Fluoride Content in Infusions of Selected Teas Available on the Polish Market—An In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Groups
2.2. Preparation of Tea Infusions
2.3. Measuring the pH of Herbal Infusions
2.4. Measuring the Buffering Capacity of Tea Infusions
- •
- pH1 is the pH of the brewed tea;
- •
- pH2 is the pH after the addition of 0.1 M HCl.
2.5. Determination of Titratable Acidity of Tea Infusions
2.6. Determination of Inorganic Phosphorus and Calcium in Tea Infusions
2.7. Determination of Fluoride Content in Tea Infusions
2.8. Statistical Analysis
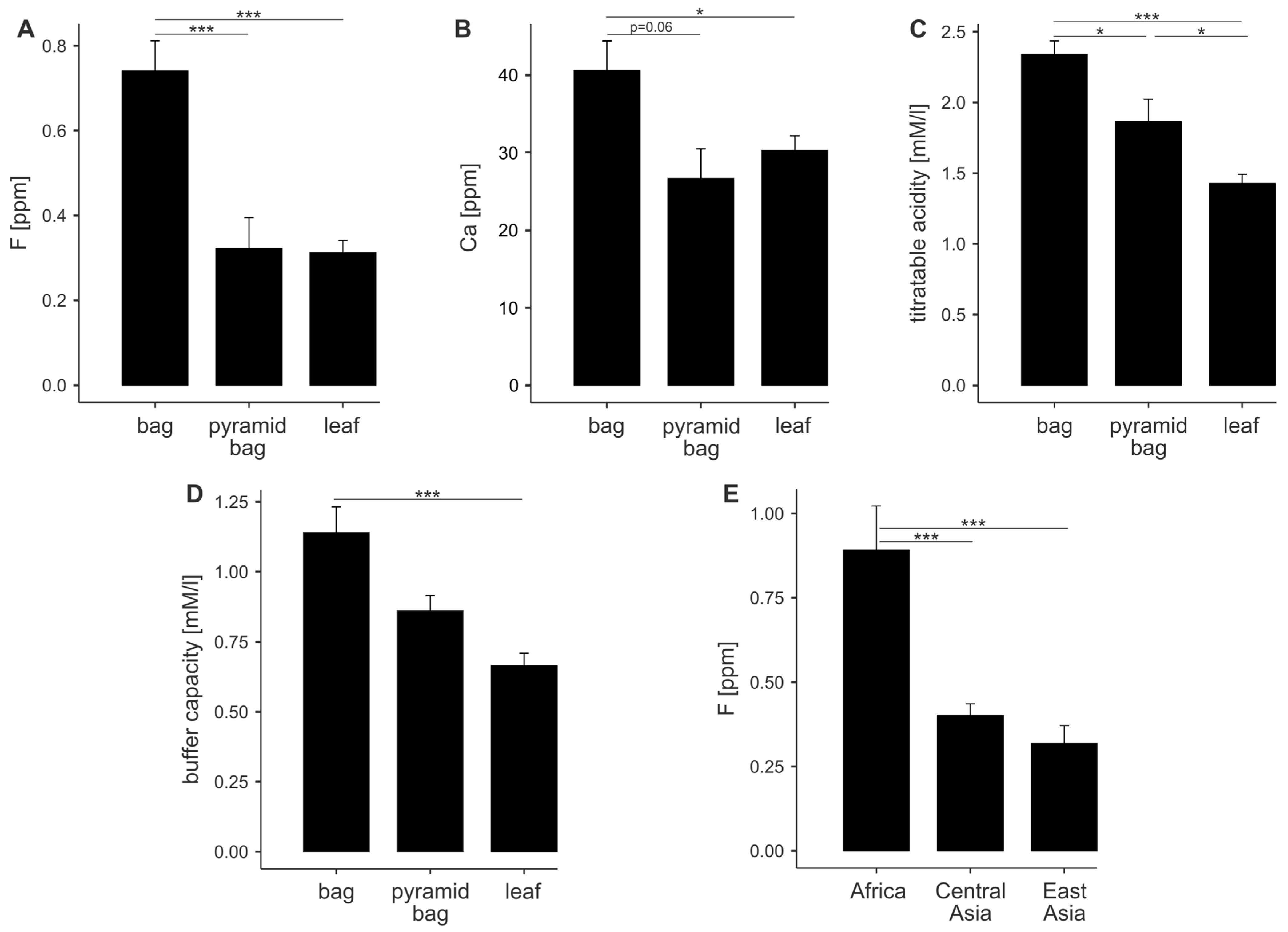
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Teas
3.2. Correlation Analysis Among Physicochemical Properties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, N.; Mukhtar, H. Tea and Health: Studies in Humans. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 6141–6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Małyszek, A.; Kiryk, S.; Kensy, J.; Kotela, A.; Michalak, M.; Kiryk, J.; Janeczek, M.; Matys, J.; Dobrzyński, M. Identification of Factors Influencing Fluoride Content in Tea Infusions: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, L.; Gurunathan, D.; Shanmugam, R. Effectiveness of White Tea-Mediated Silver Nanoparticles as an Intracanal Irrigant against Enterococcus Faecalis: An in Vitro Study. Dent. Med. Probl. 2024, 61, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.H.; Jiang, Y.M.; Caffin, N.; D’Arcy, B.; Datta, N.; Liu, X.; Singanusong, R.; Xu, Y. Phenolic Compounds in Tea from Australian Supermarkets. Food Chem. 2006, 96, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastrad, J.V.; Badanayak, P.; Goudar, G. Phenolic Compounds in Tea: Phytochemical, Biological, and Therapeutic Applications. In Phenolic Compounds—Chemistry, Synthesis, Diversity, Non-Conventional Industrial, Pharmaceutical and Therapeutic Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.-K.; Lin, C.-L.; Liang, Y.-C.; Lin-Shiau, S.-Y.; Juan, I.-M. Survey of Catechins, Gallic Acid, and Methylxanthines in Green, Oolong, Pu-Erh, and Black Teas. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 3635–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, U. PH Values and Fluoride Levels in Some Tea Brands. Ann. Acad. Med. Stetin. 2004, 50 (Suppl. 1), 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Koblar, A.; Tavčar, G.; Ponikvar-Svet, M. Fluoride in Teas of Different Types and Forms and the Exposure of Humans to Fluoride with Tea and Diet. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abanto Alvarez, J.; Rezende, K.M.P.C.; Marocho, S.M.S.; Alves, F.B.T.; Celiberti, P.; Ciamponi, A.L. Dental Fluorosis: Exposure, Prevention and Management. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2009, 14, E103–E107. [Google Scholar]
- Manjunathappa, T.H.; Devegowda, D.; Mysore, N.K.; Vishwanath, P.; Narayana, P.S. Association between Drinking Water Fluoride and the Serum Alkaline Phosphatase and Phosphate Levels in Pregnant Women and Newborn Infants. Dent. Med. Probl. 2023, 60, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Guo, W.-F.; Yang, X.-Q. Fluoride Content in Tea and Its Relationship with Tea Quality. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 4472–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, S.M.; Guha-Chowdhury, N. Total Fluoride Intake and Implications for Dietary Fluoride Supplementation. J. Public Health Dent. 1999, 59, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.H.C.; Leite, A.L.; Arana, A.; Villena, R.S.; Forte, F.D.S.; Sampaio, F.C.; Buzalaf, M.A.R. Dietary Fluoride Intake by Children Receiving Different Sources of Systemic Fluoride. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzyński, W.; Nikodem, A.; Diakowska, D.; Wiglusz, R.J.; Watras, A.; Dobrzyński, M.; Mikulewicz, M. Comparison of the fluoride ion release from nanofluorapatite-modified orthodontic cement under different pH conditions—An in vitro study. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2023, 25, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Overview on Tolerable Upper Intake Levels as Derived by the Scientific Committee on Food (SCF) and the EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA); European Food Safety Authority: Parma, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Olczak-Kowalczyk, D.; Mielczarek, A.; Jackowska, T.; Mielnik-Błaszczak, M.; Turska-Szybka, A.; Opydo-Szymaczek, J.; Jurczak, A.; Kaczmarek, U. Środki Fluorkowe w Zapobieganiu i Leczeniu Próchnicy i Erozji Zębów u Dzieci, Młodzieży i Dorosłych–Rekomendacje Polskich Ekspertów. Aktualizacja Zaleceń: Indywidualna Profilaktyka Fluorkowa u Dzieci, Młodzieży–Rekomendacje Polskich Ekspertów. Nowa Stomatol. 2022, 27, 35–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, K.; Wujczyk, M.; Dobrzynski, M.; Diakowska, D.; Wiglusz, K.; Wiglusz, R.J. In Vitro Assessment of Long-Term Fluoride Ion Release from Nanofluorapatite. Materials 2021, 14, 3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneri, F.; Iamandii, I.; Vinceti, M.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Generali, L.; Consolo, U.; Filippini, T. Fluoride Exposure and Skeletal Fluorosis: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2023, 10, 417–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Fluoride; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; ISBN 978-0-309-06403-3.
- Linhares, D.P.S.; Garcia, P.V.; Amaral, L.; Ferreira, T.; dos Santos Rodrigues, A. Safety Evaluation of Fluoride Content in Tea Infusions Consumed in the Azores—A Volcanic Region with Water Springs Naturally Enriched in Fluoride. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 179, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinowska, E.; Inkielewicz, I.; Czarnowski, W.; Szefer, P. Assessment of Fluoride Concentration and Daily Intake by Human from Tea and Herbal Infusions. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA) on a Request from the Commission Related to the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of Fluoride. EFSA J. 2005, 3, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdemoglu, S.B.; Türkdemir, H.; Gücer, S. Determination of Total and Fluoride Bound Aluminium in Tea Infusions by Ion Selective Electrode and Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Anal. Lett. 2000, 33, 1513–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovič, A.; Tavčar, G.; Ponikvar-Svet, M. Fluoride and Aluminium in Tea (Camellia sinensis L.)—Tea Quality Indicators and Risk Factors for Consumers. Molecules 2023, 28, 6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, K.; Czajczyńska-Waszkiewicz, A.; Kowalczyk-Zając, M.; Dobrzyński, M. Assessment of the influence of vegetarian diet on the occurrence of erosive and abrasive cavities in hard tooth tissues. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2011, 65, 764–769. [Google Scholar]
- Lubojanski, A.; Piesiak-Panczyszyn, D.; Zakrzewski, W.; Dobrzynski, W.; Szymonowicz, M.; Rybak, Z.; Mielan, B.; Wiglusz, R.J.; Watras, A.; Dobrzynski, M. The Safety of Fluoride Compounds and Their Effect on the Human Body—A Narrative Review. Materials 2023, 16, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Ma, L.; Shi, Y.; Han, W. The Impact of PH and Calcium on the Uptake of Fluoride by Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis L.). Ann. Bot. 2004, 93, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Ma, L.; Ruan, J. Characterization of Fluoride Uptake by Roots of Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). Plant Soil 2013, 366, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.-S.; Lin, X.-M.; Qiao, R.-Y.; Zheng, X.-Q.; Lu, J.-L.; Ye, J.-H.; Liang, Y.-R. Effect of Fluoride Treatment on Gene Expression in Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satou, R.; Oka, S.; Sugihara, N. Risk Assessment of Fluoride Daily Intake from Preference Beverage. J. Dent. Sci. 2021, 16, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Wang, J.; Shan, W.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Liu, C.; Fang, J.; Wei, S. Development of Fluorapatite Cement for Dental Enamel Defects Repair. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.; Hancock, R.; Limeback, H.; Schwartz, M.; Grynpas, M. How Does Fluoride Concentration in the Tooth Affect Apatite Crystal Size? J. Dent. Res. 2003, 82, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rošin-Grget, K. The Cariostatic Mechanisms of Fluoride. Acta Med. Acad. 2013, 42, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waugh, D.; Potter, W.; Limeback, H.; Godfrey, M. Risk Assessment of Fluoride Intake from Tea in the Republic of Ireland and Its Implications for Public Health and Water Fluoridation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Cai, H.; Zhu, X.; Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Hou, R.; Wan, X. Analysis of Naturally Occurring Fluoride in Commercial Teas and Estimation of Its Daily Intake through Tea Consumption. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, H235–H239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Hoeven, J.S.; Franken, H.C. Effect of Fluoride on Growth and Acid Production by Streptococcus Mutans in Dental Plaque. Infect. Immun. 1984, 45, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Fluoride in Drinking Water; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-309-10128-8.
- Maleki, A.; Abulmohammadi, P.; Teymouri, P.; Zandi, S.; Daraei, H.; Mahvi, A.H.; Shahsawari, S. Effect of Brewing Time and Water Hardness on Fluoride Release from Different Iranian Teas. Fluoride 2016, 49, 263–273. [Google Scholar]
- Morés, S.; Monteiro, G.C.; Santos, F.da.S.; Carasek, E.; Welz, B. Determination of Fluorine in Tea Using High-Resolution Molecular Absorption Spectrometry with Electrothermal Vaporization of the Calcium Mono-Fluoride CaF. Talanta 2011, 85, 2681–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleniacz-Trawińska, M.; Kotela, A.; Kensy, J.; Kiryk, S.; Dobrzyński, W.; Kiryk, J.; Gerber, H.; Fast, M.; Matys, J.; Dobrzyński, M. Evaluation of Factors Affecting Fluoride Release from Compomer Restorative Materials: A Systematic Review. Materials 2025, 18, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DenBesten, P.; Li, W. Chronic Fluoride Toxicity: Dental Fluorosis. Monogr. Oral Sci. 2011, 22, 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, A.L.; Sun, G.; Zhang, Y.; Grandjean, P. Developmental Fluoride Neurotoxicity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue-Choi, M.; Ramirez, Y.; Cornelis, M.C.; Berrington de González, A.; Freedman, N.D.; Loftfield, E. Tea Consumption and All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in the UK Biobank. Ann. Intern. Med. 2022, 175, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, U.; Jackowska, T.; Mielnik-Błaszczak, M.; Jurczak, A.; Olczak-Kowalczyk, D. Individualised Caries Prevention with Fluoride in Children and Adolescents–Recommendations of Polish Experts. Nowa Stomatol. 2019, 24, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition, and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for Fluoride. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piszko, P.J.; Kulus, M.; Piszko, A.; Kiryk, J.; Kiryk, S.; Kensy, J.; Małyszek, A.; Michalak, M.; Dobrzyński, W.; Matys, J.; et al. The Influence of Calcium Ions and PH on Fluoride Release from Commercial Fluoride Gels in an In Vitro Study. Gels 2025, 11, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, W. Factors Effecting Aluminum Speciation in Drinking Water by Laboratory Research. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, G.S.; Bache, B.W. Kinetics of Aluminium Fluoride Complexation in Single- and Mixed-Ligand Systems. Talanta 1992, 39, 1531–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, T.; Mathurin, F.A.; Gustafsson, J.P.; Peltola, P.; Åström, M.E. The Impact of Fluoride on Al Abundance and Speciation in Boreal Streams. Chem. Geol. 2015, 409, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romar, A.; Gago, C.; Fernández-Marcos, M.L.; Álvarez, E. Influence of Fluoride Addition on the Composition of Solutions in Equilibrium with Acid Soils. Pedosphere 2009, 19, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamalwa Wambu, E.; Jerop Kurui, A. Fluoride Adsorption onto Soil Adsorbents: The Role of PH and Other Solution Parameters. In Soil pH for Nutrient Availability and Crop Performance; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Khandare, A.L. Comparison of Fluoride Levels (Total and Extracted) in Young, Old Tea Leaves and Market Tea Samples along with Impact of Tea Infusion on Dental Fluorosis in Fluoride Endemic Villages of Nalgonda District, India. Adv. Dent. Oral Health 2019, 10, 555793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Xu, X.; Ren, Y.; Niu, H.; Yang, Y.; Hou, R.; Wan, X.; Cai, H. Fluoride Absorption, Transportation and Tolerance Mechanism in Camellia Sinensis, and Its Bioavailability and Health Risk Assessment: A Systematic Review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, S.-C.C.; Cheng, H.-W.; Fu, C.B. Potential Exposure and Risk of Fluoride Intakes from Tea Drinks Produced in Taiwan. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2008, 18, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Tea Name (Brand) | Form | Origin |
|---|---|---|
| Assam Irish Breakfast (Ronnefeldt) | Bags | India |
| Classic Black Tea (Tetley) | Bags | India |
| Classic Earl Grey (Tetley) | Bags | India |
| Darjeeling (Ronnefeldt) | Bags | India |
| Earl Grey (Ronnefeldt) | Bags | India |
| Yellow Label (Lipton) | Bags | India |
| Black with Ginger and Turmeric (Remsey) | Bags | Kenya |
| Classic Black (Remsey) | Bags | Kenya |
| Earl Grey (Lord Nelson) | Bags | Kenya |
| Earl Grey Strong Tempting Bergamot Flavour (Remsey) | Bags | Kenya |
| Earl Grey with a Hint of Lemon Bergamot Flavour (Remsey) | Bags | Kenya |
| English Breakfast (Lipton) | Bags | Kenya |
| English Teatime (Lipton) | Bags | Kenya |
| Yellow Label (Lipton) | Bags | Kenya |
| Classic Black (Lord Nelson) | Bags | Outside EU |
| Black Tea “Minutka” (Minutka) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Black Tea (Minutka) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Black Tea Earl Grey Full-Bodied (Vintage Teas) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Ceylon (Loyd) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Ceylon Black (Remsey) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Ceylon Black Tea (Big-Active) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Ceylon Earl Grey (Remsey) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Ceylon Gold (Sir William’s Tea) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Ceylon Premium Tea (Dilmah) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Classic Earl Grey (Exclusive) (Lipton) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Earl Grey (Ahmad Tea) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Earl Grey (Akbar) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Earl Grey (Loyd) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Earl Grey (Loyd) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Earl Grey (Sir William’s Tea) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Earl Grey (Teekane) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| English Breakfast (Ahmad Tea) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| English Breakfast (Ronnefeldt) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| English Breakfast (Sir William’s Tea) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| English Breakfast Tea (Remsey) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| English Tea No. 1 (Ahmad Tea) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Finest Black Tea (Eternal) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Gold (Tekkane) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Gold Tea (Loyd) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Intense Black (Lipton) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Lemon Black (Minutka) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Royal Elixir Tea (Impra Tea) | Bags | Sri Lanka |
| Eternal Finest (Eternal) | Granulate | India |
| Golden Assam (Golden Assam) | Granulate | India |
| Yellow Label (Lipton) | Granulate | Kenya |
| Black Tea (Yunnan) | Leaves | China |
| China Black Golden Silk Missing (Five o’clock) | Leaves | China |
| China Panyong Golden Needle (Five o’clock) | Leaves | China |
| Earl Grey with Lemon Zest (Lord Nelson) | Leaves | China |
| Formosa Lapsang Souchong (Five o’clock) | Leaves | China |
| Golden Yunan (Five o’clock) | Leaves | China |
| Golden Yunan Superior (Five o’clock) | Leaves | China |
| Keemun (Five o’clock) | Leaves | China |
| Yunan Black Tea (ZAS) | Leaves | China |
| Yunnan (Loyd) | Leaves | China |
| Yunnan (ZAS) | Leaves | China |
| Georgian Black Wild Op (Five o’clock) | Leaves | Georgia |
| Assam (Lord Nelson) | Leaves | India |
| Assam (ZAS) | Leaves | India |
| Assam Halmari GTGFBOP (Five o’clock) | Leaves | India |
| Assam Halmari GTGFOP1CL (Five o’clock) | Leaves | India |
| Assam Satrupa (Five o’clock) | Leaves | India |
| Assam Singlijan (Five o’clock) | Leaves | India |
| Assam Tea (Ahmad Tea) | Leaves | India |
| Assam Tonganagaon (Five o’clock) | Leaves | India |
| Ceylon Lumbini (Five o’clock) | Leaves | India |
| Darjeeling Flower Balasun (Five o’clock) | Leaves | India |
| Darjeeling Gielle (Five o’clock) | Leaves | India |
| Darjeeling Liza Hill DJ5/21 (Five o’clock) | Leaves | India |
| Darjeeling Musk Puttabang (Five o’clock) | Leaves | India |
| Darjeeling Nagr DJ2 (Five o’clock) | Leaves | India |
| Darjeeling Shree Dwarika (Five o’clock) | Leaves | India |
| Darjeeling Teesta Valley DJ11 (Five o’clock) | Leaves | India |
| Madras (Loyd) | Leaves | India |
| Madras (ZAS) | Leaves | India |
| Pure Ceylon Tea (Akbar) | Leaves | India |
| South India Nilgiri Kukicha Roasted (Five o’clock) | Leaves | India |
| Japan Black Tea (Five o’clock) | Leaves | Japan |
| Safari (Astra) | Leaves | Kenya |
| Yellow Label (Lipton) | Leaves | Kenya |
| Laos Black Saylom (Five o’clock) | Leaves | Laos |
| Nepal Arubote (Five o’clock) | Leaves | Nepal |
| Nepal Yun Chiyabari Himalayan Imperial (Five o’clock) | Leaves | Nepal |
| Kivu Lake Selected (HAYB) | Leaves | Rwanda |
| Rwanda Rukei Op (Five o’clock) | Leaves | Rwanda |
| Black Tropical Tea (Sir Adalbert’s Tea) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Ceylon (Big-Active) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Ceylon Ahinsa (Five o’clock) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Ceylon Gold (Dilmah) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Ceylon Premium Tea (Dilmah) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Ceylon Supreme (Dilmah) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Ceylon Tea (Ahmad Tea) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Ceylon Vithanakande (Five o’clock) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Dimbula (Vintage Teas) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Earl Grey (Ahmad Tea) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Earl Grey (Akbar) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Earl Grey (Loyd) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Earl Grey (Sir Adalbert’s Tea) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Earl Grey (Vintage Teas) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| English Breakfast (Ahmad Tea) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| English Breakfast (Dilmah | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| English Royal Tea (Chelton) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| English Tea No. 1 (Ahmad Tea) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Finest Top (Eternal) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Gourmet Earl Grey Tea (Dilmah) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Kandy (Vintage Teas) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Nuwara Eliya (Vintage Teas) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Organic Black Tea (Vintage Teas) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Royal Elixir Tea (Gold) (Impra Tea) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Ruhuna (Vintage Teas) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Sabaragamuwa (Vintage Teas) | Leaves | Sri Lanka |
| Darjeeling Tea (Teapigs) | Pyramid bags | India |
| English Breakfast (Teapigs) | Pyramid bags | India |
| Earl Grey (English Teashop Organic) | Pyramid bags | Sri Lanka |
| Earl Grey (Vintage Teas) | Pyramid bags | Sri Lanka |
| Earl Grey Strong (Teapigs) | Pyramid bags | Sri Lanka |
| Elegant Earl Grey (Dilmah) | Pyramid bags | Sri Lanka |
| English Breakfast (Dilmah) | Pyramid bags | Sri Lanka |
| English Breakfast (English Teashop Organic) | Pyramid bags | Sri Lanka |
| English Breakfast (Vintage Teas) | Pyramid bags | Sri Lanka |
| Maharaja Reserve Assam (Dilmah) | Pyramid bags | Sri Lanka |
| Organic Black Tea Broken Orange Pekoe KANDY (Vintage Teas) | Pyramid bags | Sri Lanka |
| Perfect Ceylon Tea (Dilmah) | Pyramid bags | Sri Lanka |
| Valley of Kings Ceylon Pekoe (Dilmah) | Pyramid bags | Sri Lanka |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Małyszek, A.; Zawiślak, I.; Kulus, M.; Watras, A.; Kensy, J.; Kotela, A.; Styczyńska, M.; Janeczek, M.; Matys, J.; Dobrzyński, M. Fluoride Content in Infusions of Selected Teas Available on the Polish Market—An In Vitro Study. Foods 2025, 14, 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142452
Małyszek A, Zawiślak I, Kulus M, Watras A, Kensy J, Kotela A, Styczyńska M, Janeczek M, Matys J, Dobrzyński M. Fluoride Content in Infusions of Selected Teas Available on the Polish Market—An In Vitro Study. Foods. 2025; 14(14):2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142452
Chicago/Turabian StyleMałyszek, Agata, Ireneusz Zawiślak, Michał Kulus, Adam Watras, Julia Kensy, Agnieszka Kotela, Marzena Styczyńska, Maciej Janeczek, Jacek Matys, and Maciej Dobrzyński. 2025. "Fluoride Content in Infusions of Selected Teas Available on the Polish Market—An In Vitro Study" Foods 14, no. 14: 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142452
APA StyleMałyszek, A., Zawiślak, I., Kulus, M., Watras, A., Kensy, J., Kotela, A., Styczyńska, M., Janeczek, M., Matys, J., & Dobrzyński, M. (2025). Fluoride Content in Infusions of Selected Teas Available on the Polish Market—An In Vitro Study. Foods, 14(14), 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142452









