Catechin-Targeted Nano-Enhanced Colorimetric Sensor Array Based on Quantum Dots—Nano Porphyrin for Precise Analysis of Xihu Longjing from Adjacent Origins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of CdTe QDs Modified with Different Ligands
2.3. Preparation of Nano Porphyrins
2.4. QDs–Nano Porphyrin Dual Signal Visualization Sensor Construction
2.5. Sample Treatment
2.6. Sample Detection and Data Analysis
2.7. Antioxidant Test of Longjing Tea
2.8. Sensory Evaluation
2.9. Determination of Catechin Compounds in Tea by HPLC-MS/MS Method
3. Results
3.1. Sensor Units Characterization
3.2. Precise Detection of Two Catechin Enantiomers
3.3. Precise Discrimination of 11 Kinds of Xihu Longjing from Adjacent Origins
3.4. Authenticity Identification of Longjing Tea
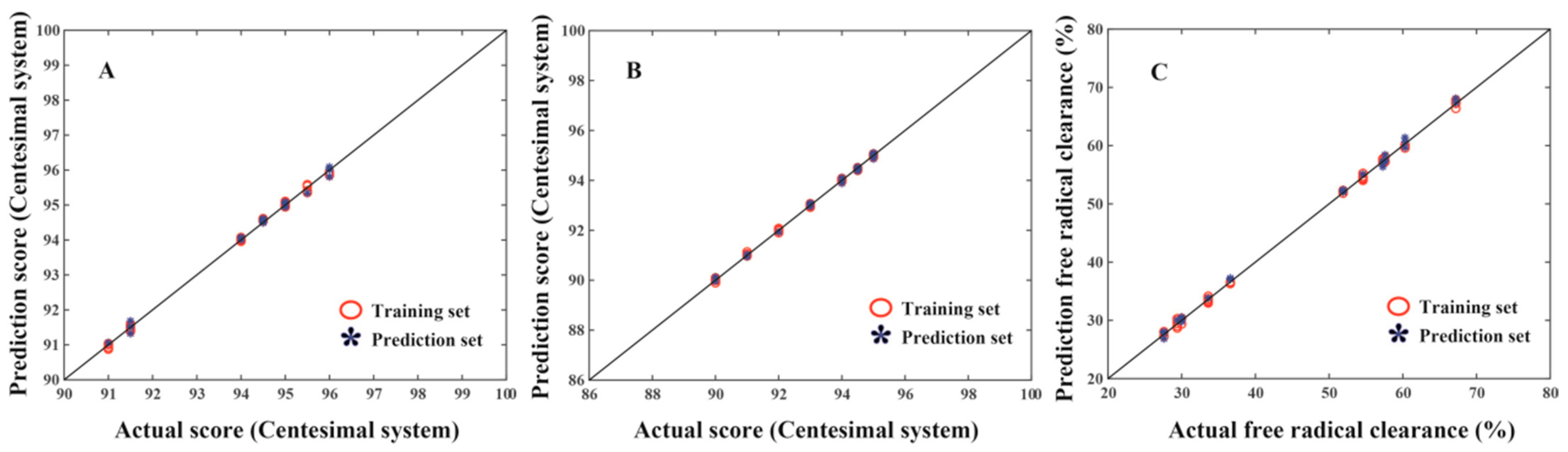
3.5. Quantitative Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity and Flavor of Longjing Teas
3.6. Stability and Anti-Interference Ability of Composite Colorimetric Sensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Yan, T.; Liu, X.; Lu, G.; Tang, X.; Hang, B. An instance-based deep transfer learning method for quality identification of Longjing tea from multiple geographical origins. Complex Intell. Syst. 2023, 9, 3409–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidinejad, A.; Boostani, S.; Babazadeh, A.; Rehman, A.; Rezae, A.; Akbari-Alavijeh, S.; Shaddel, R.; Jafari, S.M. Opportunities and challenges for the nano delivery of green tea catechins in functional foods. Food Res. Int. 2021, 142, 110186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavova-Kazakova, A.; Janiak, M.A.; Sulewska, K.; Sulewska, K.; Kancheva, V.D.; Karamać, M. Synergistic, additive, and antagonistic antioxidant effects in the mixtures of curcumin with (−)-epicatechin and with a green tea fraction containing (−)-epicatechin. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musial, C.; Kuban-Jankowska, A.; Gorska-Ponikowska, M. Beneficial Properties of Green Tea Catechins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosaka, C.; Tagata, C.; Nakagawa, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Miyake, S. Author Correction: Effects of green tea and roasted green tea on human responses. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaldeli, A.; Zakidou, P.; Paraskevopoulou, A. Volatilomics as a tool to ascertain food adulteration, authenticity, and origin. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, 1541–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Elliott, C.T.; Petchkongkaew, A.; Petchkongkaew, A.; Wu, D. The classification, detection and ‘SMART’ control of the nine sins of tea fraud. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 149, 104565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Ye, Y.; Yin, J.; Jin, J.; Liang, Y.; Liu, R.; Tang, P.; Xu, Y. Bitterness and astringency of tea leaves and products: Formation mechanism and reducing strategies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 123, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Huang, J.; Liu, Z. Pu-erh tea unique aroma: Volatile components, evaluation methods and metabolic mechanism of key odor-active compounds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 124, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhussain, N.; Nawada, S.; Schoenmakers, P. Latest Trends on the Future of Three-Dimensional Separations in Chromatography. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 11699–12106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksenov, A.A.; Laponogov, I.; Zhang, Z.; Doran, S.L.F.; Belluomo, I.; Veselkov, D.; Bittremieux, W.; Nothias, L.F.; Nothias-Esposito, M.; Maloney, K.N.; et al. Auto-deconvolution and molecular networking of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 39, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Duan, D.; Dong, C.; Li, C.; Li, G.; Zhou, Y.; Gu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Dong, D. Detection of volatile organic compounds in adulterated tea using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and Proton-transfer-reaction mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaji, H.M.; Schansker, G.; Brestic, M.; Bussotti, F.; Calatayud, A.; Ferroni, L.; Goltsev, V.; Guidi, L.; Jajoo, A.; Li, P.; et al. Frequently asked questions about chlorophyll fluorescence, the sequel. Photosynth. Res. 2016, 132, 13–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewkowska, P.; Dymerski, T.; NamieśNik, J. Use of Sensory Analysis Methods to Evaluate the Odor of Food and Outside Air. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 13, 2208–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Dong, G.; Song, D.; Liu, W.; Geng, X.; Meng, D.; Nie, L.; Liao, J.; Zhou, Q. Covalent organic framework-functionalized magnetic MXene nanocomposite for efficient pre-concentration and detection of organophosphorus and organochlorine pesticides in tea samples before gas chromatography–triple quadrupole mass spectrometry analysis. Food Chem. 2024, 459, 140352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Song, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, S.; Zhao, B.; Feng, X. A highly selective and sensitive europium-organic framework sensor for the fluorescence detection of fipronil in tea. Food Chem. 2023, 413, 135639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons, J.; Bedmar, À.; Núñez, N.; Saurina, J.; Núñez, O. Tea and Chicory Extract Characterization, Classification and Authentication by Non-Targeted HPLC-UV-FLD Fingerprinting and Chemometrics. Foods 2021, 10, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Huang, J.; Huang, J.; Wu, W.; Tong, T.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S. Identification of volatile and odor-active compounds in Hunan black tea by SPME/GC-MS and multivariate analysis. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 164, 113656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Badarla, V.R.; Kawai, A.; Ideguchi, T. Complementary vibrational spectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, J.; Sun, C.; Ye, D.; Liu, Y. Simultaneous determination of six main types of lipid-soluble pigments in green tea by visible and near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2018, 270, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, B.W.B.; Hopkins, D.L. A comparison of the Nix Colour Sensor Pro™ and HunterLab MiniScan™ colorimetric instruments when assessing aged beef colour stability over 72 h display. Meat Sci. 2018, 147, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.; Kubota, R.; Minami, T. Molecular self-assembled chemosensors and their arrays. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 429, 213607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, D. Fabrication of Fe3C/Fe-N-C nanozymes-based cascade colorimetric sensor for detection and discrimination of tea polyphenols. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 51, 100243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhen, L.; Zhang, X.; Jin, P.; Li, Y.; Huang, H. A sensor array based on the boronic acid functional nanozyme for the enhanced sensing of tea polyphenols and raw Pu-erh. Talanta 2025, 297, 128688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xue, W.; Shi, Y.; Liu, W.; Ma, R. MXene/MWCNTs-COOH/MOF-808-based electrochemical sensor for the detection of Catechin. Microchem. J. 2025, 215, 114339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Green synthesis, biomedical and biotechnological applications of carbon and graphene quantum dots. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 703–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.; Park, Y.; Cheon, B.; Park, M. Carbon Dots as an Effective Fluorescent Sensing Platform for Metal Ion Detection. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainò, G.; Yazdani, N.; Boehme, S.C.; Kober-Czerny, M.; Zhu, C.; Krieg, F.; Rossell, M.D.; Erni, R.; Wood, V.; Infante, I.; et al. Ultra-narrow room-temperature emission from single CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dots. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, V.; Ravikanth, M. Coordination chemistry of porphycenes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 516, 215999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wasson, M.C.; Shayan, M.; Berdichevsky, E.K.; Ricardo-Noordberg, J.; Singh, Z.; Papazyan, E.K.; Castro, A.J.; Marino, P.; Ajoyan, Z.; et al. A historical perspective on porphyrin-based metal–organic frameworks and their applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 429, 213615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, T.-Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, W.; Guo, W.; Lac, D.; Zhang, H.; Feng, C.; Wachsmann-Hogiu, S.; et al. A smart and versatile theranostic nanomedicine platform based on nano porphyrin. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lodi, A.; Zhang, H.; Gee, A.; Wang, H.; Kong, F.; Clarke, M.; Edmondson, M.; Hart, J.; O’ Shea, J.N.; et al. Porphyrin-fused graphene nanoribbons. Nat. Chem. 2024, 16, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Cen, T.; He, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Ying, X.; Li, S.; Jacobson, O.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; et al. Porphyrin Nanocage-Embedded Single-Molecular Nanoparticles for Cancer Nano theranostics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 8799–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yin, Q.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Hu, O.; Guo, X.; Shi, Q.; Fu, H.; She, Y. Double quantum dots-nano porphyrin fluorescence-visualized paper-based sensors for detecting organophosphorus pesticides. Talanta 2019, 199, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xu, Q.; Liu, N.; Li, Y.; Sun, N. Quantum dots photobleaching-based monochrome multiplexing in loop-mediated isothermal amplification detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Talanta 2025, 297, 128636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Che, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, C.; Fu, H.; She, Y. Dual channel sensor array based on ZnCdSe QDs—KMnO4: An effective tool for analysis of catechins and green teas. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, X.; Zhao, B.; Pang, B.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Song, F. Separation, Quantification and Structural Study of (+)-Catechin and (–)-Epicatechin by Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry Combined with Theoretical Algorithms. Chin. J. Chem. 2019, 37, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Hu, O.; Fan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, Z.; She, Y. Rational design of an “on-off-on” fluorescent assay for chiral amino acids based on quantum dots and nano porphyrin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 287, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Wu, B.; Li, H.; Zhang, M.; Cai, M.; Lang, B.; Wu, Z.; Wang, F.; Sun, J.; Zhou, P.; et al. Fluorescent/Colorimetric Dual-Mode Discriminating Gln and Val Enantiomers Based on Carbon Dots. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 14511–14832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Yu, M.; Xu, X.; Wang, Q.; Ying Hu, Y.; Fu, H.; She, Y. Nano porphyrin/CdTe quantum dots: A robust tool for effective differentiation among DNA structures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Ye, Y.; He, H.; Dong, C. Evaluation of green tea sensory quality via process characteristics and image information. Food Bioproducts Process. 2017, 117, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Wang, L.; Ding, D.; Guo, Y.; Xu, J.; Qiao, F.; Wang, H.; Shen, W. One-step synthesis of aqueous CdTe/CdSe composite QDs toward efficiency enhancement of solar cell. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 142040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atomssa, T.; Gholap, A. Characterization and determination of catechins in green tea leaves using UV-visible spectrometer. J. Eng. Technol. 2015, 7, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Cai, L.; Wu, M.; Fan, Y. Organic-Acid-Sensitive Visual Sensor Array Based on Fenton Reagent–Phenol/Aniline for the Rapid Species and Adulteration Assessment of Baijiu. Foods 2024, 13, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Lu, D.; Shi, Q.; Chen, H.; Xie, S.; Li, G.; Fu, H.; She, Y. ZnCdSe-CdTe quantum dots: A “turn-off fluorescent probe for the detection of multiple adulterants in an herbal honey. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 221, 117212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wright, M.; Zhao, Q.; Brown, R.; Wang, K.; Xue, Y. Catalytic pyrolysis of amino acids: Comparison of aliphatic amino acid and cyclic amino acid. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 112, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Masai, M.; Huang, X.; Tsuda, S.; Terao, J.; Yang, J.; Guo, X. A single-molecule electrical approach for amino acid detection and chirality recognition. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhan, C.; Huang, P.; Kang, Z. Identification and quantification of adulterated Tieguanyin based on the fluorescence hyperspectral image technique. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 120, 105343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Hou, Z.; Deng, G.; Huang, L.; Liu, N.; Ning, J.; Wang, Y. Cost-effective colorimetric sensor for authentication of protected designation of origin (PDO) Longjing green tea. Food Chem. 2023, 427, 136673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
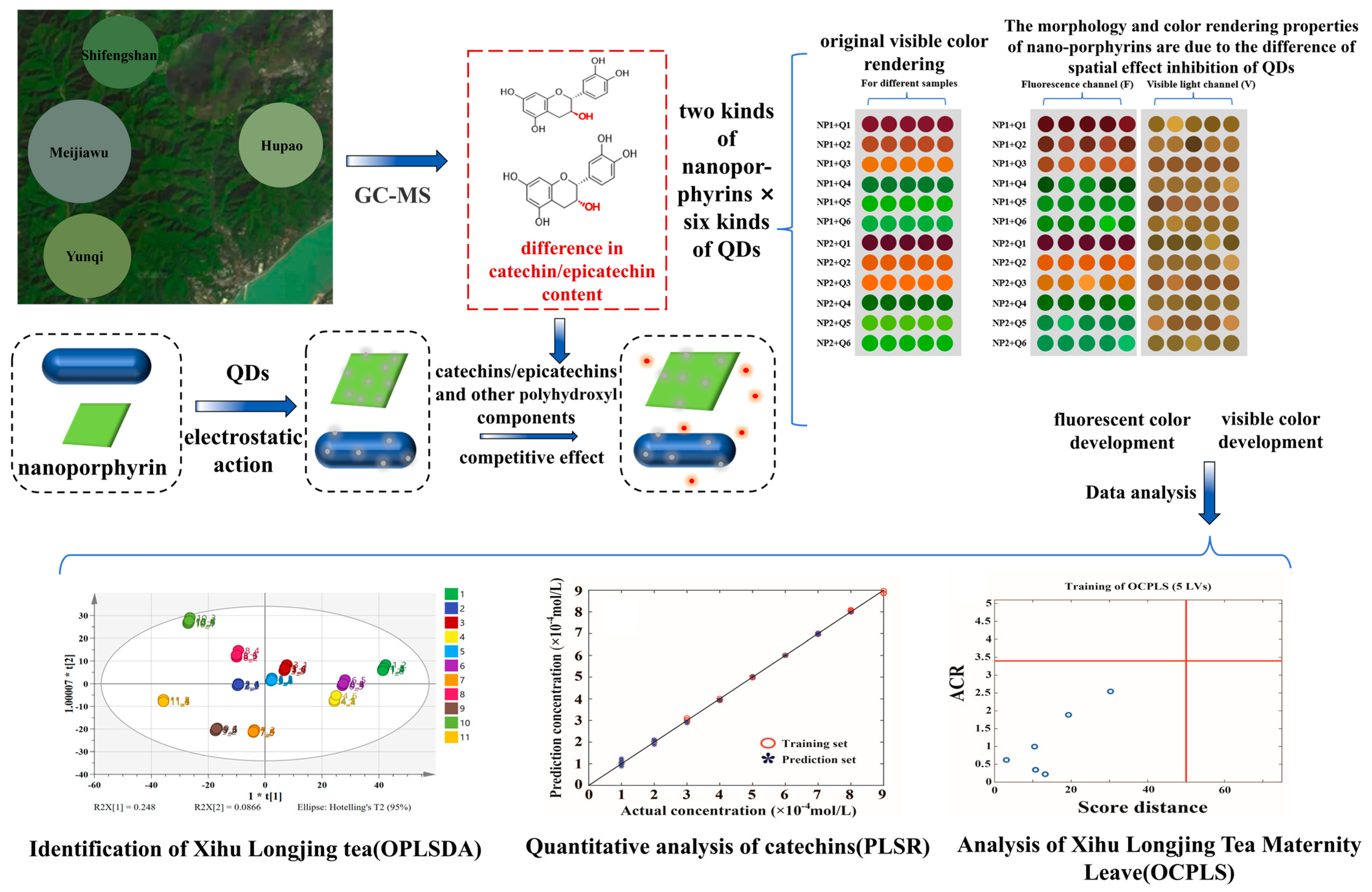
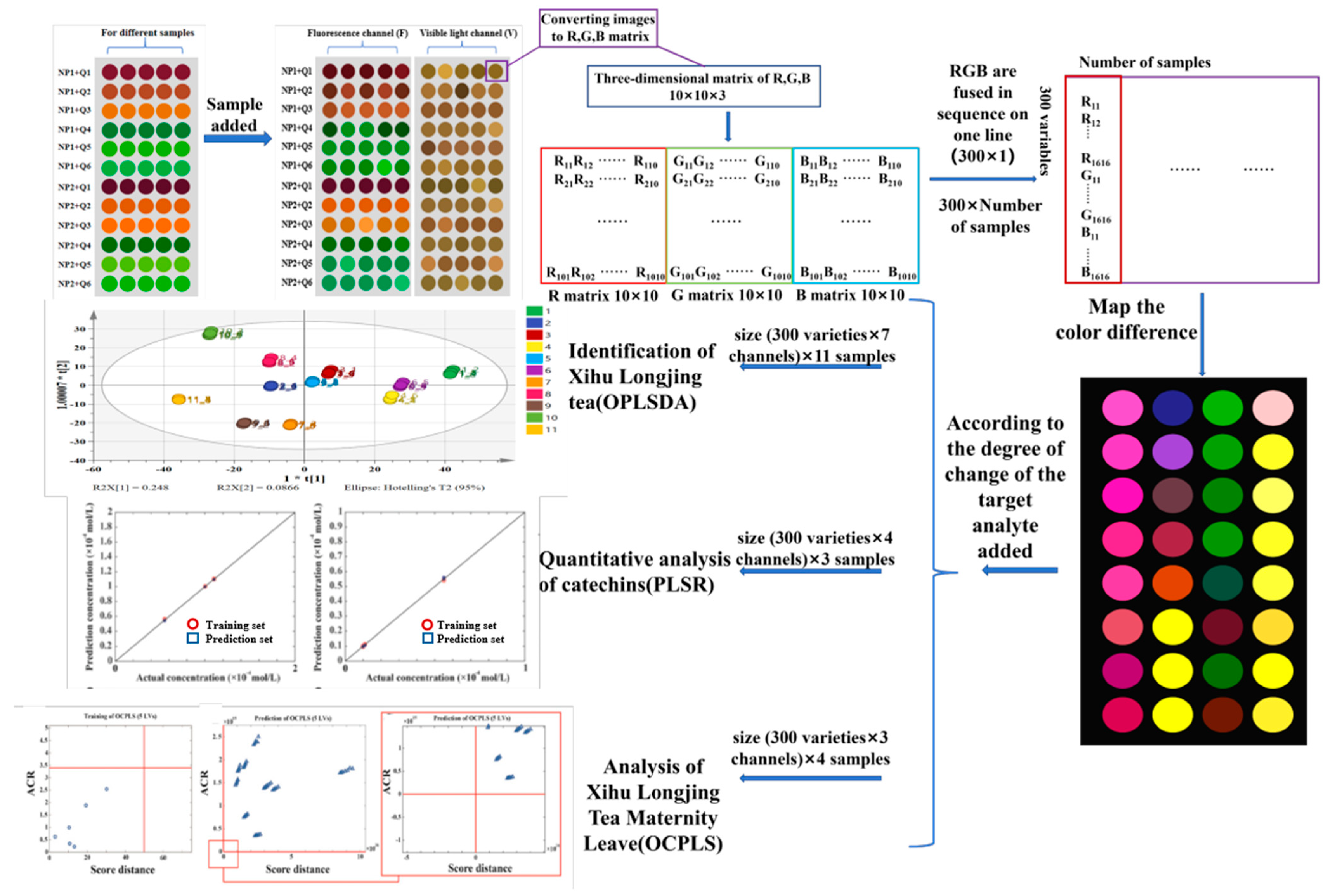

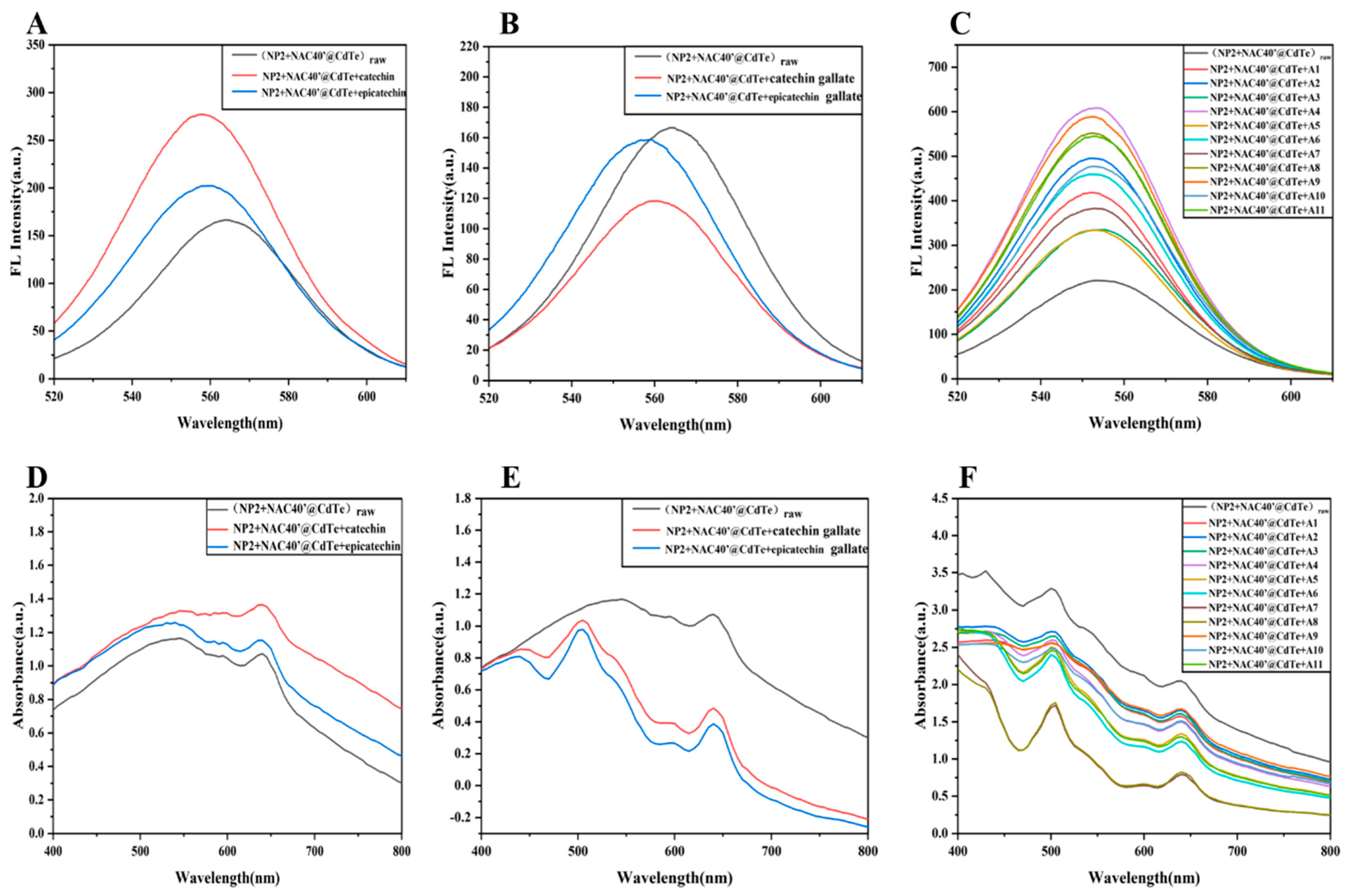
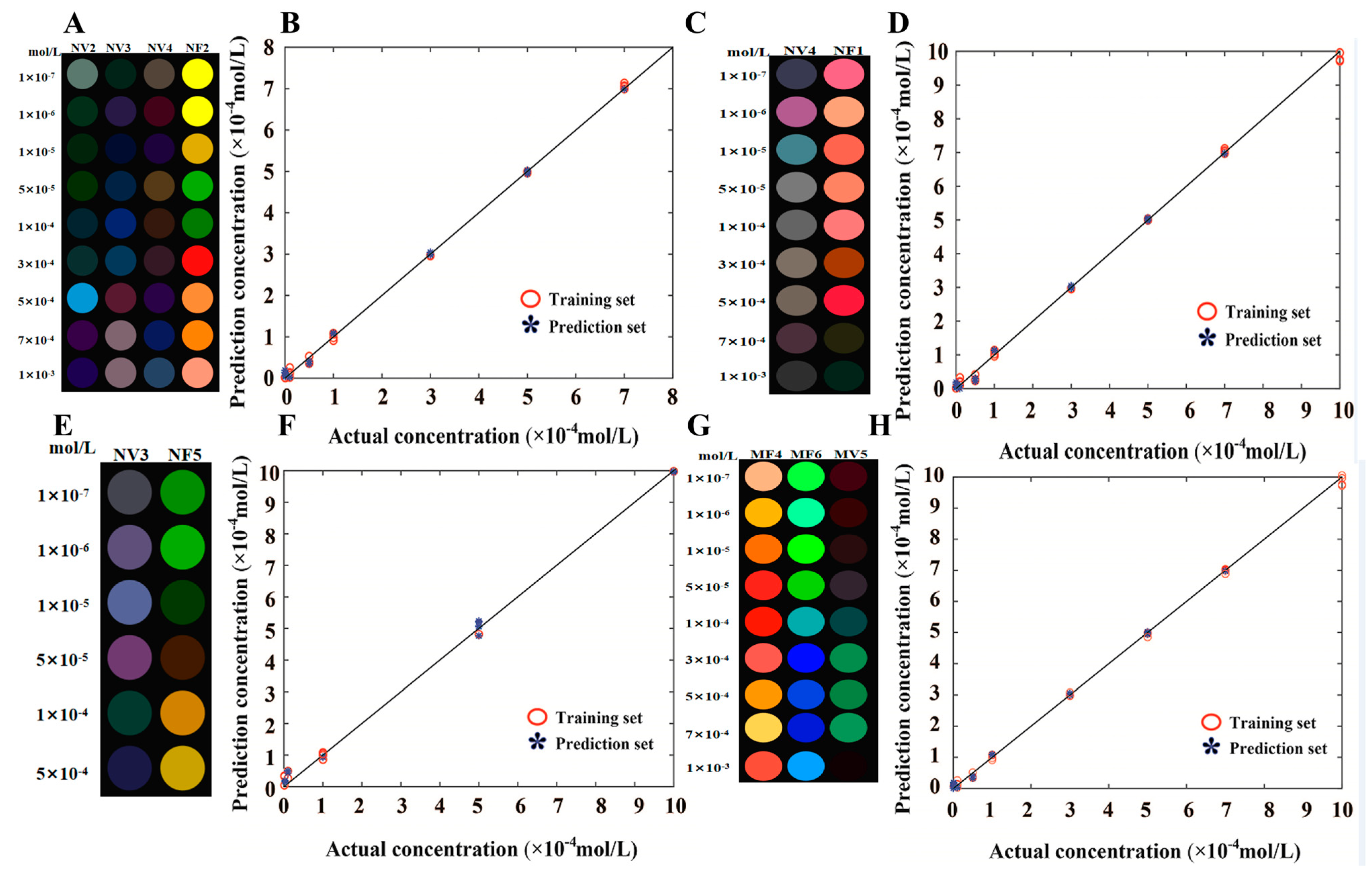


| Number | Label | Samples | Grades | Aroma | Taste Score | Total Antioxidant Capacity (∆A, ABTS mmol TE/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A1 | Sh FRET ng | Super | 94.5 | 95.0 | 0.1 |
| 2 | A2 | Shifeng | First | 91.5 | 90.0 | 0.122 |
| 3 | A3 | Meijiawu | Super | 95.0 | 95.0 | 0.192 |
| 4 | A4 | Meijiawu | First | 94.0 | 93.0 | 0.201 |
| 5 | A5 | Meijiawu | Second | 91.5 | 91.0 | 0.224 |
| 6 | A6 | Hupao | Super | 96.0 | 94.5 | 0.173 |
| 7 | A7 | Hupao | First | 95.5 | 94.0 | 0.182 |
| 8 | A8 | Hupao | Second | 95.0 | 93.0 | 0.191 |
| 9 | A9 | Yunqi | Super | 94.5 | 94.5 | 0.092 |
| 10 | A10 | Yunqi | First | 94.0 | 93.0 | 0.098 |
| 11 | A11 | Yunqi | Second | 91.0 | 92.0 | 0.112 |
| 12 | A12 | Wuniuzao | / | 91.0 | 90.0 | / |
| Channel | Channel Composition | Testing Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| NV1 | NP1 + Q1 | Visible light (V) |
| NV2 | NP1 + Q2 | Visible light (V) |
| NV3 | NP1 + Q3 | Visible light (V) |
| NV4 | NP1 + Q4 | Visible light (V) |
| NV5 | NP1 + Q5 | Visible light (V) |
| NV6 | NP1 + Q6 | Visible light (V) |
| NF1 | NP1 + Q1 | Fluorescent light (F) |
| NF2 | NP1 + Q2 | Fluorescent light (F) |
| NF3 | NP1 + Q3 | Fluorescent light (F) |
| NF4 | NP1 + Q4 | Fluorescent light (F) |
| NF5 | NP1 + Q5 | Fluorescent light (F) |
| NF6 | NP1 + Q6 | Fluorescent light (F) |
| MV1 | NP2 + Q1 | Visible light (V) |
| MV2 | NP2 + Q2 | Visible light (V) |
| MV3 | NP2 + Q3 | Visible light (V) |
| MV4 | NP2 + Q4 | Visible light (V) |
| MV5 | NP2 + Q5 | Visible light (V) |
| MV6 | NP2 + Q6 | Visible light (V) |
| MF1 | NP2 + Q1 | Fluorescent light (F) |
| MF2 | NP2 + Q2 | Fluorescent light (F) |
| MF3 | NP2 + Q3 | Fluorescent light (F) |
| MF4 | NP2 + Q4 | Fluorescent light (F) |
| MF5 | NP2 + Q5 | Fluorescent light (F) |
| MF6 | NP2 + Q6 | Fluorescent light (F) |
| Enantiomers | Detection Channel | Detection Range (mol/L) | Coefficient of Determination (R2) | Recovery Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catechin | NV2, NV3, NV4, NF2 | 1 × 10−7–1 × 10−3 | 0.99 | 95.2–103.1 |
| Epicatechin | FV4, NF1 | 1 × 10−7–1 × 10−3 | 0.99 | 94.8–102.7 |
| Catechin gallate | NV3, NV5 | 1 × 10−7–5 × 10−4 | 0.99 | 96.5–104.3 |
| Epicatechin gallate | MV5, MF4, MF6 | 1 × 10−7–1 × 10−3 | 0.99 | 95.7–103.5 |
| Label | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A6 |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| Recovery (%) | 101.31 ± 0.03 | 100.81 ± 0.03 | 98.99 ± 0.02 | 100.59 ± 0.03 | 99.44 ± 0.03 | 100.19 ± 0.03 |
| Label | A7 | A8 | A9 | A10 | A11 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| Recovery (%) | 98.91 ± 0.03 | 99.56 ± 0.02 | 100.31 ± 0.03 | 99.68 ± 0.03 | 100.49 ± 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Cai, Z.; Fan, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, M.; Fu, H.; She, Y. Catechin-Targeted Nano-Enhanced Colorimetric Sensor Array Based on Quantum Dots—Nano Porphyrin for Precise Analysis of Xihu Longjing from Adjacent Origins. Foods 2025, 14, 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193360
Liu Y, Cai Z, Fan Y, Wang X, Wu M, Fu H, She Y. Catechin-Targeted Nano-Enhanced Colorimetric Sensor Array Based on Quantum Dots—Nano Porphyrin for Precise Analysis of Xihu Longjing from Adjacent Origins. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193360
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yaqi, Zhenli Cai, Yao Fan, Xingcai Wang, Meixia Wu, Haiyan Fu, and Yuanbin She. 2025. "Catechin-Targeted Nano-Enhanced Colorimetric Sensor Array Based on Quantum Dots—Nano Porphyrin for Precise Analysis of Xihu Longjing from Adjacent Origins" Foods 14, no. 19: 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193360
APA StyleLiu, Y., Cai, Z., Fan, Y., Wang, X., Wu, M., Fu, H., & She, Y. (2025). Catechin-Targeted Nano-Enhanced Colorimetric Sensor Array Based on Quantum Dots—Nano Porphyrin for Precise Analysis of Xihu Longjing from Adjacent Origins. Foods, 14(19), 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193360




