Effect of pH-shifting on the Physicochemical Properties of Pea Proteins and Its Effect on the Texture of Hybrid Gels Formed with Casein Micelles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Suspension Preparation
2.2.2. pH Modification
2.2.3. Solubility
2.2.4. Particle Size and Zeta Potential
2.2.5. Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
2.2.6. Intrinsic Fluorescence
2.2.7. Gel Preparation
2.2.8. Water-Holding Capacity (WHC)
2.2.9. Texture Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
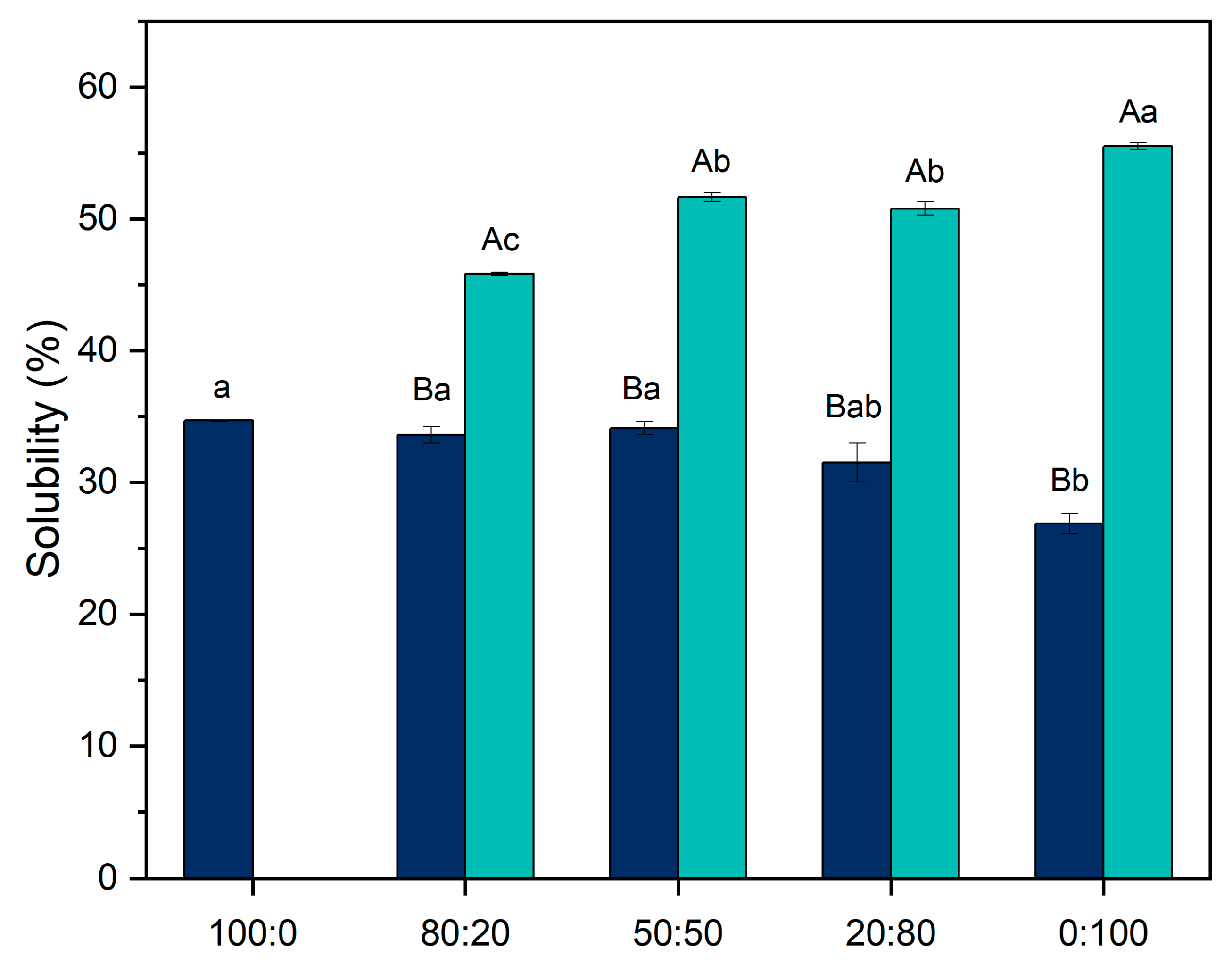
3.1. Solubility
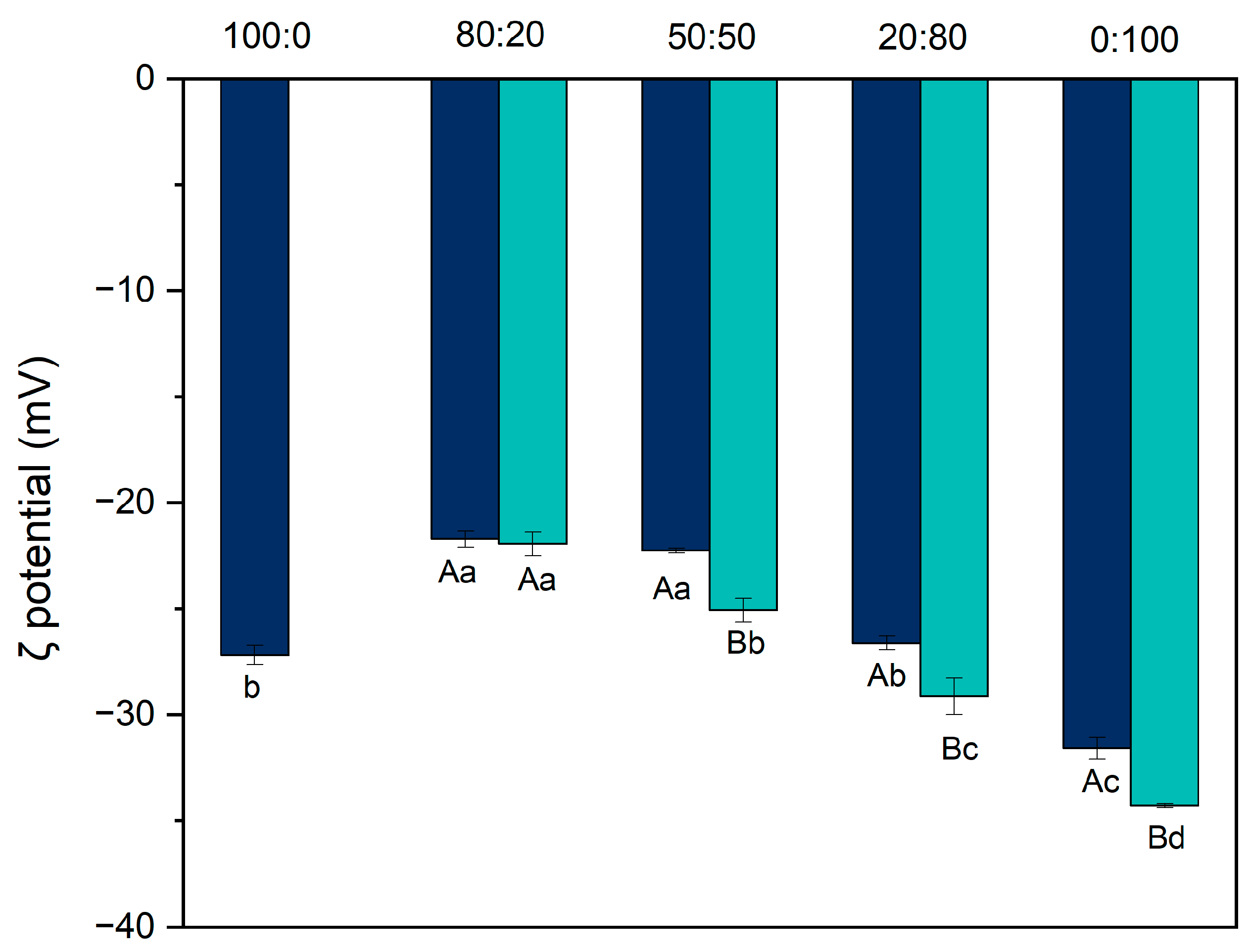
3.2. Particle Size and Zeta Potential
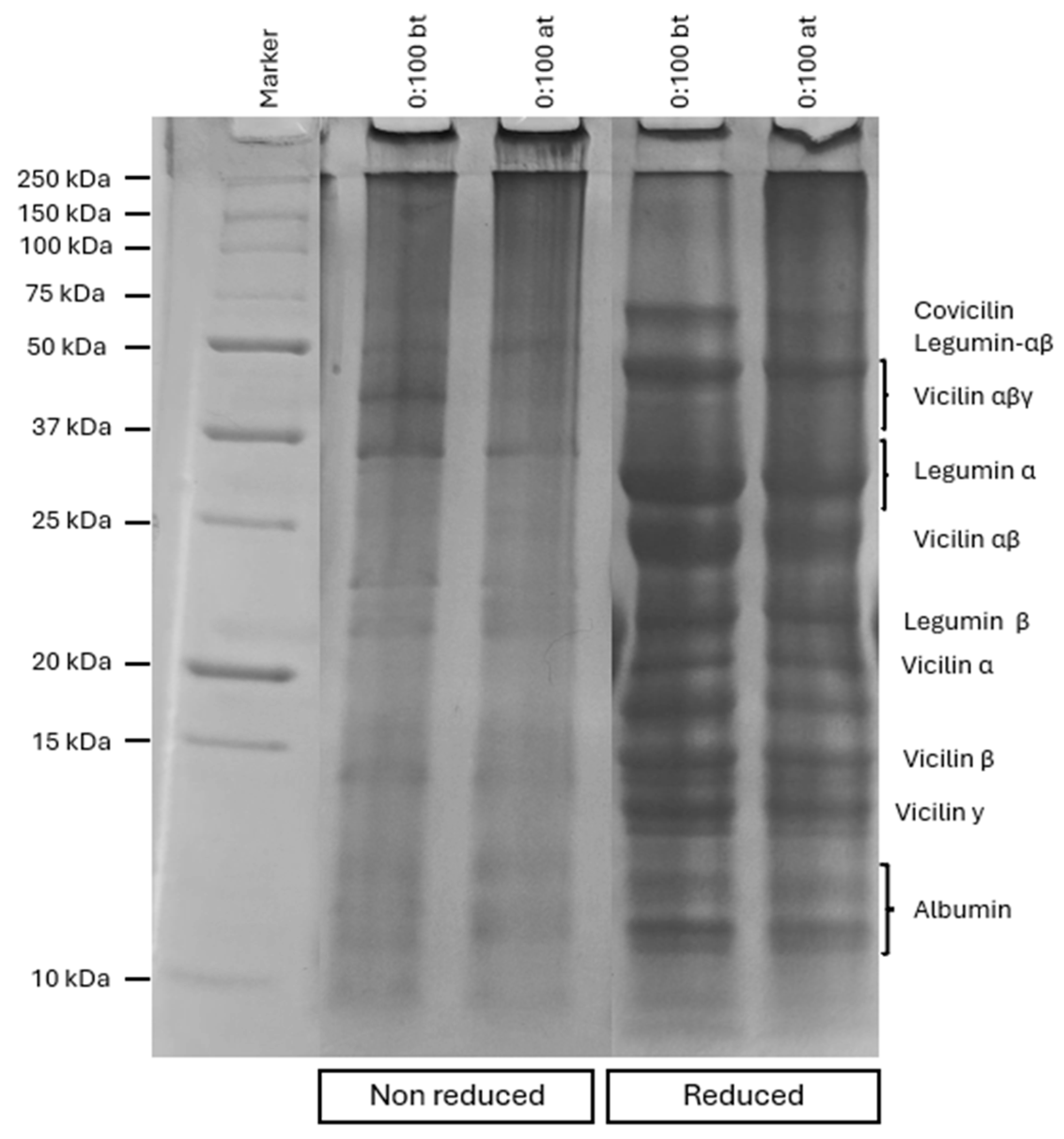
3.3. Electrophoresis
3.4. Intrinsic Fluorescence
3.5. Water-Holding Capacity
3.6. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.; Chaudhary, A.; Mathys, A. Dietary Change and Global Sustainable Development Goals. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, L.G.L.; Odelli, D.; Fernandes de Carvalho, A.; Martins, E.; Delaplace, G.; Peres de sá Peixoto Júnior, P.; Nogueira Silva, N.F.; Casanova, F. Combination of Milk and Plant Proteins to Develop Novel Food Systems: What Are the Limits? Foods 2023, 12, 2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Wang, T.; Ren, C.; Ma, W.; Wu, D.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Du, M. Advancement of Food-derived Mixed Protein Systems: Interactions, Aggregations, and Functional Properties. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 627–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliarti, O.; Kiat Kovis, T.J.; Yi, N.J. Structuring the Meat Analogue by Using Plant-Based Derived Composites. J. Food Eng. 2021, 288, 110138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Oh, H.; Choi, I.; Yoon, C.S.; Han, J. Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Rice Protein-Based Novel Textured Vegetable Proteins as Meat Analogues Produced by Low-Moisture Extrusion Cooking Technology. LWT 2022, 157, 113056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani Khiabanian, N.; Motamedzadegan, A.; Naghizadeh Raisi, S.; Alimi, M. Chemical, Textural, Rheological, and Sensorial Properties of Wheyless Feta Cheese as Influenced by Replacement of Milk Protein Concentrate with Pea Protein Isolate. J. Texture Stud. 2020, 51, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Cui, Y.; Lia, D.; Ding, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, H. The Characteristics of Soybean Protein Isolate Obtained by Synergistic Modification of High Hydrostatic Pressure and Phospholipids as a Promising Replacement of Milk in Ice Cream. LWT 2022, 160, 113223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthakumar, P.; Klepacka, J.; Bains, A.; Chawla, P.; Dhull, S.B.; Najda, A. The Current Situation of Pea Protein and Its Application in the Food Industry. Molecules 2022, 27, 5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Harb, S.; Panouillé, M.; Huc-Mathis, D.; Moulin, G.; Saint-Eve, A.; Irlinger, F.; Bonnarme, P.; Michon, C.; Souchon, I. The Rheological and Microstructural Properties of Pea, Milk, Mixed Pea/Milk Gels and Gelled Emulsions Designed by Thermal, Acid, and Enzyme Treatments. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, L.G.L.; da Silva, R.R.; Odelli, D.; Doumert, B.; Martins, E.; Casanova, F.; Marie, R.; Carvalho, A.F.; Delaplace, G.; de Sá Peixoto Junior, P.P. Acid Gelation of High-Concentrated Casein Micelles and Pea Proteins Mixed Systems. Food Res. Int. 2024, 196, 114982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mession, J.L.; Roustel, S.; Saurel, R. Interactions in Casein Micelle-Pea Protein System (Part II): Mixture Acid Gelation with Glucono-δ-Lactone. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 73, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, L.G.L.; Queiroz, L.S.; Petersen, H.O.; Marie, R.; Silva, N.F.N.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; de Sá Peixoto Júnior, P.P.; Delaplace, G.; de Carvalho, A.F.; Casanova, F. High-Intensity Ultrasound Treatment on Casein: Pea Mixed Systems: Effect on Gelling Properties. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 136178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano León, G.; Gravel, A.; Perreault, V.; Pouliot, Y.; Doyen, A. Impact of High Hydrostatic Pressure on Casein Micelle-pea Protein Systems and Comparison with Heat Treatment. Sustain. Food Proteins 2024, 2, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Huang, W.; Guo, X.; Chen, L. Strong and Elastic Pea Protein Hydrogels Formed through PH-Shifting Method. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Du, J.; Bai, Y. Effect of PH-Shifting Treatment on Structural and Heat Induced Gel Properties of Peanut Protein Isolate. Food Chem. 2020, 325, 126921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, X. Effect of PH-Shifting and Ultrasound on Soy/Potato Protein Structure and Gelation. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 159, 110672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.-S.; Cho, S.-J. Effect of PH-Shifting on the Water Holding Capacity and Gelation Properties of Mung Bean Protein Isolate. Food Res. Int. 2024, 177, 113912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Xu, J.; Gao, H.; Yu, Z.; Liang, J.; Mu, D.; Li, X.; Zhong, X.; Luo, S.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Effects of Combined High Hydrostatic Pressure and PH-Shifting Pretreatment on the Structure and Emulsifying Properties of Soy Protein Isolates. J. Food Eng. 2021, 306, 110622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldahl, J. Neue Methode Zur Bestimmung Des Stickstoffs in Organischen Körpern. Fresenius’ Z. Für Anal. Chem. 1883, 22, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Fu, W.; Li, D.; Dong, C.; Bao, Z.; Wang, C. Structure and Functionality of Whey Protein, Pea Protein, and Mixed Whey and Pea Proteins Treated by PH Shift or High-Intensity Ultrasound. J. Dairy. Sci. 2024, 107, 726–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghdadi, A.; Picart-Palmade, L.; Cunault, C.; Marchesseau, S.; Chevalier-Lucia, D. Impact of Two Thermal Processing Routes on Protein Interactions and Acid Gelation Properties of Casein Micelle-Pea Protein Mixture Compared to Casein Micelle-Whey Protein One. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ding, J.; Andrade, J.; Rababah, T.M.; Almajwal, A.; Abulmeaty, M.M.; Feng, H. Modifying the Physicochemical Properties of Pea Protein by PH-Shifting and Ultrasound Combined Treatments. Ultrason. Sonochem 2017, 38, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.X.; Ying, R.F.; Shi, L.E. Physicochemical and Functional Characteristics of Proteins Treated by a PH-Shift Process: A Review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, A.E.; Arnold, B.; Weiss, J.; Hinrichs, J. Effect of Temperature and PH on the Solubility of Caseins: Environmental Influences on the Dissociation of AS- and β-Casein. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossmann, L. Structural Properties of Pea Proteins (Pisum sativum) for Sustainable Food Matrices. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 8346–8366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emkani, M.; Moundanga, S.; Oliete, B.; Saurel, R. Protein composition and nutritional aspects of pea protein fractions obtained by a modified isoelectric precipitation method using fermentation. Foods 2023, 10, 1284413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Sun, F.; Liu, H.; Kong, B. Synergistic Modification of Pea Protein Structure Using High-Intensity Ultrasound and PH-Shifting Technology to Improve Solubility and Emulsification. Ultrason. Sonochem 2022, 88, 106099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, W.; Roopesh, M.S.; Chen, L. Pre-Treatment by Combining Atmospheric Cold Plasma and PH-Shifting to Prepare Pea Protein Concentrate Powders with Improved Gelling Properties. Food Res. Int. 2022, 154, 111028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Drositi, I.; Czaja, T.P.; Via, M.; Ahrné, L. Towards Hybrid Protein Foods: Heat- and Acid-Induced Hybrid Gels Formed from Micellar Casein and Pea Protein. Food Res. Int. 2024, 198, 115326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.C.; de Paula Ferreira, I.E.; Casanova, F.; Cavallieri, A.L.F.; Lima Nascimento, L.G.; de Carvalho, A.F.; Nogueira Silva, N.F. Colloidal and Acid Gelling Properties of Mixed Milk and Pea Protein Suspensions. Foods 2022, 11, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiá, C.; Keshanidokht, S.; Due Preisler, L.; Risbo, J.; Jensen, P.E. Plant Lipid Sources in Fermented Pea Protein Gels: Emulsion Stability and Gel Microstructure. LWT 2023, 182, 114890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.R.; Rafe, A.; Yeganehzad, S. Textural, Mechanical, and Microstructural Properties of Restructured Pimiento Alginate-Guar Gels. J. Texture Stud. 2018, 50, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Kim, D.-K.; Bae, J.H.; Kang, S.H.; Seo, K.M.; Kim, B.K.; Lee, S.Y. The Effect of Rheological Properties of Foods on Bolus Characteristics After Mastication. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 36, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Ratio | Protein Amount in the Suspension |
|---|---|
| 100:0 | 100% casein |
| 80:20 | 80% casein and 20% pea protein |
| 50:50 | 50% casein and 50% pea protein |
| 20:80 | 20% casein and 80% pea protein |
| 0:100 | 100% pea protein |
| Sample | Hardness (N) | Chewiness (N) | Resilience | Gumminess (N) | Springiness (mm) | Cohesiveness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before pH-shifting | 100:0 | 2.6735 ± 0.0224 a | 17.0898 ± 0.4235 a | 0.8947 ± 0.0103 a | 1.1628 ± 0.0503 a | 11.9540 ± 0.2416 a | 0.4342 ± 0.0288 abA |
| 80:20 | 2.1129 ± 0.0455 bA | 13.0187 ± 2.0603 bB | 0.7998 ± 0.0165 abA | 0.8699 ± 0.1400 bA | 10.9078 ± 0.2395 aA | 0.4125 ± 0.0670 abA | |
| 50:50 | 0.8241 ± 0.0080 cA | 5.7489 ± 0.2305 cA | 0.7987 ± 0.0074 abA | 0.2983 ± 0.0733 cA | 7.8289 ± 0.5428 aA | 0.3778 ± 0.0964 aB | |
| 20:80 | 0.1116 ± 0.0104 dB | 0.4765 ± 0.1002 dB | 0.7516 ± 0.0387 bA | 0.0324 ± 0.0070 dB | - | 0.2857 ± 0.0800 bcA | |
| 0:100 | 0.1452 ± 0.0100 dB | 0.5379 ± 0.0531 dA | 0.6747 ± 0.0193 cA | 0.0369 ± 0.0040 dA | - | 0.2273 ± 0.0400 cA | |
| After pH-shifting | 80:20 | 1.3828 ± 0.0571 aB | 8.6147 ± 0.7808 bA | 0.7573 ± 0.0217 aA | 0.5747 ± 0.0515 bA | 11.2789 ± 0.0283 aA | 0.4138 ± 0.0371 bA |
| 50:50 | 0.4215 ± 0.0479 bB | 2.4497 ± 0.3426 bA | 0.8108 ± 0.0093 aA | 0.1651 ± 0.0217 bB | 7.9378 ± 0.6187 aA | 0.3933 ± 0.0601 bA | |
| 20:80 | 0.5267 ± 0.0135 bA | 39.8140 ± 3.0960 aA | 0.8431 ± 0.0330 aA | 2.6644 ± 0.1999 aA | 9.5650 ± 0.2996 a | 5.2000 ± 0.4228 aA | |
| 0:100 | 0.6179 ± 0.0694 bA | 3.0360 ± 0.6526 bA | 0.7849 ± 0.0318 aA | 0.2028 ± 0.0434 bA | 7.6442 ± 1.1931 a | 0.3333 ± 0.0882 bA | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, R.R.d.; Souza, L.H.d.P.; Sousa, L.S.d.; Rodrigues, L.D.; Nogueira, G.S.; Nascimento, L.G.L.; Carvalho, A.F. Effect of pH-shifting on the Physicochemical Properties of Pea Proteins and Its Effect on the Texture of Hybrid Gels Formed with Casein Micelles. Foods 2025, 14, 2887. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162887
Silva RRd, Souza LHdP, Sousa LSd, Rodrigues LD, Nogueira GS, Nascimento LGL, Carvalho AF. Effect of pH-shifting on the Physicochemical Properties of Pea Proteins and Its Effect on the Texture of Hybrid Gels Formed with Casein Micelles. Foods. 2025; 14(16):2887. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162887
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Raiane Rodrigues da, Luis Henrique de Paula Souza, Lucas Silva de Sousa, Laura Destro Rodrigues, Gustavo Schäfer Nogueira, Luis Gustavo Lima Nascimento, and Antônio Fernandes Carvalho. 2025. "Effect of pH-shifting on the Physicochemical Properties of Pea Proteins and Its Effect on the Texture of Hybrid Gels Formed with Casein Micelles" Foods 14, no. 16: 2887. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162887
APA StyleSilva, R. R. d., Souza, L. H. d. P., Sousa, L. S. d., Rodrigues, L. D., Nogueira, G. S., Nascimento, L. G. L., & Carvalho, A. F. (2025). Effect of pH-shifting on the Physicochemical Properties of Pea Proteins and Its Effect on the Texture of Hybrid Gels Formed with Casein Micelles. Foods, 14(16), 2887. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14162887






