Temperature-Induced Structural Changes in Muscle Proteins from Giant Squid (Dosidicus gigas) Mantle: FT-IR, Circular Dichroism, and FE-SEM Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Ethical Statement
2.3. Sarcoplasmic Protein Isolation
2.4. Myofibrillar Isolation
2.5. Stromal Protein Isolation
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometers (FT-IR)
2.7. Circular Dichroism (CD)
2.8. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM)
3. Results and Discussions
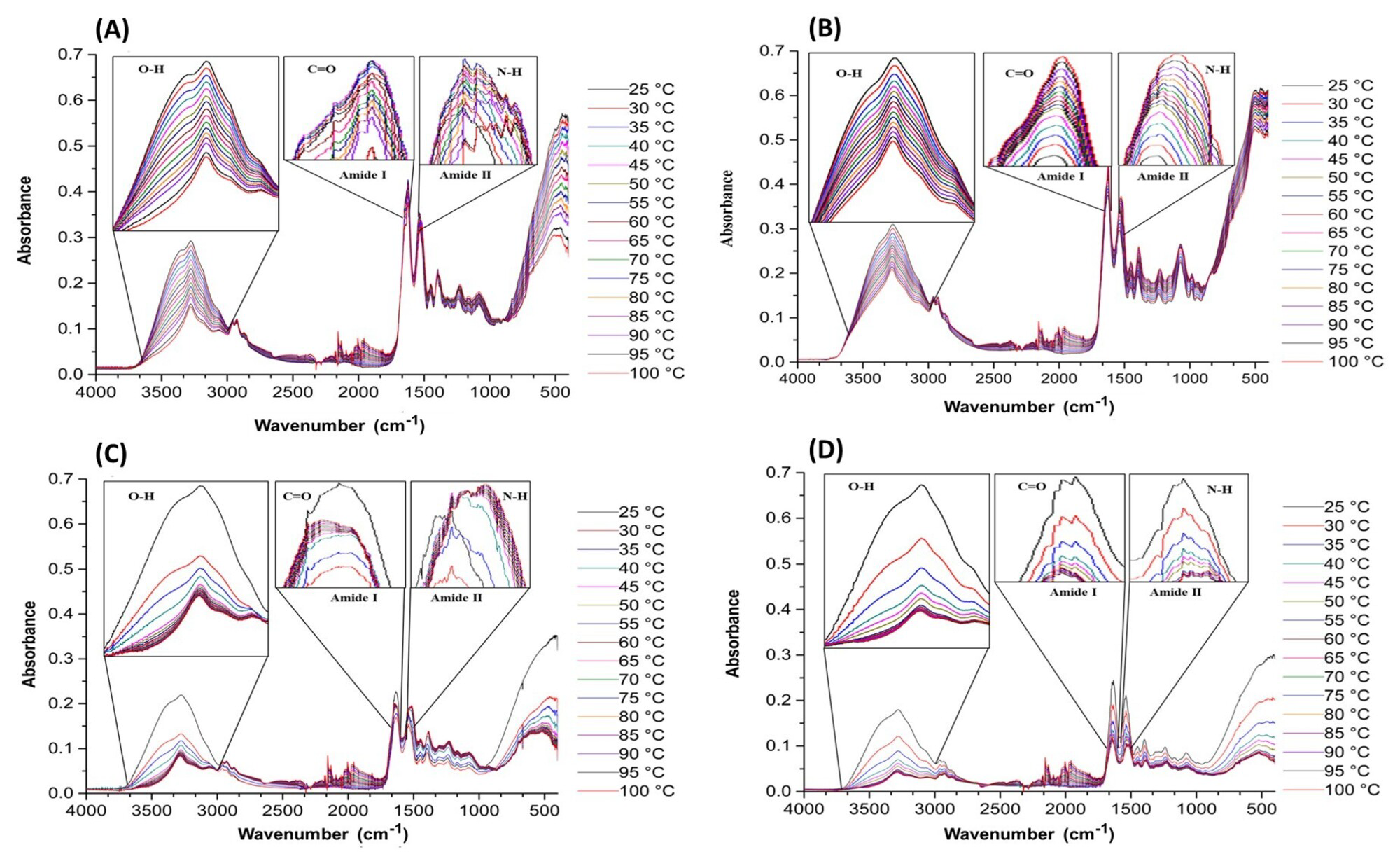
3.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
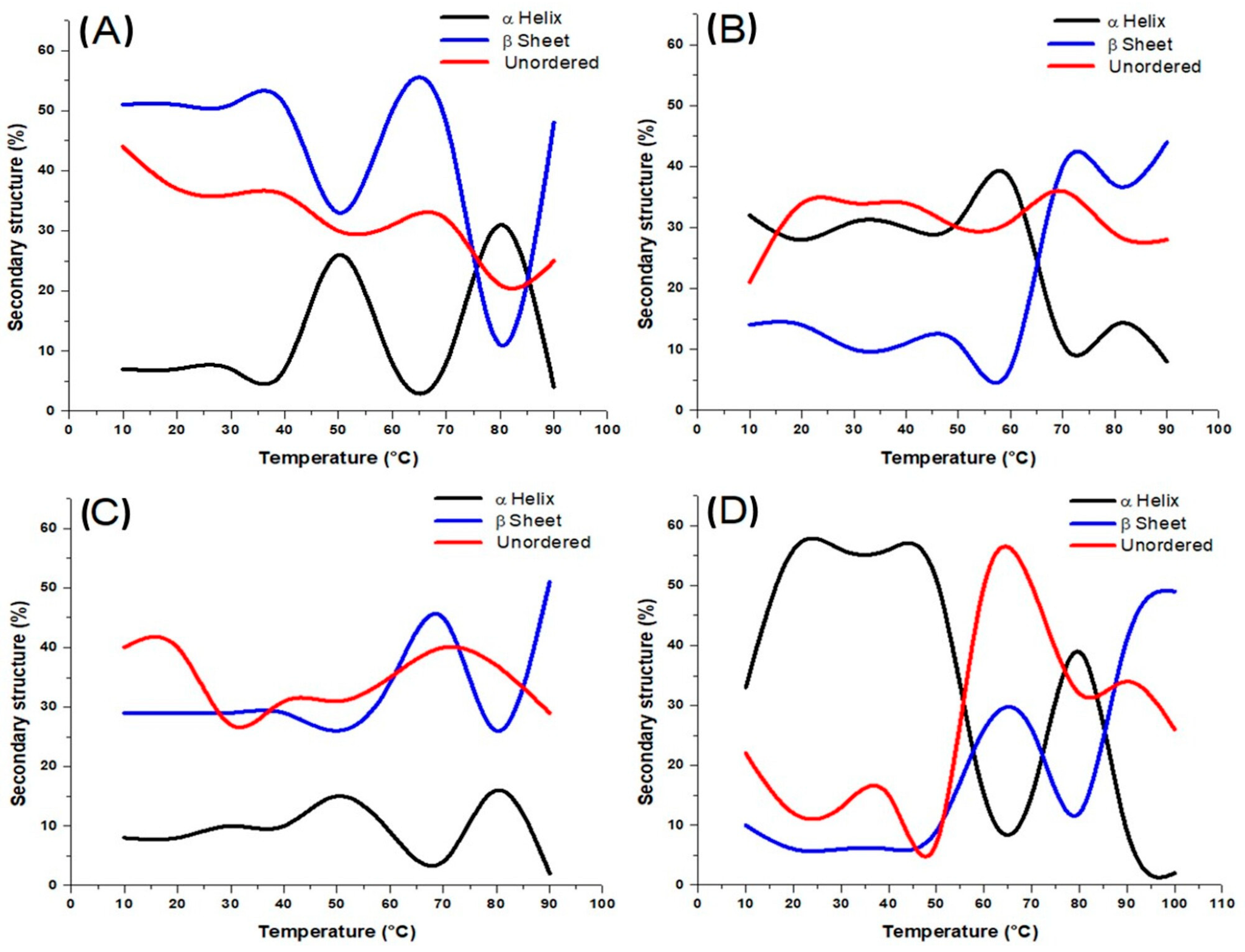
3.2. Circular Dichroism (CD)
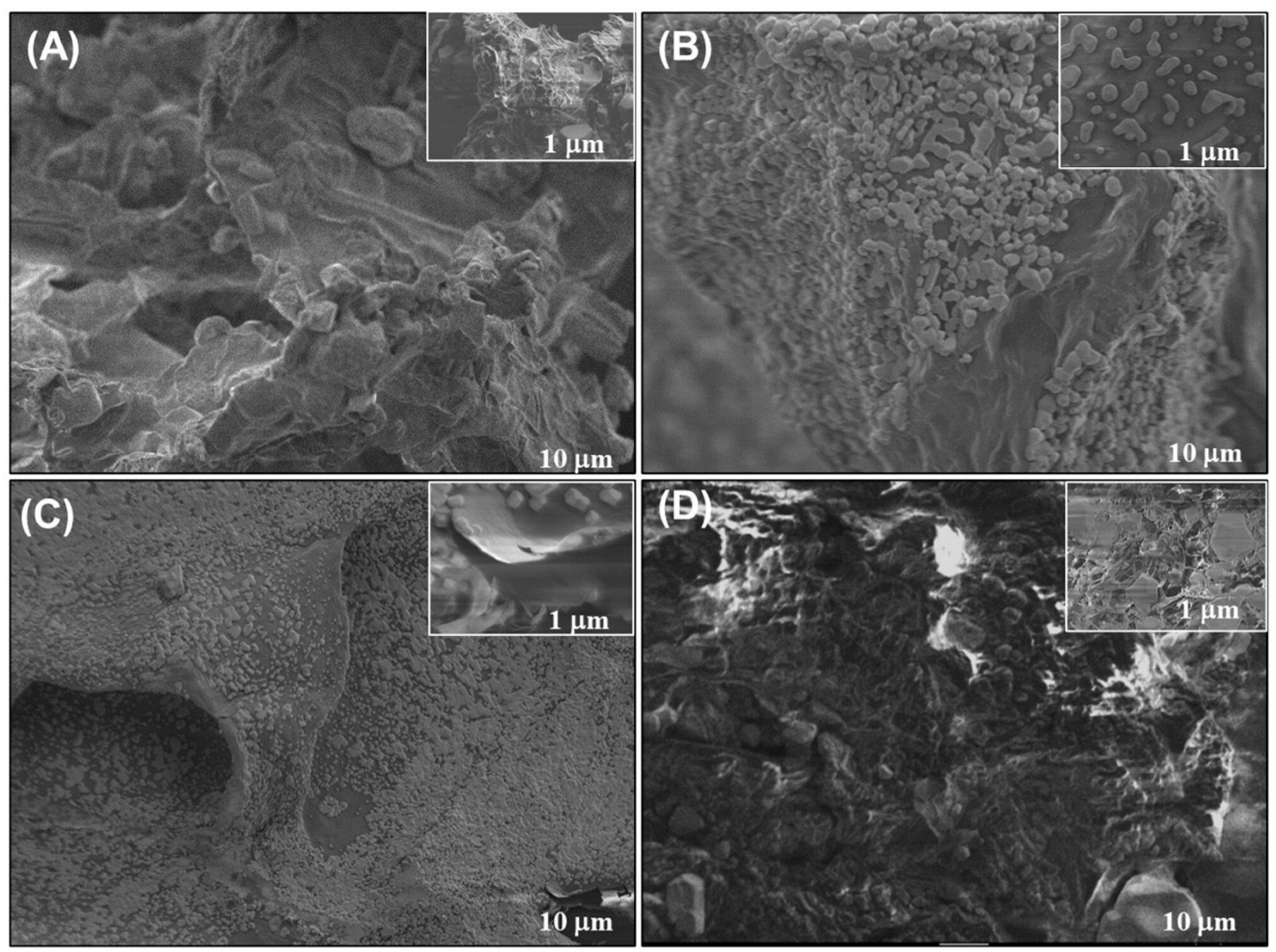
3.3. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022, Toward Blue Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Zhou, R.; Pan, W.; Lin, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Niu, F.; Li, A. Salting-in effect on muscle protein extracted from giant squid (Dosidicus gigas). Food Chem. 2017, 215, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Alonso, I.; Careche, M.; Borderías, A.J. Method for producing a functional protein concentrate from giant squid (Dosidicus gigas) muscle. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M.; Márquez-Ríos, E.; López-Corona, B.E.; Ocaño-Higuera, V.M.; Ramírez-Guerra, H.E.; Cota-Arriola, O.; Torres-Arreola, W. Physicochemical changes of pepsin-solubilized and insoluble collagen in jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) muscle after cooking process. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolano-Villaverde, I.J.; Ocaño-Higuera, V.M.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M.; Santos-Sauceda, I.; Santacruz-Ortega, H.; Cárdenas-López, J.L.; Márquez-Ríos, E. Physicochemical characterization of actomyosin–paramyosin from giant squid mantle (Dosidicus gigas). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolano-Villaverde, I.J.; Santacruz-Ortega, H.; Rivero-Espejel, I.A.; Torres-Arreola, W.; Suárez-Jiménez, G.M.; Márquez-Ríos, E. Effect of temperature on the actomyosin-paramyosin structure from giant squid mantle (Dosidicus gigas). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5377–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadena-Cadena, F.; Cárdenas-López, J.L.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M.; Cinco-Moroyoqui, F.J.; López-Zavala, A.A.; Santacruz-Ortega, H.D.C.; Rivero-Espejel, I.A. Effect of temperature and pH on the secondary structure and denaturation process of jumbo squid hepatopancreas cathepsin D. Protein Pept. Lett. 2019, 26, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, H.; Shi, H.; Dong, A.; Wang, L.; Yu, S. Progress in infrared spectroscopy as an efficient tool for predicting protein secondary structure. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formen, J.S.; Howard, J.R.; Anslyn, E.V.; Wolf, C. Circular dichroism sensing: Strategies and applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202400767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Watabe, S.; Kono, M.; Shiro, K. Muscle protein composition of sardine and mackerel. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi (Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish.) 1979, 45, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolano-Villaverde, I.J.; Santos-Sauceda, I.; Santacruz-Ortega, H.; Ramírez-Wong, B.; Brown-Bojórquez, F.; Suárez-Jiménez, G.M.; Márquez-Ríos, E. Evaluation of the gelling ability of actomyosin-paramyosin from giant squid mantle (Dosidicus gigas). Int. Food Res. J. 2020, 27, 712–719. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, M.A.; Chacon, P.; Merelo, J.J.; Morán, F. Evaluation of secondary structure of proteins from UV circular dichroism spectra using an unsupervised learning neural network. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1993, 6, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Arreola, W.; Pacheco-Aguilar, R.; Sotelo-Mundo, R.R.; Rouzaud-Sández, O.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Partial characterization of collagen from mantle, fin, and arms of jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas). CyTA–J. Food 2008, 6, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, Z.F.; Morton, J.D.; Bekhit, A.E.D.A.; Kumar, S.; Bhat, H.F. Thermal processing implications on the digestibility of meat, fish and seafood proteins. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4511–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yongsawatdigul, J.; Hemung, B.O. Structural changes and functional properties of threadfin bream sarcoplasmic proteins subjected to pH-shifting treatments and lyophilization. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, C251–C257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Deng, H.; Xiong, S.; Huang, Q. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun nanofibers of Hypophthalmichthys molitrix sarcoplasmic protein recovered by acid-chitosan flocculation coupling treatment. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzi-Plepis, A.M.D.; Goissis, G.; Das-Gupta, D.K. Dielectric and pyroelectric characterization of anionic and native collagen. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1996, 36, 2932–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Huang, H.; Lin, W.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Yang, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y. Effects of temperature on the denaturation and aggregation of Lateolabrax japonicus myosin from sea bass surimi. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walayat, N.; Xiong, Z.; Xiong, H.; Moreno, H.M.; Li, Q.; Nawaz, A.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, P.; Niaz, N. The effectiveness of egg white protein and β-cyclodextrin during frozen storage: Functional, rheological and structural changes in the myofibrillar proteins of Culter alburnus. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye-Seon, L.; Ye-Jin, O.; Seon-Yeong, H.; Jong-Young, K.; Sik, Y. Marine collagen as a promising biomaterial for biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello-Solís, S.R.; Romero-García, B. Thermal denaturation of porcine pepsin: A study by circular dichroism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2001, 28, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Matsukawa, M. Thermal stability of myosin and protective effect of F-actin on myosin affect the thermal inactivation of calcium-ATPase in unstable kuruma prawn myofibrils. Fish. Sci. 2019, 85, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Sun, B.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Xie, P. The effect of different induction methods on the structure and physicochemical properties of glycosylated soybean isolate gels. Foods 2022, 11, 3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visessanguan, W.; Ogawa, M.; Nakai, S.; An, H. Physicochemical changes and mechanism of heat-induced gelation of arrowtooth flounder myosin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Zhao, N.; Shi, X.; Sun, S.; Yu, C. Modifying the physicochemical and functional properties of water-soluble protein from mussels by high-pressure homogenization treatment. Int. J. Food Eng. 2020, 16, 20190274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeruraj, A.; Arumugam, M.; Balasubramanian, T. Isolation and characterization of thermostable collagen from the marine eel-fish (Evenchelys macrura). Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 1592–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.M.; Jess, T.J.; Price, N.C. How to study proteins by circular dichroism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2005, 1751, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.; Cox, M. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, 7th ed.; W.H. Freeman & Co: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, L.; Tu, Y.; Wu, N.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, M. Changes in texture and molecular forces of heat-induced egg white gel with adding xanthan gum. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.L.; Cox, M.M. Lehninger: Principios de Bioquímica; Ediciones Omega: Barcelona, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, C.K.W.; Chung, C.; Ogren, T.; Mutilangi, W.; McClements, D.J. Extending protein functionality: Microfluidization of heat-denatured whey protein fibrils. J. Food Eng. 2018, 223, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von der Ecken, J.; Müller, M.; Lehman, W.; Manstein, D.J.; Penczek, P.A.; Raunser, S. Structure of the F-actin–tropomyosin complex. Nature 2015, 519, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, S.S.; Yao, H.; Jiang, Z.D.; Benjakul, S.; Aubourg, S.P.; Zhang, B. The differences of muscle proteins between neon flying squid (Ommastrephes bartramii) and jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) mantles via physicochemical and proteomic analyses. Food Chem. 2021, 364, 130374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beas, V.E.; Wagner, J.R.; Crupkin, M.; Ańon, M.C. Thermal denaturation of hake (Merluccius hubbsi) myofibrillar proteins. A differential scanning calorimetric and electrophoretic study. J. Food Sci. 1990, 55, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemung, B.O.; Benjakul, S.; Yongsawatdigul, J. pH-dependent characteristics of gel-like emulsion stabilized by threadfin bream sarcoplasmic proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Li, C.; Mao, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Jia, R.; Huang, T.; Xu, D.; Yang, W. Distinctive characteristics of collagen and gelatin extracted from Dosidicus gigas skin. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 3443–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
León-Heredia, M.A.; Marquez-Rios, E.; Cadena-Cadena, F.; Santacruz-Ortega, H.; Rivero-Espejel, I.A.; Montoya-Camacho, N.; Tolano-Villaverde, I.J. Temperature-Induced Structural Changes in Muscle Proteins from Giant Squid (Dosidicus gigas) Mantle: FT-IR, Circular Dichroism, and FE-SEM Analysis. Foods 2025, 14, 2922. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172922
León-Heredia MA, Marquez-Rios E, Cadena-Cadena F, Santacruz-Ortega H, Rivero-Espejel IA, Montoya-Camacho N, Tolano-Villaverde IJ. Temperature-Induced Structural Changes in Muscle Proteins from Giant Squid (Dosidicus gigas) Mantle: FT-IR, Circular Dichroism, and FE-SEM Analysis. Foods. 2025; 14(17):2922. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172922
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeón-Heredia, Miguel A., Enrique Marquez-Rios, Francisco Cadena-Cadena, Hisila Santacruz-Ortega, Ignacio Alfredo Rivero-Espejel, Nathaly Montoya-Camacho, and Iván J. Tolano-Villaverde. 2025. "Temperature-Induced Structural Changes in Muscle Proteins from Giant Squid (Dosidicus gigas) Mantle: FT-IR, Circular Dichroism, and FE-SEM Analysis" Foods 14, no. 17: 2922. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172922
APA StyleLeón-Heredia, M. A., Marquez-Rios, E., Cadena-Cadena, F., Santacruz-Ortega, H., Rivero-Espejel, I. A., Montoya-Camacho, N., & Tolano-Villaverde, I. J. (2025). Temperature-Induced Structural Changes in Muscle Proteins from Giant Squid (Dosidicus gigas) Mantle: FT-IR, Circular Dichroism, and FE-SEM Analysis. Foods, 14(17), 2922. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14172922






