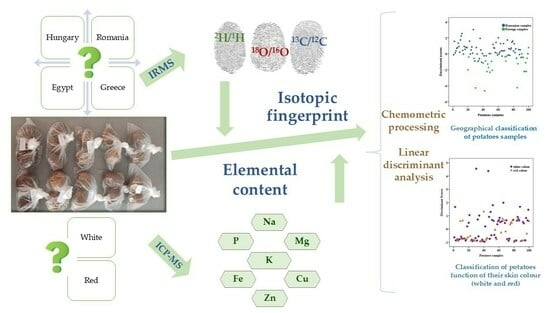
Elemental and Isotopic Fingerprints of Potatoes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Elemental Measurements
2.3. Stable Isotope Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Elemental Results
3.2. Stable Isotopes Results
3.3. Chemometric Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICP-MS | Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry |
| IRMS | Isotope ratio mass spectrometry |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
References
- Bozan, I.; Achakkagari, S.R.; Anglin, N.L.; Ellis, D.; Tai, H.H.; Strömvik, M. Pangenome analyses reveal impact of transposable elements and ploidy on the evolution of potato species. Plant Biol. 2023, 120, e2211117120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. FAOSTAT Statistical Database; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2022; Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Hosseinian, M.; Kafi, M.; Nabati, J.; Oskoueian, A. Effect of Application of Signaling Compounds on the Remobilization of Assimilates and the Leaf Senescence Induction Process in Potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.). Potato Res. 2025, 68, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Xu, X.; Zhou, S. Potato Yield Prediction Research Based on Improved Artificial Neural Networks Using Whale Optimization Algorithm. Potato Res. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mølmann, J.A.B.; Johansen, T.J. Influence of Growth Temperature on Development and Yield in a Medium Late and a Late Scandinavian Cultivar of Potato. Potato Res. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, A.; Goffart, J.-P.; Petsakos, A.; Kromann, P.; Gatto, M.; Okello, J.; Suarez, V.; Hareau, G. Global Food Security, Contributions from Sustainable Potato Agri-Food Systems. In The Potato Crop; Campos, H., Ortiz, O., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zaheer, K.; Akhtar, M.H. Potato production, usage, and nutrition—A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, J.; Gautam, S.; Scheuring, D.C.; Koym, J.W.; Vales, M.I. Variation and genetic basis of mineral content in potato tubers and prospects for genomic selection. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1301297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrivon, D. Potato facing global challenges: How, how much, how well? Potato Res. 2017, 60, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, A.; Goffart, J.-P.; Kromann, P.; Andrade-Piedra, J.; Polar, V.; Hareau, G. The Potato of the Future: Opportunities and Challenges in Sustainable Agri-food Systems. Potato Res. 2021, 64, 681–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristea, G.; Voica, C.; Feher, I.; Puscas, R.; Magdas, D.A. Isotopic and elemental characterization of Romanian pork meat in corroboration with advanced chemometric methods: A first exploratory study. Meat Sci. 2022, 189, 108825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camin, F.; Bontempo, L.; Perini, M.; Piasentier, E. Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis for Assessing the Authenticity of Food of Animal Origin. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanrar, B.; Kundu, S.; Khan, P.; Jain, V. Elemental Profiling for Discrimination of Geographical Origin of Tea (Camellia sinensis) in north-east region of India by ICP-MS coupled with Chemometric techniques. Food Chem. Adv. 2022, 1, 100073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, I.; Matos, A.S.; Epova, E.N.; Barre, J.; Cellier, R.; Ogrinc, N.; Castanheira, I.; Bordado, J.; Donard, O.F.X. Multi-element and multi-isotopic profiles of Port and Douro wines as tracers for authenticity. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2023, 115, 104988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulaudzi, N.; Combrinck, S.; Vermaak, I.; Joubert, E.; Viljoen, A. High performance thin layer chromatography fingerprinting of rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) and honeybush (Cyclopia genistoides, Cyclopia intermedia and Cyclopia subternata) teas. J. App. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2022, 30, 100378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Song, M.; Wang, K.; Fang, X.; Peng, W.; Wu, L.; Xue, X. Detection of acacia honey adulteration with high fructose corn syrup through determination of targeted α-Dicarbonyl compound using ion mobility-mass spectrometry coupled with UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2021, 352, 129312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dua, A.; Bahman, S.; Kelly, S.; Dogra, S.; Sharma, K. Authentication of Indian Honey Based on Carbon Stable Isotope Ratio Analysis—Verification of Indian Regulatory Criteria. Foods 2025, 14, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Mei, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Huan, Z.; Nie, J.; Rogers, K.M.; Nuralykyzy, B.; Li, C.; Yuan, Y. Application of Stable Isotopes and Multi Elemental Fingerprints to Verify the Origin of Premium Chinese Hainan Bananas. Foods 2025, 14, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, C.; Wang, Q.; Xu, J. Tracing the geographical origin of grain vinegar using the stable isotope ratio mass spectrometry and chemometrics. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 123, 105554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, P.; Le, M.-M.; Qi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Hu, F.-L.; Ling, T.J.; Bao, G.H. Improving flavor of summer Keemun black tea by solid-state fermentation using Cordyceps militaris revealed by LC/MS-based metabolomics and GC/MS analysis. Food Chem. 2023, 407, 135172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzano, A.; Manganiello, G.; Neglia, G.; Vinale, F.; De Nicola, D.; D’Occhio, M.; Campanile, G. A preliminary study on metabolome profiles of buffalo milk and corresponding mozzarella cheese: Safeguarding the authenticity and traceability of protected status buffalo dairy products. Molecules 2020, 25, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tömösközi-Farkas, R.; Adányi, N.; Gasztonyi-Nagy, M.; Berki, M.; Horváth, V.; Renkecz, T.; Simon, K.; Fabulya, Z.; Polgár, Z. Changes of Metabolites and Macro- and Micro-elements in Hungarian Potatoes under Organic and Conventional Farming. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. B 2016, 6, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemotomou, E.; Molyviatis, T.; Zabetakis, I. The Effect of Trace Elements Accumulation on the Levels of Secondary Metabolites and Antioxidant Activity in Carrots, Onions and Potatoes. Food Nutr. Sci. 2011, 2, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdón, B.R.; Rodríguez, L.H.; Mesa, D.R.; León, H.L.; Pérez, N.L.; Rodríguez, E.M.; Romero, C.D. Differentiation of potato cultivars experimentally cultivated based on their chemical composition and by applying linear discriminant analysis. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre, C.H.; Garcia, J.B.; Martin, S.G.; Peña Crecente, R.M. Chemometric Classification of Potatoes with Protected Designation of Origin According to Their Producing Area and Variety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8444–8451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opatić, A.M.; Nečemer, M.; Budič, B.; Lojen, S. Stable isotope analysis of major bioelements, multi-element profiling, and discriminant analysis for geographical origins of organically grown potato. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 71, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, W.A.; Coplen, T.B.; Vogl, J.; Rosner, M.; Prohaska, T. Assessment of international reference materials for stable isotope ratio analysis 2013 (IUPAC). Pure Appl. Chem. 2014, 86, 425–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coplen, T.B. Guidelines and Recommended Terms for Expression of Stable-Isotope-Ratio and Gas-Ratio Measurement Results. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2011, 25, 2538–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonel, M.; Do Carmo, E.L.; Fernandes, A.M.; Soratto, R.P.; Ebúrneo, J.A.M.; Garcia, É.L.; Dos Santos, T.P.R. Chemical composition of potato tubers: The effect of cultivars and growth conditions. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 2372–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Mu, T.; Ma, M.; Zhang, R.; Sun, Q.; Xu, Y. Nutritional evaluation of different cultivars of potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.) from China by grey relational analysis (GRA) and its application in potato steamed bread making. J. Integre. Agric. 2019, 18, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekesa, M.; Okoth, M.; Abong’, G.; Muthoni, J.; Kabira, J. Effect of soil characteristics on potato tuber minerals composition of selected Kenyan varieties. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 6, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, C.M.; Ghislain, M.; Bertin, P.; Oufir, M.; del Rosario Herrera, M.; Hoffmann, L.; Hausman, J.-F.; Larondelle, Y.; Evers, D. Andean Potato Cultivars (Solanum tuberosum L.) as a Source of Antioxidant and Mineral Micronutrients. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, C.; Restrepo-Sánchez, L.-P.; Kushalappa, A.; Rodríguez-Molano, L.-E.; Mosquera, T.; Narváez-Cuenca, C.-E. Nutritional contents of advanced breeding clones of Solanum tuberosum group Phureja. LWT 2015, 62, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Sharma, J.; Bhardwaj, V.; Sood, S.; Siddappa, S.; Goutam, U.; Dalamu, D.; Kardile, H.; Dipta, B.; Pandey, N.K. Variations in the mineral concentration among different potato (Solanum Tuberosum L.) accessions. Potato J. 2022, 48, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian, N.K.; White, P.J.; Broadley, M.R.; Ramsay, G. Variation in tuber mineral concentrations among accessions of Solanum species held in the commonwealth potato collection. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2017, 64, 1927–1935. [Google Scholar]
- Oosterhuis, D.M.; Loka, D.A.; Kawakami, E.M.; Pettigrew, W.T. Chapter Three—The Physiology of Potassium in Crop Production. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; Volume 126, pp. 203–233. [Google Scholar]
- Torabian, S.; Farhangi-Abriz, S.; Qin, R.; Noulas, C.; Sathuvalli, V.; Charlton, B.; Loka, D.A. Potassium: A Vital Macronutrient in Potato Production—A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.; Akhtar, M.E.; Mahmood-ul-Hassan, M.; Mahmood, M.M.; Safdar, M.N. Potato tuber yield and quality as affected by rates and sources of potassium fertilizer. J. Plant Nutr. 2012, 35, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Duan, Y.; Guo, T.; Zhang, P.; He, P.; Johnston, A.; Shcherbakov, A. Potassium management in potato production in Northwest region of China. Field Crops Res. 2015, 174, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Wegener, C.B.; Jurgens, H.-U.; Jansen, G. Drought stress affects bioactive compounds in potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.) relevant to non-communicable diseases. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2017, 7, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.G.; Fernelius, K.J.; Hansen, N.C.; Eggett, D.L. AVAIL phosphorus fertilizer enhancer: Meta-analysis of 503 field evaluations. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruulsema, T.W.; Peterson, H.M.; Prochnow, L.I. The science of 4R nutrient stewardship for phosphorus management across latitudes. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1295–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucon, M.-P.; Houben, D.; Reynoird, J.-P.; Mercadal-Dulaurent, A.M.; Armand, R.; Lambers, H. Advances and Perspectives to Improve the Phosphorus Availability in Cropping Systems for Agroecological Phosphorus Management. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 134, pp. 51–79. [Google Scholar]
- Hailu, G.; Nigussie, D.; Ali, M.; Derbew, B. Nitrogen and phosphorus use efficiency in improved potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) cultivars in southern Ethiopia. Am. J. Potato Res. 2017, 94, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, C.J.; Kelling, K.A.; Stark, J.C.; Porter, G.A. Optimizing phosphorus fertilizer management in potato production. Am. J. Potato Res. 2014, 91, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.G.; Hansen, N.C. Phosphorus Management in High-Yield Systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1265–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, A.; Sharma, L.K.; Zaeen, A.; Bali, S.K.; Buzza, A.; Alyokhin, A. Potato Phosphorus Response in Soils with High Value of Phosphorus. Agriculture 2020, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thor, K. Calcium—Nutrient and messenger. Front. Plant Sci.: Sec. Plant Nutr. 2019, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakova, M. The Importance of Magnesium for Potato Production: A Comprehensive Guide. Available online: https://potatoes.news/the-importance-of-magnesium-for-potato-production-a-comprehensive-guide/Daily-News (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Tamasi, G.; Cambi, M.; Gaggelli, N.; Autino, A.; Cresti, M.; Cini, R. The content of selected minerals and vitamin C for potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.) from the high Tiber Valley area, southeast Tuscany. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 41, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, M.K.; Kumar, A.; Jena, R.; Raigond, P.; Kumar, D.; Thakur, N.; Singh, B. Minerals in potato. In Potato; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 87–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, E.; Bastos, M.; Cuadrado, W.; Zárate, R.; Sarapura, V.; Yallico, L.; Tabra, F.; Bao, D. Heavy Metals in Native Potato and Health Risk Assessment in Highland Andean Zones of Junín, Peru. J. Environ. Prot. 2020, 11, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, E.; Atsan, E.; Polat, T.; Kara, K. Variation in heavy metal concentrations of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) cultivars. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2011, 21, 235–239. [Google Scholar]
- Gunko, S.; Vakuliuk, P.; Naumenko, О.; Bober, А.; Boroday, V.; Nasikovskyi, V.; Muliar, О. The Mineral Composition of Potatoes and Its Influence on the Darkening of Tubers Pulp. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 17, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šrek, P.; Hejcman, M.; Kunzová, E. Multivariate analysis of relationship between potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) yield, amount of applied elements, their concentrations in tubers and uptake in a long-term fertilizer experiment. Field Crops Res. 2010, 118, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrekidan, A.; Weldegebriel, Y.; Hadera, A.; Vander, B. Toxicological assessment of heavy metals accumulated in vegetables and fruits grown in Ginfel river near Sheba Tannery, Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 95, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millaleo, R.; Reyes-Díaz, M.; Ivanov, A.G.; Mora, M.L.; Alberdi, M. Manganese as essential and toxic element for plants: Transport, accumulation and resistance mechanisms. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2010, 10, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Pandey, S.K.; Sud, K.C.; Chanemougasoundharam, A. In vitro characterization of manganese toxicity in relation to phosphorus nutrition in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Plant Sci. 2004, 167, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya-Perales, N.S.; Maus, D.; Neimaier, A.; Escobedo-Pacheco, E.; Pumi, G. Assessment of the variation of heavy metals and pesticide residues in native and modern potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) cultivars grown at different altitudes in a typical mining region in Peru. Toxicol. Rep. 2023, 11, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakova, M. Unveiling the Hidden Potential of Rubidium: Revolutionizing Potato Farming for Improved Crop Performance. Available online: https://potatoes.news/unveiling-the-hidden-potential-of-rubidium-revolutionizing-potato-farming-for-improved-crop-performance/Daily-News (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Qiu, N.; Tian, L.; Yan, X.; Dong, H.; Zhang, M.; Han, G.; Zhou, F. The Interplay between Calcium and Strontium in Chinese Cabbage under Normal and Low Calcium Conditions. Hort. Sci. 2021, 56, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.R.; Kang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Qiu, N.W.; Chen, M.; Zhou, F. The biological effects of strontium (88Sr) on Chinese cabbage. Plant Soil. Environ. 2020, 66, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowa, I.; Woìjciak-Kosior, M.; Strzemski, M.; Dresler, S.; Szwerc, W.; Blicharski, T.; Szymczak, G.; Kocjan, R. Biofortification of soy (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) with strontium ions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5248–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójciak-Kosior, M.; Sowa, I.; Blicharski, T.; Strzemski, M.; Dresler, S.; Szymczak, G.; Wnorowski, A.; Kocjan, R.; Świeboda, R. The Stimulatory effect of strontium ions on phytoestrogens content in Glycine max (L.) Merr. Molecules 2016, 21, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresler, S.; Wójciak-Kosior, M.; Sowa, I.; Strzemski, M.; Sawicki, J.; Kováčik, J.; Blicharski, T. Effect of Long-Term Strontium Exposure on the Content of Phytoestrogens and Allantoin in Soybean. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, P.; Rachmilevitch, S.; Roitman, N.; Erel, R. Strontium as a tracer for calcium: Uptake, transport and partitioning within tomato plants. Plant Soil. 2021, 466, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roma, A.; Abete, M.C.; Brizio, P.; Picazio, G.; Caiazzo, M.; D’auria, L.G.; Esposito, M. Evaluation of Trace Elements in Potatoes (Solanum tuberosum) from a Suburban Area of Naples, Italy: The “Triangle of Death”. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; WHO. Codex General Standard for Contamination and Toxins in Food and Feed; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; Available online: https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/sh-proxy/en/?lnk=1&url=https%253A%252F%252Fworkspace.fao.org%252Fsites%252Fcodex%252FStandards%252FCXS%2B193-1995%252FCXS_193e.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2023/915 of 25 April 2023 on Maximum Levels For Certain Contaminants In Food And Repealing Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2023/915/oj/eng (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Karan, Y.B. Mineral nutrient variability of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tubers with different colors grown in Niksar, Kazova and Artova locations of Tokat Province, Turkey. Peer J. 2023, 11, e15262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, V.; Luthra, S.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Dua, V.K. Mineral content of red skinned potatoes of Eastern India. J. Hortic. Sci. 2019, 14, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdas, D.A.; Dehelean, A.; Feher, I.; Radu, S. Isotopic and multielemental fingerprinting of organically and conventionally grown potatoes. Isot. Enviro. Health. Stud. 2017, 53, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J.; Ehleringer, J.R.; Chesson, L.A.; Stange, E.; Cerling, T.E. Stable isotope ratios of tap water in the contiguous United States. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalpage, M.; Dissanayake, C.; Diyabalanage, S.; Chandrajith, R.; Frew, R.; Fernando, R. Stable Isotope and Element Profiling for Determining the Agroclimatic Origin of Cow Milk within a Tropical Country. Foods 2022, 11, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanesi, L. Chapter 19—Meat Authenticity and Traceability. In Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition, Lawrie´s Meat Science, 8th ed.; Toldra´, F., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 585–633. [Google Scholar]
- Dehelean, A.; Feher, I.; Romulus, P.; Magdas, D.A.; Covaciu, F.-D.; Kasza, A.M.; Curean, V.; Cristea, G. Influence of Geographical Origin on Isotopic and Elemental Compositions of Pork Meat. Foods 2023, 12, 4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.-M.; Kim, J.-K.; Jin, Y.-I.; Oh, Y.-T.; Prabakaran, M.; Youn, K.-J.; Kim, S.-H. Discriminative study of a potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) cultivation region by measuring the stable isotope ratios of bio-elements. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.A.; Smith, B.W. Effect of Season and Variety on the Differentiation of Geographic Growing Origin of Pistachios by Stable Isotope Profiling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 1747–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimmo, T.; Camin, F.; Bontempo, L.; Capici, C.; Tagliavini, M.; Cesco, S.; Scampicchio, M. Traceability of different apple varieties by multivariate analysis of isotope ratio mass spectrometry data. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2015, 29, 1984–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammarco, G.; Rossi, M.; Suman, M.; Cavanna, D.; Viotto, L.; Pettenà, P.; Dall, C.; Iacumin, P. Hazelnut products traceability through combined isotope ratio mass spectrometry and multi-elemental analysis. JSFA Rep. 2023, 3, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| References | U.M. | Elements | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na | Mg | P | K | Ca | ||
| This study (range, mean) | g/kg | 0.004–1.096 (0.087) | 0.475–5.4 (1.109) | 0.612–4.161 (1.707) | 5.994–23.412 (13.742) | 0.087–3.131 (0.453) |
| [30] | g/kg | 0.141–0.333 | 1.134–1.453 | - | 21.943–28.22 | 0.341–0.712 |
| [8] | g/kg | 0.102–0.468 (0.276) | 0.81–1.44 (1.14) | 2.96–4.79 (3.69) | 20.39–32.46 (25.09) | 0.19–0.79 (0.44) |
| [31] | g/kg | - | 0.38–8.00 | 3.15–4.95 | 12.95-26.60 | 0.02-1.00 |
| [32] | g/kg | - | - | - | - | 0.271–1.092 |
| [33] | g/kg | 0.007-0.12 | 0.95–1.07 | 1.62–2.20 | 19.63–24.66 | 0.10–0.15 |
| [34] | g/kg | - | 0.4–2.9 | 1.3–3.9 | 4.8–20.1 | 0.20–1.0 |
| [35] | g/kg | - | 0.8–2.2 | 2.4–5.2 | 15.0–26.9 | 0.1–0.7 |
| References | U.M. | Elements | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Zn | Cu | Cr | Ni | Mn | ||
| This study (range, mean) | mg/kg | 16.981–255.792 (73.659) | 1.779–33.642 (9.344) | <0.001–55.544 (4.580) | <0.001–21.455 (3.80) | <0.001–13.610 (2.961 | 2.412–54.627 (7.467) |
| [31] | mg/kg | 118.5–615.5 | 17.4–78.1 | 1.1–13.5 | - | - | 11.1–83.7 |
| [54] | mg/kg | 208.9–380.5 | 34.4–54.0 | 8.9–13.5 | 2.8–7.8 | 16.8–45.5 | 16.8–45.5 |
| [55] | mg/kg | - | 16.1 | 4.3 | 0.19 | 0.58 | - |
| [56] | mg/kg | - | 1.4 | 2.52 | 0.39 | 0.25 | - |
| [59] | mg/kg | - | - | 0.970–1.534 | - | - | 1.086–15.145 |
| [53] | mg/kg | 48.87–72.64 | 13.80–18.88 | 3.07–5.43 | - | 2.02–3.55 | 7.20–13.06 |
| [52] | mg/kg | 5.25–200.67 (94.531) | 13.03–26.41 (18.251) | - | - | - | - |
| [33] | mg/kg | 18.0–24.0 | 13.0–15.0 | 2.0–3.0 | - | - | 6.0–8.0 |
| [34] | mg/kg | 23.60–76.90 | 6.80–36.0 | 3.80–23.10 | - | - | 7.20–28.40 |
| [35] | mg/kg | 12.2–43.6 | 5.9–26.9 | 2.6–10.8 | - | - | 3.9–11.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voica, C.; Feher, I.; Puscas, R.; Iordache, A.M.; Cristea, G. Elemental and Isotopic Fingerprints of Potatoes. Foods 2025, 14, 2440. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142440
Voica C, Feher I, Puscas R, Iordache AM, Cristea G. Elemental and Isotopic Fingerprints of Potatoes. Foods. 2025; 14(14):2440. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142440
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoica, Cezara, Ioana Feher, Romulus Puscas, Andreea Maria Iordache, and Gabriela Cristea. 2025. "Elemental and Isotopic Fingerprints of Potatoes" Foods 14, no. 14: 2440. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142440
APA StyleVoica, C., Feher, I., Puscas, R., Iordache, A. M., & Cristea, G. (2025). Elemental and Isotopic Fingerprints of Potatoes. Foods, 14(14), 2440. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14142440