Nutritional Composition and Biological Activities of Donkey Milk: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Search Methodology
3. Nutrient Content of Donkey Milk
3.1. Proteins
3.2. Lipids
3.3. Carbohydrates
| Milk Compositions | Donkey Milk | Cow Milk | Human Milk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein (g/kg) | 12.5–21.8 | 31.0–38.0 | 9.0–17.0 |
| Fat (g/kg) | 1.0–14.0 | 35.0–39.0 | 35.0–40.0 |
| Lactose (g/kg) | 60.3–72.8 | 44.0–49.0 | 63.0–70.0 |
| Casein (g/kg) | 6.4–10.3 | 24.6–28.0 | 3.2–4.2 |
| Lactoalbumin (g/kg) | 4.9–9.3 | 5.5–7.0 | 6.8–8.3 |
3.4. Vitamins
3.5. Minerals
| Nutritional Classification | Specific Ingredients | Content |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin | Ve | 4.49 mg/kg |
| Vb1 | 4.44 μg/100 g | |
| Vb2 | 6.07 μg/100 g | |
| Vc | 5.16 mg/kg | |
| Minerals | Ca | 590 mg/kg |
| P | 513 mg/kg | |
| K | 438 mg/kg | |
| Na | 194 mg/kg | |
| Mg | 47.6 mg/kg | |
| Zn | 1.4 mg/kg | |
| Fe | 2.1 mg/kg | |
| Amino acids | Asp | 0.12% |
| Thr | 0.06% | |
| Ser | 0.07% | |
| Glu | 0.24% | |
| Gly | 0.02% | |
| Ala | 0.04% | |
| Cys | 0.04% | |
| Val | 0.07% | |
| Pro | 0.11% | |
| Mct | 0.05% | |
| Ilc | 0.06% | |
| Leu | 0.12% | |
| Tyr | 0.05% | |
| Phe | 0.10% | |
| Lys | 0.11% | |
| His | 0.04% | |
| Arg | 0.08% | |
| Proteins | CN | 6.11 g/kg |
| WP | 8.63 g/kg | |
| α-LA | 2.00 g/kg | |
| β-LG | 3.46 g/kg | |
| SA | 0.43 g/kg | |
| Ig | 0.16 g/kg | |
| LF | 0.33 g/kg | |
| LYS | 2.25 g/kg |
4. Biological Activity of Donkey Milk
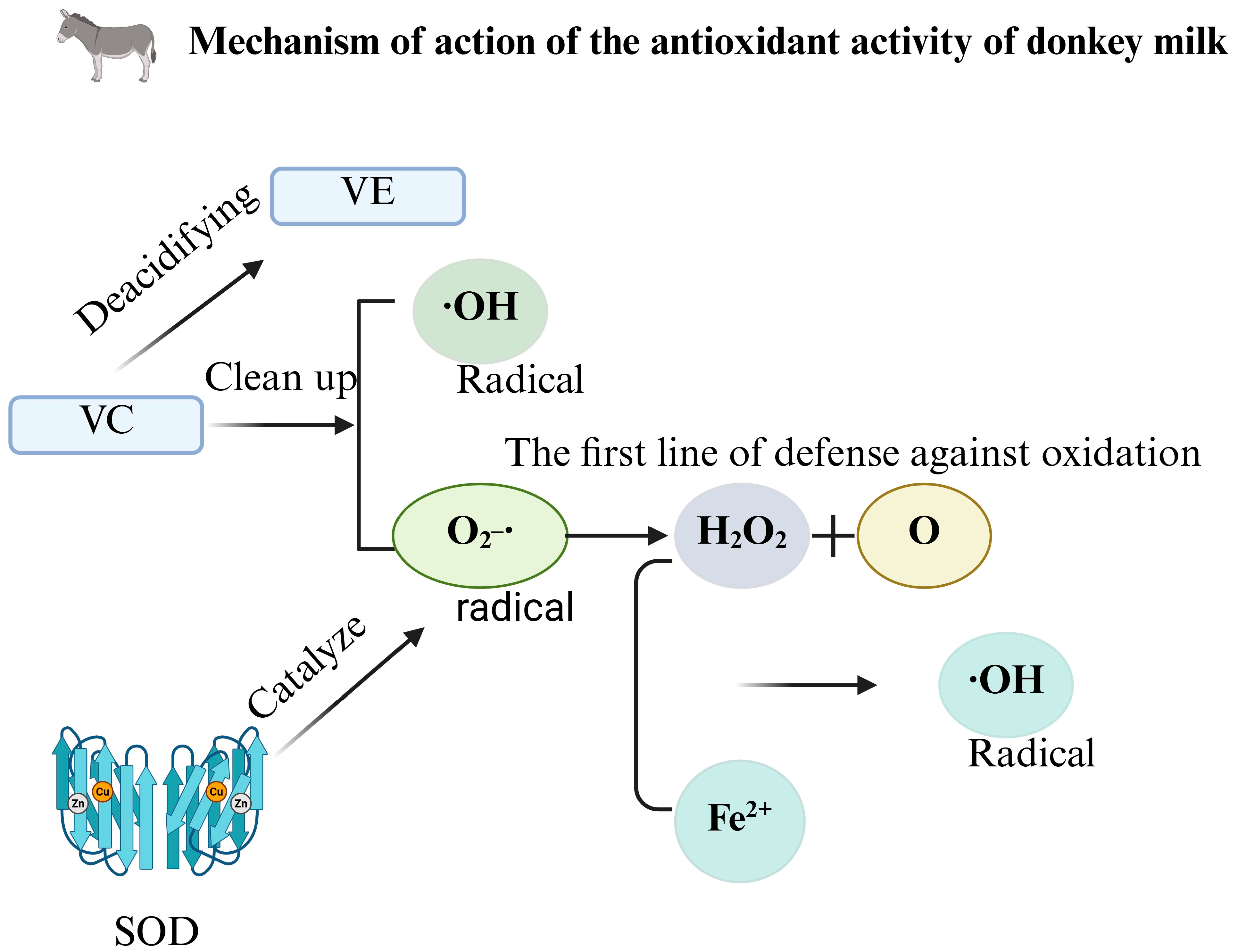
4.1. Antioxidant Activity
4.2. Antibacterial Activity
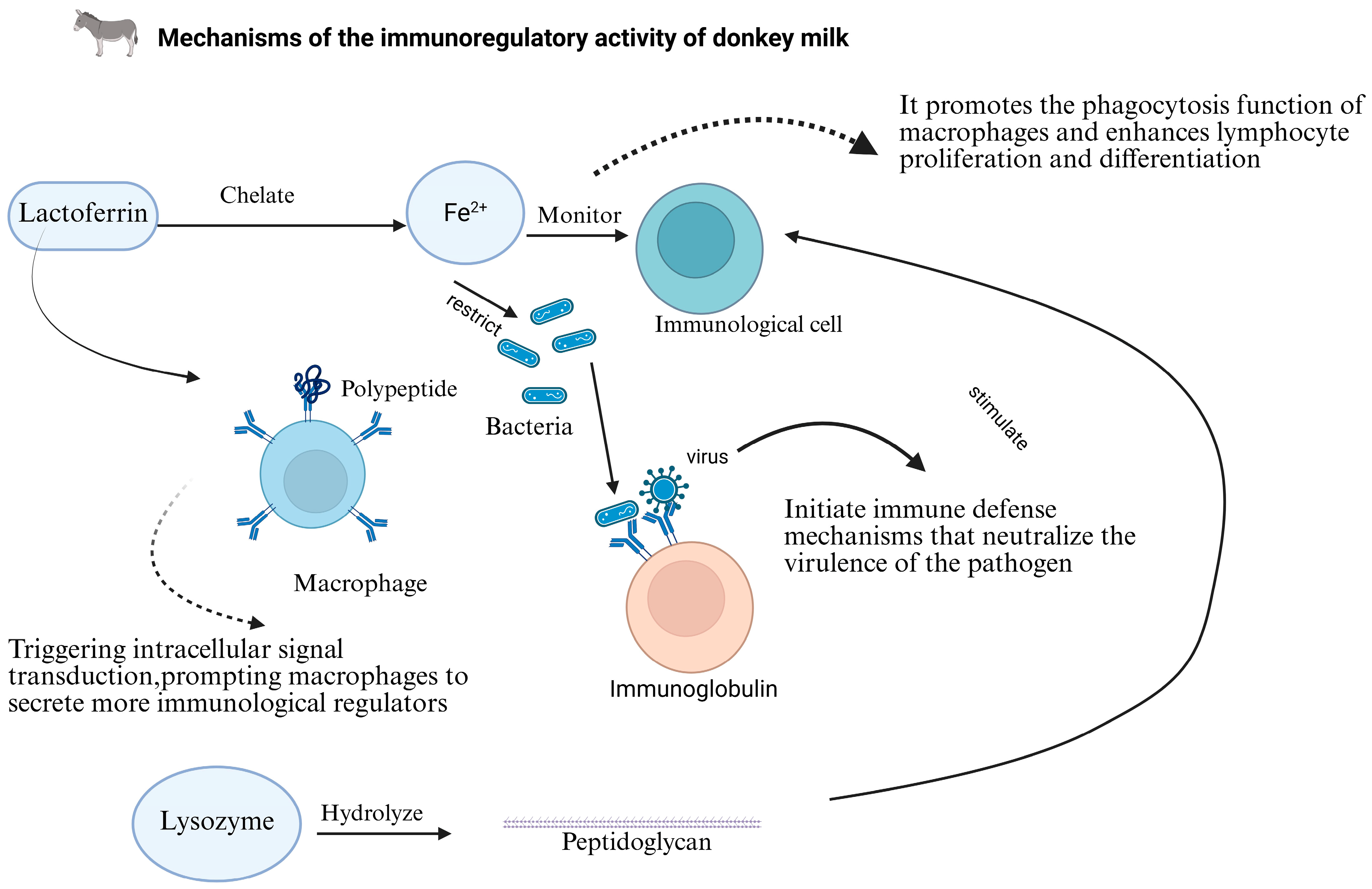
4.3. Immunomodulatory Activity
4.4. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
5. Applications of Donkey Milk
6. Challenges and Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hua, X.; A, M.; A, Y. Donkey origin, Chinese donkey breeds, and donkey output. Contemp. Livest. Poult. Breed. Ind. 2018, 3, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Hua, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, C. Origin, evolution, and research development of donkeys. Genes 2023, 13, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, G.F.; Lucena, J.E.C.; de Oliveira Barros, L. The current situation and trend of the donkey industry in South America. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2018, 65, 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Liu, G.; Wang, C. A survey report on the donkey original breeding farms in China: Current aspects and future prospective. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1126138. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, B.; Ren, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Chai, W. An Investigation of Genetic Diversity in Three Dezhou Donkey Original Breeding Farms. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11203. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, F. Feature milk: Animal husbandry sunrise industry? Agric. Econ. 2020, 12, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xue, F.; Cui, C. The current situation of the donkey industry in China. Anim. Husb. China 2025, 3, 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Keitshweditse, B.; Tsvakirai, C.Z.; Mabuza, M.L.; Tshehla, M. Towards the expansion of the functional dairy market: Determining donkey milk value propositions and identifying possible consumers. Future Foods 2024, 10, 100467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qu, H. Status and development of Shandong donkey industry. Heilongjiang Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2017, 24, 74–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C. Development status of donkey industry in Shandong Province. Feed Anim. Husb. 2019, 8, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H. Preliminary Study on the Development and Utilization of Donkey Milk in Xinjiang. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang Medical University, Xinjiang, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Ju, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, C. Progress and prospects of donkey milk. Dairy Cow Res. Cent. Shandong Acad. Agric. Sci. 2015, 8, 173–176. [Google Scholar]
- Derdak, R.; Sakoui, S.; Pop, O.L.; Muresan, C.I.; Vodnar, D.C.; Addoum, B.; Vulturar, R.; Chis, A.; Suharoschi, R.; Soukri, A.; et al. Insights on Health and Food Applications of Equus asinus (Donkey) Milk Bioactive Proteins and Peptides-An Overview. Foods 2020, 9, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertos, I.; López, M.; Jiménez, J.M.; Cao, M.J.; Corell, A.; Castro-Alija, M.J. Characterisation of Zamorano-Leonese donkey Milk as an alternative sustainably produced protein food. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 872409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.Z.; Chen, W.; Li, M.; Ren, W.; Huang, B.; Kou, X.; Wang, C. Is there sufficient evidence to support the health benefits of including donkey milk in the diet? Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1404998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Zhang, D.; Liu, P. Nutritional value and development and utilization of donkey milk. Dairy Ind. Sci. Technol. 2006, 6, 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Meena, S.; Meena, G.S.; Gautam, P.B.; Rai, D.C.; Kumari, S. A comprehensive review on donkey milk and its products: Composition, functionality and processing aspects. Food Chem. Adv. 2024, 4, 100647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; Altomonte, I.; Licitra, R. Nutritional and Nutraceutical Quality of Donkey Milk. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2018, 65, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomonte, I. Donkey milk can improve our health, and that’s why we should increase donkey milk production. J. Dairy Res. 2019, 86, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.P.; Vashisht, P.; Singh, L.; Awasti, N.; Sharma, S.; Mohan, C.; Charles, A.P.R. Donkey milk as a non-bovine alternative: A review of its nutri-functional properties, applications, and challenges. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 61, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, G.; Ji, C.; Fan, Z.; Ge, S.; Li, H.; Zhao, F. Comparative whey proteome profiling of donkey milk with human and cow milk. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 911454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proikakis, S.C.; Bouroutzika, E.V.; Anagnostopoulos, A.K.; Tsangaris, G.T. Proteomic data of Donkey’s Milk. Data Brief. 2021, 39, 107507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Shen, X.; Hong, R.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Yue, X.; Quek, S.Y. Unlocking the potential of donkey Milk: Nutritional composition, bioactive properties and future prospects. Food Res. Int. 2025, 209, 116307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimmino, F.; Catapano, A.; Villano, I.; Di Maio, G.; Petrella, L.; Traina, G.; Pizzella, A.; Tudisco, R.; Cavaliere, G. Invited review: Human, cow, and donkey milk comparison: Focus on metabolic effects. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 3072–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Luo, X.; Yue, X. Characterization and nutrition assessment of amino acids in different domains between donkey colostrum and mature milk. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 132, 106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Jiang, H. Analysis of the free amino acid composition of donkey milk and cow milk. China Dairy Ind. 2017, 10, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Vincenzetti, S.; Pucciarelli, S.; Polzonetti, V.; Polidori, P. Role of proteins and of some bioactive peptides on the nutritional quality of donkey milk and their impact on human health. Beverages 2017, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Kang, L. Characteristic chemical components and nutritional value of donkey milk. Jiangxi J. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2017, 4, 65–67. [Google Scholar]
- Cunsolo, V.; Saletti, R.; Muccilli, V.; Gallina, S.; Di Francesco, A.; Foti, S. Proteins and bioactive peptides from donkey milk: The molecular basis for its reduced allergenic properties. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martemucci, G.; D’Alessandro, A.G. Fat content, energy value and fatty acid profile of donkey milk during lactation and implications for human nutrition. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contarini, G.; Pelizzola, V.; Scurati, S.; Povolo, M. Polar lipid of donkey milk fat: Phospholipid, ceramide and cholesterol composition. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 57, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.Y.; Pang, K.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, L.; Chen, S.W.; Dong, M.L.; Ren, F.Z. Composition, physiochemical properties, nitrogen fraction distribution, and amino acid profile of donkey milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Li, X.; Shabilhaz, Y. Components test of Jiangyue donkey milk. China Dairy Ind. 2006, 34, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Baiocchi, C.; Mussap, M.; Galvano, F.; Conti, A. Donkey’s milk detailed lipid composition. Front. Biosci. 2010, 2, 537–546. [Google Scholar]
- Luoyizha, W.; Li, H.; Xu, L.; Xu, Z.Z.; Liao, X.J. Metabolomic and lipidomic analysis of donkey milk from Xinjiang and Shandong. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 325–333. [Google Scholar]
- Baloš, M.Ž.; Pelić, D.L.; Jakšić, S.; Lazić, S. Donkey milk: An overview of its chemical composition and main nutritional properties or human health benefit properties. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2023, 121, 104225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, H.; Xu, T. Chemocomposition and biological activity of donkey milk. J. Food Saf. Qual. Test. 2017, 12, 4574–4581. [Google Scholar]
- Vincenzetti, S.; Santini, G.; Polzonetti, V.; Pucciarelli, S.; Klimanova, Y.; Polidori, P. Vitamins in human and donkey milk: Functional and nutritional role. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garhwal, R.; Bhardwaj, A.; Sangwan, K.; Mehra, R.; Pal, Y.; Nayan, V.; Kumar, H. Milk from Halari donkey breed: Nutritional analysis, vitamins, minerals, and amino acids profiling. Foods 2023, 12, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, M.; Altomonte, I.; Licitra, R.; Salari, F. Technological and seasonal variations of vitamin D and other nutritional components in donkey milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8721–8725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantuz, F.; Ferraro, S.; Todini, L.; Cimarelli, L.; Fatica, A.; Marcantoni, F.; Salimei, E. Distribution of calcium, phosphorus, sulfur, magnesium, potassium, and sodium in major fractions of donkey milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 8741–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantuz, F.; Maglieri, C.; Lebboroni, G.; Salimei, E. Ca, Mg, Zn, Fe, Cu and Mn content of ass’s milk. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 8 (Suppl. S2), 703–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y. Determination of trace elements in donkey milk. Anim. Husb. Feed. Sci. 2012, 33, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Fantuz, F.; Ferraro, S.; Todini, L.; Spurio, R.; Fatica, A.; Marcantoni, F.; Salimei, E. Distribution of selected trace elements in the major fractions of donkey milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 6422–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garhwal, R.; Sangwan, K.; Mehra, R.; Kumar, N.; Bhardwaj, A.; Pal, Y.; Kumar, H. A systematic review of the bioactive components, nutritional qualities and potential therapeutic applications of donkey milk. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2022, 115, 104006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simos, Y.; Metsios, A.; Verginadis, I.; D’Alessandro, A.G.; Loiudice, P.; Jirillo, E.; Karkabounas, S. Antioxidant and anti-platelet properties of milk from goat, donkey and cow: An in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo study. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 21, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. Extraction and purification, functional characteristics, and antioxidant activity analysis of donkey serum albumin in CCA. Food Ind. Technol. 2024, 45, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.; Guo, H. The nutritional ingredients and antioxidant activity of donkey milk and donkey milk powder. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Kumari, P.; Nayan, V.; Legha, R.A.; Gautam, U.; Pal, Y.; Tripathi, B.N. Estimation of Antioxidant Potential of Indigenous Halari and French Poitu Donkey Milk by using the Total Antioxidant Capacity and Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power Essay. Asian J. Dairy Food Res. 2019, 38, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Shaikh, A.S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Tan, H. Dezhou donkey (Equus asinus) milk a potential treatment strategy for type 2 diabetes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 246, 112221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akan, E. An evaluation of the in vitro antioxidant and antidiabetic potentials of camel and donkey milk peptides released from casein and whey proteins. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 3743–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šarić, L.; Pezo, L.; Krulj, J.; Tomić, J.; Plavšić, D.; Jovanov, P.; Matić, M. Antibacterial activity of donkey’s milk against clinical isolate of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mljekarstvo ČasopisUnaprjeđenje Proizv. Prerade Mlijeka 2022, 72, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidona, F.; Sekse, C.; Criscione, A.; Jacobsen, M.; Bordonaro, S.; Marletta, D.; Vegarud, G.E. Antimicrobial effect of donkeys’ milk digested in vitro with human gastrointestinal enzymes. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spada, V.; Ferranti, P.; Chianese, L.; Salimei, E.; Addeo, F.; Picariello, G. Antibacterial potential of donkey’s milk disclosed by untargeted proteomics. J. Proteom. 2021, 231, 104007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, Q.; Khan, Z.M.; Wang, M.; Xiang, F.; Zhang, X.; Kou, X.; Li, S.; Wang, C.; Li, Y. Proteomic Profiling of Donkey Milk Exosomes Highlights Bioactive Proteins with Immune-Related Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; Salari, F.; Licitra, R.; La Motta, C.; Altomonte, I. Lysozyme activity in donkey milk. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 96, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinhua, W.X. The new force of the donkey milk Guard, lysozyme. Anim. Husb. Xinjiang 2012, 12, 62–63. [Google Scholar]
- Veronesi, M.C.; Dall’ Ara, P.; Gloria, A.; Servida, F.; Sala, E.; Robbe, D. IgG, IgA, and lysozyme in Martina Franca donkey jennies and their foals. Theriogenology 2014, 81, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brumini, D.; Criscione, A.; Bordonaro, S.; Vegarud, G.E.; Marletta, D. Whey proteins and their antimicrobial properties in donkey milk: A brief review. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2016, 96, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massouras, T.; Bitsi, N.; Paramithiotis, S.; Manolopoulou, E.; Drosinos, E.H.; Triantaphyllopoulos, K.A. Microbial profile antibacterial properties and chemical composition of raw donkey milk. Animals 2020, 10, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amati, L.; Marzulli, G.; Martulli, M.; Tafaro, A.; Jirillo, F.; Pugliese, V.; Jirillo, E. Donkey and goat milk intake and modulation of the human aged immune response. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Lau, K.Y.; Chen, J.L.; Chu, P.Y.; Huang, C.T.; Wang, W.L.; Tseng, L.M. Anti-cancer and immunomodulatory effects of cobimetinib in triple negative breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecocci, S.; Pietrucci, D.; Milanesi, M.; Pascucci, L.; Filippi, S.; Rosato, V.; Cappelli, K. Transcriptomic characterization of cow, donkey and goat milk extracellular vesicles reveals their anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, W.; Zheng, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G.; Li, L.; Zhang, N. Donkey milk inhibits tumor growth by inducing apoptosis, pyroptosis and modulation of Th1/Th2 responses in a 4T1 murine breast cancer model. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 118, 106256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liu, G.; Wang, C. Effects of donkey milk on oxidative stress and inflammatory response. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e13935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yvon, S.; Olier, M.; Leveque, M.; Jard, G.; Tormo, H.; Haimoud-Lekhal, D.A.; Eutamène, H. Donkey milk consumption exerts anti-inflammatory properties by normalizing antimicrobial peptides levels in Paneth’s cells in a model of ileitis in mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirillo, F.; Magrone, T. Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic properties of donkey’s and goat’s milk. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord.-Drug Targets (Former. Curr. Drug Targets-Immune Endocr. Metab. Disord.) 2014, 14, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirillo, F.; Jirillo, E.; Magrone, T. Donkey’s and goat’s milk consumption and benefits to human health with special reference to the inflammatory status. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinchese, G.; Cavaliere, G.; Canani, R.B.; Matamoros, S.; Bergamo, P.; De Filippo, C.; Mollica, M.P. Human, donkey and cow milk differently affects energy efficiency and inflammatory state by modulating mitochondrial function and gut microbiota. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huimin, C.; Peng, W.; Man, C.; Hong, L.; Yuxin, Z.; Zhiyu, P.; Jianjun, Y. Donkey milk supplementation alleviates renal fibrosis of chronic kidney disease by enhancing anti-inflammatory ability. J. Dairy Sci. 2025, 108, 1198–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, M.; Altomonte, I.; Tricò, D.; Lapenta, R.; Salari, F. Current knowledge on functionality and potential therapeutic uses of donkey milk. Animals 2021, 11, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarti, L.; Martini, M.; Brajon, G.; Barni, S.; Salari, F.; Altomonte, I.; Novembre, E. Donkey’s Milk in the Management of Children with Cow’s Milk protein allergy: Nutritional and hygienic aspects. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2019, 45, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiofalo, B.; Dugo, P.; Bonaccorsi, I.L.; Mondello, L. Comparison of major lipid components in human and donkey milk: New perspectives for a hypoallergenic diet in humans. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2011, 33, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenzetti, S.; Foghini, L.; Pucciarelli, S.; Polzonetti, V.; Cammertoni, N.; Beghelli, D.; Polidori, P. Hypoallergenic properties of donkey’s milk: A preliminary study. Vet Ital. 2014, 50, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Barni, S.; Sarti, L.; Mori, F.; Muscas, G.; Belli, F.; Pucci, N.; Novembre, E. Tolerability and palatability of donkey’s milk in children with cow’s milk allergy. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 29, 329–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessandri, C.; Mari, A. Efficacy of donkey’s milk in treating cow’s milk allergic children: Major concerns. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2007, 18, 625–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polidori, P.; Vincenzetti, S. Use of donkey milk in children with cow’s milk protein allergy. Foods 2013, 2, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, G.; Potortì, A.G.; Turco, V.L.; Licata, P.; Rastrelli, L.; Dugo, G. Donkey’s milk safety: POCs and PCBs levels and infant daily intake. Food Control. 2014, 46, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertino, E.; Agosti, M.; Peila, C.; Corridori, M.; Pintus, R.; Fanos, V. The donkey milk in infant nutrition. Nutrients 2022, 14, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souroullas, K.; Aspri, M.; Papademas, P. Donkey milk as a supplement in infant formula: Benefits and technological challenges. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H. Medicine and food for infants with donkey milk. Xinjiang Anim. Husb. 2013, 2, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Salvo, E.D.; Conte, F.; Casciaro, M.; Gangemi, S.; Cicero, N. Bioactive natural products in donkey and camel milk: A perspective review. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 37, 2098–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, C.; Plastina, P.; Abrego-Guandique, D.M.; Caputo, P.; Oliviero Rossi, C.; Saraceno, G.F.; Fazio, A. Characterization of exopolysaccharides isolated from donkey milk and its biological safety for skincare applications. Polysaccharides 2024, 5, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C. Autumn and winter beauty, donkey milk first! Xinjiang Anim. Husb. 2013, 2, 62. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y. Skin care effects of donkey milk and its application in cosmetics. China Dairy Ind. 2024, 3, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, J. Sarula. Research Advances on Major Components and Values of Donkey Milk and Its Application in Cosmetics. Anim. Husb. Feed Sci. 2021, 42, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; He, H.; Chen, Y.; Liao, F.; Tang, J.; Li, L.; Xiong, L. Effects of donkey milk on UVB-induced skin barrier damage and melanin pigmentation: A network pharmacology and experimental validation study. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1121498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Opportunities and Challenges of the Donkey Industry Development in Xinjiang. Herbiv. Domest. Anim. 2014, 1, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Seyiti, S.; Kelimu, A. Donkey industry in China: Current aspects, suggestions and future challenges. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2021, 102, 103642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Z.; Shi, X. Overview of innovative utilization of Texas donkey germplasm resources. Anim. Husb. China. 2022, 12, 56–58. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. Attach importance to the protection and utilization of germplasm resources to strengthen and optimize the donkey industry. Anim. Husb. Ind. 2022, 3, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Chen, H. The Development Trend and Measures of China’s Donkey Industry. J. Domest. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 2, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Song, R.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, X. Progress in the nutritional composition and detection methods of donkey milk. Livest. Vet. Today. 2024, 40, 71–73. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, C.; Song, W.; Chen, L. A comparative study of the nutritional differences between donkey milk and Holstein milk in Xinjiang. Dairy Cows China 2024, 11, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Sun, F. Research on the optimization of regional donkey industry business model. J. Hebei North Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 40, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, X.; Li, Y.; Lv, Y. Research on the development opportunities and countermeasures of donkey industry in Dezhou city under the new situation. China Livest. Poult. Seed Indust. 2023, 19, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, F.; Dalla Costa, E.; Burden, F.; Judge, A.; Minero, M. The development of guidelines to improve dairy donkey management and welfare. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 18, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S. Discussion on the development and utilization direction of donkey resources. J. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2011, 30, 39–40+42. [Google Scholar]
- Aspri, M.; Economou, N.; Papademas, P. Donkey milk: An overview on functionality, technology, and future prospects. Food Rev. Int. 2017, 33, 316–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Q.; Wei, L.; Chen, X.; Zhu, H.; Wei, J.; Zhu, M.; Khan, M.Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z. Nutritional Composition and Biological Activities of Donkey Milk: A Narrative Review. Foods 2025, 14, 2337. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132337
Xu Q, Wei L, Chen X, Zhu H, Wei J, Zhu M, Khan MZ, Wang C, Zhang Z. Nutritional Composition and Biological Activities of Donkey Milk: A Narrative Review. Foods. 2025; 14(13):2337. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132337
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Qingyu, Lin Wei, Xiuwen Chen, Hongzhen Zhu, Jinjin Wei, Mingxia Zhu, Muhammad Zahoor Khan, Changfa Wang, and Zhenwei Zhang. 2025. "Nutritional Composition and Biological Activities of Donkey Milk: A Narrative Review" Foods 14, no. 13: 2337. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132337
APA StyleXu, Q., Wei, L., Chen, X., Zhu, H., Wei, J., Zhu, M., Khan, M. Z., Wang, C., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Nutritional Composition and Biological Activities of Donkey Milk: A Narrative Review. Foods, 14(13), 2337. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14132337









