Carnosine and Acyl Carnitines as Metabolic Determinants of Muscle Phenotypic Differences Between Longissimus Dorsi and Triceps Brachii in Hanzhong Sheep
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Muscle Samples
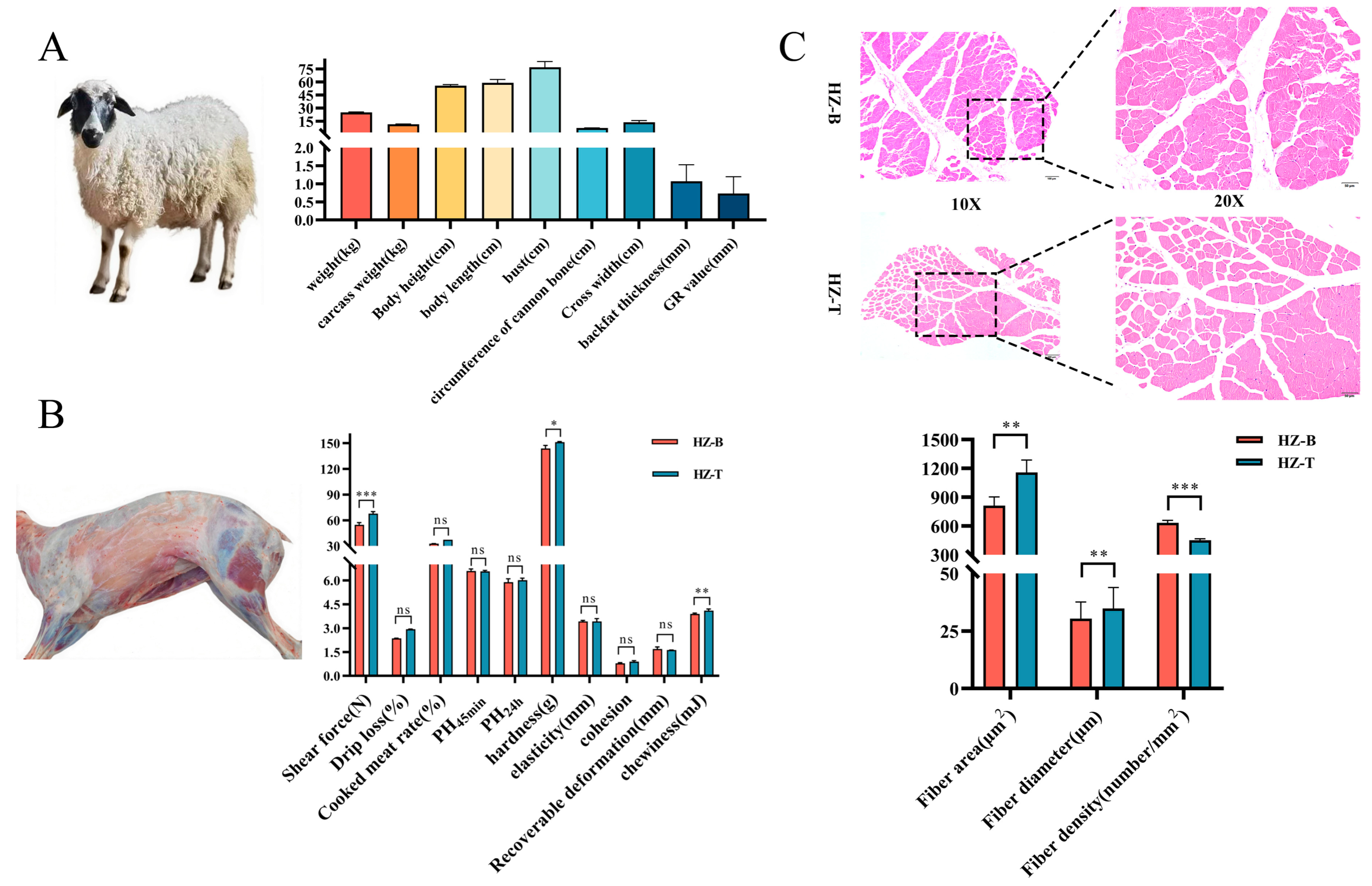
2.2. Slaughter Performance and Meat Quality Assessment
2.3. Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) Staining of Muscle Tissue
2.4. Metabolite Extraction and LC-MS Analysis
2.5. Total RNA Extraction and Transcriptomic Analysis
2.6. Comprehensive Analysis of Transcriptome and Metabolome Data
2.7. Validation of DEGs via Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.8. Statistics and Analysis of Data
3. Results
3.1. Hanzhong Sheep Exhibit Small Body Size, Slow Growth and Superior Tenderness
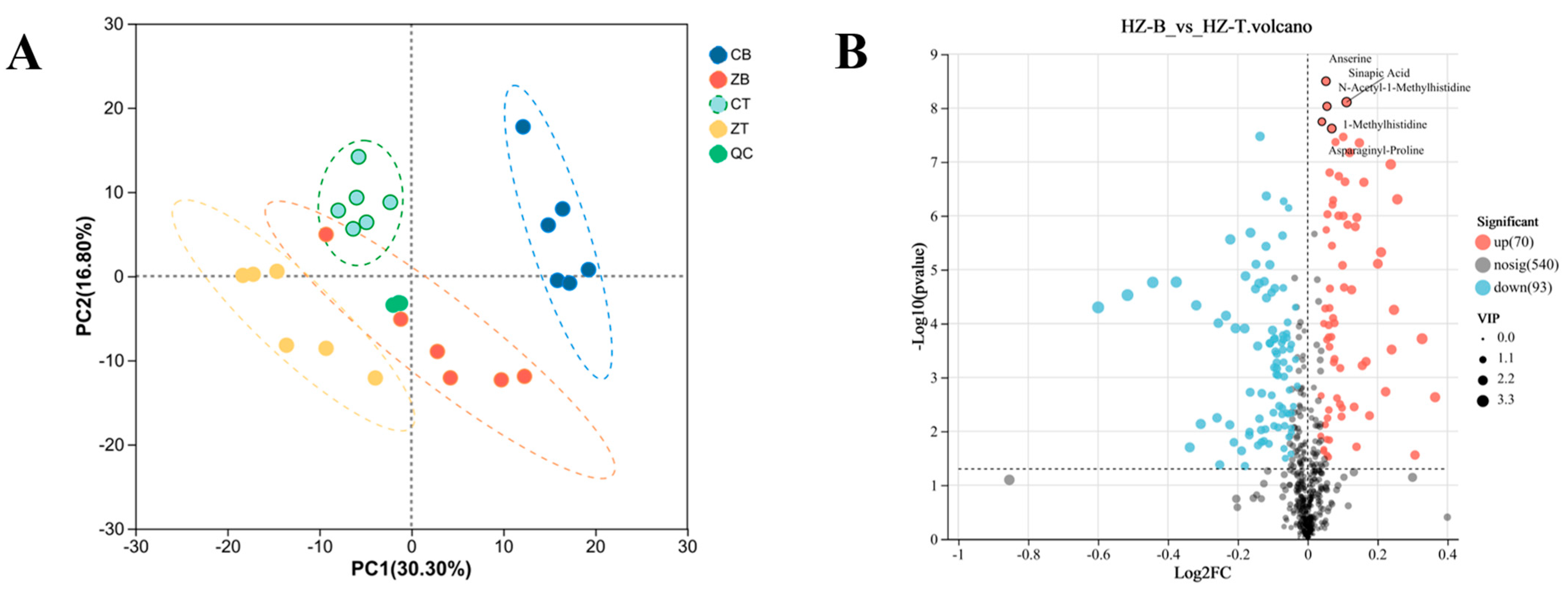
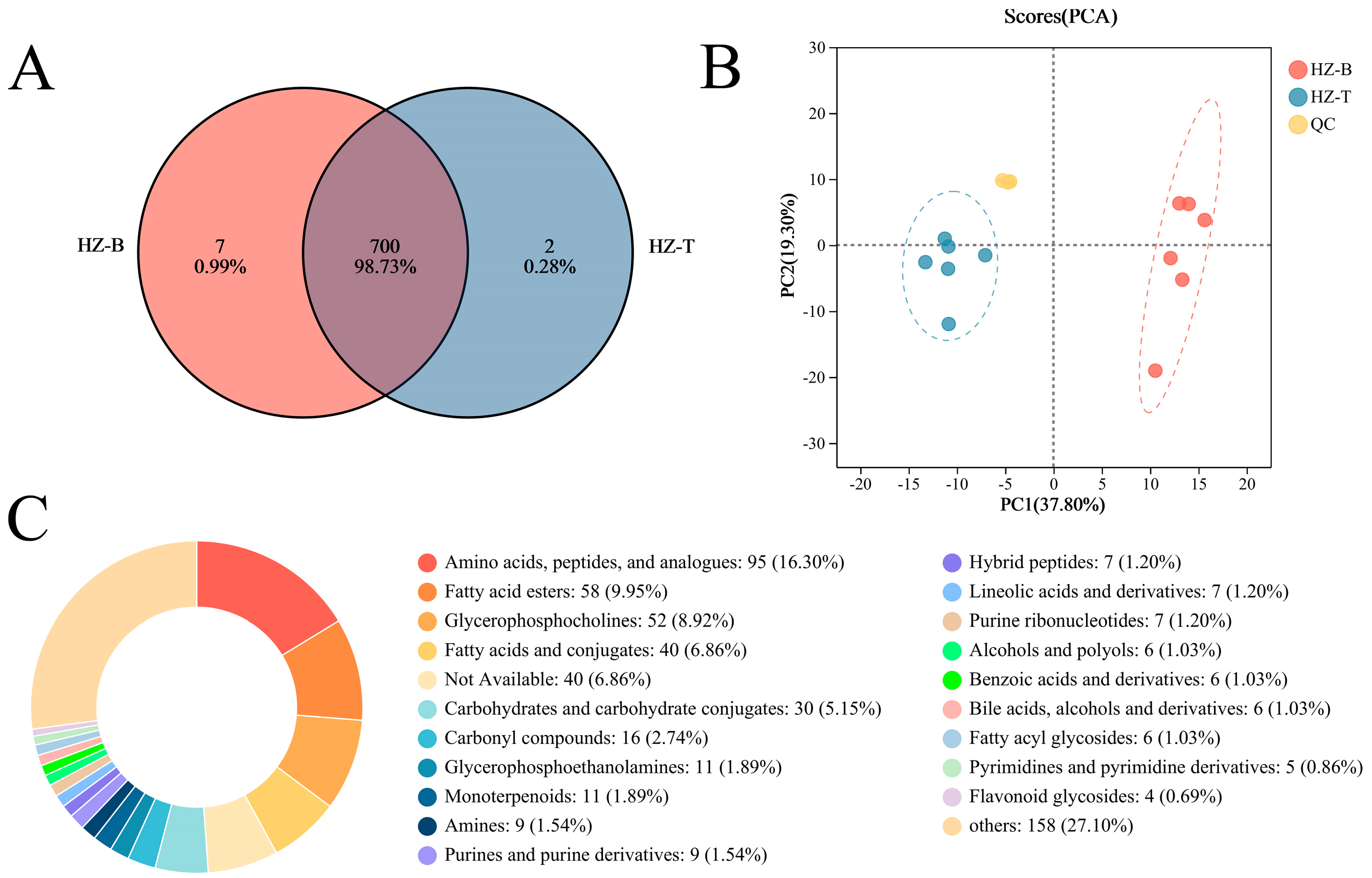
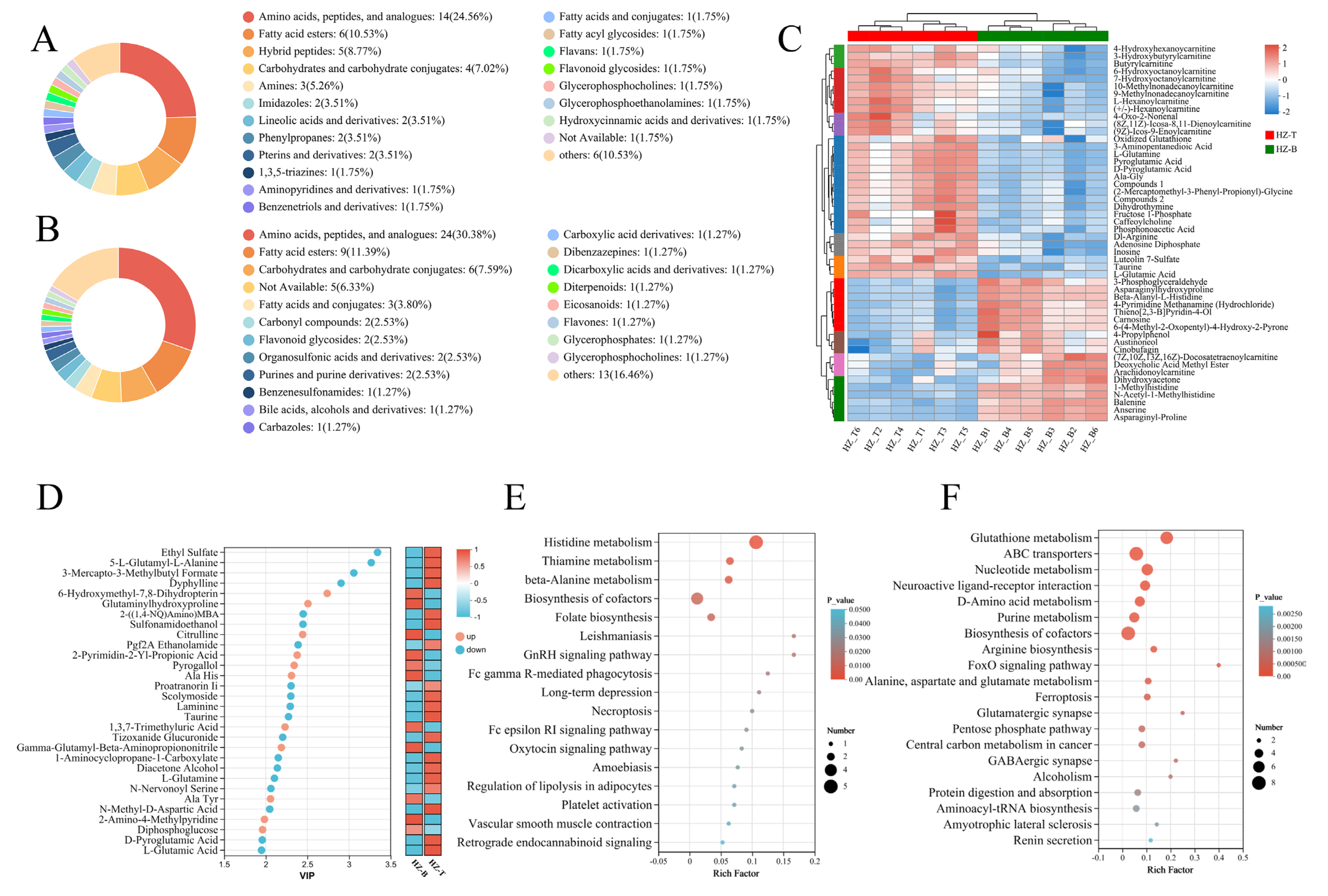
3.2. Muscle Metabolome of Hanzhong Sheep Is Compositionally Rich and Regionally Distinct
3.3. Significant Differences in Metabolite Content Between the Longissimus Dorsi and Triceps Brachii Muscles
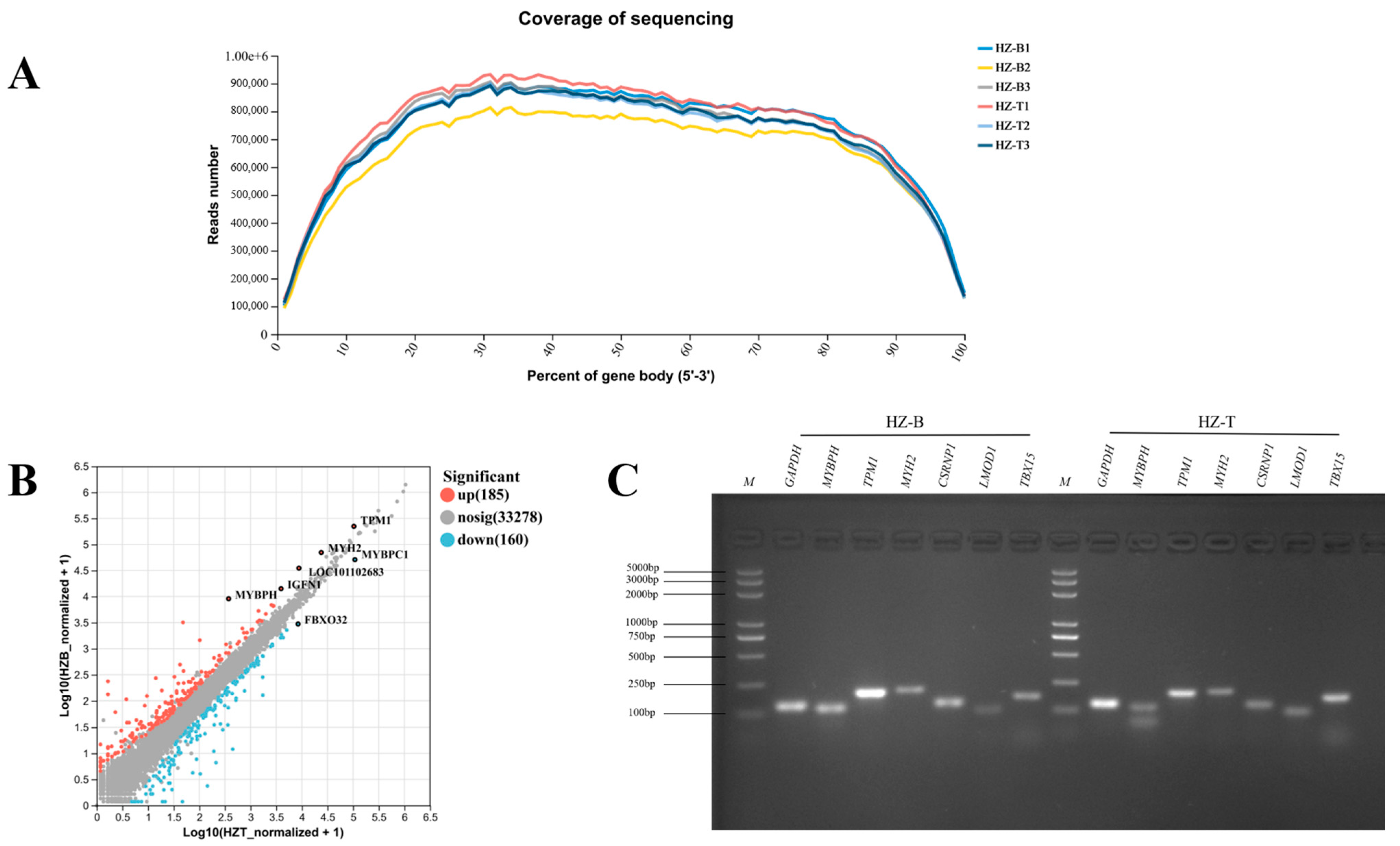
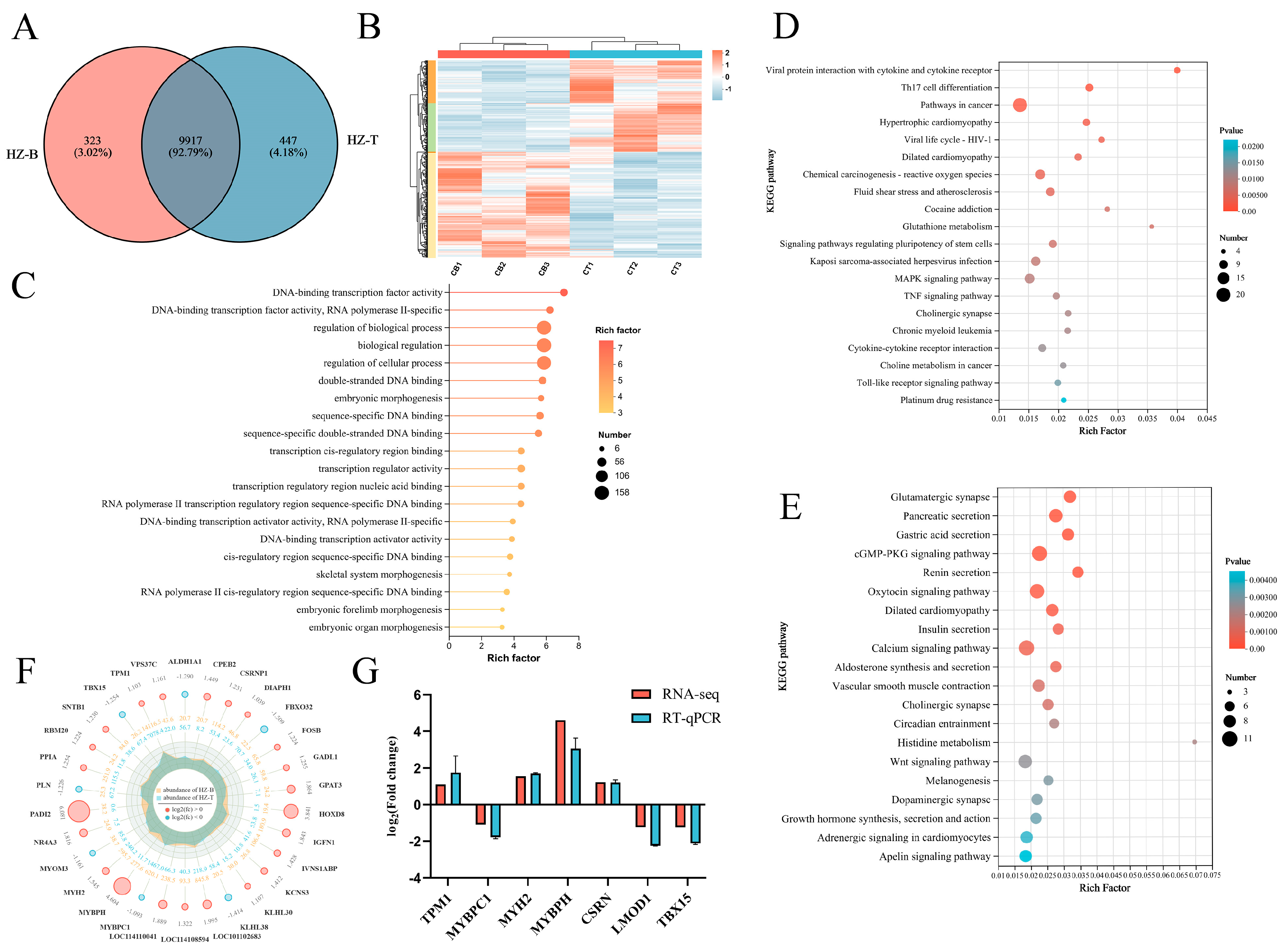
3.4. Transcriptomic Profiling Reveals Gene Expression Differences Between Muscles
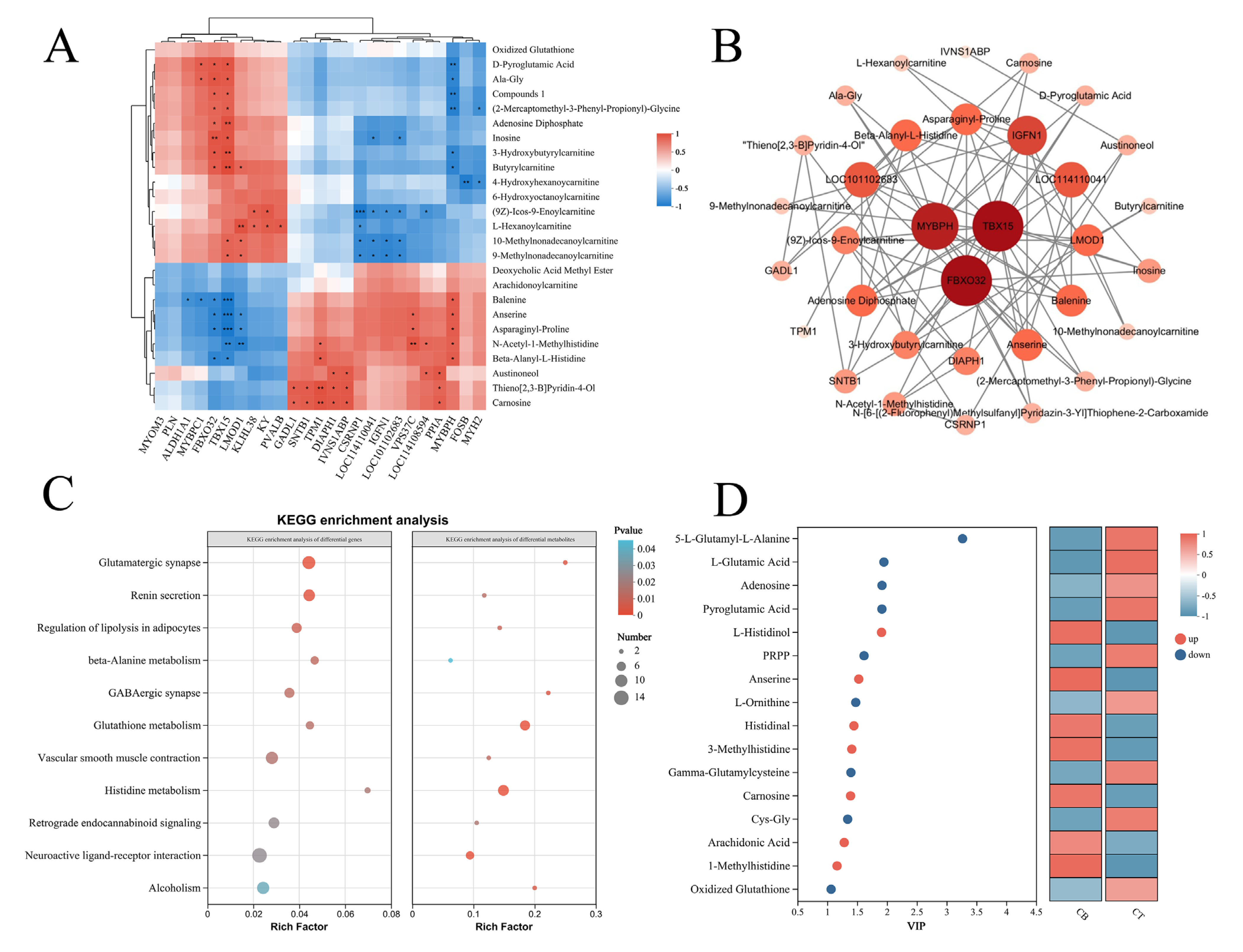
3.5. Correlation Between DEGs and DMs in Longissimus Dorsi and Triceps Brachii Muscles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
Appendix A
| Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Forward Primer (5′ to 3′) | Reverse Primer (5′ to 3′) | Amplicon Length (bp) | Annealing Temp (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | ACTGGCAAAGTGGACATCGT | TTCCCGTTCTCTGCCTTGAC | 124 | 58 |
| MYBPH | myosin-binding protein H | GGAACCTGGCTGTAGGTGAC | CGATGGTCTCCTGGATGTGG | 110 | 58 |
| TPM1 | tropomyosin 1 | GGCATGAAAGTCATTGAGAGCC | CTTCTGAGAGCTCAGCCCG | 186 | 60 |
| MYBPC1 | myosin-binding protein C1 | AAAAGCCTCAAGGCGGAAGT | TCGAATGTGTACACCCGGC | 191 | 58 |
| MYH2 | myosin-binding protein H | AAAAGCGCCAGGAGGC | TTTGCCAGATTCCTCCTTCTT | 198 | 57 |
| CSRNP1 | cysteine- and serine-rich nuclear protein 1 | ATGCCAGCTGCTTCCTCAAT | GCAAGAGGACAAGCTGAGGT | 124 | 59 |
| LMOD1 | leiomodin 1 | AAGGTAGCCAAGTATCGCCG | CTCCAGCTCCTCCATCTCCT | 93 | 59 |
| TBX15 | T-box transcription factor 15 | GCTCAGCCCTCTGAAACCTT | TTGCCTGCCTGCATGACATA | 160 | 59 |
| Sample | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Total Mapped | Error Rate (%) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | GC Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZ-B1 | 50637628 | 50280308 | 49297209 (98.04%) | 0.0122 | 98.65 | 95.6 | 51.38 |
| HZ-B2 | 50451316 | 50076994 | 48893073 (97.64%) | 0.0121 | 98.69 | 95.71 | 51.81 |
| HZ-B3 | 48301048 | 47920416 | 46882259 (97.83%) | 0.0122 | 98.66 | 95.62 | 52.65 |
| HZ-T1 | 50634370 | 50266244 | 49270916 (98.02%) | 0.0123 | 98.6 | 95.44 | 51.67 |
| HZ-T2 | 49530508 | 49215030 | 48152042 (97.84%) | 0.0122 | 98.64 | 95.57 | 53.44 |
| HZ-T3 | 46321530 | 45951396 | 44966118 (97.86%) | 0.0123 | 98.62 | 95.51 | 52.05 |
References
- Zhang, R.; Pavan, E.; Ross, A.B.; Deb-Choudhury, S.; Dixit, Y.; Mungure, T.E.; Realini, C.E.; Cao, M.; Farouk, M.M. Molecular insights into quality and authentication of sheep meat from proteomics and metabolomics. J. Proteom. 2023, 276, 104836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, A.; Fu, X.; Tang, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wu, C. Untargeted metabolomics analysis reveals comparative meat quality of different muscles and the impact of Saline-alkali land feeding on Dolang sheep (Ovis aries). BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Moon, S.S.; Song, S.; Cheng, H.; Im, C.; Du, L.; Kim, G.D. Comparative review of muscle fiber characteristics between porcine skeletal muscles. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2024, 66, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Hoa, V.B.; Song, D.H.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.W.; Bae, I.S.; Sung, P.N.; Park, J.; Song, S.; et al. Comparison of Muscle Fiber and Meat Quality Characteristics of Beef Strip Loin, Tenderloin, and Round Cuts among Jeju Black Cattle, Hanwoo, and Their Crossbreeds. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2024, 44, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognocchi, M.; Conte, G.; Mantino, A.; Foggi, G.; Casarosa, L.; Tinagli, S.; Turini, L.; Scicutella, F.; Mele, M.; Serra, A. Linseed supplementation in the diet of fattening pigs: Effect on the fatty acid profile of different pork cuts. Meat Sci. 2023, 204, 109276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, F.; Pannier, L.; Pethick, D.W.; Gardner, G.E. Intramuscular fat in lamb muscle and the impact of selection for improved carcass. Animal 2015, 9, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Liu, C.; Yang, Z.; Su, R.; Chen, X.; Hou, Y.; Hu, G.; Yao, D.; Zhao, L.; Su, L.; et al. Effects of oxidative stability variation on lamb meat quality and flavor during postmortem aging. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 2578–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Peng, L.; Guo, L.; Yang, L. From genes to phenotypes: A review of multilevel omics techniques in beef quality. Gene 2025, 962, 149416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wu, Z.; Su, Q.; Sa, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hou, S.; Gui, L. Effect of different Lys/Met ratios in a low-protein diet on the meat quality of Tibetan sheep: A transcriptomics- and metabolomics-based analysis. Food Res. 2025, 204, 115893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.T.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Zou, H.; Azeem, R.M.; Sun, W.S.; et al. Transcriptome and Metabolome Insights into Key Genes Regulating Fat Deposition and Meat Quality in Pig Breeds. Animals 2024, 14, 3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, B.; Luo, R.; Hu, X.; Bi, Y. Transcriptomics-based analysis of the effect of PI3K/AKT pathway on muscle metabolic homeostasis of cooled beach lamb during storage. Food Sci. 2024, 45, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; An, X.; Xu, Z.; Niu, C.; Geng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shi, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, R.; Yue, Y. Transcriptome-Metabolome Analysis Reveals That Crossbreeding Improves Meat Quality in Hu Sheep and Their F(1)-Generation Sheep. Foods 2025, 14, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Kuai, Z.; Yao, Z.; Lei, X.; Shi, H.; Li, J.; Liu, K.; Yin, H.; Wang, Y.; Quan, K. Exploring the influence of sex and age on the quality and flavor of Huai goat longissimus thoracis et lumborum through transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses. BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, C. The protection and utilization of the sheep breed resources in Hanzhong. Chin. Livest. Poult. Breed. Ind. 2023, 19, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.J.; Han, S.H.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.A.; Kim, Y.K.; Yoo, J.H.; Shin, M.C.; Yang, B.C.; Park, H.B.; et al. Association of functional sequence variants of the myosin heavy chain 3 gene with muscle collagen content in pigs. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2023, 65, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqin, Q.; Nishiumi, T.; Yamada, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Wu, R.; Borjigin, G. Relationships among muscle fiber type composition, fiber diameter and MRF gene expression in different skeletal muscles of naturally grazing Wuzhumuqin sheep during postnatal development. Anim. Sci. J. 2017, 88, 2033–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Du, H.; Guo, W.; Na, M.; Na, R. Effects and mechanism of the timing of alfalfa hay supplementation on rumen development of Hu lambs. J Anim Sci. 2025, 103, skaf227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.; Abanto, M.; Días, N.B.; Olate, P.; Pérez Nuñez, I.; Díaz, R.; Sepúlveda, N.; Paz, E.A.; Quiñones, J. Recent Trends in Food Quality and Authentication: The Role of Omics Technologies in Dairy and Meat Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Al-Dalali, S.; Zhou, H.; Xu, B. Influence of curing on the metabolite profile of water-boiled salted duck. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Guo, Z.; Yao, Y.; Xia, L.; Liu, R.; Song, H.; Zhang, S. Acetic acid alters rhizosphere microbes and metabolic composition to improve willows drought resistance. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Yue, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, B.; Chen, B.; Liu, J.; Lu, Z. Transcriptomics and metabolomics reveal improved performance of Hu sheep on hybridization with Southdown sheep. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, B.W.B.; Collins, D.; Kilgannon, A.K.; Hopkins, D.L. Using shear force, sarcomere length, particle size, collagen content, and protein solubility metrics to predict consumer acceptance of aged beef tenderness. J. Texture Stud. 2020, 51, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temizkan, M.C.; Bayraktaroglu, A.G.; Kahraman, T. Differential expression analysis of meat tenderness governing genes in different skeletal muscles of bovines. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 3240–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, Y.C.; Kim, B.C. The relationship between muscle fiber characteristics, postmortem metabolic rate, and meat quality of pig longissimus dorsi muscle. Meat Sci. 2005, 71, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, X.M.; Deng, B.; Xu, Z.W.; Tao, X.; Qi, K.K. Age-related changes and nutritional regulation of myosin heavy-chain composition in longissimus dorsi of commercial pigs. Animal 2013, 7, 1486–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Song, S.; Cheng, H.; Im, C.; Jung, E.Y.; Moon, S.S.; Choi, J.; Hur, S.J.; Joo, S.T.; Kim, G.D. Comparison of Meat Quality and Muscle Fiber Characteristics between Porcine Skeletal Muscles with Different Architectures. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2022, 42, 874–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldyrev, A.A.; Aldini, G.; Derave, W. Physiology and pathophysiology of carnosine. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1803–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, A.; Ida, M.; Izumo, T.; Nakai, M.; Honda, H.; Shimizu, K. l-Anserine Increases Muscle Differentiation and Muscle Contractility in Human Skeletal Muscle Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 8952–8958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Gao, F.; Zhou, G. Effects of dietary supplementation with carnosine on growth performance, meat quality, antioxidant capacity and muscle fiber characteristics in broiler chickens. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 3733–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulter, D.L. Carnitine, valproate, and toxicity. J. Child Neurol. 1991, 6, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batrukova, M.A.; Rubtsov, A.M. Histidine-containing dipeptides as endogenous regulators of the activity of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-release channels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1324, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.; Lu, X.; Sun, X.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Y. Preliminary studies on the molecular mechanism of intramuscular fat deposition in the longest dorsal muscle of sheep. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, C.; Li, S.; Xu, J.; Liu, H.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, L. Association of lipidome evolution with the corresponding volatile characteristics of postmortem lamb during chilled storage. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, P.J.; Frank, D.; Singh, T.K.; Young, O.A.; Warner, R.D. Sheepmeat flavor and the effect of different feeding systems: A review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3561–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munyaneza, J.P.; Kim, M.; Cho, E.; Jang, A.; Choo, H.J.; Lee, J.H. Association of histamine-N-methyl transferase gene polymorphisms with carnosine content in red-brown Korean native chickens. Anim. Biosci. 2024, 37, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Zhao, J.; Fan, S.; Huang, X.; Fu, H.; Liu, H.; Sun, W.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, D.; Zhu, X. PLIN5 regulates lipid metabolism via PGC-1α/Drp1 signaling in islet β-cells. Endocrine 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, I.A.; Baldassini, W.A.; Ramírez-Zamudio, G.D.; de Farias, I.; Chiaratti, M.R.; Pereira Junior, S.; Nociti, R.P.; Carvalho, P.H.V.; Curi, R.A.; Pereira, G.L.; et al. Muscle tissue transcriptome of F1 Angus-Nellore bulls and steers feedlot finished: Impacts on intramuscular fat deposition. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, R.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Tian, Y.; Kang, X.; et al. Carcass composition, meat quality, leg muscle status, and its mRNA expression profile in broilers affected by valgus-varus deformity. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Zhang, D.; Hu, B.; Wang, J.; Shen, X.; Xiao, W. FBXO32 Targets c-Myc for Proteasomal Degradation and Inhibits c-Myc Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 16202–16214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahootchi, E.; Cannon Homaei, S.; Kleppe, R.; Winge, I.; Hegvik, T.A.; Megias-Perez, R.; Totland, C.; Mogavero, F.; Baumann, A.; Glennon, J.C.; et al. GADL1 is a multifunctional decarboxylase with tissue-specific roles in β-alanine and carnosine production. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Suryakumar, G.; Singh, S.N.; Rathor, R. A comprehensive review on physiological and biological activities of carnosine: Turning from preclinical facts to potential clinical applications. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 1341–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Xian, T.; Kang, G.; Wang, H.; Feng, T. Effects of dietary l-carnosine supplementation on the growth, intestinal microbiota, and serum metabolome of fattening lambs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1525783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Zheng, M.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Lu, H.; Zhang, T. Carnosine and Acyl Carnitines as Metabolic Determinants of Muscle Phenotypic Differences Between Longissimus Dorsi and Triceps Brachii in Hanzhong Sheep. Foods 2025, 14, 3289. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193289
Li Z, Zheng M, Li W, Li J, Wang L, Wang S, Lu H, Zhang T. Carnosine and Acyl Carnitines as Metabolic Determinants of Muscle Phenotypic Differences Between Longissimus Dorsi and Triceps Brachii in Hanzhong Sheep. Foods. 2025; 14(19):3289. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193289
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhi, Miaohua Zheng, Weiwei Li, Jiayi Li, Ling Wang, Shanshan Wang, Hongzhao Lu, and Tao Zhang. 2025. "Carnosine and Acyl Carnitines as Metabolic Determinants of Muscle Phenotypic Differences Between Longissimus Dorsi and Triceps Brachii in Hanzhong Sheep" Foods 14, no. 19: 3289. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193289
APA StyleLi, Z., Zheng, M., Li, W., Li, J., Wang, L., Wang, S., Lu, H., & Zhang, T. (2025). Carnosine and Acyl Carnitines as Metabolic Determinants of Muscle Phenotypic Differences Between Longissimus Dorsi and Triceps Brachii in Hanzhong Sheep. Foods, 14(19), 3289. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193289






