Dietary Flaxseed Oil and Its Blended Oil Alleviate High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice by Improving Lipid Metabolism and Regulating Gut Microbiota
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Blended Oil and Animal Diets
2.2. Animals and Modeling
2.3. Measurement of Fasting Glycemia and Serum/Liver Biochemical Indexes
2.4. Histopathological Analysis
2.5. Assessment of SCFAs in Colon Contents
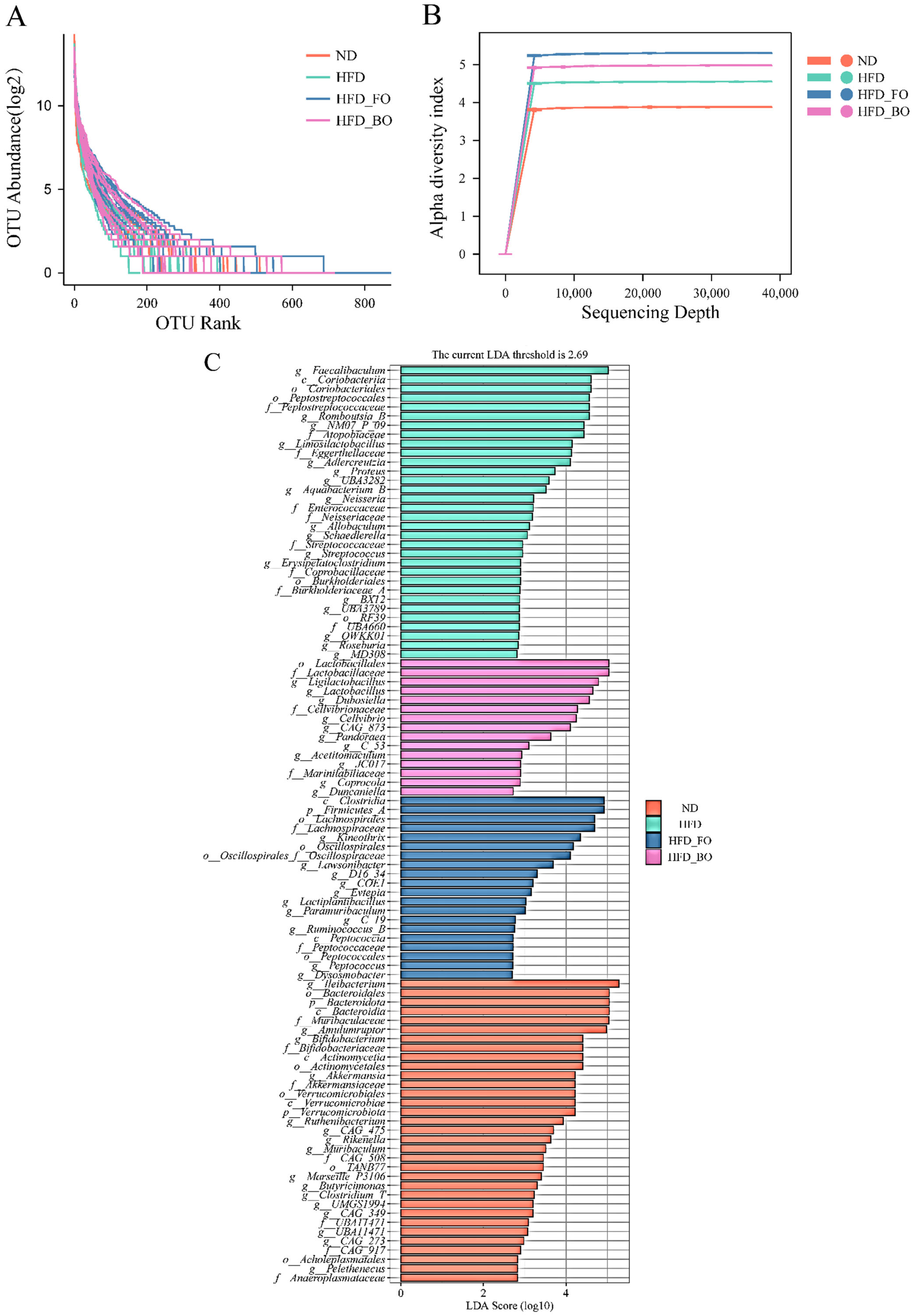
2.6. Gut Microbiota
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
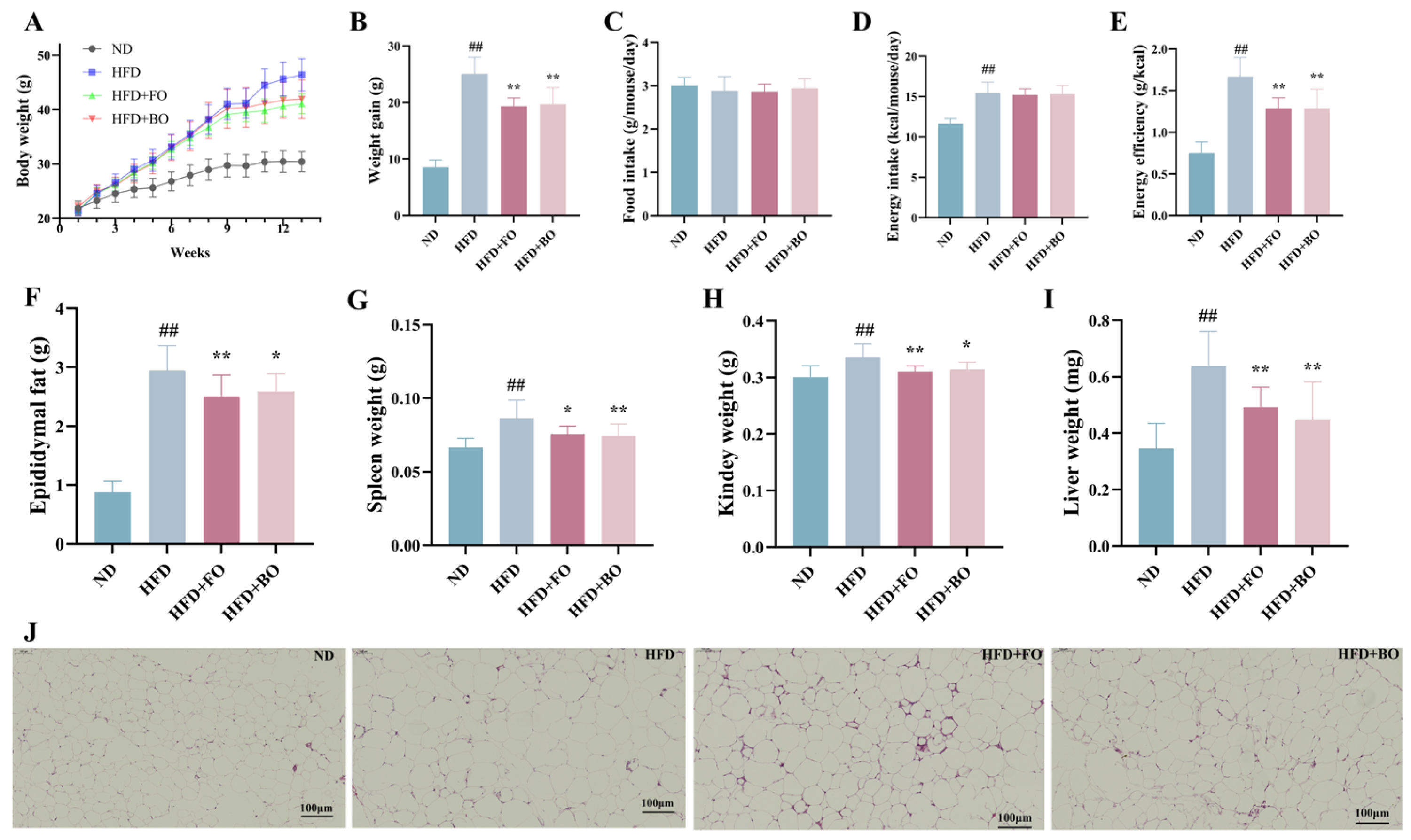
3.1. Flaxseed Oil and Blended Oil Alleviated Body Weight Gain and Fat Accumulation in HFD-Fed Mice
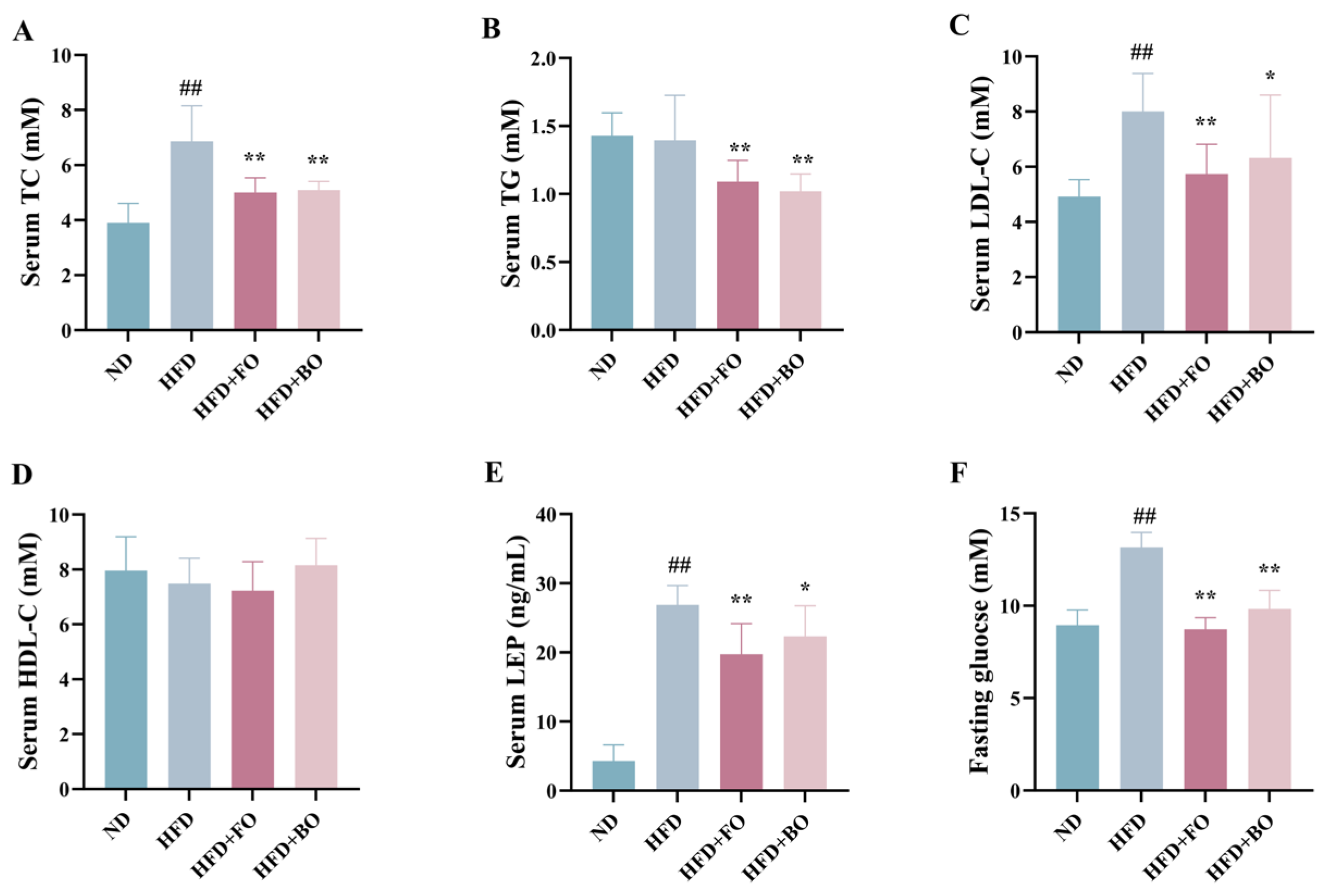
3.2. Flaxseed Oil and Blended Oil Lowered Serum Lipid and Blood Glucose Levels in HFD-Fed Mice
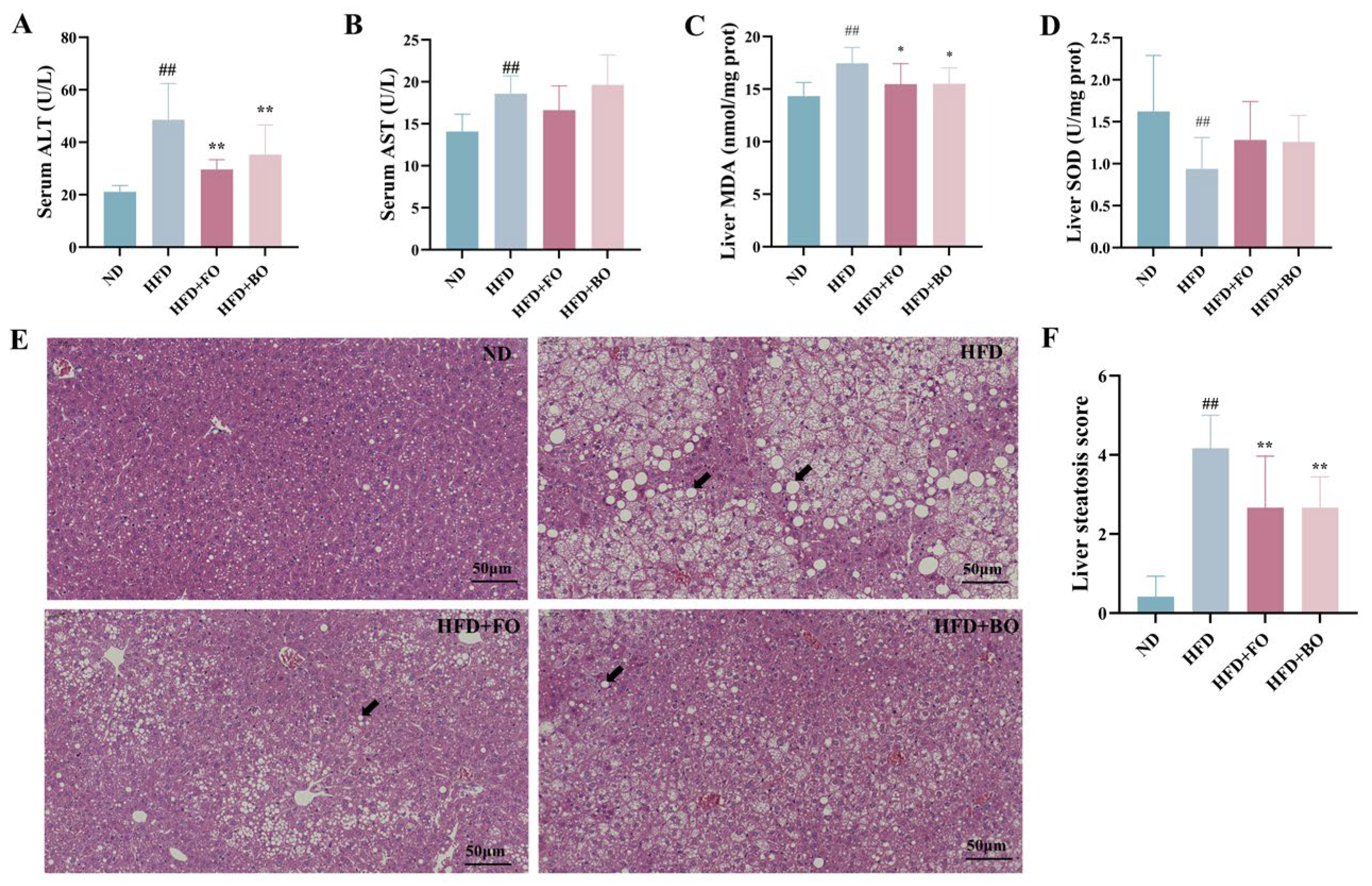
3.3. Flaxseed Oil and Blended Oil Ameliorated Hepatic Steatosis and Oxidative Stress in HFD-Fed Mice
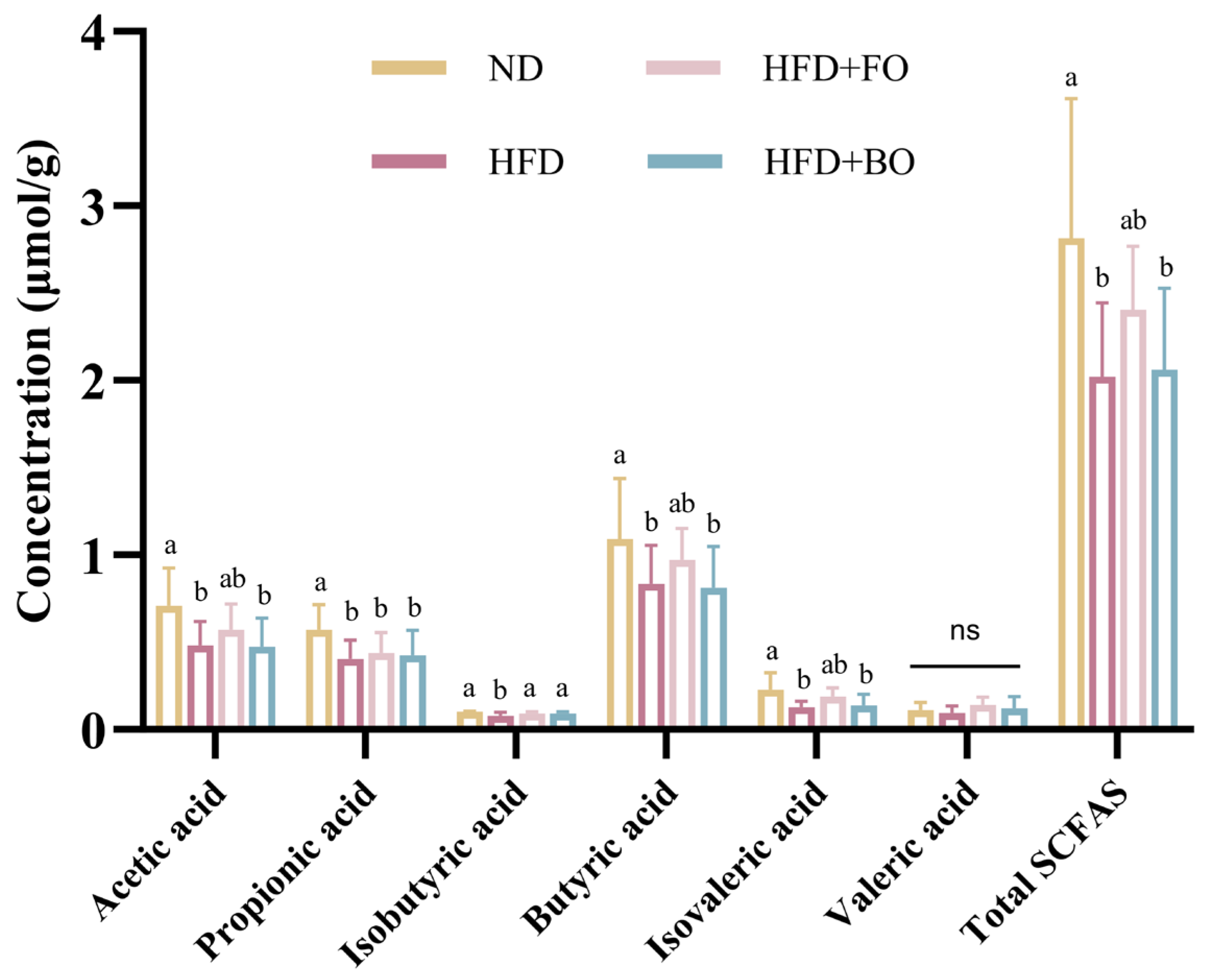
3.4. Flaxseed Oil and Blended Oil Promoted the Production of SCFAs in the Colon Contents
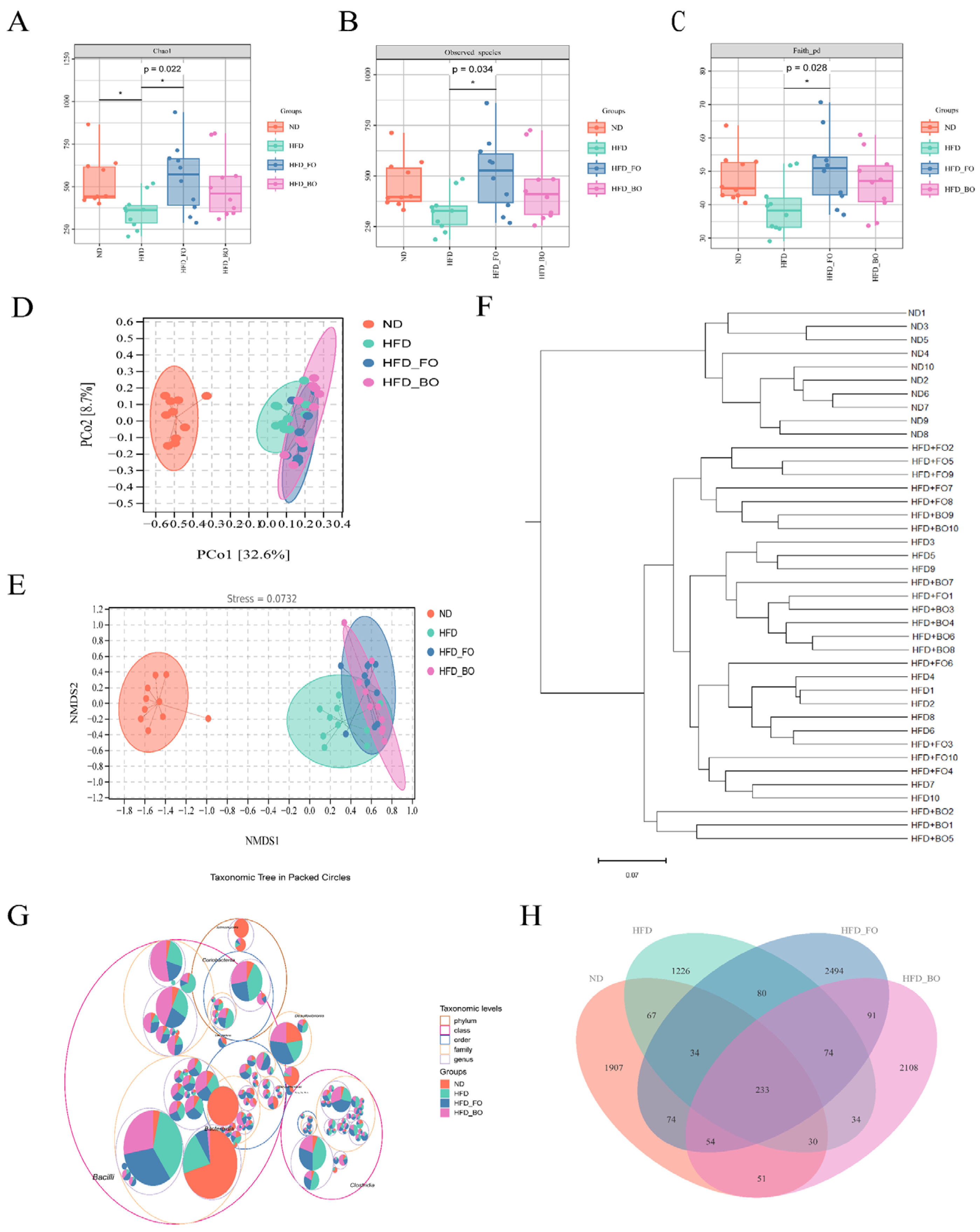
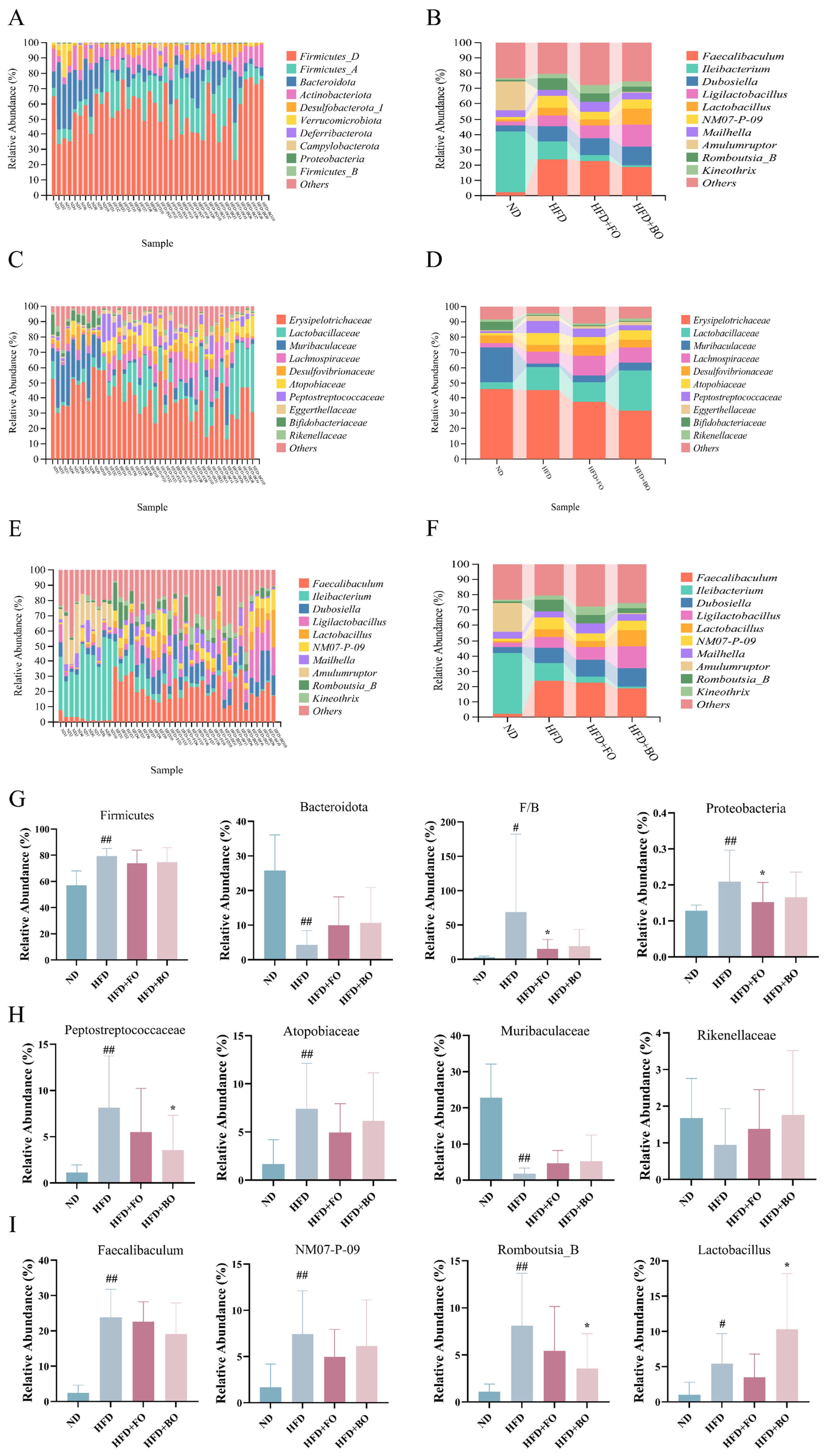
3.5. Flaxseed Oil and Blended Oil Ameliorated the HFD-Induced Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis
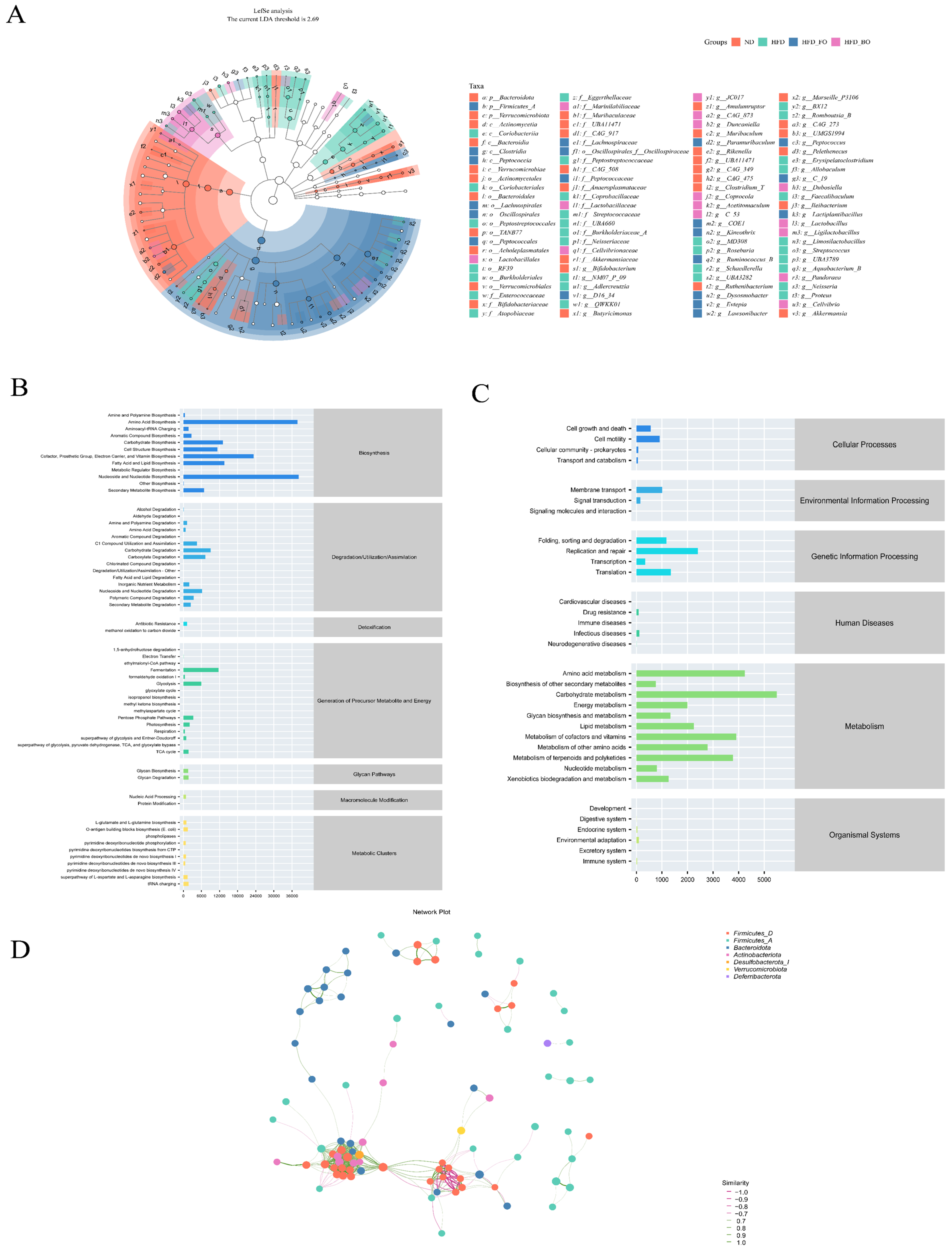
3.6. Prediction of Gut Microbial Metabolism Using PICRUSt2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Özkılıç, S.; Arslan, D. Acidic and enzymatic pre-treatment effects on cold-pressed pumpkin, terebinth and flaxseed oils. Grasas Y Aceites 2022, 73, e462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Madhagy, S.; Ashmawy, N.S.; Mamdouh, A.; Eldahshan, O.A.; Farag, M.A. A comprehensive review of the health benefits of flaxseed oil in relation to its chemical composition and comparison with other omega-3-rich oils. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Singh, B.; Kaur, A.; Singh, N. Chemical, thermal, rheological and FTIR studies of vegetable oils and their effect on eggless muffin characteristics. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e13978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, H.; Yang, X.; Ma, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, G.; Chen, X.; Ma, L.; Gao, J.; Ji, W. Associations of ω-3, ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids intake and ω-6: ω-3 ratio with systemic immune and inflammatory biomarkers: NHANES 1999–2020. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1410154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Q.; Lee, Y.-Y.; Li, K.-y.; Li, W.-z.; Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, G.-y.; Reaney, M.T.; Cai, Z.-z.; Wang, Y. Status of linusorbs in cold-pressed flaxseed oil during oxidation and their response toward antioxidants. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamyradova, N.; Özkılıç, S.Y.; Arslan, D. Blanching of olive fruits before storage at different conditions: Effects on oil yield, lipase activity and oxidation. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashempour-Baltork, F.; Torbati, M.; Azadmard-Damirchi, S.; Savage, G.P. Vegetable oil blending: A review of physicochemical, nutritional and health effects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 57, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratner, R.E. An Update on The Diabetes Prevention Program. Endocr. Pract. 2006, 12, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Laybutt, D.R.; Youngson, N.A.; Morris, M.J. Concurrent betaine administration enhances exercise-induced improvements to glucose handling in obese mice. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 2439–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.N.M.S.; Sultana, H.; Nazmul Hassan Refat, M.; Farhana, Z.; Abdulbasah Kamil, A.; Meshbahur Rahman, M. The global burden of overweight-obesity and its association with economic status, benefiting from STEPs survey of WHO member states: A meta-analysis. Prev. Med. Rep. 2024, 46, 102882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhu, L.; Ke, H.; Jiang, S.; Zeng, M. Oyster (Crassostrea gigas) polysaccharide ameliorates obesity in association with modulation of lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in high-fat diet fed mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kałużna-Czaplińska, J.; Gątarek, P.; Chartrand, M.S.; Dadar, M.; Bjørklund, G. Is there a relationship between intestinal microbiota, dietary compounds, and obesity? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 70, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Lui, E.M.K.; Xiao, M. Pu-erh tea ameliorates obesity and modulates gut microbiota in high fat diet fed mice. Food Res. Int. 2021, 144, 110360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Xia, B.; Jin, X.; Zou, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Zhao, W.; Yan, S.; Li, L.; Yuan, S.; et al. High-fiber diet mitigates maternal obesity-induced cognitive and social dysfunction in the offspring via gut-brain axis. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 923–938.e926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahe, L.K.; Astrup, A.; Larsen, L.H. Can We Prevent Obesity-Related Metabolic Diseases by Dietary Modulation of the Gut Microbiota? Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Sierra, A.; Ramos-Lopez, O.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Milagro, F.I.; Martinez, J.A. Diet, Gut Microbiota, and Obesity: Links with Host Genetics and Epigenetics and Potential Applications. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S17–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum P101-fermented Luffa cylindrica juice alleviate F-53B-induced liver steatosis in mice via the gut-liver axis. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves-de-Oliveira, D.S.; Bloise, A.M.N.L.G.; Silva, L.M.L.; Rocha-Junior, R.L.; Lima-Júnior, N.C.; Menezes, L.G.S.; Silva, E.G.S.; De Oliveira, Y.; Wanderley, A.G.; de-Brito-Alves, J.L.; et al. Maternal consumption of ɷ3 attenuates metabolic disruption elicited by saturated fatty acids-enriched diet in offspring rats. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarebanhassanabadi, M.; Shahriari Kalantari, M.; Boffetta, P.; Beiki, O.; Pakseresht, M.; Sarrafzadegan, N.; Mirzaei, M.; Kraemer, A.; Seyedhosseini, S.; Mali, S.; et al. Dietary habits and the 10-year risk of overweight and obesity in urban adult population: A cohort study predicated on Yazd Healthy Heart Project. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alim, M.A.; Mumu, T.J.; Tamanna, U.S.; Khan, M.M.; Miah, M.I.; Islam, M.S.; Jesmin, Z.A.; Khan, T.; Hasan, M.R.; Alam, M.J.; et al. Hypolipidemic effect and modulation of hepatic enzymes by different edible oils in obese Wistar rats. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seike, M.; Ashida, H.; Yamashita, Y. Dietary flaxseed oil induces production of adiponectin in visceral fat and prevents obesity in mice. Nutr. Res. 2024, 121, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, N.; Hickey, M.; Shams, R.; Rivera, C.F.; Vlahos, J.; Cense, H.A.; Demirkiran, A.; Ramkhelawon, B.; Houdijk, A.P.J. Oral ω-3 PUFA supplementation modulates inflammation in adipose tissue depots in morbidly obese women: A randomized trial. Nutrition 2023, 111, 112055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jangale, N.M.; Devarshi, P.P.; Dubal, A.A.; Ghule, A.E.; Koppikar, S.J.; Bodhankar, S.L.; Chougale, A.D.; Kulkarni, M.J.; Harsulkar, A.M. Dietary flaxseed oil and fish oil modulates expression of antioxidant and inflammatory genes with alleviation of protein glycation status and inflammation in liver of streptozotocin–nicotinamide induced diabetic rats. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranowski, M.; Enns, J.; Blewett, H.; Yakandawala, U.; Zahradka, P.; Taylor, C.G. Dietary flaxseed oil reduces adipocyte size, adipose monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 levels and T-cell infiltration in obese, insulin-resistant rats. Cytokine 2012, 59, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Xu, Z.; Huang, Q.; Wang, X.; Huang, F.; Deng, Q. Targeted microbiome metabolomics reveals flaxseed oil supplementation regulated the gut microbiota and farnesoid X receptor pathway in high-fat diet mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 2324–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO; FAO. Expert Consultation on Fats and Fatty Acids in Human Nutrition. Interim Summary of Conclusions and Dietary Recommendations on Total Fat & Fatty Acids. In World Health Organization Technical Report Series; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; pp. 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.-c.; Lin, H.; Li, Y.-t.; Zeng, Z.-l.; Yu, P.; Wen, X.-f. Effect of CCSKO on the body fat and serum lipid levels in obese mice induced by high-fat diet. China Oils Fats 2020, 45, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedossa, P.; Poitou, C.; Veyrie, N.; Bouillot, J.L.; Basdevant, A.; Paradis, V.; Tordjman, J.; Clement, K. Histopathological algorithm and scoring system for evaluation of liver lesions in morbidly obese patients. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shu, N.; Lei, Z.; Huishu, L.; Xueli, Y.; Qiang, Z.; Liwen, Z.; Liqiong, G.; Shoufang, J.; Naijun, T. Effects of PM2.5 and high-fat diet on glucose and lipid metabolisms and role of MT-COX3 methylation in male rats. Environ. Int. 2024, 188, 108780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, K.S.; Soares, N.L.; Dorand, V.A.M.; Alves, A.F.; Lima, M.S.; Pereira, R.A.; Souza, E.L.; Magnani, M.; Persuhn, D.C.; Aquino, J.S. Acerola fruit by-product alleviates lipid, glucose, and inflammatory changes in the enterohepatic axis of rats fed a high-fat diet. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, T. Extracellular vesicle miRNAs as key mediators in diet-gut microbiome-host interplay. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 136, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Wang, Q.; Yu, T.; Hu, H.; Wu, G.; Duan, X.; Jiang, R.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y. Quercetin ameliorates bone loss in OVX rats by modulating the intestinal flora-SCFAs-inflammatory signaling axis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 136, 112341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, J.; Yan, C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, D.; Li, S.; Xia, X. Punicalagin ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice through strengthening gut barrier, decreasing oxidative stress and downregulating inflammation via AMPK–NF–κB-STAT3 pathway. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Gu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Z.; Bian, Y. Naringenin prevents NAFLD in the diet-induced C57BL/6J obesity model by regulating the intestinal barrier function and microbiota. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 105, 105578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Yang, L.; Xie, M.; Yu, M.; Shi, T. Peanut-natto improved obesity of high-fat diet mice by regulating gut microbiota and lipid metabolism. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 112, 105956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.-W.; Chung, K.-S.; Heo, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-R.; Na, C.-S.; Ahn, H.-S.; Shin, Y.-K.; Lee, K.-T. Anti-obesity effect of standardized ethanol extract from the leaves of Adenocaulon himalaicum Edgew. via regulation of adipogenesis and lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells and high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 119, 106323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bays, H.E.; Fitch, A.; Christensen, S.; Burridge, K.; Tondt, J. Anti-Obesity Medications and Investigational Agents: An Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) Clinical Practice Statement (CPS) 2022. Obes. Pillars 2022, 2, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, A.; Gan, R.-Y.; Xu, X.-Y.; Mao, Q.-Q.; Zhang, P.-Z.; Li, H.-B. Effects and mechanisms of edible and medicinal plants on obesity: An updated review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2061–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Ren, F.; Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, H. Lactoferrin attenuates high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis and lipid metabolic dysfunctions by suppressing hepatic lipogenesis and down-regulating inflammation in C57BL/6J mice. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4328–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, D.; Cook, C.; Santanam, N. Omega 3 rich diet modulates energy metabolism via GPR120-Nrf2 crosstalk in a novel antioxidant mouse model. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 466–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, F.; Xu, Z.; Yin, A.; Yin, H.; Li, C.; Chen, S.-Y. DOCK2 deficiency mitigates HFD-induced obesity by reducing adipose tissue inflammation and increasing energy expenditure. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, A.; Korac, A.; Buzadzic, B.; Otasevic, V.; Stancic, A.; Daiber, A.; Korac, B. Redox implications in adipose tissue (dys)function—A new look at old acquaintances. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Hu, X.; Li, S.; Li, T. Vitexin-rhamnoside encapsulated with zein-pectin nanoparticles relieved high-fat diet induced lipid metabolism disorders in mice by altering the gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264, 130704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Park, S.; Lim, Y.; Han, S.N. Dietary supplementation with Korean pine nut oil decreases body fat accumulation and dysregulation of the appetite-suppressing pathway in the hypothalamus of high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2022, 16, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skurk, T.; Alberti-Huber, C.; Herder, C.; Hauner, H. Relationship between adipocyte size and adipokine expression and secretion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, F.; Du, L.; Peng, D.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. Fermented fruits ameliorate obesity by controlling food intake and regulating lipid metabolism in high-fat dietary mice. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 114, 106072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoe, S.; Kato, M.; Yamatoya, K. Effect of galactose-depleted and intact xyloglucan intake on glucose and lipid metabolism in diet-induced obese mice. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 113, 106026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjahjono, Y.; Foe, K.; Ratnasari Wilianto, Y.; Christianto Khudrati, W.; Yesery Esar, S.; Jafet, N.; Made Andika Bara Kusuma, I.; Ade, L.; Dian Novita, B.; Wihadmadyatami, H.; et al. HP inulin-MCT dietary fiber improves lipid metabolism and prevents non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in obese mice. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 120, 106367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura-Assis, A.; Afonso, M.S.; de Oliveira, V.; Morari, J.; dos Santos, G.A.; Koike, M.; Lottenberg, A.M.; Ramos Catharino, R.; Velloso, L.A.; Sanchez Ramos da Silva, A.; et al. Flaxseed oil rich in omega-3 protects aorta against inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress partially mediated by GPR120 receptor in obese, diabetic and dyslipidemic mice models. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 53, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Huang, S.; Deng, Q.; Tang, Y.; Yao, P.; Tang, H.; Dong, X. Flaxseed oil improves hepatic insulin resistance in obese mice through modulating mitochondrial quality control. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 53, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Bu, T.; Yang, Y.; Ni, Q. Enhancing β-cell function and identity in type 2 diabetes: The protective role of Coptis deltoidea C. Y. Cheng et Hsiao via glucose metabolism modulation and AMPK signaling activation. Phytomedicine 2024, 128, 155396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Misih, S.R.; Bloomston, M. Liver anatomy. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 90, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, S.; Luo, H.; Fu, X.; Li, W.; Li, B.; Fu, C.; Chen, F.; Xu, D.; Cao, N. Polysaccharide of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz alleviates NAFLD-induced hepatic inflammation in mice by modulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 141, 113014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.C.; Horton, J.D.; Hobbs, H.H. Human fatty liver disease: Old questions and new insights. Science 2011, 332, 1519–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Ye, S.; Jiang, R.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, J.; Meng, S. Liensinine alleviates high fat diet (HFD)-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) through suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation via regulating TAK1/AMPK signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 104, 108306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Wu, H.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X.; Li, C.; Liu, S. Noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) fruit phenolic extract supplementation ameliorates NAFLD by modulating insulin resistance, oxidative stress, inflammation, liver metabolism and gut microbiota. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Hu, J.; Yang, J.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shen, M.; Rong, L.; Xie, J. Human milk oligosaccharide 2′-fucosyllactose alleviates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis via improving intestinal barrier function and regulating gut microbiota. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Mukherjee, S.S.; Chakraborty, R.; Roy, R.R.; Pandey, A.; Patra, S.; Dey, S. The emerging role of gut microbiota in cardiovascular diseases. Indian Heart J. 2021, 73, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Shen, M.; Chen, T.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Q.; Chen, X.; Xie, J. Mesona chinensis benth polysaccharides alleviate DSS-induced ulcerative colitis via inhibiting of TLR4/MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways and modulating intestinal microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, 2200047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.-Y.; Zhao, C.-N.; Xu, X.-Y.; Tang, G.-Y.; Corke, H.; Gan, R.-Y.; Li, H.-B. Dietary plants, gut microbiota, and obesity: Effects and mechanisms. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriss, M.; Hazleton, K.Z.; Nusbacher, N.M.; Martin, C.G.; Lozupone, C.A. Low diversity gut microbiota dysbiosis: Drivers, functional implications and recovery. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Chen, T.; Li, H.; Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Kim, S.; Huang, Z.; Xie, J. An Exopolysaccharide from Genistein-Stimulated Monascus Purpureus: Structural Characterization and Protective Effects against DSS-Induced Intestinal Barrier Injury Associated with the Gut Microbiota-Modulated Short-Chain Fatty Acid-TLR4/MAPK/NF-κB Cascade Response. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Mo, S.; Shen, M.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Xie, J. Ficus pumila fruit polysaccharide attenuate ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma in mice associated with changes in microbiota involving the lung-intestinal axis. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Ouyang, J.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, W.; Liu, C.; Huang, P.; Li, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Polysaccharides from Fu brick tea ameliorate obesity by modulating gut microbiota and gut microbiota-related short chain fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2023, 118, 109356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.A.; Gu, W.; Lee, I.A.; Joh, E.H.; Kim, D.H. High Fat Diet-Induced Gut Microbiota Exacerbates Inflammation and Obesity in Mice via the TLR4 Signaling Pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; Deng, B.; Xiao, J.; Jin, J.; Huang, Z. Lipopolysaccharide and palmitic acid synergistically induced MCP-1 production via MAPK-meditated TLR4 signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Hong, J.; Xu, X.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, D.; Gu, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Gut microbiome and serum metabolome alterations in obesity and after weight-loss intervention. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaner, O.; Goday, A.; Park, Y.-M.; Lee, S.-H.; Magkos, F.; Shiow, S.-A.T.E.; Schröder, H. The gut microbiome profile in obesity: A systematic review. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 4095789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárcena, C.; Valdés-Mas, R.; Mayoral, P.; Garabaya, C.; Durand, S.; Rodríguez, F.; Fernández-García, M.T.; Salazar, N.; Nogacka, A.M.; Garatachea, N. Healthspan and lifespan extension by fecal microbiota transplantation into progeroid mice. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleissner, C.K.; Huebel, N.; Abd El-Bary, M.M.; Loh, G.; Klaus, S.; Blaut, M. Absence of intestinal microbiota does not protect mice from diet-induced obesity. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Wen, L.; Song, Y.; He, X.; Yue, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Cai, Z.; Qi, Z. DEHP exposure elevated cardiovascular risk in obese mice by disturbing the arachidonic acid metabolism of gut microbiota. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H. Lactobacillus casei Zhang exerts anti-obesity effect to obese glut1 and gut-specific-glut1 knockout mice via gut microbiota modulation mediated different metagenomic pathways. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Shen, M.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Q.; Chen, T.; Xie, J. Alleviative effects of natural plant polysaccharides against DSS-induced ulcerative colitis via inhibiting inflammation and modulating gut microbiota. Food Res. Int. 2023, 167, 112630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Song, L.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, S.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Ren, Z. Lactobacillus plantarum prevents obesity via modulation of gut microbiota and metabolites in high-fat feeding mice. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 73, 104103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, H.; Qin, N.; Ren, X.; Zhu, B.; Xia, X. Impact of food additives on the composition and function of gut microbiota: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Lu, D.; Ouyang, J.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Q.; Huang, J.; Liu, Z. Junshanyinzhen tea extract prevents obesity by regulating gut microbiota and metabolic endotoxemia in high-fat diet fed rats. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 2036–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alim, A.; Li, T.; Nisar, T.; Ali, Z.; Ren, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X. Polyphenols and pectin enriched golden kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis) alleviates high fructose-induced glucolipid disorders and hepatic oxidative damage in rats: In association with improvement of fatty acids metabolism. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 1872–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, G.Y.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Tiffany, C.R.; Mahan, S.P.; Kellom, M.; Rogers, A.W.L.; Nguyen, H.; Stevens, E.T.; Masson, H.L.P.; Yamazaki, K.; Marco, M.L.; et al. High fat intake sustains sorbitol intolerance after antibiotic-mediated Clostridia depletion from the gut microbiota. Cell 2024, 187, 1191–1205.e1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, H.G.; Coughlin, L.A.; Hussain, S.; Nguyen, V.; Channabasappa, N.; Koh, A.Y. The Impact of Lactobacillus Probiotics on the Gut Microbiota in Children With Short Bowel Syndrome. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 251, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ingredients (g) | ND | HFD | HFD+FO | HFD+BO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Casein | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| L-Cystine | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Corn Starch | 506.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Maltodextrin | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 |
| Sucrose | 68.8 | 68.8 | 68.8 | 68.8 |
| Cellulose | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Soybean Oil | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Lard | 20 | 245 | 122.5 | 122.5 |
| Flaxseed Oil | 0 | 0 | 122.5 | 0 |
| Blended Oil | 0 | 0 | 0 | 122.5 |
| Mineral Mix | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Dicalcium Phosphate | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 |
| Calcium Carbonate | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| Potassium Citrate, 1 H2O | 16.5 | 16.5 | 16.5 | 16.5 |
| Vitamin Mix | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Choline Bitartrate | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Total | 1055 | 773.8 | 773.8 | 773.8 |
| Calories supplementation (kcal %) | ||||
| Proteins | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Carbohydrates | 70 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Fats | 10 | 60 | 60 | 60 |
| Energy (kcal/g) | 3.85 | 5.24 | 5.24 | 5.24 |
| Steatosis | Lobular Inflammation | Hepatocellular Ballooning | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| the presence of steatosis in <5% of hepatocytes | none | normal hepatocytes | 0 |
| 5–33% | ≤2 foci per 20× | the liver cells were arranged in clusters, the majority of the cells maintained a round shape, the cytoplasm was lightly stained and presented a reticular configuration, and there was no significant difference in cell size | 1 |
| 34–66% | >2 | symptoms were similar to score 1, but the liver cells were enlarged and their number increased by two times | 2 |
| >66% | \ | \ | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Shen, M.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, F.; Xie, J. Dietary Flaxseed Oil and Its Blended Oil Alleviate High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice by Improving Lipid Metabolism and Regulating Gut Microbiota. Foods 2025, 14, 1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111877
Li H, Shen M, Chen X, Wu Y, Zeng F, Xie J. Dietary Flaxseed Oil and Its Blended Oil Alleviate High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice by Improving Lipid Metabolism and Regulating Gut Microbiota. Foods. 2025; 14(11):1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111877
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Haizhen, Mingyue Shen, Xianxiang Chen, Yi Wu, Fengjiao Zeng, and Jianhua Xie. 2025. "Dietary Flaxseed Oil and Its Blended Oil Alleviate High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice by Improving Lipid Metabolism and Regulating Gut Microbiota" Foods 14, no. 11: 1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111877
APA StyleLi, H., Shen, M., Chen, X., Wu, Y., Zeng, F., & Xie, J. (2025). Dietary Flaxseed Oil and Its Blended Oil Alleviate High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice by Improving Lipid Metabolism and Regulating Gut Microbiota. Foods, 14(11), 1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111877









