Thermally Stable Collagen from Black Carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) Swim Bladder: Preparation, Structure, Rheological, and Functional Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Collagen from Swim Bladders of Black Carp
2.3. Structural Characterisation
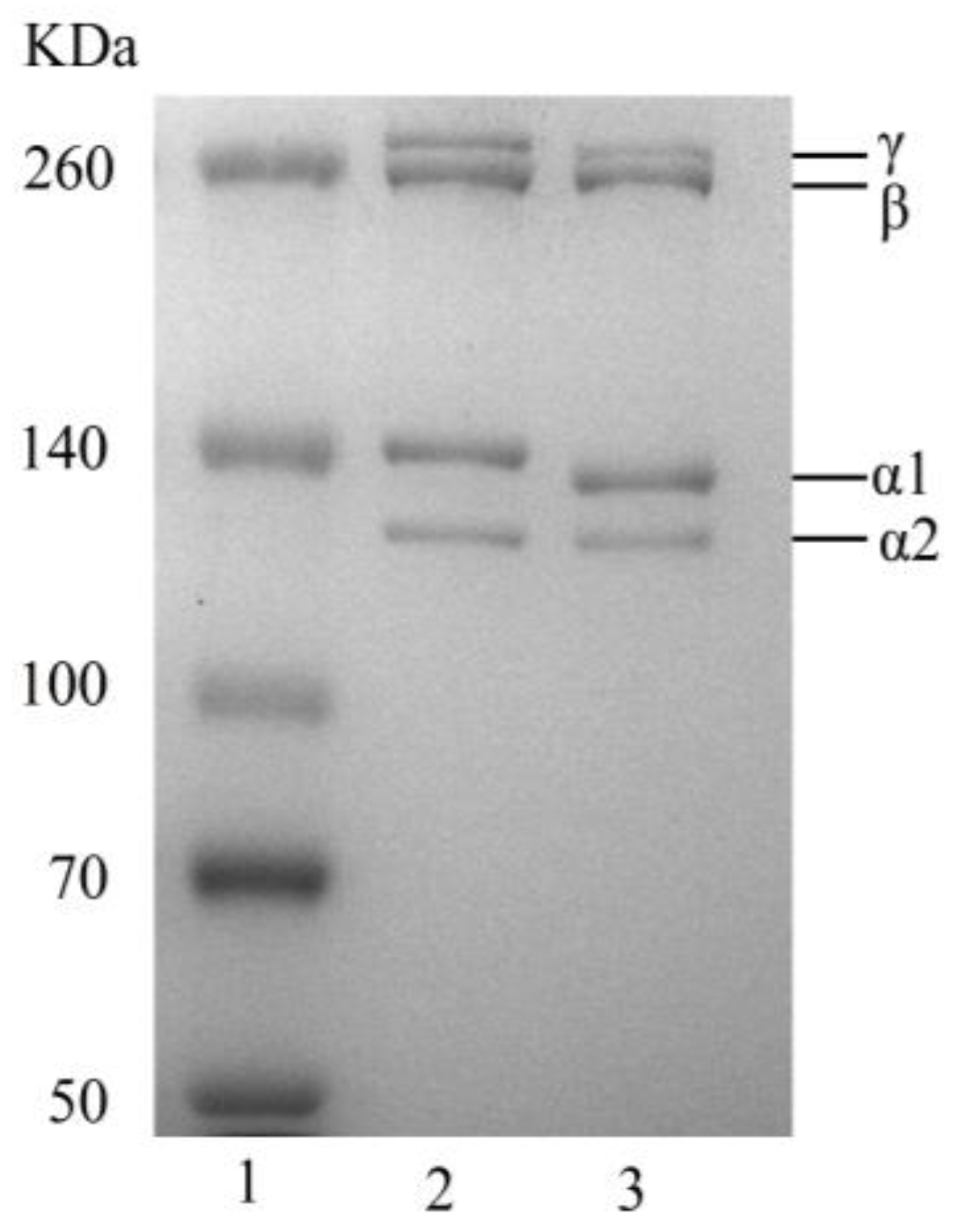
2.3.1. Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE)
2.3.2. Amino Acid Composition
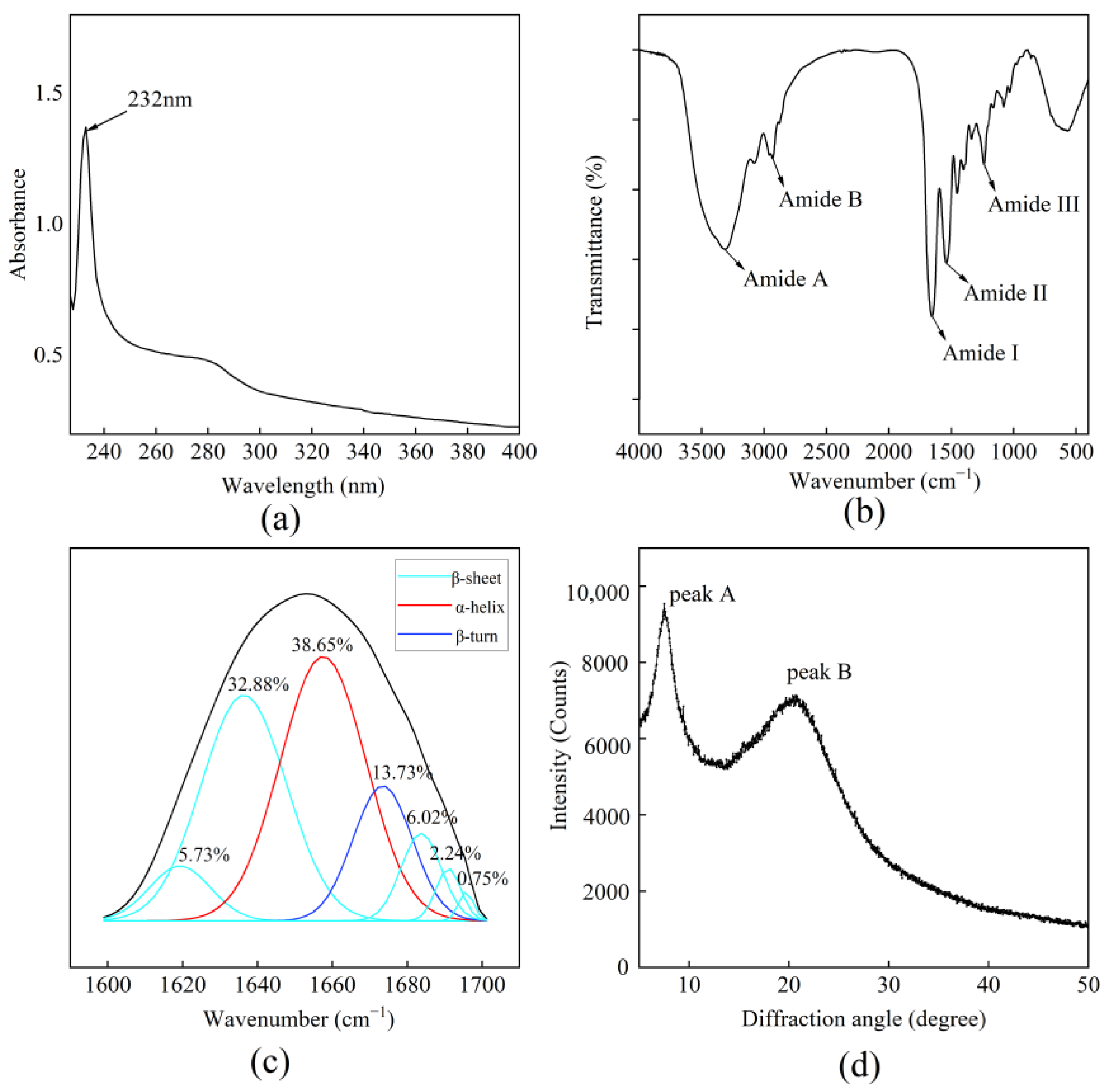
2.3.3. Ultraviolet Visible (UV) Absorption
2.3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR)
2.3.5. FTIR Spectral Curve Fitting
2.3.6. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
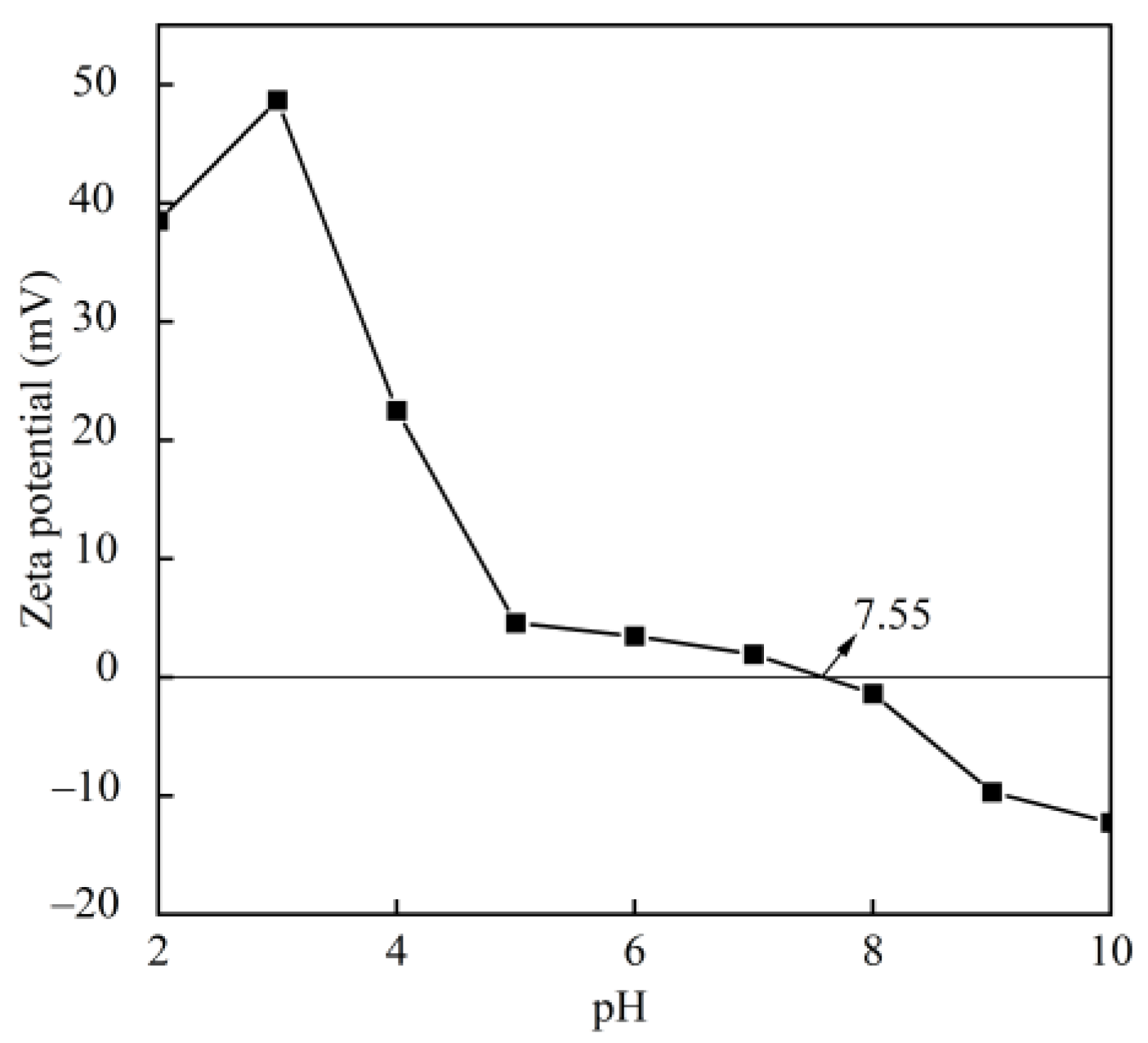
2.4. Zeta Potential
2.5. Thermal Stability
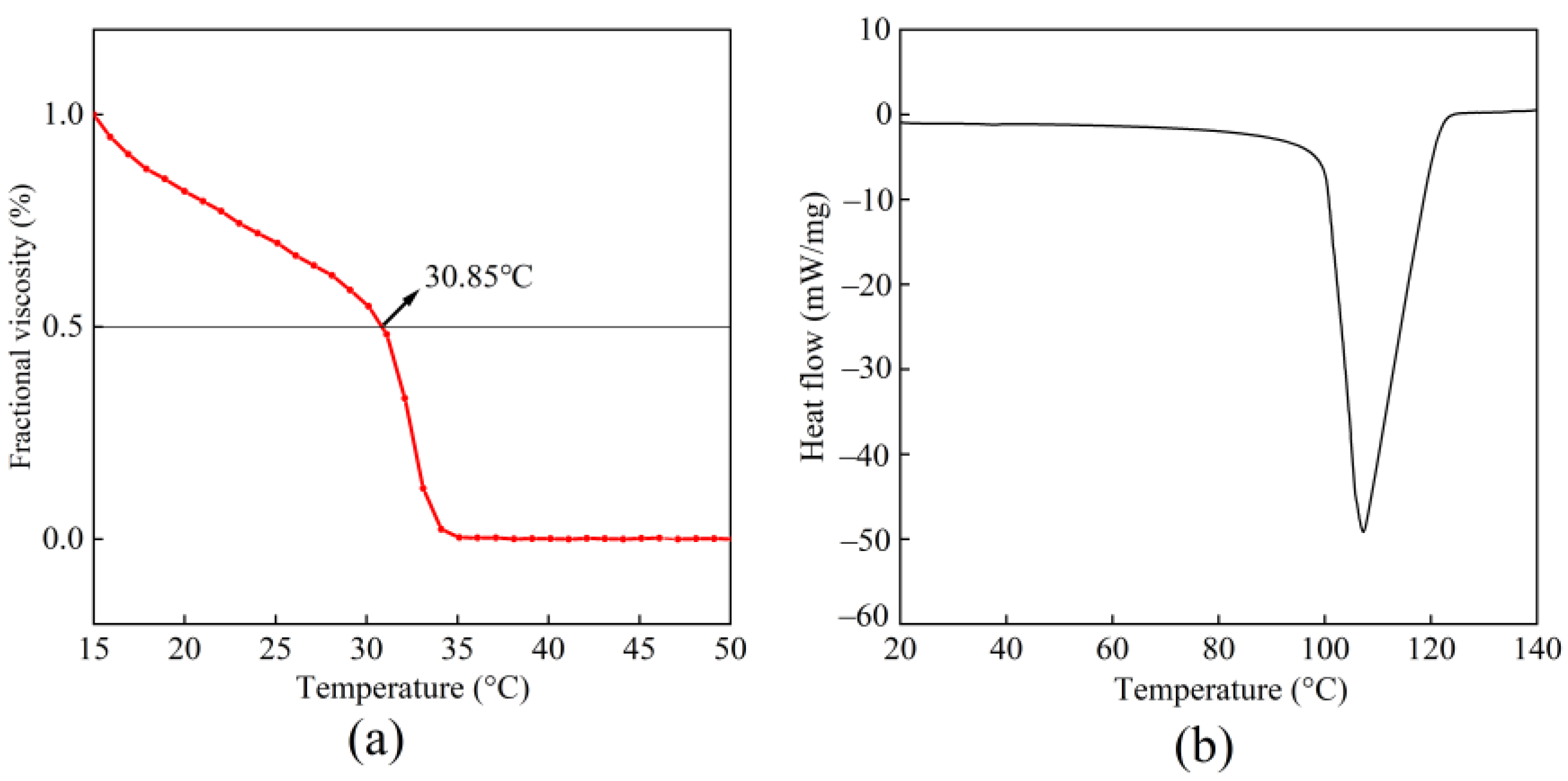
2.5.1. Denaturation Temperature (Td)
2.5.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.6. Rheological Properties
2.6.1. Dynamic Rheology
2.6.2. Steady Rheology
2.7. Functional Properties
2.7.1. Emulsifying Activity Index (EAI) and Emulsifying Stability Index (ESI)
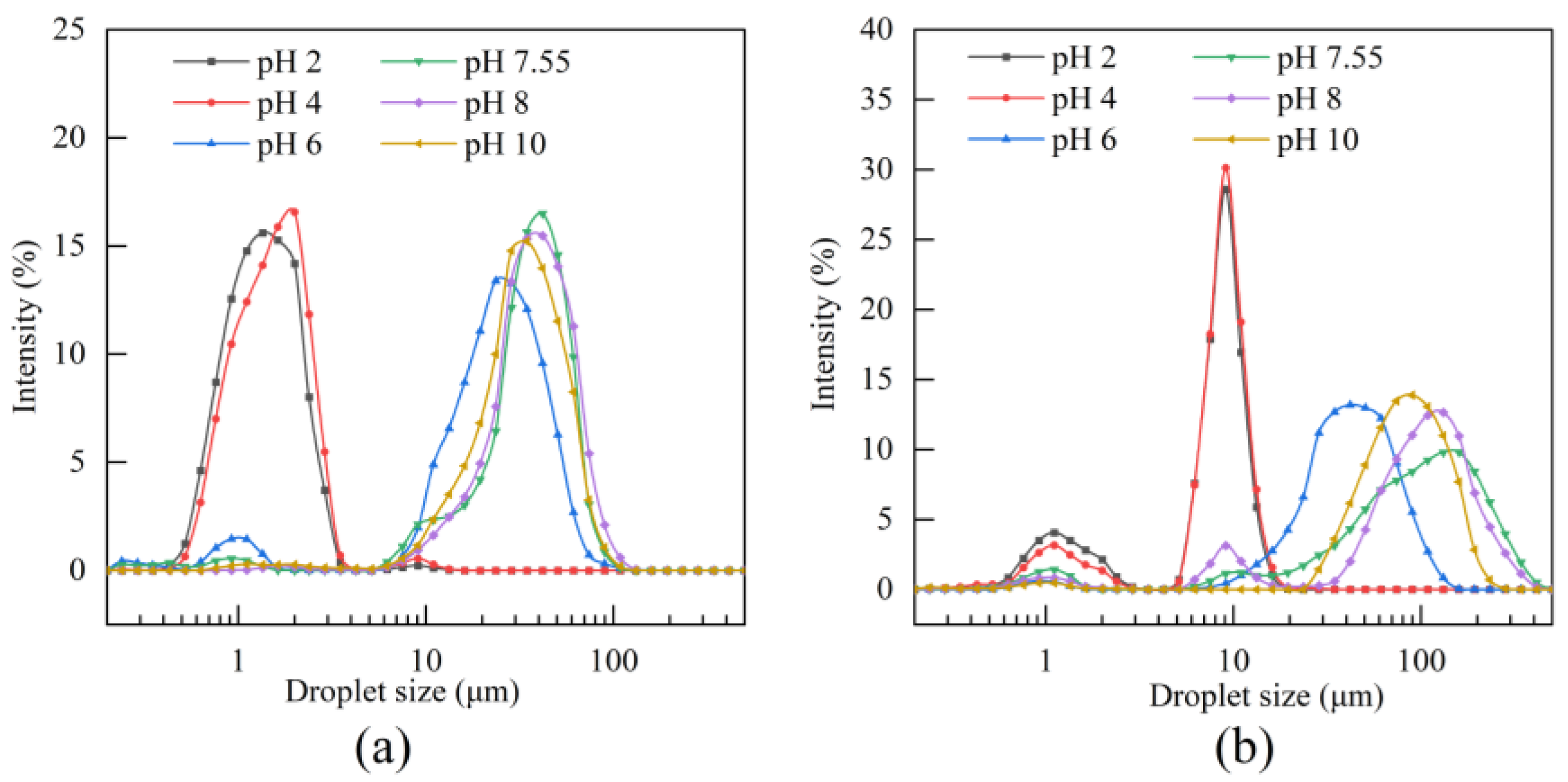
2.7.2. Particle Size Distribution
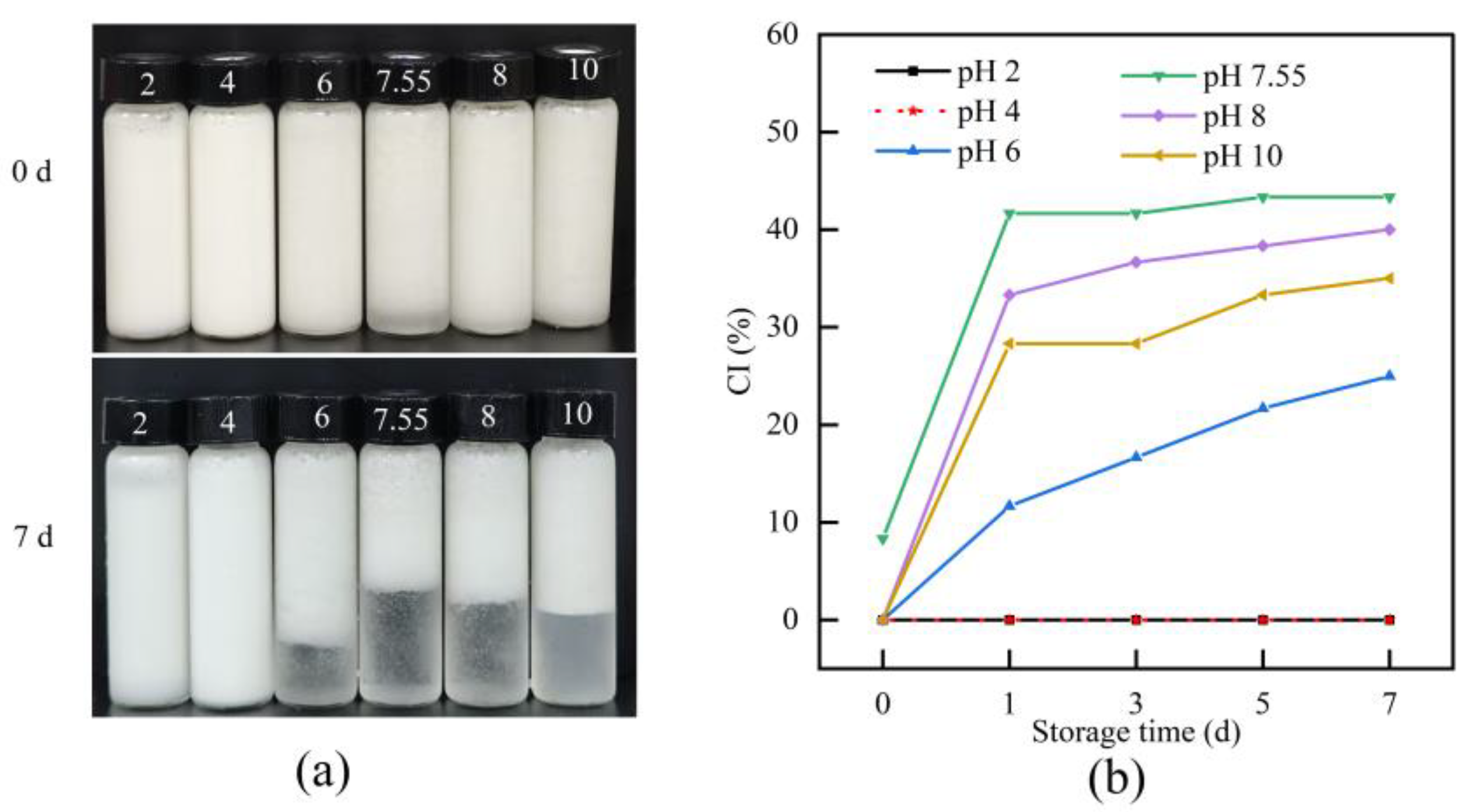
2.7.3. Creaming Index (CI)
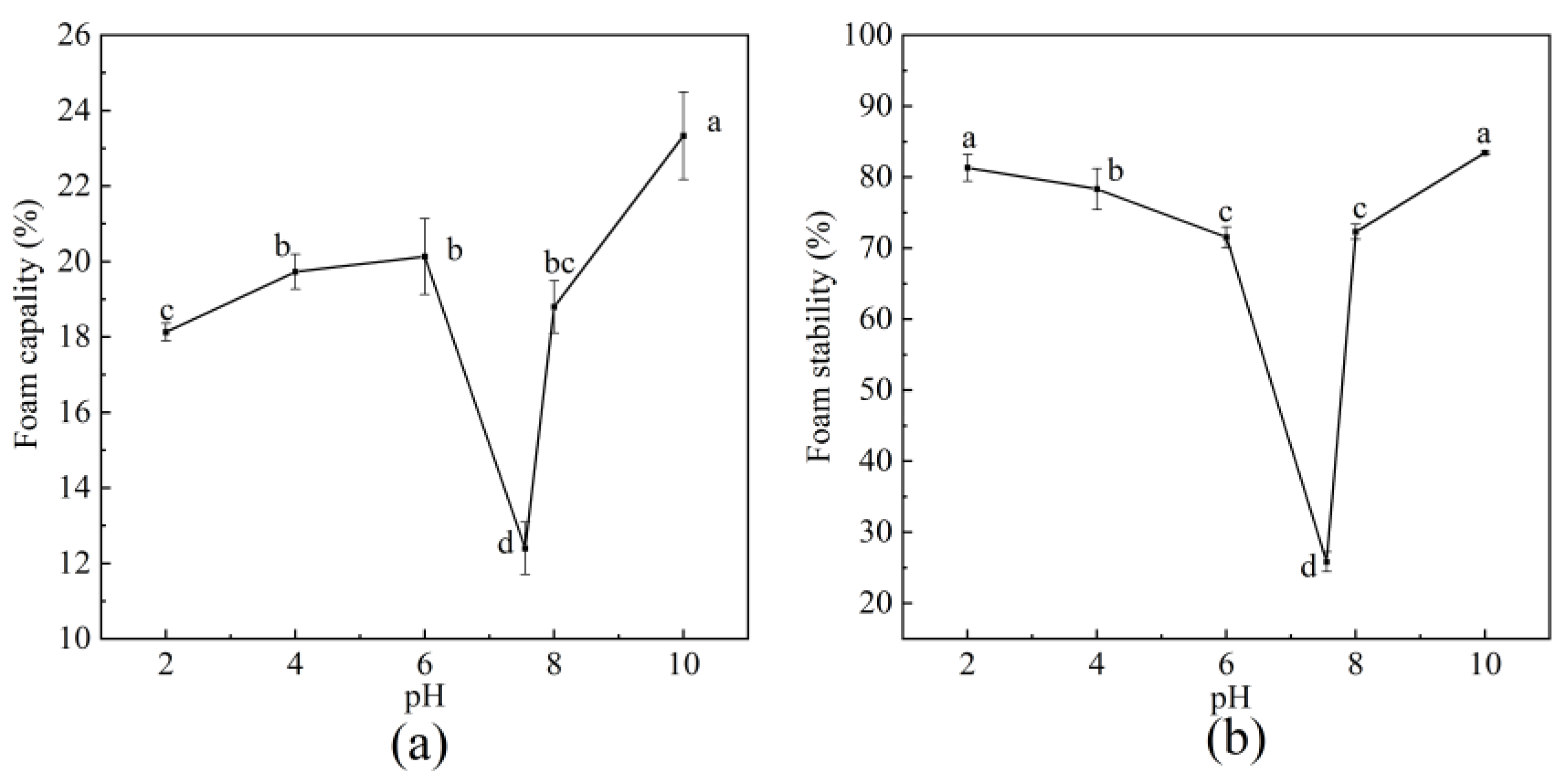
2.7.4. Foaming Capacity (FC) and Foam Stability (FS)
2.7.5. Water Absorption Capacity (WAC)
2.7.6. Oil Absorption Capacity (OAC)
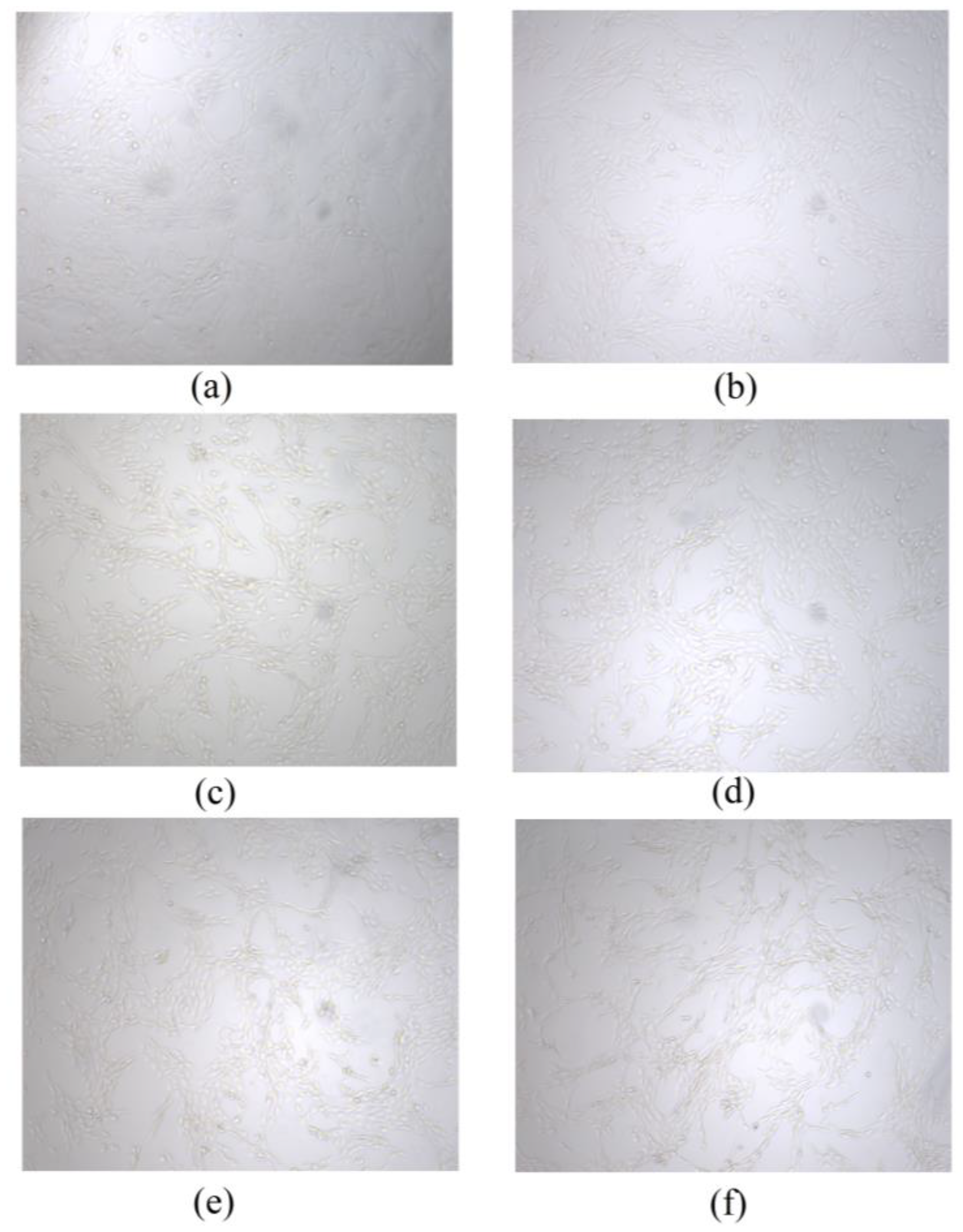
2.8. Cell Viability and Proliferation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Yield
3.2. Structural Characterisation
3.2.1. SDS–PAGE
3.2.2. Amino Acid Composition
3.2.3. UV
3.2.4. FTIR
3.2.5. Infrared Secondary Structure Fitting
3.2.6. XRD
3.3. Zeta Potential
3.4. Thermal Stability
3.5. Rheological Properties
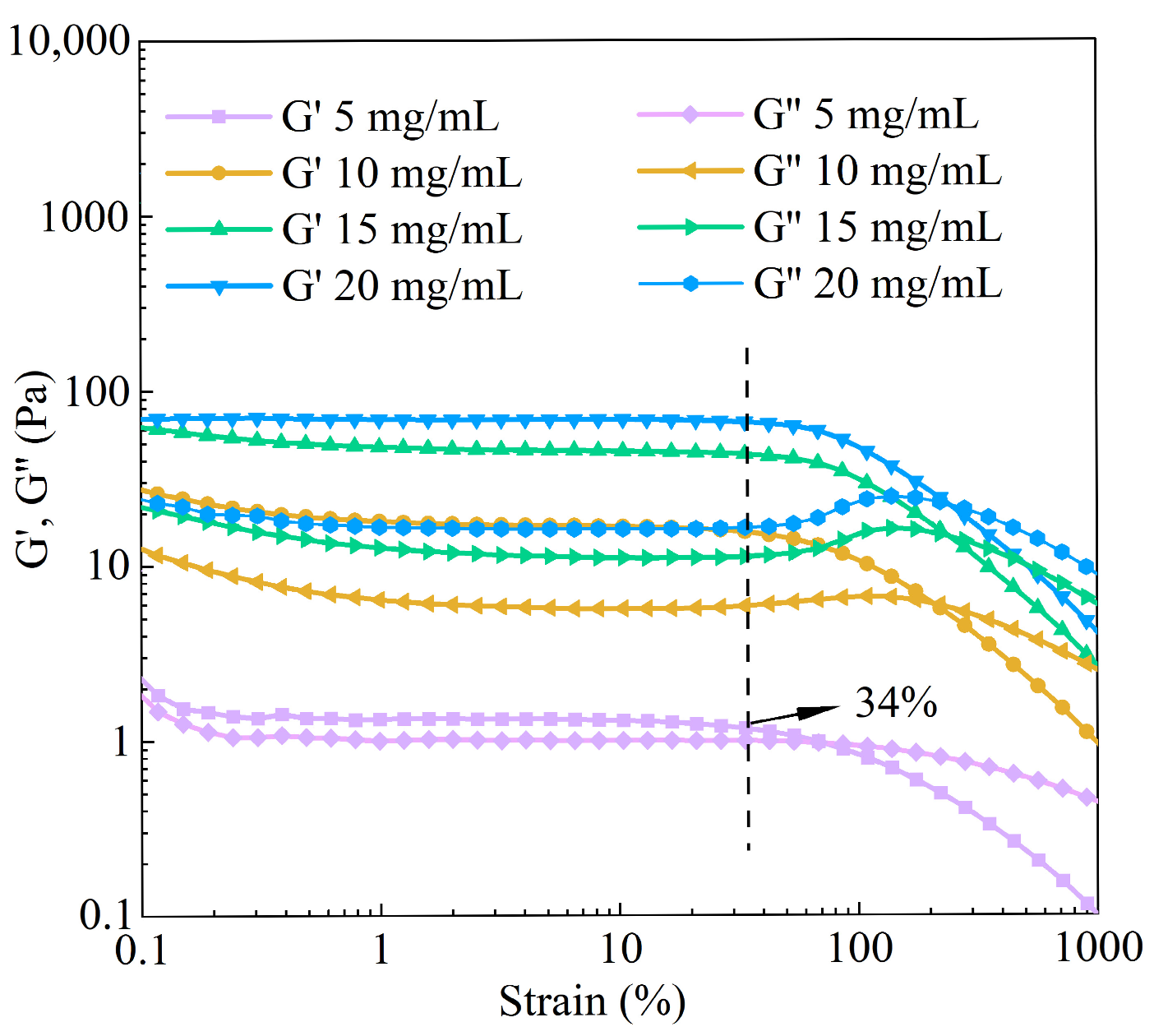
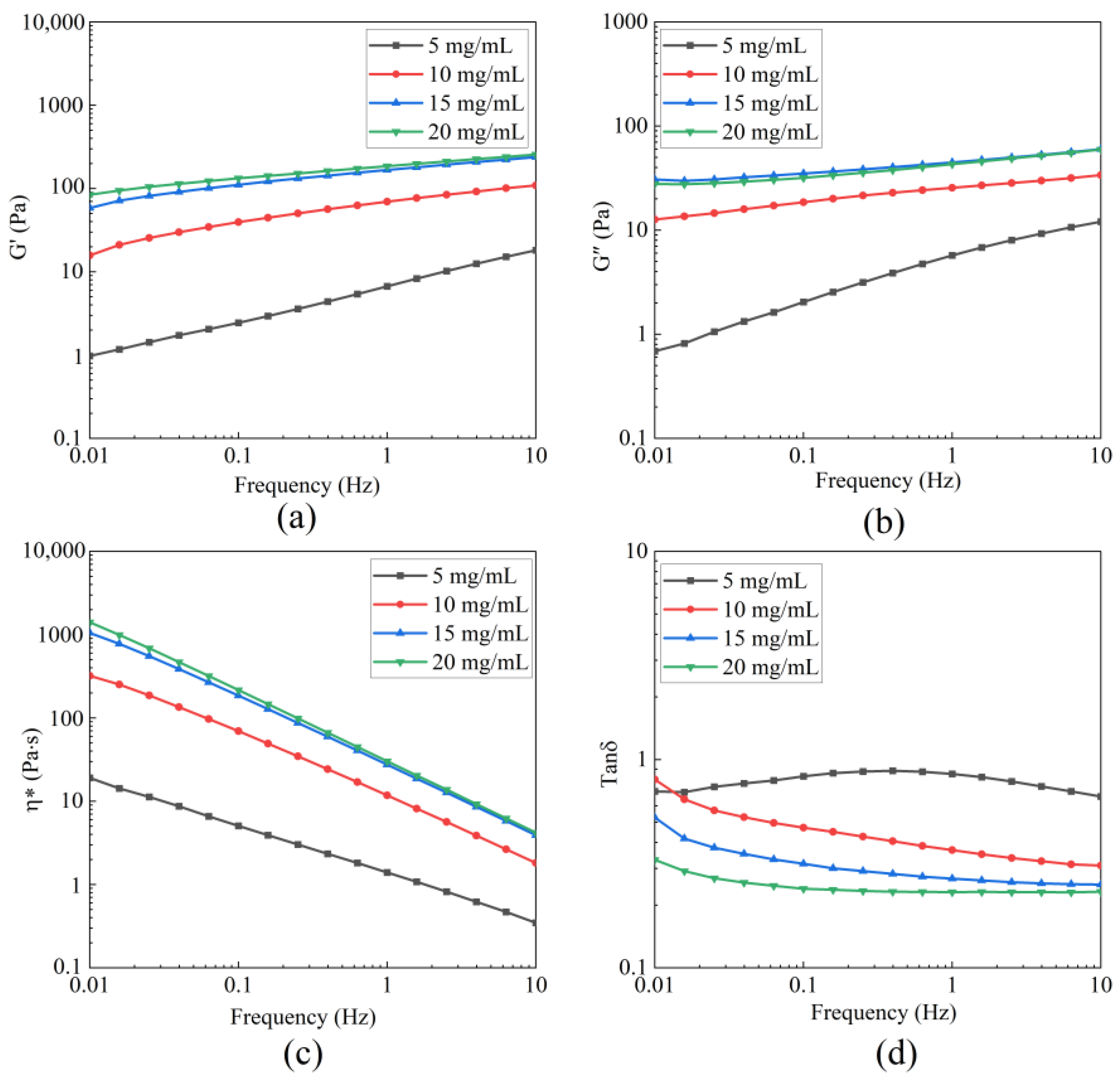
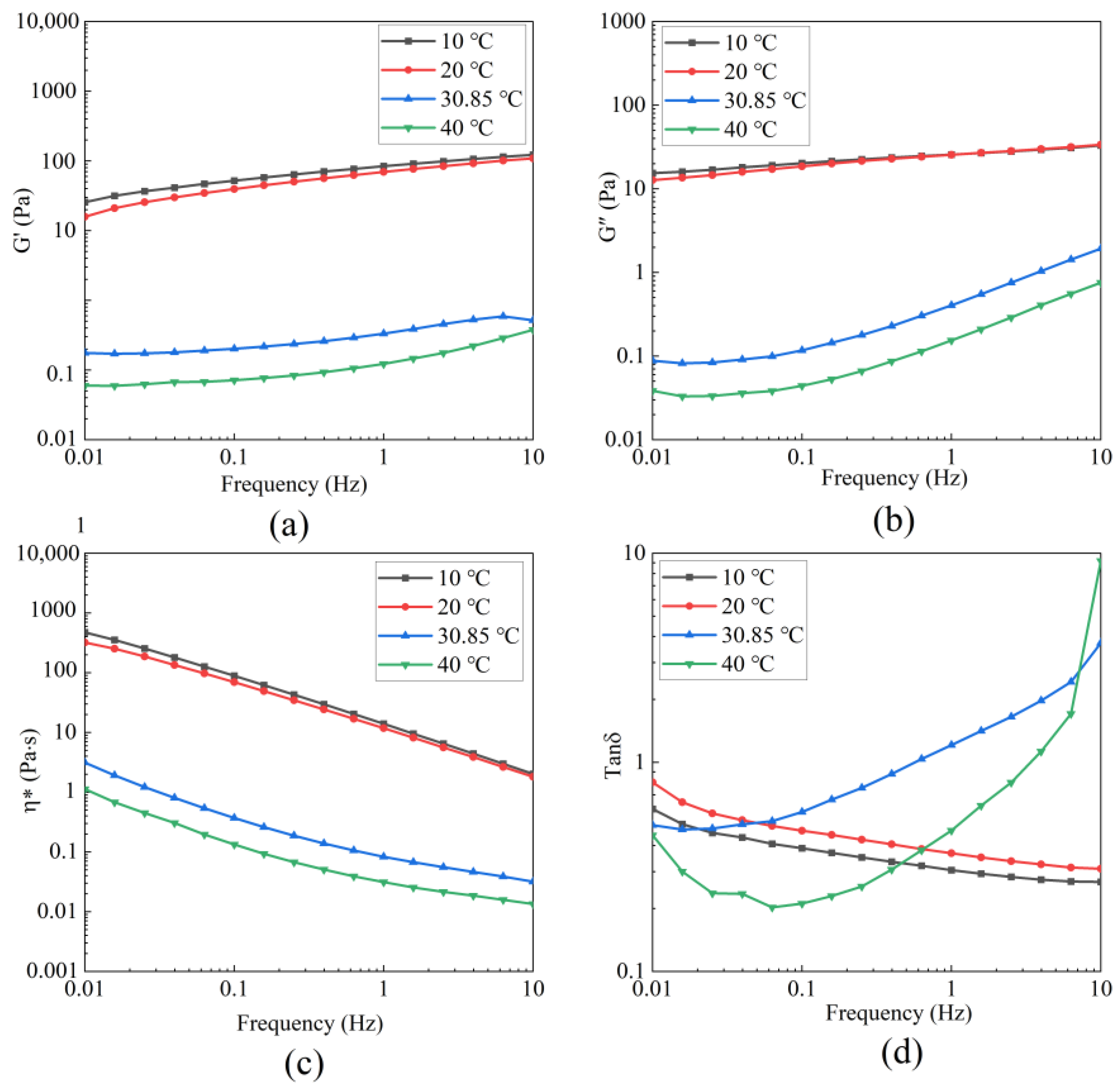
3.5.1. Dynamic Rheology
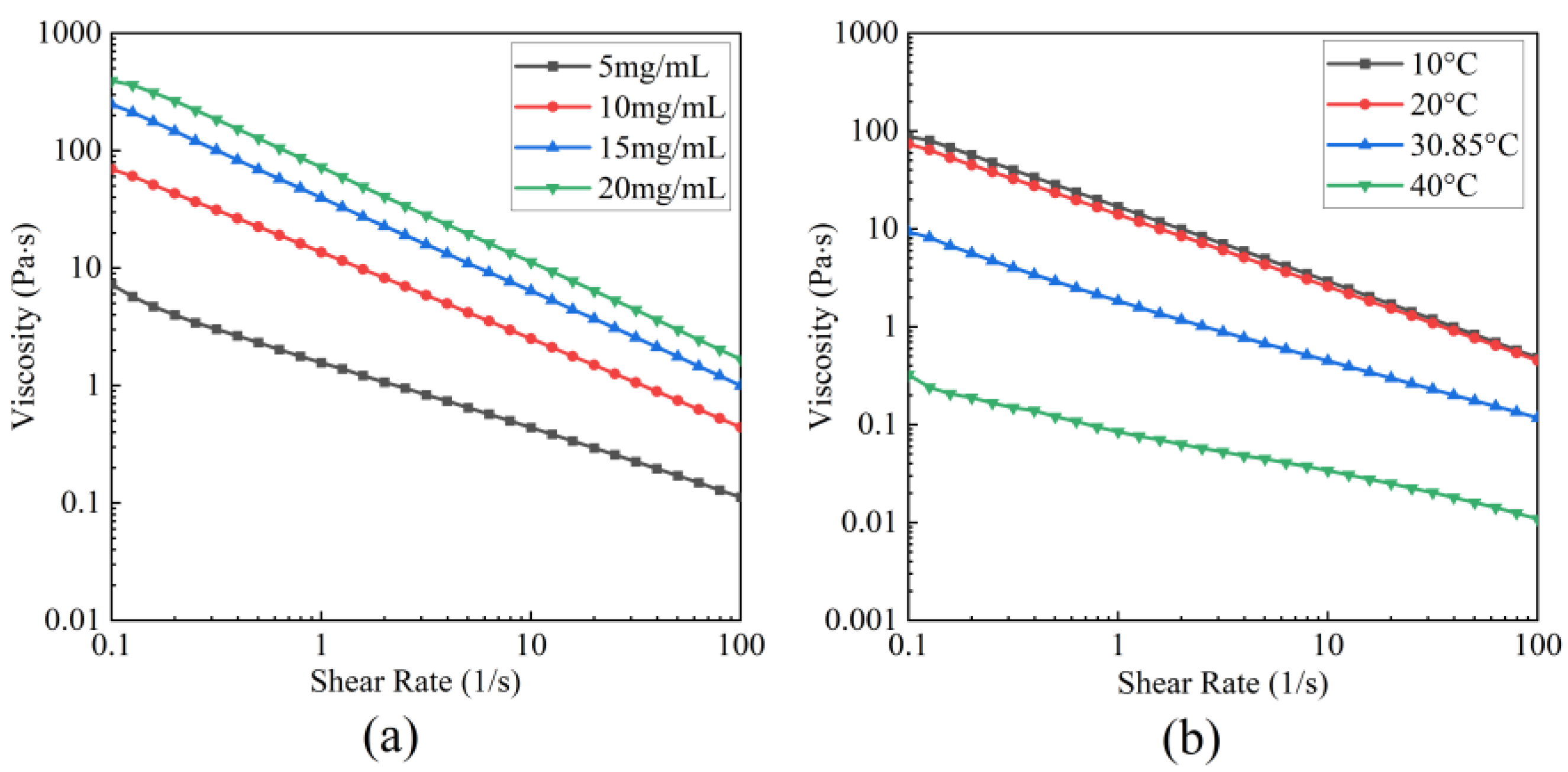
3.5.2. Steady-Shear Rheology
3.6. Functional Properties
3.6.1. EAI and ESI
3.6.2. Particle Size Distribution
3.6.3. CI
3.6.4. FC and FS
3.6.5. WAC
3.6.6. OAC
3.7. Cell Viability and Proliferation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laasri, I.; Bakkali, M.; Mejias, L.; Laglaoui, A. Marine collagen: Unveiling the blue resource-extraction techniques and multifaceted applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Ricardo, M.A.; Gómez-Contreras, P.; González-Delgado, Á.D.; Hernández-Fernández, J.; Ortega-Toro, R. Development of films based on chitosan, gelatin and collagen extracted from bocachico scales (Prochilodus magdalenae). Heliyon 2024, 10, e25194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.S.; Ke, C.; Gao, X.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Chen, J.D. Comparison of structural and physicochemical characteristics of skin collagen from chum salmon (cold-water fish) and Nile tilapia (warm-water fish). Foods 2024, 13, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelsma, T.; Wijnker, J.J.; Smid, B.; Verheij, E.; Van der Poel, W.H.M.; Wisselink, H.J. Salt inactivation of classical swine fever virus and African swine fever virus in porcine intestines confirms the existing in vitro casings model. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 238, 108424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; An, X.X.; Yang, F.M.; Xin, Z.H.; Zhao, L.Y.; Hu, Q.H. Isolation and characterisation of collagens from the skin, scale and bone of deep-sea redfish (Sebastes mentella). Food Chem. 2008, 108, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.L.; Li, B.F.; Song, W.K.; Si, L.L.; Hou, H. Characterization of pacific cod (Gadus macrocephalus) skin collagen and fabrication of collagen sponge as a good biocompatible biomedical material. Process Biochem. 2017, 63, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, C.S.; Luo, X.G.; Zhou, S.K.; Li, Y.Y.; Hou, J.H.; Tang, K.Y.; Pei, Y. Preliminarily revealing rheological behaviors of mesoscale collagen fibrils in suspension. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1311, 138723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.Y.; He, J.L.; Chen, J.D.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.S. Double-spotted pufferfish (Takifugu bimaculatus) skin collagen: Preparation, structure, cytocompatibility, rheological, and functional properties. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lin, L.; Jiang, S.T.; Lu, J.F. Characterization of acid-soluble collagen (ASC) derived from walleye pollock and silver carp skin and comparison them with the collagen from pig and duck skin. Food Chem. Adv. 2024, 4, 100746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.X.; He, J.L.; Chen, J.D.; Li, Y.S.; Zhang, X.K.; Zheng, Y.; Jia, L.Y. Valorization of fish processing by-products: Microstructural, rheological, functional, and properties of silver carp skin type I collagen. Foods 2022, 11, 2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.S.; Yang, L.H.; Wu, S.J.; Chen, J.D.; Lin, H.W. Structural, functional, rheological, and biological properties of the swim bladder collagen extracted from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 153, 112518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.X.; Lin, J.Q.; Chen, D.Q.; Duan, X.B.; Peng, Q.D.; Liu, S.P. Ecological flow assessment to improve the spawning habitat for the four major species of carp of the yangtze river: A study on habitat suitability based on ultrasonic telemetry. Water 2018, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Wang, Y.R.; Yang, R.Y.; Zhu, S.Y.; Yao, F.; Zhang, X.H.; Yang, Y.O. Effects of feeding pattern on growth, immunity and intestinal flora of GIFT tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquacult. Rep. 2025, 42, 102764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harimana, V.; Tang, X.; Le, W.; Xing, X.; Zhang, K.; Sun, Y.J.; Li, Y.R.; Ma, S.H.; Karangwa, E.; Tuyishimire, M.A. Quality parameters of black carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) raised in lotic and lentic freshwater systems. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 90, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rual Affairs of the People’s China. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2024; pp. 20–46. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.D.; Wang, G.Y.; Li, Y.S. Preparation and characterization of thermally stable collagens from the scales of lizardfish (Synodus macrops). Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewdang, O.; Benjakul, S.; Kaewmanee, T.; Kishimura, H. Characteristics of collagens from the swim bladders of yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares). Food Chem. 2014, 155, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanmangkang, S.; Maneerote, J.; Surayot, U.; Panya, A.; You, S.G.; Wangtueai, S. Physicochemical and biological properties of collagens obtained from tuna tendon by using the ultrasound-assisted extraction. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 15, 100984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongjareonrak, A.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Nagai, T.; Tanaka, M. Isolation and characterisation of acid and pepsin-solubilised collagens from the skin of brownstripe red snapper (Lutjanus vitta). Food Chem. 2005, 93, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.M.; Li, Y.H.; Li, S.Z.; Wang, W.H. Fabrication and characterization of acid soluble collagen stabilized Pickering emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 106, 105875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.Z.; Zhang, L.N.; Niu, X.R.; Zhang, Y.N.; Yang, X.Y.; Li, L. Soy protein-gellan gum noncovalent complexes stabilized emulsion: Effect of heating and pH on emulsion stability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 301, 140067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandi, G.K.; Sogi, D.S. Functional properties of rice bran protein concentrates. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.S.; Liang, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, P. Extraction and characterisation of pepsin-solubilised collagen from fins, scales, skins, bones and swim bladders of bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis). Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-López, H.; Rodríguez-Morales, S.; Enríquez-Paredes, L.M.; Villarreal-Gómez, L.J.; Olivera-Castillo, L.; Cortes-Santiago, Y.; López, M.L. Comparison of collagen characteristic from the skin and swim bladder of gulf corvina (Cynoscion othonopterus). Tissue Cell 2021, 72, 101593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.L.; Liu, H.M.; Chen, L.W.; Chen, L.L.; Zhou, C.X.; Hong, P.Z. Characterization and comparison of collagen extracted from the skin of the nile tilapia by fermentation and chemical pretreatment. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 128139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.H.; Jin, W.G.; Chen, D.J.; Dong, M.R.; Xin, X.; Li, C.Y.; Xu, Z.M. Collagens made from giant salamander (Andrias davidianus) skin and their odorants. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.R.; Shiau, C.Y.; Chen, H.H.; Huang, B.C. Isolation and characterization of acid and pepsin-solubilized collagens from the skin of balloon fish (Diodon holocanthus). Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhou, K.; Zhu, Y.C.; Zhang, W.D.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhou, H.; Yang, T.T.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, B.C. Collagen and its derivatives: From structure and properties to their applications in food industry. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshk, S.; Rezaei, M.; Abdollahi, M. Impact of ultrasound on extractability of native collagen from tuna by-product and its ultrastructure and physicochemical attributes. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 89, 106129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.G.; Nidheesh, T.; Suresh, P.V. Comparative study on characteristics and in vitro fibril formation ability of acid and pepsin soluble collagen from the skin of catla (Catla catla) and rohu (Labeo rohita). Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 804–812. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, W.; Xia, G.H.; Li, Y.C.; Shen, X.R.; Li, C. Comparison of characteristics and fibril-forming ability of skin collagen from barramundi (Lates calcarifer) and tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faralizadeh, S.; Rahimabadi, E.Z.; Bahrami, S.H.; Hasannia, S. Extraction, characterization and biocompatibility evaluation of collagen from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) skin by-product. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 22, 100454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinthusamran, S.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H. Comparative Study on Molecular characteristics of acid soluble collagens from skin and swim bladder of seabass (Lates calcarifer). Food Chem. 2013, 138, 2435–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stani, C.; Vaccari, L.; Mitri, E.; Birarda, G. FTIR investigation of the secondary structure of type I collagen: New insight into the amide III band. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 229, 118006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.C.; Yu, X.Y.; You, J.; Yin, T.; Lin, Y.L.; Chen, W.X.; Dao, L.R.; Du, H.Y.; Liu, R.; Xiong, S.B.; et al. Study of the thermodynamics and conformational changes of collagen molecules upon self-assembly. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 114, 106576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Hong, Z.; Wen, H.M.; Hong, B.H.; Lin, R.R.; Chen, W.Z.; Xie, Q.N.; Le, Q.Q.; Yi, R.Z.; Wu, H. Compositional and structural characteristics of pepsin-soluble type I collagen from the scales of red drum fish, Sciaenops ocellatus. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.D.; Li, J.Y.; Li, Z.B.; Yi, R.Z.; Shi, S.J.; Wu, K.Y.; Li, Y.S.; Wu, S.J. Physicochemical and functional properties of type I collagens in red stingray (Dasyatis akajei) skin. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.Y.; Li, Y.S.; Chen, J.D. Effect of pH on the structure, functional properties and rheological properties of collagen from greenfin horse-faced filefish (Thamnaconus septentrionalis) skin. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.Y.; Li, B.F.; Zhao, X.; Ren, G.Y.; Zhuang, Y.L.; Hou, H.; Zhang, X.K.; Chen, L.; Fan, Y. Characterization of acid-soluble collagen from the skin of walleye pollock (Theragra chalcogramma). Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeruraj, A.; Arumugam, M.; Balasubramanian, T. Isolation and characterization of thermostable collagen from the marine eel-fish (Evenchelys macrura). Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 1592–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Yeo, I.J.; Hwang, K.E.; Song, D.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Ham, Y.K.; Jeong, T.J.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, C.J. Isolation and characterization of pepsin-soluble collagens from bones, skins, and tendons in duck feet. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2016, 36, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.M.; Ma, C.Y. Conformational study of globulin from common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8046–8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.K.; Liu, D.C. Comparison of physical–chemical properties of type I collagen from different species. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, K.; Sreekumar, S.; Hemalatha, T.; Fathima, N. Physicochemical studies of asarylaldehyde crosslinked type-I collagen fibrils. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1344, 142972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, L.; Russo, F.; Natali, M.L.; Rajabimashhadi, Z.; Bagheri, S.; Mele, C.; Lionetto, F.; Sannino, A.; Gallo, N. On the effect of pepsin incubation on type I collagen from horse tendon: Fine tuning of its physico-chemical and rheological properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 256, 128489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.N.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, H.W.; Kong, M.; Dong, P.; Zhao, X.; Hou, H. Rheological properties of the swim bladder colloid from Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) and its digestive characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Han, M.Y.; Shao, X.F.; Yu, L.X.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhou, X.; Xu, X.L.; Wang, P. Colloidal structural characteristics and variation patterns of chicken skin gelatin during thermal processing. Food Chem. 2025, 493, 145920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yang, H.; Lou, A.; Jiang, S.Y.; Kang, K.L.; Wei, Y.J.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.M.; Yu, M.J.; Huang, Q. Effect of psyllium husk powder on the gelation behavior, microstructure, and intermolecular interactions in myofibrillar protein gels from Andrias davidianus. Food Chem. 2024, 458, 140266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozeri Atik, S.; Oztürk, H.I.; Akın, N. Perspectives on the yogurt rheology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Duan, L.; Tian, Z.H.; Liu, W.T.; Li, G.Y.; Hang, X.P. Rheological behavior of acylated pepsin-solubilized collagen solutions: Effects of concentration. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2015, 27, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevkani, K.; Singh, N.; Kaur, A.; Rana, J.C. Structural and functional characterization of kidney bean and field pea protein isolates: A comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Li, X.F.; Shuai, S.Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, N.; Wang, Z.M.; Jin, L.L.; Zheng, A.P. Application of rheology to hot melt extrusion: Theory and practice. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 680, 125742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollaheydaralimoazzen, M.; Sheikholeslam, M.; Poursamar, S.L.; Farzan, M.; Farzan, M.; Rafienia, M. 3D-printing of shear-thinning and self-healing gelatin/starch/halloysite-nanotube hydrogels for soft tissue engineering: An in vitro and in vivo assessment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 315, 144502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.I.; Li, Y.H.; Pan, J.F.; Liu, F.; Dai, H.J.; Fu, Y.; Huang, T.; Farooq, S.; Zhang, H. Collagen and gelatin: Structure, properties, and applications in food industry. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 128037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Shao, S.; Han, R.X.; Zhang, R.R.; Ma, X.T.; Wang, M.; Wan, Z.Q.; Zhao, D.Q.; Yan, M.M. Structural, physicochemical and functional properties of semen ziziphi spinosae protein. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 29555–29566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toniasso, D.P.W.; Giacomelli da Silva, C.; de Souza Brum Junior, B.; Somacal, S.; Emanuelli, T.; Hashime Kubota, E.; Cristina Prestes Dornelles, R.; Mello, R. Collagen extracted from rabbit: Meat and by-products: Isolation and physicochemical assessment. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 111967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunwolu, S.O.; Henshaw, F.O.; Mock, H.P.; Matros, A.; Awonorin, S. Functional properties of protein concentrates and isolates produced from cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) nut. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, M.; Undeland, I. Structural, functional, and sensorial properties of protein isolate produced from salmon, cod, and herring by-products. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 1733–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, L.; Cai, P.P.; Li, P.P.; Zhang, M.H.; Sun, Z.L.; Sun, C.; Xu, W.M.; Wang, D.Y. Effect of ultrasound assisted extraction on the physicochemical and functional properties of collagen from soft-shelled turtle calipash. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, D.; Koomsap, P.; Lamichhane, A.; Sadiq, M.B.; Ananl, A.K. Optimization of collagen extraction from chicken feet by papain hydrolysis and synthesis of chicken feet collagen based biopolymeric fibres. Food Biosci. 2018, 23, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Cai, Y.J.; Liu, T.X.; Long, Z.; Huang, L.H.; Deng, X.L.; Zhao, Q.Z.; Zhao, M.M. Effects of pretreatments on the structure and functional properties of okara protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 90, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkaczewska, J.; Wielgosz, M.; Kulawik, P.; Zajac, M. The effect of drying temperature on the properties of gelatin from carps (Cyprinus carpio) skin. Czech J. Food Sci. 2019, 37, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Amino Acid | BBC | Amino Acid | BBC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ser | 39 | Leu | 28 |
| Gly | 312 | Phe | 17 |
| His | 8 | Hyp | 55 |
| Thr | 31 | Me | 9 |
| Glu | 78 | Val | 30 |
| Asp | 58 | Tyr | 7 |
| Ala | 121 | IIe | 15 |
| Arg | 61 | Hyl | 6 |
| Pro | 84 | Try | 0 |
| Cys | 1 | Imino acids * | 139 |
| Lys | 41 | Total | 1000 |
| Concentration (mg/mL) | K | n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1.512 ± 0.366 | 0.352 ± 0.013 | 0.994 |
| 10 | 13.707 ± 0.065 | 0.288 ± 0.003 | 0.999 |
| 15 | 40.342 ± 0.239 | 0.205 ± 0.003 | 0.999 |
| 20 | 76.822 ± 1.647 | 0.263 ± 0.012 | 0.997 |
| Temperature (°C) | K | n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 17.331 ± 0.243 | 0.275 ± 0.008 | 0.999 |
| 20 | 14.068 ± 0.057 | 0.274 ± 0.002 | 0.999 |
| 30.85 | 1.841 ± 0.020 | 0.293 ± 0.006 | 0.997 |
| 40 | 0.088 ± 0.002 | 0.492 ± 0.015 | 0.986 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, L.; Li, Y.; Ke, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J. Thermally Stable Collagen from Black Carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) Swim Bladder: Preparation, Structure, Rheological, and Functional Properties. Foods 2025, 14, 3359. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193359
Wei L, Li Y, Ke C, Chen J, Zhang J. Thermally Stable Collagen from Black Carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) Swim Bladder: Preparation, Structure, Rheological, and Functional Properties. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3359. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193359
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Lichi, Yushuang Li, Cong Ke, Junde Chen, and Jing Zhang. 2025. "Thermally Stable Collagen from Black Carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) Swim Bladder: Preparation, Structure, Rheological, and Functional Properties" Foods 14, no. 19: 3359. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193359
APA StyleWei, L., Li, Y., Ke, C., Chen, J., & Zhang, J. (2025). Thermally Stable Collagen from Black Carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) Swim Bladder: Preparation, Structure, Rheological, and Functional Properties. Foods, 14(19), 3359. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193359






