Formation and Structural Characteristics of Heating-Induced Amyloid Fibrils Derived from Rice Albumin at Different pH Values
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction of Rice Albumin (RA)
2.3. Formation of Rice Albumin-Based Amyloid Fibrils (RAFs) at Different pH Values
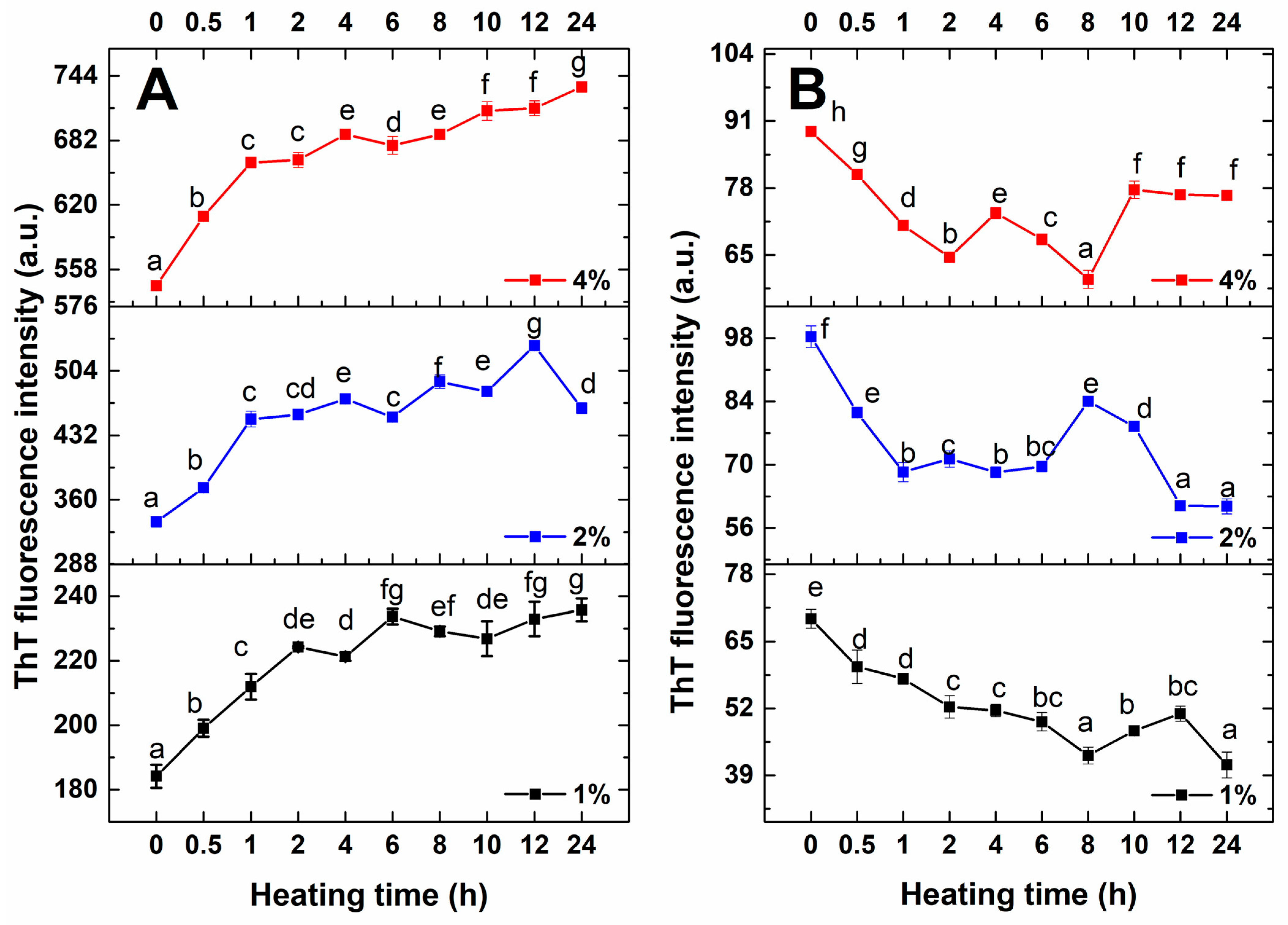
2.4. ThT Fluorescence Intensity
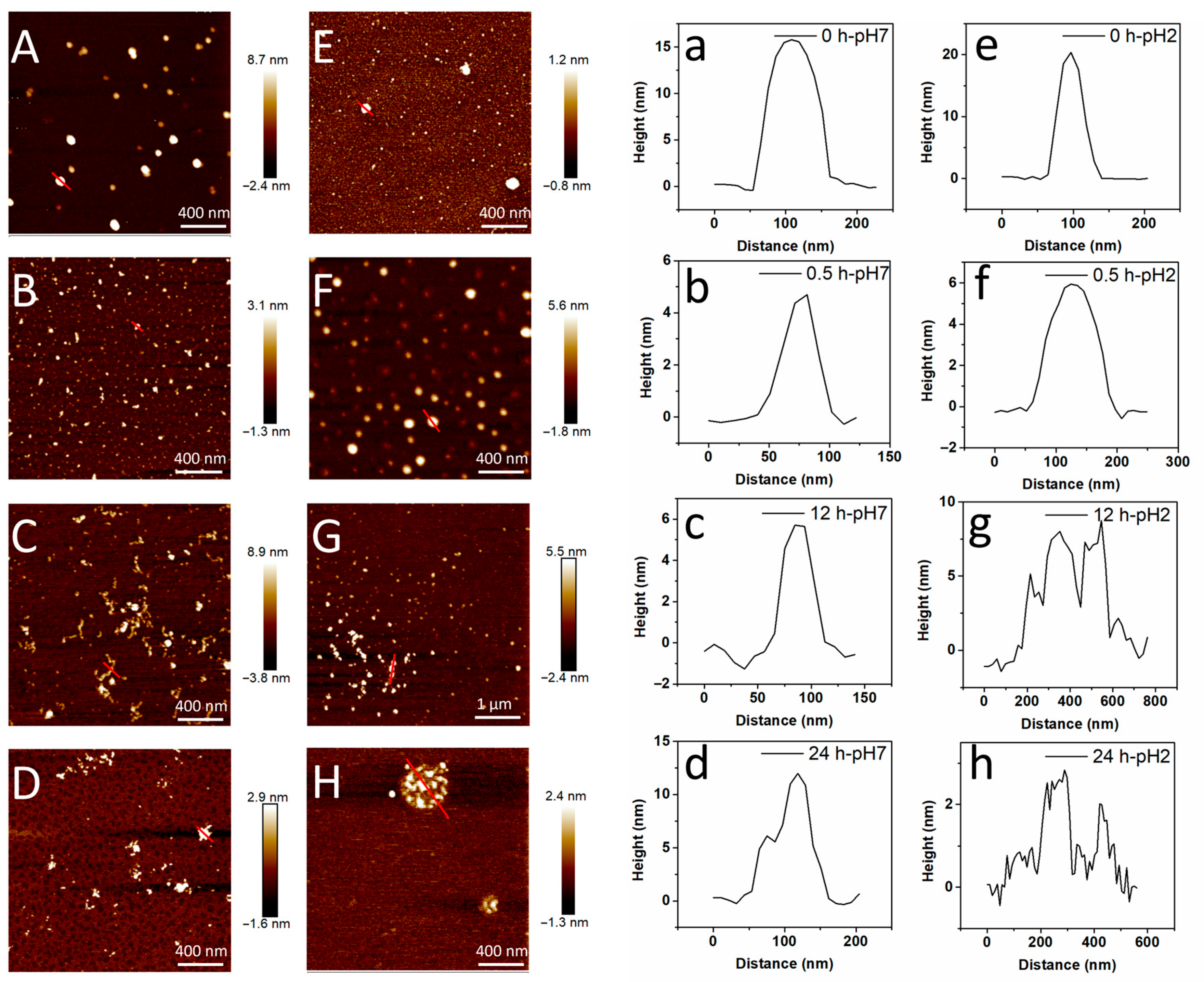
2.5. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
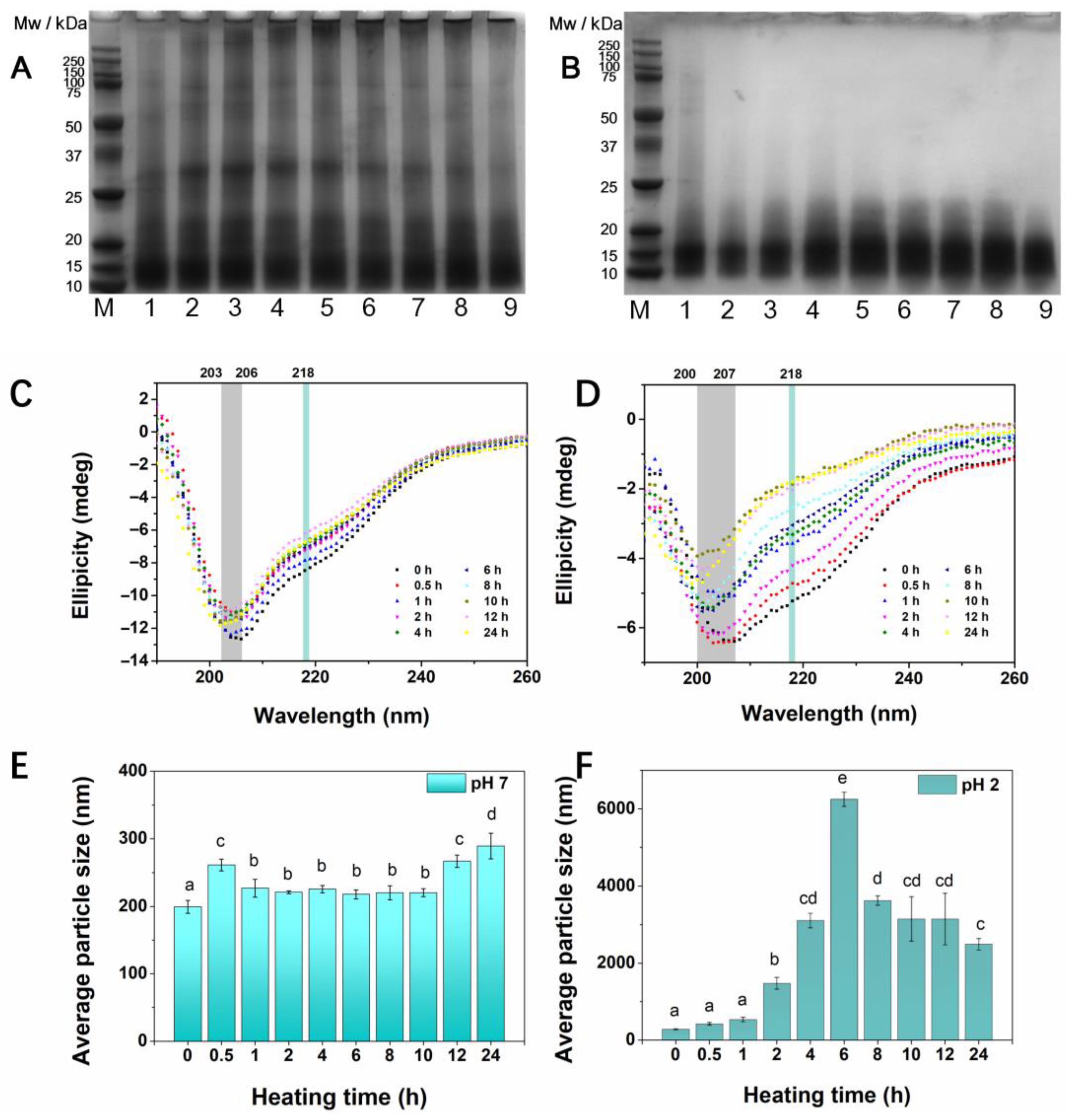
2.6. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.7. Far-UV Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectra
2.8. Average Particle Size
2.9. Solubility
2.10. Surface Hydrophobicity (H0)
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. ThT Fluorescence Intensity
3.2. Morphology Studies
3.3. SDS-PAGE
3.4. CD Spectra
3.5. Average Particle Size
3.6. Surface Hydrophobicity (H0)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RA | rice albumin |
| ThT | thioflavin T |
| Glu | glutamic acid |
| Asp | aspartic acid |
| RAFs | RA-based fibrils |
| Mw | molecular weight |
| BCA | Coomassie Blue Staining Solution and bicinchoninic acid |
| ANS | 8-Anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid |
| AFM | Atomic force microscopy |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| CD | Far-UV Circular dichroism |
| H0 | Surface hydrophobicity |
| SPSS | Statistical Product and Service Solutions |
| ANOVA | one-way analyses of variance |
References
- Cao, Y.; Mezzenga, R. Food protein amyloid fibrils: Origin, structure, formation, characterization, applications and health implications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 269, 334–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhou, J.; Soon, W.L.; Kutzli, I.; Molière, A.; Diedrich, S.; Radiom, M.; Handschin, S.; Li, B.; Li, L.; et al. Food amyloid fibrils are safe nutrition ingredients based on in-vitro and in-vivo assessment. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Wei, Z.; Xue, C. Protein fibrils from different food sources: A review of fibrillation conditions, properties, applications and research trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 121, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; He, B.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J. Plant-based protein amyloid fibrils: Origins, formation, extraction, applications, and safety. Food Chem. 2025, 469, 142559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.; Durand-Morat, A.; Nalley, L.L.; Graterol, E.; Bonatti, M.; Loaiza de la Pava, K.; Urioste, S.; Yang, W. Understanding demand for broken rice and its potential food security implications in Colombia. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 15, 100884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Zhao, S.; Liang, Y.; Luo, Y. Self-assembled nanostructures from rice protein and its fractions: Molecular approaches, physicochemical principles, and functional applications. Food Chem. 2025, 483, 144295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wang, L.; Geng, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z. Formation, structural characteristics, foaming and emulsifying properties of rice glutelin fibrils. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyst, A.M.R.; Deleu, L.J.; Luyckx, T.; Lambrecht, M.A.; Van Camp, J.; Delcour, J.A.; Van der Meeren, P. Influence of hydrophobic interfaces and shear on ovalbumin amyloid-like fibril formation in oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansens, K.J.A.; Rombouts, I.; Grootaert, C.; Brijs, K.; Van Camp, J.; Van der Meeren, P.; Rousseau, F.; Schymkowitz, J.; Delcour, J.A. Rational Design of Amyloid-Like Fibrillary Structures for Tailoring Food Protein Techno-Functionality and Their Potential Health Implications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 18, 84–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Huang, L.-H. Effect of heat-induced formation of rice bran protein fibrils on morphological structure and physicochemical properties in solutions and gels. Food Sci. Bio. Technol. 2014, 23, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pan, Z.; Yang, T.; Yang, H.; Li, L.; Li, B. Effects of ultrasonic pretreatment on fibrillation kinetics, morphologies, and functional properties of bovine serum albumin fibrils. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 149, 109520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-R.; Yang, Q.; Du, Y.-N.; Chen, H.-Q. Chitosan can improve the storage stability of ovalbumin fibrils at pH higher than isoelectric point. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 136, 108286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, T.; Dong, T.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, Z.; Feng, W.; Wang, T. Structural interplay and macroscopic aggregation of rice albumins after binding with heavy metal ions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, W. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; Agricultural chemicals, contaminants, drugs, Gaithersburg (Maryland); AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2010; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Nian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, B. Formation of pea protein amyloid fibrils to stabilize high internal phase emulsions for encapsulation of lutein. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 94, 105110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Geng, H.; Xue, W.; Chen, Z. Assembly behavior, structural characterization and rheological properties of legume proteins based amyloid fibrils. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Huang, Q. Assembly of iron-bound ovotransferrin amyloid fibrils. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, S.; Chen, P.; Jiang, Q.; Huang, W. Recent progress of plant protein-based amyloid-like nanofibrils. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 160, 110749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ma, C.-m.; Yang, Y.; Bian, X.; Liu, X.-f.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, N. Food-derived protein amyloid-like fibrils: Fibrillation mechanism, structure, and recent advances for the stabilization of emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, F.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Characterization of rice glutelin fibrils and their effect on in vitro rice starch digestibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 106, 105918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, D.; Wang, P.; McClements, D.J.; Cui, S.; Liu, H.; Leng, F.; Sun, Q.; Dai, L. Study on the formation mechanism of pea protein nanofibrils and the changes of structural properties of fibril under different pH and temperature. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 150, 109735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micsonai, A.; Wien, F. BeStSel: Analysis site for protein CD spectra-2025 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, W73–W83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L. Modifying functional properties of food amyloid-based nanostructures from rice glutelin. Food Chem. 2023, 398, 133798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L. Specific ions effect on aggregation behaviors and structural changes of amyloid fibrils from rice glutelin. Food Chem. 2024, 441, 138351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Cheng, C.Y.; Li, Q.Y.; Zhu, G.S.; Wei, Y.S.; Liu, K.L. Comparison of formation and structural characteristics of amyloid fibrils of peanut protein isolate after hydration treatment at different pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 159, 110599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.-Q.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.-R.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Chen, H.-Q. Formation and structural characteristics of pea globulin amyloid-like fibrils pretreated with low-frequency magnetic field. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 147, 109331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Jin, M.; Wang, X.; Fan, Z.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. Ability of soy protein derived amyloid fibrils to stabilize aqueous two-phase system and effect of pH on the system. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, F.G.; Mackintosh, S.H.; Gerrard, J.A. Formation of Amyloid-like Fibrils by Ovalbumin and Related Proteins under Conditions Relevant to Food Processing. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2007, 55, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzli, I.; Zhou, J.; Li, T.; Baier, S.K.; Mezzenga, R. Formation and characterization of plant-based amyloid fibrils from hemp seed protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhou, J.; Peydayesh, M.; Yao, Y.; Bagnani, M.; Kutzli, I.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Mezzenga, R. Plant Protein Amyloid Fibrils for Multifunctional Sustainable Materials. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2023, 7, 2200414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, T.; Zhang, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, L. Modification of rice protein and its components: Enhanced fibrils formation and improved foaming properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 158, 110575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herneke, A.; Lendel, C.; Johansson, D.; Newson, W.; Hedenqvist, M.; Karkehabadi, S.; Jonsson, D.; Langton, M. Protein Nanofibrils for Sustainable Food–Characterization and Comparison of Fibrils from a Broad Range of Plant Protein Isolates. ACS Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 1, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Huang, L.-H.; Wei, Z.-C. Effects of additional fibrils on structural and rheological properties of rice bran albumin solution and gel. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 239, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.L.; Guo, S.T. The Formation and Disaggregation of Soy Protein Isolate Fibril: Effects of pH. Food Biophys. 2019, 14, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagliani, L.; O’Regan, J.; Keny, A.L.; O’Mahony, J.A. Composition and protein profile analysis of rice protein ingredients. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 59, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagliani, L.; O’Regan, J.; Kelly, A.L.; O’Mahony, J.A. The composition, extraction, functionality and applications of rice proteins: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 64, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, D.T.; Ye, A.; Singh, H.; Acevedo-Fani, A. Heat-induced dissociation and association of proteins in hempseed protein bodies. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 166, 111372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Pico, J.; Zamani, S.; Castellarin, S.D.; Dee, D.R. Fibrillization of lentil proteins is impacted by the protein extraction conditions and co-extracted phenolics. Food Chem. 2024, 448, 139104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yan, S.; Li, Y. Characterization of the fibrillation of pumpkin seed protein: Kinetics, structure, and fibril-forming regions. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 165, 111254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Sui, Y.; Shi, J.; Xiong, T.; Cai, F.; Gao, X.; Mei, X. Binding interaction between rice bran albumin and sweet potato leaves polyphenol: Multi-spectroscopic and simulated molecular docking analysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 314, 144319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Yan, T.; Fu, K.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, W. Enhancement of physicochemical and techno-functional properties of soy protein isolate amyloid fibrils by moderate ultrasonic pretreatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2025, 112, 107157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ren, C.; Zou, B.; Zheng, X.; Cai, W.; Du, M.; Na, X.; Wu, C. Preheat-induced pea protein particles with anti-aggregation behaviors at virous conditions. Food Biosci. 2025, 68, 106551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Xu, C.; Lu, Z.; Li, T. Different types of anions mediated the formation of rice glutelin fibrils: Aggregation behaviors and structural characteristics. Food Chem. 2025, 471, 142760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, G.; Zeng, H.; Chen, L. Effects of high pressure homogenization on faba bean protein aggregation in relation to solubility and interfacial properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Zhu, J.; Peng, X.; Feng, J.; Dong, H.; Tong, X.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. Effects of CaCl2 concentration on fibrils formation and characteristics of soybean protein isolate and β-conglycinin/glycinin. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 142, 108769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ni, Y.; Wang, H.; Pan, T.; Yan, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, W. Ultrasonication combined with pH-shifting pretreatment promotes soy protein fibrillation: Effects of pretreatment methods on growth kinetics and various properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2026, 171, 111826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Herneke, A.; Langton, M.; Johansson, M.; Corredig, M. Effect of pH and ionic strength on heat-induced pea protein isolate aggregation and gel formation. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 167, 111393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, M.; Madadlou, A. Technological functionality and biological properties of food protein nanofibrils formed by heating at acidic condition. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 75, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Heating Time/h | Surface Hydrophobicity | |
|---|---|---|
| pH 7 | pH 2 | |
| 0 | 187.70 ± 1.99 e | 606.19 ± 10.09 f |
| 0.5 | 182.23 ±1.16 d | 613.57 ± 2.79 f |
| 1 | 186.46 ±2.64 e | 612.48 ± 8.66 f |
| 2 | 180.29 ±2.03 cd | 542.00 ± 7.17 e |
| 4 | 178.07 ±2.09 c | 542.39 ± 8.34 e |
| 6 | 191.29 ±1.62 f | 508.51 ± 7.64 d |
| 8 | 182.13 ±1.81 d | 500.15 ± 8.14 d |
| 10 | 183.13 ±2.12 d | 436.27 ± 7.71 c |
| 12 | 164.12 ±0.38 b | 385.07 ± 6.29 b |
| 24 | 145.12 ±1.41 a | 333.48 ± 5.11 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Wang, L. Formation and Structural Characteristics of Heating-Induced Amyloid Fibrils Derived from Rice Albumin at Different pH Values. Foods 2025, 14, 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173069
Li T, Wang L. Formation and Structural Characteristics of Heating-Induced Amyloid Fibrils Derived from Rice Albumin at Different pH Values. Foods. 2025; 14(17):3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173069
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ting, and Li Wang. 2025. "Formation and Structural Characteristics of Heating-Induced Amyloid Fibrils Derived from Rice Albumin at Different pH Values" Foods 14, no. 17: 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173069
APA StyleLi, T., & Wang, L. (2025). Formation and Structural Characteristics of Heating-Induced Amyloid Fibrils Derived from Rice Albumin at Different pH Values. Foods, 14(17), 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173069







