Study on Configuration Design and Numerical Simulation of Twin-Screw Extruder Cooling Die Based on Pea Protein Isolate Flow Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
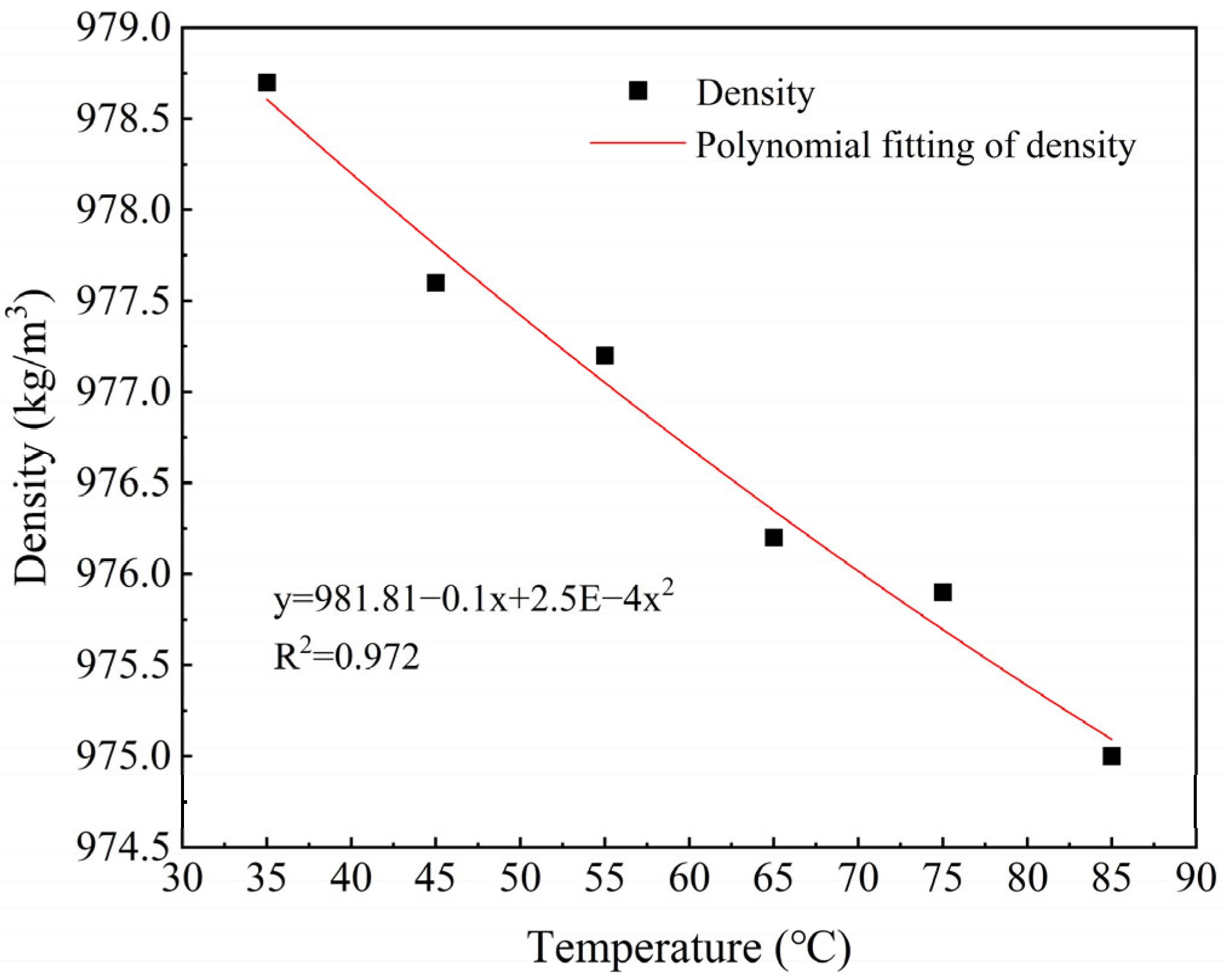
2.2. Density Measurement of PPI
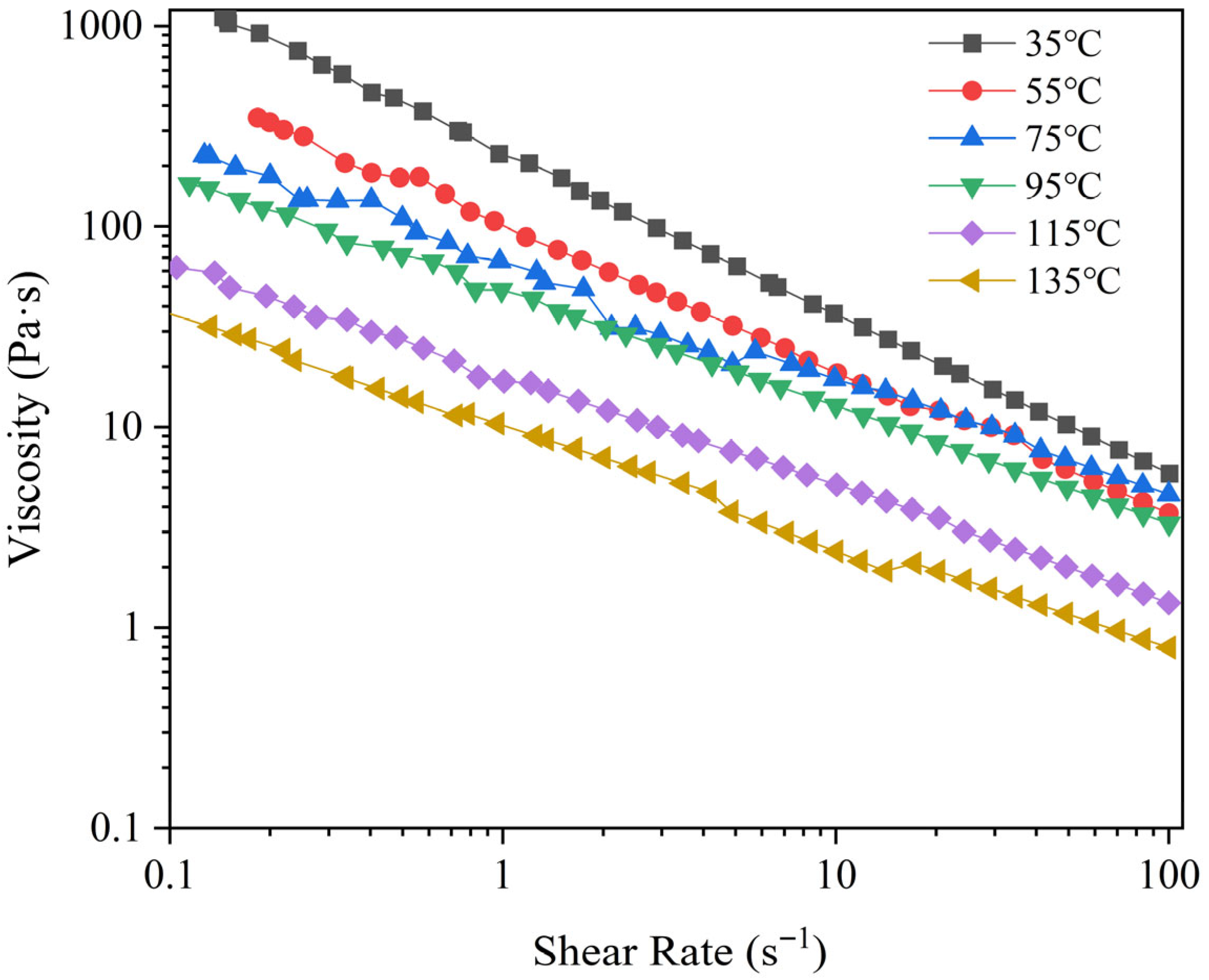
2.3. Viscosity Measurement of PPI
2.4. Determination of Thermodynamic Parameters of PPI
2.5. Design Requirements for Twin-Screw Extruder Cooling Die
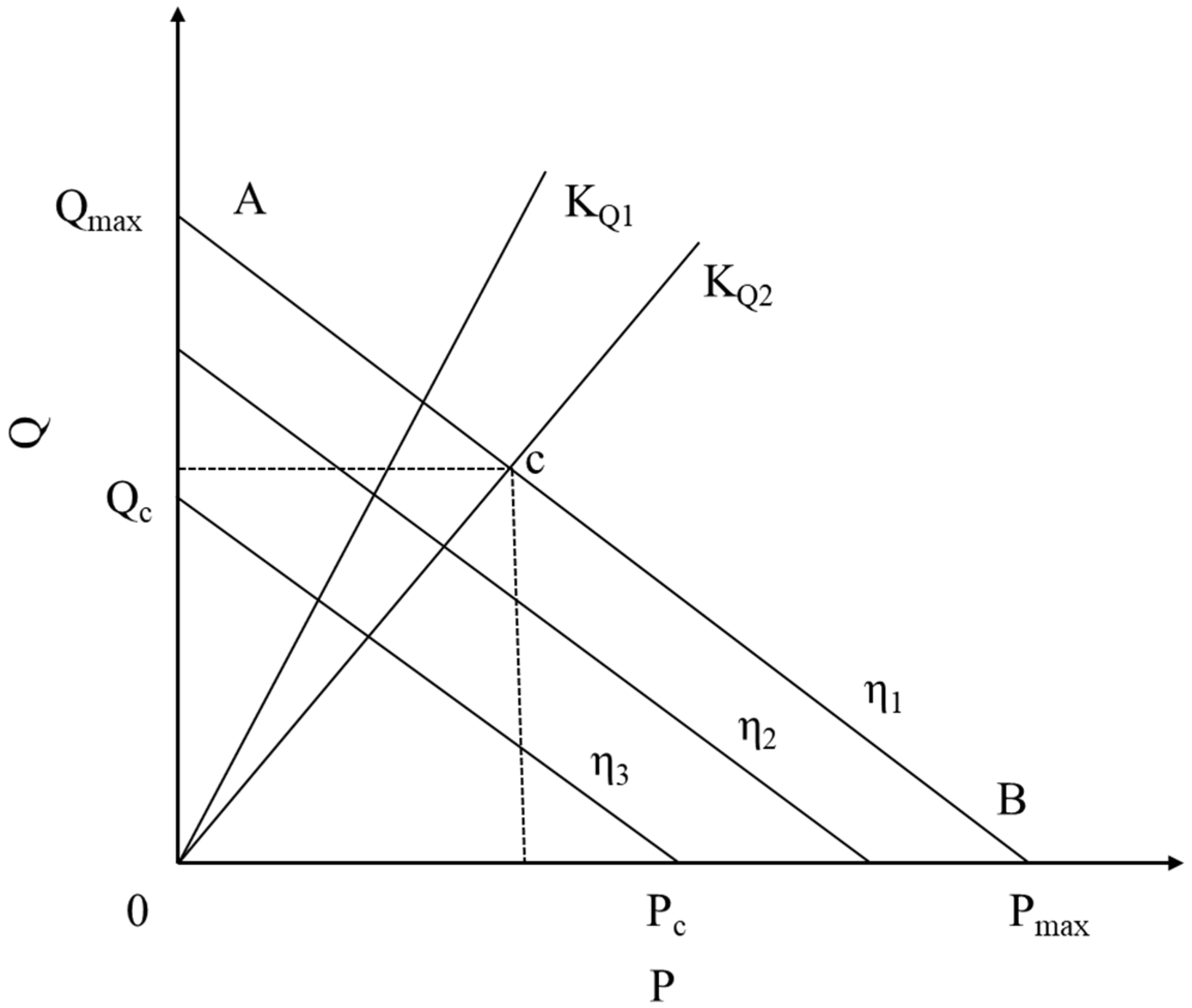
2.6. Material Flow Equation for Twin-Screw Extruder
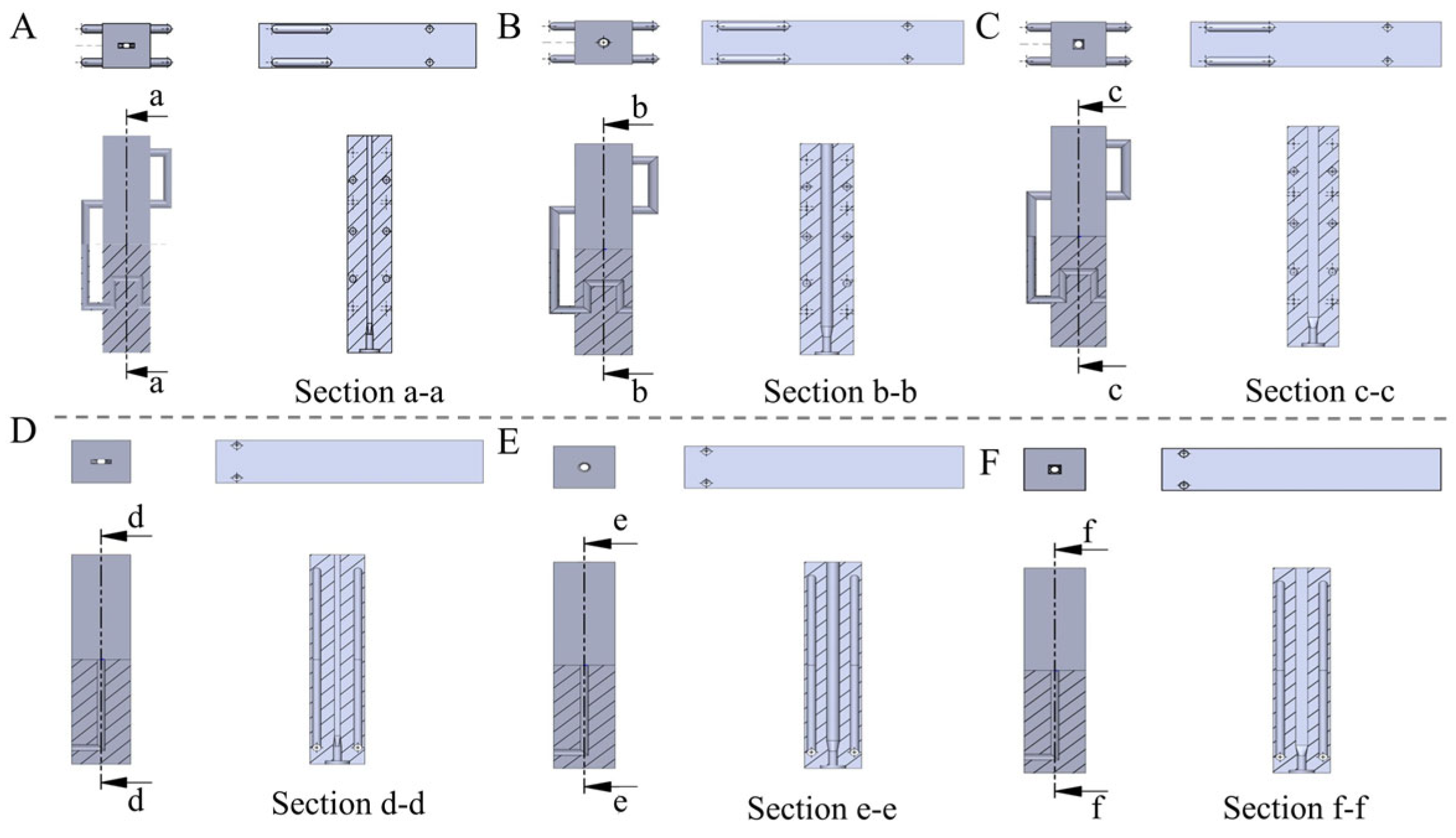
2.7. Die Flow Channel Design for Twin-Screw Extruder
2.8. Three-Dimensional Modeling and Meshing of Cooling Die
2.9. Basic Assumptions of Flow Field
- (1)
- During the cooling process, the PPI melt is assumed to fill the entire cooling die uniformly;
- (2)
- No slip occurs at the cooling die wall, i.e., the no-slip condition is applied at the wall;
- (3)
- The protein fluid is considered to flow in a laminar manner;
- (4)
- The effects of inertial forces, gravity, and other volumetric forces are neglected, as viscous forces are much greater than these;
- (5)
- No phase change occurs in the protein fluid during the cooling process.
2.10. Fluid Control Equations
- (1)
- Continuity Equation
- (2)
- Momentum Equation
- (3)
- Energy Equation
2.11. Setting of Boundary Conditions
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determination of PPI Density
3.2. Determination of PPI Viscosity
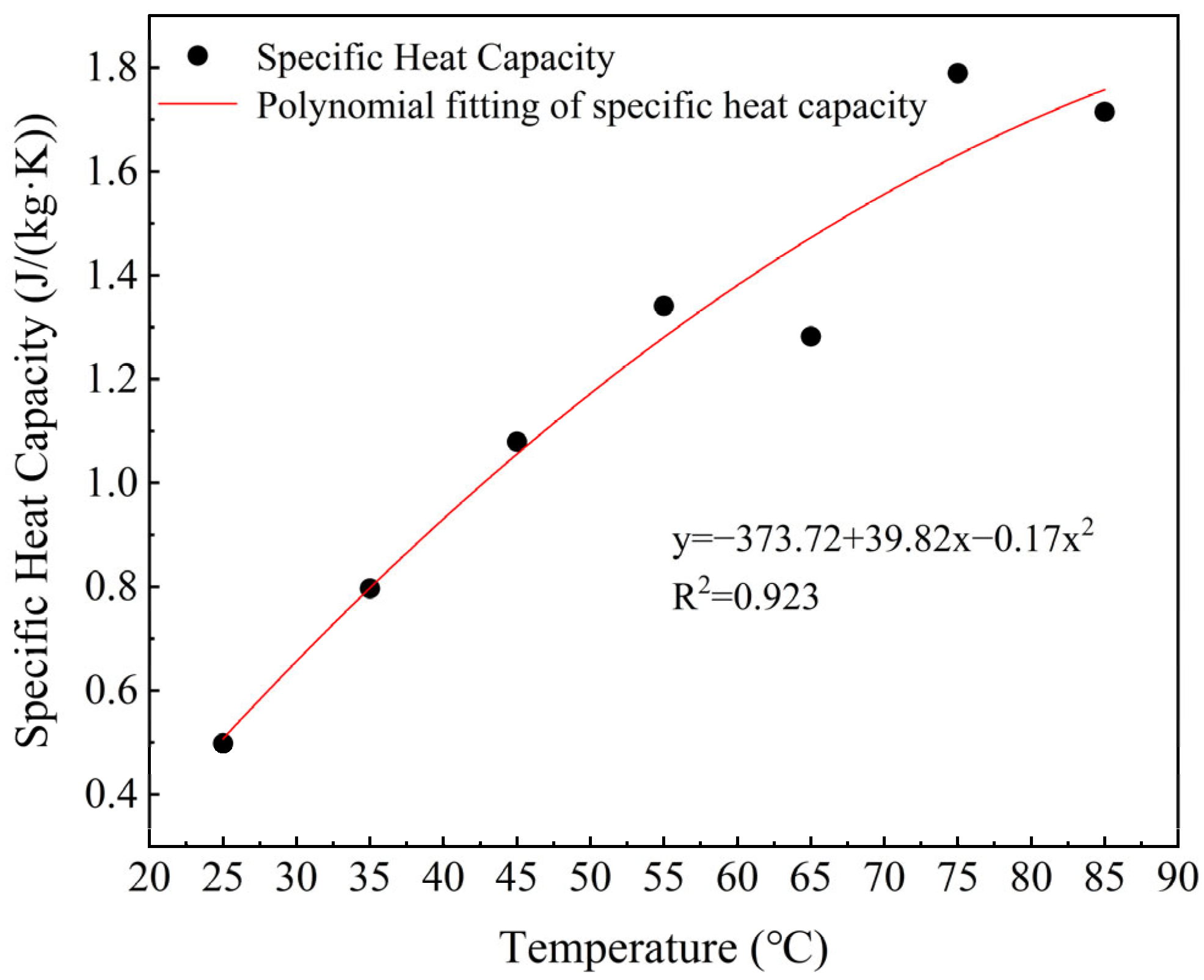
3.3. Determination of Thermodynamic Properties of PPI
3.4. Die Design Scheme
3.4.1. Material Selection for the Die
3.4.2. Determination of Die Geometric Dimensions
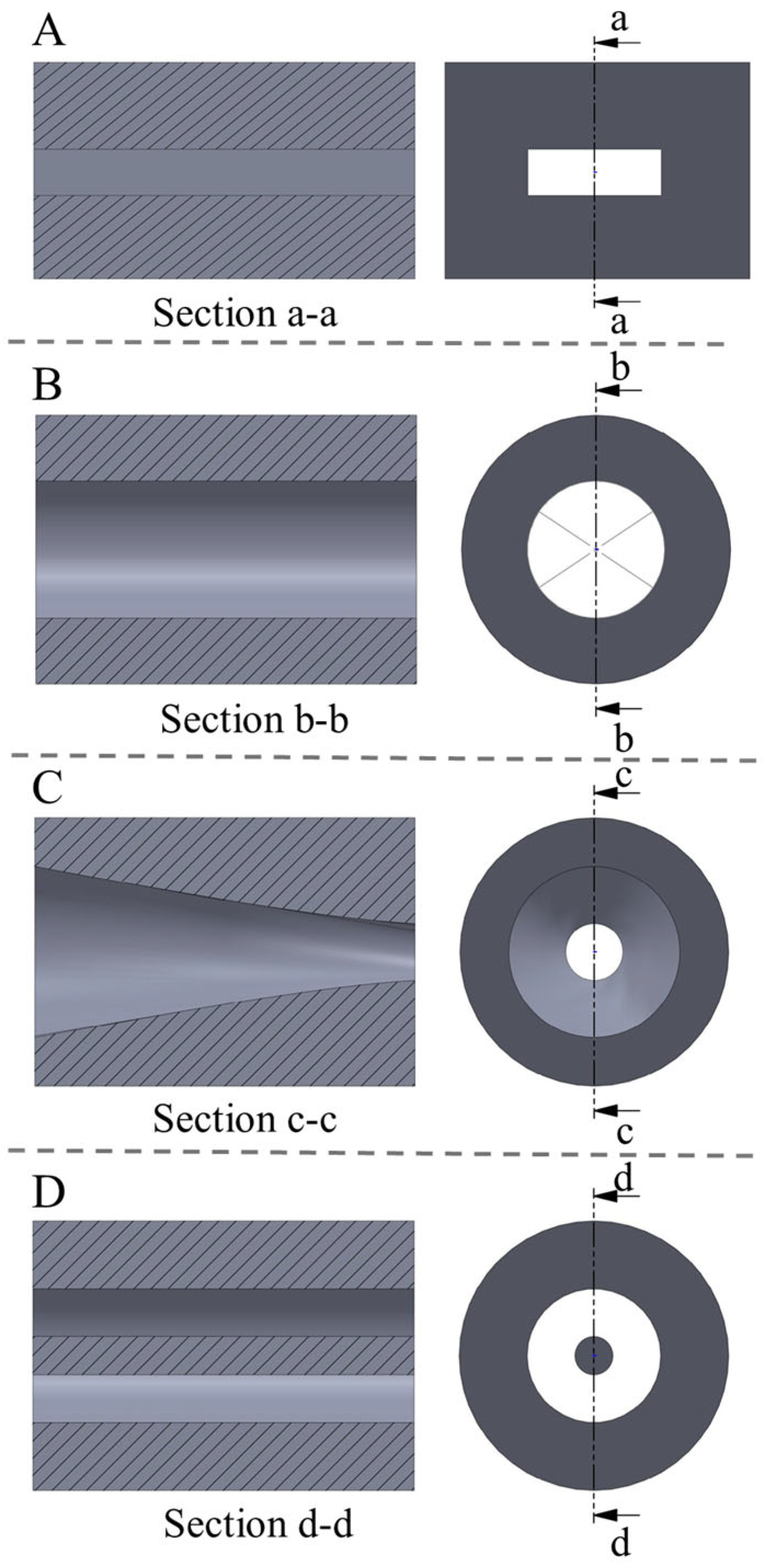
3.4.3. Layout Scheme of Die Cooling Channels
3.4.4. Summary of Die Design Scheme
3.5. Numerical Simulation Analysis of Different Cooling Die Design Schemes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, T.Y.; Yu, S.J.; Pan, Y.H.; Li, H.; Liu, X.Q.; Cao, J.N. Properties of texturized protein and performance of different protein sources in the extrusion process: A review. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, D.; Li, Y.H.; Alavi, S. Chemical and physicochemical features of common plant proteins and their extrudates for use in plant-based meat. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 131, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.W.; Hahn, J.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, Y.J. The influence of cooling die temperature gradients on the texture of high-moisture meat analogs. Food Chem. 2025, 468, 142403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- See, X.Y.; Chiang, J.H.; Law, L.; Osen, R. High moisture extrusion of plant proteins: Advances, challenges, and opportunities. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 65, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöri, P.; Aisala, H.; Liu, J.; Lille, M.; Sozer, N. Structure, texture, and sensory properties of plant-meat hybrids produced by high-moisture extrusion. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 173, 114345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornet, S.H.V.; Snel, S.J.E.; Schreuders, F.K.G.; van der Sman, R.G.M.; Beyrer, M.; van der Goot, A.J. Thermo-mechanical processing of plant proteins using shear cell and high-moisture extrusion cooking. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 3264–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, Y.; Takemitsu, H.; Kajiwara, T.; Kimura, K.; Takeuchi, T.; Tomiyama, H. Improving mixing characteristics with a pitched tip in kneading elements in twin-screw extrusion. AIChE J. 2018, 64, 1424–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.L.; Hao, H.Y.; Yang, M.; Tan, C.M.; Chen, L.; Wu, J.H.; Wang, H.Y. Enhancing cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase-mediated potato starch modification via plasma-activated water and twin-screw extrusion treatment. Food Chem. 2025, 491, 145247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Li, L. Physical modification of vegetable protein by extrusion and regulation mechanism of polysaccharide on the unique functional properties of extruded vegetable protein: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 11454–11467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, A.; Zhang, Z.N.; Zhang, T.Y.; Jiang, L.Z.; Zhou, W.B.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, X.N. Advancing molecular understanding in high moisture extrusion for plant-based meat analogs: Challenges and perspectives. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.X.; Fu, J.L.; Chang, Y.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Fang, Y.P. Structure Design for Improving the Characteristic Attributes of Extruded Plant-Based Meat Analogues. Food Biophys. 2022, 17, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaunisto, E.; Wassén, S.; Stading, M. A thermodynamical finite element model of the fibre formation process during extrusion of high-moisture meat analogues. J. Food Eng. 2024, 362, 111760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.X.; Xu, J.B.; Sun, C.X.; Zhao, Y.G.; Cao, Y.P.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Y.P. Multihole nozzle-mediated high-moisture extrusion of soy proteins into fiber-rich structures. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 151, 109819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snel, S.J.E.; Bellwald, Y.; van der Goot, A.J.; Beyrer, M. Novel rotating die coupled to a twin-screw extruder as a new route to produce meat analogues with soy, pea and gluten. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 81, 103152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.Y.; Wu, M.; Zhou, C.Y.; Wang, B. Transformation of high moisture extrusion on pea protein isolate in melting zone during: From the aspects of the rheological property, physicochemical attributes and modification mechanism. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 108016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högg, E.; Horneber, T.; Rauh, C. Modeling and experimental analysis of protein matrix solidification in cooling dies during high-moisture extrusion. Front. Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 5, 1443376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.N.; Zhu, H. Finite element analysis as a promising approach for texture development of plant-based meat analogs. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 031302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.Y.; Zhou, C.Y.; Yu, H.Z.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, M. Integrated numerical simulation and quality attributes of soybean protein isolate extrusion under different screw speeds and combinations. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 79, 103053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellwanger, F.; Pernice, L.; Karbstein, H.P.; Emin, M.A. Investigating local residence time and thermomechanical stress profile in twin-screw extrusion of plant proteins by using the moving particle semi-implicit simulation method. J. Food Eng. 2023, 359, 111665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.Y.; Hansen, J.H. Extrudate expansion model in a twin-screw extrusion cooking process considering melt rheological property. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2016, 9, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.S.; Zhang, T.Q.; Gao, F.; Zhou, C.Y.; Sun, D.Y.; Gao, Y.T.; Wu, M. The study of numerical simulation and texture of soybean protein based on high moisture extrusion with different screw elements. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 92, 103560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Sun, D.Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, C.Y.; Zhang, B.W. Study on the Function of Conveying, Kneading Block and Reversing Elements on the Mixing Efficiency and Dispersion Effect inside the Barrel of an Extruder with Numerical Simulation. Foods 2023, 12, 3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Wang, C.; Jiang, L.H.; Zeng, J.M. Numerical simulation and die optimization design of extrusion process for a complex hollow aluminum alloy multi-hole die. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Chemical, Metallurgical Engineering (ICCMME 2013), Zhuhai, China, 10–11 December 2013; pp. 1778–1783. [Google Scholar]
- Hasanvand, E.; Rafe, A. Rheological and structural properties of rice bran protein-flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) gum complex coacervates. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdek, K.D.; Faller, J.F. Use of a dual orifice die for on-line extruder measurement of flow behavior index in starchy foods. J. Food Eng. 2002, 55, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, A.; Kalyon, D.M. Mechanisms of Mixing in Single and Co-Rotating Twin-Screw Extruders. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1995, 35, 1325–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pom, G.K.; Lehel, F.R.P.; Nsoga, V.N.; Edongue, H.; Azese, M.N.; Nganbe Ii, M.M.; Eny, G.E.; Hona, J. Numerical study of the effects of variable viscosity on a fluid flow between two stretchable disks fixed at different temperatures. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2025, 2550108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.Y.; Zhang, B.W.; Zhou, C.Y.; Ren, W.K.; Wu, M. Effect of high-moisture extrusion process on quality attribute and fibrous formation mechanism of pea protein: Insight into dynamic changes of textural protein. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2023, 89, 103486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, S.M.; Knoerzer, K.; Sellahewa, J.; Emin, M.A.; Arcot, J. Effect of different heat-treatment times and applied shear on secondary structure, molecular weight distribution, solubility and rheological properties of pea protein isolate as investigated by capillary rheometry. J. Food Eng. 2017, 208, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsegaye, B.; Barman, S.; Bovagne, L.; Ellwanger, F.; Kaunisto, E.; Lorén, N.; Kádár, R.; Stading, M. Rheological properties of pea protein melts used for producing meat analogues. Appl. Rheol. 2025, 35, 20250036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebalia, I.; Della Valle, G.; Kristiawan, M. Extrusion of pea snack foods and control of biopolymer changes aided by rheology and simulation. Food Bioprod. Process. 2022, 135, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahi, M.R.; Mohebbi, M.; Razavi, S.M.A. Designation and characterization of cold-set whey protein isolate-low acyl gellan gum emulsion-filled gel for enhancing limonene flavor perception: A study on structure, breakdown characteristics, and sensory perception in the human mouth. J. Food Eng. 2024, 383, 112245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, T.; Delaplace, G.; Riaublanc, A.; Dememe, M.; Derensy, A.; Della Valle, G. A general viscosity model for high moisture extrudates of pea protein isolates/gluten blend. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 033120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högg, E.; Rauh, C. Towards a Better Understanding of Texturization during High-Moisture Extrusion (HME)-Part II: Characterization of Thermophysical Properties of High-Moisture Meat Analogues. Foods 2023, 12, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.N.; Hu, L.; Xiang, Y.P.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Shao, J.H. Interactions between myofibrillar protein and konjac glucomannan at critical thermal phase transition temperatures: Aggregation, cross-linking, and protein conformational changes. Food Res. Int. 2025, 207, 116094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Q.; Yuan, Y.Q.; Wu, C.; Hu, Y.Y.; Zhou, S.Y.; Luan, G.Z. Heat-induced aggregation of subunits/polypeptides of soybean protein: Structural and physicochemical properties. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, M.; Tsukushi, I. Prediction of the heat capacity of main-chain-type polymers below the glass transition temperature. Polym. J. 2020, 52, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, J.; Roth, E.; Moss, M. Thermal conductivity of Inconel 718 and 304 stainless steel. Int. J. Thermophys. 1987, 8, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.M. A review of the design optimization of conformal cooling channels in injection molds. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 138, 2653–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, D.; Mutoh, Y. Fatigue Limit Prediction of the Matrix of 17-4PH Stainless Steel Based on Small Crack Mechanics. J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 2013, 135, 021407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortis, G.; Cortese, L. Effective Ductile Fracture Characterization of 17-4PH and Ti6Al4V by Shear-Tension Tests: Experiments and Damage Models Calibration. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyony, V.; Fayolle, F.; Jury, V. Die dimensions impact on fibrous plant protein formation during high moisture extrusion. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.X.; Gu, Z.H.; Sun, C.X.; Zhao, Y.G.; Cao, Y.P.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Y.P. Inducing melt elongation flow and controlling cooling temperature facilitate the texturization of high-moisture soy protein extrudates. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 157, 110452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietsch, V.L.; Werner, R.; Karbstein, H.P.; Emin, M.A. High moisture extrusion of wheat gluten: Relationship between process parameters, protein polymerization, and final product characteristics. J. Food Eng. 2019, 259, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittek, P.; Ellwanger, F.; Karbstein, H.P.; Emin, M.A. Morphology Development and Flow Characteristics during High Moisture Extrusion of a Plant-Based Meat Analogue. Foods 2021, 10, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendler, C.; Duchardt, A.; Karbstein, H.P.; Emin, M.A. Effect of Oil Content and Oil Addition Point on the Extrusion Processing of Wheat Gluten-Based Meat Analogues. Foods 2021, 10, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, C.; Scharfe, M.; Hinrichs, J. Texturization of renneted casein-based gel particles by sheet die extrusion: Mechanical properties and numerical analysis of flow characteristics. J. Food Eng. 2020, 278, 109938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.L.; Yang, M.; Wu, J.H.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, H.Y. The potential of plasma-activated water in safe and sustainable food production: A comprehensive review of recent advances and future trends. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölker, R.; Jäger, A.; Ben Khalifa, N.; Tekkaya, A.E. Controlling Heat Balance in Hot Aluminum Extrusion by Additive Manufactured Extrusion Dies with Conformal Cooling Channels. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 14, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

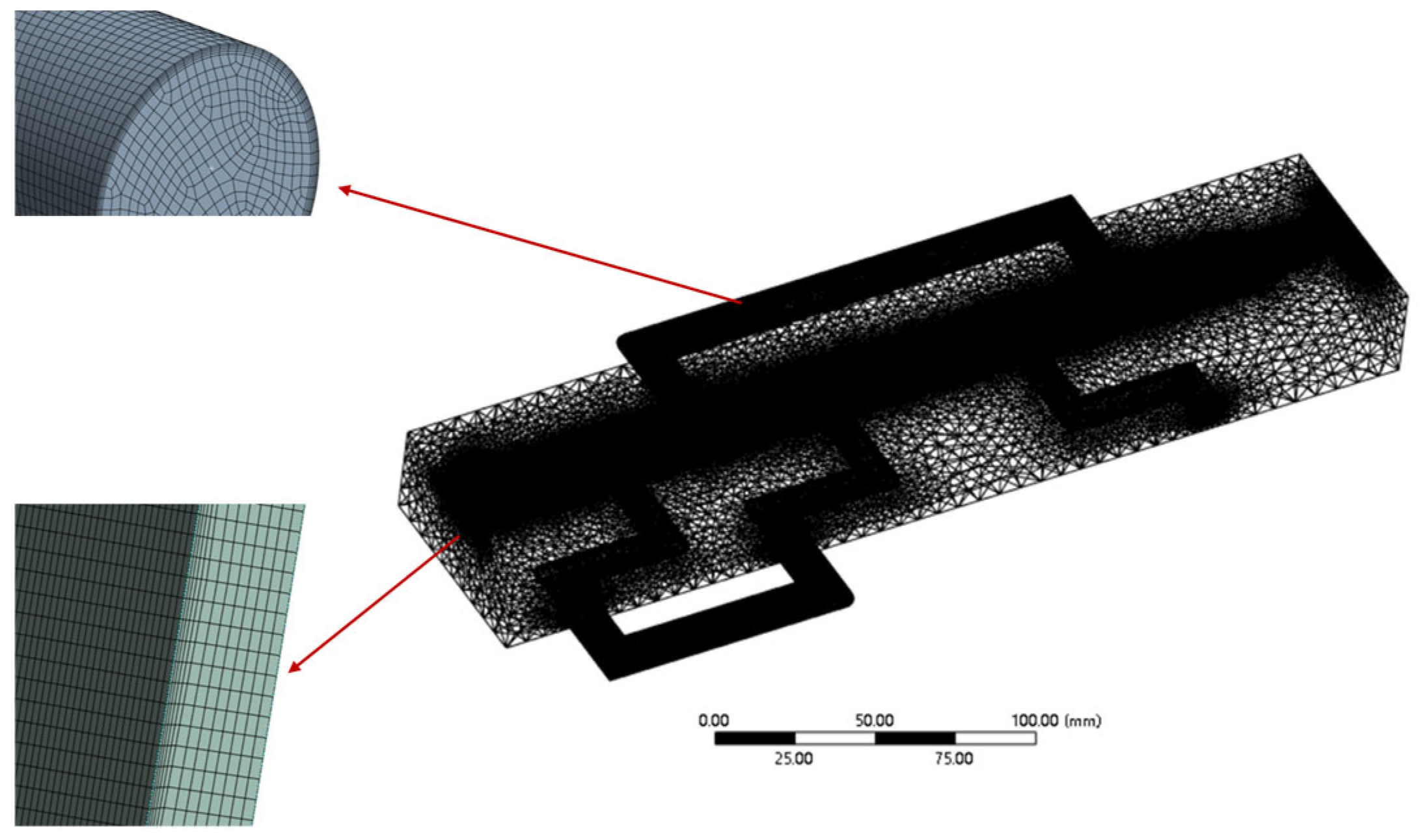


| Mesh Density | Number of Elements (×106) | Outlet Average Velocity (m/s) | Centerline Temperature (°C) | Difference vs. Finer Mesh (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coarse | 0.420 | 0.220 | 141.200 | 5.800 |
| Medium | 0.780 | 0.220 | 143.100 | 2.100 |
| Fine | 1.150 | 0.230 | 143.900 | 0.000 |
| Temperature (°C) | K (Pa·sn) | n (Dimensionless) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 35 | 236.100 ± 2.450 a | 0.200 ± 0.010 e | 0.999 |
| 55 | 102.350 ± 1.450 b | 0.280 ± 0.020 d | 0.997 |
| 75 | 65.200 ± 1.480 c | 0.400 ± 0.050 c | 0.991 |
| 95 | 47.680 ± 0.390 d | 0.430 ± 0.010 ab | 0.998 |
| 115 | 17.970 ± 0.220 e | 0.440 ± 0.010 a | 0.996 |
| 135 | 9.840 ± 0.100 f | 0.430 ± 0.020 ab | 0.998 |
| Parameter | Rectangular Die | Square Die | Circular Die |
|---|---|---|---|
| Center–wall ΔT at 200 mm (°C) | 12.400 | 10.200 | 7.800 |
| Average heat transfer coefficient (W/m2·K) | 128.000 | 112.000 | 95.000 |
| Viscosity at center (Pa·s) | 6.200 ± 0.100 a | 7.400 ± 0.200 b | 8.100 ± 0.200 c |
| Viscosity at wall (Pa·s) | 45.800 ± 0.800 a | 36.200 ± 0.600 b | 30.000 ± 0.500 c |
| Wall/center viscosity ratio | 7.400 | 4.900 | 3.700 |
| Center–wall velocity difference (m/s) | 0.024 | 0.021 | 0.019 |
| Max. wall shear rate (s−1) | 3.420 | 2.870 | 2.150 |
| Corner shear rate (s−1) | 0.960 | 0.960 | 1.120 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, M.; Zhang, X.; Wu, M.; Zhang, T.; Zou, F.; Yang, S. Study on Configuration Design and Numerical Simulation of Twin-Screw Extruder Cooling Die Based on Pea Protein Isolate Flow Properties. Foods 2025, 14, 3137. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173137
Yang M, Zhang X, Wu M, Zhang T, Zou F, Yang S. Study on Configuration Design and Numerical Simulation of Twin-Screw Extruder Cooling Die Based on Pea Protein Isolate Flow Properties. Foods. 2025; 14(17):3137. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173137
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Miao, Xun Zhang, Min Wu, Tianqi Zhang, Fanglei Zou, and Shuqi Yang. 2025. "Study on Configuration Design and Numerical Simulation of Twin-Screw Extruder Cooling Die Based on Pea Protein Isolate Flow Properties" Foods 14, no. 17: 3137. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173137
APA StyleYang, M., Zhang, X., Wu, M., Zhang, T., Zou, F., & Yang, S. (2025). Study on Configuration Design and Numerical Simulation of Twin-Screw Extruder Cooling Die Based on Pea Protein Isolate Flow Properties. Foods, 14(17), 3137. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173137






