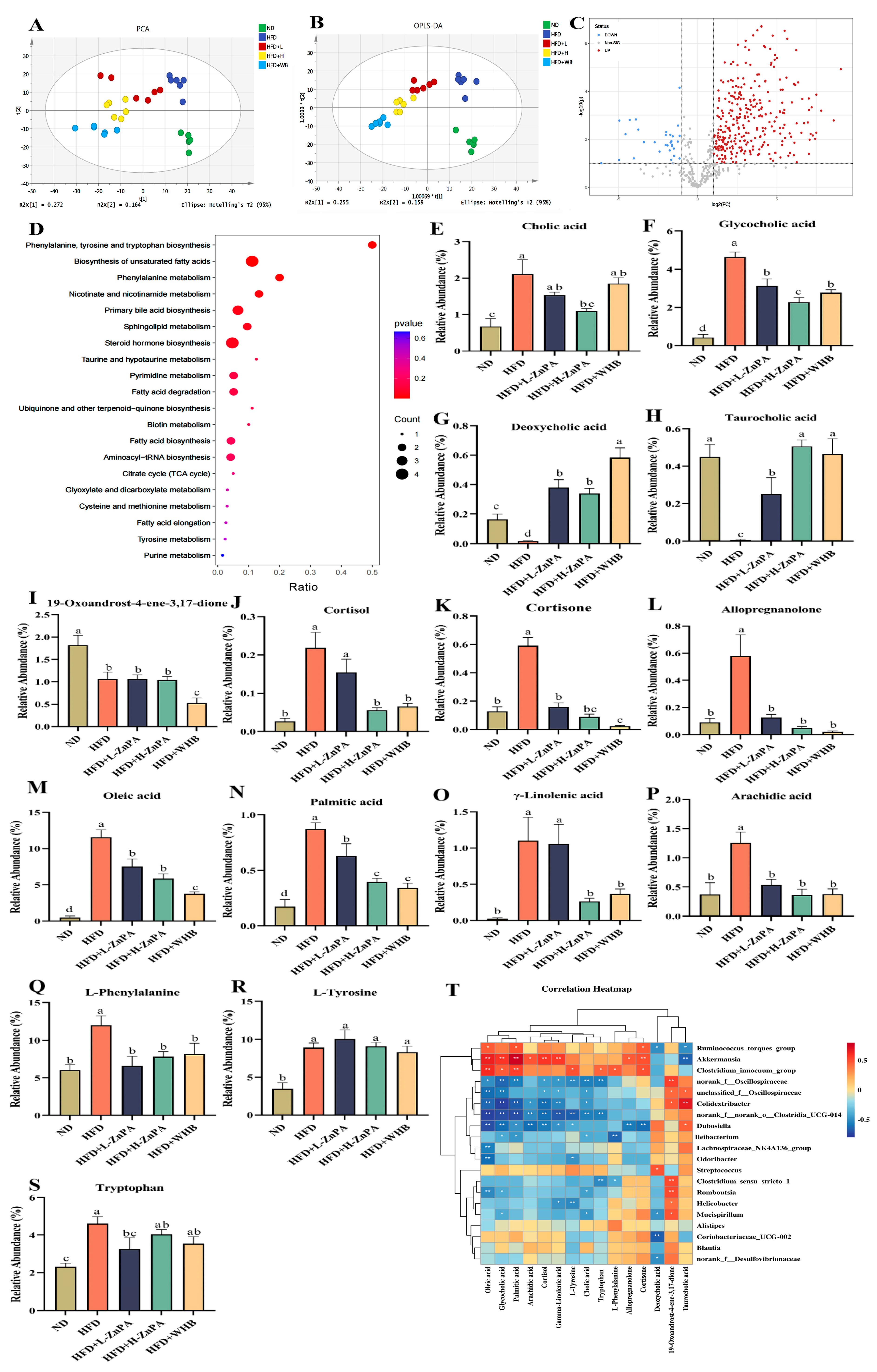
| Group | ND | HFD | HFD+L-ZnPA | HFD+L-ZnPA | HFD+WHB | Normal Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.09 ± 0.46 b | 6.12 ± 0.60 a | 4.18 ± 0.40 b | 3.41 ± 0.53 b | 2.47 ± 0.34 c | 2.0–3.5 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 0.46 ± 0.08 c | 0.90 ± 0.03 a | 0.72 ± 0.03 b | 0.51 ± 0.05 c | 0.43 ± 0.07 c | 0.3–0.6 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 0.84 ± 0.06 a | 0.33 ± 0.07 d | 0.51 ± 0.04 c | 0.59 ± 0.05 bc | 0.69 ± 0.06 b | 0.7–1.2 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 0.61 ± 0.02 c | 0.90 ± 0.04 a | 0.72 ± 0.10 b | 0.63 ± 0.04 bc | 0.60 ± 0.02 c | 0.2–0.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, P.; Zhao, A.; Zhan, M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X. Wheat Bran-Derived Zinc Phytate Mitigates Hepatic Inflammation and Metabolic Disorders Associated with Gut Microbiota-FXR–PGC-1α Signaling in High-Fat Diet-Fed C57BL/6J Mice. Foods 2025, 14, 3367. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193367
Yu P, Zhao A, Zhan M, Zhang L, Yang C, Zhao Y, Yang X. Wheat Bran-Derived Zinc Phytate Mitigates Hepatic Inflammation and Metabolic Disorders Associated with Gut Microbiota-FXR–PGC-1α Signaling in High-Fat Diet-Fed C57BL/6J Mice. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3367. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193367
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Pinglian, Aiqing Zhao, Mingfang Zhan, Liansheng Zhang, Chengcheng Yang, Yan Zhao, and Xingbin Yang. 2025. "Wheat Bran-Derived Zinc Phytate Mitigates Hepatic Inflammation and Metabolic Disorders Associated with Gut Microbiota-FXR–PGC-1α Signaling in High-Fat Diet-Fed C57BL/6J Mice" Foods 14, no. 19: 3367. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193367
APA StyleYu, P., Zhao, A., Zhan, M., Zhang, L., Yang, C., Zhao, Y., & Yang, X. (2025). Wheat Bran-Derived Zinc Phytate Mitigates Hepatic Inflammation and Metabolic Disorders Associated with Gut Microbiota-FXR–PGC-1α Signaling in High-Fat Diet-Fed C57BL/6J Mice. Foods, 14(19), 3367. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193367




